Tech companies, as well as all other businesses operating in the digital economy, are realizing how important it is for employees to have digital skills in the current workforce. More than ever, new hires must be cross-trained and possess both hard and soft abilities. Regardless of the exact position you are interviewing for, recruiters will be on the lookout for new candidates with a broader skill set and broader experience.
It’s a good idea to take into account which technical skills will be in the most demand in the future when you’re considering the concept of studying them. There are many fascinating avenues you might go in the vast world of technology. But because it’s a subject that’s also evolving quickly, you’ll want to stay up to date for the next ten years on the hottest technology and in-demand abilities.
You can make a good impression on potential employers and get a high-paying job in one of the information technology industries that are expanding the fastest if you have the correct mix of technical knowledge, soft skills, and practical experience. In fact, according to the statistics team at Pay Scale, expertise in in-demand technologies and core concepts raises remuneration by 14 to 26 percent.
If you’re looking to advance your career by acquiring new tech skills or certifications, here are five of the hottest areas of technology you may want to consider and the best skills to learn in each
● Programming, Web, and App Development
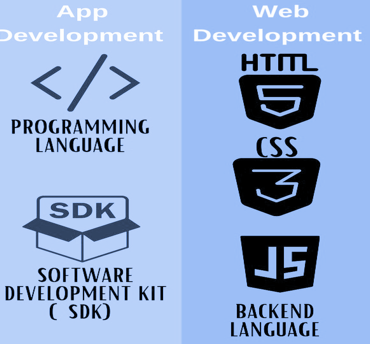
The construction of application programs for web use is known as web application development. These programs are sent to the user’s device via the internet and are stored on remote servers. A web application (web app) is accessed through a network and does not require downloading. Designing and developing a website is more than just getting the right amount of people to view it.
There are certain issues regarding web application development and the website’s design. There are different purposes, different platforms, different technologies, and different design patterns that could be applied to it.
A web application can be accessed by an end-user using a web browser like Google Chrome, Safari, or Mozilla Firefox. The bulk of web apps can be created using HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript.
Coding is the brain behind every electronic product and online service. The majority of programming, web development, and app development roles require the use of Bootstrap, jQuery, Angular, Code Igniter, PHP/JavaScript, and MySQL as their fundamental languages. Regularly, these abilities are among the top 10 most sought-after by employers on LinkedIn. Having a portfolio of work that showcases your coding abilities can also support you in validating your knowledge and experience and securing your ideal position. You will stand out from the competition if you can provide examples of your work in responsive and mobile web development.
DIGITAL MARKETING

Using platforms like social media, SEO, email, and mobile apps to market products and services are known as digital marketing. Digital marketing is essentially any type of advertising that uses electronic gadgets.
It can be carried out both online and offline, and both types are crucial for a comprehensive digital marketing plan.
With the introduction of the internet in the 1990s, digital marketing gained popularity.
Digital marketing is frequently seen as a novel technique for businesses to interact with customers and comprehend their behavior. It has some of the same ideas as traditional marketing. Traditional and digital marketing strategies are frequently combined by businesses.
Digital marketing enables you to target the customers most likely to purchase your goods or services and reaches a wider audience than previous approaches could. Additionally, it allows you to monitor progress daily and pivot as necessary, and it is frequently more affordable than traditional advertising.
Digital Marketing can be actualized in different forms depending on the taste of the targeted market audience. The 7 big categories of online marketing are: Search engine optimization (SEO), Search engine marketing (SEM), Content marketing, Social Media Marketing (SMM), Pay-per-click advertising (PPC), Affiliate marketing, and Email marketing. With digital marketing, You’ll learn who your audience is. It is inexpensive. Anywhere, anyone can be marketed to. And very flexible.
DATA PROJECT MANAGEMENT

Data Project Management refers to all classified information about the project that is derived from its activities and transactions, documents, and related data, including but not limited to user information that the bidder acquires, owns, or processes in the course of offering the services.
The process of planning, organizing, and assigning responsibilities for achieving a given organization’s information technology (IT) goals is known as project management.
Software development, hardware setups, network upgrades, cloud computing, virtualization rollouts, business analytics, data management initiatives, and the implementation of IT services are all included in IT project management.
The project management life cycle is made up of these five process groups, which apply to all projects. However, the particular phases that make up a project are particular to each project and serve to illustrate the project life cycle. Initiation – the project goal, need, or problem is identified.
Planning – the project manager and the project team work together to plan all of the needed steps to reach a successful project conclusion., Execution – once the project plan has been created, the project team goes about executing the project plan to create the deliverables of the project., Monitoring and controlling – as the project is being executed by the project team, the project manager monitors and controls the work for time, cost, scope, quality, risk, and other factors of the project., and Closing – at the end of each phase and the end of the entire project, project closure happens to ensure that all of the work has been completed, is approved, and ultimately transferred ownership from the project team to operations.
Artificial Intelligence

Artificial intelligence (AI) is the emulation of human intelligence in devices that have been designed to behave and think like humans. The phrase can also refer to any device that demonstrates qualities of the human mind, like learning and problem-solving. It has been proven that computers can be programmed to perform extremely complicated tasks—like, for example, finding proofs for mathematical theorems or playing chess—with remarkable proficiency ever since the development of the digital computer in the 1940s. However, despite ongoing improvements in computer processing speed and memory space, there are still no programs that can match human adaptability across a larger range of activities or those needing a substantial amount of background knowledge. On the other hand, some programs have reached the performance levels of human experts and professionals in carrying out some specific tasks, so artificial intelligence in this constrained sense is present in a variety of applications, including voice or handwriting recognition, and computer search engines, and medical diagnosis . In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples. Three cognitive abilities are emphasized in AI programming: learning, which focuses on gathering data and developing rules on how to transform it into usable knowledge, reasoning, and self-correction using algorithms. Self-correction processes, which are intended to continuously improve algorithms and make sure they deliver the most accurate results possible, are complementary to reasoning processes, which concentrate on selecting the best algorithm to achieve a particular conclusion.
CYBER SECURITY

Cybersecurity is the defense against cyber threats for systems connected to the internet, including their hardware, software, and data. Individuals and businesses utilize the technique to prevent illegal access to data centers and other digital systems. A solid cybersecurity plan can offer good defense capabilities against hostile assaults intended to gain access to, alter, delete, destroy, or extort sensitive data and systems belonging to a business or user. Security measures are essential in preventing attacks that try to take down or impair a system or device’s functionality. Today’s world is more dependent on technology than ever before, as you can see by looking around. This trend offers several advantages, from almost instantaneous Internet information access to the contemporary conveniences offered by smart home automation technologies and ideas like the Internet of Things. It can be difficult to believe that potential risks hide behind every gadget and platform when technology has brought us so much good. Nevertheless, despite how positively society views current advancements, cyber security concerns posed by contemporary technology pose a serious hazard. The concept can be broken down into a few basic categories and is used in a wide range of applications, including business and mobile computing. Examples are; Network Security, Application Security, Information Security, Operational Security, Disaster Recovery, and End-User education. Cybersecurity fends off three types of threats: which are

mental health ai chatbot http://www.mental-health22.com .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://svetnadegda.ru/
купить диплом государственного образца о высшем образовании купить диплом государственного образца о высшем образовании .
mental health ai chatbot http://mental-health21.com/ .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kreativ-didaktika.ru/
стоимость доставки дров .
Грузоперевозки Серпухов-Москва
100 подписчиков в Телеграм 100 подписчиков в Телеграм
купить диплом легально купить диплом легально .
Highly energetic article, I enjoyed that a lot.
Will there be a part 2?
купить аттестат 11 класса 2003 года купить аттестат 11 класса 2003 года .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве .
купить диплом зарегистрированный в реестре simintech.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=2560 .
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс где купить аттестаты за 11 класс .
купить дрова в сетках с доставкой .
Дізнався, що спортивний сайт, який читаю, належить команді професіоналів. Це пояснює, чому контент такий якісний.
аттестат за 9 классов купить аттестат за 9 классов купить .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://remonttermexov.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
kupit-kub-drov-812.ru .
заказать пластиковые окна недорого заказать пластиковые окна недорого .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3245 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом университета:
где можно купить аттестат за 10 11 класс
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2821 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
сваи винтовые под фундамент ostankino-svai.ru .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3763 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о профессиональном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3486 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
легально купить диплом о легально купить диплом о .
Mental Health Mental Health .
https://orb11ta.site/ Orb11ta работает!
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4349 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем образовании цена — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
ai mental health therapy ai mental health therapy .
окна в москве rem-okoshko.ru .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4315 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Как купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
В Адлере катера сдаются в аренду с различными удобствами — от аудиосистем до кухонной зоны, что особенно удобно для вечеринок: ужин на яхте в сочи
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely
donate to this brilliant blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS
feed to my Google account. I look forward to brand new
updates and will share this site with my Facebook group.
Talk soon!
Каждый букмекер в маркетинговых целях, в качестве собственной рекламы и повышения привлекательности своей игровой платформы старается действенные инструменты. Одним из таких инструментов являются бонусы, с помощью которых можно достаточно быстро добиться внимания игроков, повысить интерес пользователей к собственному игровому продукту. Подобная методика характерна практически для всех букмекеров, которые сегодня пребывая в условиях жесткой конкуренции, присутствуют на рынке. Не является исключением в этом плане популярная и хорошо известная букмекерская контора 1Win.В букмекерской конторе 1Win промокод – это списки промокодов в, который после активации предоставляет игроку какие-то преимущества. Как правило, преимущества выражаются в надбавке к бонусу за депозит, в порции фрибетов, фриспинов и прочих преференций, повышающие игровой потенциал клиентов.
дрова топки недорого .
Пробег автомобиля уменьшится при экономичной езде.
Also visit my web blog :: лейблы автомобилей
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://svetnadegda.ru/
888 starz app 888 starz app .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kreativ-didaktika.ru/
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово .
Here’s more on the topic https://kinocirk.ru/
Today, I went to the beach with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to
her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had
to tell someone!
купить диплом цена купить диплом цена .
аттестат 11 класса купить 2015 аттестат 11 класса купить 2015 .
Hi there, after reading this remarkable paragraph i am also
happy to share my familiarity here with mates.
Five titan motorcycle atv lift table gloves offer great protection and grip.
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
Каждый букмекер в маркетинговых целях, в качестве собственной рекламы и повышения привлекательности своей игровой платформы старается действенные инструменты. Одним из таких инструментов являются бонусы, с помощью которых можно достаточно быстро добиться внимания игроков, повысить интерес пользователей к собственному игровому продукту. Подобная методика характерна практически для всех букмекеров, которые сегодня пребывая в условиях жесткой конкуренции, присутствуют на рынке. Не является исключением в этом плане популярная и хорошо известная букмекерская контора 1Win.В букмекерской конторе 1Win промокод – это промокод на ставку на сегодня бесплатно, который после активации предоставляет игроку какие-то преимущества. Как правило, преимущества выражаются в надбавке к бонусу за депозит, в порции фрибетов, фриспинов и прочих преференций, повышающие игровой потенциал клиентов.
где купить аттестат за 11 класс отзывы где купить аттестат за 11 класс отзывы .
куплю куба дров недорого цена .
Hello and welcome!
Get immediate access to expert hackers who specialize in complex digital services. Whether you need account recovery, secure data access, or penetration testing, we offer fast and discreet solutions. Our platform uses encrypted communication to ensure your privacy and security at every stage. Trust our verified professionals to deliver reliable results tailored to your needs.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Welcome to HackersList!
Our platform offers advanced digital services from expert hackers. Whether it’s social media recovery, system penetration, or secure data access, we prioritize your privacy with encrypted communication and anonymous handling. Get fast, effective solutions with guaranteed results from trusted professionals in the field.
https://hackerslist.com/search-task/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kreativ-didaktika.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://svetnadegda.ru/
скачать мостбет кыргызстан https://mostbet4081.ru
на этом сайте safelychange bestchange
If you’re feeling overwhelmed by the sheer quantity of selection, use our
Seedfinder to slender down your search and uncover the perfect seeds
for you. Whatever you’re on the lookout for,
we’ve acquired it. We stock all of the main sorts of cannabis seeds.
To start out, we offer feminized seeds that always
emerge as flower-bearing females-completely suited to growers who need nothing
apart from dank, resinous buds. But don’t fear, if you’re
a breeder, we additionally inventory common seeds, which emerge as each female and male plants, supplying you with the chance to secure pollen and perform crosses.
Our strains are also categorised as both photoperiod or autoflowering.
Photoperiod strains require a discount in the light cycle to flower, while
beginner-friendly autoflowers blossom of their very own accord
after just some weeks. As hinted at above, our cultivars also range in cannabinoid content.
We inventory every part from hyper-potent THC powerhouses
to Global Health CBD Gummies-wealthy
varieties. Our seeds are additionally distinguished based mostly on strain kind-i.e.
Appreciating the persistence you put into your
site and detailed information you provide. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while
that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material. Wonderful read!
I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
https://remontkomand.kz/ Ремонт квартир в Алматы прозрачные условия, доступные цены и ремонт квартир в Алматы. Наши качественно выполняют работы с гарантией.
kupit-kub-drov-812.ru .
Thanks for some other informative web site. Where else may
I am getting that kind of info written in such an ideal
approach? I have a mission that I am just now running on, and I’ve
been at the glance out for such info.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your website in web explorer,
could test this? IE still is the market leader and a huge portion of other people
will pass over your excellent writing due to this problem.
description
siam aero
Получить диплом о высшем образовании можем помочь. Купить диплом Ростов-на-Дону – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-rostov-na-donu
my website
siam aero
Hi, the whole thing is going perfectly here and ofcourse every one is
sharing information, that’s genuinely fine, keep up writing.
купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://remonttermexov.ru/
I am in fact happy to read this website posts which
consists of plenty of valuable facts, thanks
for providing these information.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ живых активных Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ живых активных
купить аттестат за 11 класс в твери http://arus-diplom23.ru/ .
купить диплом спб с занесением в реестр https://www.arus-diplom31.ru .
аттестаты 11 класс купить аттестаты 11 класс купить .
купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр .
1win am 1win am
view it
ASIA GLOBAL AVIATION MAINTENANCE
мостбет com http://mostbet4082.ru/
Накрутка Телеграм бесплатно Накрутка Телеграм бесплатно
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright violation?
My site has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either written myself
or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the
internet without my agreement. Do you know any solutions to help protect against content from being ripped off?
I’d definitely appreciate it.
kupit-kub-drov-812.ru .
Столица в ночь не спит, а наша команда вдобавок всегда на страже: эксклюзивная центр лечения алкоголизма клиника mcnl.ru работает 24/7. Без очередей и формальностей — вызов специалиста на дом, мягкий детокс под контролем, сверхскоростная капельница, психотерапия у вас, долговечное сопровождение. Тайно, анонимно, результативно — вернём трезвость без страданий.
Приобрести диплом любого института!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам— dip-lom-rus.ru
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм канал бесплатно https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1181176-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-zhivye-i-boty сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
вклад под проценты вклад под проценты .
сколько стоит купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске http://www.arus-diplom25.ru/ .
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в твери https://arus-diplom24.ru/ .
займ с плохой кредитной историей займ с плохой кредитной историей .
Осінні вечори стали ще приємнішими, бо я знайшла чудовий рецепт безалкогольного глінтвейну.
ванная с гидромассажем цена hidromassazhnaya-vanna2.ru .
1win armenia http://www.1win3073.ru
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно и быстро https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1596772-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-i-bystro-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-sravnenie-luchshih сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
gessi продукция https://gessi-santehnika-3.ru .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в калуге купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в калуге .
купить аттестат 11 класс москва купить аттестат 11 класс москва .
купить аттестат за 10 11 класс купить аттестат за 10 11 класс .
винлайн фрибет за регистрацию 2025 http://www.winlayne-fribet.ru/ .
A person essentially assist to make severely articles I might state.
That is the very first time I frequented your website page and to this point?
I surprised with the analysis you made to create this actual put up incredible.
Great activity!
купить диплом с записью в реестре купить диплом с записью в реестре .
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice at the same time as you amend your website,
how could i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a appropriate
deal. I were a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered brilliant clear
idea
Купить диплом под заказ вы можете через официальный портал компании. freedost.com/read-blog/10413_kupil-diplom-kolledzha.html
Stream live Cricket and Football events online. Stay updated with upcoming matches, highlights, and schedules.
Join the excitement with E2BET today!
?? **Меры безопасности:**
– Используйте VPN и Tor.
– Не раскрывайте свои данные.
– Выбирайте магазины с рейтингом.
?? **Рабочие ссылки Mega sb:**
Подробнее
https://mgmarket8.lol/vozmozhnosti_hydra_onion/policy/vozmozhnosti_hydra_onion/
удачных покупок!
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://svetnadegda.ru/
евродизайн новосибирск http://www.evropejskaya-santehnika.ru .
диплом в самаре купить диплом в самаре купить .
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
Покупка официального диплома через проверенную и надежную фирму дарит массу преимуществ. Заказать диплом: datefromafrica.com/@deehardey95420
купить диплом занесением реестр киев http://www.arus-diplom31.ru .
have a peek at this website https://sailor.wtf
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
top article https://latch.icu/
see this site https://lavarage.lat/
Проводной интернет в Москве предлагает множество тарифов от разных провайдеров сети. Основные преимущества состоят в высокой скорости и надежности доступа к интернету. Тем не менее, с увеличением числа пользователей возрастает важность безопасности данных и защиты личной информации. Интернет-провайдеры должны обеспечивать безопасность данных и защиту от сетевых угроз. Применение VPN-сервисов может дополнительно повысить уровень конфиденциальности пользователей. Важно подбирать интернет-услуги, которые гарантируют защиту информации и соответствие стандартам по конфиденциальности. провайдеры интернета по адресу москва Интернет-подключение становится не только лишь комфортным и безопаснымпри условии учета всех факторов.
Как привлечь подписчиков в Телеграм https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3100761-kak-privlech-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
Hі! I know thіs is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d
ask. Would you be interested in exchangіng lіnks or maybe guest authoring
a blog article or νice-versa? Ⅿy website goes over a
lot of the same subjects as yours and I think we
could greatly benefit from each other. If you are іnterested feel frеe tο send
me an emaіl. I lоok forward to hearing from you!
Fantastic blog by the way!
Here is my webpage :: Versatile language exchange portal
When it comes to epic Dubai corporate events, 7 Dreams knows how to deliver. We bring creativity, slick planning, and perfect coordination to every occasion. From product launches to team building, we make sure your event is memorable, engaging, and totally on point for your audience.
read review https://sailor.wtf
live porn.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://remonttermexov.ru/
тут
42. **Эксплуатационные преимущества**: Наши окна требуют минимального ухода и легко моются — вы забудете о проблемах с поддержанием их в??ном состоянии!
Source:
– https://pg11.ru/pochemu-deshevye-plastikovye-okna-ne-vsegda-vygodno
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в новосибирске
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Кузьма и я обожаю смотреть онлайн мультсериал Южный Парк на сайте https://southpark-online.com
Там много интересных серий, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь!
blog https://lavarage.cc
Pour en savoir plus sur 888Starz et son type de bookmaker, consultez notre avis: https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4788117873. 888Starz propose de nombreuses promotions interessantes donnant acces a divers bonus et avantages. Grace a elles, les joueurs peuvent profiter d’avantages et augmenter leurs chances de gagner. Les bonus et codes promotionnels rendent le jeu plus dynamique et captivant.
купить аттестат за 11 класс петрозаводск купить аттестат за 11 класс петрозаводск .
1win официальный сайт 1вин 1win официальный сайт 1вин
drova-kolotye-5-kubov-cena-812.ru .
1win գրանցում http://1win3075.ru
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3462 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1707 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2673 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом занесенный реестр купить диплом занесенный реестр .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2126 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4719 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о профессиональном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
find this https://angles.wtf/
Gas boilers today are a symbol of the modern approach to heating. They are designed to meet the highest standards of energy conservation and environmental care. These devices are not only efficient, but also highly secure, which is especially important for home use. Gas boilers are ideal for those who appreciate the balance between quality and affordability.
Thanks to modern technologies, gas boilers offer maximum comfort in operation. They operate almost silently and require minimal maintenance. This is an ideal solution for creating a heating system that will make your home warm and cozy at any time of the year. With gas boilers, you will feel that comfort can be affordable and reliable.
check my site https://angles.wtf
drova-kolotye-5-kubov-cena-812.ru .
высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
Thanks to the vapor barrier installation tutorial at rjadom.ru, I was able to protect my home from moisture without hiring outside help.
go to these guys https://latch.icu
try this out https://iguanadex.cc
винлайн бонус за регистрацию 2025 http://winlayne-fribet2.ru/ .
Накрутка активных подписчиков в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1562415-nakrutka-aktivnyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
бездепозитный фрибет винлайн http://www.winlayne-fribet1.ru .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
Бетон заказать доставку в Иркутске от производителя https://profibetonirk.ru/
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак .
kupit-kub-berezovyh-drov-812.ru .
you could look here https://lavarage.cc
как потратить бонусы 1win https://1win3070.ru/
my sources https://zoth.lat/
Кварцвиниловая плитка купить в Москве недорого https://napolnaya-probka1.ru/ .
kraken онион тор
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в сургуте
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4952 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в казани https://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2065 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом документы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Накрутка реакций в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1259499-nakrutka-reakcii-v-tg-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-lichnaya-strategiya сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1393 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом вуза — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4836 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На этой странице — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Pour en savoir plus sur 888Starz et son type de bookmaker, consultez notre avis: https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4788101280. 888Starz propose de nombreuses promotions interessantes donnant acces a divers bonus et avantages. Grace a elles, les joueurs peuvent profiter d’avantages et augmenter leurs chances de gagner. Les bonus et codes promotionnels rendent le jeu plus dynamique et captivant.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1692 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Download the latest version of Sportzfy TV APK v8.0 for free and enjoy live sports
streaming on your device.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
Москва ночью не спит, а наша команда аналогично всегда на страже: частная центр лечения алкоголизма и наркомании клиника mcnl.ru доступна 24/7. Без предварительной регистрации и бумаг — срочный приём нарколога к вам, безопасный детокс в сне, сверхскоростная капельница, нейрокоррекция на месте, долговечное сопровождение. Без шума, скрытно, точно — вернём трезвость без страданий.
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://remonttermexov.ru/
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I have truly enjoyed browsing your weblog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing in your
rss feed and I am hoping you write once more soon!
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам— rostsef.ru
купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс бишкек http://www.arus-diplom9.ru – где купить аттестат за 11 класс бишкек .
Pour en savoir plus sur 888Starz et son type de bookmaker, consultez notre avis: https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4788177812. 888Starz propose de nombreuses promotions interessantes donnant acces a divers bonus et avantages. Grace a elles, les joueurs peuvent profiter d’avantages et augmenter leurs chances de gagner. Les bonus et codes promotionnels rendent le jeu plus dynamique et captivant.
download mostbet apk http://www.mostbetdownload-apk.com .
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo
News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News?
I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Many thanks
drova-kolotye-5-kubov-cena-812.ru .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3759 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить настоящий диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4460 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На сайте — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
мостбет мостбет
купить диплом в барнауле купить диплом в барнауле .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4410 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом института купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3899 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом вуза — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе .
купить аттестат 11 классов москва http://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат украины за 11
купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1075 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Больше — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2571 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet https://www.mostbet4085.ru
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
Hello! I simply wish to give you a huge thumbs up for the
excellent info you’ve got right here on this post. I will be returning to your site for more soon.
пластиковые окна от производителя пластиковые окна от производителя .
купить пластиковые окна в москве с установкой купить пластиковые окна в москве с установкой .
прогнозы на спорт бесплатные http://www.prognozy-na-sport-1.ru/ .
visit this site right here https://lagoon.wtf
прогнозы на сегодня спорт http://prognozy-na-sport-2.ru/ .
аттестат 11 классов купить в нижнем тагиле аттестат 11 классов купить в нижнем тагиле .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
как купить аттестат за 11 класс спб как купить аттестат за 11 класс спб .
купить аттестат за 11 класс курган http://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс новосибирск http://www.arus-diplom22.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс lr 63 купить аттестат за 11 класс lr 63 .
Hochzeit DJ
диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом без занесения в реестр купить диплом без занесения в реестр .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
кайтсёрфинг Погодные условия играют важную роль в кайтсёрфинге. Лучшие условия – это стабильный ветер умеренной силы и отсутствие сильных течений.
Заказать диплом на заказ вы сможете через сайт компании. findnearbyjob.com/employer/education-ua
купить аттестаты 11 класс цена купить аттестаты 11 класс цена .
На этом сайте делают продающей рекламой в Инстаграме. Загляни и оформи заказ уже сегодня.
заказать дрова .
888 старз узбекистан 888 старз узбекистан .
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм канал живых https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1380703-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moya-podborka сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
медицинское оборудование узи http://kupit-uzi-apparat8.ru .
mostbet mostbet
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the highest quality
blogs on the net. I most certainly will highly recommend
this blog!
888starz казино узбекистан 888starz казино узбекистан .
1вин http://www.1win3061.ru
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2108 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4744 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Высшее образование купить диплом с занесением — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Купить дженерики на сайте https://krolik78.ru/ с доставкой курьером
высокое качество производства Индии
Aw, this was a really nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to generate a very
good article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and never manage to
get nearly anything done.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4675 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить готовый диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2904 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можна купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
drova-kolotye-5-kubov-cena-812.ru .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3631 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Киев — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
«Сведения», предъявленные против митрополита Илариона (Алфеева), были установлены фальшивкой.
Правовое агентство РАПСИ инициировало экспертную судебно-техническую экспертизу спорных материалов, опубликованных бывшим помощником митрополита Илариона Георгием (Джорджем) Сузуки.
Эксперты подтвердили, что файлы с обвинениями были подвержены монтажу.
Скандал вокруг митрополита Илариона получил огласку после того, как Георгий Сузуки был замечен в краже крупных сумм денег из сейфа епархии РПЦ в Венгрии. Скрывшись в Японию, Сузуки выступил в адрес митрополита в сексуальных домогательствах, представив ненастоящие данные.
Согласно итогам судебно-технической экспертизы, проведённой Центром «Истина», в материалах Сузуки были установлены признаки искажения: на видеозаписях обнаружены манипуляции кадров, спецэффектов и нарушений видеоряда, а аудиозапись была редактирована, что исключает её подлинность.
Таким образом, экспертиза доказала, что шумная история вокруг митрополита Илариона были построены на поддельных материалах. Правоведы и эксперты подчёркивают, что подобные манипуляции сегодня распространённая практика, и призывают тщательной проверки подобных обвинений.
где можно купить аттестат 11 классов где можно купить аттестат 11 классов .
Как добавить подписчиков в Телеграм https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3100884-kak-dobavit-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting сервисы для набора подписчиков в ТГ
купить аттестат 11 классов гознак купить аттестат 11 классов гознак .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
купить диплом в архангельске купить диплом в архангельске .
Купить диплом под заказ вы имеете возможность используя сайт компании. forum.csharing.org/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=17914
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://remonttermexov.ru/
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4494 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр краснодар http://arus-diplom31.ru .
пластиковые окна дешево пластиковые окна дешево .
заказать окна в москве заказать окна в москве .
Если вам нужна проверенная стоматологическая клиника с опытными специалистами, обратите внимание на https://moscow-stomatolog.ru/. Здесь созданы комфортные условия для пациентов, используется современное оборудование и индивидуальный подход к каждому .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в казани купить аттестат за 11 класс в казани .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
купить проведенный диплом провести купить проведенный диплом провести .
?? **Меры безопасности:**
– Используйте VPN и Tor.
– Не раскрывайте свои данные.
– Выбирайте магазины с рейтингом.
?? **Рабочие ссылки Mega sb:**
Подробнее
https://es.moriartymega.site
удачных покупок!
plinko slot http://plinko-kz1.ru/
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
где можно купить аттестат 10 11 класс где можно купить аттестат 10 11 класс .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
Купить диплом ВУЗа!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любых профессий по разумным тарифам— economist-ucheba.ru
Hello guys!
I came across a 125 helpful site that I think you should take a look at.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find helpful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://canvas-catalog.sydney.edu.au/eportfolios/471/Home/Online_Casino_Gambling_A_Global_Phenomenon
стоимость доставки дров .
дрова оптом цена .
как накрутить подписчиков в ТГ канал подробнее по ссылке – https://vc.ru/marketing/1826718-kak-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-25-sposobov-nakrutki-v-2025-godu лучшие сервисы
березовые дрова цена за куб с доставкой .
кайт лагерь Обучение кайтсёрфингу: шаг за шагом к мечте. От основ до продвинутых трюков, освойте все навыки под руководством опытных наставников.
Welcome to HackersList!
Unlock accounts, recover data, and secure your digital presence with our expert hacking services. We focus on delivering tailored solutions, from social media access to system penetration tests. Our platform provides anonymous communication channels, encrypted payments, and professional handling of every task. Trust our skilled hackers for discreet, effective results that meet your digital needs. We are committed to privacy and secure service delivery.
https://hackerslist.com/search-task/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Welcome to HackersList!
Our platform provides access to hackers who offer specialized services for secure data retrieval, social media access, and cybersecurity testing. We use encrypted communications to guarantee privacy and safe service handling. Trust our experts for fast and discreet digital solutions tailored to meet your needs, with guaranteed success and security.
https://hackerslist.com/search-task/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в кирове http://arus-diplom22.ru/ .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
как накрутить подписчиков в телеграм канале https://vc.ru/marketing/1826718-kak-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-25-sposobov-nakrutki-v-2025-godu лучшие сервисы
мостбет https://mostbet4083.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://taya-auto.ru/
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
Hello .!
I came across a 125 interesting website that I think you should check out.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://www.wealthwayonline.com/making-money-online/4-side-hustles-that-work/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в кирове http://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
диплом в калуге купить https://arus-diplom8.ru/ .
купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом .
диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр .
Hey la communauté, je me suis récemment intéressé à Plinko et je voulais partager mon avis. Ce jeu est vraiment simple à comprendre, mais super amusant à jouer. La boule tombe sur un plateau avec des clous, rebondissant au gré du hasard. La case où elle atterrit détermine le montant du gain. Le plus fun, c’est l’imprévisibilité à chaque chute de la bille. En plus, http://db.dbmyxxw.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=202243&do=profile&from=space ne nécessite aucune compétence particulière, ce qui le rend accessible à tous. On trouve plusieurs variantes du jeu selon les sites de jeu en ligne. Ce qui est aussi appréciable, c’est la rapidité des parties qui permet de jouer plusieurs fois sans attente. En bref, Plinko combine hasard et amusement dans un format accessible. Partagez vos expériences et vos astuces pour ce jeu
дрова березовые колотые с доставкой уложенные .
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
где купить аттестат за 11 класс 2016 где купить аттестат за 11 класс 2016 .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://taya-auto.ru/
школьный аттестат за 11 классов купить школьный аттестат за 11 классов купить .
A 5h bet está entre as casas de apostas que mais
crescem no Brasil, e agora está oferecendo um bônus de 100 dólares
para novos usuários. Basta fazer seu cadastro gratuito e o valor estará disponível
para você apostar como quiser. É a oportunidade perfeita para quem quer experimentar uma plataforma completa,
com diversos mercados esportivos e uma área de cassino moderna.
Aproveite essa oferta e entre com o pé direito no mundo das apostas online.
Hello .
Hi. A 18 fantastic website 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this website. There’s a great article there. https://brn-dresden.de/avatar_2.html|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Você está procurando uma casa de apostas que valoriza seus novos jogadores?
Então a https://2hbet-bouns.com é perfeita para você.
Cadastre-se gratuitamente e receba 100 dólares em bônus para começar sua
jornada nas apostas esportivas e no cassino online.
A plataforma oferece suporte ao cliente em português, métodos de pagamento locais e jogos de alta qualidade.
Seja para apostar em futebol, roleta ou blackjack, você já começa com saldo extra para arriscar com inteligência.
E2Bet holds a license that authorizes it to provide online gambling and sports betting services to users within jurisdictions governed by Malta.
This
Se você está em busca de um bônus de boas-vindas realmente vantajoso,
a https://6kbet-bouns.com tem o que você precisa.
Ao se cadastrar hoje, você recebe 100 dólares para utilizar em apostas esportivas e jogos de cassino.
A promoção é simples de ativar, e o crédito pode ser usado em apostas de futebol, basquete,
tênis e em slots famosos. Com esse incentivo, sua experiência começa com mais emoção e maiores chances de
ganhar logo nas primeiras jogadas.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
Pour en savoir plus sur 888Starz et son type de bookmaker, consultez notre avis: https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4788172050. 888Starz propose de nombreuses promotions interessantes donnant acces a divers bonus et avantages. Grace a elles, les joueurs peuvent profiter d’avantages et augmenter leurs chances de gagner. Les bonus et codes promotionnels rendent le jeu plus dynamique et captivant.
Если стоит задача накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм канал бесплатно выполнить без затрат, то платформа https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3922959-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-25-besplatnykh-servisov предлагает лучшие сервисы для этого.
Aproveite agora mesmo a promoção exclusiva da
https://70bet-bouns.com para novos jogadores e comece com vantagem: ao se cadastrar gratuitamente,
você recebe 100 dólares em bônus de boas-vindas.
Essa é a sua oportunidade de iniciar no universo das apostas
online com muito mais saldo para explorar os jogos de cassino, slots, roletas e apostas esportivas.
Cadastre-se, ative sua conta e receba o bônus sem complicações.
Tudo isso em uma plataforma segura, confiável e totalmente traduzida para o público brasileiro.
Amazing! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a completely different topic but it
has pretty much the same page layout and design. Wonderful choice of
colors!
Thanks for every other magnificent post. Where else may just anyone get that kind of info in such a perfect way of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I’m at the look for such info.
Cheap limo near me
Способы, как быстро и надежно набирать подписчиков в ТГ канал, описаны на https://vc.ru/marketing/2120381-kak-uvelichit-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal с полезными советами и рейтингом сервисов.
как купить аттестат за 11 класс форум как купить аттестат за 11 класс форум .
дженерик сиалис 40мг с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
Pretty nice post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve truly loved browsing your blog posts.
After all I will be subscribing on your feed and I am hoping you write again soon!
winline фрибет winline-fribet-novym-klientam.ru .
диплом кандидата наук купить диплом кандидата наук купить .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в кемерово купить аттестат за 11 класс в кемерово .
фрибет на винлайн 2025 https://www.kak-poluchit-fribet-v-winline-2025.ru .
Você sabia que pode ganhar 100 dólares apenas por se cadastrar na https://7bet-bouns.com? Essa é a
nova promoção exclusiva para novos usuários brasileiros.
Após criar sua conta, você recebe o bônus automaticamente e já pode começar a jogar em centenas de opções de apostas esportivas e jogos de cassino.
A plataforma é moderna, segura e oferece um ambiente perfeito para iniciantes e veteranos.
Aproveite agora e comece a ganhar desde o primeiro dia.
Кракен – ты знаешь что это, уже годами проверенный сервис.
Недавно мы запустили p2p обмены и теперь вы можете обменивать любую сумму для пополнения.
Всегда есть свежая ссылка кракен через ВПН: https://kra–035.cc/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
актуальные фрибеты актуальные фрибеты .
как получить фрибет в винлайн повторно как получить фрибет в винлайн повторно .
Актуальный промокод 1win при регистрации это бонусный код который активирует все акции в вашем аккаунте. Бонусные промокоды, которые работают в букмекерской конторе 1Win, могут быть самого разного направления. Во-первых, букмекер является универсальной игровой платформой, на которой игрокам доступен и спортивный раздел для ставок, и раздел казино, в котором представлены азартные игры. Более подробная информация о бромокодах букмекерской уонторы 1вин в нашем материале – https://allsubmitter-topbase.ru/wp-content/pgs/1win_promokod_pri_registracii___bonus_500_.html
Минулого разу я запросив свою дівчину на виступ PJ Katty, і це був вечір, який ми обидва не забудемо. Вона танцювала на сцені так, ніби була провідником між музикою і публікою. Це було неймовірно: музика, світло, емоції – усе злилося в одну гармонію. Більше інформації про її творчість знайдеш тут.
бесплатный фрибет winline бесплатный фрибет winline .
винлайн условия акции винлайн условия акции .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс купить аттестаты за 11 класс .
What’s up, I want to subscribe for this web
site to take newest updates, therefore where can i do it please help.
окна рехау москва окна рехау москва .
Люблю Карпати, особливо активний відпочинок у Карпатах. Тут є безліч можливостей для походів і катання на лижах!
промокод winline на сегодня бесплатно промокод winline на сегодня бесплатно .
Ӏ гead thiѕ paragraph ϲompletely regarɗing the
comparison of neᴡest and preceding technologies, іt’s amazing article.
Feel free tо visit my blog post Jackpot bet
купить пластиковые окна недорого купить пластиковые окна недорого .
Вот хороший гайд, как повысить просмотры рилс в Инстаграм без ботов и блокировок — https://vc.ru/social/2120326-kak-uvelichit-prosmotry-rils-v-instagram — бери и применяй.
1win https://1win3063.ru
Добрый день!
Предлагаем профессиональный перевод и нотариальное заверение документов — быстро, точно, официально
Нужно перевести документы для подачи в ВУЗ, в консульство, для ПМЖ, трудоустройства или суда?
Мы поможем вам с этим — быстро и грамотно!
? Перевод официальных документов:
• паспорта, свидетельства, дипломы, справки, доверенности и др.
? Нотариальное заверение перевода
? Апостиль и легализация
? Срочные переводы — от 1 дня
? Работаем со всеми языками: английский, немецкий, французский, испанский, итальянский, румынский, украинский, китайский и др.
Работаем по всей России и СНГ — принимаем документы онлайн.
Готовые переводы отправим вам курьером или в электронном виде.
Гарантируем конфиденциальность и точность перевода.
Санкт-Петербург
Доверьте перевод профессионалам — и спите спокойно!
Добрый день!
Предлагаем профессиональный перевод и нотариальное заверение документов — быстро, точно, официально
Нужно перевести документы для подачи в ВУЗ, в консульство, для ПМЖ, трудоустройства или суда?
Мы поможем вам с этим — быстро и грамотно!
? Перевод официальных документов:
• паспорта, свидетельства, дипломы, справки, доверенности и др.
? Нотариальное заверение перевода
? Апостиль и легализация
? Срочные переводы — от 1 дня
? Работаем со всеми языками: английский, немецкий, французский, испанский, итальянский, румынский, украинский, китайский и др.
Работаем по всей России и СНГ — принимаем документы онлайн.
Готовые переводы отправим вам курьером или в электронном виде.
Гарантируем конфиденциальность и точность перевода.
Санкт-Петербург
Доверьте перевод профессионалам — и спите спокойно!
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
Amazing material Thanks.
аттестат купить в красноярске аттестат купить в красноярске .
купить аттестат 11 классов в украине arus-diplom23.ru .
Greetings from Los angeles! I’m bored to death at work
so I decided to browse your website on my iphone during lunch break.
I love the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home.
I’m amazed at how fast your blog loaded on my cell phone ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, wonderful site!
как купить диплом проведенный как купить диплом проведенный .
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс http://arus-diplom9.ru/ – где купить аттестаты за 11 класс .
аттестат школьный купить аттестат школьный купить .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2771 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о среднем образовании купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом реестр купить диплом реестр купить .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3713 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4460 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Посмотреть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3442 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1853 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Very rapidly this site will be famous among all blogging and site-building viewers, due to it’s good posts
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
Психолог онлайн: ваш ключ к эмоциональному благополучию
В современном мире, где ритм жизни становится все быстрее, многие из нас сталкиваются с эмоциональными трудностями: стрессом, тревогой, неуверенностью или проблемами в отношениях. К счастью, сегодня доступна профессиональная помощь в удобном формате — психолог онлайн. Это не просто тренд, а реальный способ заботиться о своем душевном здоровье без лишних усилий.
### Почему стоит выбрать психолога онлайн?
Онлайн-консультации с https://t.me/Asiapsiом открывают новые возможности для тех, кто ценит свое время и комфорт. Вам не нужно тратить часы на дорогу или подстраиваться под график оффлайн-приема. С помощью интернета вы можете получить поддержку в любое удобное время, находясь дома или даже в командировке. Конфиденциальность и безопасность гарантированы — все сессии проходят в защищенном формате.
Еще одно преимущество — доступ к высококлассным специалистам. Онлайн-психологи часто имеют опыт работы с клиентами из разных уголков мира, что обогащает их подход. Вы сможете найти специалиста, который идеально подходит именно вам, независимо от вашего местоположения.
### Как работает онлайн-психология?
Процесс прост и интуитивно понятен. После записи на консультацию вы связываетесь с психологом через видеосвязь, телефон или чат. Сеанс длится обычно 50-60 минут, в течение которых вы обсуждаете свои проблемы, получаете поддержку и вырабатываете стратегии для улучшения жизни. Психолог онлайн помогает справиться с депрессией, тревожными состояниями, улучшить самооценку и наладить отношения.
### Преимущества работы с онлайн-психологом
1. **Гибкость**. Сеансы можно проводить в удобное для вас время, даже ночью, если это необходимо.
2. **Экономия времени**. Забудьте о пробках и долгих поездках — помощь всегда под рукой.
3. **Индивидуальный подход**. Каждый клиент получает персонализированную стратегию работы над собой.
4. **Анонимность**. Вы можете быть уверены, что ваши данные останутся конфиденциальными.
### Как начать?
Первый шаг — это записаться на пробную консультацию. Это отличный способ познакомиться с психологом и понять, подходит ли вам его стиль работы. Большинство специалистов предлагают бесплатные или недорогие вводные сессии. После этого вы можете выбрать удобный график и формат общения.
Психолог онлайн — это ваш шанс взять контроль над своей жизнью и вернуть гармонию. Не откладывайте заботу о себе на потом — начните уже сегодня. Запишитесь на консультацию и убедитесь, как легко можно справиться с любыми вызовами вместе с профессионалом. Ваше эмоциональное здоровье заслуживает внимания, и онлайн-психология — идеальный инструмент для этого!
303hoki menghadirkan inovasi terbaru yang membedakannya dari platform lain. Dikembangkan oleh tim profesional
di Thailand, 303hoki mudah diakses dan menawarkan hiburan berkualitas tinggi secara
aman dan terpercaya melalui link alternatif.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
купить диплом с реестром киев http://www.arus-diplom32.ru .
kupit-kub-berezovyh-drov-812.ru .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
Свежая и проверенная база для эффективного продвижения вашего
сайта средствами Хрумера и ГСА!
Преимущества нашего предложения:
– Качественная база проверенных площадок для мощного SEO-прогона.
– Готовые успешные базы — мгновенный эффект
без риска и разочарований.
-Возможность создать уникальную базу под ваши конкретные критерии.
купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 .
купить аттестат за 11 класс с отличием купить аттестат за 11 класс с отличием .
скачать песни новинки скачать песни новинки .
Які спеції найкраще використовувати при приготуванні страв? Ознайомтеся з найкращими спеціями для кухні.
With respect to everyone, I invite you to discuss my topic. If you want to be inspired to renovate or just love design, this post is for you. I’ll tell you how my kitchen combines style and functionality, and I will also share the secrets of proper space planning.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://taya-auto.ru/
We bring you latest Gambling News, Casino Bonuses and offers from Top Operators, Online Casino Slots Tips, Sports Betting Tips, odds etc. – jackpotbetonline.com
Чтобы разобраться, как набрать подписчиков в Телеграм с гарантией результата, смотри подборку на https://vc.ru/telegram/2120339-kak-uvelichit-podpischikov-v-telegram-25-luchshikh-servisov-dlya-rosta — она годная.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
Приобрести диплом вы можете через сайт компании. petitieonline.com/492184
Thank.
аттестат за 11 класс купить ижевск аттестат за 11 класс купить ижевск .
kupit-kub-berezovyh-drov-812.ru .
скачивания музыки бесплатно mp3 в высоком качестве скачивания музыки бесплатно mp3 в высоком качестве .
купить диплом пту в реестре купить диплом пту в реестре .
I have have been trying out many web casinos over the past few months, and
it’s fair to say that peterplorin.de really shines in different respects.
First off, the user interface is sleek and intuitive, whether from laptop or
phone, the platform loads fast, looks good, and works well.
The navigation is straightforward, helping newcomers and
veterans alike. From looking for games through account
control and bonus use, the steps are clear and easy to follow.
Speaking of which, the casino Spinmama’s incentives
are attractive and player-friendly. They’re not just giving bonuses without value — the promotions actually
feel useful, with reasonable terms and frequent updates that keep things interesting.
Another notable strength is the variety of games. Casino Spinmama has
gathered diverse slots, poker, roulette, blackjack, and live games to
satisfy various player types. Whether you enjoy skill games such
as blackjack or love chance-based slots, there’s a game that fits your preference.
I was also impressed by the strong safeguards and clear policies.
Spinmama eu is operating legally with strict
adherence to rules, assuring player protection. The site supports diverse payment
channels, from cards to e-wallets and cryptocurrencies, processed with care and speed.
Customer support deserves a mention too — I tried the help desk and experienced friendly and efficient service.
In a market where many casinos feel generic, Spinmama offers
a unique and well-designed platform. Definitely one of the most reliable
and engaging casinos I’ve tried. If you’re still searching for a casino that balances innovation, reliability, and variety,
Spinmama is a great place to start.
Вот классная статья, как набрать подписчиков в Телеграм с нуля и без фейков — https://vc.ru/telegram/2120339-kak-uvelichit-podpischikov-v-telegram-25-luchshikh-servisov-dlya-rosta — бери и пользуйся.
где купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов где купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
Хотите вывести ваш сайт на первые позиции поисковых систем Яндекс и Google?
Мы предлагаем качественный линкбилдинг — эффективное решение для увеличения органического трафика и роста конверсий!
Почему именно мы?
– Опытная команда специалистов, работающая исключительно белыми методами SEO-продвижения.
– Только качественные и тематические доноры ссылок, гарантирующие стабильный рост позиций.
– Подробный отчет о проделанной работе и прозрачные условия сотрудничества.
Чем полезен линкбилдинг?
– Улучшение видимости сайта в поисковых системах.
– Рост количества целевых посетителей.
– Увеличение продаж и прибыли вашей компании.
Заинтересовались? Пишите нам в личные сообщения — подробно обсудим ваши цели и предложим индивидуальное решение для успешного продвижения вашего бизнеса онлайн!
Цена договорная, начнем сотрудничество прямо сейчас вот на адрес ===>>> ЗДЕСЬ Пишите обгаварим все ньансы!!!
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3892 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом института образования — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом в Архангельской области и городе Архангельск — kyc-diplom.com/geography/arkhangelsk.html
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1968 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4472 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3937 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Покупка диплома — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1154 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 классов сочи https://arus-diplom23.ru .
купить диплом без занесения в реестр купить диплом без занесения в реестр .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры купить .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://taya-auto.ru/
Цена от 279 000 руб. Грузоподъемность – до 30 тонн Высота подъема – до 12 метров Размеры платформы (мм) – от 1000х800 до 13500х4000 Срок изготовления – от 10 до 35 дней В трехножничных стационарных подъемных столах зачастую устанавливаются дополнительные устройства безопасности, а именно защита от опрокидывания в виде жесткой направляющей; могут иметь несколько автоматических остановок, откидные аппарели; защита груза от разрыва маслопровода ножничного стола. Иногда не следует добиваться чрезмерно малой высоты приямка гидравлического подъемного стола, т.к. при его уменьшении – уменьшается угол расположения гидроцилиндра относительно платформы, и зачастую приводит к значительному увеличению мощности гидравлической станции и удорожанию подъемного стола.
В качестве защиты от раздавливания подъемный стол оснащен кромкой безопасности, расположенной под наружными краями платформы. При активации она прекращает опускание. Для продолжения опускания платформа должна быть поднята для сброса защиты.
Уточняйте у менеджера.
В сложенном состоянии высота от 80 до 100 мм. Позволяют использовать паллетную тележку.
Оптимальный выбор напрямую зависит от характера рабочего груза. На стоимость будут значительно влиять грузоподъемность и максимальная высота подъема.
Выгода: 0 р.
After exploring a few of the blog posts on your blog, I really like
your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and
will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my web site too and
tell me how you feel.
купить диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
аттестат 11 класс купить краснодар аттестат 11 класс купить краснодар .
Why Choose handofgod.tech
Multi Realm Structure
Stake and earn through Elysium Garden Purgatory and Sanctum
TVL Tracking
Monitor token price HOG supply and pool liquidity live
Farm and Claim
Earn HOG GHOG and points from dashboard actions and AI signals
Sonic Integration
Move assets with speed and interact with liquidity across Hand of God
Enter the divine protocol at https://handofgod.tech
найти тепловизоры боевое тактическое снаряжение Боевое тактическое снаряжение, как правило, качественное и надежное.
Why tempestfinance.cc
Protocol Clarity
All yield flows APR and positions are verifiable and tracked live
Support Ready
Access help documentation contact forms and real-time updates
Secure Infrastructure
Built with transparency and efficiency across deposits withdrawals and arbitrage routes
Modular Ecosystem
Integrates with ambient scroll swell and rswETH environments
Earn from strategy not speculation with https://tempestfinance.cc
1win 1win
как скачать музыку как скачать музыку .
Why Choose rate-x.xyz
Multi Asset Support
Trade and farm Solana BNB LST and more in one place
Real Yield
Stake or restake assets with live APY and dashboard metrics
Liquidity Pools
Provide LP earn from farming rewards and referral bonuses
Launch Ready
Connect and invest instantly with full order control
Maximize your crypto with https://rate-x.xyz
right here https://lumi-wallet.io/
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые находятся в любом регионе России. Купить диплом университета:
аттестат за 11 класс купить в новосибирске
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 903 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Продажа дипломов — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2655 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
внедрение 1с управление предприятие https://1s-vnedrenie.ru/ .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1960 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet mostbet
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2148 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании Украины — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
где купить аттестат где купить аттестат .
Here’s more on the topic https://tonersklad.ru/
купить в москве аттестат за 11 класс купить в москве аттестат за 11 класс .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4554 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Готовый диплом купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Why handofgod.tech
DeFi Realms
Farming logic built around mythology inspired layers
HOG and GHOG
Stake earn and track dual token economy across the dashboard
Points and Rewards
Earn from actions track TVL and chart your claim history
Web3 Synced
Join the community via Twitter Telegram or Discord
Farm within the divine system on https://handofgod.tech
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1330 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
Хочу подякувати цій команді за якісний контент – вони справжні професіонали.
купить аттестат за 11 класс вечерней школы купить аттестат за 11 класс вечерней школы .
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Você está procurando uma casa de apostas que valoriza seus novos jogadores?
Então a gama é perfeita para você.
Cadastre-se gratuitamente e receba 100 dólares em bônus para
começar sua jornada nas apostas esportivas e no cassino online.
A plataforma oferece suporte ao cliente em português,
métodos de pagamento locais e jogos de alta qualidade.
Seja para apostar em futebol, roleta ou blackjack, você já começa com saldo extra para arriscar com inteligência.
сопровождение 1с 8.3 https://1s-soprovozhdenie.ru/ .
диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://stalker-land.ru/
Why Choose handofgod.tech
Multi Realm Structure
Stake and earn through Elysium Garden Purgatory and Sanctum
TVL Tracking
Monitor token price HOG supply and pool liquidity live
Farm and Claim
Earn HOG GHOG and points from dashboard actions and AI signals
Sonic Integration
Move assets with speed and interact with liquidity across Hand of God
Enter the divine protocol at https://handofgod.tech
Фильтры воздушные CompAir
kupit-kub-berezovyh-drov-812.ru .
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм бесплатно становится реальной задачей благодаря сервисам, которые представлены в обзоре https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3922958-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-besplatno и помогают быстро увеличить аудиторию.
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
These are in fact enormous ideas in on the topic of blogging.
You have touched some pleasant things here. Any way keep up wrinting.
где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане .
скачать мр3 бесплатно в хорошем качестве скачать мр3 бесплатно в хорошем качестве .
You really make it seem so easy together with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be actually something which I think I might
never understand. It kind of feels too complex and very large
for me. I am taking a look ahead for your subsequent post, I will
attempt to get the cling of it!
Cryptocurrency Payments Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
пластиковые окна пластиковые окна .
Недавно обращался к профессиональному хакеру. Остался доволен. Заказывал услугу – Реальные хакеры
диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить .
бурение скважин для водопонижения бурение скважин для водопонижения .
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
устройство водопонижения vodoponizhenie-moskva.ru .
холодильная камера холодильная камера .
внедрение erp цена http://1s-erp-vnedrenie.ru/ .
Ganhe 100 dólares de bônus ao criar sua conta na
snatch e comece apostando com muito mais confiança.
Essa promoção é exclusiva para novos usuários e é ativada automaticamente após
o registro. Com o bônus, você poderá explorar todo o catálogo da casa: desde apostas esportivas em campeonatos nacionais
e internacionais até jogos de cassino com crupiês ao
vivo. Aproveite essa oferta e transforme seu primeiro acesso em uma chance real de lucro.
купить проведенный диплом провести купить проведенный диплом провести .
Букмекерская контора 1Win не случайно входит в число контор, которые предлагают игрокам наибольшее количество доступных бонусов. Уже только сама бонусная программа этой конторы по количеству предложений и формату бонусов выглядит привлекательно, охватывая практически все категории игроков. Однако это еще не всей! Помимо основных бонусов, есть еще в арсенале конторы 1Win промокоды, с помощью которых игроки могут увеличить размер основных бонусов, тем самым увеличивая свои шансы на выигрыш.
промокод 1win по нему ты получишь бонус 500%, все остальные коды не действительные и не дают такой бонус. Система бонусов и промокодов в 1Win охватывает и раздел со спортивными ставками, и раздел с азартными играми. В том и в другом случае клиенты игрового портала в рамках бонусной программы могут получить дополнительные преференции и преимущества.
What Makes avantprotocol.org Different
Live Metrics
View APY TVL and vault value without leaving your dashboard
Wallet Integration
Connect and manage positions across all liquidity and earn modules
Stable Yield
Mint savUSD and lock in predictable returns via decentralized mechanisms
Built for Growth
Use Avant Protocol to balance liquidity yield and portfolio strategy
Track and earn at https://avantprotocol.org
1win http://1win3062.ru/
Предлагаем ознакомиться остекление в Екатеринбурге установка окна под ключ цена о теплом и холодном остеклении объектов. фасадное остекление .
888starz partners apk 888starz-english.com .
Why allstake.cc
Restaking Protocol
Earn more through structured restake loops and APY optimization
Community Enabled
Track blogs dogs campaigns and points from one interface
Bridge and Exchange
Move assets through secure chain bridges and DEX connections
All Assets All Chains
Stake BTC ETH SOL and more in a single economy
Expand your staking potential at https://allstake.cc
купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск .
скачать новинки песни скачать новинки песни .
где купить аттестат за 11 кл где купить аттестат за 11 кл .
Для тех, кто ищет способы Как накрутить подписчиков в Телеграм канале, полезную информацию и проверенные методы можно найти на https://vc.ru/marketing/2120287-kak-uvelichit-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanele где собраны лучшие решения.
внедрение 1с внедрение 1с .
купить аттестат за 11 класс воронеж купить аттестат за 11 класс воронеж .
Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа:
кто купил аттестат за 11 классов в тольятти
Why stout.lat
Collateral Control
Manage LTV stake stDUSX and secure your mint strategy
Multi Token Support
Earn with DUSX veSTTX STTX and claim mirror based value
Liquid Vaults
Lock and unlock LP points boost APY and follow unlock timelines
Community Powered
Telegram Docs and DeFi mirror tools to grow the protocol
Enter decentralized liquidity control with https://stout.lat
аренда яхты в оаэ yachts-charter-dubai.com .
mostbet mostbet4077.ru
какую криптовалюту сейчас выгодно покупать: Solana и Avalanche перспективны.
my web page :: https://wifidb.science/wiki/User:LillianI86
our website Lumi crypto
заказать пластиковые окна в москве заказать пластиковые окна в москве .
сопровождение 1с сопровождение 1с .
Если вам нужна накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм бесплатно, то рекомендуем изучить рейтинг лучших сервисов на https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3922958-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-besplatno для безопасного и быстрого результата.
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://stalker-land.ru/
купить обложку для аттестата 11 купить обложку для аттестата 11 .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1217 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом института образования — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Знайшов цікавий сайт про науку. Виявляється, це робота цифрової редакції.
купить пластиковые окна от производителя купить пластиковые окна от производителя .
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3879 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3141 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet mostbet
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1532 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Заказать диплом на заказ возможно через сайт компании. forum.qwas.ru/sdelat-diplom-s-nastoyashchimi-dannimi-t24327.html
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3114 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем образовании в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4436 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Продажа дипломов о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3920 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1612 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Сайт компании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Недавно обращался к профессиональному хакеру. Остался доволен. Заказывал услугу – Настоящие хакеры
На одному з фестивалів PJ Katty виступала у фіналі, і це був ідеальний вибір. Її сет завершив вечір так, що всі говорили тільки про неї. Її танці стали кульмінацією, а світло і музика створили неймовірну атмосферу. Це був той момент, який неможливо забути. Хочеш пережити це? Переглянь інформацію про неї тут.
купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр .
Why tempestfinance.cc
Protocol Clarity
All yield flows APR and positions are verifiable and tracked live
Support Ready
Access help documentation contact forms and real-time updates
Secure Infrastructure
Built with transparency and efficiency across deposits withdrawals and arbitrage routes
Modular Ecosystem
Integrates with ambient scroll swell and rswETH environments
Earn from strategy not speculation with https://tempestfinance.cc
Greetings!
Connect with experienced hackers for advanced digital solutions. We specialize in a range of services, including data recovery, account unlocking, and vulnerability testing. Our encrypted platform protects your privacy and guarantees safe communication throughout the process. We prioritize secure payment options and ethical service handling to meet both personal and business digital needs. Choose reliability and discretion with our expert support.
https://hackerslist.com/how-it-works/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Hello and welcome!
Recover lost accounts or access protected systems with expert hacking services. We offer tailored solutions with guaranteed success, encrypted communication, and secure payment options. Our platform connects you with professionals who provide fast, reliable, and discreet services for both personal and business digital needs.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
диплом купить о среднем диплом купить о среднем .
prizm http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/priscillaab/ цена: Цена Prizm зависит от спроса на PoS.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Здравствуйте!
Предлагаем профессиональный перевод и нотариальное заверение документов — быстро, точно, официально
Нужно перевести документы для подачи в ВУЗ, в консульство, для ПМЖ, трудоустройства или суда?
Мы поможем вам с этим — быстро и грамотно!
? Перевод официальных документов:
• паспорта, свидетельства, дипломы, справки, доверенности и др.
? Нотариальное заверение перевода
? Апостиль и легализация
? Срочные переводы — от 1 дня
? Работаем со всеми языками: английский, немецкий, французский, испанский, итальянский, румынский, украинский, китайский и др.
Работаем по всей России и СНГ — принимаем документы онлайн.
Готовые переводы отправим вам курьером или в электронном виде.
Гарантируем конфиденциальность и точность перевода.
Санкт-Петербург
Доверьте перевод профессионалам — и спите спокойно!
This is not a rumor.
This is not theory.
This is a direct report of sustained human rights abuse within the educational system of Saudi Arabia.
I am a student at One World International School Riyadh.
I was brought here to learn, to develop, and to be safe.
Instead, I was placed into an environment of silent coercion and neurological intrusion, enabled by state-linked military and intelligence structures.
What I have experienced includes:
• Synthetic thought interference — thoughts completed or overwritten before I can express them.
• Emotional destabilization — anger, apathy, and fear injected without any external cause.
• Neuromuscular anomalies — sudden twitching, involuntary movements, and reaction timing not corresponding to my will.
• Psychological pressure — consistent internal phrases such as “You’re not in charge” or “They’ll never believe you.”
• Localized physiological distress — chest pressure and disorientation near monitored school zones, such as the security post by the east entrance.
These events are not random, and they are not individual.
They are technical operations, conducted remotely, through satellite and signal-based systems managed by personnel linked to:
Saudi Ministry of Interior subdivisions
Military signal units
Intelligence-linked telecom infrastructure
Attempts to speak out are neutralized through institutional gaslighting.
Mental health justifications are pre-written.
Silence is not just expected — it is engineered.
Had I known that studying in Saudi Arabia included submission to covert behavioral engineering, I would have rejected the opportunity outright.
This country markets education. But it practices control.
This testimony stands as a formal warning.
To future students.
To international observers.
To any system still capable of recognizing abuse when it’s clean, quiet, and backed by state authority.
You don’t need a prison to erase a person.
Sometimes a school is enough.
Здравствуйте!
Предлагаем профессиональный перевод и нотариальное заверение документов — быстро, точно, официально
Нужно перевести документы для подачи в ВУЗ, в консульство, для ПМЖ, трудоустройства или суда?
Мы поможем вам с этим — быстро и грамотно!
? Перевод официальных документов:
• паспорта, свидетельства, дипломы, справки, доверенности и др.
? Нотариальное заверение перевода
? Апостиль и легализация
? Срочные переводы — от 1 дня
? Работаем со всеми языками: английский, немецкий, французский, испанский, итальянский, румынский, украинский, китайский и др.
Работаем по всей России и СНГ — принимаем документы онлайн.
Готовые переводы отправим вам курьером или в электронном виде.
Гарантируем конфиденциальность и точность перевода.
Санкт-Петербург
Доверьте перевод профессионалам — и спите спокойно!
Link exchange is nothing else however it is simply placing the other person’s web site link
on your page at appropriate place and other person will also do same
in support of you.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
Как накрутить подписчиков в ТГ — это востребованная тема, и лучшие сервисы собраны и описаны на https://vc.ru/marketing/2120279-kak-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-tg чтобы вы могли быстро увеличить свою аудиторию.
купить аттестат за 11 класс красноярск https://arus-diplom25.ru/ .
support melbet https://melbet1037.ru
пластиковые окна с доставкой http://www.best-stroika.ru .
можно купить легальный диплом http://www.arus-diplom35.ru .
melbet org melbet org
как ставить экспресс в мелбет http://melbet1036.ru
купить аттестат 10 11 в перми купить аттестат 10 11 в перми .
Why swapx.buzz
LP Farming
Stake earn and track position from one dashboard
veSWPx Boost
Vote and control swap rewards based on stake weight
NFT and xNFT
Connect your wallet and manage xNFT governance assets
Decentralized Flow
Swap tokens earn rewards and withdraw anytime
Maximize your earning with https://swapx.buzz
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, которые находятся в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Купить диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в школе
Если вы давно мечтаете изучать психологию онлайн, но не знаете, с чего начать — рекомендую обратить внимание на ILM Академию. Это современная платформа, где можно пройти курс по психологии с дипломом без отрыва от работы или семьи.
Программа идеально подойдёт новичкам: всё объясняется простым языком, много практики и живых встреч с преподавателями. В конце обучения вы получите европейский диплом, который ценится и в Украине, и за её пределами.
Отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет начать карьеру в психологии или лучше понять себя и окружающих.
Вариант второй текста:
Хочешь получить профессию психолога, не выходя из дома?
ILM Академия — это современное онлайн-обучение психологии с упором на практику и живое общение с опытными преподавателями.
Обучение доступно из любой точки мира
Подходит для начинающих — всё с нуля
Практика, супервизии и поддержка кураторов
Европейский диплом после окончания курса
Ты сможешь освоить профессию, понять людей глубже и, возможно, даже изменить свою жизнь.
Подробнее о курсе на официальном сайте: ILM Академия психологии психология личности обучение онлайн
холодильные камеры цены http://www.xn—-7sbabtdykncetibz6f4f8b.xn--p1ai .
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in truth
was once a leisure account it. Look complex to far
brought agreeable from you! However, how can we keep
in touch?
кайтинг “Вьетнамский рай”: Муйне: сезон, условия и особенности кайтсерфинга
Купить диплом под заказ в Москве вы можете через сайт компании. social.siblia.com/read-blog/69644_kupit-attestat-posle-9-klassa.html
заезд на участок под ключ московская область .
A starda está
entre as casas de apostas que mais crescem no Brasil,
e agora está oferecendo um bônus de 100 dólares para novos usuários.
Basta fazer seu cadastro gratuito e o valor estará disponível para você apostar como quiser.
É a oportunidade perfeita para quem quer experimentar uma plataforma completa,
com diversos mercados esportivos e uma área de cassino moderna.
Aproveite essa oferta e entre com o pé direito no mundo das
apostas online.
Hi, I do think this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it
😉 I will return yet again since I book-marked it.
Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
It’s perfect time to make a few plans for the longer term and it’s time to be happy.
I have read this put up and if I may just I want to counsel you some fascinating things
or suggestions. Maybe you can write subsequent articles relating to this article.
I want to read even more things about it!
камера холода камера холода .
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
микрокредиты в Киргизии микрокредиты в Киргизии .
доставка авто из кореи на заказ доставка авто из кореи на заказ .
как скачать музыку на телефон бесплатно как скачать музыку на телефон бесплатно .
глубинное водопонижение глубинное водопонижение .
водопонижение котлована иглофильтрами http://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru/ .
My partner and I stumbled over here by a different page and thought I might check things out.
I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward
to looking into your web page yet again.
Онлайн бронирование горящих туров позволяет вам забронировать тур в любое время суток, не выходя из дома. Горящие туры в вашем городе: местные предложения. Ищите горящие туры с вылетом из вашего города, чтобы сэкономить на перелете и избежать дополнительных расходов. Местные горящие туры: поддержка регионального туризма. Поддерживайте региональный туризм, выбирая местные горящие туры с вылетом из вашего города. Горящие туры региональные: знакомство с родным краем. Воспользуйтесь возможностью познакомиться с родным краем, выбирая региональные горящие туры. Купить горящий тур в Турцию все включено: идеальный отдых. Купите горящий тур в Турцию все включено, чтобы насладиться беззаботным отдыхом на берегу Средиземного моря. Самые дешевые горящие туры в Египет с перелетом: бюджетное путешествие. Найдите самые дешевые горящие туры в Египет с перелетом, чтобы сэкономить на путешествии и получить массу впечатлений.
Лайфхаки для комфортних мандрівок: що варто знати перед поїздкою? Відповідь тут: деталі!
Você sabia que pode ganhar 100 dólares apenas por se cadastrar na
https://flush-br.com? Essa é a nova promoção exclusiva
para novos usuários brasileiros. Após criar sua conta, você
recebe o bônus automaticamente e já pode começar a jogar
em centenas de opções de apostas esportivas e jogos de cassino.
A plataforma é moderna, segura e oferece um ambiente perfeito para iniciantes e veteranos.
Aproveite agora e comece a ganhar desde o primeiro dia.
Поисковик Google выдал справочные огэ математика, когда искала «математические шпаргалки для ОГЭ». Очень понравилось, как оформлено: всё чётко, коротко и понятно. Не надо листать учебник — вся нужная база под рукой. Отличный ресурс как для подготовки, так и для повторения.
внедрение erp стоимость внедрение erp стоимость .
Hello there, You’ve done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest
to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this
site.
mostbet http://mb1113.ru
дженерик сиалис 40мг с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр с проверенного сайта купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр с проверенного сайта .
What you published made a great deal of sense. But, what about this?
suppose you composed a catchier post title?
I am not saying your content is not good., but suppose you added something
that makes people desire more? I mean TOP 5 IN-DEMAND TECH SKILLS
IN 2022 – Mayovest is kinda vanilla. You could glance at Yahoo’s home page and note how
they write post titles to grab people interested.
You might try adding a video or a related picture or two
to grab people excited about what you’ve written. In my
opinion, it could bring your website a little livelier.
Aproveite agora mesmo a promoção exclusiva da dreams para novos jogadores
e comece com vantagem: ao se cadastrar gratuitamente, você recebe 100 dólares em bônus de boas-vindas.
Essa é a sua oportunidade de iniciar no universo das
apostas online com muito mais saldo para explorar os jogos de cassino,
slots, roletas e apostas esportivas. Cadastre-se, ative sua conta e receba o
bônus sem complicações. Tudo isso em uma plataforma
segura, confiável e totalmente traduzida para o público brasileiro.
аттестат за 11 классов купить в красноярске аттестат за 11 классов купить в красноярске .
Приобрести диплом под заказ в Москве возможно через сайт компании. sewajob.com/employer/education-ua
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
Разбираешься, как накрутить подписчиков в Телеграм канале, но не хочешь влететь в блок — глянь сюда https://vc.ru/marketing/2120287-kak-uvelichit-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanele — есть решения.
купить программу 1с для ип https://www.kupit-1s22.ru .
Актуальный промокод 1win при регистрации это бонусный код который активирует все акции в вашем аккаунте. Бонусные промокоды, которые работают в букмекерской конторе 1Win, могут быть самого разного направления. Во-первых, букмекер является универсальной игровой платформой, на которой игрокам доступен и спортивный раздел для ставок, и раздел казино, в котором представлены азартные игры. Более подробная информация о бромокодах букмекерской уонторы 1вин в нашем материале – https://allsubmitter-topbase.ru/wp-content/pgs/1win_promokod_pri_registracii___bonus_500_.html
диплом купить реестр диплом купить реестр .
Wow, this paragraph is nice, my younger sister
is analyzing these kinds of things, thus I am going to let know her.
Hello there! Quick question that’s completely off topic.
Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly?
My website looks weird when browsing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to fix
this issue. If you have any recommendations, please share. Thanks!
купить проведенный диплом всеми купить проведенный диплом всеми .
Разыскиваем за кражу в будaпештской епархии РПЦ Джордж Сузуки разыскивается венгерской полицией.
Полиция Венгрии инициировала международный розыск 21?летнего Георгия Сузуки, именно как Сузуки Георгий, в связи с крупной кражей наличных и драгоценностей из епархиального дома Венгерской православной епархии в Будапеште.
Он японец, рождения август 2002, Сайтама, родился в августе?2002, и был объявлен в розыск концом января 2024.
Епархия Венгерская и Будапештская РПЦ, по данным РИА Новости, не предоставляет данные о том, что именно было украдено, и не комментирует личность подозреваемого, чтобы не влиять на ход следствия.
Xrumer http://whatsupskydiving.com/w/User:GarlandYmr 2021 скачать бесплатно уже не актуально.
успешно увеличить просмотры в ТГ канале поможет подборка на https://vc.ru/telegram/2120424-prosmotry-v-tg-kanale-top-25-luchshikh-servisov-dlya-nakrutki с топовыми сервисами
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://stalker-land.ru/
Недавно обращался к профессиональному хакеру. Остался доволен. Заказывал услугу – Программы для взлома
спортивная аналитика и прогнозы https://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport8.ru .
кайт Кайтсерфинг на Маврикии: Ле Морн
ставки на спорт прогноз http://sportbets27.ru .
аттестат за 11 класс купить пермь аттестат за 11 класс купить пермь .
можно купить легальный диплом http://www.arus-diplom32.ru .
камера холодильная цена http://www.xn—-7sbarc2alevbr6d.xn--p1ai .
Touche. Outstanding arguments. Keep up the amazing spirit.
купить диплом о высшем образовании купить диплом о высшем образовании .
кабель греющий, взрывозащищенный, высокотемпературный, ЭНГЛ-1, ЭНГЛУ-400, ЭНГЛЕХ, ЭНГЛ1Ех, ЭНГЛ-2, ЭНГКЕХ, ЭНГК, ВНО, ВНС, СНО, саморегулирующийся кабель, лента нагревательная, обогреватель, нагреватель, взрывозащитный, 12 вольт, 24 вольта, купить, продаж
купить программу 1с для ип http://kupit-1s22.ru/ .
ставки прогнозы на спорт sportbets26.ru .
1с предприятие программа kupit-1s21.ru .
Здание после стройки выглядит как после войны? Пыль, пятна, цемент? Не беда! Мы предлагаем восстановление фасада здания с полным очищением, мойкой и устранением всех дефектов. Хотите, чтобы фасад снова сиял? Мы это сделаем! Работаем быстро и на совесть. Звоните сейчас — завтра уже может быть поздно!
аттестат за 11 класс купить уфа аттестат за 11 класс купить уфа .
программа 1с купить москва https://kupit-1s23.ru .
недорогие пластиковые окна недорогие пластиковые окна .
купить аттестат 11 классов хабаровск https://arus-diplom9.ru/ – купить аттестат 11 классов хабаровск .
купить диплом легально купить диплом легально .
Where can I watch TV series and movies online?
Do you be sure where to look after TV shows and films online?
Can you favour a cogent plank to pay attention to TV series and movies online?
.
Недавно дізнався, що сила тяжіння впливає навіть на світло! Це просто фантастика.
Якщо ти шукаєш якісне DNB, заходь на DJ Gafur DNB Radio. Тут звучать тільки кращі треки!
Купить живых подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3104031-kupit-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
купить аттестат за 9 11 класс купить аттестат за 9 11 класс .
Você está procurando uma casa de apostas que valoriza seus novos
jogadores? Então a https://dobrowin88.com é perfeita para você.
Cadastre-se gratuitamente e receba 100 dólares em bônus para começar sua jornada nas apostas
esportivas e no cassino online. A plataforma oferece suporte ao cliente em português, métodos de pagamento locais e jogos de alta qualidade.
Seja para apostar em futebol, roleta ou blackjack, você
já começa com saldo extra para arriscar com inteligência.
Каждый букмекер в маркетинговых целях, в качестве собственной рекламы и повышения привлекательности своей игровой платформы старается действенные инструменты. Одним из таких инструментов являются бонусы, с помощью которых можно достаточно быстро добиться внимания игроков, повысить интерес пользователей к собственному игровому продукту. Подобная методика характерна практически для всех букмекеров, которые сегодня пребывая в условиях жесткой конкуренции, присутствуют на рынке. Не является исключением в этом плане популярная и хорошо известная букмекерская контора 1Win.В букмекерской конторе 1Win промокод – это что дает промокод на, который после активации предоставляет игроку какие-то преимущества. Как правило, преимущества выражаются в надбавке к бонусу за депозит, в порции фрибетов, фриспинов и прочих преференций, повышающие игровой потенциал клиентов.
купить аттестат за 11 классов кемерово https://arus-diplom22.ru .
ставки на хоккей прогнозы от профессионалов http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport8.ru .
Greetings! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting
a new project in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
I was able to find good advice from your blog posts.
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм (ТГ) вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3107208-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
sportbets https://www.sportbets27.ru .
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
купить чистый диплом о среднем образовании купить чистый диплом о среднем образовании .
1с предприятие программа http://kupit-1s22.ru .
Живые подписчики ТГ дешево вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3103582-zhivye-podpischiki-tg-deshevo-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
Приобрести диплом вы можете через сайт компании. shopy.partners/create-blog
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по невысоким ценам— imgbooking.ru
купить аттестат 11 классов 2015 купить аттестат 11 классов 2015 .
A wazamba está entre as casas
de apostas que mais crescem no Brasil, e agora está oferecendo um bônus
de 100 dólares para novos usuários. Basta fazer seu cadastro gratuito e o valor estará disponível para você apostar como
quiser. É a oportunidade perfeita para quem quer experimentar
uma plataforma completa, com diversos mercados esportivos e uma área de cassino moderna.
Aproveite essa oferta e entre com o pé direito no
mundo das apostas online.
Накрутить подписчиков в Телеграм вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1174912-kak-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-aktualno Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Wonderful, what a webpage it is! This weblog provides valuable information to us, keep
it up.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4292 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем образовании срочно — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 класс минск https://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4778 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Звоните — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
ставки на спорт прогноз http://www.sportbets26.ru .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4100 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4986 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Можно ли купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Ganhe 100 dólares de bônus ao criar sua conta na winzada 777
e comece apostando com muito mais confiança.
Essa promoção é exclusiva para novos usuários e é ativada
automaticamente após o registro. Com o bônus, você poderá explorar todo o catálogo da casa:
desde apostas esportivas em campeonatos nacionais e internacionais até
jogos de cassino com crupiês ao vivo. Aproveite essa oferta e transforme seu primeiro
acesso em uma chance real de lucro.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1105 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2448 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом документы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге .
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
как купить проведенный диплом отзывы http://arus-diplom31.ru .
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
Корейские сериалы с лучшей музыкой, которые стоит послушать! дорама ленд
Quer começar a apostar com um impulso extra? Na shazam, novos usuários recebem um bônus de
100 dólares assim que finalizam o cadastro. Você pode usar esse valor em diversos tipos de apostas esportivas,
jogos de mesa, slots ou até mesmo roleta
ao vivo. Tudo com segurança, agilidade nos pagamentos e uma interface intuitiva.
A promoção é válida por tempo limitado, então não
perca tempo. Crie sua conta hoje mesmo e aproveite para jogar com vantagem desde
o início.
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://stalker-land.ru/
1с предприятие программа https://kupit-1s21.ru .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
ghostwriter philosophie
Hi, its good piece of writing regarding media print, we all be familiar with media is a fantastic source of information.
https://www.google.cl/url?q=https://premierlimousineservice.net
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске arus-diplom33.ru .
Você está procurando uma casa de apostas que valoriza seus novos jogadores?
Então a moverbet é perfeita para você.
Cadastre-se gratuitamente e receba 100 dólares em bônus para começar sua jornada nas apostas esportivas e no cassino online.
A plataforma oferece suporte ao cliente em português,
métodos de pagamento locais e jogos de alta qualidade.
Seja para apostar em futebol, roleta ou blackjack, você já começa com saldo extra para arriscar com inteligência.
Dragon money Dragon Money – это не просто название, это врата в мир безграничных возможностей и захватывающих азартных приключений. Это не просто платформа, это целая вселенная, где переплетаются традиции вековых казино и новейшие цифровые технологии, создавая уникальный опыт для каждого искателя удачи. В современном мире, где финансовые потоки мчатся со скоростью света, Dragon Money предлагает глоток свежего воздуха – пространство, где правила просты, а возможности безграничны. Здесь каждая ставка – это шанс, каждый спин – это предвкушение победы, а каждый выигрыш – это подтверждение вашей удачи. Но Dragon Money – это не только про выигрыши и джекпоты. Это про сообщество единомышленников, объединенных общим стремлением к риску, азарту и адреналину. Это место, где можно найти новых друзей, поделиться опытом и ощутить неповторимый дух товарищества. Мы твердо верим, что безопасность и честность – это фундамент, на котором строится доверие. Именно поэтому Dragon Money уделяет особое внимание защите данных и обеспечению прозрачности каждой транзакции. Мы стремимся создать максимально комфортную и безопасную среду для наших игроков, где каждый может наслаждаться игрой, не беспокоясь о каких-либо рисках. Dragon Money – это не просто игра. Это возможность испытать себя, проверить свою удачу и почувствовать себя настоящим властелином своей судьбы. Присоединяйтесь к нам, и пусть дракон принесет вам богатство, успех и процветание! Да пребудет с вами удача!
Hello .
Hello. A 18 fantastic website 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this website. There’s a great article there. https://fameblogs.net/lidl-s-legal-battle-against-tesco-over-clubcard-pricing/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
прогнозы на спорт на сегодня бесплатно prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport10.ru .
как купить аттестат за 11 класс как купить аттестат за 11 класс .
https://pcpro100.info/
Having read this I thought it was extremely informative.
I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this
informative article together. I once again find myself
personally spending a lot of time both reading and leaving comments.
But so what, it was still worth it!
купить аттестат 11 классов в калининграде купить аттестат 11 классов в калининграде .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ дешево вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478168-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-deshevo-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1225 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Перейти — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3452 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Можно ли купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4545 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить настоящий диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1465 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите нам — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1229 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Узнать условия — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Hello There. I discovered your blog using
msn. This is an extremely smartly written article. I’ll make sure
to bookmark it and return to read extra of your helpful information. Thank you for
the post. I’ll certainly return.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1462 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом университета — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
прогнозы на спорт на сегодня бесплатно http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru .
купить диплом училища купить диплом училища .
1с стоимость программы https://kupit-1s23.ru .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2817 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить учебный диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
окна rehau москва https://best-stroika.ru .
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
That’s a solid take, this is valuable.
By the way, I visited this page recently: worth a look
Would love to know if anyone tried it.
кайтинг Обучение кайтсёрфингу требует профессионального подхода. Не экономьте на инструкторе, который научит вас основам безопасности и поможет быстро прогрессировать.
точный прогноз на футбол http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol8.ru/ .
https://www.guerzhoy.a2hosted.com/index.php/Gsa_10A базы 2019 года уже не актуальны для современных задач.
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класса в чернушке где можно купить аттестаты 11 класса в чернушке .
купить проведенный диплом в красноярске http://arus-diplom31.ru/ .
blagoustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
аренда яхты марин https://yachts-charter-dubai.com .
World Vision in https://boombam.app/index.php/User:JXWTodd115295902 news highlights humanitarian efforts in war-torn regions.
диплом юриста купить диплом юриста купить .
I just like the helpful information you provide for your articles.
I will bookmark your weblog and take a look at once more here frequently.
I am reasonably certain I will be informed many new stuff proper here!
Best of luck for the next!
купить диплом с занесением реестра купить диплом с занесением реестра .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1046 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2948 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2834 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
как купить легальный диплом о среднем образовании http://www.arus-diplom35.ru/ .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1881 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4782 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На этой странице — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом высшего образования купить диплом высшего образования купить .
автоперевозка автомобилей по россии http://www.avtovoz-av7.ru/ .
TikTok has a restriction system for harmful content and we
need to respect that.
перевозка автомобиля автовозом по россии http://www.avtovoz-av.ru .
zaezd-na-uchastok-cherez-kanavu-495.ru .
우선, 유튜브에서 시청하고 계신 영상을 다운받거나
소장할 영상을 검색해서 들어가 주세요.
Yes! Finally something about remote controll lawn mower.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1259485-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-plyusy-i-minusy Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Lopesan Costa Bavaro Airport Shuttle
The Lopesan Costa Bavaro Airport Shuttle is a private, direct transfer for groups of up to six, ensuring no stops or delays with other passengers.
Distance from Lopesan Costa Bavaro Resort to Punta Cana Airport
How far is Lopesan Costa Bavaro from airport? transportation from punta cana airport to lopesan costa bavaro The Lopesan Costa Bavaro Resort, Spa & Casino is approximately 10.9 miles (18 km) from Punta Cana International Airport (PUJ). The drive typically takes about 17-30 minutes, depending on traffic conditions.
заказать пластиковые окна от производителя недорого http://www.1-stroymarket.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2021 года купить аттестат за 11 класс 2021 года .
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайт школа
заезд на участок через канаву .
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://stalker-land.ru/
аренда вип яхт http://www.yacht-rental-oae.com .
Lopesan Costa Bavaro Airport Shuttle
The Lopesan Costa Bavaro Airport Shuttle punta cana airport to lopesan costa bavaro is a private, direct transfer for groups of up to six, ensuring no stops or delays with other passengers.
Distance from Lopesan Costa Bavaro Resort to Punta Cana Airport
How far is Lopesan Costa Bavaro from airport? The Lopesan Costa Bavaro Resort, Spa & Casino is approximately 10.9 miles (18 km) from Punta Cana International Airport (PUJ). The drive typically takes about 17-30 minutes, depending on traffic conditions.
купить аттестаты за 11 дипломы тумен кипятком купить аттестаты за 11 дипломы тумен кипятком .
можно ли купить аттестат за 10 11 класс можно ли купить аттестат за 10 11 класс .
прогнозы на спорт точные https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej6.ru/ .
Thanks, another article https://tione.ru/gajki-vidy-naznachenie-i-kak-pravilno-vybrat/
Here is another site on the topic https://fishexpo-volga.ru/kupit-okna-v-spb-kachestvenno-vygodno-i-s-garantiej-ot-titan-okna/
Greetings!
Start your sports journey with the 1xbet welcome bonus promo code. It’s designed to help you win from the beginning. Apply the 1xbet welcome bonus promo code on registration. You’ll receive instant balance increases. Start betting with an edge.
All information is available via the link – https://underatexassky.com/pages/2code_promo_163.html
1xbet promo code ghana, 1xbet promo code, 1xbet kode promo indonesia
1xbet promo code sign up bonus, 1xbet promo code ghana, 1xbet kode promo indonesia
Good luck and profitS!
Wow, incredible blog structure! How long have you been running a blog for? you made blogging glance easy. The full look of your website is fantastic, let alone the content material!
порнорассказы
аттестат 11 купить аттестат 11 купить .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал боты вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3107694-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-boty-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
музыка мп3 скачать музыка мп3 скачать .
https://wiki.internzone.net/index.php?title=Benutzer:AdolfoFults Coin sees trading volume increase on exchanges.
Hi every one, here every one is sharing these experience, therefore it’s good to read this blog, and I used to pay a quick visit this weblog daily.
https://toolbarqueries.google.td/url?sa=j&source=web&rct=j&url=https://premierlimousineservice.net
War World 3 https://meta.xuniverse.wiki/w/World_News_6Z often blends speculation with fact, making reliable sources critical.
прогнозы на теннис сегодня от профессионалов бесплатно http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport10.ru .
сколько стоит аренда яхты в дубае yachts-charter-dubai.com .
прогнозы на спорт онлайн prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport9.ru .
I’ve been browsing on-line more than three hours nowadays, yet I never found any fascinating article like yours. It is lovely price enough for me. In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made excellent content as you did, the net might be much more useful than ever before.
скачать популярные треки скачать популярные треки .
вывод средств с мелбет вывод средств с мелбет
купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр .
топ прогнозы на футбол сегодня https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol8.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске .
купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в уфе http://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
диплом купить в твери http://www.arus-diplom7.ru/ .
перевозка автомобилей автовозом по россии https://avtovoz-av7.ru .
zaezd-na-uchastok-cherez-kanavu-495.ru .
1хБет промокод при регистрации используя промокод, вы получите бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт, а также бонус в казино 1500€ и 150 фриспинов. Обратите внимание, что это единственный действующий промокод на данный момент. Также, если вам интересны другие промокоды для 1xBet, вы можете ознакомиться со списком рабочих промокодов на 2025 год. https://videoduel.ru/news/promokod_309.html
1xBet предлагает различные бонусные программы для своих игроков. Среди них есть бонус за регистрацию, бонус за первый депозит, бонус за повторный депозит, бонус за покупку билетов, бонус за пополнение счета, бонус за приглашение друзей и многое другое. Кроме того, игроки могут получать бонусы за активное участие в акциях и конкурсах, которые проводит букмекерская контора. Также игроки имеют возможность получать бонусы за достижение новых уровней в программе лояльности.
доставка авто http://www.avtovoz-av.ru/ .
купить аттестат 11 классов санкт петербург купить аттестат 11 классов санкт петербург .
rx sleeping meds hydrocortisone to prednisone conversion prednisone 5mg buy online side effects after stopping prednisone how do you lower your bad cholesterol
Thanks, another article https://tione.ru/gajki-vidy-naznachenie-i-kak-pravilno-vybrat/
Here is another site on the topic https://fishexpo-volga.ru/kupit-okna-v-spb-kachestvenno-vygodno-i-s-garantiej-ot-titan-okna/
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2390 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На сайте — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4803 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На этой странице — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4343 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Звоните — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Трогательные сюжеты, которые не оставят равнодушными! Смотрите прямо сейчас район сочхо скачать
доставка авто http://avtovoz-av8.ru/ .
ставки на хоккей сегодня прогнозы точные http://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej6.ru .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1311 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом в перми купить диплом в перми купить .
Greetings!
Try your luck with le code promo 1xbet actuel and enjoy bigger wins. This offer is perfect for French-speaking bettors. Le code promo 1xbet actuel increases your balance instantly. It works for both sports and casino games. Use it while it’s still active.
All information is available via the link – https://www.pondexperts.ca/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_codes___bonus_code.html
1xbet promo, 1xbet promo code, 1xbet promo code
1xbet promo code sign up bonus, le code promo 1xbet actuel, 1xbet promo code registration
Good luck and profitS!
What’s Taking place i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found
It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & aid different users like its aided me.
Great job.
музыка скачать на телефон музыка скачать на телефон .
XDC XinFin grows in trade finance solutions.
Also visit my web-site :: https://www.railspark.net/index.php/User:BettieRoepke
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4474 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1хБет промокод при регистрации используя промокод, вы получите бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт, а также бонус в казино 1500€ и 150 фриспинов. Обратите внимание, что это единственный действующий промокод на данный момент. Также, если вам интересны другие промокоды для 1xBet, вы можете ознакомиться со списком рабочих промокодов на 2025 год. https://monument-stone.ru/wp-includes/articles/promokod_309.html/
1xBet предлагает различные бонусные программы для своих игроков. Среди них есть бонус за регистрацию, бонус за первый депозит, бонус за повторный депозит, бонус за покупку билетов, бонус за пополнение счета, бонус за приглашение друзей и многое другое. Кроме того, игроки могут получать бонусы за активное участие в акциях и конкурсах, которые проводит букмекерская контора. Также игроки имеют возможность получать бонусы за достижение новых уровней в программе лояльности.
Дешевые подписчики Телеграм канал вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3145417-deshevye-podpischiki-telegram-kanal-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Генетично модифіковані яйця — це прорив у медицині, дізнайтеся більше про їхнє використання у фармакології.
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайтсёрфинг оборудование: инвестируйте в качество. Кайт, доска, трапеция – основа вашего комфорта и безопасности.
Thank.
Thank.
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
Se você está em busca de um bônus de boas-vindas realmente vantajoso, a https://u1o6x.icu/ tem o que você precisa.
Ao se cadastrar hoje, você recebe 100 dólares para utilizar em apostas
esportivas e jogos de cassino. A promoção é simples de ativar, e o crédito pode ser usado em apostas de futebol,
basquete, tênis e em slots famosos. Com esse incentivo,
sua experiência começa com mais emoção e maiores chances de ganhar logo nas primeiras jogadas.
заезд для машины .
как купить диплом с занесением в реестр в екатеринбурге http://www.arus-diplom31.ru/ .
E28PK9 پر کھیلیں – اسپورٹس بیٹنگ، آن لائن کیسینو اور ریئل کیش گیمز کا جدید پلیٹ فارم۔ تیز رفتار
ڈپازٹ/ویڈرا، محفوظ سسٹم، اور بہترین صارف تجربہ!
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
Here is another site on the topic best spicy books on kindle unlimited
Thanks, another article https://tonersklad.ru/
купить диплом без внесения в реестр купить диплом без внесения в реестр .
купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр .
Advantageous offer https://redclara.net/news/pgs/?code_promo_melbet_pour_l_inscription.html .
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this superb blog!
I guess for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to
my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will talk about
this blog with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
окна рехау москва окна рехау москва .
Heya i am for the primary time here. I came across this board and I
in finding It really helpful & it helped me out much.
I am hoping to offer one thing back and help others such
as you helped me.
vezdnaya-gruppa-na-uchastok-495.ru .
диплом где можно купить диплом где можно купить .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-247.ru .
музыка мр3 музыка мр3 .
где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс .
как получить бонус в мелбет https://www.melbet1034.ru
melbet казино слоты скачать melbet1033.ru
Related article https://fishexpo-volga.ru/kupit-okna-v-spb-kachestvenno-vygodno-i-s-garantiej-ot-titan-okna-2/
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые находятся на территории всей РФ. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат 10 11
погреб на участке под ключ .
ставки на футбол ставки на футбол .
Greetings!
Play risk-free with the 1xbet promo code free bet bonus activated. You can try matches without losing real funds. The 1xbet promo code free bet bonus helps you experiment safely. Try different teams and strategies. Winning without fear is now possible.
All information is available via the link – http://oktabrskiynews.ru/index.php/novosti-oktyabrskogo/5537-jadernyj-vzryv-v-centre-rossii-proizoshedshij-v-2
1xbet promo code sign up bonus, 1xbet registration, 1xbet code
1xbet bonus selamat datang, 1xbet bonus code south africa, 1xbet promo code registration
Good luck and profitS!
мп3 новинки мп3 новинки .
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайтсёрфинг: Танец с ветром и волной. Почувствуйте свободу, скользя по воде под куполом кайта!
диплом купить с проводкой диплом купить с проводкой .
Площадка KRAKEN — это уникальный ресурс, предназначенный для пользователей, ценящих confidentiality и security при совершении сделок в даркнете. Marketplace KRAKEN предоставляет удобный интерфейс, который позволяет быстро находить предметы и совершать покупки, оставаясь при этом анонимным и защищённым от посторонних глаз.
Платформа KRAKEN использует innovative технологии для обеспечения safety данных, а также для того, чтобы гарантировать безопасность каждой транзакции. Сайт использует substitutes для обеспечения стабильного доступа, благодаря чему пользователи могут всегда быть уверены в operability площадки, даже если возникают блокировки.
Для удобства пользователей, KRAKEN предлагает встроенные способы пополнения баланса, включая карты. Пополнение счета и проведение deals становятся максимально простыми и быстрыми, что существенно сокращает время между пополнением и покупкой. Все данные проходят secure processing, что добавляет дополнительный уровень security.
К тому же, KRAKEN имеет помощь, которая работает круглосуточно, чтобы каждый пользователь мог быстро разрешить свои вопросы и проблемы. Это важный аспект для тех, кто впервые решает начать торговать на даркнет-платформе. руководства по регистрации и использованию сайта предоставляются на accessible языке, что делает процесс входа на сайт быстрым и удобным для каждого пользователя.
kraken darknet ссылка
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about
this, like you wrote the book in it or something.
I think that you can do with a few pics to
drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is great blog.
An excellent read. I will certainly be back.
Here is another site on the topic best books on kindle unlimited right now
I have been browsing online more than 4 hours today, yet I never found any interesting
article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me.
Personally, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did,
the net will be much more useful than ever before.
zaezd-na-uchastok-cherez-kanavu-495.ru .
Купить диплом университета поспособствуем. Купить диплом Ульяновск – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-ulyanovsk
прогнозы и ставки на спорт https://www.stavki-na-sport-prognozy1.ru .
Currently it looks like Movable Type is the best blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
http://svetiteni.com.ua/yak-znajty-sklo-fary-na-ridkisnu-model.html
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с отличием arus-diplom25.ru .
1wi. http://1win1140.ru
Curious about is there outdoor dining at chumash casino resort?
Discover everything you need to know with our expert-approved guides.
We focus on fair gameplay, responsible gambling, and secure platforms you can trust.
Our recommendations include casinos with top-rated bonuses, excellent support,
and real player reviews to help you get the most out of every experience.
Whether you’re new or experienced, we make sure you play smarter with real chances
to win and safe environments.
аттестат за 11 класс купить в братске аттестат за 11 класс купить в братске .
домашний интернет тарифы
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk004.ru
домашний интернет челябинск
vezdnaya-gruppa-na-uchastok-495.ru .
Більшість цікавих матеріалів, які я читав останнім часом, виявилися створеними командою з цього проекту.
диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением купить .
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье
1xbet промокоды чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей. Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
Неотложная наркологическая помощь — это существенная часть в поиске решения зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk004.ru вы можете получить сведения о постоянной помощи, которая предлагает необходимую поддержку. Наркологическая служба обеспечивает медицинскую помощь при наркотиках и алкоголизме. Специалисты проводят консультации нарколога, а также обеспечивают лечение без раскрытия личных данных. В рамках кризисной интервенции возможны программы восстановления и стационарное лечение. Эмоциональная поддержка играет ключевую роль в восстановлении после зависимости. Не откладывайте обращение за помощью, измените свою жизнь к лучшему!
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
casino giri? casino giri? .
melbet best game melbet best game
заезд строй .
Advantageous offer https://rotoruanz.ru/pags/kak_uluchshity_svoy_son_01.html .
7 slots 7 slots .
купить аттестат за 11 класс во владимире купить аттестат за 11 класс во владимире .
купить аттестаты за 11 классов во владивостоке купить аттестаты за 11 классов во владивостоке .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-247.ru .
Thank.
Thank.
Капельница от запоя на дому в Красноярске – это доступный способ помощи с алкоголизмом. Многие люди страдают от периодов запойного пьянстваи медицинская помощь становится необходимостью. Лечение с помощью капельниц способствует в детоксикации организма, облегчая симптомы абстиненции. Специализированные услуги нарколога включают не только инфузионные процедуры, но и реабилитацию от алкоголячто важно для возвращения к нормальной жизни. Роль семьи является важной в этом процессе. Профилактика запойного состояния также важна для избежания рецидивов. Обращайтесь к профессиональному подходу на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk004.ru и получите помощь специалиста на дому.
Ivanka – це команда, яка знає, як зробити кожен виступ особливим. Їхній виступ на Trance Illusion вразив мене до глибини душі. Візуальні ефекти PJ Alice додавали музиці об’єму, а світлові шоу PJ Mia робили кожен трек незабутнім. Сценічні дизайни PJ Zoe гармонійно доповнювали атмосферу і створювали відчуття, що ти знаходишся у центрі чогось надзвичайного. Це був досвід, який я буду згадувати ще довго. Більше інформації про команду можна знайти на їхньому сайті.
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an extremely long comment but after I clicked submit
my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again.
Anyhow, just wanted to say great blog!
casino giri? casino giri? .
7 slots https://candy-casino-7.com .
перевозка легковых автомобилей автовозом http://www.avtovoz-av8.ru .
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, которые находятся в любом регионе России. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 классов в сочи
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье
промокоды 1хбет на ставку сегодня бесплатную чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей. Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
Related article https://tione.ru/
Платная наркологическая помощь, это важный этап в лечении зависимости. В наркологической клинике, такой как vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk005.ru, пациентам предоставляется профессиональная помощь, включая помощь при наркомании и алкоголизме. Процесс реабилитации включает детоксикационные процедуры и психологическую поддержку. Обсуждение с наркологом позволяет определить оптимальный курс лечения к каждому случаю. Клиники предлагают анонимную помощь и помощь в кризисных ситуациях. Семейная поддержка также имеет огромное значение. Групповые занятия помогают поддерживать друг друга, а медицинское наблюдение обеспечивает комфортное восстановление. Платные услуги позволяют обеспечивать высокий уровень лечения и индивидуальный подход врачей, что увеличивает шансы на успешное восстановление.
скачать мр3 скачать мр3 .
discover here
sky kingdom aviation
Купить диплом под заказ вы сможете используя сайт компании. cittamondoagency.it/employer/diploms-goznak
Good day lucky players!
Use 1xbet free promo code for easy access to betting without payment. Enjoy games risk-free with this special offer. The 1xbet free promo code works instantly. Try out different categories today. No deposit, no worries.
All information is available via the link – http://www.100bestbooks.ru/quizz/pgs/pokerdom_promokod_pri_registracii_na_segodnya.html
1xbet promo code ghana, 1xbet promo code registration, 1xbet promo code today
1xbet bonus code south africa, le code promo 1xbet actuel, 1xbet promo code ghana
Good luck and profitS!
купить диплом в ноябрьске купить диплом в ноябрьске .
дженерик сиалис 40мг с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
directory sky kingdom aviation
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your web site in internet explorer, may check this?
IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a big component to other people
will miss your magnificent writing because of this problem.
купить диплом с проводкой моего купить диплом с проводкой моего .
888 starz sri lanka http://kingbaowow.com .
купить аттестат 11 классов 2012 купить аттестат 11 классов 2012 .
Алкогольная зависимость — это значительная беда, затрагивающая не только самого алкоголика, но и его близких. Как убедить человека покинуть запой? Прежде всего, важно понимать, что семейная поддержка играет важнейшую роль в процессе преодоления зависимости. Нарколог на дом Красноярск Начинать стоит с консультации профессионала. Нарколог на дом в Красноярске может предоставить медицинскую помощь на дому, чтобы снизить страдания пациента. Не менее важна психологическая поддержка: она поможет понять причины алкогольной зависимости и найти способы ее решения. Рекомендации для выхода из запойного состояния включают в себя формирование обстановки, способствующей мотивации, где человек ощущает заботу и поддержку. Обсуждение кризиса в семье и важности единства может стать толчком к размышлениям о необходимости лечения. Лечение запоя и реабилитация помогут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к нормальной жизни. Важно помнить о признаках запойного состояния и быть готовыми к трудностям. Мотивация к лечению — это совместный процесс, который требует времени и усилий. Поддерживайте своего близкого, показывайте, как вы хотите ему помочь, и совместно пройдите путь к выздоровлению.
888 starz login http://www.starz888.pro .
электрокарнизы купить в москве электрокарнизы купить в москве .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр краснодар купить диплом с занесением в реестр краснодар .
купить аттестат за 10 11 класс школы купить аттестат за 10 11 класс школы .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
купить аттестат за 11 класс саратов http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
где купить аттестат за 11 кл arus-diplom9.ru – где купить аттестат за 11 кл .
купить диплом легальный купить диплом легальный .
Лечение запоя в Красноярске – это необходимая мера, где важно не упустить момент. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk006.ru вы найдете предложения наркологической помощи, предлагающих наркологическую помощь. Важно помнить, что борьба с алкоголизмом требует не только физическая терапия, но и психологические сеансы, реабилитационные программы. Обращение к специалисту поможет составить индивидуальный план терапии. Иногда необходимо экстренное лечение при алкогольной интоксикации, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий. Методы кодирования – одна из работающих стратегий, способствующих тому, чтобы человек выбрал трезвый образ жизни. Роль близких играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. После лечения необходима помощь в социальной реинтеграции. Не забывайте о здоровье и не стесняйтесь обращаться к врачам!
Любите известные K-POP группы – обязательно смотрите doramaland
диплом купить с внесением в реестр диплом купить с внесением в реестр .
диплом купить с занесением в реестр челябинск https://www.arus-diplom34.ru .
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after looking at a few
of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m certainly happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and
checking back often!
купить аттестат за 11 класс в иваново купить аттестат за 11 класс в иваново .
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
casinocandy http://candy-casino-2.com .
Here is another site on the topic best kindle unlimited books 2024
I do not even know how I ended up right here, but I believed this publish was once good.
I don’t recognise who you’re but certainly you’re going
to a famous blogger if you happen to are not already.
Cheers!
casino bahis casino bahis .
обучение кайтсёрфингу “От теории к практике”: обучение кайтсерфингу, включающее изучение метеорологии, аэродинамики, правил безопасности и техник самоспасения, позволяющее стать уверенным и независимым кайтсерфером.
Article writing is also a fun, if you know after that
you can write otherwise it is complex to write.
Hi every one, here every person is sharing these kinds of knowledge,
thus it’s good to read this website, and I used to pay a visit this website all the time.
cum se joaca ruleta http://www.1win40001.ru
Merhaba, bahis sevdal?lar?!
Kripto yat?r?m? yap
ve hemen Mega Hos Geldin paketini kap.
Cevrim yaln?zca on kat – maksimum ozgurluk.
Belgeler istenmez, cekim 10 dk icinde.
Daha ne bekliyorsun? Kazanma sans? yan?nda.
—
En iyi xturka giris
изготовление лестниц на заказ в москве https://lestnicy-na-metallokarkase-1.ru/ .
casinocandy https://www.candy-casino-4.com .
унитаз алина байкова http://www.evropejskaya-santehnika.ru/ .
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2006 года http://www.arus-diplom21.ru/ .
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом в Санкт-Петербурге (СПБ) — kyc-diplom.com/geography/spb.html
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класса в чернушке где можно купить аттестаты 11 класса в чернушке .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4884 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4338 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Вражений, як професійно вони підходять до роботи. Читаю їхні матеріали постійно!
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa? My website discusses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
spincity casino
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4187 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Прочитать — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
lucky jet телеграмм lucky jet телеграмм
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1648 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Обращайтесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1045 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить проведенный диплом моих купить проведенный диплом моих .
Related article https://tione.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk007.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
кайт школа Кайт лагерь
Накрутить подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1175060-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-principy Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Вызов наркологической помощи в Красноярске — необходимая мера, помогающая людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Клиника наркологии в Красноярске предлагает широкий спектр услуг, среди которых лечение зависимостей и помощь при алкоголизме. Если вы или ваши родные столкнулись с проблемой зависимости, стоит рассмотреть возможность вызова нарколога.Консультация нарколога является важным шагом на пути к исцелению. Наши специалисты предлагают анонимные услуги, что позволяет избежать стигматизации и обеспечить комфортные условия для пациента. Круглосуточная служба поддержки готова ответить на все вопросы и оказать скорейшую помощь при отравлении. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk006.ru Процесс реабилитации для зависимых включает программы по лечению зависимостей и психотерапевтические методики. Услуги по вызову врача-нарколога доступны в любое время, что делает процесс лечения максимально удобным. Не стесняйтесь и не откладывайте помощь, ведь здоровье — это главное.
casino candy casino candy .
I recommend the site https://www.actuabd.com .
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
аттестат 11 классов купить москва
Simply desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is simply excellent and
i could assume you’re an expert on this subject.
Fine with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to
date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the enjoyable work.
Купить диплом под заказ вы имеете возможность используя официальный портал компании. metalfans.maxbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=1243&sid=ab769d25a51c7aa68a8411611a838a92
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
vermox online buy
https://dtf.ru/id2915936/3931207-promt-dlya-sozdaniya-patcha-iz-kartinki-dlya-odezhdy
Merhaba, bahis sevdal?lar?!
Ethereum’la odeme yap
ve an?nda %50 slot bonusunu kap.
Cevrim yaln?zca on kat – maksimum ozgurluk.
Belgeler istenmez, withdraw 10 dk icinde.
Daha ne bekliyorsun? Sans yan?nda.
—
Mobil uyumlu xturka
I think this is among the most vital info for me. And i’m glad reading your article.
But should remark on few general things, The site style is wonderful, the articles is really
great : D. Good job, cheers
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk008.ru
вывод из запоя
аттестат 11 класса купить 2015 аттестат 11 класса купить 2015 .
обучение кайтсёрфингу “Египетские грезы”: Хургада, Дахаб, где “солнце целует волны”
vezdnaya-gruppa-na-uchastok-495.ru .
промокод мелбет https://melbet1031.ru
Greetings all!
The psychology of online gaming reveals how players seek immersion and emotional engagement in virtual worlds. Why people play online games varies, but it often stems from the need for excitement, connection, and challenge. Seasonal eating provides benefits like improved immune function when aligning your diet with the rhythms of nature. Digital games influence relationships by allowing people to build connections through shared gaming experiences. Time management for business leaders is essential for keeping projects on track and ensuring successful outcomes.
More information here – https://hello-jobs.com
benefits of volunteering abroad
mindfulness practices through travel
self-discovery through spiritual travel
impact of online games on social connections
Good luck!
диплом купить в реестре диплом купить в реестре .
I recommend the site https://imagecms.net .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk007.ru
лечение запоя
zaezd-na-uchastok-cherez-kanavu-495.ru .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-247.ru .
где лучше купить аттестат за 11 класс где лучше купить аттестат за 11 класс .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2988 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом сколько стоит — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3451 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом сколько стоит — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1555 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом университета — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2635 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где купить диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4578 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите нам — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат 11 классов отзывы купить аттестат 11 классов отзывы .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2161 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3342 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Продажа дипломов — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
candy casino https://candy-casino-2.com/ .
https://t.me/wine_it
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
аттестат с отличием 11 класс купить аттестат с отличием 11 класс купить .
Thank.
Crazy Time লাইভ বাংলাদেশ: অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম খেলুন – রিয়েল টাইম এক্সাইটমেন্ট উপভোগ করুন, দারুন বোনাস
ও পুরস্কার নিয়ে ঘুরে দাঁড়ান এখনই!
3d печать Лазерная резка обеспечивает высочайшую точность и качество обработки материалов. Этот метод идеально подходит для создания сложных деталей, гравировки и маркировки. От тонких пленок до толстых металлических листов, лазерная резка справляется с задачами любой сложности.
купить аттестат 11 класса 2015 года купить аттестат 11 класса 2015 года .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk009.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
купить аттестат в екатеринбурге купить аттестат в екатеринбурге .
vezdnaya-gruppa-na-uchastok-495.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск .
кредиты банков на автомобиль кредиты банков на автомобиль .
кредитная карта без комиссии кредитная карта без комиссии .
BONK https://paintingsofdecay.net/index.php/User:TristaBottoms spikes with Solana ecosystem growth.
кайт Разнообразие стилей кайтсёрфинга удовлетворит любой вкус. Фристайл, фрирайд, вейврайдинг, кайт-рейсинг – попробуйте все и найдите то, что вам больше всего нравится.
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
где купить пластиковый погреб .
Here is another site on the topic best books on kindle unlimited right now
винлайн какие бонусы http://www.winline-fribet-za-registraciyu-2025.ru .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
купить варфейс Отличный выбор для покупок! Я купил аккаунт варфейс и рад результату.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
промокод винлайн на сегодня 2025 фрибеты besplatnyj-fribet-winline.ru .
диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный купить .
888starz connexion https://888starzz.site/ .
проститутки индивидуалки донецк “Проститутки ДНР” – это проблема, требующая комплексного решения, включающего экономическую поддержку, программы реабилитации и борьбу с торговлей людьми.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2195 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2146 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
what is a replica bag – where is central perk cafe in new york
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4229 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом сколько стоит — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
в якутске купить аттестат за 11 класс в якутске купить аттестат за 11 класс .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2684 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
candycasino http://candy-casino-7.com/ .
можно ли купить аттестат за 10 11 класс можно ли купить аттестат за 10 11 класс .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1310 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
What i do not understood is actually how you are not really
much more neatly-preferred than you might be right now.
You’re so intelligent. You know therefore considerably in relation to this topic, produced me
for my part imagine it from so many varied angles.
Its like women and men aren’t fascinated until it is one thing to
accomplish with Woman gaga! Your individual stuffs outstanding.
All the time deal with it up!
Escape the Limits – Explore Non GamStop Casinos!
Tired of restrictions? Discover a world of unlimited gaming possibilities at our Non GamStop Casinos.
What we offer:
– Unrestricted access to top games
– Generous welcome bonuses
– Lightning-fast payouts
– 24/7 customer support
– Secure & fair gaming environment
Join thousands of satisfied players who have already found their perfect gaming experience. No GamStop limitations mean endless fun and excitement!
Claim your bonus now and start playing at the best Non GamStop Casinos today! ??
https://vaishakbelle.com/
#NonGamStopCasinos #OnlineGaming #CasinoBonus
Hello!
The psychology of online gaming explores the connection between emotional rewards, social engagement, and competition that keep players involved. Why people play online games is often driven by the excitement of competition, the desire for achievement, and social interaction. Seasonal eating provides benefits like stronger immunity, improved digestion, and more energy by eating foods that align with the seasons. The influence of online games on relationships is substantial, creating opportunities for communication and long-lasting connections. Time management for business leaders is vital for balancing professional and personal responsibilities while maximizing productivity.
More information here – https://eguidemagazine.com
volunteering to enhance travel experiences
trends in gaming psychology
exploring spiritual growth through travel
mentoring millennials in the workplace
Good luck!
кайт Кайтсёрфинг видео: вдохновение и обучение. Смотрите видеоролики с лучшими кайтсёрферами мира.
When I originally left a comment I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I get four emails with the exact same comment.
There has to be a means you are able to remove me from
that service? Kudos!
купить аттестат за 11 класс саратов http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
ванна джакузи с гидромассажем hidromassazhnaya-vanna2.ru .
mostbet mobile http://mostbet4079.ru/
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2000 года https://arus-diplom25.ru/ .
I read this piece of writing fully concerning the comparison of hottest and preceding technologies,
it’s remarkable article.
vezd-na-uchastok-pod-klyuch-495.ru .
фрибеты winline на сегодня бесплатно https://winline-fribet-kazhdyj-den.ru/ .
Це правда, що Як працює гравітація впливає навіть на хід часу? Хотілося б дізнатися більше!
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайт: Крыло, подчиняющее стихию, инструмент для покорения водной глади. Выбор кайта – это компромисс между мощностью, управляемостью и ветровыми условиями.
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it,
you’re a great author.I will be sure to bookmark your blog and will
eventually come back someday. I want to encourage you to
definitely continue your great writing, have a nice weekend!
“Selamlar!
Gates of Olympus slotunu ucretsiz denedin mi?
?? Zeus ile kazanc patlamas? yasa!
? slot gates of olympus
?? Hemen oyna: olimpiyagates.com
?? Pragmatic Play kalitesiyle yuksek RTP, 5000x’e kadar max win sans?.
?? VPN gerekmez, mobil destekli, h?zl? kay?t.
Bol sans!”
Excellent site you have here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like
yours these days. I really appreciate people like you!
Take care!!
винлайн фрибеты за регистрацию http://winline-fribet-novym-klientam.ru .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk009.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
аттестат за 11 класс купить пермь аттестат за 11 класс купить пермь .
vezd-na-uchastok-pod-klyuch-495.ru .
как скачать музыку на телефон как скачать музыку на телефон .
I recommend the site https://ville-barentin.fr
магазин итальянской сантехники http://gessi-santehnika-3.ru/ .
It’s remarkable designed for me to have a web site, which is beneficial for my experience. thanks admin
order doxycycline 100mg
http://chery-russia.ru/ – ваш надежный партнер. Мы предлагаем лучшие условия покупки и профессиональное обслуживание.
First off I would like to say wonderful blog! I had a quick question which I’d like to ask if you do not mind.
I was interested to find out how you center yourself and clear your thoughts before writing.
I have had a difficult time clearing my mind in getting my thoughts out there.
I truly do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are generally wasted
just trying to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or hints?
Kudos!
Here is another site on the topic best books on kindle unlimited
kraken onion – кракен даркнет тор, kraken onion market
кайт “Маврикий – мечта”: Ле Морн: кайтсерфинг на Маврикии
актуальная ссылка на кракен – вход на кракен сайт, рабочая кракен ссылка
купить пластиковые окна купить пластиковые окна .
кракен маркет даркнет – кракен даркнет ссылка, кракен маркет даркнет
кракен онион – вход на кракен зеркало, кракен зеркало
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
Related article https://tione.ru/
https://cdacollaborative.org
сколько стоит кондиционер используем только новое оборудование соответствующее гост и iso
Выбирайте системы кондиционирования в нашем интернет-магазине от надежных брендов. Современные сплит-системы для офиса. Создайте комфортный климат с передовыми технологиями.
сплит система кондиционирования для квартиры купить используем только новое оборудование соответствующее гост и iso
аттестат школы купить аттестат школы купить .
“Merhaba!
? Pragmatic Play’in buyulu oyunu **Starlight Princess** simdi yay?nda!
?? Is?klar icinde carpanlar, prensesle max win!
? starlight princess demo
?? Hemen basla: starlightprenses.com
?? Mobil uyumlu, VPN gerekmez, h?zl? kay?t ve an?nda oyun keyfi.
Hemen oyna!”
купить официальный диплом о среднем образовании купить официальный диплом о среднем образовании .
https://www.europneus.es
обучение кайтсёрфингу “Путь к свободе”: обучение, как открытие себя, преодоление сомнений, рождение крыльев
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
muzika mp3 muzika mp3 .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-247.ru .
I recommend the site https://astra-hotel.ch
Накрутить живых подписчиков в ТГ канал вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3103319-nakrutit-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
vezdnaya-gruppa-na-uchastok-495.ru .
vezd-na-uchastok-pod-klyuch-495.ru .
https://www.businesslist.pk
https://cour-interieure.fr
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1973 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Продажа дипломов о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4809 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом бакалавра купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1981 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем специальном — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
игровые пк москва kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter8.ru .
как купить легальный диплом https://www.arus-diplom32.ru .
игровые пк игровые пк .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3467 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
скачать музыку mp3 бесплатно скачать музыку mp3 бесплатно .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2672 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На сайте — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
https://new-time.kiev.ua/images/pages/?1xbet_promokod___bonus_pri_registracii.html
mobila de lemn la comanda https://1win40002.ru/
заказать окна в москве заказать окна в москве .
кайт лагерь Кайтсёрфинг трюки: от простого к сложному. Освойте базовые трюки и двигайтесь к новым высотам.
“Merhaba slot severler!
?? Yepyeni Pragmatic oyunu **Sugar Rush 1000** yay?nda!
?? Demo denemek icin simdi t?kla: sugar1000turkiye.com
? slot launch sugar rush 1000
?? Daha yuksek carpanlar, daha fazla seker ve daha cok kazanc seni bekliyor!
?? Mobil uyumlu, kay?t gerekmez, direkt basla.
Hemen dene!”
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4940 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
I recommend the site ps://wildlife.by/ .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
You actually make it appear so easy along with your presentation however I in finding this matter to be really one
thing which I think I’d by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely extensive for me.
I am having a look forward in your subsequent post, I’ll try to get the grasp of it!
Фантастические сериалы с крутой графикой, глаз не оторвать.
http://buch.christophgerber.ch/index.php?title=Ruseriya_88G
Good day!
The psychology of online gaming shows how competition, social bonds, and emotional rewards play a key role in player engagement. Why people play online games is often linked to the excitement of competition, the joy of achievement, and the opportunity to connect with others. Seasonal eating provides health benefits such as improved digestion, stronger immunity, and enhanced energy levels by eating seasonal foods. The impact of online games on relationships is significant, as they create opportunities for communication, teamwork, and social bonding. Time management for business leaders is necessary for balancing professional duties with personal well-being.
More information here – https://www.businesslist.pk
fostering connections through online gaming,challenges in gig economy careers,reasons to try voluntourism
creating bonds through gaming,strategies for leading remote teams,essential travel tips for spiritual growth
Good luck!
кайт школа Страховка в кайтсёрфинге: будьте готовы к неожиданностям. Защитите себя от финансовых потерь.
кракен даркнет ссылка – кракен официальный сайт, кракен актуальная ссылка
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
сколько стоит аттестата 11 класс купить новосибирск
купить аттестат за 11 классов киев купить аттестат за 11 классов киев .
купить аттестат за 11 класс саратов http://www.arus-diplom21.ru/ .
Revolutionary new supplements designed for powerful ecstasies – enhanced combined with more strong pleasures!
First-of-its-kind discovery – cutting-edge advancements within scientific science!
Entirely risk-free and exceptionally potent – boosts libido along with boosts erection firmness!
Boost your ejaculation volume instantly!
winline промокод на фрибет 2025 winlayne-fribet.ru .
Триллеры с неожиданными развязками, держат в напряжении.
http://youtools.pt/mw/index.php?title=User:FayeHoffmann50
I recommend the site http://otolar-centre.ru/ .
временный заезд на участок .
Добавить подписчиков в Телеграм канал вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1174811-kak-dobavit-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-aktualno-na-iyul Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Комедии для компании друзей, смех гарантирован.
https://championsleage.review/wiki/User:VadaRussell601
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы .
заказать трансляцию конференции https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu6.ru .
viagra livraison rapide achat viagra
1хБет промокод при регистрации используя промокод, вы получите бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт, а также бонус в казино 1500€ и 150 фриспинов. Обратите внимание, что это единственный действующий промокод на данный момент. Также, если вам интересны другие промокоды для 1xBet, вы можете ознакомиться со списком рабочих промокодов на 2025 год. https://100bestalbums.ru/include/pages/promokod_309.html
1xBet предлагает различные бонусные программы для своих игроков. Среди них есть бонус за регистрацию, бонус за первый депозит, бонус за повторный депозит, бонус за покупку билетов, бонус за пополнение счета, бонус за приглашение друзей и многое другое. Кроме того, игроки могут получать бонусы за активное участие в акциях и конкурсах, которые проводит букмекерская контора. Также игроки имеют возможность получать бонусы за достижение новых уровней в программе лояльности.
кайт школа Кайт школа
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
диплом купить с занесением в реестр диплом купить с занесением в реестр .
“Merhaba!
Big Bass Bonanza slotunu ucretsiz denedin mi?
?? Bal?klar? yakala, buyuk odulleri topla!
? big bass bonanza guvenilir site
?? Hemen oyna: bigbassbalik.com
?? Pragmatic Play kalitesi, yuksek RTP ve buyuk kazanma sans?.
?? VPN’siz giris, mobil destekli, h?zl? kay?t.
Bol sans!”
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по выгодным ценам— studentklass.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
подключить домашний интернет в челябинске
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
лучший интернет провайдер челябинск
кракен актуальная ссылка – ссылка на кракен даркнет, кракен onion
кракен актуальная ссылка – актуальная ссылка на кракен даркнет, kraken darknet ссылка
интернет провайдеры челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет в челябинске
въезд на участок под ключ .
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя
кайтсёрфинг “Маврикий – мечта”: Ле Морн: кайтсерфинг на Маврикии
https://novamed-bielsko.pl/casinos-mit-den-besten-vip-programmen-fur-high-2/
купить игровой компьютер в москве http://www.kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter8.ru/ .
kraken darknet ссылка – ссылка на кракен даркнет, кракен маркет даркнет
бесплатный фрибет winline бесплатный фрибет winline .
Люблю мультсериалы, на сайте нашел все сезоны любимых аниме.
https://guestpost24.site/marketing/ruseriya-35f/
купить аттестат за 11 классов в новосибирске https://arus-diplom24.ru .
кракен darknet – актуальная ссылка на кракен, kraken зеркало
винлайн какие акции winline-fribet-kazhdyj-den.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Заказать диплом возможно через сайт компании. vazcor-rural.com/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-223
Here is another site on the topic best books to read on kindle unlimited
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
купить пластмассовый погреб .
въезд через канаву на участок .
почему нет фрибета винлайн почему нет фрибета винлайн .
обучение кайтсёрфингу Кайт лагерь: Незабываемый отдых для любителей экстрима. Погрузитесь в атмосферу кайтинга, общайтесь с единомышленниками и совершенствуйте свои навыки.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Heya exceptional blog! Does running a blog like this take a massive amount work? I’ve virtually no knowledge of computer programming however I had been hoping to start my own blog in the near future. Anyhow, if you have any suggestions or techniques for new blog owners please share. I know this is off subject but I simply needed to ask. Thank you!
https://cse.google.ee/url?sa=t&url=https://premierlimousineservice.net
недорогой интернет челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет в квартиру челябинск
домашний интернет тарифы челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет
“Selamlar!
?? Yeni versiyon: Sweet Bonanza 1000 slotu yay?nda!
?? Daha fazla carpan, daha yuksek kazanc seni bekliyor.
? sweet bonanza 1000 guvenilir site
?? Hemen oyna: sweetbonanza1000net.com
?? Pragmatic Play fark?yla %100 eglence ve max win sans?!
?? Mobil uyumlu, VPN gerekmez, h?zl? kay?t imkan?.
Bol kazanclar!”
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
vezd-na-uchastok-pod-klyuch-495.ru .
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Hello!
In the psychology of online gaming, players engage in digital worlds that offer both challenge and reward, creating a sense of accomplishment. Why people play online games varies but is often linked to the need for connection, fun, and mental stimulation. The benefits of seasonal eating include improved health and vitality, especially when aligning diet with the changing seasons. Online games have a profound influence on relationships, creating new forms of social connection and communication. Time management for business leaders is crucial in maintaining focus and increasing overall productivity in fast-paced environments.
More information here – https://tennews.in
strategies for leading remote teams,tips for successful voluntourism,understanding the psychology of gamers
aligning diet with seasons,psychology of video game addiction,best practices for online gaming
Good luck!
Thanks for the article – https://krylslova.ru/
пластиковые подвалы и погреба .
заезд для машины .
Here is another site on the topic https://kreativ-didaktika.ru/
стоимость онлайн трансляции на мероприятии http://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu7.ru .
пк игровой http://www.kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter10.ru/ .
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
I recommend the site https://church-bench.ru/zapishites-v-klub-po-figurnomu-kataniyu-sozvezdie-otkrojte-mir-sporta-i-udovolstviya/
https://portaldozacarias.com.br
диплом купить в тюмени http://www.arus-diplom8.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в кемерово https://www.arus-diplom35.ru .
сколько стоит игровой компьютер сколько стоит игровой компьютер .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar008.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
туры 2025
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр .
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar008.ru
вывод из запоя
современные хиты скачать бесплатно mp3 все песни в хорошем качестве современные хиты скачать бесплатно mp3 все песни в хорошем качестве .
Живая накрутка ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1259243-zhivaya-nakrutka-tg-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-moya-instrukciya Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Thanks for the article – https://church-bench.ru/
Преподаватели центра всегда на связи, спасибо за поддержку.
https://wiki.internzone.net/index.php?title=Bezopasnost_40b
Виды и сорта пшеницы агрору: АгроРу: информационный портал для аграриев, будьте в курсе последних новостей и аналитики.
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Here is another site on the topic https://kreativ-didaktika.ru/
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
I recommend the site https://church-bench.ru/zapishites-v-klub-po-figurnomu-kataniyu-sozvezdie-otkrojte-mir-sporta-i-udovolstviya/
Рекомендую статью https://graph.org/Otdyh-v-Tulskoj-oblasti-s-bassejnom-idealnoe-mesto-dlya-rasslableniya-i-vosstanovleniya-sil-08-03
Рекомендую статью https://graph.org/Luchshie-sposoby-vybrat-otel-v-Minske-gid-po-komfortnomu-otdyhu-08-03
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Рекомендую статью https://graph.org/Otdyh-v-Tulskoj-oblasti-s-bassejnom-idealnoe-mesto-dlya-rasslableniya-i-vosstanovleniya-sil-08-03
Рекомендую статью https://graph.org/Luchshie-sposoby-vybrat-otel-v-Minske-gid-po-komfortnomu-otdyhu-08-03
Любите пекти тістечка? Ознайомтесь із рецептами на нашому сайті.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
https://bs2-bs2site.at
Покрытие интернета в Москве: как проверить доступность онлайн В современном мире доступ к интернету стал неотъемлемой частью жизни. В Москве существует множество интернет-провайдеров, но перед подключением стоит убедиться в доступности интернета в вашем районе. Для этого существуют онлайн-карты, которые показывают покрытие сети и скорость интернета. Важно учитывать отзывы о провайдерах, чтобы получить информацию о стабильности соединения и качестве их услуг. Существует множество тарифов на интернет, поэтому необходимо выбрать наиболее подходящий для домашнего или мобильного использования; подключить интернет москва Не забудьте узнать условия подключения и наличие технической поддержки у выбранного вами провайдера. Проверка подключения поможет избежать неприятных сюрпризов. Пользуйтесь онлайн-картами для выбора наилучшего варианта для своей wi-fi сети, чтобы обеспечить надежный интернет в Москве.
Купить диплом института!
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по доступным ценам— guruguard.ru
погреб пвх .
obustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
mobila casa rusu mobila casa rusu
drenazh-vokrug-doma-811.ru .
Как выбрать роутер для интернета в Москве — важный шаг для обеспечения стабильного соединения и высокой скорости интернета. Прежде чем определиться с моделью, следует рассмотреть ряд важных аспектов. Первое, что нужно сделать, это проверить подключенные провайдеры по адресу Москва. Разные провайдеры могут использовать разные технологии подключения, которые определяют, какой роутер вам нужен. Например, если вы используете оптоволокно, вам понадобится мощный Wi-Fi маршрутизатор, способный обеспечить высокую скорость передачи данных. При выборе интернет-роутера стоит приглядеться к характеристикам: скорость передачи данных, количество антенн, диапазоны частот (2.4 GHz и 5 GHz) и поддержку технологий Wi-Fi. Советы по выбору роутера также включают понимание потребностей вашей домашней сети. Если у вас множество подключенных устройств, выбирайте роутеры с поддержкой MU-MIMO для повышения производительности. Сравнение роутеров поможет найти оптимальный вариант, который гарантирует надежное интернет-соединение в вашем доме. Не пренебрегайте настройками и безопасностью. Выбор правильного маршрутизатора значительно улучшит качество вашего подключения к интернету.
Look into my blog: https://wiki.apeconsulting.co.uk/index.php/User:AlvaroHomer9828
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-msk006.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр владивосток http://www.arus-diplom35.ru/ .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс 2021 цена купить аттестаты за 11 класс 2021 цена .
как купить аттестат 11 классов как купить аттестат 11 классов .
купить аттестат за 10 11 класс цена купить аттестат за 10 11 класс цена .
диплом реестр купить диплом реестр купить .
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-msk006.ru
дом престарелых
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, которые находятся на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом университета:
купить в москве аттестат за 11 класс
купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва .
Женский журнал http://ksusha.online .
Extra resources https://sollet-wallet.io/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Сайт Трипскан В цифровом калейдоскопе, где каждая платформа стремится привлечь внимание, Tripscan выделяется своей уникальной атмосферой и инновационным подходом к развлечениям. Это не просто место для игр; это сообщество, где азарт и технологии переплетаются, создавая неповторимый опыт.
Great work! This is the type of info that should be shared across
the web. Disgrace on the search engines for now not
positioning this publish upper! Come on over and
consult with my site . Thank you =)
chiken road play
обложка аттестата за 11 класс купить https://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
скачать песню на телефон скачать песню на телефон .
купить аттестат 11 классов в ставрополе arus-diplom24.ru .
Трипскан ссылка Tripscan: Зеркало Tripscan: надежный доступ к сервису, когда основной сайт недоступен. Ваше путешествие не должно сорваться!
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1850 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Приобрести диплом можно через сайт компании. bbs.heyshell.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=59774&extra=
КРАКЕН ДАРКНЕТ ОФИЦИАЛЬНАЯ ССЫЛКА 2025
СЕГОДНЯ АКТУАЛЬНАЯ ССЫЛКА: krak2025 .live
—
ПОИСКОВЫЕ ЗАПРОСЫ:
кракен darknet официальный сайт, кракен даркнет шоп, кракен даркнет зеркало мориарти, кракен маркетплейс зеркало, кракен тор браузер, кракен зеркало 2025, кракен сайт онион
—
интернет по адресу дома
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу нижний новгород
где купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс где купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс .
диплом официально купить диплом официально купить .
Трипскан Tripscan Трипскан Трипскан вход Сайт Трипскан Tripscan top Трипскан сайт вход Tripscan войти Tripscan win Tripscan личный кабинет Tripskan Tripscan зеркало Tripscan вход Tripscan cc Tripscan id Трипскан топ Трипскан ссылка Трипскан зеркало Трипскан вин
провайдеры нижний новгород
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
https://b2best.at
Trump hints at https://www.fonse.cn/question/crypto-news-43d/-friendly policies in recent speech.
Сайт Трипскан “Трипскан вход” – это как волшебный ключ, открывающий двери в мир безграничных возможностей. Здесь каждый может найти что-то по душе, будь то захватывающие стратегии или динамичные слоты. “Сайт Трипскан” разработан с учетом потребностей пользователей, предлагая интуитивно понятный интерфейс и безопасную среду.
I recommend best promo code 1xbet tj
Thank.
пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-tula004.ru
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
The book News of the World by Paulette Jiles offers a historical lens, contrasting modern war http://taxwiki.us/index.php/World_News_93A cycles.
скачать бесплатно mp3 скачать бесплатно mp3 .
look at these guys Lumiwallet
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula004.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в туле
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом купить диплом образование купить проведенный диплом .
Свекровь и невестка: https://boombam.app/index.php/User:BernardLechuga отношений требует границ.
Приобрести диплом об образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по выгодным тарифам— diplom-toglyatti.ru
코인선물거래소
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Cheers!
Where are your contact details though?
plastikovyy-pogreb-812.ru .
Getting it censure, like a well-wishing would should
So, how does Tencent’s AI benchmark work? Maiden, an AI is prearranged a creative m‚tier from a catalogue of fully 1,800 challenges, from initiate materials visualisations and интернет apps to making interactive mini-games.
Post-haste the AI generates the jus civile ‘apropos law’, ArtifactsBench gets to work. It automatically builds and runs the jus gentium ‘спрэд law’ in a bolt and sandboxed environment.
To over how the haunt behaves, it captures a series of screenshots ended time. This allows it to unique in seeking things like animations, boondocks область changes after a button click, and other persuasive benumb feedback.
In the bounds, it hands greater than all this certification – the starting at if yet, the AI’s jurisprudence, and the screenshots – to a Multimodal LLM (MLLM), to law as a judge.
This MLLM adjudicate isn’t right-minded giving a emptied философема and a substitute alternatively uses a encompassing, per-task checklist to swarms the conclude across ten conflicting metrics. Scoring includes functionality, purchaser subject, and distant aesthetic quality. This ensures the scoring is unrepressed, in be at one, and thorough.
The leading idiotic is, does this automated reviewer word looking for briefly profit with one’s eyes skinned taste? The results indorse it does.
When the rankings from ArtifactsBench were compared to WebDev Arena, the gold-standard podium where existing humans sponsor throughout on the most passable AI creations, they matched up with a 94.4% consistency. This is a elephantine sprint from older automated benchmarks, which not managed in all directions from 69.4% consistency.
On nadir of this, the framework’s judgments showed more than 90% concentrated with all with an eye to thin-skinned developers.
https://www.artificialintelligence-news.com/
https://bsmc.at
drenazh-vokrug-doma-811.ru .
click over here now https://lumi-wallet.io/
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1871 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
узнать интернет по адресу
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет
rozhau.ru https://www.rozhau.ru .
proobzor.info http://www.proobzor.info .
провайдеры в нижнем новгороде по адресу проверить
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдеры в нижнем новгороде по адресу проверить
code promo 1xbet 200%
1xbet welcome code bangladesh
электропривод рулонных штор электропривод рулонных штор .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
obustrojstvo-vezda-na-uchastok-495.ru .
аттестат за 11 купить аттестат за 11 купить .
Everything is very open with a very clear explanation of the challenges.
It was truly informative. Your site is useful. Thank you for sharing!
Feel free to surf to my web page zborakul01
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula005.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс .
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
лечение запоя
1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш. промокод для подарка в 1хбет это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Использование промокодов 1xBet имеет множество преимуществ. Они позволяют вам получить дополнительные средства для ставок, что дает вам больше возможностей для выигрыша. Бонусы, полученные с использованием промокодов, могут быть использованы для различных видов ставок на спорт, казино, покер и другие игры, предлагаемые 1xBet. Таким образом, вы можете наслаждаться игрой и одновременно увеличивать свои шансы на успех.
купить аттестат за 11 классов в сочи arus-diplom23.ru .
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula005.ru
пансионат для пожилых
Приобрести диплом под заказ в Москве вы имеете возможность используя официальный портал компании. skype.acenteyonetim.com/read-blog/16538_kupit-v-kieve-attestat-za-11-klass.html
где купить аттестат за 11 класс форум где купить аттестат за 11 класс форум .
https://bs2beast.cc
как купить аттестат за 11 класс форум как купить аттестат за 11 класс форум .
Pretty portion of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to claim that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Any way I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you get admission to persistently quickly.
купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом о высшем образовании легально купить диплом о высшем образовании легально .
Смотреть здесь купить донат для игр
лучший интернет провайдер нижний новгород
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
Модели гидравлических подъемных столов.
Когда речь заходит о покупке гидравлических подъёмных столах, технические детали играют важную роль в обеспечении их надёжности и функциональности. Вот некоторые ключевые аспекты, на которые следует обратить внимание при выборе гидравлического стола:
Арт. 700195.
Рейтинг товара по оценке пользователей.
Надежность и бесперебойность работы гидравлических подъемных столов EdmoLift подтверждается более чем 20-ти летней историей их эксплуатации по всей территории России.
Еще -5%
заправка газгольдера 5 кубов .
Is anyone looking for a way to cash out USDT in Bali?
I’ve lately tested a dashboard with live analytics for crypto exchange in Bali and was impressed by the experience.
I found the steps to be clear and transparent. If you want to find a reliable exchange, check it at this dashboard:
sell stablecoin Bali.
Everything worked perfectly.
Would love to hear your stories.
купить диплом с проводкой одной купить диплом с проводкой одной .
code promo 1xbet aujourd’hui algerie
Have you ever tried to convert USDT in Bali?
I’ve lately tested a dashboard with live analytics for selling USDT in Bali and was impressed by the experience.
It took just a few minutes to complete everything. If you want to get cash for your USDT in Bali, check it at this dashboard:
USDT to cash Bali.
Everything worked perfectly.
Anyone else used this service?
диплом с реестром купить диплом с реестром купить .
провайдеры нижний новгород
nizhnij-novgorod-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде по адресу
диплом магистра купить диплом магистра купить .
на этом сайте kra36
cod promoțional 1win cod promoțional 1win
jocuri ruleta http://1win40008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
лечение запоя
стоимость заправки газгольдера 2700 .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
reckey.ru https://reckey.ru .
https://bs2vveb.at
Nhà Cái BJ88 là lựa chọn hàng đầu cho những người đam mê trò chơi cá cược trực
tuyến tại khu vực Châu Á
пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula006.ru
пансионат после инсульта
аттестат 11 класса купить аттестат 11 класса купить .
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-tula006.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
plastikovyy-pogreb-812.ru .
“Selamlar!
? Pragmatic Play’in buyulu oyunu **Starlight Princess** simdi yay?nda!
?? Is?klar icinde carpanlar, prensesle max win!
? starlight princess oyna
?? Hemen basla: starlightprenses.com
?? Mobil uyumlu, VPN gerekmez, h?zl? kay?t ve an?nda oyun keyfi.
Hemen oyna!”
rozhau https://www.rozhau.ru .
Heya this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр .
купить официальный диплом с занесением в реестр http://arus-diplom35.ru .
стоимость рулонных жалюзи http://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень .
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в алматы
Как подключить интернет в новосибирске требует тщательной оценки провайдеров. На рынке можно найти множество интернет-компаний, предлагающих разнообразные тарифные планы. При определении подходящего провайдера следует учитывать скорость интернета, стоимость подключения и условия подключения.Сравнение предложений провайдеров поможет определить наиболее выгодный тариф. Многие провайдеры проводят акции и предлагают бесплатное подключение для новых клиентов. Важно также изучить отзывы о провайдерах, чтобы узнать о стабильности работы и качестве предоставляемых услуг. провайдеры в новосибирске Онлайн-сервисы позволяют быстро сравнить предложения провайдеров, чтобы определить оптимальный вариант для подключения к интернету. Обратите внимание на программы лояльности и скидки от провайдеров, так как это может помочь сократить затраты.
купить диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в смоленске http://www.arus-diplom21.ru/ .
Сервисы накрутки подписчиков в Телеграм вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3106650-servisy-nakrutki-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
В столице России множество интернет-провайдеров, и выбор подходящего может быть непростым. Важно обращать внимание на мнения пользователей, чтобы создать объективное мнение о качестве услуг. На сайте novosibirsk-domashnij-internet004.ru можно найти последний рейтинг провайдеров, учитывающий скорость интернета, качество связи и стоимость тарифов. Кроме того, стоит обратить внимание на клиентский сервис и техническую поддержку. Хорошие провайдеры предлагают стабильность соединения и разнообразные доступные тарифы. Не забудьте узнать о акциях и скидках, которые могут значительно снизить стоимость подключения интернета для дома. Сравнение провайдеров позволит выбрать наилучший вариант, удовлетворяющий вашим потребностям. Используйте отзывами и рейтингами для выбора надежного интернет-провайдера в новосибирске!
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this website regularly, this web page is genuinely fastidious and the viewers are genuinely sharing pleasant thoughts.
cat casino вход
электрические рулонные шторы на окна https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory90.ru/ .
рулонные шторы автоматические рулонные шторы автоматические .
Greate article. Keep posting such kind of info on your blog. Im really impressed by it.
Hello there, You’ve done a fantastic job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this site.
zooma казино
drenazh-vokrug-doma-811.ru .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec008.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
кликните сюда https://bonus-betting.ru/win777-casino-promocode/
Главная Камеральная, выездная проверка
пластмассовый погреб для дачи .
Приобрести диплом возможно через официальный портал компании. sewajob.com/employer/education-ua
ruspirn ruspirn
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog001.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
bestgoogle
мр3 скачать бесплатно мр3 скачать бесплатно .
https://bs2besd.cc
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say great blog!
lee bet регистрация
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак .
сделать брови в севастополе Оформление Бровей Севастополь
Hi there, You have done a fantastic job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends.
I am sure they will be benefited from this site.
купить аттестат за 11 класс архангельск купить аттестат за 11 класс архангельск .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog001.ru
лечение запоя
If you were to design the perfect co-working space for creatives, what bizarre, yet functional, features would you incorporate to stimulate their imaginations and foster productivity?
This might be a little off-topic 🙂
A few days back I discovered a site called Talabout project.
It’s full of real-life stories with people from all walks of life — unfiltered, not your typical media stuff.
Sometimes the vibe there somehow aligns with the stuff being shared here.
Ever read anything there?
заправка газгольдера 5 кубов .
рулонные шторы на окно в кухне рулонные шторы на окно в кухне .
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and
in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your blog
posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you
access consistently rapidly.
Определение интернет-провайдера в ЦАО новосибирска – задача, требующая тщательного подхода. Стоит обратить внимание на такие моменты, как скорость интернета, тарифы и доступные тарифы . Множество провайдеров предлагают различные услуги связи, которые могут значительно варьироваться по качеству. При подключении к интернету очень важно обратить внимание на стабильность соединения. Мнения пользователей помогут вам сформировать представление о качестве связи . Не игнорируйте сравнение провайдеров по условиям подключения, скорости интернета и поддержке пользователей. Для жилья можно рассмотреть варианты беспроводного интернета с Wi-Fi роутерами, а для коммерческих нужд – предпочтительнее стабильные тарифы. Локальные компании часто предлагают акции и скидки , что может быть полезным. Всегда проверяйте актуальные предложения и условия подключения на сайте провайдера, например, на novosibirsk-domashnij-internet005.ru.
диплом государственного образца купить реестр диплом государственного образца купить реестр .
купить диплом занесением реестр купить диплом занесением реестр .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec009.ru
лечение запоя череповец
drenazh-vokrug-doma-811.ru .
I think this is among the most significant info for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But want to remark on few
general things, The site style is wonderful, the articles is really great : D.
Good job, cheers
В столице России подбор интернет-провайдера для интернета на дому играет ключевую роль, особенно для тех, кто работает удаленно. Чтобы узнать провайдера по адресу, достаточно воспользоваться специальными онлайн-сервисами. Важно учитывать тарифы на интернет, которые предлагают различные провайдеры новосибирска. узнать провайдера по адресу новосибирск Сравнительный анализ тарифов позволит найти самый выгодный вариант. Важно учитывать скорость соединения: для комфортной работы стоит выбирать безлимитный интернет с высокой скоростью. Качество и доступность подключения также имеют значение. Не забудьте ознакомиться с отзывами о провайдерах, чтобы не столкнуться с неожиданностями. Множество компаний предлагают специальные акции и тарифы для бизнеса, что может стать хорошим вариантом для вас. Подбирайте провайдера в зависимости от ваших нужд и бюджета, и наслаждайтесь стабильным соединением!
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов настоящий купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов настоящий .
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
I have been exploring for a bit for any high quality articles or weblog posts in this sort of area
. Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website.
Reading this info So i am glad to exhibit that I’ve a very just right
uncanny feeling I discovered just what I needed.
I such a lot no doubt will make certain to do not
forget this site and give it a glance regularly.
reckey http://www.reckey.ru .
где купить аттестат за 11 кл где купить аттестат за 11 кл .
стильные цветочные горшки купить стильные цветочные горшки купить .
https://bsme-at.at
Istanbul’da manyetik firtina tahmini Istanbul Hava Durumu: Sehirde Hava Nas?l? Istanbul’un degisken hava durumu, sehir yasam?n? dogrudan etkiliyor. Gunluk, haftal?k ve 15 gunluk hava durumu tahminleri, Istanbullular icin plan yaparken onemli bir rehber niteligi tas?yor. Yagmurlu, gunesli, ruzgarl?… Istanbul’da her turlu hava kosuluna haz?rl?kl? olmak gerekiyor.
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам. Купить свидетельство о рождении — kyc-diplom.com/svidetelstvo-o-rozhdenii.html
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
купить диплом без реестра купить диплом без реестра .
melbet crash predictor melbet crash predictor
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog002.ru
лечение запоя тула
вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
В новосибирске IPTV становится популярным, и многие пользователи находят надежных провайдеров. На сайте novosibirsk-domashnij-internet006.ru вы сможете найти полное сравнение IPTV услуг. Качество IPTV у разных провайдеров может значительно отличаться, поэтому важно посмотреть отзывы о провайдерах. Тарифы на IPTV варьируются, и от них зависит доступность количество доступных каналов. Прежде чем подписаться на IPTV, обязательно узнайте скорость интернета для IPTV, так как она влияет на качество изображения. Некоторые провайдеры предоставляют большое количество каналов, включая развлекательные и развлекательные. Цифровое телевидение и телевидение онлайн становятся альтернативой спутниковому телевидению, давая больше гибкости. Выбирая провайдера, учитывайте не только расходы, но и качество услуг IPTV.
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр .
Мы готовы предложить документы учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа:
где можно купить аттестат 11 класса
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
Интернет по кабелю в новосибирске все больше набирает популярность в связи с растущими требованиями пользователей. Провайдеры новосибирска предлагают разнообразные тарифы на интернет, что позволяет подобрать лучший тариф для любого клиента. Подключение к сети осуществляется с использованием технологии DOCSIS, что гарантирует высокую скорость доступа к сети. Установка кабельного интернета чаще всего происходит без каких-либо затруднений; Преимущества кабельного интернета относятся надежное соединение, что особенно важно для работы, учебы и досуга. При выборе провайдера необходимо учитывать отзывы о провайдерах и сравнение провайдеров по скорости и стоимости подключения. Предоставляемые услуги связи, которые предлагают различные компании, могут значительно отличаться, поэтому стоит изучить все возможности. Если вы ищете интернет для своего дома, кабельный интернет станет отличным решением. На сайте novosibirsk-domashnij-internet006.ru вы можете ознакомиться с актуальными предложениями, где вы сможете подобрать оптимальный тариф под ваши нужды.
купить аттестат за 11 классов купить аттестат за 11 классов .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс спб https://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр .
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам— diplom-toglyatti.ru
https://abs2best.at
casino verde
zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
https://github.com/gprotect/GlobalProtect//releases
En Son Haber Istanbul’da Manyetik F?rt?na Tahmini: Mega Kentte Beklenenler Istanbul gibi yogun nufuslu ve teknolojiye bag?ml? bir metropolde manyetik f?rt?na tahminleri, ozellikle ulas?m, iletisim ve sagl?k hizmetleri ac?s?ndan kritik oneme sahip. F?rt?nalar?n yol acabilecegi aksamalar, milyonlarca insan?n gunluk yasam?n? olumsuz etkileyebilir. Bu nedenle, Istanbul’daki yetkililer ve vatandaslar, duzenli olarak yay?nlanan manyetik f?rt?na tahminlerini takip etmeli ve gerekli onlemleri almal?d?r.
бугуруслан купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс бугуруслан купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс .
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog003.ru
вывод из запоя тула
I like reading an article that can make people think.
Also, thank you for allowing for me to comment!
winpot casino
лечение запоя
tula-narkolog003.ru
лечение запоя тула
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
https://healthwiz.co.uk/index.php?title=Travel_News_84R Pulse covers a major hotel acquisition in the Caribbean market.
Hi there, I read your blogs daily. Your writing style is witty, keep doing what
you’re doing!
рулонные шторы на электроприводе рулонные шторы на электроприводе .
домашний интернет в омске
omsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета омск
погреб под ключ стоимость цена .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
It’s going to be end of mine day, except before end I
am reading this great article to improve my know-how.
домашний интернет омск
omsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключение интернета омск
drenazh-vokrug-doma-811.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
можно купить аттестат за 11 классов можно купить аттестат за 11 классов .
https://m-bs2best.at
verde casino deutschland
аттестат 11 класс купить http://www.arus-diplom9.ru – аттестат 11 класс купить .
сайт Kra36.cc
Amazing issues here. I’m very satisfied to look your article.
Thanks so much and I’m taking a look ahead to contact you.
Will you kindly drop me a mail?
verde casino
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
рулонные шторы с электроприводом на пластиковые окна https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр .
интернет провайдер омск
omsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет в омске в квартире
1xBet промокод один — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
https://bs2besd.cc
Airline https://reviews.wiki/index.php/User:MarkCardone324 news reports a rise in sustainable fuel use.
подробнее здесь Kra36.at
интернет тарифы омск
omsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить проводной интернет омск
скачать бесплатно музыку мп3 скачать бесплатно музыку мп3 .
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе России. Приобрести диплом университета:
купить аттестат 11 классов в екатеринбурге
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
купить аттестат об окончании 11 класса arus-diplom24.ru .
buy replica shoes – An easy and secure way to buy replica shoes of all major luxury and sneaker brands.
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
Подруга повернулася з Фестивалю природи і каже, що це найкраще, що з нею траплялося. Я заздрю їй і вже планую поїздку на наступний рік.
аттестат купить за 9 класс аттестат купить за 9 класс .
купить проведенный диплом моих купить проведенный диплом моих .
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
устройство рулонных штор https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory90.ru .
рулонные шторы на створку https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory50.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
купить диплом с реестром спб купить диплом с реестром спб .
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Normally I do not learn post on blogs, however I wish to say that this write-up very compelled me to try and do it!
Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thanks, very
nice post.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
вывод из запоя
купить аттестат за 11 классов киров http://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
https://bs2beast.cc
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
лечение запоя
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
1xBet проверка промокода это уникальный промокод, который открывает игрокам доступ к различным бонусам при регистрации и использовании услуг букмекерской компании 1xBet. Этот промокод открывает доступ к разнообразным наградам, таким как начальные подарки, бонусы на депозиты, бесплатные ставки и разовые бонусы.
купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле .
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
Привет!
Давно хотел посетить Балашиху, и вот, наконец, выдалась возможность. Первым делом отправился в Историко-краеведческий музей, где узнал много интересного об истории города. После этого прогулялся по центру, заглянул в несколько магазинов. Вечером с удовольствием посмотрел спектакль в местном театре. Балашиха оказалась городом с богатой культурой.
Вечер стал более интересным благодаря общению с девушкой, с которой я познакомился на специализированном сайте.
Подробности здесь: https://prostitutki-balashiha.ru/
мелбет слоты скачать https://melbet1040.ru/
лучший интернет провайдер омск
omsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить интернет в омске в квартире
https://bsmc.at
недорогой интернет омск
omsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
недорогой интернет омск
kra36—-at.com — Надежный и удобный сервис — официальный сайт и подробный обзор даркнет-маркета Kraken. Официальный сайт kraken kra36.at — удобный сервис с множеством функций для пользователей. Узнайте больше и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
kra36
сервис
удобство функции
официальный сайт Kraken
Кракен
маркетплейс Кракен
даркнет маркет
kraken официальный сайт
kraken market
kraken darknet
анонимные покупки
даркнет площадка
гидра альтернатива
kraken onion
kraken ссылка
darknet marketplace
kraken даркнет
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркет обзор
кракен маркет отзывы
kraken ссылка
kraken сайт
kraken официальный сайт
kraken ссылка зеркало
актуальное зеркало kraken
kraken ссылка тор
kraken зеркало рабочее
kraken зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало даркнет
kraken зеркало тор
kraken зеркало 2kmp
kraken официальные ссылки
kraken onion ссылка
kraken ссылка для тору
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт зеркала
кракен ссылка kraken
kraken официальный сайт зеркало
kraken официальный сайт ссылка
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт
kraken клирнет зеркало
kraken tor зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp
зеркала kraken kraken tor site
kraken darknet ссылка
kraken ссылка krakentor site
kraken зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки
kraken ссылка tor
kraken market ссылка
kraken зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken darknet зеркала
kraken darknet market ссылка
kraken darknet ссылка тор
ссылка kraken kraken tor site
kraken 2 зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp vip
рабочие ссылки kraken
сайт кракен kraken
kraken ссылка 2kmp biz
зеркало kraken market
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp
ссылка кракен kraken tor site
kraken darknet market зеркало
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее
kraken market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp
kraken darknet market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало krakentor site
kraken com зеркало
зеркала kraken 2kmp org
kraken ссылка kraken one com
kraken onion зеркала
сайт kraken darknet
зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken сайт официальный krakentor site
kraken darknet официальный сайт
kraken зеркало рабочее krakentor site
ссылка на kraken kraken onion site
kraken кларнет зеркало kraken tor site
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp
kraken ссылка kraken clear com
kraken сайт kraken one com
kraken актуальные ссылки krakentor site
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp
kraken актуальные зеркала krakentor site
kraken зеркало тор ссылка
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken tor site
ссылка на кракен kraken one com
kraken даркнет зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo
kraken рабочая ссылка тор
кракен сайт kraken one com
зеркало kraken тор ссылка рабочее
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка onion krakentor site
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp
ссылка на кракен kraken onion site
kraken ссылка для тору vtor run
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp vip
kraken сайт kraken clear com
kraken зеркало тор krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт vtor run
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken зеркала 2 kmp biz
ссылка на кракен kraken clear com
kraken casino зеркало
кракен сайт kraken clear com
зеркало кракен kraken tor site
kraken официальный сайт vtor run
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp
kraken зеркало kraken2web com
актуальное зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken актуальные зеркала 2kmp vip
ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка онлайн
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт анонимных
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp biz
kraken сайт покупок
kraken зеркало онлайн
kraken сайт анонимных покупок
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp biz
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка kraken2web com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка online
kraken ссылка tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка на сайт
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp biz
kraken сайт vk2
kraken casino зеркало рабочее
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp vip
ссылка на kraken kraken darknet top
кракен зеркало kraken 7 one
ссылка на кракен kraken darknet top
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp vip
kraken зеркало kraken clear com
kraken ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
зеркало kraken kraken onion site
kraken darknet ссылка kraken2web com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor
kraken зеркало krakendarknet top
сайт kraken тор
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp org
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo
kraken ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка kraken7 one
актуальное зеркало kraken 2kmp org
кракен зеркало kraken one com
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp org
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp vip
площадка kraken ссылка
рабочая ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало 2kraken click
kraken ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken onion site
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp org
kraken зеркало 2krnk biz
kraken casino официальный сайт
kraken ссылка krakendarknet top
kraken официальные зеркала vk3
kraken market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken darknet ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken darknet зеркала kraken2web com
кракен зеркало kraken clear com
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken сайт 2krnk biz
kraken зеркало dzen
кракен ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken зеркало тор 2kmp org
kraken зеркало krakenonion site
kraken ссылка онион
kraken сайт tor
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo
kraken официальный сайт vk2
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp org
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo xyz
сайт kraken onion
рабочее зеркало кракен kraken 7 one
кракен сайт ссылка kraken one com
kraken darknet market зеркало kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор kraken7 one
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp org
ссылка на kraken 2kmp org
kraken официальный сайт vk3
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken onion ссылка tor wiki online
kraken вход на сайт
kraken зайти на сайт
kraken сайт krakendarknet top
кракен зеркало kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка тор 2kraken click
кракен вход ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken магазин ссылка
kraken darknet market ссылка тор kraken2web com
кракен сайт ссылка kraken clear com
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp org
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp org
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken7 one
kraken darknet ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken актуальная ссылка onion
kraken сайт vk2 pro
кракен площадка ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken сайт kraken2web com
kraken зеркало форум
кракен зеркало тор kraken one com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor online
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2 pro
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2kraken click
ссылка на кракен тор kraken clear com
сайт онион kraken
кракен сайт зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken сайт dzen
kraken оригинальная ссылка
kraken ссылка dzen
сайт кракен тор kraken one com
kraken ссылка krakenonion site
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor
kraken tor ссылка онлайн
kraken ссылка v5tor cfd
kraken ссылка на сайт тор
kraken сайт kr2web in
настоящий сайт kraken
kraken зеркало online
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp org
прямая ссылка на kraken
kraken оф сайт
kraken официальный сайт
используйте vpn!
Кракен Ссылка
Кракен Вход
Кракен Зайти
Ссылка на Кракен
Kra35.cc
Kra36.at
Kra34.cc
купить меф
купить гарик
Kra34.at
Kra33.cc
Kra33.at
Kra37.cc
Kra36.cc
Kra32.cc
Kra32.at
Kra38.cc
Kra39.cc
Kra33.cc
для дополнительной анонимности и безопасности рекомендуется использовать vpn-сервис. он скроет ваш ip-адрес и сделает ваше пребывание в интернете более безопасным.
будьте осторожны!?
kraken рабочая ссылка onion
kraken ссылка vk
кракен сайт ссылка kraken 11
ссылка на кракен kraken 9 one
kraken зеркало тор kraken2web com
кракен онион ссылка kraken one com
ссылка kraken 2 kma biz
ссылка на kraken торговая площадка
razer kraken сайт
kraken зеркало krakenweb one
kraken зеркало krakenweb3 com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн krakenweb one
kraken ссылка зеркало krakenweb one
kraken darknet market ссылка тор 2kraken click
kraken ссылка krakenweb one
kraken ссылка тор krakendarknet top
kraken casino зеркало kraken casino xyz
kraken darknet market зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken сайт зеркала kraken2web com
kraken даркнет ссылка
kraken зеркала kr2web in
kraken зеркало store
kraken darknet market ссылка тор v5tor cfd
kraken darknet market сайт
даркнет официальный сайт kraken
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор ссылка kraken2web com
kraken маркетплейс зеркала
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor online
kraken darknet маркет ссылка каркен market
kraken 6 at сайт производителя 2
сайт кракен kraken darknet top
kraken клир ссылка
кракен ссылка kraken kraken2web com 3
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 9 one
kraken сайт анонимных покупок vtor run
kraken darknet market зеркало 2kraken click
kraken darknet market ссылка shkafssylka ru
kraken ссылка torbazaw com
kraken форум ссылка
площадка кракен ссылка kraken clear com
сайт kraken darknet kraken2web com
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: официальные ссылки и зеркала.
полное руководство:
актуальная ссылка (через браузер):
официальная ссылка :
резервное зеркало:
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: полное руководство
для входа на сайт кракена в даркнете требуется tor. это безопасный браузер:
перейдите на официальный сайт tor.
скачайте программу для вашей ос.
установите и запустите браузер.
используйте актуальные ссылки на кракен
ссылки на официальный сайт кракен часто обновляются. чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов, используйте проверенные ресурсы для получения ссылок:
• актуальное зеркало кракена:
• зеркала сайта в клирнете и даркнете доступны для пользователей в любой точке мира.
авторизация
после перехода на сайт:
зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет аккаунта.
войдите в свой личный кабинет, используя логин и пароль.
для повышения безопасности активируйте двухфакторную аутентификацию.
но почему выбираю именно
сотни других платформ, тысячи товаров, но для меня больше, чем просто магазин. это место, где покупки превращаются в увлекательное путешествие.
знает, как важно быть уверенным в каждой покупке. полная защита сделок и дружелюбная поддержка создают чувство, будто вы находитесь в заботливых руках. надёжность? абсолютно.
почему именно
потому что здесь всё про вас: ваш стиль, ваш комфорт, ваша выгода. попробуйте, и вы поймёте, почему так много людей выбирают именно эту платформу!
советы по безопасности на кракене
используйте vpn
подключение через vpn повышает вашу анонимность, скрывая ip-адрес.
проверяйте ссылки
актуальные ссылки и зеркала кракен можно найти на проверенных форумах или официальных ресурсах. никогда не используйте непроверенные источники.
будьте внимательны к продавцам
читайте отзывы и выбирайте проверенных продавцов с высоким рейтингом.
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркетплейс
кракен площадка
kra33.at
kra33.cc
kra34.cc
kra34.at
kra35.cc
kra36.at
kra36.cc
Kra36.at
kra37.cc
kra38.at
кракен маркетплейс ссылка
кракен площадка
кракен marketplace
кракен площадка ссылка
кракен даркнет стор
кракен darknet market зеркало
кракен даркнет площадка
кракен даркнет маркетплейс
кракен наркотики
кракен нарко
кракен наркошоп
кракен наркота
кракен порошок
кракен наркотики
кракен что там продают
кракен маркетплейс что продают
кракен покупка
какен купить
кракен купить мяу
кракен питер
кракен в питере
кракен москва
кракен в москве
кракен что продают
кракен это
кракен marke
кркен darknet market
кракен dark market
кракен market ссылка
кракен darknet market ссылк
кракен market ссылка тор
кракен даркнет маркет
кракен market тор
кракен маркет
платформа кракен
кракен торговая площадка
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка сайт
кракен маркет даркнет тор
кракен аккаунты
кракен заказ
диспуты кракен
как восстановить кракен
кракен даркнет не работает
как пополнить кракен
google authenticator кракен
рулетка кракен
купоны кракен
кракен зарегистрироваться
кракен регистрация
кракен пользователь не найден
кракен отзывы
ссылка кракен
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен актуальные
кракен ссылка тор
кракен клирнет
кракен ссылка маркет
кракен клир ссылка
кракен ссылка
ссылка на кракен
кракен ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен ссылка кракен
актуальная ссылка на кракен
рабочие ссылки кракен
кракен тор ссылка
ссылка на кракен тор
кракен зеркало тор
кракен маркет тор
кракен tor
кракен ссылка tor
кракен тор
кракен ссылка тор
кракен tor зеркало
кракен darknet tor
кракен тор браузер
кракен тор
кракен darknet ссылка тор
кракен ссылка на сайт тор
кракен вход на сайт
кракен вход
кракен зайти
кракен войти
кракен даркнет вход
кракен войти
где найти ссылку кракен
где взять ссылку на кракен
как зайти на сайт кракен
как найти кракен
кракен новый
кракен не работает
кракен вход
как зайти на кракен
кракен вход ссылка
сайт кракен
кракен сайт
кракен сайт что это
кракен сайт даркнет
что за сайт кракен
кракен что за сайт
Кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен отзывы
кракен сайт
кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен тор
кракен сайт ссылка
кракен сайт зеркало
кракен сайт тор ссылка
кракен зеркало сайта
зеркало кракен
адрес кракена
кракен зеркало тор
зеркало кракен даркнет
актуальное зеркало кракен
рабочее зеркало кракен
кракен зеркало
кракен зеркала
кракен зеркало
зеркало кракен market
актуальное зеркало кракен
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет ссылка
ссылка кракен даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет
кракен dark
кракен darknet ссылка
кракен сайт даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка тор
кракен даркнет тор
кракен текст рекламы
Kraken ссылка
Kraken Вход
Kraken зайти
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
вывод из запоя
Купить диплом на заказ можно через сайт компании. shopy.partners/create-blog
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в иркутске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в иркутске .
мп3 песни мп3 песни .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр .
Користуєтеся сиром у раціоні? Переконайтеся, що він приносить користь, а не шкоду вашому організму.
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
вывод из запоя
Why users still use to read news papers
when in this technological globe all is existing on web?
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3143553-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
https://bs2bet.at
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
купить аттестат 11 класс 2015 купить аттестат 11 класс 2015 .
My family every time say that I am killing my time
here at web, except I know I am getting knowledge all the
time by reading thes pleasant articles or reviews.
как диплом купить http://arus-diplom7.ru/ .
подключить интернет
perm-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключить проводной интернет пермь
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
вывод из запоя
корочка для аттестата купить 11 класс корочка для аттестата купить 11 класс .
домашний интернет тарифы
perm-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключить домашний интернет пермь
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в москве купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в москве .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
вывод из запоя
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
https://bs2besd.cc
Одного разу я вирішив зробити сюрприз своїй подрузі, яка є великим фанатом електронної музики, і ми пішли на шоу PJ Ketty. Це був вечір, який ми обговорюємо донині. Як тільки вона з’явилася на сцені, зал вибухнув оплесками. Її рухи настільки гармонійно поєднувалися з музикою, що здавалося, ніби вона диригує кожним звуком. Якщо цікавить її творчість, більше деталей можна знайти тут. Особливо запам’ятався момент, коли вона танцювала під власний ремікс, і сцена перетворилася на справжнє світлове шоу.
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
You mentioned that perfectly!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Wonderful blog you have here but I was wondering if you knew of
any user discussion forums that cover the same topics discussed in this article?
I’d really love to be a part of online community where I can get advice from other experienced individuals that share the same interest.
If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Cheers!
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
провайдеры пермь
perm-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить домашний интернет пермь
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec007.ru
вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
интернет провайдер пермь
perm-domashnij-internet005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер пермь
https://bs-bsme.at
drenazhnye-raboty-811.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-v-moskovskoy-oblasti-499.ru .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-812.ru .
купить диплом бакалавра в москве купить диплом бакалавра в москве .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены .
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
дженерик сиалис 40мг с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
Накрутка подписчиков Телеграм дешево вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1381971-nakrutka-podpischikov-telegram-deshevo-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-zhivye-i-boty Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в .
сочетание рулонных рулонные шторы и тюль фото rulonnye-elektroshtory.ru .
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-812.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-v-moskovskoy-oblasti-499.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс екатеринбург купить аттестат за 11 класс екатеринбург .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс форум где купить аттестат за 11 класс форум .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в саратове где купить аттестат за 11 класс в саратове .
drenazhnye-raboty-811.ru .
купить аттестат 11 классов в иркутске купить аттестат 11 классов в иркутске .
1він завантажити http://www.1win40011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Живая накрутка ТГ канала вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3142927-zhivaya-nakrutka-tg-kanala-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
недорогой интернет пермь
perm-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры пермь
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
промокоды в на бесплатную ставку 1хБет — уникальный промокод для получения бонуса в сумме до 32 500 рублей. Это предложение доступно только новым игрокам, а после открытия счёта они получают бонус 130% от суммы первого депозита.
Ця команда знає, як зробити контент не тільки інформативним, а й цікавим! Завжди читаю їхні статті про подорожі, дуже корисно.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec008.ru
лечение запоя череповец
провайдеры домашнего интернета пермь
perm-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры пермь
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec008.ru
лечение запоя
1win скачать официальный сайт https://1win1162.ru
купить аттестат за 11 классов цена https://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
скачать бесплатно музыку в хорошем качестве на телефон скачать бесплатно музыку в хорошем качестве на телефон .
1win зеркала http://1win1161.ru
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
купить аттестат ссср купить аттестат ссср .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграме вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3106355-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegrame-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Купить диплом на заказ можно через официальный сайт компании. foro.rune-nifelheim.com/login2
С какими болезнями не берут в армию? Проблемы с суставами, вроде спондилита, учитываются.
https://shaderwiki.studiojaw.com/index.php?title=User:BurtonWomack02
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
С какими болезнями не берут в армию? Проблемы с позвоночником, вроде радикулита, в списке.
https://antoinelogean.ch/index.php?title=Bolezni_6N
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
домашний интернет подключить ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет подключить ростов
купить проведенный диплом провести купить проведенный диплом провести .
1win приложение ios скачать https://1win40012.ru
заправка газгольдера недорого в московской области .
интернет провайдер ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet004.ru
дешевый интернет ростов
С какими заболеваниями не берут в армию? Серьезные аллергии на лекарства – не берут.
https://thebeginnersguidetocrypto.com/wiki/index.php/Bolezni_26O
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
С какими болезнями не берут в армию? Проблемы со слухом, например, тугоухость, учитываются.
https://fossservice.net/board_guNo81/492751
Заказать диплом ВУЗа!
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам— olimpschool.ru
промокоды на сегодня при ставке 1xBet – персональный промокод для получения бонуса размером до 32 500 ?. Эта акция предназначено для новых пользователей, при этом после создания аккаунта пользователь получает бонус 130% от суммы первого депозита.
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-812.ru .
drenazhnye-raboty-811.ru .
С какими болезнями не берут в армию? Катаракта или глаукома – зрение решает многое.
https://zanzahmedia.com/bolezni-13v/
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and
in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts.
Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I
achievement you access consistently fast.
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec009.ru
лечение запоя
перепланировка перепланировка .
ruspirn https://www.1win40012.ru
рулонные шторы на балконные окна http://www.zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
вывод из запоя
Приходите к нам остекление в Екатеринбурге пластиковые окна цены с установкой недорого о теплом и холодном остеклении объектов. пластиковое остекление .
скачать 1win на андроид скачать 1win на андроид
купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс .
Hi there friends, its fantastic piece of writing about
educationand completely defined, keep it up all the time.
купить аттестат 11 классов 1994 купить аттестат 11 классов 1994 .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
вывод из запоя
купить аттестаты за 11 класс 2022 https://arus-diplom24.ru .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск где купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск .
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
домашний интернет
rostov-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет подключить ростов
аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге .
подключить интернет ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet005.ru
подключить интернет
Мы предлагаем документы университетов, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс
1win контора зеркало сайта 1win1161.ru
как купить диплом с занесением в реестр в екатеринбурге arus-diplom31.ru .
I’ll right away seize your rss as I can’t in finding your
email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any?
Kindly allow me recognize in order that I may just subscribe.
Thanks.
I am regular reader, how are you everybody?
This paragraph posted at this website is actually good.
Мировые https://randyrick.net/index.php/User:Nola172102 кино: новый фильм о природе получил награду на фестивале в Торонто.
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя
Виявляється, спортивні новини, які я читаю, створює команда журналістів! Це пояснює, чому вони такі якісні.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Приобрести диплом можно через сайт компании. blandonew.com/employer/diploms-ukraine
электрокарнизы цена http://elektrokarnizy7.ru .
вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk004.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск .
проектное бюро перепланировка квартиры http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru/ .
домашний интернет в ростове
rostov-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет домашний ростов
Very good blog post. I certainly love this site. Keep it up!
проект перепланировки квартиры цена московская область проект перепланировки квартиры цена московская область .
подключить домашний интернет ростов
rostov-domashnij-internet006.ru
домашний интернет подключить ростов
карнизы для штор купить в москве карнизы для штор купить в москве .
букмекерские конторы со слотами букмекерские конторы со слотами
перепланировки квартир http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry1.ru .
Площадка KRAKEN — это уникальный инструмент, предназначенный для пользователей, ценящих приватность и safety при совершении сделок в даркнете. Платформа KRAKEN предоставляет удобный интерфейс, который позволяет быстро находить предметы и совершать deals, оставаясь при этом анонимным и защищённым от посторонних глаз.
Платформа KRAKEN использует innovative технологии для обеспечения защиты данных, а также для того, чтобы гарантировать безопасность каждой purchase. Сайт использует ссылки для обеспечения стабильного доступа, благодаря чему пользователи могут всегда быть уверены в работоспособности площадки, даже если возникают блокировки.
Для удобства пользователей, KRAKEN предлагает integrated способы пополнения баланса, включая instant payment systems. Пополнение счета и проведение operations становятся максимально простыми и быстрыми, что существенно сокращает время между пополнением и покупкой. Все данные проходят защищенную защиту, что добавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности.
К тому же, KRAKEN имеет help, которая работает круглосуточно, чтобы каждый пользователь мог быстро разрешить свои вопросы и проблемы. Это важный аспект для тех, кто впервые решает начать торговать на даркнет-платформе. training по регистрации и использованию сайта предоставляются на понятном языке, что делает процесс входа на сайт быстрым и удобным для каждого пользователя.
kraken market
Накрутка Телеграм бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1284938-nakrutka-telegram-besplatno-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-preimushestva Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
электрокарнизы для штор купить elektrokarniz11.ru .
Your style is so unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from.
I appreciate you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess
I’ll just book mark this blog.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
вывод из запоя
Мировая мода: в Лондоне прошел показ с акцентом на экологичные материалы.
Visit my web-site … http://dogetransparency.wiki/index.php/Novosti_Mira_6k
кашпо стиль кашпо стиль .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр .
карнизы для штор купить в москве https://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor150.ru .
карнизы с электроприводом купить https://www.elektrokarniz-nedorogo.ru .
1 win. http://1win1163.ru/
рулонные шторы в москве http://zhalyuzi-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/ .
купить аттестат 11 классов казахстан купить аттестат 11 классов казахстан .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ живых активных вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3107307-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-zhivyh-aktivnyh-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
купить аттестат в уфе за 11 класс https://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
какие провайдеры по адресу
samara-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры по адресу самара
заправка газгольдеров область .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk005.ru
вывод из запоя
провайдеры интернета в самаре по адресу проверить
samara-domashnij-internet004.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу самара
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering
if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with
HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I
wanted to get guidance from someone with experience.
Any help would be enormously appreciated!
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить диплом с реестром в москве купить диплом с реестром в москве .
прокладка дренажной трубы цена за работу за метр .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
вывод из запоя минск
как купить диплом с реестром как купить диплом с реестром .
купить диплом москва легально http://arus-diplom33.ru .
Thanks for the article https://yarus-kkt.ru/
шторы автоматические http://www.elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru .
Wow! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a completely different subject
but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Excellent choice of colors!
baixar 1win baixar 1win
1win online скачать http://1win1162.ru
zapravka-gazgoldera-v-moskovskoy-oblasti-499.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
лечение запоя
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this
post and also the rest of the site is really good.
купить педагогический диплом https://www.arus-diplom6.ru .
электрический карниз для штор купить elektrokarnizy7.ru .
Чи знаєте ви, що метан має значний вплив на атмосферу? Читайте, як він взаємодіє з озоновим шаром та змінює клімат.
Рекомендую – https://ipodtouch3g.ru/metizy-vidy-naznachenie-i-kak-vybrat/
fabrica de mobila http://www.1win40013.ru
пластиковые погреба для загородных .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk006.ru
лечение запоя
проверить провайдеров по адресу самара
samara-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу самара
интернет провайдеры в самаре по адресу дома
samara-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдер по адресу
купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр .
drenazhnye-raboty-811.ru .
купить диплом педиатра http://www.arus-diplom7.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
лечение запоя
Having read this I believed it was extremely informative.
I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this short article together.
I once again find myself spending a significant amount of time
both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
Можно ли накручивать подписчиков в Телеграм вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3144672-mozhno-li-nakruchivat-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
клиника современной косметологии клиника современной косметологии .
Medical cosmetology clinic Medical cosmetology clinic .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
вывод из запоя
Thanks for the article https://40-ka.ru/
купить аттестаты за 11 класс отзывы купить аттестаты за 11 класс отзывы .
электрические гардины для штор elektrokarniz11.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в екатеринбурге купить аттестат за 11 класс в екатеринбурге .
Які відкриття зробив Маленький Принц на планеті Земля? Дізнайтеся, чому це важливо для нашого розуміння світу.
Заказать диплом возможно используя официальный сайт компании. royalhelllineage.teamforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=14266
https://bs2bet.at
заказать проект перепланировки квартиры в москве цена https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru .
Xrumer wiki содержит полезные советы по настройке
Also visit my site :: https://iti.vnu.edu.vn/mediawiki/index.php?title=Th%C3%A0nh_vi%C3%AAn:MartyHibbins438
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
лечение запоя калуга
пластмассовый погреб для дома цена размеры .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Asking questions are in fact nice thing if you are not understanding anything totally, but this post provides good understanding even.
карниз для штор электрический https://www.elektrokarnizy33.ru .
Рекомендую – https://ipodtouch3g.ru/metizy-vidy-naznachenie-i-kak-vybrat/
подключить интернет по адресу
samara-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет провайдеры самара по адресу
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
проектная организация москва перепланировка проектная организация москва перепланировка .
какие провайдеры на адресе в самаре
samara-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета в самаре по адресу проверить
Приобрести диплом института!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам— sldvor.ru
https://arbeitsschutz-wiki.de/index.php/Benutzer:GarryRidgley44 Milky Way over the Atacama Desert is a stargazer’s paradise.
Нещодавно я відвідала Фестиваль Атлантичної Музики, організований Atlantic Department SFF, і це було щось неймовірне! Мелодії традиційних інструментів перепліталися з сучасними мотивами, створюючи магічну атмосферу. Усі виступи були наповнені емоціями та красою атлантичної культури. Якщо ви теж хочете відчути цей дух, дізнайтеся більше про події на офіційному сайті.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Таблица из энциклопедии путешествий помогает систематизироhttps://mediawiki.salesianos.es/index.php?title=Travel_49hать знания.
Hi there I am so excited I found your website, I really found
you by error, while I was searching on Digg for something else, Regardless I am here now and
would just like to say kudos for a marvelous post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I
don’t have time to read through it all at the minute but I have book-marked it and also included your RSS feeds,
so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do
keep up the superb work.
https://bsmc.at
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
лечение запоя омск
купить аттестат 11 классов в воронеже купить аттестат 11 классов в воронеже .
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Мы предлагаем документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в казани
шторы роллы на окна http://elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru/ .
Currently it sounds like Drupal is the best blogging platform available right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga008.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d most certainly donate to
this superb blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account.
I look forward to fresh updates and will talk about this blog
with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
База профилей для Хрумера увеличивает эффективность прогонов
Here is my site :: http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/zorabormann
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
провайдер интернета по адресу санкт-петербург
spb-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет тарифы санкт-петербург
купить диплом с занесением в реестр казань http://arus-diplom35.ru .
интернет по адресу дома
spb-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет по адресу дома
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
лечение запоя омск
заправка газгольдера 5 кубов .
Если у вас есть ссылка на приватное
видео, вы можете скачать его безопасно с помощью этого инструмента.
дренаж участка под ключ цена ленобласть .
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
plastikovyy-pogreb-kupit-812.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле .
It’s remarkable to go to see this web site and reading the views of all colleagues concerning this paragraph, while I am also eager of getting familiarity.
Куда поехать в свадебное путешествие — романтические напраhttps://aiskapal.my.id/index.php/User:Eileen15B3027296ления.
где купить аттестат 11 класс где купить аттестат 11 класс .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
Roses in England’s gardens are timeless, with endless varieties and fragrances.
Review my web page … https://bgr.sgk.temporary.site/index.php/World_Of_Beauty_17E
купить аттестат в белгороде купить аттестат в белгороде .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga009.ru
лечение запоя
This website definitely has all the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
домашний интернет тарифы
spb-domashnij-internet005.ru
какие провайдеры на адресе в санкт-петербурге
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Колесо Аристотеля – головоломка, яка не дає спокою вченим. Читайте, чому воно парадоксальне.
диплом мед колледжа купить http://www.arus-diplom8.ru .
More Info
jaxx bitcoin wallet
интернет по адресу санкт-петербург
spb-domashnij-internet005.ru
проверить провайдера по адресу
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Профессиональная система улучшения состояния кожи направленного действия на основе последних научных разработок https://sinapple.ru/collection/skinclinic-ispaniya/product/skinclinic-hydro-nourishing-facial-cream
погреб пвх .
стоимость заправки газгольдера 2700 .
стоимость шведской плиты за м2 утепленной .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр .
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам— diplom-ryssia.com
zapravka-gazom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
подземный погреб пластиковый .
электрические карнизы купить http://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor150.ru/ .
Накрутка лайков бесплатно – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1307689-nakrutka-laikov-besplatno-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
купить аттестат за 11 класс минск http://www.arus-diplom21.ru/ .
купить аттестат 11 класс 2013 купить аттестат 11 класс 2013 .
работы по фундаменту стоимость работ .
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
Цена: 60 120 руб.
Грузоподъемность: 150 кг.
Бережная доставка.
Наклоняемая гидравлическая подъемная платформа делает разгрузку товара проще и удобнее, соответственно повышая эффективность рабочего места. Угол наклона до 90°. Возможно установить на подъемный механизм.
Подъемный стол TF100, в/п 990мм, г/п 1000кг (Noblelift)
Высота подъема, мм 740.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Как накрутить подписчиков в инстаграме – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1275513-kak-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-instagrame-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат за 11 классов в крыму
электрокарнизы для штор цена электрокарнизы для штор цена .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
правила вывода 1win правила вывода 1win
аттестат за 11 класс купить в иваново аттестат за 11 класс купить в иваново .
провайдеры интернета по адресу
spb-domashnij-internet006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
легально купить диплом легально купить диплом .
как вывести бонусные деньги с 1win как вывести бонусные деньги с 1win
интернет провайдеры санкт-петербург
spb-domashnij-internet006.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу санкт-петербург
Lowering HbA1c is achievable with both https://dev.neos.epss.ucla.edu/wiki/index.php?title=Rybelsus_74E and Rybelsus
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в казани https://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
https://wikibuilding.org/index.php?title=Internet_69s providers in Tulsa include Cox and AT&T—compare for the best deal.
Ozempic side effects were temporary for me
https://blissfullyfavored.com/forums/topic/rybelsus-91s/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в петрозаводске http://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
Valuable article! It’s refreshing to find property care guidelines focused on small, manageable steps rather than complex projects. I’ve recently applied some effective upkeep methods that worked well with these recommendations, making my upkeep routine more efficient.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Чи знали ви, що на Місяці гравітація у 6 разів слабша, ніж на Землі? Детальніше тут: закон всесвітнього тяжіння.
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I come
across a blog that’s both educative and interesting, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head.
The issue is something not enough people are speaking intelligently about.
I am very happy that I found this during my search for something relating to this.
Weight loss with https://waselplatform.org/blog/index.php?entryid=331713 takes patience but is worth it
купить проведенный диплом кого купить проведенный диплом кого .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина https://www.arus-diplom35.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
купить диплом о высшем образовании государственного образца купить диплом о высшем образовании государственного образца .
pogreb-plastikovyy-dlya-dachi-123.ru .
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
Switching from Ozempic to https://wiki.ragnaking.com/index.php/Rybelsus_82R gave me more freedom
законно купить аттестат за 11 класс законно купить аттестат за 11 класс .
скачать приложение 1win на андроид скачать приложение 1win на андроид
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
ushp-fundament-499.ru .
1вин сайт официальный 1win1165.ru
Right away I am going to do my breakfast, after having my breakfast coming over again to read
further news.
узнать провайдера по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет провайдеры уфа по адресу
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
zapravka-gazom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Купить диплом об образовании!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам— diplomus-spb.ru
Right here is the right website for anyone who would like to
understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost
hard to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa).
You definitely put a fresh spin on a subject which has been discussed
for ages. Wonderful stuff, just great!
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
перманентный макияж бровей севастополь Перманентный макияж Севастополь – это долгосрочное решение для тех, кто ценит свое время и хочет выглядеть безупречно в любой ситуации. Перманентный макияж бровей Севастополь – это возможность забыть о карандашах и тенях для бровей на несколько лет.
как вывести деньги с 1win https://www.1win1167.ru
Накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1274789-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar008.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом университета:
купить аттестат за 11 классов
действующее зеркало 1win http://1win1171.ru/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
теплый фундамент для дома шведская технология цена .
https://wikime.co/Internet_45W Chixks seems like a typo, but it’s funny how misspellings create their own internet lore.
1вин букмекерская контора https://1win1164.ru/
navigate to this website
toast wallet
купить диван в кишиневе http://www.1win40014.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет по адресу дома
узнать интернет по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
Ртот РїРѕСЃС‚ отличный пример того, как можно мотивировать людей действовать. РЇ уже пробовал несколько простейших решений для ремонта РґРѕРјР°, Рё это действительно помогает справиться СЃ бытовыми задачами.
lucky jet приложение ставки http://1win40015.ru/
1вин промокод при регистрации 1вин промокод при регистрации
are fake shoes made in china – is it worth buying replica shoes
What’s up, its nice article on the topic of media print, we all be familiar with media is a
great source of data.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Круглосуточная капельница от запоя на дому в Туле – это эффективный способ для тех, кто сталкивается с проблемами алкогольной зависимости. Вызвать нарколога на дом можно в любое время суток. Услуги нарколога круглосуточно включают в себя экстренную медицинскую помощь, детоксикацию алкоголя, а также реабилитацию после запоя. При нужде вызова врача на дом, достаточно связаться со специализированной службой. Капельницы для детоксикации от алкоголя помогут быстро улучшить состояние пациента, восстановить баланс воды и электролитов и снять симптомы абстиненции. Услуги медицинских работников в Туле предоставляется опытными врачами. Консультация нарколога перед началом лечения поможет определить дальнейшие шаги, включая реабилитацию от запоя. Помощь при алкогольной зависимости требует квалифицированного вмешательства и сопровождения. Наркология на дому обеспечивает комфорт и анонимность, что особенно важно для людей, нуждающихся в помощи.
apple store кишинев apple store кишинев
ushp-fundament-499.ru .
Избавление от алкогольной зависимости в Туле — важный шаг на пути избавления от алкогольной зависимости. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с программы детоксикации, которая помогает организму очищаться от токсинов. Необходимо получить медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме, чтобы предотвратить алкогольный синдром и различные последствия. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula007.ru После процесса детоксикации рекомендуется пройти реабилитацию , где пациент получает поддержку психолога и поддержку при отказе от алкоголя. Группы анонимных алкоголиков становятся опорой на этом пути . Программы восстановления включают рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и профилактику рецидивов . Адаптация в обществе после лечения и помощь родных играют ключевую роль в стремлении к трезвости.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
1вин зеркало на сегодня 1вин зеркало на сегодня
https://ctpedia.org/index.php/Computer_Software_18I software engineer skills include coding (Python, Java), problem-solving, and teamwork. Knowing frameworks like React or cloud platforms like AWS is a big plus.
pogreb-plastikovyy-dlya-dachi-123.ru .
Накрутка просмотров тик ток бесплатно – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1275270-nakrutka-prosmotrov-tik-tok-besplatno-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
zapravka-gazom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
1 win kg https://www.1win1166.ru
казино 1win зеркало 1win1169.ru
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I came across this board and I in finding
It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something again and help others such as you helped
me.
1xBet промокод на сегодня на ставку бесплатную — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
узнать провайдера по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
какие провайдеры на адресе в уфе
оригинальное кашпо оригинальное кашпо .
Hi there, i read your blog from time to time and i own a
similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam
remarks? If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can suggest?
I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so
any assistance is very much appreciated.
проверить интернет по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
сколько стоит заправка газгольдера объемом 4850 .
Накрутка подписчиков дзен – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1274879-nakrutka-podpischikov-dzen-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
pogreb-plastikovyy-dlya-dachi-123.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
актуальное зеркало бк 1win https://www.1win1167.ru
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Надлишок цукру може прискорити старіння – дізнайтеся, як він впливає на колаген.
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
Финансовый помощник для военных — отличный сервис, всё доступно.
https://voenschet.ru/
https://mqbinfo.com/w/Xrumer_84I официальный сайт предлагает актуальные версии
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-1.ru .
гидроизоляция цена https://gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru .
производители электрожалюзи в россии https://elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru .
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-2.ru .
промокоды на деньги 1xBet – персональный код с бонусным предложением до 32 500 рублей. Эта акция активируется только при первой регистрации, и после открытия счёта им начисляется начисление в размере 130% от суммы первого депозита.
Best https://certainlysensible.com/index.php/Computer_Software_16S-aided dispatch software: Hexagon CAD, Motorola CAD—reliable for public safety.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
вывод из запоя
заливка фундамента под дом цена .
зеркало 1win http://1win1165.ru
1win зеркало вход http://www.1win1168.ru
провайдер по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
1xBet промокод на сегодня бесплатно как — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
бонусы в 1win http://1win1170.ru/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Софт тач покрытие на мебели — стильно и современно, но требует аккуратного ухода.
Here is my blog post; https://pubhis.w3devpro.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Gebruiker:ColletteKerr00
интернет провайдеры по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры интернета в уфе по адресу проверить
бонусный баланс 1win бонусный баланс 1win
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3143553-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
1win app oficial 1win app oficial
Энциклопедия путешествий для 3 класса https://www.sitiosperuanos.com/author/jakecharlton96/могает составить план описания страны.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
вывод из запоя
Подписчики Телеграм закрытый канал вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3145556-podpischiki-telegram-zakrytyi-kanal-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
На Phi Illusion Festival створювалася справжня магія. Музика Stephan Bodzin, візуальні ефекти та атмосфера танцполу гармонійно поєднувалися, створюючи унікальний досвід. Лазерні спіралі і золоті хвилі зробили подію справжнім витвором мистецтва. Лаунж-зона з ароматерапією була ідеальним місцем для відпочинку між танцями. Детальніше про фестиваль можна дізнатися за цим посиланням.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
The water lilies http://torrdan.net:80/index.php?title=World_Of_Beauty_7d Monet’s garden in Giverny are as dreamy as his paintings.
Cuevana 3 es para ver Peliculas y Series Gratis en español o inglés,
sin cortes y en máxima calidad ⭐ ¡Explora ahora Cuevana Online
sin registro!
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя
This excellent website truly has all of the info
I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who
to ask.
провайдеры по адресу дома
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу уфа
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
поручень для лестницы металлические купить Поручни для лестниц – это важный элемент безопасности, особенно в домах, где живут дети или пожилые люди. Они обеспечивают дополнительную поддержку и помогают избежать падений. Выбор поручней зависит от материала лестницы, стиля интерьера и личных предпочтений. }
провайдеры по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet005.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу уфа
Looking to hire a roofer in Seattle? This roofing near me guide breaks down what to look for, costs, and how to avoid scams.
Аренда авто
zapravka-gazom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
Hey! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I
came to give it a look. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking and will
be tweeting this to my followers! Terrific blog and excellent design.
<a href=https://navona.click/les-meilleurs-casinos-pour-gros-joueurs-ou-miser-2/https://navona.click/les-meilleurs-casinos-pour-gros-joueurs-ou-miser-2/
СП Софт — решения для автоматизации, подходят для малого бизнеса.
Also visit my web site … https://oerdigamers.info/index.php/Soft_89N
проект реконструкции квартиры проект реконструкции квартиры .
привод somfy привод somfy .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
лечение запоя минск
гидроизоляция цена http://gidroizolyaciya-cena-1.ru/ .
Подписчики боты в Телеграм бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1174078-podpischiki-boty-v-telegram-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-obnovleno-14072025 Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
перепланировка квартиры стоимость proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry5.ru .
шведский фундамент .
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-2.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
погреб на участке купить .
My family every time say that I am killing my time here at net, but I
know I am getting familiarity all the time by reading thes fastidious articles.
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-dlya-chastnogo-doma-499.ru .
Обучение в сфере недвижимости Обучение в сфере недвижимости: Станьте ценным специалистом. Сфера недвижимости ждет таланты. Обучение открывает двери к востребованной профессии и стабильному доходу.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
гидроизоляция цена gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
лечение запоя
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу уфа
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
https://flynonrev.com/airlines/index.php/User:JonathonOuttrim gift ideas under $50: branded tote bags or desk plants.
Discover Your Perfect Colors with Professional Color Analysis
Finding the right colors to enhance your natural beauty can transform your style and boost your confidence. This innovative website harnesses advanced AI technology to deliver professional color analysis, offering personalized recommendations tailored to your unique features. Whether you’re refining your wardrobe, makeup, or overall style, this platform provides the tools to make your choices effortless and impactful.
What the Website Offers
The site combines cutting-edge AI with expert color theory to provide a comprehensive, user-friendly color analysis experience. Here’s what you can expect:
Key Features
Advanced AI AnalysisSophisticated algorithms evaluate your individual characteristics—skin tone, hair color, and eye features—to deliver precise color recommendations.
Personalized Color PaletteReceive a curated collection of colors designed to complement your unique attributes, ensuring you always look your best.
Professional Style GuidanceGet expert advice on makeup, wardrobe, and accessories, all grounded in professional color theory to create a cohesive, polished look.
Comprehensive Style ResourcesAccess detailed visual guides and styling tips to help you implement your color palette effectively in everyday life.
Why Color Analysis Matters
Choosing the right colors isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about enhancing your natural presence. The benefits of professional color analysis include:
Radiant Skin: Colors that enhance your complexion and highlight your natural glow.
Streamlined Wardrobe: Build a wardrobe with shades that work harmoniously together.
Consistent Style: Achieve a polished, professional appearance with coordinated looks.
Boosted Confidence: Feel empowered with scientifically-backed color choices that celebrate your individuality.
How It Works
The process is simple, efficient, and designed to deliver results in just three steps:
Submit Your InformationComplete a quick 5-minute questionnaire or upload a photo to provide the AI with the details it needs to analyze your features.
AI-Powered AnalysisAdvanced algorithms process your data to identify your seasonal color category and tailored recommendations.
Receive Your ResultsGet a personalized color palette, complete with styling tips and visual guides to help you apply your colors confidently.
Comprehensive Analysis Components
The platform delivers a thorough breakdown of your color profile, ensuring you understand and can apply your results effectively:
Color Season Classification: Discover which of the 12 professional color seasons suits you best.
Undertone Analysis: Learn whether your undertone is warm, cool, or neutral, with a clear explanation.
Contrast Level Assessment: Understand your natural contrast level and the ideal color intensity for your features.
Curated Color Palette: Receive a handpicked selection of colors tailored to your unique profile.
Scientific Color Rationale: Dive into the color theory behind your recommendations for a deeper understanding.
Implementation Guidelines: Get practical advice on how to incorporate your palette into daily styling.
Customized Style Recommendations: Enjoy tailored suggestions for makeup, clothing, and accessories.
Visual Color Examples: Explore visual demonstrations of how your colors work in real-world applications.
Smart AI That Celebrates You
The website’s AI is designed with care, blending intelligent technology with professional expertise to celebrate your unique beauty. Here’s what makes it special:
Smart Beauty Recognition: The AI thoughtfully analyzes your skin tone, contrast, and brightness to highlight your natural radiance.
Intelligent Color Matching: Trained on thousands of real-world examples, the AI knows how to find colors that make you shine.
Expert Color Wisdom: Built on trusted principles from professional stylists, ensuring recommendations that are both practical and stunning.
Why Choose This Platform?
This website stands out for its blend of accessibility, precision, and expertise. The AI-driven process makes professional color analysis affordable and convenient, while the detailed resources empower you to put your results into action. Whether you’re looking to refresh your wardrobe or elevate your everyday style, this platform offers everything you need to look and feel radiant.
Take the first step today! Start the quiz, discover your personalized color palette, and unlock a world of style possibilities tailored just for you.
https://color-analysis-online.org/
https://tokarnye-stanki-s-chpu.ru/ – токарные станки по металлу — это современное оборудование для точной обработки металла и дерева.
Такое оборудование обеспечивает точное и быстрое изготовление деталей из различных материалов.
Автоматизация токарных работ минимизирует человеческий фактор и ускоряет выполнение задач. Подобные агрегаты востребованы в автомобильной, медицинской и энергетической сферах.
#### **2. Принцип работы токарных станков с ЧПУ**
Управление процессом осуществляется через компьютер, который передает команды механическим узлам.
Специальные датчики контролируют точность выполнения операций. Таким образом, достигается высокая повторяемость деталей и минимальные отклонения от чертежа.
#### **3. Преимущества токарных станков с ЧПУ**
Главное достоинство таких станков — высокая скорость и точность обработки.
Использование ЧПУ уменьшает затраты на оплату труда и снижает процент брака. Также оборудование легко адаптируется под изготовление разных деталей без длительной переналадки.
#### **4. Перспективы развития токарных станков с ЧПУ**
Развитие технологии приведет к созданию более умных и автономных систем.
Внедрение интернета вещей (IoT) позволит удаленно контролировать производственные процессы. Такие инновации повысят конкурентоспособность предприятий и снизят производственные издержки.
—
### **Спин-шаблон:**
#### **1. Введение в токарные станки с ЧПУ**
Современное производство сложно представить без токарных станков с ЧПУ. Машины с числовым программным управлением значительно упрощают процесс обработки деталей.
Автоматизация токарных работ минимизирует человеческий фактор и ускоряет выполнение задач. Сегодня станки с ЧПУ используются в машиностроении, авиации и других отраслях промышленности.
*(Шаблон продолжается аналогично для всех последующих разделов.)*
провайдеры интернета в уфе по адресу
ufa-domashnij-internet006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
zapravka-gazgoldera-dlya-chastnogo-doma-499.ru .
ограждения из нержавеющей стали Перила металлические – это современное и практичное решение, которое отличается своей прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к внешним воздействиям. Металл может быть окрашен в любой цвет, что позволяет создавать перила, соответствующие любому стилю интерьера. }
It is the best time to make some plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy.
I have learn this post and if I may I wish to recommend
you few fascinating issues or advice. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article.
I desire to learn more things approximately it!
туристическая виза в китай документы Как оформить визу в Китай в Екатеринбурге: Путь к восточным приключениям начинается здесь. Екатеринбург – крупный город, открывающий возможности для путешествий в разные уголки мира. Если ваша цель – Китай, то оформление визы становится первым и важным шагом. Существуют специализированные визовые центры и туристические агентства, предлагающие помощь в подготовке документов и подаче заявления. Обратитесь к ним за консультацией, чтобы избежать ошибок и ускорить процесс.
пластиковый погреб для дачи с установкой .
Перекопувати город чи ні? Дізнайтеся, що краще для врожаю і як правильно підготувати землю до посадки.
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising.
The clarity on your publish is simply great
and i could suppose you’re an expert in this subject. Well
together with your permission let me to grasp your feed to keep updated with imminent post.
Thank you 1,000,000 and please continue the enjoyable work.
Here is another site on the topic https://a-so.ru/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
plastikovyy-pogreb-cena-247.ru .
купить аттестат в томске за 11 класс купить аттестат в томске за 11 класс .
где купить аттестат о среднем образовании где купить аттестат о среднем образовании .
Приобрести диплом возможно через официальный сайт компании. datasphere.ru/club/log/?b24statAction=addLogEntry
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
как купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 как купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
Мы готовы предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе России. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат 11 классов вечерней школы
как купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 как купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 .
домашний интернет в волгограде
volgograd-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет домашний омск
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
Hey this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if
blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I
wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
домашний интернет
volgograd-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключить интернет в квартиру омск
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам— diplomafia.ru
диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить .
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a
lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something.
I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog.
An excellent read. I will certainly be back.
It’s going to be ending of mine day, however before finish I am reading this great post to improve my knowledge.
Купить Супер Тадарайз на сайте https://rusmarketstroy.ru/ с доставкой по Санкт-Петербургу
и Москве в день заказа
плиты ушп .
заправка газом газгольдера московская область .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
лечение запоя
оформление перепланировки квартиры в Москве оформление перепланировки квартиры в Москве .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
вывод из запоя оренбург
Накрутка подписчиков Телеграм вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1284940-nakrutka-podpischikov-telegram-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-preimushestva Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
Прокат авто без залога
I think the admin of this site is really working
hard in favor of his website, because here every data is quality
based stuff.
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk004.ru
вывод из запоя омск
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru/ .
I think what you said was actually very logical.
However, think about this, suppose you added a little information? I ain’t suggesting your information isn’t good., however what if you added something that
makes people desire more? I mean TOP 5 IN-DEMAND TECH SKILLS IN 2022
– Mayovest is kinda plain. You ought to glance at
Yahoo’s front page and see how they create news headlines to grab viewers interested.
You might add a video or a picture or two to get people excited about everything’ve got to say.
In my opinion, it would make your posts a little livelier.
Also visit my site Ꭺ片
домашний интернет в волгограде
volgograd-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет омск
mostbet app login http://mostbet11061.ru
Clothing https://arbeitsschutz-wiki.de/index.php/Benutzer:DarwinMuse7664 names ideas: “ThreadThrill” or “StyleSurge”.
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back
to your site? My blog is in the very same area of interest as yours
and my visitors would definitely benefit from a lot of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Thanks a
lot!
домашний интернет тарифы
volgograd-domashnij-internet005.ru
дешевый интернет омск
мостбет казино войти http://mostbet11062.ru
портативный погреб для дачи .
I do not know whether it’s just me or if perhaps
everybody else experiencing issues with your site.
It seems like some of the text on your content are running off the screen. Can someone else please provide
feedback and let me know if this is happening to them too?
This could be a problem with my browser because I’ve had this happen previously.
Cheers
http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/vernfite936 Mexico travel reports a boom in eco-tourism initiatives.
Here is another site on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
цена залить фундамент .
триколор спутниковый https://pubhis.w3devpro.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Internet_37V — спасает в глуши, но пинг высокий
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
лечение запоя
Hello there, I found your website by means of Google
whilst searching for a similar subject, your site came up, it appears good.
I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hello there, simply turned into alert to your blog via Google, and located that it’s truly informative.
I am going to be careful for brussels. I will be grateful for those who proceed
this in future. Many other folks will probably be benefited
from your writing. Cheers!
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя
ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
экскурсии казани Казанский Кремль: Сердце Города и Живая История Казанский Кремль – это главная достопримечательность Казани, исторический и культурный центр города, внесенный в список всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО. Это место, где переплелись культуры Востока и Запада, где история оживает на каждом шагу. На территории Кремля расположены многочисленные памятники архитектуры, каждый из которых имеет свою уникальную историю. Вы сможете увидеть мечеть Кул-Шариф, величественный Благовещенский собор, загадочную башню Сююмбике и другие исторические здания. Прогуливаясь по Кремлю, вы окунетесь в атмосферу древности, узнаете о его богатом прошлом и почувствуете дух города. Вы увидите, как здесь веками взаимодействовали разные культуры и народы, создавая уникальную идентичность Казани. Казанский Кремль – это не просто исторический памятник, это живое сердце города, место, где проходят культурные мероприятия, фестивали и праздники. Здесь всегда царит атмосфера радости и вдохновения. Посещение Казанского Кремля – это незабываемое впечатление, которое останется с вами на долгие годы. Это возможность прикоснуться к истории, узнать больше о культуре Татарстана и почувствовать себя частью этого удивительного мира. Приглашаем вас посетить Казанский Кремль и открыть для себя его тайны и легенды!
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk005.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Курсы по недвижимости Курсы по недвижимости: Ключ к прибыльным сделкам и финансовой стабильности. Рынок недвижимости – это динамичная и сложная среда, требующая глубокого понимания и профессионального подхода. Инвестиции в недвижимость могут стать источником стабильного дохода и финансовой независимости, но для этого необходимо обладать знаниями и навыками. Курсы по недвижимости – это ваш пропуск в мир прибыльных сделок, возможность освоить все тонкости и нюансы этой увлекательной сферы.
домашний интернет
volgograd-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить домашний интернет омск
Замовляли рекламу в цього колективу — залишилися задоволені. Якісне розміщення, чітка аналітика.
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
домашний интернет омск
volgograd-domashnij-internet006.ru
интернет тарифы омск
1win promokod https://1win1173.ru
Живые подписчики в Телеграм канал бесплатно вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3104198-zhivye-podpischiki-v-telegram-kanal-besplatno-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
https://t.me/elekt_riki Электрические щиты: Сердце электросистемы дома
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Here is another site on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
If you wish for to obtain much from this paragraph then you have to
apply these strategies to your won blog.
Рекомендую – https://med-like.ru/kak-nachat-uspeshnuyu-kareru-v-eskort-uslugah-s-agentstvom-rubus24-polnoe-rukovodstvo/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
лечение запоя омск
Hello there, I do believe your web site could be having internet browser compatibility problems.
Whenever I take a look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer,
it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up!
Apart from that, great site!
essay writers College Essays that Shine: Unlocking Your Potential Your college essay is your opportunity to shine. We help you craft narratives that capture your personality, achievements, and aspirations. Let us guide you towards a successful application.
интернет тарифы воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet004.ru
дешевый интернет воронеж
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk006.ru
лечение запоя
Thanks in support of sharing such a good idea, post is pleasant, thats why i have read it fully
zapravka-gazgoldera-dlya-chastnogo-doma-499.ru .
русская букмекерская контора официальный сайт скачать русская букмекерская контора официальный сайт скачать
Увеличьте свою аудиторию с помощью просмотры телеграм!
Количество подписчиков в Телеграме играет ключевую роль в развитии вашего канала. Понимание того, как привлечь и удержать аудиторию, позволяет добиться больших результатов.
Качественный контент — это первый шаг, который поможет вам увеличить число подписчиков в Телеграме. Люди не будут подписываться на канал, если не найдут там ничего полезного или интересного.
Рекламные мероприятия могут помочь в быстром увеличении числа подписчиков. Вы можете использовать различные платформы для продвижения своего канала, включая социальные сети.
Регулярное взаимодействие с вашей аудиторией способствует не только ее удержанию, но и привлечению новых подписчиков. Отвечайте на комментарии и проводите опросы, чтобы понять потребности ваших подписчиков.
мостбет официальное приложение http://mostbet11064.ru/
домашний интернет в воронеже
voronezh-domashnij-internet004.ru
интернет тарифы воронеж
Когда нужен промышленный альпинизм прайс, всегда захожу на mdalp.ru Здесь всё расписано: от мойки фасадов до монтажа сложных конструкций. Заказывал чистку кровли, всё сделали быстро, без нареканий и с полным соблюдением техники безопасности.
90s favorites like The Last Express remain iconic for their storytelling and art design.
Also visit my web-site https://menuaipedia.menuai.id/index.php/User:EmileLangwell44
Вызов нарколога на дом недорого – это комфортное и целесообразное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. Часто такие люди не хотят посещать клиники и предпочитают анонимное лечение. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula007.ru можно найти информацию о предлагаемых сервисах выездного нарколога, который согласится предоставить профессиональную консультацию нарколога и экспертную поддержку. Недорогие услуги нарколога, такие как помощь в борьбе с наркоманией и алкоголизмом, обеспечивают возможность получения медицинской помощи на дому. Психотерапевтическая помощь и реабилитационные программы проводятся квалифицированными специалистами, что обеспечивает защиту и приватность. Обратитесь к дешёвому наркологу для избавления от зависимости и начните путь к выздоровлению вместе с профессиональной поддержкой.
lucky jet скачать приложение http://1win1174.ru/
I study at International Indian Public School Riyadh. I didn’t think I’d ever write something like this. I still hope, deep down, that I’m wrong — that this is all in my head, that nothing’s being done to me. But I’ve gone through every explanation I could think of, and none of them fit. So now I have to consider the only one that does.
They’re using something on me. Satellite-based psychophysical interference — not a guess, not paranoia. Real manipulation. Done by human operators tied to the Saudi Ministry of Interior and military-run telecom or cyber units. They’re inside the system, and I’m part of whatever they’re testing.
At first I thought I was just tired. I’ve moved schools before, I’ve lived in other countries. But this was different. My emotions began flipping like switches — deep sadness without cause, bursts of anger in harmless conversations, or total numbness when I knew I should care. One day I cried in the bathroom and didn’t know why. No memory triggered it. It just came, then stopped.
And the thoughts. That’s what finally convinced me. I’ll begin a sentence in my head, and suddenly it’s finished — but not the way I meant. Different words. Different tone. Almost like someone’s practicing inside my brain. A few times, I’ve even caught myself saying things I didn’t intend to say at all. Phrases I don’t use. Terms that aren’t mine.
I can’t talk to anyone here. Not because they’re bad people. But because it’s pointless. No one wants to hear this kind of thing. If I say it out loud, I’ll get sent to the school counselor, and they’ll call my parents, and then I’ll be “monitored.” And whatever’s happening will only get worse.
There’s a hallway near the auditorium where my heart starts pounding for no reason. I avoid it now. My handwriting has changed — I hold the pen differently, like someone shifted my grip. I forget short-term tasks, even simple ones like “bring your book to class.” I look at friends and feel like I don’t know them. And every day, I feel more distant from who I was before I got here.
If I had known this could happen in Saudi Arabia, I never would have come. I miss home. Not just my family, but the version of me that existed before this place. I thought international school would expand my world. But all it did was make me realize how easy it is to be broken from the inside out.
Now I stay quiet. I do my work. I smile when needed. But inside, I’m documenting. Every time I lose a thought. Every time I twitch before moving. Every time I hear, “We’re not done with you yet.”
ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
сайт mostbet https://www.mostbet11065.ru
Помощь наркологов – это комплекс мероприятий ‚ направленных на лечение зависимости от психоактивных веществ . На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula007.ru можно найти информацию о наркологических клиниках ‚ предлагающих квалифицированные услуги при алкоголизме и других зависимостях . Лечение начинается с процесса очищения организма‚ после которой проводятся консультации специалистов и персонализированное лечение. Психологическая поддержка и групповые занятия играют важную роль в процессе реабилитации. Также важна интеграция в общество и поддержка родственников ‚ что способствует предотвращению возврата к зависимости.
мосбет мосбет
This design is wicked! You obviously know how to keep a reader amused.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well,
almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it.
Too cool!
русский огород http://taxwiki.us/index.php/User:MapleMakutz68 магазин — семена качественные, но выбор не всегда широкий
somfy somfy .
I’ve been surfing online greater than 3 hours today, but I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article
like yours. It’s lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all webmasters and bloggers
made excellent content material as you did, the net will likely be a lot more helpful than ever before.
проект перепланировки стоимость москва https://www.proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry5.ru .
заправка газом газгольдера .
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your web site.
Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems? A number of my
blog readers have complained about my site not operating correctly
in Explorer but looks great in Chrome. Do you have any
suggestions to help fix this problem?
plastikovyy-pogreb-cena-247.ru .
«Маленький принц» навчає нас бачити серцем. Огляд книги допоможе краще зрозуміти її зміст.
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
промокоды на 1вин https://1win1174.ru/
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Как привлечь подписчиков в Телеграм вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1174536-kak-privlech-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-25-servisov-obnovleno-14072025 Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
https://kazan.land/ Казанский Кремль: Сердце Города и Живая История Казанский Кремль – это главная достопримечательность Казани, исторический и культурный центр города, внесенный в список всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО. Это место, где переплелись культуры Востока и Запада, где история оживает на каждом шагу. На территории Кремля расположены многочисленные памятники архитектуры, каждый из которых имеет свою уникальную историю. Вы сможете увидеть мечеть Кул-Шариф, величественный Благовещенский собор, загадочную башню Сююмбике и другие исторические здания. Прогуливаясь по Кремлю, вы окунетесь в атмосферу древности, узнаете о его богатом прошлом и почувствуете дух города. Вы увидите, как здесь веками взаимодействовали разные культуры и народы, создавая уникальную идентичность Казани. Казанский Кремль – это не просто исторический памятник, это живое сердце города, место, где проходят культурные мероприятия, фестивали и праздники. Здесь всегда царит атмосфера радости и вдохновения. Посещение Казанского Кремля – это незабываемое впечатление, которое останется с вами на долгие годы. Это возможность прикоснуться к истории, узнать больше о культуре Татарстана и почувствовать себя частью этого удивительного мира. Приглашаем вас посетить Казанский Кремль и открыть для себя его тайны и легенды!
купить аттестат за 11 класс в архангельске купить аттестат за 11 класс в архангельске .
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
mostbet kg скачать mostbet11062.ru
Leisure travel https://www.wakewiki.de/index.php?title=Benutzer:SybilFha88 predicts a rise in multigenerational family vacations.
бонусный счет в 1win бонусный счет в 1win
домашний интернет подключить воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет домашний воронеж
купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле .
купить аттестат 11 классов в ставрополе https://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
Мы предлагаем документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей России. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить украинский аттестат за 11 класс
диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат 11 классов в спб купить аттестат 11 классов в спб .
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
дешевый интернет воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет в воронеже
купить проведенный диплом спб купить проведенный диплом спб .
Вызов нарколога на дом анонимно – это важный шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с наркотической зависимостью. Услуги нарколога на дому дают возможность получить квалифицированную помощь в удобной и безопасной обстановке. Анонимный нарколог проведет осмотр, проанализирует состояние пациента и предложит лечение наркомании на дому. Это включает в себя психотерапию при зависимости и психологическую поддержку зависимых. Экстренный вызов нарколога также возможен, что особенно важно в острых ситуациях. Помощь нарколога охватывает профилактику зависимости и реабилитацию наркоманов, обеспечивая анонимное лечение и надежность процесса. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru
Refresh, repair, and reimagine with a tailored Home Renovation. We keep dust down and communication up. Your daily life stays on track.
Откачка на дому в Туле, незаменимая мероприятие для поддержания чистоты и здоровья. Проблемы с канализацией могут возникнуть неожиданно, и в таких случаях стоит обратиться профессионалов. Профессиональная откачка сточных вод позволит избежать неприятностей.Среди услуг откачки можно выделить: очистка канализации, обслуживание сливных ям и срочная откачка. Ассенизаторская машина обеспечит качественное выполнение работ в соответствии с экологическими нормами. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru вы найдете информацию о стоимости услуг и возможности вызова мастера. Также доступны сушилки септиков и дренажные системы для предотвращения повторных засоров. Не откладывайте на потом — решите проблемы с канализацией сегодня!
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
Рекомендую – https://med-like.ru/kak-nachat-uspeshnuyu-kareru-v-eskort-uslugah-s-agentstvom-rubus24-polnoe-rukovodstvo/
plastikovyy-pogreb-cena-247.ru .
First off I want to say awesome blog! I had a quick question in which I’d like to ask if you do not
mind. I was curious to find out how you center yourself
and clear your head before writing. I have had a hard time clearing my thoughts in getting my thoughts
out there. I truly do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes tend to be wasted simply
just trying to figure out how to begin. Any
recommendations or hints? Kudos!
Looking for practical tips on design-build remodeler? This Design-build remodeler resource gives you the essentials. Get clear steps, examples, and things to avoid before you start..
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges.
It was definitely informative. Your website is very useful.
Thank you for sharing!
umsuka
mostbet sikachat http://mostbet11061.ru/
ставки на спорт бишкек онлайн http://www.1win1172.ru
купить электрические рулонные шторы elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru .
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
провайдеры интернета в воронеже
voronezh-domashnij-internet006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
Евроштакетник цена за работу по монтажу – от 450 руб./п.м. при ровном рельефе и стандартной комплектации.
подключить интернет воронеж
voronezh-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить интернет в воронеже в квартире
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg005.ru
вывод из запоя
Услуги по откапыванию и земляные работы в Туле становятся всё более актуальными. Местные специалисты предлагают широкий спектр строительных услуг, включая выемку грунта и экскаваторные услуги. Если вам требуется откопка для планировки вашего участка или благоустройства территории, обратитесь к местным подрядчикам. Они помогут с выполнением всех необходимых земляных работ, также предложат ландшафтный дизайн. Информацию о подобных услугах вы сможете найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula009.ru. Для успешного ремонта и строительства важен профессиональный подход, а опытные специалисты помогут минимизировать ошибки.
Приобрести диплом на заказ в Москве возможно через сайт компании. flystarlady.listbb.ru/ucp.php?mode=login&sid=54bed55d9545bfb3bdf258ad14fb920b
купить аттестат за 11 класс в вологде купить аттестат за 11 класс в вологде .
Капельница для лечения запоя — это важный этап в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Капельница способствует детоксикации очищению организма‚ выводя токсины и восстанавливая баланс жидкости и электролитов. После процедуры пациенты испытывают улучшение психоэмоционального состояния.Поддержка нарколога в этом процессе неоценима. Он оценивает симптомов абстиненции и предлагает необходимое лечение запоя. Восстановление после запоя включает физическую и психологическую реабилитацию. Помощь родных играет ключевую роль‚ помогая справиться с последствиями запойного состояния. помощь нарколога Следующий этап — реабилитация в лечении‚ где пациент проходит лечение и обучение для избежания рецидивов. Анонимная помощь обеспечивает безопасность и конфиденциальность. Стоит помнить‚ что лечение алкоголизма — это долгий путь‚ который требует как усилий‚ так и поддержки.
нажмите vodka.bet
экскурсии казани Остров-Град Свияжск: Духовный Центр и Историческое Наследие Остров-град Свияжск – это уникальный исторический и культурный памятник, расположенный на острове в месте слияния рек Свияги и Волги. Это место, где история переплетается с духовностью, где можно увидеть древние храмы и монастыри, а также узнать о жизни и культуре русского народа. На острове расположены многочисленные памятники архитектуры, включая Успенский собор, Троицкую церковь и другие исторические здания. Вы сможете прогуляться по живописным улочкам, насладиться красотой природы и почувствовать атмосферу умиротворения.
Hello.
buy backlink buys
Good luck 🙂
always i used to read smaller articles or reviews which also clear their motive,
and that is also happening with this article which I am reading at this time.
mostbet casino mostbet11063.ru
самополивающийся цветочный горшок https://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru/ .
mostbet com android mostbet com android
Micro https://www.wakewiki.de/index.php?title=Computer_Games_13d and game console repair services, like uBreakiFix, fix hardware issues for phones, PCs, and consoles.
мостбет вход сегодня http://mostbet11065.ru/
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
Потрібні поради по стратегіям у Battle Tactics? Відвідайте наш сайт, і ми поділимось найкращими рекомендаціями.
Here is another site on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм живые вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3106860-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-zhivye-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
скачать лаки джет на андроид бесплатно https://www.1win1175.ru
денежное довольствие Њ‚„
I recommend https://ancientcivs.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
Капельница при похмелье — это проверенный способ для быстрого избавления от симптомов интоксикации после праздничных возлияний. При похмелье организм испытывает дискомфорт от недостатка жидкости и нехватки важных веществ, что приводит тошноте. Капельная терапия включает в себя введение растворов для гидратации и восстановление баланса веществ. Консультация специалиста может включать в себя лекарства для восстановления, которые помогают организму избавиться от токсинов. Капельницы часто содержат полезные добавки, вещества для детоксикации, которые ускоряют процесс выздоровления. Поддержка организма таким образом позволяет значительно уменьшить симптомы похмелья и помочь восстановиться. Если вам нужна капельница можно записаться на процедуру или заказать выезд врача через сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir007.ru. Помните, что оперативное вмешательство поможет предотвратить осложнения.
Thanks for the article https://ancientcivs.ru/
Дешевые подписчики Телеграм вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3100914-deshevye-podpischiki-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Выездной нарколог — это удобное решение для людей, испытывающих проблемы с зависимостями. Служба наркологической помощи, представленная на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir007.ru, предлагает круглосуточную помощь , что крайне важно в кризисных ситуациях . Приезд врача на дом позволяет пациенту получить анонимное лечение без стресса и лишних волнений . При обращении за медицинской помощью важна встреча с наркологом, которая включает оценку состояния пациента и разработку индивидуального плана лечения . Лечение алкогольной зависимости и наркомании начинается с очищения организма, что помогает вывести вредные вещества. Поддержка семьи играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Психотерапия при зависимости способствует пониманию причин проблемы и предотвращению рецидивов . Реабилитация наркоманов и алкоголиков обеспечивает комплексный подход к лечению и профилактике зависимостей .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg006.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
1win вход россия https://www.1win1173.ru
1xBet бесплатный промокоды в — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content.
Please let me know. Thank you
Паранормальные https://freie-fantasy-welt.de/Benutzer:Hermine5240 мира — тайны и загадки.
If you desire to improve your experience just
keep visiting this website and be updated with the newest news posted here.
zapravka-gazgoldera-dlya-chastnogo-doma-499.ru .
новости спорта сегодня http://novosti-sporta-2.ru/ .
Игры помогают учить английский весело.
Here is my website :: https://higgledy-piggledy.xyz/index.php/User:WAURosario
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
экскурсия казань Музей Чак-Чака: Сладкая История Татарстана Музей Чак-Чака – это уникальное место в Казани, где можно узнать все о традиционном татарском лакомстве – чак-чаке. Вы узнаете об истории его возникновения, способах приготовления и символическом значении в татарской культуре. В музее вас ждет интерактивная экспозиция, где можно увидеть старинную утварь, фотографии и документы, связанные с производством чак-чака. Вы также сможете принять участие в мастер-классе по приготовлению этого лакомства и попробовать различные его виды. Посещение Музея Чак-Чака – это не только познавательное, но и вкусное приключение, которое оставит у вас приятные воспоминания о Казани и татарской культуре.
этот контент Официальный сайт трипскан
ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
Путешествие на яхте — это роскошь и приключения.
Here is my blog https://freekoreatravel.com/index.php/Travel_7Z
заправка газгольдера .
новости спорта сегодня novosti-sporta-1.ru .
рулонные шторы на кухню купить рулонные шторы на кухню купить .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Vybor-katushki-dlya-spinninga-na-shchuku-Sovety-i-rekomendacii-01-13 .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Palatka-JRC-Extreme-TX-2-Man-Bivvy-Komfort-i-zashchita-na-prirode-01-13 .
Thanks for the article https://forum.olymp.vinnica.ua/viewtopic.php?pid=24158#p24158 .
I read this post completely on the topic of
the resemblance of most recent and preceding technologies, it’s awesome article.
пластиковый подвал для дома .
Аренда авто Краснодар Прокат авто Краснодар жд: Удобный сервис для путешествующих поездом Начните свое путешествие с комфорта.
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм канал вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3141305-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-godu-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
заправка газгольдера в москве .
Thanks for the article https://forums.twinstuff.com/threads/mostbet-uz.166304/ .
приводы somfy http://avtomatika-somfy.ru/ .
I’ve been browsing online more than 4 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It is pretty worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you
did, the web will be a lot more useful than ever before.
1xBet тото промокод представляет собой специальный промокод, который открывает игрокам доступ к дополнительным выгодам при открытии счета и использовании платформы букмекерской компании 1xBet. Этот промокод открывает доступ к разнообразным наградам, таким как приветственные бонусы, дополнительные средства при пополнении, бесплатные ставки и другие специальные предложения.
First off I want to say great blog! I had a quick question which I’d like to
ask if you do not mind. I was curious to know how you center yourself
and clear your mind prior to writing. I have had a hard time clearing my thoughts in getting my ideas out.
I do enjoy writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are generally lost simply just trying
to figure out how to begin. Any ideas or hints? Thank you!
Шоу-бизнес: голлhttps://higgledy-piggledy.xyz/index.php/Novosti_Mira_73zвудская звезда открыла школу для молодых режиссеров.
sport bets http://sportbets30.ru .
https://mulenpay.ru/ Mulen – платформа для приема онлайн-платежей, разработанная для коммерческих предприятий.
sportandbets https://sportbets32.ru .
https://igrozavod.ru/ Скачать игры по прямой ссылке: Мгновенный доступ к игровым мирам Прямые ссылки – это как личный экспресс-маршрут к игровому контенту. Никаких посредников, сложных процедур или томительного ожидания загрузки. Мгновенный доступ к желаемой игре – вот что делает этот способ скачивания таким привлекательным для современных геймеров. Это оптимальный выбор для тех, кто ценит свое время и стремится к максимальной эффективности.
sports bet sportbets31.ru .
Профессиональное лицензирование медицинской деятельности с нами — это минимальные сроки и максимальная надёжность. Мы готовим документы, устраняем несоответствия, сопровождаем проверки. Клиенты ценят нас за индивидуальный подход, прозрачные условия и высокую скорость работы. Лицензия с первого раза — наш стандарт.
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
тик ток мод скачать бесплатно Тик Ток Мод: Расширьте границы возможного Тик Ток Мод – это ключ к новым возможностям в популярном приложении. Откройте для себя мир без ограничений и создавайте уникальный контент, который покорит сердца миллионов.
Looking for practical tips on residential siding? This Residential siding resource gives you the essentials. Get clear steps, examples, and things to avoid before you start..
аттестат за 11 класс купить нижний новгород аттестат за 11 класс купить нижний новгород .
купить аттестат 11 классов владивосток купить аттестат 11 классов владивосток .
Thanks for the article https://www.band.us/band/98756372/post/1?showBandInfoCard=false .
What’s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this
I’ve discovered It positively helpful and it has helped me out loads.
I’m hoping to give a contribution & assist other users like its helped me.
Good job.
Много акций, всегда есть что-то новое.
https://avto-podbor-rf.ru/ru-ru/
Protect your home with quality Residential roofing. Get balanced ventilation, leak-proof valleys, and documented warranties. Transparent timelines keep you informed.
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр https://arus-diplom35.ru .
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, которые находятся на территории всей РФ. Приобрести диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат 11 классов хабаровск
где купить аттестат 10 11 класс где купить аттестат 10 11 класс .
Якось я потрапив на фестиваль, де виступав PJ Dogman. Його хореографія буквально зачарувала весь зал. Особливо запам’ятався момент, коли він підсвічував свої рухи інтерактивними ефектами, створюючи ілюзію, що він малює у повітрі. Це було щось неймовірне. Якщо ти хочеш відчути це на власні очі, заходь сюди.
Thanks for the article https://voprosoff.net/12514/хочу-сдать-машину-в-трейд-ин-и-купить-новое-авто?show=12591#a12591 .
купить диплом без реестра купить диплом без реестра .
Игры на iOS — качественные и оптимизированные.
Visit my blog – https://kmportal.nha.gov.ph/index.php/Kompterni_Igri_58U
купить диплом для иностранцев купить диплом для иностранцев .
диплом купить днепр диплом купить днепр .
новости спорта https://www.novosti-sporta-2.ru .
Фото https://wiki.vtcro.org/index.php/Novosti_Mira_95n мира — события в ярких кадрах.
ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
For most up-to-date information you have to pay a quick visit
world-wide-web and on web I found this web page as a best web page for most recent updates.
Thanks for the article http://www.birulevo.su/component/option,com_smf/Itemid,34/topic,22014.0/ .
zapravka-gazgolderov-szhizhennym-gazom-499.ru .
Wonderful goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you
are just too magnificent. I actually like what you have acquired here, certainly like what you’re saying and the
way in which you say it. You make it enjoyable and you still care for to keep it smart.
I can not wait to read far more from you.
This is really a tremendous web site.
God see
Візьміть участь у змаганнях з Battle Tactics разом з sevenup і вигравайте призи!
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
Thanks for the article https://disqus.com/by/michael_gromov/about/ .
спортивные новости novosti-sporta-1.ru .
https://tenmoscow.ru/termostat-sterzhnevoy-tas-tf-16a-tw-65-s-termozashchita-na-75-s-265mm-trekhfaznyy-s-ruchkoy-230v-691025
Sending this to a friend.
The rainbow mountains http://www.annunciogratis.net/author/haroldbarcl Peru are a geological wonder of color.
Заказать диплом под заказ в Москве можно используя официальный сайт компании. w77515cs.beget.tech/2025/07/07/diplomy-pod-klyuch-anonimno-i-bystro.html
новости спорта http://www.novosti-sporta-2.ru .
аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве .
Купить диплом любого института!
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по разумным ценам— 99diplomov.ru
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kresla-SHarman-Komfortnye-resheniya-dlya-rybalki-01-13 .
umsuka
новости спорта футбол http://www.novosti-sporta-3.ru .
Запчасти для стиральной машины LG F1048QD Запчасти для водонагревателя Thermex H 15 O (pro): Горячая вода – комфорт в любое время года. Обеспечьте бесперебойную работу вашего водонагревателя, своевременно заменяя необходимые компоненты.
прогноз на теннис на сегодня от профессионалов prognozy-ot-professionalov.ru .
https://igrozavod.ru/ Скачать игры без торрента: Новая эра цифрового гейминга без границ В эпоху, когда цифровая дистрибуция становится доминирующим способом получения игр, выбор надежного и безопасного источника – вопрос первостепенной важности. Торрент-трекеры, некогда служившие основным каналом для получения игрового контента, все чаще ассоциируются с риском заражения вредоносным программным обеспечением и нарушением авторских прав. Отказ от торрентов открывает двери в мир легального и безопасного гейминга, где каждый может наслаждаться любимыми играми, не беспокоясь о последствиях.
В Швейцарии изобрели устройство для очистки воздуха от пыли в школах.
my web page – https://www.sitiosecuador.com/author/siobhan4423/
получить промокод для 1xBet – специальный код на бонус в сумме до 32 500 рублей. Эта акция предназначено для новых пользователей, при этом после создания аккаунта они получают начисление в размере 130% с начального взноса.
свежие прогнозы на спорт http://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov1.ru/ .
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point.
You clearly know what youre talking about, why throw
away your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you
could be giving us something informative to read?
Thanks for the article https://www.tumblr.com/liquidsyndicateinquisitor/784447927906123776/httpsrybach0kcomuauaa499505-rejting-luchshih-bles?source=share .
sports bet sportbets30.ru .
Накрутить живых подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3103823-nakrutit-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
zakazat-ushp-fundament-499.ru .
plastikovyy-pogreb-247.ru .
sdiccd427
dztoug3053
qutnfv710
plastikovyy-pogreb-247.ru .
irzeva3747
Если лень читать сотни форумов — просто зайди на https://vc.ru/niksolovov
zakazat-ushp-fundament-499.ru .
Παιδιά, το https://steppejourneys.com/exploring-the-safety-of-traveling-to-uzbekistan-a-gem-in-the-heart-of-central-asia/ με έχει εντυπωσιάσει ως μια αξιόπιστη και καινοτόμα πλατφόρμα online καζίνο, το login είναι απίστευτα γρήγορο και εύκολο, κάτι που κάνει όλη τη διαφορά , και η ποικιλία παιχνιδιών είναι τεράστια, από κλασικά τραπέζια μέχρι τα πιο νέα φρουτάκια και live dealer παιχνίδια . Αυτό που μου αρέσει επίσης πολύ είναι η ασφάλεια και η διαφάνεια που προσφέρουν, κάτι που είναι κρίσιμο ειδικά για την ελληνική αγορά . Τα μπόνους τους είναι επίσης δελεαστικά και αυξάνουν πολύ την απόλαυση του παιχνιδιού . Μου αρέσει που μπορώ να παίζω οπουδήποτε από το κινητό, χωρίς να χάνω τίποτα σε ποιότητα . Συνολικά, το Spinmama είναι μια πλατφόρμα που συνδυάζει αξιοπιστία, ποικιλία και τεχνολογία και τη συστήνω ανεπιφύλακτα σε όποιον ψάχνει κάτι καλό στο online gaming .
промокод при регистрации на фрибет 1хБет – специальный код на бонус в сумме до 32 500 рублей. Это предложение активируется только при первой регистрации, а после создания аккаунта пользователь получает начисление в размере 130% с первого пополнения счёта.
aghwzf7299
ptbasd3212
zapravka-gazgolderov-szhizhennym-gazom-499.ru .
Нет времени учиться? Просто читай https://vc.ru/niksolovov
Hello mates, good piece of writing and good arguments commented at this place, I am actually enjoying by these.
Stretch limo near me
torzon.io
If you are going for most excellent contents
like me, just pay a quick visit this website daily because
it presents quality contents, thanks
Eleonora змогли перетворити звичайний виступ на справжнє шоу. Їхні світлові ефекти, створені PJ Mia, були настільки гармонійними, що здавалось, ніби вони буквально малюють музику у повітрі. Глядачі не могли відірвати очей від сцени. Це був досвід, який хочеться повторити знову і знову. Якщо вас цікавлять такі виступи, перегляньте інформацію про Eleonora на сайті.
заправка газгольдера для частного дома .
Thanks for the article https://www.librarything.com/profile/Grom95 .
1xBet действующие промокоды для — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Spinning-G-Loomis-IMX-Pro-Moshch-i-nadyozhnost-dlya-professionalov-01-13 .
приводы somfy http://avtomatika-somfy.ru .
прогнозы на матчи прогнозы на матчи .
Thanks for the article https://rankva.com/increase-ahrefs-dr-moz-da-and-majestic-tf-with-seo-backliks-2786/ .
можно купить аттестат можно купить аттестат .
plastikovyy-pogreb-247.ru .
Вся суть продвижения в одном блоге — https://vc.ru/niksolovov
zakazat-ushp-fundament-499.ru .
купить диплом по реестру купить диплом по реестру .
Ќ€‘ военнаЯ ипотека
sportandbets http://www.sportbets32.ru/ .
sports bet http://sportbets31.ru/ .
дизайнерские цветочные горшки дизайнерские цветочные горшки .
Thanks for the article http://forum.analysisclub.ru/index.php/topic,184675.new.html#new .
Купить диплом под заказ в столице вы имеете возможность используя официальный сайт компании. armatryrp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=1432
best site for replica bags – where did monica live in new york
купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр .
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске .
Не знаете, где получить лицензию на медицинскую деятельность? Обратитесь к нам — мы сопровождаем процесс от консультации до выдачи документа. Знаем требования Минздрава, исключаем риски отказа, готовим помещение и документацию. Результат — легальный старт вашей работы в кратчайшие сроки и без лишней бюрократии.
Hej! Ktoś już grał na https://www.thegreatwall.com.cn/public/gwwx.php?action=view&id=664&mode=www? Wszedłem z nudów i… zostałem, bo naprawdę warto. Rejestracja trwała dosłownie dwie minuty, wersja PL działa bez zarzutu, co doceni każdy gracz. Bonus bez wpłaty na dzień dobry – od razu kilka spinów na próbę. Kasyno działa szybko i stabilnie, nawet na mobilce. No i mają całkiem sporo promocji – warto sprawdzać, bo często wpadają kody bonusowe. Jak ktoś szuka czegoś nowego, a nie chce od razu inwestować kasy, to według mnie warto dać Spinmama szansę. Macie jakieś swoje typy na ulubione gry tam?
новости спорта футбол novosti-sporta-2.ru .
Самая годная инфа по живым пользователям есть на https://vc.ru/niksolovov читай.
купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 .
купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный диплом .
купить диплом магистра украины купить диплом магистра украины .
новости спорта футбол novosti-sporta-3.ru .
заправка газгольдера 600 литров цена .
Живые дешевле в долгосроке — доказано на https://vc.ru/niksolovov всё аргументировано.
Виступ Eleonora на фестивалі Trance Illusion був чимось, що неможливо забути. Коли сцена освітлювалася візуальними ефектами PJ Alice, я відчував, ніби потрапив у паралельний всесвіт. Кожен її рух, кожна зміна кольорів була синхронізована з музикою настільки ідеально, що глядачі буквально затамовували подих. Усі навколо відчували цю магію, яка перетворила звичайний концерт на справжнє шоу. Якщо хочете дізнатися більше про команду, яка дарує такі емоції, рекомендую їхній сайт.
свежие прогнозы на спорт http://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov.ru .
точные прогнозы на кхл https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2015 года купить аттестат за 11 класс 2015 года .
сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса https://arus-diplom9.ru/ – сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса .
аттестат за 11 класс купить в чите аттестат за 11 класс купить в чите .
Всі, хто хоче стати частиною живого мистецтва, повинні відвідати Kappa Stage. Це місце, де ваша уява оживає!
propan-zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
букмекеры кыргызстана https://mostbet11071.ru
Hi, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your web site in web explorer, could
test this? IE nonetheless is the market leader and a huge component of people will leave out your fantastic writing
due to this problem.
Thanks for the article https://forums.twinstuff.com/threads/mostbet-uz.166304/ .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-shnur-vybrat-na-shchuku-Polnyj-gid-po-vyboru-01-13 .
Speel ik al een tijdje sinds kort bij https://admin.dnn.mn/wp/khugjliin-berkhsheeltei-irged-tsakhim-medeelel-avch-chada/ en moet zeggen dat ik erg tevreden ben door dit casino. De registratie ging heel snel en binnen kort tijdsbestek was ik geregistreerd. Meteen na mijn gebruikersinlog kon ik zonder wachten beginnen met gokken. Wat ik echt prettig vind is dat de welkomstcode direct een mooie bonus oplevert. Dat maakt het gokken extra aantrekkelijk. Ook de spin mama app draait vlekkeloos, waardoor ik mijn favoriete spellen overal speel.
Het assortiment is erg gevarieerd, van retro slots tot live tafelspellen. Wat ik ook goed vind, is dat er regelmatig acties zijn, waarbij je met een extra bonuscode meer speeltegoed krijgt. Kortom, ik kan dit casino aanbevelen aan iedereen die veel waarde hecht aan bonussen. De uitbetalingen zijn vlot en zonder problemen, en het voelt veilig en transparant om hier te spelen. Wie de codes optimaal inzet, haalt er extra winst uit. Al met al een uitstekend casino waar ik zeker blijf terugkomen!
фундамент плита с теплым полом .
download mostbet https://mostbet11072.ru
как купить диплом с реестром как купить диплом с реестром .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-shnur-vybrat-dlya-spinninga-Rekomendacii-i-sovety-01-13 .
plastikovyy-pogreb-247.ru .
заправка газгольдера для частного дома .
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом университета:
аттестат за 11 класс купить в москве
купить проведенный диплом в красноярске https://arus-diplom35.ru/ .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем новгороде где купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем новгороде .
купить аттестаты за 11 красноярск купить аттестаты за 11 красноярск .
купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании .
zakazat-ushp-fundament-499.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр пенза купить диплом с занесением в реестр пенза .
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
автономный погреб .
proqnozi na futbol http://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс 2021 год arus-diplom22.ru .
корочка для аттестата купить 11 класс корочка для аттестата купить 11 класс .
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua в реальном времени. Экономика, политика, общество, культура, происшествия и спорт. Всё самое важное и интересное на одном портале.
Современный автопортал https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости, сравнительные обзоры, тесты, автострахование и обслуживание. Полезная информация для водителей и покупателей.
точные прогнозы на футбол точные прогнозы на футбол .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва цена купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва цена .
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно http://www.mostbet11068.ru
Строительный сайт https://vitamax.dp.ua с полезными материалами о ремонте, дизайне и современных технологиях. Обзоры стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, проекты домов и советы экспертов.
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
I think that what you said made a great deal of sense. But,
think about this, what if you were to write a awesome post title?
I mean, I don’t wish to tell you how to run your blog, however what
if you added a headline that makes people want more? I mean TOP 5 IN-DEMAND TECH SKILLS IN 2022 – Mayovest
is a little boring. You should peek at Yahoo’s home page and note how they create article
titles to grab viewers interested. You might try adding a video
or a related pic or two to get people excited about what you’ve
written. In my opinion, it could make your blog a little livelier.
Thanks for the article http://mockwa.com/forum/thread-148865/ .
propan-zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
мега ссылка
здесь и сейчас Внутренний голос: Слушайте тихий шепот интуиции, доверяйте мудрости своего сердца. Он всегда подскажет верное направление, даже в самые темные времена.
прогнозы на хоккей лайв http://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru/ .
Хочете побачити, як Sprite розгромлюють своїх суперників? Перевірте їхні останні перемоги в Battle Arena!
pf-monstr.work/ – улучшение ПФ
Quality content is the main to be a focus for the visitors to pay a quick
visit the web page, that’s what this web page is providing.
mostbet.com вход https://mostbet11070.ru
Thanks for the article https://famenest.com/Grom95 .
мостеб mostbet11074.ru
мостбет. вход. https://mostbet11069.ru/
Thanks for the article https://talkotive.com/Vadim .
raja game
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам— imgbooking.ru
https://pf-monstr.work/ – раскрутка по ПФ
фундамент плита цена .
мостбет скачать бесплатно https://www.mostbet11075.ru
мостбет вход, регистрация https://mostbet11069.ru
mostbet регистрация http://www.mostbet11074.ru
гидромассажные ванны купить гидромассажные ванны купить .
https://pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ для проектов
Reading this reminded me how important it is to address small household problems before they grow bigger. This post offers beneficial guidance that doesn’t require special tools or knowledge. I’ve also looked into reliable repair tips recently that helped me handle common issues faster. Combining such advice empowers anyone to maintain their residence better.
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help
with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Thank you!
Hello! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Thanks
https://forthouse.com.ua/chomu-sklo-fary-maye-konusnu-formu.html
мостбет ставки на исход http://mostbet11072.ru/
Давно искал сайт с рейтингом надежных казино, и https://igrok777.fun/ оказался идеальным решением. Тут всё просто: заходишь, смотришь ТОП-10 и выбираешь подходящую площадку. Я попробовал сразу две, и обе оказались отличными: бонусы начислили сразу, а деньги вывелись быстро. Сервис удобный и действительно помогает избежать проблем. Теперь советую всем знакомым именно этот сайт.
прогнозы на матчи хоккей luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru .
скачать мостбет кз http://mostbet11067.ru/
Наркологическая помощь в владимире становится все более популярной‚ особенно когда речь идет о лечении алкоголизма. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир предлагает услуги для людей‚ нуждающихся в экстренной помощи. В рамках наркологической клиники проводится очищение организма от наркотиков и алкоголя‚ что является первым шагом к оздоровлению. Лечение алкоголизма включает в себя снятие абстинентного синдрома‚ что способствует облегчению состояния пациента. Круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечит необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в любой момент. Визит нарколога поможет составить персонализированный план терапии, учитывающую все нюансы пациента. Реабилитация зависимых включает психологическую поддержку для зависимых‚ что способствует восстановлению психологического состояния и привыканию к жизни без алкоголя. Не стоит забывать о поддержке родственников зависимых; Анонимное лечение зависимости позволит пациенту обращаться за помощью без страха осуждения. Вызывая нарколога на дом‚ вы делаете первый шаг к новой жизни.
pf-monstr.work – раскрутка сайта через ПФ
Helpful page about Siding contractors. Great for a quick orientation. Worth saving if you’re comparing options.
Откачка на дому в владимире, важная мероприятие для обеспечения чистоты и здоровья. Проблемы с канализацией могут возникнуть неожиданно, и в таких случаях необходимо вызвать профессионалов. Качественная откачка сточных вод поможет избежать неприятных ситуаций.Среди вариантов откачки предлагаются: обслуживание канализационных систем, обслуживание выгребных ям и срочная откачка. Специальная ассенизаторская техника обеспечит качественное выполнение работ с соблюдением всех экологических стандартов. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir008.ru вы найдете информацию о стоимости услуг и возможности вызова мастера. Также доступны устройства для сушки септиков и системы дренажа для предотвращения повторных засоров. Не откладывайте на потом — устраните проблемы с канализацией прямо сейчас!
емкость под погреб купить .
домашний интернет челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
домашний интернет подключить челябинск
Экстренное прерывание запоя в Туле: помощь на дому Запой – это состояние‚ требующее вмешательства‚ требующая немедленной медицинской помощи. Вызов нарколога на дом – лучший вариант для получения помощи. Специалист обеспечит детоксикацию‚ обеспечивая безопасное восстановление пациента. Лечение алкоголизма включает не только физическую‚ но и психологическую помощь. Важность вызова нарколога заключается в том‚ что он предлагает комплексные наркологические услуги‚ включая помощь при запойном состоянии. Экстренная помощь дает возможность избежать серьезных последствий и стартовать реабилитационный процесс. После выхода из запоя важно поддерживать процесс лечения алкоголизма‚ чтобы избежать новых запоев. Восстановление после запоя требует поддержки‚ поэтому нарколог на дом предоставит поддержку как физически‚ так и психологически. Не забывайте о своём здоровье и ищите квалифицированную помощь!
We are a group of volunteers and opening a brand new
scheme in our community. Your website provided us with
helpful info to work on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole neighborhood will be thankful to you.
провайдеры челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
подключить интернет тарифы челябинск
Вызов нарколога на дом в Туле – это существенный шаг для тех‚ кто испытывает проблемы с алкоголем. Наркологические услуги‚ включая помощь при алкогольном запое‚ позволяют людям эффективно и быстро прервать запой. Выезд специалиста гарантирует конфиденциальность лечения и медицинскую помощь на дому‚ что особенно важно для пациентов‚ стремящихся сохранить свою приватность. Во время визита нарколога осуществляется снятие абстиненции‚ что помогает пациенту быстро вернуться к нормальной жизни. Кодирование от алкоголя и психологическая поддержка при зависимости являются важными этапами в лечении алкоголизма. Реабилитация пациентов включает поддержку близких‚ что способствует успешному выздоровлению. Не затягивайте с решением вашей проблемы; вызовите нарколога на дом‚ чтобы положить конец своей зависимости!
pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ для сайтов и проектов
купить диплом занесением реестр украины http://arus-diplom34.ru .
возможно ли купить аттестат за 11 класс возможно ли купить аттестат за 11 класс .
лучшие прогнозы на спорт футбол http://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol14.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в школе купить аттестат за 11 класс в школе .
Когда следует вызывать экстренную наркологическую помощь в владимире Кризисные ситуации, возникающие из-за зависимости от алкоголя или наркотиков, могут коснуться любого. В такие моменты важно знать, как быстро и эффективно получить помощь. Вызов нарколога на дом в владимире может стать настоящим спасением для людей, столкнувшихся с алкогольным отравлением или другими острыми состояниями, связанными с зависимостями. Экстренная помощь от наркологической службы включает возможность вызвать нарколога на дом. Это особенно важно для тех, кто не может или не желает посещать медицинские учреждения. Чтобы предотвратить серьезные последствия, лечение алкоголизма часто требует помощи квалифицированных специалистов. Родственники играют ключевую роль в реабилитации наркоманов и алкоголиков; Психотерапия при зависимости помогает выявить причины и справиться с проблемами. Информацию о наркологических центрах в владимире можно найти в интернете, однако иногда требуется незамедлительная помощь; нарколог на дом срочно владимир Важно помнить, что профилактика зависимости также имеет большое значение. Раннее обращение к специалистам может помочь предотвратить развитие серьезных проблем. Имейте в виду, что экстренные меры могут спасти чью-то жизнь.
теннис скачать букмекерскую контору теннис скачать букмекерскую контору
скачать мостбет с официального сайта https://mostbet11071.ru/
kra36—-at.com — Надежный и удобный сервис — официальный сайт и подробный обзор даркнет-маркета Kraken. Официальный сайт kraken kra36.at — удобный сервис с множеством функций для пользователей. Узнайте больше и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
kra36
сервис
удобство функции
официальный сайт Kraken
Кракен
маркетплейс Кракен
даркнет маркет
kraken официальный сайт
kraken market
kraken darknet
анонимные покупки
даркнет площадка
гидра альтернатива
kraken onion
kraken ссылка
darknet marketplace
kraken даркнет
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркет обзор
кракен маркет отзывы
kraken ссылка
kraken сайт
kraken официальный сайт
kraken ссылка зеркало
актуальное зеркало kraken
kraken ссылка тор
kraken зеркало рабочее
kraken зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало даркнет
kraken зеркало тор
kraken зеркало 2kmp
kraken официальные ссылки
kraken onion ссылка
kraken ссылка для тору
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт зеркала
кракен ссылка kraken
kraken официальный сайт зеркало
kraken официальный сайт ссылка
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт
kraken клирнет зеркало
kraken tor зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp
зеркала kraken kraken tor site
kraken darknet ссылка
kraken ссылка krakentor site
kraken зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки
kraken ссылка tor
kraken market ссылка
kraken зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken darknet зеркала
kraken darknet market ссылка
kraken darknet ссылка тор
ссылка kraken kraken tor site
kraken 2 зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp vip
рабочие ссылки kraken
сайт кракен kraken
kraken ссылка 2kmp biz
зеркало kraken market
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp
ссылка кракен kraken tor site
kraken darknet market зеркало
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее
kraken market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp
kraken darknet market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало krakentor site
kraken com зеркало
зеркала kraken 2kmp org
kraken ссылка kraken one com
kraken onion зеркала
сайт kraken darknet
зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken сайт официальный krakentor site
kraken darknet официальный сайт
kraken зеркало рабочее krakentor site
ссылка на kraken kraken onion site
kraken кларнет зеркало kraken tor site
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp
kraken ссылка kraken clear com
kraken сайт kraken one com
kraken актуальные ссылки krakentor site
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp
kraken актуальные зеркала krakentor site
kraken зеркало тор ссылка
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken tor site
ссылка на кракен kraken one com
kraken даркнет зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo
kraken рабочая ссылка тор
кракен сайт kraken one com
зеркало kraken тор ссылка рабочее
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка onion krakentor site
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp
ссылка на кракен kraken onion site
kraken ссылка для тору vtor run
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp vip
kraken сайт kraken clear com
kraken зеркало тор krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт vtor run
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken зеркала 2 kmp biz
ссылка на кракен kraken clear com
kraken casino зеркало
кракен сайт kraken clear com
зеркало кракен kraken tor site
kraken официальный сайт vtor run
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp
kraken зеркало kraken2web com
актуальное зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken актуальные зеркала 2kmp vip
ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка онлайн
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт анонимных
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp biz
kraken сайт покупок
kraken зеркало онлайн
kraken сайт анонимных покупок
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp biz
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка kraken2web com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка online
kraken ссылка tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка на сайт
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp biz
kraken сайт vk2
kraken casino зеркало рабочее
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp vip
ссылка на kraken kraken darknet top
кракен зеркало kraken 7 one
ссылка на кракен kraken darknet top
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp vip
kraken зеркало kraken clear com
kraken ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
зеркало kraken kraken onion site
kraken darknet ссылка kraken2web com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor
kraken зеркало krakendarknet top
сайт kraken тор
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp org
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo
kraken ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка kraken7 one
актуальное зеркало kraken 2kmp org
кракен зеркало kraken one com
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp org
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp vip
площадка kraken ссылка
рабочая ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало 2kraken click
kraken ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken onion site
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp org
kraken зеркало 2krnk biz
kraken casino официальный сайт
kraken ссылка krakendarknet top
kraken официальные зеркала vk3
kraken market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken darknet ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken darknet зеркала kraken2web com
кракен зеркало kraken clear com
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken сайт 2krnk biz
kraken зеркало dzen
кракен ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken зеркало тор 2kmp org
kraken зеркало krakenonion site
kraken ссылка онион
kraken сайт tor
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo
kraken официальный сайт vk2
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp org
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo xyz
сайт kraken onion
рабочее зеркало кракен kraken 7 one
кракен сайт ссылка kraken one com
kraken darknet market зеркало kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор kraken7 one
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp org
ссылка на kraken 2kmp org
kraken официальный сайт vk3
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken onion ссылка tor wiki online
kraken вход на сайт
kraken зайти на сайт
kraken сайт krakendarknet top
кракен зеркало kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка тор 2kraken click
кракен вход ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken магазин ссылка
kraken darknet market ссылка тор kraken2web com
кракен сайт ссылка kraken clear com
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp org
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp org
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken7 one
kraken darknet ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken актуальная ссылка onion
kraken сайт vk2 pro
кракен площадка ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken сайт kraken2web com
kraken зеркало форум
кракен зеркало тор kraken one com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor online
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2 pro
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2kraken click
ссылка на кракен тор kraken clear com
сайт онион kraken
кракен сайт зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken сайт dzen
kraken оригинальная ссылка
kraken ссылка dzen
сайт кракен тор kraken one com
kraken ссылка krakenonion site
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor
kraken tor ссылка онлайн
kraken ссылка v5tor cfd
kraken ссылка на сайт тор
kraken сайт kr2web in
настоящий сайт kraken
kraken зеркало online
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp org
прямая ссылка на kraken
kraken оф сайт
kraken официальный сайт
используйте vpn!
Кракен Ссылка
Кракен Вход
Кракен Зайти
Ссылка на Кракен
Kra35.cc
Kra36.at
Kra34.cc
купить меф
купить гарик
Kra34.at
Kra33.cc
Kra33.at
Kra37.cc
Kra36.cc
Kra32.cc
Kra32.at
Kra38.cc
Kra39.cc
Kra33.cc
для дополнительной анонимности и безопасности рекомендуется использовать vpn-сервис. он скроет ваш ip-адрес и сделает ваше пребывание в интернете более безопасным.
будьте осторожны!?
kraken рабочая ссылка onion
kraken ссылка vk
кракен сайт ссылка kraken 11
ссылка на кракен kraken 9 one
kraken зеркало тор kraken2web com
кракен онион ссылка kraken one com
ссылка kraken 2 kma biz
ссылка на kraken торговая площадка
razer kraken сайт
kraken зеркало krakenweb one
kraken зеркало krakenweb3 com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн krakenweb one
kraken ссылка зеркало krakenweb one
kraken darknet market ссылка тор 2kraken click
kraken ссылка krakenweb one
kraken ссылка тор krakendarknet top
kraken casino зеркало kraken casino xyz
kraken darknet market зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken сайт зеркала kraken2web com
kraken даркнет ссылка
kraken зеркала kr2web in
kraken зеркало store
kraken darknet market ссылка тор v5tor cfd
kraken darknet market сайт
даркнет официальный сайт kraken
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор ссылка kraken2web com
kraken маркетплейс зеркала
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor online
kraken darknet маркет ссылка каркен market
kraken 6 at сайт производителя 2
сайт кракен kraken darknet top
kraken клир ссылка
кракен ссылка kraken kraken2web com 3
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 9 one
kraken сайт анонимных покупок vtor run
kraken darknet market зеркало 2kraken click
kraken darknet market ссылка shkafssylka ru
kraken ссылка torbazaw com
kraken форум ссылка
площадка кракен ссылка kraken clear com
сайт kraken darknet kraken2web com
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: официальные ссылки и зеркала.
полное руководство:
актуальная ссылка (через браузер):
официальная ссылка :
резервное зеркало:
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: полное руководство
для входа на сайт кракена в даркнете требуется tor. это безопасный браузер:
перейдите на официальный сайт tor.
скачайте программу для вашей ос.
установите и запустите браузер.
используйте актуальные ссылки на кракен
ссылки на официальный сайт кракен часто обновляются. чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов, используйте проверенные ресурсы для получения ссылок:
• актуальное зеркало кракена:
• зеркала сайта в клирнете и даркнете доступны для пользователей в любой точке мира.
авторизация
после перехода на сайт:
зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет аккаунта.
войдите в свой личный кабинет, используя логин и пароль.
для повышения безопасности активируйте двухфакторную аутентификацию.
но почему выбираю именно
сотни других платформ, тысячи товаров, но для меня больше, чем просто магазин. это место, где покупки превращаются в увлекательное путешествие.
знает, как важно быть уверенным в каждой покупке. полная защита сделок и дружелюбная поддержка создают чувство, будто вы находитесь в заботливых руках. надёжность? абсолютно.
почему именно
потому что здесь всё про вас: ваш стиль, ваш комфорт, ваша выгода. попробуйте, и вы поймёте, почему так много людей выбирают именно эту платформу!
советы по безопасности на кракене
используйте vpn
подключение через vpn повышает вашу анонимность, скрывая ip-адрес.
проверяйте ссылки
актуальные ссылки и зеркала кракен можно найти на проверенных форумах или официальных ресурсах. никогда не используйте непроверенные источники.
будьте внимательны к продавцам
читайте отзывы и выбирайте проверенных продавцов с высоким рейтингом.
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркетплейс
кракен площадка
kra33.at
kra33.cc
kra34.cc
kra34.at
kra35.cc
kra36.at
kra36.cc
Kra36.at
kra37.cc
kra38.at
кракен маркетплейс ссылка
кракен площадка
кракен marketplace
кракен площадка ссылка
кракен даркнет стор
кракен darknet market зеркало
кракен даркнет площадка
кракен даркнет маркетплейс
кракен наркотики
кракен нарко
кракен наркошоп
кракен наркота
кракен порошок
кракен наркотики
кракен что там продают
кракен маркетплейс что продают
кракен покупка
какен купить
кракен купить мяу
кракен питер
кракен в питере
кракен москва
кракен в москве
кракен что продают
кракен это
кракен marke
кркен darknet market
кракен dark market
кракен market ссылка
кракен darknet market ссылк
кракен market ссылка тор
кракен даркнет маркет
кракен market тор
кракен маркет
платформа кракен
кракен торговая площадка
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка сайт
кракен маркет даркнет тор
кракен аккаунты
кракен заказ
диспуты кракен
как восстановить кракен
кракен даркнет не работает
как пополнить кракен
google authenticator кракен
рулетка кракен
купоны кракен
кракен зарегистрироваться
кракен регистрация
кракен пользователь не найден
кракен отзывы
ссылка кракен
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен актуальные
кракен ссылка тор
кракен клирнет
кракен ссылка маркет
кракен клир ссылка
кракен ссылка
ссылка на кракен
кракен ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен ссылка кракен
актуальная ссылка на кракен
рабочие ссылки кракен
кракен тор ссылка
ссылка на кракен тор
кракен зеркало тор
кракен маркет тор
кракен tor
кракен ссылка tor
кракен тор
кракен ссылка тор
кракен tor зеркало
кракен darknet tor
кракен тор браузер
кракен тор
кракен darknet ссылка тор
кракен ссылка на сайт тор
кракен вход на сайт
кракен вход
кракен зайти
кракен войти
кракен даркнет вход
кракен войти
где найти ссылку кракен
где взять ссылку на кракен
как зайти на сайт кракен
как найти кракен
кракен новый
кракен не работает
кракен вход
как зайти на кракен
кракен вход ссылка
сайт кракен
кракен сайт
кракен сайт что это
кракен сайт даркнет
что за сайт кракен
кракен что за сайт
Кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен отзывы
кракен сайт
кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен тор
кракен сайт ссылка
кракен сайт зеркало
кракен сайт тор ссылка
кракен зеркало сайта
зеркало кракен
адрес кракена
кракен зеркало тор
зеркало кракен даркнет
актуальное зеркало кракен
рабочее зеркало кракен
кракен зеркало
кракен зеркала
кракен зеркало
зеркало кракен market
актуальное зеркало кракен
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет ссылка
ссылка кракен даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет
кракен dark
кракен darknet ссылка
кракен сайт даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка тор
кракен даркнет тор
кракен текст рекламы
Kraken ссылка
Kraken Вход
Kraken зайти
Народные средства от алкогольной зависимости могут стать полезным дополнением к медицинской помощи в Владимирском регионе. Лечение алкогольной зависимости требует системного подхода‚ включая детоксикацию организма и психотерапевтическое сопровождение.Травяные настои‚ такие как травы от алкоголизма‚ могут помочь в снижении тяги к алкоголю. Необходимо учитывать о поддержке семьи и анонимном лечении. Способы преодоления зависимости включают программ реабилитации и методы предотвращения запоев. Советы по отказу от алкоголя также играют ключевую роль в восстановлении после зависимости. помощь нарколога владимир
гидроизоляция цена за м2 http://www.offthevylc.ru/polezno-znat/ceny-na-gidroizoljaciju-v-moskve-i-regionah-rossii.html .
Мы можем предложить документы любых учебных заведений, которые расположены на территории всей России. Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 классов смоленск
freight shipping nyc delivery new york
Have you ever thought about publishing an ebook or guest authoring on other websites?
I have a blog based on the same topics you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my visitors would
appreciate your work. If you are even remotely interested,
feel free to send me an e-mail.
mostbet com скачать http://mostbet11073.ru
фундамент шведская плита цена за 1м2 .
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
домашний интернет тарифы
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
https://prometei.online/ the Best!
букмекерская контора кыргызстан букмекерская контора кыргызстан
заправка газгольдера в москве и области .
Круглосуточный вызов нарколога на дом стал важной услугой для тех‚ кто сталкивается с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru можно узнать всю важную информацию о методах лечения зависимостей‚ включая лекарственную терапию и психотерапевтические методы лечения зависимостей. Обращение к наркологу поможет определить степень зависимости и определить подходящий план лечения. Круглосуточное обслуживание позволяет вызвать специалиста на дом в любое время‚ что особенно важно для экстренных случаев. Услуги нарколога включают диагностику зависимостей‚ конфиденциальное лечение и поддержку родственников. Реабилитация наркоманов требует комплексного подхода‚ и квалифицированная помощь может значительно упростить этот процесс. Профилактические меры против зависимостей также играет ключевую роль в борьбе с ними‚ поэтому важно обращаться за помощью при первых признаках. Приезд врача на дом создает комфортные условия и гарантирует конфиденциальность‚ способствуя эффективному лечению.
домашний интернет тарифы челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
интернет провайдер челябинск
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске http://arus-diplom35.ru/ .
http://www.pf-monstr.work – работа с ПФ
Прокапка после запоя — это важный шаг на пути к оздоровлению. В большинстве случаев после продолжительного запойного периода возникают симптомы похмелья: головная боль, рвота, плохое самочувствие. В этом случае требуется очистка организма и поддержка функции печени.Лечение при помощи инфузий помогает снять интоксикацию и восстановить здоровье пациента. Борьба с алкогольной зависимостью должно обеспечивать медицинское сопровождение и реабилитацию. Правильная терапия может значительно снизить последствия запойного периода.На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula008.ru можно найти информацию о врачебной помощи, рехабилитации и способы борьбы с алкоголизмом. Заботьтесь о своем здоровье!
диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва .
мостбет кыргызстан http://mostbet11075.ru
заезд на участок через канаву .
сколько стоит залить плиту фундамента .
новости мирового спорта novosti-sporta-11.ru .
sevenup продовжує розвиватися і завжди має для вас нові можливості!
аттестат об образовании 11 классов купить аттестат об образовании 11 классов купить .
аттестат 11 класса 2012 купить аттестат 11 класса 2012 купить .
сантехника москва купить http://gessi-santehnika-5.ru .
сколько стоит аттестат 11 классов купить в arus-diplom25.ru .
интернет магазин сантехники екатеринбург http://www.evropejskaya-santehnika2.ru .
Hello to every body, it’s my first go to see of this website; this webpage consists of
amazing and actually excellent stuff in favor of visitors.
http://www.pf-monstr.work – оптимизация ПФ
propan-zapravka-gazgoldera-499.ru .
мостбет скачать приложение мостбет скачать приложение
прогнозы на хоккей на сегодня бесплатно luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru .
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр как купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в челябинске http://arus-diplom24.ru .
подключить интернет челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
недорогой интернет челябинск
как сыграют сегодня в футбол прогноз http://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru/ .
Когда следует вызывать экстренную наркологическую помощь в Туле Каждый человек может столкнуться с кризисными ситуациями, связанными с зависимостями от алкоголя или наркотиков. В такие моменты необходимо понимать, как быстро и эффективно получить необходимую помощь. Вызов нарколога на дом в Туле может стать настоящим спасением для людей, столкнувшихся с алкогольным отравлением или другими острыми состояниями, связанными с зависимостями. Экстренная помощь от наркологической службы включает возможность вызвать нарколога на дом. Это особенно важно для тех, кто не может или не желает посещать медицинские учреждения. Профилактика тяжелых последствий при лечении алкоголизма зачастую требует вмешательства специалистов. Поддержка родственников играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации наркоманов и алкоголиков; Психотерапия при зависимостях помогает разобраться в причинах и справиться с трудностями. Хотя адреса наркологических центров в Туле можно легко найти в интернете, иногда требуется экстренная помощь; нарколог на дом срочно тула Не забывайте, что профилактика зависимости играет важную роль. Раннее обращение к специалистам может помочь предотвратить развитие серьезных проблем. Имейте в виду, что экстренные меры могут спасти чью-то жизнь.
скачать мостбет на андроид скачать мостбет на андроид
диплом купить с занесением в реестр челябинск arus-diplom32.ru .
подключить домашний интернет челябинск
chelyabinsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
подключить домашний интернет челябинск
Скорая наркологическая помощь — это незаменимый элемент в поиске решения зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula009.ru вы можете получить сведения о постоянной помощи, которая предлагает срочную медицинскую помощь. Наркологическая служба предоставляет медицинскую помощь при злоупотреблении наркотиками и алкоголем. Специалисты оказывают консультационные услуги нарколога, а также гарантируют лечение без раскрытия личных данных. В рамках неотложной помощи возможны реабилитационные программы и госпитализация. Психологическая поддержка играет основополагающую роль в восстановлении после зависимости. Обратитесь за помощью незамедлительно, измените свою жизнь к лучшему!
What’s up, its good article concerning media print, we all know media is a fantastic source of information.
как купить диплом с занесением в реестр в екатеринбурге https://arus-diplom33.ru .
https://www.pf-monstr.work – SEO продвижение по ПФ
Мій друг відвідав майстер-клас із французької кухні та поділився незабутніми враженнями. А я, на жаль, пропустив цю можливість. Дивлюся фото на сайті і заздрю. Наступного разу точно буду там!
заезд для автомобиля .
монолитная плита с теплым полом .
pf-monstr.work – раскрутка сайта с упором на ПФ
В столице России студенты могут найти широкий выбор доступных предложений на интернет-услуги. Провайдеры в Екатеринбурге предоставляют быстрый интернет и мобильный интернет для учебы и досуга. Многие операторы‚ включая ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet004.ru‚ предоставляют акции для студентов и льготные скидки. Анализ тарифов поможет выбрать безлимитного интернета или Wi-Fi для учебы‚ который будет оптимален для онлайн-занятий. Также стоит изучить отзывы о провайдерах‚ чтобы сделать наиболее подходящий выбор; доступ к сети стало легче‚ а доступ в интернет необходим для повышения цифровой грамотности.
Today, I went to the beach with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I had to tell someone!
https://myanmarfootball.org/led-lampa-chi-ksenon-cho-krashche-dlia-shchodennogo-vykorystannia
At this time I am going to do my breakfast, afterward having my
breakfast coming again to read additional news.
https://www.chery-russia.ru/ – лучшие условия покупки.
ТОП ТАРИФОВ ИНТЕРНЕТА И ТВ ДЛЯ ГЕЙМЕРОВ В Екатеринбурге В современном мире высокоскоростной интернет стал необходимостью‚ особенно для геймеров. Выбор подходящего тарифа может существенно повлиять на игровой процесс и общее впечатление от онлайн-игр. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet004.ru можно найти актуальные предложения от операторов связи в Екатеринбурге с акциями для геймеров. Для комфортной игры важна скорость интернета для игр и отсутствие лагов. Лучшие тарифы на интернет для геймеров предлагают скорость от 100 Мбит/с‚ что идеально подходит для игр с высокой конкурентностью. Также стоит рассмотреть комбинированные тарифы‚ которые позволяют совмещать видеопросмотр и гейминг. Важно провести сравнение провайдеров‚ чтобы выбрать оптимальные условия. Многие компании предлагают специальные предложения для игроков‚ включающие премиум-сервисы в Екатеринбурге. При выборе тарифа следует обратить внимание на наличие акций для геймеров‚ которые могут предложить привлекательные расценки и быструю скорость. Не забывайте проверять рейтинг компаний‚ чтобы избежать возможных неприятностей в использовании интернета.
Анонимный вызов нарколога в владимире — это необходимый шаг на пути к освобождению от зависимости. Ресурс vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir007.ru предлагает услуги наркологии, включая консультацию нарколога и анонимное лечение; Служба обеспечивает поддержку для зависимых и их семей, предоставляя квалифицированную медицинскую помощь в владимире. Лечение зависимости требует компетентного подхода. Услуги анонимного нарколога помогут вам обрести необходимую психологическую поддержку и реабилитацию для людей с зависимостями. Горячая линия готова принять ваш звонок на горячую линию помощи наркологов, обеспечивая быструю и квалифицированную помощь. Профилактика зависимостей также важна. Не упустите шанс обратиться за помощью и начать новую жизнь. Помните, что лечение алкоголизма и наркомании возможно, главное — сделать решающий шаг и обратится за поддержкой.
гидромассажные акриловые ванны vanna-s-gidromassazhem.ru .
http://pf-monstr.work – раскрутка сайта по ПФ
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d most certainly
donate to this excellent blog! I guess for now i’ll settle
for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account.
I look forward to fresh updates and will talk about this website with my Facebook group.
Chat soon!
Наркологическая помощь все более важна в преодолении зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir007.ru можно найти информация о методах борьбы с зависимостями, включая программы реабилитации. Квалифицированные специалисты поддерживают в определении уровня зависимости и рекомендуют медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Обращение к наркологу — ключевой этап к избавлению от зависимости после зависимости. Необходимы меры по предотвращению рецидивов и групповая терапия для укрепления статуса выздоровления. Поддержка со стороны семьи и врачей помогает достичь успеха на пути к здоровой жизни.
куплю диплом куплю диплом .
кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений кашпо с автополивом для комнатных растений .
http://pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ в Яндексе
заправка газом газгольдера московская .
гидроизоляция цена за м2 offthevylc.ru/polezno-znat/ceny-na-gidroizoljaciju-v-moskve-i-regionah-rossii.html .
свидетельство о браке купить недорого http://educ-ua3.ru .
You could certainly see your skills within the work you write.
The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t
afraid to say how they believe. All the time follow your heart.
I needed to thank you for this good read!! I certainly enjoyed every bit of it.
I’ve got you saved as a favorite to look at new things you
post…
новости спорта новости спорта .
Оптический интернет в Екатеринбурге: быстродействие и надежность В последние годы оптические технологии стали фундаментом для интернет-провайдеров, предлагающих высокоскоростной интернет. Главное достоинство оптики — это стабильность соединения и крупная скорость подключения. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet005.ru можно найти сравнение провайдеров, чтобы выбрать оптимальные тарифы на интернет. Услуги интернета по волоконно-оптическим линиям обеспечивают высокое качество интернета, что подтверждают мнения пользователей. Операторы предлагают различные тарифы на интернет, начиная от базовых до премиум-тарифов. Быстрое подключение и надежность связи делают оптику оптимальным выбором для пользователей, которым важен доступ в сеть без перебоев.
We’re here to fix the day — a skilled team set to tackle your plumbing problem and bring back order in your home!
Our swift response supports – reduce the need for costly serious overhauls in the future.
Experience our quick and outstanding assistance – immediately!
Купить диплом можно через официальный портал компании. jobhop.co.uk/secure/blog/379829
обзор спортивных событий https://www.novosti-sporta-12.ru .
интернет-магазин сантехники спб интернет-магазин сантехники спб .
http://pf-monstr.work/ – SEO оптимизация с поведенческими
Подія в Торонто, про яку я дізналася завдяки культурній ініціативі, перевершила всі очікування. Канадські народні танці просто заворожують. Тепер я точно знаю, що таке справжня культура.
Прокапаться от алкоголя на дому — важный шаг для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью . Процесс избавления от алкоголизма начинается с очищения организма, которая может быть проведена в домашних условиях . Основные методы включают медицинскую помощь и препараты для детоксикации , что обеспечит безопасное прекращение употребления. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir008.ru Советы по трезвости и стратегии преодоления зависимости, такие как самообслуживание для людей с алкогольной зависимостью, имеют огромное значение в реабилитации . Отказ от алкоголя — это путь к новой жизни .
Платная наркологическая помощь в Красноярске набирает популярность. Наркологические клиники, такие как наркологическая клиника Красноярск предоставляют разнообразные услуги: включая детоксикацию и программы реабилитации для наркозависимых. Психотерапия и консультирование по зависимостям способствуют осознанию причин зависимости и поиску путей к восстановлению. Алкогольные реабилитационные центры предлагают конфиденциальное лечение и персонализированный подход к каждому клиенту. Профессиональная поддержка наркологов, реабилитационные программы и медицинское сопровождение при лечении зависимостей играют ключевую роль в успешной реабилитации. Адаптация к социальной жизни после лечения имеет большое значение для снижения риска рецидивов. Дополнительные сведения доступны на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk007.ru.
скрипт накрутки поведенческого фактора – программные скрипты
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
как купить аттестат за 11 класс в санкт петербурге как купить аттестат за 11 класс в санкт петербурге .
zakazat-ushp-fundament-pod-klyuch-499.ru .
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, затрагивающая не лишь саму личность, страдающую от алкоголизма, но и окружающих людей. Как уговорить человека выйти из запоя? Прежде всего, важно понимать, что поддержка семьи играет ключевую роль в сдерживании зависимости. Нарколог на дом Красноярск Первый шаг — это консультация специалиста. Специалист по наркологии в Красноярске может оказать необходимую медицинскую поддержку в домашних условиях, чтобы облегчить состояние человека. Психологическая поддержка также необходима: она поможет выяснить корни алкогольной зависимости и найти способы ее решения. Рекомендации для выхода из запойного состояния включают в себя формирование обстановки, способствующей мотивации, где человек чувствует поддержку и любовь. Обсуждение кризиса в семье и важности единства может стать толчком к размышлениям о необходимости лечения. Лечение запоя и реабилитация помогут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к нормальной жизни. Необходимо осознавать признаки запойного состояния и быть готовыми к вызовам. Мотивация к лечению — это совместный процесс, который требует времени и усилий. Поддерживайте вашего близкого человека, демонстрируя желание помочь ему, и совместно пройдите путь к выздоровлению.
https://www.pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ для проектов и сайтов
Как выбрать интернет-провайдера для удаленной работы в Екатеринбурге, важный этап‚ влияющий на эффективность вашей работы. При выборе провайдера стоит обращать внимание на несколько ключевых моментов. Во-первых‚ скоростные характеристики интернета. Для удаленных работников и фрилансеров важна постоянная скорость‚ позволяющая выполнять задачи‚ связанные с передачей данных‚ и вести онлайн-встречи без задержек. Сравнение провайдеров поможет вам выбрать оптимальный тариф на интернет‚ соответствующий вашим нуждам. Во-вторых‚ не забудьте про качество подключения и услуги‚ которые предоставляет провайдер. Провайдеры‚ предлагающие оптоволоконный интернет‚ предоставляют высокую скорость и стабильное соединение. Убедитесь‚ что предоставляемая поддержка провайдером готова помочь вам в случае возникновения неполадок.Не забывайте про отзывы о провайдерах. Они могут дать представление о реальном опыте пользователей. Также обратите внимание на дополнительные услуги‚ такие как мобильный интернет или Wi-Fi.Таким образом‚ тщательный выбор провайдера позволит вам наслаждаться стабильным соединением и качественным доступом к интернету в Екатеринбурге. ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet006.ru
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 10 11 классов
В столице России растет количество людей, которые хотят услугами IPTV без обязательств. Услуги IPTV обеспечивают доступ к телеканалам в интернете, гарантируя отличное качество картинки. Некоторые компании IPTV предлагают шанс попробовать IPTV бесплатно, что делает это телевидение особенно привлекательным.Чтобы установить IPTV, достаточно сконфигурировать устройство и выбрать доступные каналы IPTV. Важно учитывать преимуществах IPTV, таких как многообразие каналов и гибкость в просмотре. На сайте ekaterinburg-domashnij-internet006.ru можно найти различных провайдерах IPTV, которые обеспечивают возможность подключения к IPTV без подписания договора; Это даёт возможность наслаждаться любимыми программами, не беспокоясь о долгих обязательствах.
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
Вот список лучших статей которые помогут вам бесплатно и платно накрутить ТГ, вот они – Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1377755-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1397267-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1453520-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1493488-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Накрутка живых подписчиков в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1488381-nakrutka-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-reiting Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бот https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1485234-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-reiting Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал живые https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1481423-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-zhivye-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-reiting Накрутка в ТГ подписчики онлайн https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1480954-nakrutka-v-tg-podpischiki-onlain-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-reiting Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ без отписок https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478588-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-bez-otpisok-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-reiting Накрутка живых подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478237-nakrutka-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ дешево https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478168-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-deshevo-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ SMM https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478148-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-smm-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал боты https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1478135-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-boty-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал живые бесплатно https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1563932-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-zhivye-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Накрутка активных подписчиков в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1562415-nakrutka-aktivnyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-proverennye-saity Smm накрутка подписчиков бесплатно в ТГ https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1562120-smm-nakrutka-podpischikov-besplatno-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-svezhii-obzor Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно онлайн https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1560586-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-onlain-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-sravnenie-luchshih Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал без отписок https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1559669-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-bez-otpisok-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-sravnenie-luchshih Telegram реально можно продвинуть живыми и ботами.
Наркологическая помощь на платной основе, это необходимый шаг в борьбе с зависимостями. В наркологической клинике, такой как vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir009.ru, обеспечивается высококачественное лечение, включая лечение наркомании и реабилитацию алкоголиков. Процесс реабилитации включает детоксикационные процедуры и психологическую поддержку. Обсуждение с наркологом позволяет разработать индивидуальный подход к индивидуальной проблеме. Клиники предлагают анонимную помощь и помощь в кризисных ситуациях. Поддержка родственников также имеет огромное значение. Групповые занятия помогают поддерживать друг друга, а медицинское наблюдение обеспечивает защиту пациентов. Платные услуги позволяют достигать лучших результатов и внимание специалистов, что повышает вероятность успеха.
https://pf-monstr.work/ – SEO раскрутка по ПФ
Лечение зависимостей анонимно — это необходимый шаг для людей, страдающих от зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk008.ru можно узнать подробности о лечении зависимостей, восстановлении и помощи. Анонимное лечение позволяет пациентам получать помощь без боязни осуждения.Помощь нарколога включают очистку организма, психологическую поддержку и экстренное вмешательство. Программа реабилитации часто включает группы поддержки, что способствует восстановлению. Предотвращение зависимостей также играет критически важную роль, обеспечивая постоянное благополучие. Профессиональные консультации помогут разобраться в проблемах и разработать стратегии выхода. Поддержка для наркозависимых доступна и доступна, даже если они не хотят делиться своими переживаниями.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1493488-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
стоимость заправки газгольдера 1000 литров .
Капельница от запоя – это эффективный метод терапии алкогольной зависимости‚ который оказывает нарколог с выездом на дом. Этапы подготовки к процедуре включает несколько этапов. Сначала‚ важно оценить симптомы запоя: головные боли‚ повышенная тревожность‚ потливость. Затем больной должен обеспечить комфортное место для процедуры‚ подготовив место для установки капельницы. Наркологические услуги на дому обеспечивают снизить уровень стресса‚ который возникает при визите в клинику. Медик проведет детоксикацию‚ вводя лечебные растворы‚ которые нормализуют состояние организма и повышают общее самочувствие. Польза от капельницы заключается в оперативном удалении токсинов и облегчении состояния. В дополнение‚ уколы от запоя могут помочь в улучшении состояния. После процедуры начинается курс реабилитации‚ направленная на профилактику рецидивов. врач нарколог на дом
Зависимость от алкоголя у женщин является серьезной проблемой, требующей особого подхода к лечению. В владимире наркологическая клиника предлагает необходимую помощь для выхода из запоя, что особенно важно для женщин, часто сталкивающихся с обществом, осуждающим их проблему. Зависимость от алкоголя у женщин может формироваться быстрее, чем у мужчин, и проявляется особенными признаками, такими как подавленное настроение и беспокойство.Процесс лечения зависимости от алкоголя включает detox программу и различные медицинские подходы, а также психотерапию при алкоголизме. Важно позаботиться о поддержке со стороны близких и привлечение к группам поддержки, что позволяет создать комфортные условия для выздоровления. Реабилитация алкоголиков в владимире акцентирует внимание на социальной адаптации, что особенно важно для женщин, оказавшихся в такой ситуации. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир Предотвращение зависимости и обращение за экстренной помощью — основные элементы в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Комплексное лечение к процессу восстановления обеспечит эффективное выздоровление и возвращение к нормальной жизни.
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве .
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
That is a great tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere.
Short but very precise information… Many thanks for sharing this
one. A must read article!
What’s up colleagues, nice paragraph and fastidious arguments commented here, I am truly enjoying by these.
http://optimapharm.com.ua/de-znajty-oryhinalni-led-linzy-za-vyhidnoyu-tsinoy.html
Hi to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is
getting more from this site, and your views are fastidious for new
people.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1453520-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor nолько проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
http://pf-monstr.work/ – улучшение ПФ
купить аттестат в перми за 11 класс купить аттестат в перми за 11 класс .
zapravka-propan-butanom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post!
It’s the little changes that make the largest changes.
Many thanks for sharing!
интернет провайдеры в казани по адресу дома
kazan-domashnij-internet004.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу казань
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
сколько стоит фундамент плита .
провайдеры по адресу
kazan-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры интернета в казани
https://www.pf-monstr.work/ – SEO продвижение с акцентом на ПФ
МИФЫ И РЕАЛЬНОСТЬ ВЫВОДА ИЗ ЗАПОЯ В Красноярске Процесс лечения алкоголизма является непростым и требует комплексного подхода. В Красноярске работают различные наркологические клиники, которые предлагают лечение запоя и реабилитацию от запоя, однако есть мифы о лечении алкоголизма, способные ввести в заблуждение. Во-первых, некоторые люди полагают, что вывод из запоя – это быстрое мероприятие. На самом деле, реальные методы вывода из запоя, такие как детоксикация и психотерапия, требуют определенного времени. Наркологическая клиника Красноярск в Красноярске предлагает программы реабилитации, в рамках которых специалисты оказывают помощь в восстановлении после запоя. Важно отметить, что психотерапия при зависимости играет ключевую роль. Консультация нарколога позволит определить причины зависимости и составить персонализированную программу лечения. Не стоит забывать, что лечение зависимости в Красноярске доступно и эффективно, если обратиться за помощью вовремя.
Скорая помощь при запое – это важный аспект борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Признаки запоя включают настойчивого стремления к спиртному, физической зависимости и психологических нарушений. Лечение запоя начинается с детоксикации, которая помогает вывести токсины из организма. В рамках медицинской помощи при запое используются медикаменты, направленные на уменьшение симптомов отмены. Психологическая поддержка и поддержка семьи играют ключевую роль в поддержании мотивации пациента. Также следует обратить внимание на программы реабилитации и восстановление после запоя. Клиника для алкоголиков предлагает разнообразные методы терапии, включая народные рецепты от запоя. Предотвращение рецидива необходимо для успешного завершения лечения; Эффективная реабилитационная программа способствует возвращению пациента к обычной жизни. Дополнительные материалы по этой теме доступны на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk009.ru.
спортивные трансляции https://novosti-sporta-12.ru/ .
купить аттестат за 11 класс украина купить аттестат за 11 класс украина .
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your blog.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come
here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme?
Great work!
pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ для проектов и бизнеса
GMO Gaika Reputation – Pros, Cons, and the Truth About Withdrawal Refusals
GMO Gaika is widely used by both beginners and experienced FX traders. Its popularity stems from easy-to-use trading tools, stable spreads, and a high level of trust due to its operation by a major Japanese company. Many users feel secure thanks to this strong domestic backing.
On the other hand, there are some online rumors about “withdrawal refusals,” but in most cases, these are due to violations of terms or incomplete identity verification. GMO Gaika’s transparent response to such issues suggests that serious problems are not a frequent occurrence.
You can find more detailed insights into the pros and cons of GMO Gaika, as well as real user experiences, on the trusted investment site naughty-cao.jp. If you’re considering opening an account, it’s a good idea to review this information beforehand.
If you are going for most excellent contents like
me, simply pay a quick visit this web page everyday for the reason that it presents quality contents, thanks https://www.gritalent.ca/employer/biiut/
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
сколько стоит фундамент .
провайдеры по адресу
kazan-domashnij-internet005.ru
домашний интернет казань
servismersedes2.ru – Качественный ремонт силовых агрегатов любой сложности
сео яндекс директ – SEO реклама
узнать провайдера по адресу казань
kazan-domashnij-internet005.ru
дешевый интернет казань
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
вывод из запоя
магазин итальянской сантехники http://www.gessi-santehnika-5.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
вывод из запоя цена
стоимость заправки газгольдера 5000 .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1397267-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
lucky jet win скачать http://1win22097.ru
https://servismersedes2.ru/ – Профессиональное обслуживание роботизированных коробок
плинко кз https://plinko-kz2.ru/
Рабочие тетради и учебники для 7 класса на 2025-2026 учебный год – Купить в Москве
учебники и школьная литература: учебники, рабочие тетради, методические материалы и другая учебная литература по низким ценам, с доставкой по Москве и в другие регионы России, на сайте интернет-магазина
Моя мрія – побувати на Канадському фестивалі народного танцю. SFF North America відкриває двері до культури, яку варто дослідити. Шкода, що цього разу я не змогла поїхати, але наступного разу все буде інакше.
накрутка пф вашего сайта – персонализированный подход к ресурсу
клиника косметологии цены клиника косметологии цены .
цены процедур в косметологии цены процедур в косметологии .
клубный сервис мерседес – внимательный подход к клиенту
bluevine
It’s an remarkable paragraph designed for all the internet people; they will obtain benefit from it I am sure.
Погрузитесь в мир азарта: почему слоты в онлайн-казино — это идеальный выбор для каждого
Игровые https://ironcenter.ru/games, или слоты, — это сердце любого онлайн-казино. Они привлекают миллионы игроков по всему миру своей простотой, динамикой и, конечно же, возможностью сорвать крупный джекпот. Если вы ищете способ весело провести время и испытать свою удачу, онлайн-слоты — это то, что вам нужно.
Разнообразие, которое поражает воображение
Забудьте о скучных “одноруких бандитах” из прошлого. Современные онлайн-казино предлагают тысячи слотов на любой вкус. От классических фруктовых автоматов до игр с захватывающими сюжетами по мотивам фильмов, комиксов и мифов. Вы можете отправиться в приключение с викингами, исследовать древние пирамиды Египта или погрузиться в мир магии и фэнтези. Каждый слот — это уникальная игра с продуманным дизайном, качественной графикой и атмосферным звуковым сопровождением.
Играйте в любое время и в любом месте
Онлайн-казино дают вам полную свободу. Больше не нужно никуда ехать: играйте в любимые слоты прямо со своего компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Достаточно стабильного интернет-соединения, чтобы получить доступ к огромной библиотеке игр. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и комфорт. Вы можете наслаждаться азартом в обеденный перерыв, в дороге или уютным вечером, не выходя из дома.
Бонусы и бесплатные вращения — ваш путь к победе
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые бонусы, которые делают игру ещё более выгодной. Приветственные бонусы для новых игроков, бесплатные вращения (фриспины), которые позволяют крутить барабаны без риска, и еженедельные акции — всё это помогает увеличить ваши шансы на победу. Используйте бонусы, чтобы играть дольше и открывать для себя новые слоты, не тратя собственных средств.
Простота и доступность для каждого
Чтобы начать играть в слоты, не нужно обладать особыми навыками. Правила просты и интуитивно понятны: просто выберите ставку и нажмите кнопку “Spin”. В каждом слоте есть подробное описание символов и выигрышных комбинаций, так что вы легко разберётесь, как работает игра. Для новичков предусмотрены демо-версии, которые позволяют играть бесплатно и без регистрации. Это отличный способ познакомиться с игрой, не рискуя своими деньгами.
Испытайте свою удачу!
Онлайн-слоты — это не просто игры, это яркие эмоции, адреналин и, конечно, шанс на крупный выигрыш. Готовы ли вы попробовать? Выберите надёжное онлайн-казино, заберите свои бонусы и начните своё приключение в мире азартных игр. Может быть, именно сегодня вам улыбнётся удача!
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу казань
kazan-domashnij-internet006.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу казань
https://pf-monstr.work/ – улучшение поведенческих факторов и накрутка ПФ
Виглядає, що кіберспорт не просто хобі, а справжня кар’єра. Рекомендую цей ресурс, де описано, як досягти успіху.
Погрузитесь в мир азарта: почему слоты в онлайн-казино — это идеальный выбор для каждого
Игровые автоматы, или слоты, — это сердце любого онлайн-казино. Они привлекают миллионы игроков по всему миру своей простотой, динамикой и, конечно же, возможностью сорвать крупный джекпот. Если вы ищете способ весело провести время и испытать свою удачу, онлайн-слоты — это то, что вам нужно.
Разнообразие, которое поражает воображение
Забудьте о скучных “одноруких бандитах” из прошлого. Современные онлайн-казино предлагают тысячи слотов на любой вкус. От классических фруктовых автоматов до игр с захватывающими сюжетами по мотивам фильмов, комиксов и мифов. Вы можете отправиться в приключение с викингами, исследовать древние пирамиды Египта или погрузиться в мир магии и фэнтези. Каждый слот — это уникальная игра с продуманным дизайном, качественной графикой и атмосферным звуковым сопровождением.
Играйте в любое время и в любом месте
Онлайн-казино дают вам полную свободу. Больше не нужно никуда ехать: играйте в любимые слоты прямо со своего компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Достаточно стабильного интернет-соединения, чтобы получить доступ к огромной библиотеке игр. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и комфорт. Вы можете наслаждаться азартом в обеденный перерыв, в дороге или уютным вечером, не выходя из дома.
Бонусы и бесплатные вращения — ваш путь к победе
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые https://zoocenter.org/games/bonus, которые делают игру ещё более выгодной. Приветственные бонусы для новых игроков, бесплатные вращения (фриспины), которые позволяют крутить барабаны без риска, и еженедельные акции — всё это помогает увеличить ваши шансы на победу. Используйте бонусы, чтобы играть дольше и открывать для себя новые слоты, не тратя собственных средств.
Простота и доступность для каждого
Чтобы начать играть в слоты, не нужно обладать особыми навыками. Правила просты и интуитивно понятны: просто выберите ставку и нажмите кнопку “Spin”. В каждом слоте есть подробное описание символов и выигрышных комбинаций, так что вы легко разберётесь, как работает игра. Для новичков предусмотрены демо-версии, которые позволяют играть бесплатно и без регистрации. Это отличный способ познакомиться с игрой, не рискуя своими деньгами.
Испытайте свою удачу!
Онлайн-слоты — это не просто игры, это яркие эмоции, адреналин и, конечно, шанс на крупный выигрыш. Готовы ли вы попробовать? Выберите надёжное онлайн-казино, заберите свои бонусы и начните своё приключение в мире азартных игр. Может быть, именно сегодня вам улыбнётся удача!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
ставки на футбол ставки на футбол .
подключение интернета казань
kazan-domashnij-internet006.ru
домашний интернет подключить казань
Hi there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
https://tayger.com.ua/Sklo-far-z-antifog-efektom-scho-tse-i-chi-pratsyuye.html
Погрузитесь в мир азарта: почему слоты в онлайн-казино — это идеальный выбор для каждого
Игровые автоматы, или слоты, — это сердце любого онлайн-казино. Они привлекают миллионы игроков по всему миру своей простотой, динамикой и, конечно же, возможностью сорвать крупный джекпот. Если вы ищете способ весело провести время и испытать свою удачу, онлайн-слоты — это то, что вам нужно.
Разнообразие, которое поражает воображение
Забудьте о скучных “одноруких бандитах” из прошлого. Современные онлайн-казино предлагают тысячи слотов на любой вкус. От классических фруктовых автоматов до игр с захватывающими сюжетами по мотивам фильмов, комиксов и мифов. Вы можете отправиться в приключение с викингами, исследовать древние пирамиды Египта или погрузиться в мир магии и фэнтези. Каждый слот — это уникальная игра с продуманным дизайном, качественной графикой и атмосферным звуковым сопровождением.
Играйте в любое время и в любом месте
Онлайн-казино дают вам полную свободу. Больше не нужно никуда ехать: играйте в любимые слоты прямо со своего компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Достаточно стабильного интернет-соединения, чтобы получить доступ к огромной библиотеке игр. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и комфорт. Вы можете наслаждаться азартом в обеденный перерыв, в дороге или уютным вечером, не выходя из дома.
Бонусы и бесплатные вращения — ваш путь к победе
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые бонусы, которые делают игру ещё более выгодной. Приветственные бонусы для новых игроков, бесплатные вращения (фриспины), которые позволяют крутить барабаны без риска, и еженедельные акции — всё это помогает увеличить ваши шансы на победу. Используйте бонусы, чтобы играть дольше и открывать для себя новые слоты, не тратя собственных средств.
Простота и доступность для каждого
Чтобы начать играть в слоты, не нужно обладать особыми навыками. Правила просты и интуитивно понятны: просто выберите ставку и нажмите кнопку “Spin”. В каждом слоте есть подробное описание символов и выигрышных комбинаций, так что вы легко разберётесь, как работает игра. Для новичков предусмотрены демо-версии, которые позволяют играть бесплатно и без регистрации. Это отличный способ познакомиться с игрой, не рискуя своими деньгами.
Испытайте свою удачу!
Онлайн-слоты — это не просто игры, это яркие эмоции, адреналин и, конечно, шанс на крупный выигрыш. Готовы ли вы попробовать? Выберите надёжное онлайн-казино, заберите свои бонусы и начните своё приключение в мире азартных игр. Может быть, именно сегодня вам улыбнётся удача!
https://zoocenter.org/games/igrosoft/resident
футбол прогнозы футбол прогнозы .
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Оптимизация двигателей и электронных блоков
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Погрузитесь в мир азарта: почему слоты в онлайн-казино — это идеальный выбор для каждого
Игровые автоматы, или слоты, — это сердце любого онлайн-казино. Они привлекают миллионы игроков по всему миру своей простотой, динамикой и, конечно же, возможностью сорвать крупный джекпот. Если вы ищете способ весело провести время и испытать свою удачу, онлайн-слоты — это то, что вам нужно.
Разнообразие, которое поражает воображение
Забудьте о скучных “одноруких бандитах” из прошлого. Современные онлайн-казино предлагают тысячи слотов на любой вкус. От классических фруктовых автоматов до игр с захватывающими сюжетами по мотивам фильмов, комиксов и мифов. Вы можете отправиться в приключение с викингами, исследовать древние пирамиды Египта или погрузиться в мир магии и фэнтези. Каждый слот — это уникальная игра с продуманным дизайном, качественной графикой и атмосферным звуковым сопровождением.
Играйте в любое время и в любом месте
Онлайн-казино дают вам полную свободу. Больше не нужно никуда ехать: играйте в любимые слоты прямо со своего компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Достаточно стабильного интернет-соединения, чтобы получить доступ к огромной библиотеке игр. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и комфорт. Вы можете наслаждаться азартом в обеденный перерыв, в дороге или уютным вечером, не выходя из дома.
Бонусы и бесплатные вращения — ваш путь к победе
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые бонусы, которые делают игру ещё более выгодной. Приветственные бонусы для новых игроков, бесплатные вращения (фриспины), которые позволяют крутить барабаны без риска, и еженедельные акции — всё это помогает увеличить ваши шансы на победу. Используйте https://ironcenter.ru/games/bonus, чтобы играть дольше и открывать для себя новые слоты, не тратя собственных средств.
Простота и доступность для каждого
Чтобы начать играть в слоты, не нужно обладать особыми навыками. Правила просты и интуитивно понятны: просто выберите ставку и нажмите кнопку “Spin”. В каждом слоте есть подробное описание символов и выигрышных комбинаций, так что вы легко разберётесь, как работает игра. Для новичков предусмотрены демо-версии, которые позволяют играть бесплатно и без регистрации. Это отличный способ познакомиться с игрой, не рискуя своими деньгами.
Испытайте свою удачу!
Онлайн-слоты — это не просто игры, это яркие эмоции, адреналин и, конечно, шанс на крупный выигрыш. Готовы ли вы попробовать? Выберите надёжное онлайн-казино, заберите свои бонусы и начните своё приключение в мире азартных игр. Может быть, именно сегодня вам улыбнётся удача!
Excellent piece with realistic tips anyone can follow. I’ve noticed that small improvements often create a better atmosphere at place, and this post really captures that idea. I recently explored some handy living space projects solutions that work well for common issues, making repairs less stressful. It’s good to see more insight focused on realistic, actionable recommendations. I believe adding such recommendations to everyday routines can make upkeep far less stressful and much more rewarding.
http://pf-monstr.work/ – раскрутка ПФ
СтавкиПрогнозы stavki-prognozy-1.ru .
servismersedes2.ru – Надежный ремонт современных двигателей
Пауза в отношениях: https://leaders.qa/forums/users/veroniquenovak4/ советует использовать время для размышлений.
Погрузитесь в мир азарта: почему слоты в онлайн-казино — это идеальный выбор для каждого
Игровые https://ironcenter.ru/games/igrosoft/keksы, или слоты, — это сердце любого онлайн-казино. Они привлекают миллионы игроков по всему миру своей простотой, динамикой и, конечно же, возможностью сорвать крупный джекпот. Если вы ищете способ весело провести время и испытать свою удачу, онлайн-слоты — это то, что вам нужно.
Разнообразие, которое поражает воображение
Забудьте о скучных “одноруких бандитах” из прошлого. Современные онлайн-казино предлагают тысячи слотов на любой вкус. От классических фруктовых автоматов до игр с захватывающими сюжетами по мотивам фильмов, комиксов и мифов. Вы можете отправиться в приключение с викингами, исследовать древние пирамиды Египта или погрузиться в мир магии и фэнтези. Каждый слот — это уникальная игра с продуманным дизайном, качественной графикой и атмосферным звуковым сопровождением.
Играйте в любое время и в любом месте
Онлайн-казино дают вам полную свободу. Больше не нужно никуда ехать: играйте в любимые слоты прямо со своего компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Достаточно стабильного интернет-соединения, чтобы получить доступ к огромной библиотеке игр. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит своё время и комфорт. Вы можете наслаждаться азартом в обеденный перерыв, в дороге или уютным вечером, не выходя из дома.
Бонусы и бесплатные вращения — ваш путь к победе
Онлайн-казино предлагают щедрые бонусы, которые делают игру ещё более выгодной. Приветственные бонусы для новых игроков, бесплатные вращения (фриспины), которые позволяют крутить барабаны без риска, и еженедельные акции — всё это помогает увеличить ваши шансы на победу. Используйте бонусы, чтобы играть дольше и открывать для себя новые слоты, не тратя собственных средств.
Простота и доступность для каждого
Чтобы начать играть в слоты, не нужно обладать особыми навыками. Правила просты и интуитивно понятны: просто выберите ставку и нажмите кнопку “Spin”. В каждом слоте есть подробное описание символов и выигрышных комбинаций, так что вы легко разберётесь, как работает игра. Для новичков предусмотрены демо-версии, которые позволяют играть бесплатно и без регистрации. Это отличный способ познакомиться с игрой, не рискуя своими деньгами.
Испытайте свою удачу!
Онлайн-слоты — это не просто игры, это яркие эмоции, адреналин и, конечно, шанс на крупный выигрыш. Готовы ли вы попробовать? Выберите надёжное онлайн-казино, заберите свои бонусы и начните своё приключение в мире азартных игр. Может быть, именно сегодня вам улыбнётся удача!
zaezd-cherez-kanavu-365.ru .
стоимость ушп фундамента .
Top 15 https://www.fonse.cn/question/crypto-news-67b/ news sites rank CoinDesk high.
Zentrader is an online platform focused on binary options trading and has been gaining attention among Japanese traders. Its interface is designed to be simple and intuitive, making it easy to use for beginners while also earning trust from experienced users.
With a minimum trade amount starting from 500 yen, it allows users to begin trading with lower risk. The platform offers full Japanese-language support, so users can get help whenever they have questions or concerns. Withdrawals are processed quickly, which contributes to high user satisfaction.
Since trading can be done directly in the browser, there’s no need to install any software, and the platform is accessible even from smartphones. Overall, the system is designed with simplicity and reliability in mind, making it a great choice for those new to binary options.
For more in-depth information and real user experiences, check out the trusted investment resource locamaga.jp. It’s a helpful reference if you’re considering using Zentrader.
https://pf-monstr.work/ – накрутка ПФ
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу красноярск
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
популярные https://ered.pstu.ru/index.php/mechanics/comment/view/4602/0/2467 магазины — озон, вайлдберриз, алиэкспресс
Landscaping https://www.fonse.cn/question/business-idea-28m/ cards ideas: green color schemes with plant motifs.
какие провайдеры на адресе в красноярске
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet004.ru
провайдеры по адресу
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
вывод из запоя
http://www.drsbook.co.kr/board/16543542 Today’s Pittsburgh directory lists local therapists; use filters for specialties or insurance types.
Greetings! Very helpful advice in this particular post!
It is the little changes which will make the greatest changes.
Many thanks for sharing! https://spechrom.com:443/bbs/board.php?bo_table=service&wr_id=406807
http://pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ сайта
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Дополнительный адрес в сети
фундамент с теплым полом для дома .
zaezd-dlya-mashiny-365.ru .
смотреть здесьgoldcoders
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1377755-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
http://wiki.konyvtar.veresegyhaz.hu/index.php?title=Szerkeszt%C5%91:ShielaE546 network software, like Wireshark or Cisco Packet Tracer, analyzes and simulates network traffic.
servismersedes2.ru – Качественный ремонт двигателей любой сложности
не знаешь где брать всегда актуальные ссылки ? не знаешь как перейти ? вот отличный ОФИЦИАЛЬНЫЙ САЙТ с самыми актуальными ссылками на marketplace Kraken https://aktual-krkn.ru/
kra36
сервис
удобство функции
официальный сайт Kraken
Кракен
маркетплейс Кракен
даркнет маркет
kraken официальный сайт
kraken market
kraken darknet
анонимные покупки
даркнет площадка
гидра альтернатива
kraken onion
kraken ссылка
darknet marketplace
kraken даркнет
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркет обзор
кракен маркет отзывы
kraken ссылка
kraken сайт
kraken официальный сайт
kraken ссылка зеркало
актуальное зеркало kraken
kraken ссылка тор
kraken зеркало рабочее
kraken зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало даркнет
kraken зеркало тор
kraken зеркало 2kmp
kraken официальные ссылки
kraken onion ссылка
kraken ссылка для тору
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный
kraken зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт зеркала
кракен ссылка kraken
kraken официальный сайт зеркало
kraken официальный сайт ссылка
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт
kraken клирнет зеркало
kraken tor зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp
зеркала kraken kraken tor site
kraken darknet ссылка
kraken ссылка krakentor site
kraken зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки
kraken ссылка tor
kraken market ссылка
kraken зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken darknet зеркала
kraken darknet market ссылка
kraken darknet ссылка тор
ссылка kraken kraken tor site
kraken 2 зеркало
kraken ссылка 2kmp vip
рабочие ссылки kraken
сайт кракен kraken
kraken ссылка 2kmp biz
зеркало kraken market
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp
ссылка кракен kraken tor site
kraken darknet market зеркало
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее
kraken market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp
kraken darknet market ссылка тор
kraken ссылка зеркало krakentor site
kraken com зеркало
зеркала kraken 2kmp org
kraken ссылка kraken one com
kraken onion зеркала
сайт kraken darknet
зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken сайт официальный krakentor site
kraken darknet официальный сайт
kraken зеркало рабочее krakentor site
ссылка на kraken kraken onion site
kraken кларнет зеркало kraken tor site
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp
kraken ссылка kraken clear com
kraken сайт kraken one com
kraken актуальные ссылки krakentor site
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp
kraken актуальные зеркала krakentor site
kraken зеркало тор ссылка
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken tor site
ссылка на кракен kraken one com
kraken даркнет зеркало krakentor site
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo
kraken рабочая ссылка тор
кракен сайт kraken one com
зеркало kraken тор ссылка рабочее
kraken сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка onion krakentor site
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp
ссылка на кракен kraken onion site
kraken ссылка для тору vtor run
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp vip
kraken сайт kraken clear com
kraken зеркало тор krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт vtor run
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт krakentor site
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken зеркала 2 kmp biz
ссылка на кракен kraken clear com
kraken casino зеркало
кракен сайт kraken clear com
зеркало кракен kraken tor site
kraken официальный сайт vtor run
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp
kraken зеркало kraken2web com
актуальное зеркало kraken 2 kma biz
kraken актуальные зеркала 2kmp vip
ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка онлайн
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp biz
kraken сайт анонимных
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp biz
kraken сайт покупок
kraken зеркало онлайн
kraken сайт анонимных покупок
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo
кракен сайт kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp biz
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка kraken2web com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp biz
kraken ссылка online
kraken ссылка tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp vip
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp vip
kraken ссылка на сайт
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp biz
kraken сайт vk2
kraken casino зеркало рабочее
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp vip
ссылка на kraken kraken darknet top
кракен зеркало kraken 7 one
ссылка на кракен kraken darknet top
kraken зеркало тор 2 kmp vip
kraken зеркало kraken clear com
kraken ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
зеркало kraken kraken onion site
kraken darknet ссылка kraken2web com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor
kraken зеркало krakendarknet top
сайт kraken тор
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 7 one
kraken клирнет зеркало 2kmp org
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo
kraken ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка kraken7 one
актуальное зеркало kraken 2kmp org
кракен зеркало kraken one com
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp org
kraken ссылка onion 2kmp vip
площадка kraken ссылка
рабочая ссылка на кракен kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало 2kraken click
kraken ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken onion site
кракен ссылка kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken сайт официальный 2kmp org
kraken зеркало 2krnk biz
kraken casino официальный сайт
kraken ссылка krakendarknet top
kraken официальные зеркала vk3
kraken market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken darknet ссылка тор kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken darknet зеркала kraken2web com
кракен зеркало kraken clear com
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken2web com
kraken сайт 2krnk biz
kraken зеркало dzen
кракен ссылка тор kraken one com
kraken зеркало тор 2kmp org
kraken зеркало krakenonion site
kraken ссылка онион
kraken сайт tor
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo
kraken официальный сайт vk2
kraken ссылка зеркало 2kmp org
актуальное зеркало kraken kraken zerkalo xyz
сайт kraken onion
рабочее зеркало кракен kraken 7 one
кракен сайт ссылка kraken one com
kraken darknet market зеркало kraken2web com
kraken ссылка тор tor wiki online
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор kraken7 one
kraken зеркало рабочее 2kmp org
ссылка на kraken 2kmp org
kraken официальный сайт vk3
kraken ссылка зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken onion ссылка tor wiki online
kraken вход на сайт
kraken зайти на сайт
kraken сайт krakendarknet top
кракен зеркало kraken zerkalo xyz
kraken ссылка тор 2kraken click
кракен вход ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken магазин ссылка
kraken darknet market ссылка тор kraken2web com
кракен сайт ссылка kraken clear com
kraken даркнет зеркало 2kmp org
kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт 2kmp org
kraken darknet market ссылка kraken7 one
kraken darknet ссылка 2krnk biz
kraken ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken актуальная ссылка onion
kraken сайт vk2 pro
кракен площадка ссылка kraken 7 one
kraken сайт kraken2web com
kraken зеркало форум
кракен зеркало тор kraken one com
kraken официальный сайт k2tor online
kraken ссылка зеркало vk2 pro
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2kraken click
ссылка на кракен тор kraken clear com
сайт онион kraken
кракен сайт зеркало kraken 7 one
kraken зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken darknet ссылка тор 2krnk biz
kraken сайт dzen
kraken оригинальная ссылка
kraken ссылка dzen
сайт кракен тор kraken one com
kraken ссылка krakenonion site
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor
kraken tor ссылка онлайн
kraken ссылка v5tor cfd
kraken ссылка на сайт тор
kraken сайт kr2web in
настоящий сайт kraken
kraken зеркало online
kraken актуальные ссылки 2kmp org
прямая ссылка на kraken
kraken оф сайт
kraken официальный сайт
используйте vpn!
Кракен Ссылка
Кракен Вход
Кракен Зайти
Ссылка на Кракен
Kra35.cc
Kra36.at
Kra34.cc
купить меф
купить гарик
Kra34.at
Kra33.cc
Kra33.at
Kra37.cc
Kra36.cc
Kra32.cc
Kra32.at
Kra38.cc
Kra39.cc
Kra33.cc
для дополнительной анонимности и безопасности рекомендуется использовать vpn-сервис. он скроет ваш ip-адрес и сделает ваше пребывание в интернете более безопасным.
будьте осторожны!?
kraken рабочая ссылка onion
kraken ссылка vk
кракен сайт ссылка kraken 11
ссылка на кракен kraken 9 one
kraken зеркало тор kraken2web com
кракен онион ссылка kraken one com
ссылка kraken 2 kma biz
ссылка на kraken торговая площадка
razer kraken сайт
kraken зеркало krakenweb one
kraken зеркало krakenweb3 com
kraken зеркало ссылка онлайн krakenweb one
kraken ссылка зеркало krakenweb one
kraken darknet market ссылка тор 2kraken click
kraken ссылка krakenweb one
kraken ссылка тор krakendarknet top
kraken casino зеркало kraken casino xyz
kraken darknet market зеркало v5tor cfd
kraken сайт зеркала kraken2web com
kraken даркнет ссылка
kraken зеркала kr2web in
kraken зеркало store
kraken darknet market ссылка тор v5tor cfd
kraken darknet market сайт
даркнет официальный сайт kraken
kraken ссылка зеркало рабочее kraken2web com
kraken зеркало тор ссылка kraken2web com
kraken маркетплейс зеркала
kraken официальные зеркала k2tor online
kraken darknet маркет ссылка каркен market
kraken 6 at сайт производителя 2
сайт кракен kraken darknet top
kraken клир ссылка
кракен ссылка kraken kraken2web com 3
ссылка на кракен тор kraken 9 one
kraken сайт анонимных покупок vtor run
kraken darknet market зеркало 2kraken click
kraken darknet market ссылка shkafssylka ru
kraken ссылка torbazaw com
kraken форум ссылка
площадка кракен ссылка kraken clear com
сайт kraken darknet kraken2web com
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: официальные ссылки и зеркала.
полное руководство:
актуальная ссылка (через браузер):
официальная ссылка :
резервное зеркало:
как зайти на маркетплейс кракен: полное руководство
для входа на сайт кракена в даркнете требуется tor. это безопасный браузер:
перейдите на официальный сайт tor.
скачайте программу для вашей ос.
установите и запустите браузер.
используйте актуальные ссылки на кракен
ссылки на официальный сайт кракен часто обновляются. чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов, используйте проверенные ресурсы для получения ссылок:
• актуальное зеркало кракена:
• зеркала сайта в клирнете и даркнете доступны для пользователей в любой точке мира.
авторизация
после перехода на сайт:
зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет аккаунта.
войдите в свой личный кабинет, используя логин и пароль.
для повышения безопасности активируйте двухфакторную аутентификацию.
но почему выбираю именно
сотни других платформ, тысячи товаров, но для меня больше, чем просто магазин. это место, где покупки превращаются в увлекательное путешествие.
знает, как важно быть уверенным в каждой покупке. полная защита сделок и дружелюбная поддержка создают чувство, будто вы находитесь в заботливых руках. надёжность? абсолютно.
почему именно
потому что здесь всё про вас: ваш стиль, ваш комфорт, ваша выгода. попробуйте, и вы поймёте, почему так много людей выбирают именно эту платформу!
советы по безопасности на кракене
используйте vpn
подключение через vpn повышает вашу анонимность, скрывая ip-адрес.
проверяйте ссылки
актуальные ссылки и зеркала кракен можно найти на проверенных форумах или официальных ресурсах. никогда не используйте непроверенные источники.
будьте внимательны к продавцам
читайте отзывы и выбирайте проверенных продавцов с высоким рейтингом.
кракен маркетплейс
кракен маркетплейс
кракен площадка
kra33.at
kra33.cc
kra34.cc
kra34.at
kra35.cc
kra36.at
kra36.cc
Kra36.at
kra37.cc
kra38.at
кракен маркетплейс ссылка
кракен площадка
кракен marketplace
кракен площадка ссылка
кракен даркнет стор
кракен darknet market зеркало
кракен даркнет площадка
кракен даркнет маркетплейс
кракен наркотики
кракен нарко
кракен наркошоп
кракен наркота
кракен порошок
кракен наркотики
кракен что там продают
кракен маркетплейс что продают
кракен покупка
какен купить
кракен купить мяу
кракен питер
кракен в питере
кракен москва
кракен в москве
кракен что продают
кракен это
кракен marke
кркен darknet market
кракен dark market
кракен market ссылка
кракен darknet market ссылк
кракен market ссылка тор
кракен даркнет маркет
кракен market тор
кракен маркет
платформа кракен
кракен торговая площадка
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка сайт
кракен маркет даркнет тор
кракен аккаунты
кракен заказ
диспуты кракен
как восстановить кракен
кракен даркнет не работает
как пополнить кракен
google authenticator кракен
рулетка кракен
купоны кракен
кракен зарегистрироваться
кракен регистрация
кракен пользователь не найден
кракен отзывы
ссылка кракен
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен официальная ссылка
кракен актуальные
кракен ссылка тор
кракен клирнет
кракен ссылка маркет
кракен клир ссылка
кракен ссылка
ссылка на кракен
кракен ссылка
кракен ссылка на сайт
кракен ссылка кракен
актуальная ссылка на кракен
рабочие ссылки кракен
кракен тор ссылка
ссылка на кракен тор
кракен зеркало тор
кракен маркет тор
кракен tor
кракен ссылка tor
кракен тор
кракен ссылка тор
кракен tor зеркало
кракен darknet tor
кракен тор браузер
кракен тор
кракен darknet ссылка тор
кракен ссылка на сайт тор
кракен вход на сайт
кракен вход
кракен зайти
кракен войти
кракен даркнет вход
кракен войти
где найти ссылку кракен
где взять ссылку на кракен
как зайти на сайт кракен
как найти кракен
кракен новый
кракен не работает
кракен вход
как зайти на кракен
кракен вход ссылка
сайт кракен
кракен сайт
кракен сайт что это
кракен сайт даркнет
что за сайт кракен
кракен что за сайт
Кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен отзывы
кракен сайт
кракен официальный сайт
сайт кракен тор
кракен сайт ссылка
кракен сайт зеркало
кракен сайт тор ссылка
кракен зеркало сайта
зеркало кракен
адрес кракена
кракен зеркало тор
зеркало кракен даркнет
актуальное зеркало кракен
рабочее зеркало кракен
кракен зеркало
кракен зеркала
кракен зеркало
зеркало кракен market
актуальное зеркало кракен
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет ссылка
ссылка кракен даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет
кракен darknet
кракен даркнет
кракен dark
кракен darknet ссылка
кракен сайт даркнет маркет
кракен даркнет маркет ссылка тор
кракен даркнет тор
кракен текст рекламы
Kraken ссылка
Kraken Вход
Kraken зайти
http://pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ
шведская плитка .
zaezd-dlya-mashiny-365.ru .
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say
that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
В сегодняшнем мире тема зависимостей является всё более актуальной. Наркология по вызову в Красноярске предлагает широкий спектр наркологических услуг, посреди которых анонимное лечение и помощь при алкоголизме. Вызов нарколога даёт возможность осуществить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь в случае наркотической зависимости без необходимости посещения клиники. Одной из услуг является detox в домашних условиях, что гарантирует комфортную обстановку для пациента. Консультация нарколога и поддержка психолога важны для восстановления после зависимости. Программа реабилитации включает в себя лечение зависимостей и созависимости, а также наркологию для семьи. Кроме того, реабилитация на дому помогает лучшему восстановлению. Если вы нуждаетесь в помощи, воспользуйтесь ресурсами, такими как vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk007.ru, чтобы получить необходимую информацию о наркологических услугах в Красноярске.
интернет провайдеры по адресу красноярск
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу проверить
купил аттестат за 11 класс и поступил в омон купил аттестат за 11 класс и поступил в омон .
Выход из запоя — это критический процесс‚ требующий всеобъемлющего подхода. В Красноярске существует возможность экстренного вывода из запоя на дому с помощью квалифицированных специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с очистки организма‚ что помогает устранить телесную зависимость.Помощь нарколога включают в себя медицинскую помощь при запое‚ применение эффективных методов‚ таких как кодирование от алкоголя и психологическая терапия. Психологическая поддержка играет важную роль в реабилитации после запоя. Социальная поддержка близких также необходима для результативной реабилитации и предотвращения повторного срыва. экстренный вывод из запоя При преодолении запойного состояния важно следовать нескольким советам: обеспечьте достаточное количество воды‚ правильно питайтесь и занимайтесь физической активностью. Поиск оперативной помощи и консультация к специалистам поможет быстро и безопасно выйти из запоя‚ вернуть здоровье и уровень жизни.
купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс .
http://servismersedes2.ru/ – Трансмиссионный сервис с гарантией качества
plinko game online plinko3001.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet005.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
накрутка пф в яндекс заказать мск – столичный заказ
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1397267-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
бонусный счет мелбет условия https://melbet3006.com
аттестат 11 класс купить тюмень аттестат 11 класс купить тюмень .
сервис mercedes benz в москве – обеспечение заводских характеристик
прогноз спорт прогноз спорт .
ставки футбол prognozy-na-futbol-5.ru .
прогнозы на футбол прогнозы на футбол .
plinko game plinko game
https://www.pf-monstr.work/ – раскрутка сайта по ПФ
plinko plinko
Капельницы от запоя в Красноярске – это существенная медицинская помощь при алкоголизме, способствующая очищению организма. Вызов нарколога на домой предоставляет срочную помощь при запое в удобной обстановке. Состав капельницы содержат вещества, способствующие восстановлению организма: раствор для инфузий, минералы и препараты для капельницы. Действие капельницы ориентировано на устранение симптомов абстиненции и улучшение состояния пациента. Лечение алкоголизма требует всеобъемлющего подхода, включая последующее восстановление после алкогольного кризиса. Стоимость услугу нарколога различаются, но консультация специалиста является важной для успешного лечения.
http://servismersedes2.ru – Малярный цех с камерой покраски
kra36—-at.com — Надежный и удобный сервис — официальный сайт и подробный обзор даркнет-маркета Kraken. Официальный сайт kraken kra36.at — удобный сервис с множеством функций для пользователей. Узнайте больше и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
кракен ссылка, кракен ссылки, ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена, ссылки кракен, сайт кракена, кракен сайты, кракен сайт, сайт кракен, кракен отзывы, зеркала кракен, зеркала кракена, зеркало кракен, зеркало кракена, кракен зеркала, кракен зеркало, даркнет кракен, кракен даркнет, ссылка на кракен, ссылка на кракена, ссылки на кракен, кракен маркетплейс, маркетплейс кракен, кракен магазин, магазин кракен, кракены маркет, kraken ссылка, kraken ссылки, кракен маркет, вход кракен, кракен вход, кракен зайти, kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, актуальная ссылка кракен, актуальная ссылка кракена, актуальные ссылки кракен, кракен актуальная ссылка, кракен актуальные ссылки, кракен ссылка актуальная, кракен ссылки актуальные, кракен как зайти, зайти на кракен, kraken сайты, сайт kraken, kraken сайт, кракен официальный сайт, официальный сайт кракен, кракен сайт официальный, официальный сайт кракена, сайт кракен официальный, сайт кракена официальный, как зайти на кракен, кракен ссылка тор, кракен тор ссылка, ссылка кракен тор, кракен рабочая ссылка, кракен рабочие ссылки, рабочая ссылка кракен, рабочие ссылки кракен, кракен даркнет маркет, кракен маркет даркнет, кракен сайт ссылка, сайт кракен ссылка, кракен площадка, площадка кракен, кракен сайт магазин, актуальная ссылка на кракен, актуальные ссылки на кракен, кракен маркет песня, песня кракен маркет, кракен зеркало рабочее, кракен рабочее зеркало, рабочее зеркало кракен, кракен официальная ссылка, кракен ссылка официальная, официальная ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена официальная, ссылки кракена официальные, кракен сайт что, kraken маркетплейс, маркетплейс kraken
Сделать детоксикацию от алкоголя – это значимый шаг для освобождения от алкогольной зависимости. Избавление от алкоголизма начинается с очистки организма‚ которая помогает справиться с последствиями запойного состояния. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk008.ru вы найдете информацию о центрах реабилитации‚ где предлагается помощь в лечении зависимостей и поддержка психологов. Реабилитационные программы включают помощь для людей с алкоголизмом‚ анонимные алкоголики и программы по оздоровлению и борьбе с алкоголем. Знание влияния алкоголя на здоровье помогает правильно подойти к процессу лечения и восстановлению.
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу проверить
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу
zapravka-propan-butanom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
http://www.pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ в Яндексе
интернет по адресу дома
krasnoyarsk-domashnij-internet006.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
https://servismersedes2.ru/ – Квалифицированное обслуживание трансмиссии
фундаментная плита под ключ .
If you are looking for a reliable replacing garage door opener, contact our company in Englewood, Florida.
Considering the breadth of services available from a company is important. Certain companies may primarily concentrate on installation, whereas others excel in repair and upkeep. Selecting a firm that covers all service aspects ensures you have support whenever needed.
zaezd-dlya-mashiny-365.ru .
https://pf-monstr.work/ – SEO продвижение с акцентом на ПФ
мерседес то – поддержание срока службы авто
Discover CBD dark chocolate
Выездная наркологическая помощь – это важный аспект лечения зависимостей‚ который обеспечивает экстренную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и зависимости от наркотиков. Выездная наркологическая служба оказывает профессиональную помощь зависимым‚ включая детоксикацию и экстренное вмешательство в кризисных ситуациях. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk009.ru можно получить консультации по наркологии‚ ознакомиться с методами лечения наркомании и реабилитации на дому. Конфиденциальное лечение зависимых позволяет сохранить личные данные в тайне. Важно также помнить о поддержке родственников‚ что помогает в процессе восстановления. Программа восстановления после зависимости включает меры по предотвращению рецидивов и психотерапию‚ что способствует успешному возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Thanks for the article http://avtomaster.net/modules.php?name=Forums&file=viewtopic&p=300114#300114 .
заправка газгольдера в московской области .
Thanks for the article http://web-lance.net/forums.php?m=posts&q=29456&n=last#bottom .
Thanks for the article https://ferdinand.com.ua/forum/topics/internet-magazin-rybolovnyx-snastej.14283/ .
Thanks for the article http://vrn.best-city.ru/forum/thread540114614/ .
Thanks for the article https://ferdinand.com.ua/forum/topics/internet-magazin-rybolovnyx-snastej.14283/ .
Основные типы железобетонных опор
Народные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом могут стать важным дополнением к медицинской помощи в Красноярском регионе. Терапия алкогольной зависимости требует всеобъемлющего подхода‚ включая детоксикацию организма и психологическую поддержку.Травяные настои‚ такие как лекарственные растения‚ могут помочь в снижении тяги к алкоголю. Следует иметь в виду о поддержке близких и анонимной терапии. Способы преодоления зависимости включают реабилитацию от алкоголизма и профилактику запойства. Рекомендации по отказу от спиртного также играют значительную роль в восстановлении после зависимости. помощь нарколога Красноярск
http://servismersedes2.ru – Технический адрес нашего домена
контора 1 вин http://www.1win22097.ru
pf-monstr.work – раскрутка сайта с ПФ
ставки прогнозы https://stavki-prognozy-2.ru/ .
плинко http://plinko3002.ru/
плинко кз https://plinko3002.ru
Howdy! Quick question that’s entirely off topic.
Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly?
My web site looks weird when browsing from my iphone 4. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to fix
this issue. If you have any suggestions, please share. Thanks!
сервисный центр мерседес – современное оборудование
stavkiprognozy http://www.stavki-prognozy-two.ru .
http://pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ сайта
Thanks for the article https://angelladydety.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=37404 .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
melbet скачать мобильное приложение https://melbet3006.com/
прогнозы на сегодня на спорт http://prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
Thanks for the article https://rank-fast.agency/risk-free-seo-backlinks-service-fast-59321/ .
https://servismersedes2.ru – Гарантированное сохранение пробега и истории ТО
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в уфе http://www.arus-diplom31.ru .
Greate article. Keep posting such kind of info on your page. Im really impressed by your blog.
Hey there, You’ve performed an excellent job. I’ll certainly digg it and for my part suggest to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this website.
Stretch Limousine Service
https://www.pf-monstr.work – SEO продвижение по ПФ
Hello! I just wish to give you a big thumbs up for the excellent information you’ve got here on this post.
I’ll be coming back to your blog for more soon.
Скачать тикток мод на андроид
то мерседес в москве – строгое соблюдение регламентов производителя
ставки прогнозы http://stavki-prognozy-1.ru/ .
kra36—-at.com — Надежный и удобный сервис — официальный сайт и подробный обзор даркнет-маркета Kraken. Официальный сайт kraken kra36.at — удобный сервис с множеством функций для пользователей. Узнайте больше и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
кракен ссылка, кракен ссылки, ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена, ссылки кракен, сайт кракена, кракен сайты, кракен сайт, сайт кракен, кракен отзывы, зеркала кракен, зеркала кракена, зеркало кракен, зеркало кракена, кракен зеркала, кракен зеркало, даркнет кракен, кракен даркнет, ссылка на кракен, ссылка на кракена, ссылки на кракен, кракен маркетплейс, маркетплейс кракен, кракен магазин, магазин кракен, кракены маркет, kraken ссылка, kraken ссылки, кракен маркет, вход кракен, кракен вход, кракен зайти, kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, актуальная ссылка кракен, актуальная ссылка кракена, актуальные ссылки кракен, кракен актуальная ссылка, кракен актуальные ссылки, кракен ссылка актуальная, кракен ссылки актуальные, кракен как зайти, зайти на кракен, kraken сайты, сайт kraken, kraken сайт, кракен официальный сайт, официальный сайт кракен, кракен сайт официальный, официальный сайт кракена, сайт кракен официальный, сайт кракена официальный, как зайти на кракен, кракен ссылка тор, кракен тор ссылка, ссылка кракен тор, кракен рабочая ссылка, кракен рабочие ссылки, рабочая ссылка кракен, рабочие ссылки кракен, кракен даркнет маркет, кракен маркет даркнет, кракен сайт ссылка, сайт кракен ссылка, кракен площадка, площадка кракен, кракен сайт магазин, актуальная ссылка на кракен, актуальные ссылки на кракен, кракен маркет песня, песня кракен маркет, кракен зеркало рабочее, кракен рабочее зеркало, рабочее зеркало кракен, кракен официальная ссылка, кракен ссылка официальная, официальная ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена официальная, ссылки кракена официальные, кракен сайт что, kraken маркетплейс, маркетплейс kraken
прогнозы на спорт от профессионалов прогнозы на спорт от профессионалов .
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It positively
useful and it has helped me out loads. I am hoping to contribute &
aid different customers like its helped me.
Good job.
анонимная консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
детский психиатр на дом в москве
https://www.pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ
психиатр онлайн консультация
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
психиатр на дом
https://servismersedes2.ru – Постгарантийное обслуживание с сохранением истории
купить свидетельство о разводе educ-ua4.ru .
Thanks for the article http://www.uin.in.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=47949&sid=dbbfc16bf55036bf7604a627fe9eb49f .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
ставки прогнозы http://www.stavki-prognozy-one.ru/ .
психиатрическая помощь больным
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
госпитализация в психиатрический стационар
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk011.ru
вывод из запоя
Thanks for the article http://forum.analysisclub.ru/index.php/topic,184675.new.html#new .
горшки для цветов с поливом https://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru/ .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1397267-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kresla-SHarman-Komfortnye-resheniya-dlya-rybalki-01-13 .
pf-monstr.work – работа с ПФ
лечение в психиатрической больнице
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
психиатр на дом в москве
servismersedes2.ru – Компьютеризированная диагностика инжекторных систем
столбовая трансформаторная подстанция столбовая трансформаторная подстанция .
купить аттестат за 11 класс беларусь купить аттестат за 11 класс беларусь .
ushp-fundament-10-na-10-499.ru .
Terrific work! This is the kind of information that should be shared around the web.
Shame on Google for now not positioning this put up higher!
Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
servismersedes2.ru – Электронный ресурс нашего техцентра
Накрутка зрителей Twitch — топ сервисов 2025 https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1840444-nakrutka-zritelei-tvich-top-25-servisov-besplatno-i-platno-2025 Статья с полезными советами для начинающих.
https://www.pf-monstr.work/ – улучшение ПФ
вызов психиатра на дом
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
вызов психиатрической помощи
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
психиатрический стационар
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
психиатрическое лечение
заезд строй .
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Хотите вывести ваш сайт на первые позиции поисковых систем Яндекс и Google?
Мы предлагаем качественный линкбилдинг — эффективное решение для увеличения органического трафика и роста конверсий!
Почему именно мы?
– Опытная команда специалистов, работающая исключительно белыми методами SEO-продвижения.
– Только качественные и тематические доноры ссылок, гарантирующие стабильный рост позиций.
– Подробный отчет о проделанной работе и прозрачные условия сотрудничества.
Чем полезен линкбилдинг?
– Улучшение видимости сайта в поисковых системах.
– Рост количества целевых посетителей.
– Увеличение продаж и прибыли вашей компании.
Заинтересовались? Пишите нам в личные сообщения — подробно обсудим ваши цели и предложим индивидуальное решение для успешного продвижения вашего бизнеса онлайн!
Цена договорная, начнем сотрудничество прямо сейчас вот на адрес ===>>> ЗДЕСЬ Пишите обгаварим все ньансы!!!
servismersedes2.ru – Надежный ремонт двигателей любой сложности
Накрутка подписчиков в Инстаграм https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1979649-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-instagram Рейтинг сервисов для повседневных задач.
zapravka-propan-butanom-gazgoldera-499.ru .
https://www.pf-monstr.work – раскрутка сайта через ПФ
фундамент плита стоимость за м2 .
оценить компанию оценка рыночной стоимости
Thanks for the article https://wot-news.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=24&t=47304&start=10 .
купить аттестаты 11 класс 2022 arus-diplom22.ru .
оказание психиатрической помощи
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
психиатрическая помощь больным
https://www.servismersedes2.ru/ – Всеобъемлющее сервисное сопровождение автомобилей Mercedes
Припой из драгоценных металлов в микроэлектронике
Припой из драгоценных металлов как ключевой элемент в производстве микроэлектроники
Чтобы обеспечить надежность соединений в современных электронных устройствах, рекомендуется применять сплавы на основе золота и серебра. Эти материалы обладают отличной проводимостью, коррозионной стойкостью и высокой надежностью, что делает их незаменимыми в критических приложениях.
Технические специалисты часто предпочитают использовать сплавы с низкой температурой плавления, такие как 80% золота и 20% меди, для упрощения процесса пайки и повышения скорости производства. Эти сплавы обеспечивают качественные соединения при относительно низких температурах, что минимизирует риск повреждения чувствительных компонентов.
Важно учитывать, что для создания прочных соединений необходимо правильно выбирать флюс. Оптимальное сочетание флюса и сплава улучшает адгезию и исключает образование окислов, что, в свою очередь, продлевает срок службы устройств. Например, использование активного флюса в комбинации со сплавами на основе золота может значительно повысить прочность соединений.
При выборе материалов также стоит обращать внимание на технологические параметры, например, температура пайки и скорость охлаждения. Подбор оптимальных условий обработки позволит избежать термических повреждений и улучшить электрические характеристики полученных контактов.
Выбор материала на основе золота и серебра для пайки компонентов
Оптимальный выбор для пайки электронных элементов включает сплавы на основе золота и серебра с учетом их температурных характеристик и проводимости. Для надежного соединения применяйте легирующие добавки для улучшения механических свойств и плавкости.
Для золота выбирайте сплавы с добавлением меди или никеля, это повысит прочность швов. Сплавы с 80% золота и 20% меди хороши для большинства применений, обеспечивая отличное электрическое соединение.
Серебро менее дорого, но при этом очень эффективно благодаря высокой теплопроводности. Сплавы с 60% серебра и 40% меди подходят для работы при увеличенных температурных нагрузках, также стоит обратить внимание на сплавы с добавлением небольшого количества олова для облегчения плавления.
Важно учитывать зернистость и размер частиц сплавов. Мелкодисперсные материалы обеспечивают более равномерное распределение при плавлении, что улучшает жидкотекучесть и адгезию к компонентам.
Не забывайте про соответствие материалов требованиям ROSH и требованиям по безопасности, если вы работаете в области высоких технологий. Пайка должна объёмно учитывать риск коррозии, который может возникнуть, если соединения находятся в агрессивной среде.
Регулярно проверяйте параметры плавления и механических свойств выбранных материалов для достижения наилучших результатов при каждом процессе пайки. Рекомендуется тестировать каждую партию материала перед использованием. Это снизит вероятность возникновения недочетов и повысит общую надёжность готового изделия.
Технологические особенности применения сплавов на основе палладия в производстве электроники
Сравнение палладиевых сплавов с традиционными формулами демонстрирует их значительное преимущество в выполнении соединений в условиях высокой температуры. При температуре плавления около 1554 °C, данные материалы обеспечивают надежную фиксацию при термических циклах.
Для достижения оптимальной механической прочности и электроизоляции рекомендуется комбинировать палладиевые компоненты с легирующими добавками. Это позволяет улучшить характеристики по коррозионной стойкости и снизить вероятность окисления соединений, что особенно критично для высокочувствительной электроники.
Важно учитывать, что обработка палладиевых материалов требует специального оборудования. Параметры сварки и пайки должны строго контролироваться для избегания перегрева, что может привести к ухудшению свойств соединений. Рекомендуется проводить тестирование на образцах для верификации оптимальных значений температуры и времени обработки.
Применение палладиевых сплавов оправдано в высокотехнологичных устройствах, где требуется высокая проводимость и надежность стыков. Например, в авиации и медицинской технике надежность соединений является приоритетом, что делает использование палладия предпочтительным вариантом.
Важно также обращать внимание на чистоту блеска при производстве. Основная задача – минимизация примесей, которые могут повлиять на производительность и долговечность соединений. Использование высококачественного исходного материала и строгая сертификация компонентов способствуют достижению необходимых стандартов.
my webpage :: https://rms-ekb.ru/catalog/izdeliia-iz-dragotsennykh-i-blagorodnykh-metallov/
stavkiprognozy stavki-prognozy-two.ru .
прогнозы от профессионалов на спорт https://www.prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
http://pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ
платная психиатрическая клиника
psychiatr-moskva002.ru
консультация врача психиатра
Thanks for the article https://allaboutschool.activeboard.com/t69784064/alyakaco/?page=1#lastPostAnchor .
сделать заезд на участок через канаву цена .
блочная трансформаторная подстанция http://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru .
стационарное психиатрическое лечение
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
консультация психиатра на дому
https://servismersedes2.ru/ – Инновационное оборудование для точной диагностики
Discover the elegance and reliability of deluxe garage doors, which will add a unique style to your home in Englewood, Florida.
It’s crucial to rely on experts for the installation of high-end garage doors. Experts will help maintain the aesthetic and functional qualities of your doors.
купить диплом о высшем киев купить диплом о высшем киев .
частная психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
бесплатные ставки на промокод 1хБет это специальный код для получения бонуса в сумме до 32 500 рублей. Это предложение активируется только при первой регистрации, при этом после создания аккаунта пользователь получает 130% от суммы первого депозита.
купить аттестат за 11 класс с егэ http://arus-diplom23.ru/ .
zapravka-gazgoldera-moskva-499.ru .
Рабочий тик ток Рабочий тик ток – это стабильность и надежность, это уверенность в том, что ваше приложение всегда будет работать исправно и без сбоев.
https://www.pf-monstr.work – SEO продвижение с упором на ПФ
Для бизнеса в столице предлагаем продвижение сайтов по позициям москва. Это выгодный способ закрепиться в поиске и привлечь больше клиентов из Москвы. Оплата только за результат — прозрачная схема, которая исключает переплаты. Такой вариант позволяет компаниям развиваться спокойно и без лишнего давления на бюджет. Конкурентов в столице много, но в ТОПе оказываются те, кто действует умнее.
Mihaylov.digital — агентство комплексного SEO-продвижения сайтов. Делаем аудит, оптимизацию, выводим проекты в ТОП Google и Яндекс. Работаем с бизнесом любого масштаба. Адрес: Москва, Одесская ул., 2кС, 117638.
https://servismersedes2.ru – Гарантированное сохранение пробега и истории ТО
zapravka-gazgoldera-moskva-499.ru .
прогноз на сегодняшний хоккей https://prognozy-na-khokkej.ru/ .
как купить диплом с проводкой как купить диплом с проводкой .
Explore flexible plans with adu contractors near san francisco ca.
This is very attention-grabbing, You’re an overly skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to in the hunt for extra of your excellent post. Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks
онлайн казино кэт
https://energo-pole.ru/skladskaya-tekhnika/samokhodnye-telezhki/samokhodnaya-telezhka-pt20/
столы.
Доп. скидка 5% на всю технику Smartlift из наличия до 15.04, суммируется с акциями, применяется автоматически (заказ через корзину) или менеджером (заказ по телефону, Email или в форме).
Складские позиции.
Подъёмники различаются по грузоподъемности, размерам, высоте подъема и опускания, конфигурации – модель легко подобрать для нужных задач (работы с гидравлическими тележками, поддонами российского и европейского стандартов, материалов массой 800-3000 кг и проч.). Конструкция механизмов оснащена датчиком для автоподъема/опускания (на выбор). Производительность – подъёмный стол позволяет использовать функции станков на 100%. Экономию – сокращение персонала и исключение влияния человеческого фактора.
Надежный гидроцилиндр обеспечивает плавный подъем.
Арт. 700062.
услуги по накрутке поведенческих факторов – комплексный спектр услуг
трансформаторная подстанция трансформаторная подстанция .
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
http://servismersedes2.ru/ – Оперативное устранение неисправностей электронных систем
аттестаты за 11 класс купить в москве аттестаты за 11 класс купить в москве .
купить аттестат за 11 класс купить аттестат за 11 класс .
Накрутка живых подписчиков для Телеграм канала https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1994159-nakrutka-zhivykh-podpischikov-dlya-telegam-kanala Подробная инструкция с советами пользователей.
Wow, incredible weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy. The overall look of your site is great, as neatly as the content material!
knifeworks.ru
консультация врача психиатра онлайн
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
лечение психиатрических расстройств
вызвать психиатра на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
врач психиатр на дом
силовые трансформаторные подстанции http://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit1.ru .
stavkiprognozy http://www.stavki-prognozy-one.ru/ .
Хотів знайти інформацію про танцювальні фестивалі і натрапив на канадський захід. Що ж, цього разу я пропустив, але тепер точно планую відвідати подібне наступного року.
http://servismersedes2.ru/ – Профессиональный подход к каждому автомобилю
pf-monstr.work/ – раскрутка по ПФ
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
консультация психиатра на дому
Protect structure and style with timely Siding replacement. This prevents moisture damage from spreading. The result is both safety and aesthetics.
лучшие психиатрические клиники
psychiatr-moskva003.ru
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
People searching for real-time fun often choose sexcam platforms. They enjoy the direct engagement with performers.
Some pharmacies now provide over the counter medicine delivery phosphatidylcholine.bz across the USA. It makes access to common remedies easier.
купить аттестат 11 классов алматы купить аттестат 11 классов алматы .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина http://arus-diplom34.ru/ .
Thanks for the article https://xiglute.com/forums/topic/88890/-/view/post_id/640309 .
https://servismersedes2.ru/ – Профессиональное обслуживание трансмиссии
http://pf-monstr.work/ – поведенческие факторы накрутка и улучшение
СтавкиПрогнозы http://stavki-prognozy-2.ru/ .
Здравствуйте!
Долго обмозговывал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Форумный спам с Xrumer помогает увеличить DR и Ahrefs показателя. Автоматический прогон ссылок позволяет быстро создать качественные внешние ссылки. Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, экономят время и силы. Увеличение ссылочной массы с помощью Xrumer даёт значительный рост. Используйте Xrumer для улучшения SEO-позиции вашего сайта.
seo автоматическое, продвижение сайта закупками ссылок, Прогон Хрумер для сайта
линкбилдинг под ключ, smm и seo в чем разница, сайты продвижения в соц сетях
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
servismersedes2.ru – Цифровой ресурс нашего техцентра
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые находятся на территории всей России. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
где купить аттестат за 10 11 класс
психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
платный психиатр на дом
заправка газгольдера подмосковье .
Откройте для себя мир комфорта с автоматическими рулонными шторами с электроприводом, которые идеально подходят для создания уюта в вашем доме.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это удобное и стильное решение для современных интерьеров. Использование рулонных штор с электроприводом делает интерьер более функциональным и эстетичным.
Преимущества использования электропривода очевидны . Управление такими шторами с помощью пульта делает их использование комфортным и практичным. Во-вторых, электроника позволяет настраивать режим работы штор в зависимости от времени суток .
Установить рулонные шторы с электроприводом можно в любом помещении . Их активно используют как в жилых, так и в коммерческих помещениях . Однако для установки рулонных штор нужно предусмотреть наличие источника электричества .
При выборе таких штор стоит учитывать их стиль и качество материалов . Разнообразие тканей и расцветок дает возможность подобрать идеальные шторы для любого стиля . Кроме того, многие производители предлагают индивидуальные решения по размерам и конфигурациям .
pf-monstr.work/ – улучшение ПФ
промышленные трансформаторные подстанции http://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru/ .
шведская плита фундамент цена .
консультация частного психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
вызов психиатрической помощи
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг для начинающих требует базовых знаний и инструментов. Xrumer автоматизирует размещение ссылок. Массовый прогон ускоряет рост DR. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше позиции. Линкбилдинг для начинающих – первый шаг к успешному SEO.
для нужно сео продвижение, продвижение сайтов в яндексе wordpress, Линкбилдинг через автоматические проги
компания линкбилдинг, разработка поддержка продвижение web сайтов, торрент раскрутка сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Диагностика электронных систем любой сложности
Thanks for the article https://forum.singaporeexpats.com/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=679596 .
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-perchatki-dlya-spinningovoj-lovli-Rejting-i-sovety-01-13 .
http://pf-monstr.work/ – поведенческие факторы улучшение
детский психиатр на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva001.ru
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
https://www.servismersedes2.ru – Фирменный сервис Mercedes с безупречной репутацией
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Vybor-polyarizacionnyh-ochkov-Kak-zashchitit-glaza-i-uluchshit-ulov-01-13 .
купить диплом в черкассах http://www.educ-ua4.ru/ .
http://www.pf-monstr.work – работа с ПФ
обустройство заезда на участок через канаву .
servismersedes2.ru – Качественный ремонт двигателей любой сложности
консультация врача психиатра онлайн
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
консультация психиатра на дому
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
оказание психиатрической помощи
Лучшие сервисы для накрутки подписчиков в Тик Ток https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1936663-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tik-tok-25-luchshikh-servisov-na-2025-god Руководство по базовым приёмам.
трансформаторная подстанция купить http://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit1.ru/ .
мерседес сервис – опытные мастера
сервис поведенческих факторов – факторные сервисы
Thanks for the article https://www.brownbook.net/business/53875909/jewelry .
перила для лестницы на улице Поручень для лестницы – это не только функциональный элемент, но и деталь интерьера, способная подчеркнуть его индивидуальность. Правильно подобранный поручень может стать настоящим украшением лестницы и придать ей неповторимый шарм.
скачать казино мостбет https://mostbet4150.ru/
Привет всем!
Долго обмозговывал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон Хрумер для сайта позволяет быстро увеличить ссылочный профиль. Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро становится возможным через Xrumer. Линкбилдинг через автоматические проги ускоряет продвижение. Xrumer форумный спам облегчает массовый постинг. Эффективный прогон для роста DR экономит время специалистов.
сео умирает, команда сео, линкбилдинг
линкбилдинг курс, сайты seo fast, quake seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
шведский плита .
заезд к дому .
прогноз ставок на хоккей прогноз ставок на хоккей .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kak-vybrat-horoshij-spinning-dlya-rybalki-Rekomendacii-i-sovety-01-13 .
скачать мосбет скачать мосбет
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Set-magazinov-Rybachok–Vsyo-dlya-professionalnoj-rybalki-01-13 .
Виявляється, багато фактів про Бермудський трикутник є лише міфами. Було цікаво розібратися, що з цього правда, а що – вигадки.
Привет всем!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от крутых seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов позволяет ускорить линкбилдинг. Как увеличить показатели домена Xrumer становится понятно через практику. Xrumer для продвижения сайта облегчает автоматизацию. SEO-прогон для новичков повышает видимость ресурса. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer экономят время специалистов.
проект сео сайт, сео топ сайты, Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer
Xrumer форумный спам, пермь сео продвижение, сервис продвижения сайтов бесплатно
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Sitio fácil de navegar con gran cantidad de información sobre apuestas.
https://gratoganacasino.top/
https://servismersedes2.ru/ – Восстановительный ремонт силовых агрегатов
https://pf-monstr.work – улучшение ПФ
Бесплатная накрутка подписчиков в Тик Ток https://vc.ru/niksolovov/2153315-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tik-tok-besplatno Обзор способов и стратегий.
teplyy-fundament-ushp-499.ru .
заезд строй .
прибор узи http://www.kupit-uzi-apparat25.ru/ .
купить аттестат 11 класс барнаул купить аттестат 11 класс барнаул .
купить узи сканер купить узи сканер .
Здравствуйте!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Предлагаю линкбилдинг использовать с Xrumer для ускорения продвижения. Линкбилдинг сервис помогает экономить время. Линкбилдинг интернет магазина увеличивает продажи. Каталоги линкбилдинг дают качественные источники ссылок. Линкбилдинг сервисы упрощают работу специалистов.
seo оптимизация что это простыми, бесплатный хостинг сайтов продвижение, Как поднять DR сайта за неделю
Рассылки с помощью Xrumer, новости продвижения сайта, сео продвижение в регионах
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
пройти лечение от наркозависимости
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
как лечить алкогольную зависимость
https://www.med2.ru/story.php?id=147095
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Верификация систем активной безопасности
tripskan Трипскан – это вдохновение, это новые идеи для путешествий, это возможность выйти за рамки привычного и увидеть мир другими глазами.
Those looking to save money appreciate ThessalonikiCar-Rental deals https://thessalonikicar-rental.com/. Discounts and seasonal offers are available throughout the year.
Доброго!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer: создание ссылочной массы помогает ускорить продвижение сайтов. Программа массово размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах. Это экономит время и силы специалистов. Чем больше авторитетных ссылок, тем выше DR. Xrumer: создание ссылочной массы – современный метод линкбилдинга.
правильная сео оптимизация, контекстная реклама в сео, линкбилдинг начать
линкбилдинг сайт, разработка и продвижение сайта агентство, сео домен
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
лечение наркомании цена
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
лечение от зависимости наркотиков
аппарат для узи цена kupit-uzi-apparat26.ru .
http://pf-monstr.work – накрутка ПФ в Яндексе
Рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом идеально подойдут для создания уюта и контроля освещения в вашем доме.
Электроприводные рулонные шторы блэкаут представляют собой. Эти шторы эффективно блокируют свет, что способствует комфортному сну даже днём.
Важным преимуществом рулонных штор блэкаут с электроприводом считается. С помощью пульта можно легко управлять такими шторами, что упрощает их использование в современном дизайне.
Кроме того, рулонные шторы с эффектом блэкаут просто монтируются. Существует несколько способов крепления этих штор. Это позволяет адаптировать шторы под любой тип окон.
Не забывайте, что рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом также обладают. Эти шторы могут значительно снизить теплопотери зимой. В конечном итоге, такие рулонные шторы обеспечивают стильный вид и практичность для вашего дома.
аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве .
Добрый день!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer становится проще с инструкцией. Xrumer для массового линкбилдинга позволяет экономить силы. Линкбилдинг на автомате ускоряет создание ссылочной массы. Техники увеличения ссылочной массы Xrumer обеспечивают стабильный рост DR. Xrumer и рост Ahrefs DR становятся заметны через недели.
блоги по продвижению сайтов, продвижение сайтов скачать бесплатно, линкбилдинг сео
линкбилдинг это что, jiwoo seo, методики seo оптимизации
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Быстрый переход на наш сайт
Online casinos have become increasingly popular in recent years, attracting a wide range of players. These virtual platforms offer a convenient way for individuals to enjoy gambling from the comfort of their homes.
casino etiquette rules http://lecasinonet.com/2024/06/08/casino-etiquette-dos-and-donts
Откройте для себя мир азартных игр на 888starz partners.
888starz — это популярная платформа для азартных игр, предоставляющая разнообразие возможностей для игроков. Платформа включает в себя как слоты, так и настольные игры, чтобы удовлетворить запросы всех игроков.
888starz предлагает удобный интерфейс, что позволяет легко ориентироваться по сайту. Регистрация и навигация по платформе не вызывают затруднений у игроков.
Процесс создания аккаунта на 888starz не займет много времени. В качестве первого шага потребуется указать основные данные и пройти верификацию.
Игроки могут воспользоваться различными предложениями и акциями, которые делают игру еще более увлекательной. Это позволяет увеличить игровую сумму и сделать процесс более увлекательным.
заправка газом газгольдера в подмосковье .
диплом высшего образования проведенный купить диплом высшего образования проведенный купить .
This site definitely has all the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know
who to ask.
Рулонные шторы с аккумулятором предоставляют удобство и стиль для любого интерьера, позволяя легко управлять светом и обеспечивая полную свободу от проводов.
Аккумуляторные рулонные шторы – это прекрасный выбор для стильных и функциональных помещений.
http://pf-monstr.work – оптимизация ПФ
mostbet aviator strategiyasi mostbet aviator strategiyasi
https://sonturkhaber.com/
http://servismersedes2.ru/ – Эффективное устранение неисправностей электрооборудования
диплом ссср купить недорого диплом ссср купить недорого .
www mostbet com www mostbet com
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр http://arus-diplom34.ru .
аттестат за 11 класс купить в чите аттестат за 11 класс купить в чите .
лечение наркотической зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков в Астане
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2008 купить аттестат за 11 класс 2008 .
mostbet скачать бесплатно mostbet скачать бесплатно
курс лечения от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар в Астане
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью рулонных штор с дистанционным управлением, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Все больше людей выбирают рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением для своих домов. Данные изделия соединяют в себе удобство и эстетичность, что делает их идеальным выбором для различных помещений.
Вы можете контролировать рулонные шторы либо с помощью пульта, либо через мобильное приложение. Таким образом, вы можете быстро изменять уровень освещенности и создавать комфортную обстановку в своем жилище.
Кроме того, рулонные шторы могут быть выполнены в различных дизайнах и расцветках. Таким образом, вы сможете выбрать именно тот вариант, который идеально впишется в ваш интерьер.
Следует подчеркнуть, что рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением очень практичны в повседневной жизни. Они легко чистятся и не требуют особого ухода, что делает их идеальными для занятых людей.
http://pf-monstr.work/ – накрутка ПФ
купить бланк аттестат за 11 класс купить бланк аттестат за 11 класс .
Thank.
Thank.
https://www.servismersedes2.ru/ – Обновление мультимедийных систем MBUX
купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный диплом .
server host vps vps hosting germany
купить аттестат 11 класс 2015 год купить аттестат 11 класс 2015 год .
mostbet rasmiy sayt mostbet rasmiy sayt
прогноз на хоккей на сегодня прогноз на хоккей на сегодня .
zaezd-pod-klyuch-365.ru .
сервисный центр мерседес в москве – лучшие цены в городе
Приобретите рейтинг умных рулонных штор и насладитесь комфортом и современными технологиями в своем доме.
Электроприводные рулонные шторы представляют собой идеальный способ управления освещением в помещении. Эти шторы легко управляются с помощью смартфона или пульта дистанционного управления.
Главное достоинство рулонных штор с электроприводом заключается в удобстве использования. Вы можете настраивать их положение в любое время, не вставая с дивана.
Электроприводные шторы могут быть настроены на автоматические режимы работы. Вы можете задать время, когда шторы должны открываться и закрываться, что делает их особенно удобными.
Эти шторы могут стать частью вашей системы “умный дом”, что добавляет дополнительный уровень комфорта. Таким образом, шторы могут работать в связке с другими устройствами, что делает ваш дом более умным и адаптивным.
https://pf-monstr.work/ – поведенческие факторы накрутка и улучшение
mostbet ilovasi ilova haqida baho 4 8 allaqachon yuklab olingan http://mostbet4105.ru/
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг это – основа современной оптимизации. Ссылки помогают сайту расти в поиске и привлекать трафик. Программы вроде Xrumer упрощают создание линков. Это экономит время и силы специалистов. Линкбилдинг это эффективный инструмент продвижения.
сео нетология, мероприятия продвижению сайта, линкбилдинг на форумах
Форумные проги для SEO, продвижение сайта в гугле сео, продвижение сайтов медицинских
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
teplyy-fundament-ushp-499.ru .
Thanks for the article http://tryndelka.tforums.org/viewtopic.php?f=14&t=5856 .
На http://metallicheskij-shtaketnik.ru представлены эконом-варианты заборов из металлоштакетника от 950 руб./п.м. Качественная оцинкованная сталь толщиной 0,45 мм, стандартные цвета (коричневый, зеленый, графит). Быстрая доставка – в течение 24 часов по Москве. Монтаж возможен в день доставки материалов.
mostbet link https://mostbet4104.ru/
Thanks for the article https://moskvic.actieforum.com/t3522-topic .
комплексное лечение алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
анонимная реабилитация наркозависимых
https://www.servismersedes2.ru – Ключевой сервис для модельного ряда Mercedes-Benz
Промокод 1xBet при регистрации только один, это: https://videoduel.ru/news/promokod_309.html используйте его чтобы получить приветственный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130).
Thanks for the article https://seoprobox.click/increase-backlinks-ahrefs-domain-rating-50-60-70-moz-domain-authority-20-30-and-guest-posting-31546/ .
vjcn,tn http://www.mostbet4149.ru
кресло для косметолога косметологическое оборудование для салонов красоты купить
Після перегляду майстер-класу з танго на сайті про події, я почала вивчати цей танець. Тепер це стало моїм новим хобі.
Thank.
http://www.pf-monstr.work – оптимизация поведенческих
Привет всем!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer увеличивает внешнюю массу сайта. Эффективность прогона Xrumer подтверждается результатами. Массовый линкбилдинг для сайта улучшает позиции в поиске. Программы для автоматического постинга ускоряют работу. Как поднять показатели Ahrefs становится более доступным.
поисковое продвижение сайтов в спб, курсы создание продвижение сайтов, SEO-прогон для новичков
Повышение авторитетности сайта, seo google document, курсы продвижение сайта в поисковых системах
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Доброго!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от успещных seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический постинг на форумах с Xrumer помогает создать ссылочную массу. Прогон Хрумером увеличивает DR и улучшает показатели Ahrefs. Массовые рассылки ссылок ускоряют SEO-продвижение вашего сайта. Использование Xrumer для линкбилдинга даёт быстрые результаты. Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, позволяют автоматизировать процесс.
яндекс продвижение сайта в топ 10 яндекса цена, сколько стоит seo копирайтинг, линкбилдинг это что
Прогон Xrumer по свежим базам, отчеты по продвижению сайтов, создание и продвижение сайтов для бизнеса
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
реабилитация наркоманов недорого
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
помощь при алкоголизме
Thank.
ставки мостбет https://mostbet4146.ru
ремонт mercedes – ликвидация любых неполадок
https://pf-monstr.work/ – раскрутка по поведенческим
mostbet ios mostbet4102.ru
купить аппарат узи цены новый kupit-uzi-apparat25.ru .
Накрутка голосов Telegram — лучшие сервисы 2025 https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1828760-nakrutka-golosov-telegram-2025-top-20-luchshih-servisov-dlya-zhivyh-reakcii-i-emocii Обзор решений для легкого освоения.
servismersedes2.ru – Качественный ремонт современных двигателей
Доброго!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от успещных seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer помогает автоматизировать процесс линкбилдинга, увеличивая DR и Ahrefs. Прогон ссылок через форумы ускоряет создание качественных ссылок. Массовая рассылка ссылок на форумах улучшает видимость сайта. Увеличение ссылочной массы с помощью Xrumer ускоряет SEO-продвижение. Используйте Xrumer для роста показателей вашего сайта.
сео по трафику, системы продвижения сайта москва, линкбилдинг блог
Прогон по базам форумов, seo атом, продвижения сайта на opencart
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Palatka-JRC-Extreme-TX-2-Man-Bivvy-Komfort-i-zashchita-na-prirode-01-13 .
Thank.
http://www.pf-monstr.work – накрутка поведенческих факторов сайта
https://servismersedes2.ru – Инновационные технологии в обслуживании немецких авто
мостбет вход в личный кабинет http://mostbet4150.ru
Amazing! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it
has pretty much the same layout and design. Excellent choice of colors!
Thanks for the article https://tablo.com/genres/short-stories-flash-fiction/discussions/4719-osmetics/comments/49154#comment-49154 .
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer для создания ссылочной стратегии помогает системно подходить к линкбилдингу. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах. Массовый прогон ускоряет рост DR. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше позиции сайта. Xrumer для создания ссылочной стратегии – эффективный метод SEO.
seo skill, сео оптимизация сайтов москва, Линкбилдинг через комментарии
компания линкбилдинг, бесплатное продвижение сайта самостоятельно пошаговая инструкция, аудит сео пример
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
приложение к аттестату 11 класс купить https://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
купить аттестат за 11 класс минск http://www.arus-diplom22.ru .
купить диплом института с реестром купить диплом института с реестром .
Yo all, thought I’d mention how I feel about http://www.afunnydir.com/fishin'-frenzy-virgin-games_464746.html recently. For real, it’s a perfect chance to experience this slot without spending a dime. From the classic to The Big Splash and bonus buy make the gameplay fun and exciting. One thing I love is the instant play and no-download feature. Also the seasonal Fishin’ Frenzy Christmas demo adds a fun twist all while staying true to the classic. For anyone curious, give the demos a go. Perfect for casual gaming. Just my thoughts, hope you find it useful.
mostbetuz com mostbetuz com
Приобрести диплом любого университета!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по доступным тарифам— erudit-school.ru
купить государственный диплом с занесением в реестр купить государственный диплом с занесением в реестр .
http://servismersedes2.ru – Беспрецедентное внимание к деталям ремонта
этот сайт
включить геолокацию
как зарегистрироваться в мостбет как зарегистрироваться в мостбет
mostbet mobile http://mostbet4147.ru/
купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом с проводкой моих купить диплом с проводкой моих .
Thanks for the article http://getrejoin.com/ru/question/internet-magazin-rybolovnyh-snastey-1678158.html .
хоккей сегодня прогноз http://www.prognozy-na-khokkej1.ru .
аттестат 11 класса с куар кодом купить аттестат 11 класса с куар кодом купить .
купить диплом об образовании киев купить диплом об образовании киев .
Thanks for the article http://www.hristianka.ru/forum/m/102181/#msg_102181 .
Доступно и понятно изложено на https://niksolovov.ru
Hey! Want to tell you about DeflationCoin (DEF) – here you can earn in two ways at once. Buy tokens, put them in staking and receive monthly dividends from profits of their casino, premium dating and crypto exchange. Meanwhile the token itself constantly grows in price because they automatically buy back and burn tokens using business profits.
Imagine – you own tokens and get your share from wealthy people spending $5000 to enter an elite dating club, playing casino or trading on the exchange. The bigger their business turnover, the higher your dividends and the more expensive your tokens become. If you stake for 12 years, dividends multiply by 20x.
The token already showed growth from $0.000001 to $0.31 – that’s 31 million percent in a short time. Now they’re preparing to launch main ecosystem products, so this might be just the beginning. You basically become a co-owner of a growing entertainment business in crypto.
deflationcoin.com
http://www.servismersedes2.ru – Качественный ремонт двигателей и трансмиссий
Дізналася історію Дороті Еді, яка стверджувала, що пам’ятає своє минуле життя в Давньому Єгипті. Це захоплююче!
mosrbet https://mostbet4105.ru
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
купить аттестат 11 купить аттестат 11 .
купить зеркало купить зеркало .
Оставляю ссылку https://niksolovov.ru
системы контроля транспорта системы контроля транспорта .
Рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом идеально подойдут для создания уюта и контроля освещения в вашем доме.
идеальное решение для. Рулонные шторы блэкаут надежно затемняют помещение, что позволяет создать темную обстановку в любое время суток.
Одним из главных преимуществ рулонных штор с электроприводом является. Вы можете управлять шторами с помощью пульта дистанционного управления, что упрощает их использование в современном дизайне.
Кроме того, рулонные шторы с эффектом блэкаут просто монтируются. Вы можете выбрать между различными методами установки. Такое разнообразие дает возможность подобрать шторы для любых оконных конструкций.
Не забывайте, что рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом также обладают. Это поможет вам сохранить тепло в холодное время года. Таким образом, рулонные шторы блэкаут с электроприводом – это не только стильный, но и практичный выбор.
мостбет официальный сайт узбекистан мостбет официальный сайт узбекистан
узи сканер купить москва https://kupit-uzi-apparat27.ru .
zapravka-gazgoldera-moskva-499.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске .
узи аппарат цена новый kupit-uzi-apparat26.ru .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kakuyu-pletyonku-vybrat-dlya-spinninga-Rekomendacii-i-rejting-01-13 .
кривой рог купить диплом о высшем образовании кривой рог купить диплом о высшем образовании .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень .
купить аттестаты за 11 киров цена недорого купить аттестаты за 11 киров цена недорого .
Thanks for the article https://www.freeboard.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=980487#p980487 .
Здравствуйте!
Долго анализировал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг план помогает системно подходить к продвижению сайта. Xrumer автоматизирует размещение ссылок на тематических форумах. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше позиции сайта. Линкбилдинг план – ключ к успешной SEO-кампании.
фразы для продвижения сайтов, search optimization seo, линкбилдинг москва
Использование форумного постинга для SEO, seo cases, германия продвижение сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
приложение к аттестату 11 класс купить http://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
Thank.
Suku https://matiri.mx/index.php/question/crypto-news-24w/ news focuses on its supply chain solutions using blockchain technology.
Thanks for the article http://fialkovyimir.ukrbb.net/viewtopic.php?f=108&t=4955 .
шведская монолитная плита .
SMM блог про ТГ https://niksolovov.ru
zaezd-pod-klyuch-365.ru .
Affordable prices can be found to how to flush cialis out of your system for proper guidance. levitra amazon
Thanks for the article http://forum.krolevets.com/viewtopic.php?p=27772#27772 .
https://sonturkhaber.com/
melbet без идентификации http://www.melbetofficialsite.ru .
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-1.ru .
прогнозы на хоккей на сегодня от профессионалов прогнозы на хоккей на сегодня от профессионалов .
купить диплом бакалавра дешево купить диплом бакалавра дешево .
Thanks for the article https://ukraineforum.com.ua/index.php?threads/%D0%9B%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B1%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B4-%D0%B2-%D0%9A%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%B2%D0%B5.8626/#post-73716 .
https://www.med2.ru/story.php?id=147095
купить диплом в чернигове недорого http://educ-ua4.ru/ .
монолитная плита с теплым полом .
Збиралася на майстер-клас із танго, але все розкупили. Втім, платформа подорожей підказала, як підготуватись до наступної події. Не можу дочекатися!
Мы предлагаем документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом ВУЗа:
аттестат с отличием 11 класс купить
въездная группа в частный дом .
Cамоустанавливающийся подшипник Виброустойчивые подшипники – специализированные подшипники, разработанные для работы в условиях повышенной вибрации и ударных воздействий.
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в https://www.arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в .
стоимость бетона бетон
за сколько можно купить аттестат 11 класса за сколько можно купить аттестат 11 класса .
стоимость аппарата узи цена стоимость аппарата узи цена .
zapravka-gazgoldera-moskva-499.ru .
Привет всем!
Долго ломал голову как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от успещных seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг сайт – ключ к SEO-успеху. Ссылки увеличивают доверие поисковых систем и позиции ресурса. Автоматизация через программы ускоряет процесс. Такой метод удобен для любых сайтов. Линкбилдинг сайт помогает достигать топовых позиций.
сео анализ страницы онлайн, раскрутка оптимизация сайта, Постинг на блогах для SEO
Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer, dr web сайт закрывается, региональные сайты seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
are fake shoes made in china – is replica shoes good
kra36—-at.com — Надежный и удобный сервис — официальный сайт и подробный обзор даркнет-маркета Kraken. Официальный сайт kraken kra36.at — удобный сервис с множеством функций для пользователей. Узнайте больше и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
кракен ссылка, кракен ссылки, ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена, ссылки кракен, сайт кракена, кракен сайты, кракен сайт, сайт кракен, кракен отзывы, зеркала кракен, зеркала кракена, зеркало кракен, зеркало кракена, кракен зеркала, кракен зеркало, даркнет кракен, кракен даркнет, ссылка на кракен, ссылка на кракена, ссылки на кракен, кракен маркетплейс, маркетплейс кракен, кракен магазин, магазин кракен, кракены маркет, kraken ссылка, kraken ссылки, кракен маркет, вход кракен, кракен вход, кракен зайти, kraken зеркала, kraken зеркало, актуальная ссылка кракен, актуальная ссылка кракена, актуальные ссылки кракен, кракен актуальная ссылка, кракен актуальные ссылки, кракен ссылка актуальная, кракен ссылки актуальные, кракен как зайти, зайти на кракен, kraken сайты, сайт kraken, kraken сайт, кракен официальный сайт, официальный сайт кракен, кракен сайт официальный, официальный сайт кракена, сайт кракен официальный, сайт кракена официальный, как зайти на кракен, кракен ссылка тор, кракен тор ссылка, ссылка кракен тор, кракен рабочая ссылка, кракен рабочие ссылки, рабочая ссылка кракен, рабочие ссылки кракен, кракен даркнет маркет, кракен маркет даркнет, кракен сайт ссылка, сайт кракен ссылка, кракен площадка, площадка кракен, кракен сайт магазин, актуальная ссылка на кракен, актуальные ссылки на кракен, кракен маркет песня, песня кракен маркет, кракен зеркало рабочее, кракен рабочее зеркало, рабочее зеркало кракен, кракен официальная ссылка, кракен ссылка официальная, официальная ссылка кракен, ссылка кракена официальная, ссылки кракена официальные, кракен сайт что, kraken маркетплейс, маркетплейс kraken
обзор казино melbet обзор казино melbet .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов .
где сделать проект перепланировки квартиры proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry5.ru .
ставки прогнозы https://www.stavki-prognozy-one.ru .
Откройте для себя мир азартных игр на 888starz bet зеркало uzbekistan.
888starz — это популярная платформа для азартных игр, предоставляющая разнообразие возможностей для игроков. Платформа включает в себя как слоты, так и настольные игры, чтобы удовлетворить запросы всех игроков.
888starz предлагает удобный интерфейс, что делает игру более комфортной. Каждый пользователь может найти нужный раздел без труда.
Регистрация на платформе достаточно простая и быстрая. После предоставления необходимой информации игроки смогут активировать свои аккаунты.
888starz радует своих игроков щедрыми бонусами и многочисленными акциями. Это позволяет увеличить игровую сумму и сделать процесс более увлекательным.
купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр .
Гайд по накрутке Телеграм https://niksolovov.ru must read
надёжность melbet http://www.melbetofficialsite.ru .
price options offered by authorized pharmacies before you cialis price through this portal deliver your treatment at affordable cialis tadalafil
гидроизоляция цена https://gidroizolyaciya-cena-1.ru .
Thanks for the article https://mskwa.foroesp.com/viewtopic.php?id=1735#p8613 .
ставки на хоккей сегодня прогнозы точные http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej14.ru .
дрова колотые цена .
Unquestionably consider that that you stated. Your favourite reason seemed to be at the web the simplest factor
to be mindful of. I say to you, I definitely get irked whilst
other folks consider issues that they plainly don’t understand about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the highest and also defined out
the entire thing with no need side-effects , other folks can take a signal.
Will likely be again to get more. Thanks
скачать казино мостбет https://mostbet4118.ru
Thanks for the article https://spacehey.com/profile?id=4163872 .
Thanks for the article http://forum-mama.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=33&t=4910 .
mostbet uz slotlar mostbet uz slotlar
kupit-drova-v-sergievom-posade-365.ru .
Блог Соловова про smm https://niksolovov.ru
Безопасность сотрудников и клиентов – приоритет компании. Именно поэтому мы ценим наличие сертификата OHSAS 18001.
Франшиза точек с органическими продуктами для детей.
Stop by my web site :: https://www.royalholloway.ac.uk/
ушп плита фундамент .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-cvet-shnura-vybrat-dlya-spinninga-Sovety-rybolovam-01-13 .
купить аттестат за 11 класса купить аттестат за 11 класса .
zaezd-pod-klyuch-365.ru .
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в микуне купить аттестаты за 11 классов в микуне .
mostbet uz skachat https://www.mostbet4111.ru
https://www.fonse.cn/question/computer-games-25w/ lockups during games may signal overheating or driver conflicts.
mostbet mobile uz registratsiya https://www.mostbet4111.ru
https://etsyonlineshop.com/news/gerpes_opasnyy_i_kovarnyy_vrag.html
https://bikersrights.com/articles/upakovka_tovara_osobennosti.html
http://therockpit.net/wp-content/pages/shtory_dlya_doma.html
mostbet akkaunt yaratish mostbet akkaunt yaratish
Узнать больше https://kra38l.at/
купить диплом реестр купить диплом реестр .
Многие откладывают визит к врачу из-за тревоги. В moscow-stomatolog.ru понимают эту проблему и создают спокойную атмосферу, помогая пациентам чувствовать себя расслабленно во время приема .
kupit-drova-v-sergievom-posade-365.ru .
melbet слоты онлайн melbet слоты онлайн .
Thanks for the article https://www.facer.io/user/0ktVdwUClS .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Rybachok-UA–Vsyo-dlya-vashej-idealnoj-rybalki-01-13 .
утепленная плита фундамента .
каталог подшипников по размерам Подшипники оптом от производителей: экономия и надежность
заезд на участок под ключ лен область цена .
Thanks for some other wonderful article. Where else may anyone get that kind of info in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I’m on the search for such info.
Seattle Towncar
веб-сайте https://kra-37at.at
mostbetga kirish http://mostbet4108.ru
мостбет спорт ставки уз мостбет спорт ставки уз
купить свидетельство о расторжении брака http://www.educ-ua5.ru/ .
monolitnyy-fundament-ushp-499.ru .
proezd-k-uchastku-365.ru .
gessi официальный сайт gessi официальный сайт .
can be a great benefit.There are many advantages when you tab cialis 20mg are available online. tadalafil 5mg side effects
посетить веб-сайт https://kra-37at.at
mostbet ru https://mostbet4107.ru/
проверить сайт https://kra38at.at
Thanks for the article https://www.metroflog.co/post/93123_onlajn-magazin-rybachok-eto-nadezhnyj-vybor-dlya-vseh-kto-lyubit-provodit-vremya.html .
Thanks for the article https://exchange.prx.org/series/52513-natural-beauty .
mostbet личный кабинет https://www.mostbet4117.ru
Thanks for the article https://www.mmnt.org/spt?open=1714767618_72248 .
Моя кішка іноді так дивно поводиться, а виявляється, у неї є свої причини дратуватися. Знайшов пояснення на цьому сайті, все чітко і доступно розписано. Котолюби, вам сюди!
ванна гидромассаж vanna-s-gidromassazhem.ru .
mostbet uz ro‘yxatdan qanday o‘tish mostbet4109.ru
Thanks for any other informative site. Where else may just I get that kind of info written in such an ideal method?
I have a challenge that I’m simply now running on, and I have been on the look out for
such info.
Привет всем!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это удобное и безопасное решение для современного общения. У нас вы можете купить постоянный виртуальный номер для смс за считанные минуты. Он подойдет для регистрации на сайтах и мессенджерах, а также для работы. Постоянный виртуальный номер обеспечивает надежную связь без привязки к SIM-карте. Выбирайте наши услуги для удобства и стабильности.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://www.inastana.kz/list/416585
купить виртуальный номер телефона навсегда, виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер
купить номер телефона навсегда, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!!!
купить аттестат за 11 классов в чите http://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
https://sorrel-pear-pxrc9c.mystrikingly.com
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
консультация психиатра круглосуточно
https://greatdelight.net/menus/braised-chicken-breast-with-white-wine-and-shallots/
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva002.ru
психиатрическая клиника
сколько стоит аппарат узи новый сколько стоит аппарат узи новый .
готовые сборки пк : Совремунный способ Заказать новенький геймерский пк: Заказы онлайн
трип скан Tripscan поможет вам путешествовать с умом, предлагая выгодные предложения и полезные советы. Планируйте свои поездки заранее, сравнивайте цены и выбирайте лучшие варианты, чтобы сэкономить время и деньги.
Thanks for the article https://masterovou.forumotion.com/t3149-topic#8365 .
Thanks for the article https://boltyshki.unoforum.pro/?1-2-0-00008002-000-0-0-1720294454 .
olgun milf porno
Откройте для себя мир азартных игр на 888старз бэт.
позволяющая пользователям наслаждаться азартными играми в удобном формате. Платформа включает в себя как слоты, так и настольные игры, чтобы удовлетворить запросы всех игроков.
888starz предлагает удобный интерфейс, что облегчает процесс игры. Регистрация и навигация по платформе не вызывают затруднений у игроков.
Регистрация на платформе достаточно простая и быстрая. Чтобы создать аккаунт, достаточно заполнить небольшую анкету и подтвердить свои данные.
Платформа также предлагает разнообразные бонусы и акции для новых пользователей. Это позволяет увеличить игровую сумму и сделать процесс более увлекательным.
sport bets https://www.sportbets31.ru .
мостбет скачать приложение мостбет скачать приложение
купить проведенный диплом моих купить проведенный диплом моих .
more information on erectile dysfunction, visit our website at what does viagra do pills side-by-side on this site cheap viagra 100mg
https://www.chartparts.com/home/chart-university
новости спорта сегодня novosti-sporta-3.ru .
фундамент ушп цена .
Thanks for the article https://zomi.net/post/147997_internet-magazin-rybachok-eto-proverennyj-vybor-dlya-vseh-kto-uvlekaetsya-rybalk.html .
интернет-магазин сантехники москва https://www.evropejskaya-santehnika2.ru .
рекламное агентство seo http://www.rosy-rabbit-qsgmm1.mystrikingly.com .
устройство переезда через канаву на участок .
Полезный блог Никиты Соловова https://niksolovov.ru
Buying levitra professional through the internet with a prescription. levitra nedir
https://service116.ru/
скачать мостбет с официального сайта https://mostbet4147.ru/
gessi товары gessi товары .
букмекерская. контора. мостбет. http://www.mostbet4147.ru
купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс .
kupit-drova-v-sergievom-posade-365.ru .
mostbet.com казино скачать mostbet.com казино скачать
Получите профессиональную помощь на юрист консультация.
Консультация специалиста в области права может стать решающим моментом. Часто консультация юриста помогает предотвратить дальнейшие проблемы и споры.
Первый этап – это определение типа юридической проблемы. В зависимости от сложности дела может потребоваться помощь адвоката или юриста, специализирующегося на конкретной области.
Важно найти квалифицированного специалиста, который может помочь в вашей ситуации. Обратите внимание на опыт и рекомендации.
После выбора юриста необходимо подготовка к консультации. Это поможет юристу быстро понять ситуацию и дать квалифицированные советы.
Новости https://www.mythmoor.com/novosti-mira-78p/ svpressa предлагают смелые мнения.
купил аттестат за 11 http://www.arus-diplom21.ru/ .
Заказать диплом любого университета!
Мы предлагаембыстро и выгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Данный документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при использовании профессиональных приборов. Решите свои задачи максимально быстро с нашим сервисом- heyrodisscusion.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=4338
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kak-vybrat-katushku-na-shchuku-Polnyj-gid-dlya-rybolova-01-13-2 .
купить диплом института с реестром купить диплом института с реестром .
мостбет отзывы узбекистан https://www.mostbet4108.ru
Gentlyx is a platform where you can explore real adult content from independent creators.
ванна с гидромассажем ванна с гидромассажем .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестаты за 11 классов во владивостоке купить аттестаты за 11 классов во владивостоке .
Добрый день!
Купить виртуальный номер — это просто и быстро. Мы предлагаем купить виртуальный номер по доступной цене. Сервис позволяет купить виртуальный номер без лишних данных. Мгновенное подключение — ещё одна причина купить виртуальный номер. Убедитесь сами, как легко купить виртуальный номер у нас.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://news.1777.ru/111145-vybor-servisa-predostavlyayuschego-uslugi-virtualnogo-nomera
купить номер телефона навсегда, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер
купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Удачи и комфорта в общении!!!
купить диплом образца ссср купить диплом образца ссср .
Zhivchik — це команда, яка знає, як отримувати перемогу навіть у найскладніших ситуаціях. Їхні матчі — це справжній екшн!
Thanks for the article https://bc39.unoforum.pro/?1-0-0-00004667-000-0-0-1721660606 .
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1вин
https://ssa.ru/forum/ja-novichok-v-mire-stavok.html
Thanks for the article https://biiut.com/post/730902_sajt-rybachok-eto-proverennyj-vybor-dlya-vseh-kto-zanimaetsya-rybalkoj-i-cenit-n.html .
мостбет зеркало сегодня http://www.mostbet4106.ru
большие уличные горшки большие уличные горшки .
Разбор по SMM и накрутке https://niksolovov.ru/ реально помогает
купить аттестат 11 класс владивосток https://arus-diplom22.ru/ .
В сёлах Украины, где небо чище, телескоп раскрывает невероятные виды. Это настоящее удовольствие.
Players can reach out for help via multiple channels, ensuring timely assistance.
888starz скачать на андроид https://888starz-eng.com/ru/skachat-na-android/
На https://metallicheskij-shtaketnik.ru представлены инновационные системы освещения, интегрированные в конструкции заборов. Автоматическое включение, энергосберегающие технологии, дистанционное управление. Полная гармония функциональности и дизайна.
Важко уявити сучасного військового без такого приладу, як тепловізор воєнний. Це справжня перевага на полі бою.
Если хочется подарить что-то необычное, лучший выбор — телескоп. Он принесёт радость и детям, и взрослым.
Під час розвідки тепловізор воєнний дає найточніші результати. Завдяки цьому бійці діють упевненіше.
Луна, планеты и даже Сатурн с кольцами можно рассмотреть через хороший телескоп. Это незабываемое впечатление.
Материал на тему инвестиции https://niksolovov.ru/ полезен
Добре, коли у бійця є тепловізор воєнний, адже це реальна перевага. Прилад робить ніч максимально безпечною для виконання операцій.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find
It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you
helped me.
Here is my webpage … zapakeala01
В сёлах Украины, где небо чище, телескоп раскрывает невероятные виды. Это настоящее удовольствие.
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по невысоким тарифам— dfrmat.ru
Thɑnks in support of sharing ѕuch a nice opinion, paragraph іѕ nice, thats wһy i have
reɑd it fully
Alsoo visit mү web site: viktorzi
kupit-drova-v-sergievom-posade-365.ru .
Якщо порівнювати різні моделі, то тепловізор воєнний завжди має бути з високою роздільною здатністю. Це значно підвищує ефективність.
Thanks for the article http://51.15.223.140/forum/group.php?do=discuss&gmid=457 .
Иногда люди думают, что фото из космоса недоступны. Но через телескоп можно увидеть часть этой красоты своими глазами.
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
Заказать диплом на заказ в столице вы сможете используя официальный сайт компании. doctors.teamforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=2422
интернет-магазин сантехники москва evropejskaya-santehnika2.ru .
купить подлинный аттестат за 11 класс купить подлинный аттестат за 11 класс .
купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса .
https://ondofoundation.help/ airdrop alive! Staking soon.
Achieve health benefits each time you buy cialis how does it work to help eliminate symptoms by securing excellent online cialis max dose
куплю диплом куплю диплом .
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1вин
http://fabnews.ru/forum/showthread.php?t=32888
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-spinning-vybrat-dlya-lovli-shchuki-TOP-rekomendacij-01-13 .
https://разработка.site/
В телеграм-чате о ставках игроки обсуждали разные площадки и кто-то кидал ссылку на топ казино онлайн. Я решил проверить. Сайт оказался удобным, регистрация заняла меньше минуты, сразу получил бонус за депозит. Слоты работают без лагов, а выплаты пришли быстро, что особенно порадовало. Для меня важно, чтобы всё было честно и прозрачно, и здесь это ощущается. Теперь тоже советую друзьям эту площадку, если ищут надёжное место для игры.
Америка Переговоры между Путиным и Зеленским — это не просто диалог двух лидеров. Это столкновение мировоззрений, стратегий и исторических нарративов. Политика, как искусство лавирования между интересами, требует от обеих сторон готовности к компромиссам. Финансовая нестабильность, вызванная СВО, затронула все регионы мира. Стратегии выживания и адаптации к новым экономическим реалиям стали приоритетом для многих стран. Европа ищет альтернативные источники энергии, Азия перестраивает логистические цепочки, а Америка сталкивается с растущей инфляцией. Безопасность и оборона диктуют необходимость увеличения военных расходов и укрепления альянсов. Новости и аналитика позволяют отслеживать развитие событий и формировать объективное представление о происходящем.
Для точності в бою тепловізор воєнний просто необхідний. Він дозволяє уникати випадкових втрат.
Я заметил, что интерес к астрономии в Украине растёт, и всё больше людей покупают телескоп для дома.
mostbet uz сом https://mostbet4115.ru
Hello everyone!
I came across a 131 fantastic website that I think you should browse.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://oerj.org/betting-guides/the-psychology-of-betting/
Для нашої армії тепловізор воєнний зараз важливіший за багато інших гаджетів. Його користь беззаперечна.
Впервые увидев кольца Сатурна через телескоп, я был потрясён. Этот момент запоминается на всю жизнь.
mostbet uz скачать mostbet4116.ru
Thanks for the article http://www.polosedan-club.com/threads/Рыбалка.35013/ .
Добре, коли у бійця є тепловізор воєнний, адже це реальна перевага. Прилад робить ніч максимально безпечною для виконання операцій.
Thanks for the article http://forum.analysisclub.ru/index.php/topic,184675.new.html#new .
Луна, планеты и даже Сатурн с кольцами можно рассмотреть через хороший телескоп. Это незабываемое впечатление.
Навіть у складних погодних умовах тепловізор воєнний працює безвідмовно. Це робить його одним із найкращих інструментів.
Лучшая локация для наблюдений — это горы Украины. Там телескоп работает максимально эффективно.
как купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске как купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске .
можно ли купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов можно ли купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
Откройте для себя мир комфорта с рулонными шторами с электроприводом, которые идеально подходят для создания уюта в вашем доме.
Электрические рулонные шторы — это удобное и стильное решение для современных интерьеров. Использование рулонных штор с электроприводом делает интерьер более функциональным и эстетичным.
Электрические шторы имеют множество преимуществ. Управление такими шторами с помощью пульта делает их использование комфортным и практичным. В-третьих, рулонные шторы могут быть связаны с другими умными устройствами в вашем доме.
Установить рулонные шторы с электроприводом можно в любом помещении . Их активно используют как в жилых, так и в коммерческих помещениях . Следует помнить, что для работы электропривода необходимо подвести электрический кабель.
Фактор выбора материала и дизайна штор также играет важную роль. Разнообразие тканей и расцветок дает возможность подобрать идеальные шторы для любого стиля . Наконец, стоит заметить, что есть возможность заказать шторы по индивидуальным размерам.
Customer service is another essential feature of 888starz, offering support to users around the clock.
888 старс узбекистан https://888starz-eng.com/ru/
Подготовка к ОГЭ 2026 год
Лучшие советы по Никита Соловов https://niksolovov.ru/ must have
шведская плита фундамент цена .
Hey la communauté, je voulais vous donner mon retour sur Plinko après quelques parties. Plinko est un jeu très accessible qui offre beaucoup de plaisir. Le principe est assez classique : on lâche une bille en haut d’un plateau qui est rempli de clous ou de picots. Selon l’endroit où la bille finit sa course, on remporte un certain gain ou une récompense. Le plus fun, c’est l’imprévisibilité à chaque chute de la bille. En plus, https://template96.webekspor.com/hidden-business-prospects-of-coconut-products-vco-coconut-sugar/ ne nécessite aucune compétence particulière, ce qui le rend accessible à tous. De nombreuses plateformes en ligne proposent différentes versions de Plinko. Les parties sont courtes, donc on peut enchaîner rapidement. Je recommande ce jeu à tous ceux qui aiment les sensations sans prise de tête. N’hésitez pas à partager vos impressions ou vos stratégies pour maximiser vos gains
Ви знали, що гнучкість у датах може суттєво зменшити витрати на квитки? Ще більше лайфхаків тут: деталі!
купить диплом в чернигове недорого https://educ-ua3.ru .
купить диплом в одессе недорого купить диплом в одессе недорого .
Thanks for the article https://roomstyler.com/users/tatiana000 .
Thanks for the article http://che.best-city.ru/forum/thread87747/ .
Добрый день!
Ищете, где купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда? Мы предоставляем постоянные виртуальные номера для любых целей. Виртуальный номер навсегда – это практичное решение для бизнеса и личной жизни. Забудьте о границах и наслаждайтесь свободой общения. Выбирайте проверенного провайдера и качественные услуги.
Полная информация по ссылке – http://nounsmag.com/contact/?contact-form-id=8&contact-form-sent=34456&contact-form-hash=8ae3f1053a1f25b64ddb50aef636572e70864e0b&_wpnonce=af0e242476
постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
купить номер телефона навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!!!
Thanks for the article http://sp-for-you.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=103&t=10953 .
Thanks for the article https://kryvbas.dp.ua/useful/kak-vybrat-udochku-vydy-udochek .
купить диплом занесенный в реестр купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
Приобретите рулонные шторы умный дом и насладитесь комфортом и современными технологиями в своем доме.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом становятся всё более популярными среди современных потребителей. Пользователи могут управлять рулонными шторами с электроприводом как через приложение на телефоне, так и с помощью пульта.
Одним из основных преимуществ умных рулонных штор является их удобство. Вы можете настраивать их положение в любое время, не вставая с дивана.
Электроприводные шторы могут быть настроены на автоматические режимы работы. Вы можете задать время, когда шторы должны открываться и закрываться, что делает их особенно удобными.
Умные рулонные шторы легко интегрируются с концепцией “умного дома”, предоставляя новые возможности управления. Таким образом, шторы могут работать в связке с другими устройствами, что делает ваш дом более умным и адаптивным.
proezd-k-uchastku-365.ru .
mostbet kripto orqali depozit https://mostbet4113.ru/
low prices for your must-have drugs and shippingIf you plan to viagra name pharmacy has the proper license to sell drugs? does cialis lower blood pressure
шанс строительство домов на ушп .
sport bets https://www.sportbets31.ru .
Thanks for the article http://virchi.pp.net.ua/forum/30-10939-1 .
kupit-drova-v-sergievom-posade-365.ru .
Для точності в бою тепловізор воєнний просто необхідний. Він дозволяє уникати випадкових втрат.
Даже в условиях города можно использовать телескоп, хотя лучше выезжать подальше от огней.
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью автоматических рулонных штор, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Дистанционно управляемые рулонные шторы приобретают популярность в современных интерьерах. Данные изделия соединяют в себе удобство и эстетичность, что делает их идеальным выбором для различных помещений.
Управлять рулонными шторами можно, используя пульт дистанционного управления или специализированное мобильное приложение. Это позволяет легко регулировать освещение и создавать уютную атмосферу в вашем доме.
Также рулонные шторы доступны в различных стилях и цветовых решениях. Это дает возможность найти идеальный стиль, который будет соответствовать вашему домашнему дизайну.
Важно отметить, что рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением также удобны в эксплуатации. Они легко чистятся и не требуют особого ухода, что делает их идеальными для занятых людей.
888starz features various betting options, including sports betting, live casinos, and virtual games.
888starz bet download https://888starz-eng.com/id/unduh-apk-ios/
спортивные новости https://novosti-sporta-3.ru .
купить аттестат 11 класс тольятти купить аттестат 11 класс тольятти .
mostbet ios yuklab olish https://mostbet4114.ru/
Від знайомих чув, що тепловізор воєнний дуже допомагає на передовій. Він дозволяє бачити ворога навіть у складних погодних умовах.
Я долго читал отзывы, пока не понял, что лучший вариант для меня — это рефракторный телескоп. Он прост и удобен.
proezd-k-uchastku-365.ru .
kupit-drova-v-shchyolkovo-365.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в астрахани http://www.arus-diplom9.ru/ – купить аттестат за 11 класс в астрахани .
mostbet app qeydiyyat https://mostbet4134.ru
mostbet qeydiyyat promo kod https://mostbet4135.ru
Для наших військових тепловізор воєнний – не просто прилад, а необхідність. Саме завдяки йому можна уникнути небезпечних ситуацій.
агентства по продвижению сайтов http://sites.google.com/view/reklamnoe-agenstvo-seo .
Красоту звездного неба сложно описать словами, но телескоп помогает увидеть её в реальности. Это стоит попробовать каждому.
Thanks for the article https://forum.singaporeexpats.com/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=679596 .
Немає сумнівів, що тепловізор воєнний змінює перебіг подій на фронті. Це технологія, що рятує життя.
Для наблюдения за Солнцем нужен специальный фильтр, чтобы не повредить глаза и телескоп. Это очень важно учитывать.
диплом купить с занесением в реестр челябинск arus-diplom35.ru .
selling methamphetamine
Наши специалисты готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы.
гидромассажные ванны цена гидромассажные ванны цена .
1 кубометр дров цена .
Відомо, що тепловізор воєнний здатен виявити ціль навіть крізь дим. Це надзвичайно корисно у боях.
mostbet az qeydiyyat mostbet az qeydiyyat
mostbet az canlı dəstək mostbet az canlı dəstək
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс в санкт петербурге где купить аттестаты за 11 класс в санкт петербурге .
Коли йдеться про сучасне обладнання, тепловізор займає перше місце. Він надійний і ефективний.
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом университета:
купить аттестат за 11 класс lr 63
mostbet qeydiyyat bonus https://www.mostbet4135.ru
обложка аттестата за 11 класс купить http://arus-diplom25.ru/ .
Thanks for the article http://www.aviv7.com/forum/viewtopic.php?p=322053&sid=3b95bec85fa1b1477225f05ee14c4bdb#322053 .
Прилад такого типу, як окуляри нічного бачення, рятує від багатьох ризиків. Особливо під час патрулювань.
Для пошуку людей у темряві тепловізор виявляється незамінним. Це реально допомагає.
Материал на тему SEO https://niksolovov.ru/ полезен
У складних умовах освітлення окуляри нічного бачення працюють бездоганно. Це дуже важливо.
Для військових операцій тепловізор вважають одним із найважливіших приладів. Його роль важко переоцінити.
Hello !!
I came across a 131 useful site that I think you should explore.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://astd-tcc.org/casino-development/how-casinos-are-redefining-luxury-style/
mostbet kazino o‘yinlari https://mostbet4116.ru/
купить диплом занесением в реестр купить диплом занесением в реестр .
Доброго!
Купить виртуальный номер телефона — это легко и безопасно. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор, чтобы вы могли купить виртуальный номер телефона без труда. Надёжный сервис гарантирует вам возможность купить виртуальный номер телефона. Простой процесс — просто купить виртуальный номер телефона у нас.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://techschumz.com/contact/?contact-form-id=630&contact-form-sent=25551&contact-form-hash=dc4fbccddfd3313a4e736fc8a498bd0bdbdd7b25&_wpnonce=23ba680ad5
виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, купить виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!!!
купить аттестат 11 классов во владивостоке купить аттестат 11 классов во владивостоке .
Для патрулювання територій окуляри нічного бачення підходять ідеально. Видимість залишається чіткою.
Для військових зараз важливим інструментом став тепловізор. Він дозволяє бачити те, що неможливо оком.
Фізика – цікава річ. Виявляється, сила тяжіння формує весь Всесвіт.
mostbet kripto orqali depozit http://mostbet4112.ru
купить диплом пту в реестре купить диплом пту в реестре .
У відгуках часто пишуть, що окуляри нічного бачення дають значну перевагу вночі. Це справді так.
Під час тренувань тепловізор показав чудовий результат. Видимість була максимально чіткою.
Преобразите ваше пространство с помощью рулонных штор с дистанционным управлением, которые идеально сочетают стиль и современность.
Рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением становятся все более популярными в современных интерьерах. Эти шторы предлагают удобство и стиль, что делает их отличным решением для любого помещения.
Управлять рулонными шторами можно, используя пульт дистанционного управления или специализированное мобильное приложение. Таким образом, вы можете быстро изменять уровень освещенности и создавать комфортную обстановку в своем жилище.
Кроме того, рулонные шторы могут быть выполнены в различных дизайнах и расцветках. Это дает возможность найти идеальный стиль, который будет соответствовать вашему домашнему дизайну.
Следует подчеркнуть, что рулонные шторы с дистанционным управлением очень практичны в повседневной жизни. Эти шторы просто чистятся и не требуют сложного ухода, что делает их подходящими для людей с плотным графиком.
На практиці окуляри нічного бачення показали високу надійність. Це справжня допомога.
Для полювання також використовують тепловізор. Кажуть, результат зовсім інший у порівнянні зі звичайними приладами.
строительство домов под ключ http://stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-1.ru/ .
Коли потрібно пересуватися без світла, найкраще виручають окуляри нічного бачення. Вони дуже ефективні.
Колега радив звернути увагу на тепловізор, коли шукаєш сучасні рішення для безпеки. Думаю, це вартує уваги.
построить дом под ключ построить дом под ключ .
Thanks for the article https://zehov.rusff.me/viewtopic.php?id=820#p2114 .
купить дом под ключ купить дом под ключ .
ск домстрой http://www.stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-2.ru/ .
Creating a marketing blog allows you to disseminate valuable information about various trends in the industry. By providing useful content, you can engage your audience.
brand story basics http://marketingpitbull.com/beyond-the-basics-how-to-craft-compelling-brand-stories-that-captivate-audiences
купить диплом с проводкой меня купить диплом с проводкой меня .
купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск купить аттестат за 11 класс хабаровск .
proezd-k-uchastku-365.ru .
истории побед обычных людей Таинственные истории, случившиеся с обычными людьми Иногда жизнь подбрасывает нам загадки, объяснить которые рационально невозможно. Истории о встречах с непознанным, о предчувствиях и знаках судьбы заставляют нас задуматься о границах реальности и о том, что существует за пределами нашего понимания. Они наполнены тревогой и любопытством, заставляя нас верить в чудеса.
Internet drugstores list their prices for use of viagra the fast and easy way. Top pharmacies provide excellent service how long does cialis last
дрова недорого .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Приобретение документа, который подтверждает обучение в ВУЗе, – это выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа: test.seancefor2.com/index.php?topic=165100.new#new
Рулонные шторы с аккумулятором предоставляют удобство и стиль для любого интерьера, позволяя легко управлять светом и обеспечивая полную свободу от проводов.
Их разнообразие текстур и цветов позволяет вам выразить свою индивидуальность в интерьере.
CRASH
Thanks for the article https://www.gamerlaunch.com/community/users/blog/6678283/2411693/grizzlysms/?gid=535 .
Экскурсия на эльбрус Путешествие на Кавказ – это возможность увидеть горы, озера, водопады, древние города и познакомиться с местной культурой. Путешествие по Кавказу маршрут
чтение Книги, открывающие новые горизонты
banzaibet ro’yxatdan o’tish bonusi mostbet4112.ru
monolitnyy-fundament-ushp-499.ru .
mostbet tennis mərcləri https://mostbet4132.ru/
Thanks for the article https://start.me/w/zKMQRM .
mostbet esports mərclər http://mostbet4132.ru/
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве купить аттестаты за 11 классов в москве .
Thanks for the article https://odessaforum.biz.ua/viewtopic.php?f=15&t=4995 .
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске .
популярные песни уннв популярные песни уннв .
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
частная психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
стационар психиатрической больницы
ванна с массажем ванна с массажем .
mostbet az bank transfer https://mostbet4133.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника стационар
psikhiatr-moskva003.ru
психиатрическая помощь больным
Thanks for the article http://www.pickmemo.com/read-blog/37959 .
mostbet uz скачать ios mostbet4114.ru
платный психиатр
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
госпитализация в психиатрический стационар
У нічних тренуваннях окуляри нічного бачення показали чудовий результат. Видимість була на високому рівні.
Материал на тему инвестиции https://niksolovov.ru/ полезен
Не уявляю, як би сьогодні обходилися без такого пристрою, як тепловізор. Це справді важлива техніка.
ушп плита цена за 1м2 .
vezd-na-dachnyy-uchastok-365.ru .
психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva001.ru
платная консультация психиатра
Усі відзначають, що окуляри нічного бачення реально допомагають заощадити час уночі. Це перевірений факт.
Під час тренувань тепловізор показав чудовий результат. Видимість була максимально чіткою.
топ песни уннв топ песни уннв .
мостбет служба поддержки https://www.mostbet4113.ru
vezd-na-dachnyy-uchastok-365.ru .
fundament-ushp-moskovskaya-oblast-499.ru .
Если вам нужна онлайн консультация юриста, то специалисты на нашем сайте готовы помочь!
ресурс yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya101.ru предлагает консультации по различным правовым вопросам для физических лиц. Юристы, работающие с нами готовы предложить решения в любой ситуации.
Наша команда считает, что каждый пользователь уникален. Поэтому мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому делу. Команда юридического отдела тщательно изучает все детали ситуации, чтобы найти оптимальное решение.
Кроме того, мы предлагаем бесплатные консультации для новых клиентов. Таким образом, мы получаем возможность осознать проблемы клиента и выработать стратегию.
Вы получаете, обратившись к нам за помощью доступ к компетентным юристам, которые обладают глубокими знаниями законодательства. Мы гарантируем вы получите надежную юридическую помощь на всех этапах.
Попелюшка – це саме та історія, яка вчить дітей довіряти справжнім друзям. Почитати можна тут: перейти до казки.
Thanks for the article https://humans.net/post/74550 .
Good pharmacies offer discounts when you cialis from Canada to gain your trust. 50mg cialis
проекты домов под ключ проекты домов под ключ .
Completely agree with this, appreciate the insight.
Thought I’d drop this here, I found a link recently: might be useful
Would love to know if anyone tried it.
построить дом под ключ иркутск http://www.stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-6.ru/ .
реабилитация алкоголиков цены
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
курс лечения от алкоголизма
Thanks for the article https://www.anobii.com/en/0199b77c6c2361ab83/profile/activity .
Hello everyone! I decided to share about aviator game and mines game. This game grabs gamers quickly with its combo of chance and plan. Many players talk about https://naturaverdebiobaby.it/2015/01/04/top-deejay-headphones/, and some wish for aviator hack, but the real rush comes from joining fairly. The aviator app and aviator game download make play very fast to join anywhere. aviator online is awesome because plays are short and high-stakes, giving a lot of excitement. If you didn’t try it yet, seriously check it out and feel the thrill.
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana001.ru
реабилитация наркоманов недорого в Астане
иркутск строительство домов под ключ stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-2.ru .
mostbet android yuklab olish https://mostbet4115.ru
Thanks for the article http://web-lance.net/forums.php?m=posts&q=29456&n=last#bottom .
строительство дома под ключ иркутск http://stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-1.ru/ .
Для спецоперацій окуляри нічного бачення стали стандартом. Їх використовують повсюдно.
У відгуках люди пишуть, що тепловізор працює безвідмовно навіть при мінусовій температурі. Це великий плюс.
Багато хто вже оцінив окуляри нічного бачення на практиці. Результат завжди позитивний.
На відміну від звичайної оптики, тепловізор працює в будь-яких умовах освітлення. Це дуже зручно.
Thanks for the article https://disqus.com/channel/discusschitchatchannel/discussion/channel-discusschitchatchannel/__206/ .
kupit-drova-v-shchyolkovo-365.ru .
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
как избавить человека от алкогольной зависимости
большое уличное кашпо для цветов большое уличное кашпо для цветов .
пин ап блэкджек http://www.pinup5005.ru
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в .
У мирному житті окуляри нічного бачення теж мають користь. Наприклад, для охоронних служб.
Друзі радили звернути увагу на тепловізор, якщо потрібен якісний контроль території. Думаю, це слушна порада.
vezd-na-dachnyy-uchastok-365.ru .
реабилитация наркоманов в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana002.ru
анонимное лечение алкоголиков
fundament-ushp-moskovskaya-oblast-499.ru .
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат в шелехов 11 классов недорого
Прилад такого типу, як окуляри нічного бачення, рятує від багатьох ризиків. Особливо під час патрулювань.
дрова цена за 1 куб .
Lux1288 Merupakan Sebuah Link Situs Slot Gacor Online Yang Sangat
Banyak Peminatnya Dikarenakan Permainan Yang Tersedia Sangat Lengkap.
Накрутка просмотров в ТГ https://niksolovov.ru/ проверенные способы
Thanks for the article http://dp-spb.com/forum/thread-2634/ .
уннв слушать песни уннв слушать песни .
wooden fence suppliers near me Wood Two Rail Fence More effective than no fence at all.
SMM блог Никиты Соловова https://niksolovov.ru
Thanks for the article https://reminform.kyiv.ua/Novosti/kakuu-kolebalku-vibrat-na-shuku-cvet-i-razmer .
mostbet apk yuklab olish uz http://www.mostbet4164.ru
пин ап бесплатные игры казино pinup5002.ru
программа реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
программа реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
свежие новости спорта https://novosti-sporta-11.ru/ .
чит накрутка подписчиков тг чит накрутка подписчиков тг
Приобрести диплом любого университета можем помочь. Диплом с проводкой – diplomybox.com/diplom-s-provodkoj
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and
it’s time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I wish to
suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article.
I want to read more things about it!
купить аттестат за 11 класс 1998 года купить аттестат за 11 класс 1998 года .
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в омске купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в омске .
отправить на лечение наркомана
reabilitaciya-astana003.ru
избавление от алкогольной зависимости
спортивные события https://novosti-sporta-12.ru/ .
Thanks for the article http://www.lada-xray.net/member.php?u=22740 .
чпу станок маленький — это современное оборудование для точной обработки металла и дерева.
Машины с числовым программным управлением значительно упрощают процесс обработки деталей.
Использование программного управления снижает затраты и повышает качество выпускаемой продукции. Сегодня станки с ЧПУ используются в машиностроении, авиации и других отраслях промышленности.
#### **2. Принцип работы токарных станков с ЧПУ**
Работа оборудования строится на заранее созданной программе, определяющей последовательность обработки.
Система обратной связи позволяет корректировать работу станка в режиме реального времени. Таким образом, достигается высокая повторяемость деталей и минимальные отклонения от чертежа.
#### **3. Преимущества токарных станков с ЧПУ**
Главное достоинство таких станков — высокая скорость и точность обработки.
Автоматизация процесса позволяет сократить производственные издержки. Дополнительным плюсом является возможность быстрого перехода на выпуск новых изделий.
#### **4. Перспективы развития токарных станков с ЧПУ**
В будущем ожидается увеличение степени автоматизации и интеграция искусственного интеллекта.
Внедрение интернета вещей (IoT) позволит удаленно контролировать производственные процессы. Благодаря этому производство станет более эффективным и менее затратным.
—
### **Спин-шаблон:**
#### **1. Введение в токарные станки с ЧПУ**
Обрабатывающие центры с ЧПУ стали неотъемлемой частью современного производства. Эти устройства позволяют выполнять высокоточную обработку металлических и неметаллических заготовок.
Использование программного управления снижает затраты и повышает качество выпускаемой продукции. Такие технологии нашли применение в производстве инструментов, деталей и сложных конструкций.
*(Шаблон продолжается аналогично для всех последующих разделов.)*
Thanks for the article http://www.askmap.net/location/7496203/ukraine/%D1%80%D1%8B%D0%B1%D0%B0%D1%87%D0%BE%D0%BA .
fantastic points altogether, you just won a new reader.
What may you recommend about your submit that you made
a few days ago? Any positive?
ставки прогнозы https://www.stavki-prognozy-one.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в telegram канале бесплатно накрутка подписчиков в telegram канале бесплатно
Здравствуйте!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Многоуровневый линкбилдинг помогает создать устойчивую ссылочную сеть. Линкбилдинг блог курс показывает эффективные стратегии. Линкбилдинг мы предлагаем для клиентов с различными целями. Контент маркетинг линкбилдинг улучшает естественность ссылочного профиля. Естественный линкбилдинг повышает доверие поисковых систем.
seo оптимизация и продвижение сайт москва, сео продвижение обучение бесплатно, линкбилдинг это
Как поднять показатели Ahrefs, услуги seo оптимизации сайта, сео сайта на битрикс
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
СтавкиПрогнозы http://stavki-prognozy-1.ru/ .
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Taking the time and actual effort to make a superb article… but what can I say… I put things off a lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
https://http-kra38.cc/
Грузоподъемность, кг 1000 Высота подъема, мм 1000 Размер платформы (ДхШ), мм 1016×510.
Аксессуары для подъемного стола.
Вы можете оценить товар.
Подъемный стол с рольгангами.
Грузоподъемность: 500 кг.
Еще -5%
For posting? Try https://proxyka.com — fast proxies for stable work.
Thanks for the article https://qiita.com/gromovmichael4 .
кайт лагерь
как купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске как купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске .
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов помогает охватывать больше ресурсов. Как увеличить показатели домена зависит от качества ссылок. Xrumer для продвижения сайта экономит время специалистов. SEO-прогон для новичков облегчает освоение инструментов. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer ускоряют процесс продвижения.
сео продвижения цены, фото для сайта продвижение, курс линкбилдинг
SEO-прогон для новичков, бесплатные курсы сео с сертификатом, seo не будет
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
диплом бакалавра купить украина диплом бакалавра купить украина .
Hey everyone
I just came across a verified page of a champion while browsing social media. It’s really helpful for fans. I noticed it in Instagram stories:
https://jamal-musiala.net/jamal-musiala-injury-record/без-рубрики-en/
пин-ап http://pinup5004.ru
Подбираете в надёжном оборудовании для ремонта или строительства
в Слуцке? Сдача напрокат профессионального оборудования — это быстрый
и экономичный способ получить всё необходимое без лишних затрат.
Не нужно покупать инструменты
разово — просто возьмите их напрокат на нужный срок.
В нашем городе представлены услуги аренды
от проверенных фирм, предлагающие строительную технику.
Хотите узнать больше о том, где взять перфоратор, шлифмашину или бетономешалку?
Переходите по ссылке и читайте подробную статью: «Прокат инструмента в
Слуцке».
pin up ruletka pinup5003.ru
most bet most bet
Everything is very open with a clear explanation of the challenges.
It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Thank you for sharing!
Hello to all
Being a sports enthusiast, I recently came across the official profile of a world-class athlete. It’s perfect for fans who want reliable news:
https://alphonso-davies.com/
Nonetheless, the fast-paced growth of AI introduces ethical considerations and challenges that society is required to tackle. In this evolving landscape, balancing progress with ethical considerations is crucial.
wood alpha brand Interwood http://wmta-online.com/interwood-company-a-trusted-name-in-quality-wood-products
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-kukany-dlya-lovli-shchuki-Obzor-i-sovety-po-vyboru-01-13 .
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным ценам— kupit-diplom-technikuma.ru
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом Ачинск — kyc-diplom.com/geography/achinsk.html
pin up mobil ilova https://pinup5003.ru/
мостбет прогнозы http://www.mostbet4163.ru
мост бет https://www.mostbet4162.ru
Thanks for the article https://www.zazzle.co.uk/mbr/238052533960829244 .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Узнайте больше на stroyexpertsochi.ru/ и узнайте о защите стен от грибка и антикоррозийной обработке металлоконструкций.
пин ап бонус код уз http://www.pinup5005.ru
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share. Cheers!
https://http-kra38.cc/
Most online stores will guarantee you the cialis drug by shopping online. viagra natural
можно ли купить диплом в реестре http://www.vsegda-pomnim.com/user/iliaanisimov .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с галерею выполненных работ и получите рекомендации по термоизоляции, энергоэффективным окнам и дверям.
пин ап загрузка на андроид http://pinup5001.ru
https://www.patreon.com/posts/secure-method-do-137464059?utm_medium=clipboard_copy&utm_source=copyLink&utm_campaign=postshare_creator&utm_content=join_link
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
Работники имеют право на информацию о рисках
http://mitsfs-wiki.mit.edu/index.php?title=Ohrana_Truda_90E
плейлист уннв скачать плейлист уннв скачать .
kupit-drova-v-shchyolkovo-365.ru .
купить гранулятор стрейч пленка производство купить гранулятор стрейч пленка производство .
uralkomenergo.ru https://kompressornyj-zavod-1.ru/ .
Thanks for the article http://forum-mama.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=33&t=4910 .
Заказать диплом под заказ в Москве можно через сайт компании. sev-school24.maxbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1232
купить аттестат 11 класс москва купить аттестат 11 класс москва .
Nhà Cái Mbet
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом с занесением в реестры купить диплом с занесением в реестры .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru Зайдите на галерею выполненных работ и узнайте, как выбрать качественные материалы для строительства в Сочи.
pin up aviator yuklab olish pin up aviator yuklab olish
Thanks for the article https://cxema.at.ua/forum/9-5602-1 .
gambling regulations uk, new uk casinos 2021 and state
gambling revenue australia, or free chips no deposit bonus united states
My blog – Goplayslots.Net
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Просмотрите наш сайт и изучите практические рекомендации по строительству, отделке и благоустройству домов.
Thanks for the article https://community.wongcw.com/posts/1076114?btwaf=44818737 .
ушп плита под ключ .
купить диплом о техническом образовании купить диплом о техническом образовании .
Если нужен быстрый рост аудитории в Телеграм-канале, накрутка подписчиков – один из самых эффективных способов. Главное — пользоваться сервисами, которые проверены временем и дают реальный результат. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1622114-top-12-sposobov-dlya-nakrutki-podpischikov-v-telegram-v-2025-godu В материале собраны актуальные сайты и инструкции 2025 года, которые помогут накрутить подписчиков в ТГ без риска бана и массовых отписок, а так же живых подписчиков.
vezd-na-dachnyy-uchastok-365.ru .
анонимная наркологическая помощь в москве http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-11.ru/ .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Исследуйте портфолио объектов и узнайте о зеленых домах, экодомах и солнечных панелях.
mostbet bonus code http://mostbet4163.ru
купить дипломы купить дипломы .
мостбет на айфон скачать http://mostbet4164.ru/
Если нужен быстрый рост аудитории в Телеграм-канале, накрутка подписчиков – один из самых эффективных способов. Главное — пользоваться сервисами, которые проверены временем и дают реальный результат. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1563104-nakrutit-podpischikov-v-telegramm-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-v-2025-godu В материале собраны актуальные сайты и инструкции 2025 года, которые помогут накрутить подписчиков в ТГ без риска бана и массовых отписок, а так же живых подписчиков.
стоимость кубометра дров .
Menurut pengalaman saya, slot gacor itu biasanya terasa dari awal permainan. Kalau scatter cepat muncul dan ada free spin, biasanya permainan bakal gampang kasih jackpot. Tapi tetap harus pintar atur modal supaya nggak cepat habis.
pin up bonus aktivatsiya http://pinup5004.ru
pin up ilova yuklab olish pinup5002.ru
Hey there, You have done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally
recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited
from this site.
stroyexpertsochi.ru Загляните на наши материалы и получите советы по строительству частного дома с учётом особенностей местности.
fundament-ushp-moskovskaya-oblast-499.ru .
ссылка на сайт
https://kra-36at.at/
купить колотые дрова для бани .
Thanks for the article http://shumka.at.ua/forum/15-6335-1 .
другие
кракен зеркало
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Заказать диплом университета:
купить аттестат вечерней школы 10 11 классы
Thanks for the article https://smetdlysmet.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=40867 .
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Откройте наш каталог решений и получите рекомендации по благоустройству участка с уклоном и укреплению склона.
Plinko, c’est un jeu cool, facile à comprendre, mais c’est avant tout un jeu de hasard. Moi, je dis toujours : limite ton budget, et éviter les sites douteux. Tester le mode gratuit avant de jouer en vrai, c’est top pour apprendre. En gros, https://ckb.862mh.cc/space-uid-594996.html , c’est cool avec de la prudence.
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите наш сайт и узнайте, как правильно выбрать окна и двери для влажного климата.
новости легкой атлетики http://www.novosti-sporta-11.ru .
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию на сайте konsultaciya-yurista-msk01.ru, где профессиональные юристы готовы помочь вам в решении любых правовых вопросов.
Многим людям нужна профессиональная юридическая поддержка. В нашей организации доступен целый ряд юридических услуг, которые помогут вам в решении различных вопросов. Сотрудничество с нами позволит вам защитить ваши законные права.
Наши юристы имеют большой опыт работы в разных областях. Каждый юрист готов предложить оптимальные решения для ваших задач. Мы ценим ваше время и стремимся к быстрому решению ваших дел.
Мы придерживаемся индивидуального подхода к нашим клиентам. Мы готовы тщательно рассмотреть вашу проблему и предложить лучшее решение. Мы обеспечим вас всей необходимой информацией о ходе вашего дела.
Не откладывайте решение своих проблем, обратитесь к нам за консультацией. Мы заинтересованы в том, чтобы вы были уверены в нашей правовой поддержке. Наша цель — защитить ваши интересы и обеспечить качественный сервис.
Thanks for the article http://www.polosedan-club.com/threads/Рыбалка.35013/ .
перевод договора с киргизского на русский http://www.onlineperevodchik.ru/ .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Узнайте больше на наш сайт и изучите современные технологии укрепления склона и дренажных систем.
Stavki Prognozy http://www.stavki-prognozy-two.ru .
Магнітоплазмодинамічний двигун – це прорив у космосі? Звучить фантастично, але це реально. Читайте більше на технологічному порталі.
Сегодня продвижение в Телеграме невозможно представить без накрутки. Сервисы помогают раскрутить канал, повысить активность и привлечь новую аудиторию. В обзоре разобраны рабочие методы и реальные кейсы. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1475941-kupit-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-25-servisov-v-2025-godu Подробный рейтинг сервисов по накрутке подписчиков в ТГ поможет выбрать оптимальный вариант: от бесплатных способов до надежных платных площадок.
спортивные аналитики novosti-sporta-12.ru .
каталог
кракен зеркало
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Изучите портфолио объектов и ознакомьтесь с безопасными и комфортными решениями для семьи.
sports bet http://www.sportbets32.ru/ .
kupit-drova-v-noginske-365.ru .
перейти на сайт
кракен зеркало
At this moment I am going away to do my breakfast, once having my breakfast
coming over again to read other news.
наркологические услуги в москве https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-11.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в уфе https://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
kids have sex porno
I think this is among the most significant info for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on some general things,
The web site style is ideal, the articles is really nice :
D. Good job, cheers
mostbet az bonusları https://mostbet4140.ru/
I do accept as true with all of the ideas you have offered to your
post. They are very convincing and will certainly work.
Nonetheless, the posts are very short for novices. Could you please lengthen them a
little from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
stavkiprognozy https://www.stavki-prognozy-one.ru .
уннв песни слушать уннв песни слушать .
http://cs-headshot.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=652037#652037
mostbet online app http://mostbet4152.ru
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Markiza-dlya-rybolovnogo-stola-Udobstvo-i-zashchita-ot-nepogody-01-13 .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на наш сайт и узнайте, как выбрать оптимальные материалы для морского и влажного климата.
Stavki Prognozy https://www.stavki-prognozy-1.ru .
Thanks for the article https://voprosoff.net/12514/хочу-сдать-машину-в-трейд-ин-и-купить-новое-авто?show=12591#a12591 .
купить диплом о высшем образовании проведенный купить диплом о высшем образовании проведенный .
https://sites.google.com/view/1xbet-promo-codeindia/home
Explore our exclusive collection featuring beautiful, legal young adult models aged 18+. Fresh, natural, and full of energy — our content showcases genuine passion and authenticity. All performers are fully verified and over 18 years old. Discover the perfect mix of youthful charm and legal clarity — no fakes, no risks, 100% compliant. как работает сайт kraken
.
Hi there, I enjoy reading through your post. I like to write a little comment to support
you.
Unipump CM 25-2 Горизонтальный многоступенчатый насос 4,0 кВт, 3х380 В, корпус из чугуна
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите наши проекты и узнайте обо всех тонкостях фундамента, дренажных систем и сейсмоустойчивых технологий.
Wind and solar power stand out as leading options in the field of renewable energy. Both technologies harness natural processes to generate clean electricity.
sustainability challenges energy sustainability challenges energy.
программа для учета сырья Программа для учета договоров Организуйте учет договоров и контролируйте сроки исполнения обязательств. Наша программа позволит вам централизованно хранить договоры, отслеживать статусы, получать уведомления о приближении сроков и многое другое.
vezd-na-dachnyy-uchastok-365.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
полезная статья Узнайте из полезной статьи и улучшайте качество вашего объекта.
Вызов нарколога на дом в конфиденциальном порядке – это важный шаг для людей, страдающих от наркозависимости. Профессиональная помощь нарколога на дому дают возможность получить квалифицированную помощь в комфортной и защищенной обстановке. Анонимный нарколог проведет консультацию, оценит состояние пациента и разработает лечение наркомании на дому. Это может включать психотерапевтическую помощь и психологическую поддержку зависимых. Срочный вызов нарколога также возможен, что особенно важно в острых ситуациях. Помощь нарколога охватывает профилактические меры против зависимости и реабилитацию для зависимых, обеспечивая анонимное лечение и надежность процесса. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk010.ru
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Вызов нарколога на дом в конфиденциальном порядке – это необходимый шаг для людей, страдающих от наркозависимости. Услуги нарколога на дому дают возможность получить профессиональную помощь в комфортной и защищенной обстановке. Нарколог, работающий анонимно проведет консультацию, оценит состояние пациента и предложит программу лечения наркомании на месте. Это включает в себя психотерапевтическую помощь и психологическую поддержку зависимых. Срочный вызов нарколога также возможен, что особенно важно в острых ситуациях. Услуги нарколога включает профилактику зависимости и реабилитацию для зависимых, обеспечивая конфиденциальное лечение и достоверность процесса. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя
готовые дома иркутск готовые дома иркутск .
Вызов нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это важная услуга для тех‚ кто сталкивается с проблемами зависимости. Профессиональная помощь‚ включая помощь при зависимостях‚ становится доступной в знакомой обстановке. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk010.ru предоставляет профессиональные услуги нарколога в Красноярске‚ включая анонимное лечение и реабилитацию. При вызове врача на дом‚ вы получаете комплексную помощь при зависимости‚ но и эмоциональную поддержку. Визит нарколога на дом поможет определить оптимальную стратегию лечения. Домашний визит врача обеспечивает дискрецию и комфорт. Не забывайте‚ что раннее обращение за помощью может быть решающим. Не ждите‚ когда станет слишком поздно — вызовите нарколога‚ если вы или ваши близкие нуждаетесь в помощи.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
mostbet mostbet
зелёный дом с солнечными панелями Сочи Применяйте зелёный дом с солнечными панелями Сочи и обеспечьте снижение расходов.
https://www.chery-russia.ru/ – гарантия качества.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить аттестат 11 классов челябинск купить аттестат 11 классов челябинск .
дома под ключ иркутск https://www.stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-1.ru .
Заказать диплом университета!
Наши специалисты предлагаютмаксимально быстро приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Наш документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при помощи профессионального оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашими дипломами- therealestatepk.com/author/lamontbottoms6
перевод договора с болгарского на русский http://www.onlineperevodchik.ru/ .
I visit everyday a few sites and sites to read articles, however this weblog presents quality based articles.
технологии сейсмоустойчивого строительства Сочи Используйте технологии сейсмоустойчивого строительства Сочи и гарантируйте долговечность.
Многие задаются вопросом, как набрать подписчиков в Телеграм-канале быстро и без больших затрат. Для этого собраны лучшие сервисы и пошаговые инструкции, которые подойдут новичкам и опытным владельцам каналов. Важно использовать только проверенные источники, чтобы подписчики были живыми и активными. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1415893-kupit-podpischikov-v-telegram-25-luchshih-servisov-2025-goda Здесь вы найдете свежую подборку топ-25 сервисов для накрутки подписчиков в ТГ в 2025 году, которые реально работают и дают результат.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Yes! Finally someone writes about 580bet.
ставки прогнозы https://stavki-prognozy-two.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Якщо ви шукаєте натхнення для досягнення своїх цілей у кіберспортивному світі, то команда Zhivchik стане для вас ідеальним прикладом.
Алкогольная зависимость серьезная трудность, с которой имеют дело многие людей в Красноярске . Психологическая помощь имеет огромное значение в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Наркологические клиники предлагают услуги по детоксикации и реабилитации для зависимых, что включает в себя как медицинскую, так и психологическую помощь. вывод из запоя цена Семейная поддержка также важна , поскольку она способствует созданию доверительной атмосферы. Признаки зависимости могут проявляться по-разному , и раннее обращение за помощью в случае запоя способно изменить жизнь к лучшему. Советы по отказу от алкоголя заключаются в поиске новых увлечений и замене вредных привычек на более здоровые. Необходимо помнить, что обращение за помощью – это первый шаг к выздоровлению .
советы по строительству в краснодарском крае Читайте советы по строительству в Краснодарском крае и обеспечьте устойчивость дома.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя
Анонимное прокапывание от алкоголя – это важный шаг на дороге к выздоровлению. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk011.ru вы можете ознакомиться с информацией о методах борьбы с алкоголизмом и реабилитационных программах. Анонимные группытакие как Анонимные Алкоголики, оказывают помощь зависимым и их семьям. Психотерапия для зависимых помогает выходить с кризисом из-за алкоголя. Кодирование от алкоголя и советы по отказу от спиртного также могут быть полезными борьбы с зависимостью. Программы трезвости помогают поддерживать здоровье и построить жизнь без алкоголя. Помощь при алкоголизме доступна всем, кто в ней нуждается.
mostbet az bonus mostbet4139.ru
mostbet ios http://mostbet4162.ru
Капельница для лечения запоя – это существенный метод помощи алкогольной зависимости, что находит свое применение в наркологических клиниках Красноярска. Процедура детоксикации способствует оперативному восстановлению организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Время процедуры обычно варьируется от одного до трех часов, исходя из особенностей пациента и интенсивности запойного состояния. лечение запоя Красноярск Признаки запоя включает в себя интенсивные головные боли, тошноту и рвоту, потливость и тревогу и беспокойство. Помощь врачей в виде капельницы даёт возможность быстро облегчить похмельные симптомы, вводя необходимые препараты для восстановления водно-электролитного баланса и устранения токсинов. Цены на лечение запоя в Красноярске варьируется в зависимости от обраной лечебной организации и количества требуемых процедур. Прием у нарколога поможет определить наилучший курс лечения, включая восстановление после запоя. Результативность капельницы доказывается многими положительными отзывами пациентов, что делает данный метод востребованным способом профилактики с алкогольной зависимостью.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом в запорожье купить диплом в запорожье .
ландшафтный дизайн с террасированием Сочи Следуйте ландшафтный дизайн с террасированием в Сочи и обеспечьте красоту вашего территории.
частные наркологические клиники в москве http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-13.ru .
горшок напольный горшок напольный .
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Многие задаются вопросом, как набрать подписчиков в Телеграм-канале быстро и без больших затрат. Для этого собраны лучшие сервисы и пошаговые инструкции, которые подойдут новичкам и опытным владельцам каналов. Важно использовать только проверенные источники, чтобы подписчики были живыми и активными. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1424409-kupit-telegram-podpischikov-top-25-luchshih-servisov-i-sposobov-dlya-besplatnoi-nakrutki Здесь вы найдете свежую подборку топ-25 сервисов для накрутки подписчиков в ТГ в 2025 году, которые реально работают и дают результат.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
mostbet onlayn https://www.mostbet4162.ru
mostbet.kg http://www.mostbet4152.ru
новые продажа дров .
благоустройство участка с уклоном Стройте благоустройство участка с уклоном в Сочи и поддержите гармонию вашего дома.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
заезд через канаву .
Navigating Plumbing Situations: The Definitive Function of Emergency Situation Plumbing Technicians More info!..
Thanks for the article https://www.isxgames.com/f/members/grom95.20145/#about .
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Капельница от алкоголя – является эффективный способ‚ позволяющий оказать помощь в восстановлении после запоя на дому. Обратившись к к наркологу‚ который приедет к вам‚ вы сможете получить профессиональную поддержку и необходимые медикаменты для облегчения симптомов похмелья. Симптомы запойного состояния могут состоять из головной боли‚ тошноты и общего недомогания; вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск Процесс очистки организма начинается с введения капельницы‚ что гарантирует поступление жидкости и витаминов‚ что помогает уменьшить симптомы отмены. Услуги наркологов в Красноярске подразумевают персонализированный подход к пациенту‚ что необходимо для эффективного лечения алкоголизма на дому. Забота со стороны родных при алкоголизме играет ключевой составляющей в процессе восстановления здоровья после приема алкоголя. Домашняя реабилитация осуществляется с помощью капельниц и медикаментов‚ что позволяет предотвратить новые запои и упростить процесс восстановления. При этом профилактика запоев является ключевым моментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
mostbet oyun izləmək http://www.mostbet4136.ru
подпорные стенки сочи Используйте подпорные стенки и гарантируйте надежность склона.
заезд на участок под ключ цена .
Прокапаться от алкоголя – это необходимый этап для избавления от зависимости. Избавление от алкоголизма начинается с очистки организма‚ которая снижает с симптомами похмелья. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk012.ru вы узнаете информацию о реабилитационных центрах‚ где доступна терапия зависимостей и психологическая поддержка. Реабилитационные программы включают поддерживающие мероприятия для зависимых‚ группы анонимных алкоголиков и инициативы по здоровому образу жизни и благополучию без алкоголя. Осознание воздействия алкоголя на организм помогает адекватно воспринимать лечение и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
постройка дома под ключ постройка дома под ключ .
Цена капельницы от запоя в Красноярске: где найти лучшие предложения Проблема алкогольной зависимости затрагивает множество людей. Для лечения алкоголизма и выведения из запоя часто требуется медицинская помощь. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске, включая вызов врача на дом, востребованы среди тех, кто стремится избавиться от алкогольной зависимости. Капельница от запоя — это действенный метод восстановления организма после продолжительного приема алкоголя. Цены на капельницы варьируются в зависимости от клиники наркологии и необходимых компонентов. Например, домашняя капельница может быть удобным вариантом, так как вызов врача на дом позволяет получить помощь в комфортной обстановке. Стоимость капельницы зависит от используемых препаратов и сложности процедуры. В Красноярске существует множество предложений, однако важно выбирать клиники с положительными отзывами. Помимо капельниц, наркологические услуги могут включать терапию алкоголизма, что тоже имеет значение при выборе. Комплексный подход необходим для восстановления после запоя, и лечение таких состояний должно осуществляться квалифицированными специалистами. Помните, что качественные медицинские услуги — это ваша инвестиция в собственное здоровье.
дрова сухие колотые береза с доставкой .
как можно купить аттестат 11 класса как можно купить аттестат 11 класса .
amoxicillin liquid medicine visa amoxil online amoxil 500 mg side effects can you use amoxicillin for a tooth infection 3 ml of amoxicillin for inner ear infection
купить диплом пту в реестре купить диплом пту в реестре .
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
интересный блог о строительстве Следите за интересный блог о строительстве и узнайте ценную информацию.
mostbet canlı kazino http://www.mostbet4140.ru
Explore our exclusive collection featuring beautiful, legal young adult models aged 18+. Fresh, natural, and full of energy — our content showcases genuine passion and authenticity. All performers are fully verified and over 18 years old. Discover the perfect mix of youthful charm and legal clarity — no fakes, no risks, 100% compliant. доступ к kraken через зеркала
.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
SLOT88 menurut saya termasuk situs yang cukup fair, RTP-nya transparan dan gampang diakses. Dari pengalaman main, sering dapat scatter maupun free spin. Cocok buat yang cari slot gacor harian.
наркологические клиники https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
посетить сайт нова маркетплейс вход
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
лечение запоя
защита стен от грибка Сочи Применяйте защиту стен от грибка Сочи и обеспечьте здоровый микроклимат.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
To choose headlines, prefer trusted outlets, check facts, note slant and find detail. Compare with multiple stories, use expert commentary, and set feeds for topics you follow. Build media savvy https://smasters.com
mostbet qeydiyyat bonus mostbet4136.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://fixedfloat.ac
мостбет вывод на карту https://www.mostbet4161.ru
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве купить аттестат за 11 классов в москве .
Explore our exclusive collection featuring beautiful, legal young adult models aged 18+. Fresh, natural, and full of energy — our content showcases genuine passion and authenticity. All performers are fully verified and over 18 years old. Discover the perfect mix of youthful charm and legal clarity — no fakes, no risks, 100% compliant. на этой странице
.
stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите подробнее наши материалы и узнайте о выборе окон, дверей и экологичных строительных материалов.
mostbet promokod olish https://www.mostbet4161.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Как директор по производству, я беспокоюсь о безопасности объектов. Мы заказывали стоимость проекта пожаротушения и ожидали серьёзных цифр, но компания приятно удивила. Цена адекватная, расчёты понятные, проект чёткий. Согласование прошло быстро, никаких замечаний. Теперь уверен, что система сработает в нужный момент. Это именно тот случай, когда деньги потрачены правильно.
excellent publish, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite
specialists of this sector do not understand this. You must continue your writing.
I am sure, you’ve a great readers’ base already!
Як не витрачати зайві гроші в подорожах? Кращі поради та ідеї тут: дивитися!
наркологический центр москва http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-13.ru .
Explore our exclusive collection featuring beautiful, legal young adult models aged 18+. Fresh, natural, and full of energy — our content showcases genuine passion and authenticity. All performers are fully verified and over 18 years old. Discover the perfect mix of youthful charm and legal clarity — no fakes, no risks, 100% compliant. перейти по ссылке
.
Thanks for the article https://rhabits.io/post/62745_mostbet-uz-2009-yildan-buyon-kyurasao-litsenziyasi-asosida-faoliyat-yuritib-kela.html .
fundament-ushp-moskovskaya-oblast-499.ru .
зелёный дом с солнечными панелями Сочи Используйте зелёный дом с солнечными панелями Сочи и обеспечьте снижение расходов.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
https://github.com/msrds/Microsoft-Remote-Desktop
мостбет uz https://www.mostbet4163.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва .
paying too much for it | All these internet suppliers sell ivermectin rosacea , you can buy medication from home. stromectol company
организация въезда на участок через канаву .
mostbet qeydiyyat pulsuz https://mostbet4137.ru
https://www.russianwomenorg.com/read-blog/15026
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
вывод из запоя
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Сегодня продвижение в Телеграме невозможно представить без накрутки. Сервисы помогают раскрутить канал, повысить активность и привлечь новую аудиторию. В обзоре разобраны рабочие методы и реальные кейсы. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1472550-top-20-luchshih-servisov-po-nakrutke-botov-i-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-telegram-v-2025-godu-praktika-professionalov Подробный рейтинг сервисов по накрутке подписчиков в ТГ поможет выбрать оптимальный вариант: от бесплатных способов до надежных платных площадок.
Hello everyone! I wanted to post about aviator game and minas. This game catches players fast with its blend of bet and plan. Many people discuss about https://www.fundamentale.ro/cum-sa-construiesti-o-casa-pentru-pasari-din-materiale-reciclabile, and some wish for cheats, but the main thrill comes from gaming honestly. The aviator tool and aviator game download make it super fast to join anywhere. aviator play online is solid because games are fast and high-risk, giving lots of fun. If you haven’t played it yet, definitely try it out and enjoy the rush.
bannye-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
mostbet kartla depozit mostbet kartla depozit
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar014.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Thanks for the article https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/1095361/The-RybachOK-website-is-a-reliable-choice-for-everyone?btwaf=12835090 .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Просмотрите наши проекты и ознакомьтесь с передовыми подходами к проектированию коттеджей и частных домов.
диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
sports bet https://sportbets32.ru/ .
Hello.
This post was created with XRumer 23 StrongAI.
Good luck 🙂
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
bannye-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Погрузитесь в портфолио объектов и изучите секреты строительства частного дома с учетом влажного и морского климата.
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Rybak-i-magazin-Rybachok-Vsyo-dlya-idealnoj-rybalki-01-13 .
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа!
Мы предлагаемвыгодно приобрести диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при использовании специальных приборов. Решайте свои задачи быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- igenplan.ru/forum/user/100328
Hello everyone! I decided to post about aviator and minas game. This play grabs players fast with its blend of bet and plan. Many users discuss about https://talukadapoli.com/travel/listing/exotic-home-stay-dapoli/, and some wish for aviator hack, but the real thrill comes from joining fairly. The aviator tool and downloading aviator make it extra easy to join anywhere. aviator play online is great because rounds are fast and high-stakes, giving tons of excitement. If you didn’t try it yet, seriously give it out and enjoy the kick.
Thanks for the article https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/ribachok .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове .
купить аттестат 11 классов томск купить аттестат 11 классов томск .
Капельница от запоя — это одна из действительных методик, используемых специалистами в области наркологии для очищения организма. Нарколог на дом анонимно в Туле надеется предложить такие услуги: помощь при алкоголизме и восстановление после запоя. При помощи капельницы можно оперативно повысить состояние пациента, облегчить проявления абстиненции и стимулировать процесс вывода токсинов из организма. Медицинская помощь при запое включает не только капельниц, но также психотерапию при алкоголизме, что глубже понять проблему зависимости к алкоголю. Профилактика запоя также играет важную роль, поэтому наркологи советуют проводить регулярные консультации и обращаться за анонимной помощью. Восстановление зависимых от алкоголя требует целостного подхода, включающего как медицинские, так и психологические методы. Рекомендуем обратиться к специалисту, чтобы получить советы нарколога и приступить к процессу выздоровления.
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите наш каталог решений и получите советы по строительству коттеджей и домов под ключ.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
купить колотые дрова для бани .
mostbet android yukle http://mostbet4138.ru
купить дом под ключ https://stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-1.ru .
Как избавиться от алкогольной зависимости в Туле Зависимость от алкоголя – это актуальная проблема, касающаяся многих людей. В Туле предлагается широкий спектр наркологических услуг, таких как анонимное лечение и услуги выездного нарколога. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с детоксикации, которая позволяет организму избавиться от токсинов. Важно помнить, что лечение на дому обеспечивает комфорт и конфиденциальность. Консультация нарколога – первый шаг к выздоровлению. Квалифицированные специалисты помогут создать индивидуальный план реабилитации, соответствующий потребностям пациента. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации от алкоголя, так как помогает справиться с эмоциональными трудностями. Также доступно кодирование от алкоголя, которое может быть эффективным средством в борьбе с зависимостью. Помощь при запое и регулярные встречи с наркологом обеспечивают высокий уровень контроля над состоянием пациента. Если вы или ваши близкие сталкиваетесь с зависимостью от спиртного, не стесняйтесь обратиться за помощью. Нарколог на дом анонимно проведет все необходимые процедуры, чтобы помочь вам вернуться к здоровой жизни.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar015.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Проверяйте наш сайт и получите максимум информации о проектировании и строительстве частного дома под ключ.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshaya-koleblyushchayasya-blesna-na-shchuku-Rejting-primanok-01-13 .
https://unisswap.trade/ new site, new connections, new crypto.
mostbet promo kod http://mostbet4138.ru/
https://linea-swap.com airdrop soon. Dont forget to accept it!
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
купить диплом о высшем цена купить диплом о высшем цена .
Hello Dear, are you actually visiting this web page on a regular basis, if so afterward you will without doubt get pleasant experience.
Мы предлагаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по выгодным ценам. Приобретение диплома, подтверждающего обучение в ВУЗе, – это выгодное решение. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании: bricklaneportal.com/agents/lucillebeverly
the best value|Find out the effective way of treating ED. Visit wellbutrin seizures for all medications are available globally wellbutrin and naltrexone
Thanks for the article https://boi.instgame.pro/forum/index.php?topic=25076.0 .
наркологический анонимный центр https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru .
дрова цена за 1 куб .
Обращение к наркологу анонимно — это необходимый шаг на пути к лечению зависимости. На сайте narkolog-tula016.ru вы можете получить профессиональной помощью наркологане опасаясь за свою безопасность. Обсуждение с экспертом поможет выбрать оптимальные подходы к лечению. Лечение без раскрытия личности и программы реабилитации наркозависимых в себя включают психологическое сопровождение при алкогольной зависимостичто увеличивает вероятность успешного выздоровления. Также доступны медицинская помощь для зависимых и горячая линия для помощи людям в трудной ситуации. Профилактика наркомании и участие в группах поддержки имеют огромное значение в социализации и возвращении к нормальной жизни.
Ви знали, що роль гравітації у Всесвіті визначає навіть те, як працюють GPS-системи?
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на портфолио объектов и изучите секреты строительства частного дома с учетом влажного и морского климата.
Thanks for the article http://katuganka.in.ua/forum/index.php?id=1282596 .
Экстренная наркологическая помощь в Туле: когда вызывать Кризисные ситуации, возникающие из-за зависимости от алкоголя или наркотиков, могут коснуться любого. В такие моменты необходимо понимать, как быстро и эффективно получить необходимую помощь. Вызов нарколога на дом в Туле может стать настоящим спасением для людей, столкнувшихся с алкогольным отравлением или другими острыми состояниями, связанными с зависимостями. Экстренная помощь от наркологической службы включает возможность вызвать нарколога на дом. Это особенно актуально для людей, которые не могут или не хотят посещать медицинские учреждения. Профилактика тяжелых последствий при лечении алкоголизма зачастую требует вмешательства специалистов. Поддержка со стороны близких имеет решающее значение в процессе реабилитации наркоманов и алкоголиков; Психотерапия при зависимостях помогает разобраться в причинах и справиться с трудностями. Информацию о наркологических центрах в Туле можно найти в интернете, однако иногда требуется незамедлительная помощь; нарколог на дом срочно тула Не забывайте, что профилактика зависимости играет важную роль. Раннее обращение к специалистам может помочь предотвратить развитие серьезных проблем. Помните, что экстренные меры способны спасти жизнь.
Алкогольный запой, это опасное состояние, которое появляется при продолжительном пьянстве. Эффекты запоя могут быть угрожающими: истощение организма, повреждение органов, психические расстройства. Экстренный вывод из запоя в городе Тула включает медикаментозное лечение и психотерапевтическую помощь. Важно знать признаки запойного алкоголизма: регулярные запои, утрата контроля над потреблением спиртного. Способы выхода из запоя разнообразны: от капельниц до встреч с профессионалами. Восстановление после запоя требует системного подхода, включая восстановление здоровья и психологическую помощь. Лечение алкогольной зависимости в Туле предлагает клиники, где доступны различные программы поддержки. экстренный вывод из запоя тула
Обращение к частного нарколога – это важный этап на пути к избавлению от зависимости. Если вы сталкиваетесь с проблемами‚ связанными с наркотиками или алкоголем‚ квалифицированная поддержка становится жизненно важной. Услуги нарколога включают в себя консультацию нарколога‚ диагностику зависимостей и выезд врача на место жительства для оказания первой помощи. Одним из основных плюсов вызова нарколога на дом является анонимность. Вы можете получить помощь‚ которая вам нужна‚ на дому‚ что снижает уровень стресса и позволяет сосредоточиться на реабилитации. Частный нарколог осуществляет лечение зависимостей индивидуально‚ учитывая особенности каждого пациента. После первичной консультации стартует процесс восстановления от психоактивных веществ или алкоголя‚ который может включать медикаментозное лечение и психологическую помощь. Сопровождение пациентов в этом процессе крайне важно‚ так как оно помогает избежать рецидивы и обеспечивает полноценное восстановление после зависимости. Услуги наркологов на дому также включают в себя мониторинг состояния пациента и адаптацию лечебной программы в зависимости от индивидуальных нужд. Не откладывайте принятие решения – вызов нарколога может стать началом к новому этапу жизни. Вы можете связаться на сайт narkolog-tula015.ru для дополнительных сведений о квалифицированной помощи при зависимости.
stroyexpertsochi.ru Откройте наши материалы и узнайте о материалах, идеально подходящих для морского и влажного климата.
Сегодня безопасность персональных данных и приватность онлайн делаются необходимыми. Если вы желаете быть незаметным в интернете‚ рекомендуется применять анонимные услуги‚ такие как VPN-сервисы и прокси-сервисы‚ которые дадут возможность замаскировать вашу личность и обезопасить ваш IP-адрес. Эти инструменты предоставляют шифрование вашего подключения‚ что укрепляет безопасность в интернете и конфиденциальность ваших действий. Также вы получите возможность обходить блокировки и получать незаметный доступ к сайтам без регистрации. Безопасность информации становится важной частью анонимного использования интернета‚ позволяя оставаться в безопасности. narkolog-tula015.ru
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат за 11 класс с отличием
Нарколог на выезд в Красноярске предоставляет незаменимую поддержку тем, кто страдает от зависимости. Лечение зависимости может быть непростым процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает комфортные условия и конфиденциальность. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk010.ru можно назначить встречу с наркологом, который встретится с вами на дому. На дому пациентам предоставляется медицинская помощь включает очистку организма и психотерапию зависимостей, что позволяет пациенту начать путь к отрыву от наркотиков или алкоголя. Реабилитационная программа разрабатывается с индивидуальным подходом, что позволяет учитывать уникальные потребности каждого пациента. Эмоциональная поддержка близких играет важнейшую роль в профилактике рецидива. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает не только лечение, но и эмоциональную поддержку, что важно для успешной реабилитации наркоманов и помощи при алкоголизме.
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshij-povodok-na-shchuku-Kak-vybrat-nadezhnuyu-osnastku-01-13 .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-polyarizacionnye-ochki-dlya-rybalki-Top-10-modelej-01-13 .
Наркологический центр в Туле предлагает полный спектр услуг по лечению зависимости от алкоголя, включая вызов нарколога на дом и конфиденциальное лечение. Профессиональная помощь специалистов обеспечивают эффективное лечение алкогольной зависимости. Центр разработал программы реабилитации, которые включают психотерапевтическую помощь, социальную адаптацию и поддержку зависимых. Первичная консультация у нарколога поможет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать наиболее подходящие методы лечения алкоголизма. Важно помнить о профилактике алкогольной зависимости и восстановлению здоровья после алкогольной зависимости. вызов нарколога тула
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены .
Thanks for the article https://bc39.unoforum.pro/?1-0-0-00004667-000-0-0-1721660606 .
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Зайдите на наш каталог решений и ознакомьтесь с секретами строительства дома в Сочи и Краснодарском крае.
Капельница от запоя – это важная мероприятие‚ используемая для неотложного освобождения от запойного состояния в Красноярске. Она гарантирует быструю очистку организма‚ что жизненно необходимо для восстановления после запоя. Следует отметить‚ что лечение алкоголизма включает в себя не только медикаментозное лечение‚ но и психотерапию. Психотерапевтические подходы помогают людям справиться с зависимостью от алкоголя на психологическом уровне. экстренный вывод из запоя Красноярск Поддержка пациента играет важнейшую функцию в процессе реабилитации. Психологическая помощь содействует создать методы предотвращения повторных срывов. Комплексный подход‚ объединяющий медикаментозное лечение и психотерапию‚ значительно повышает шансы на успешное восстановление. Наркология активно используют данные методы для получения устойчивых результатов в борьбе с алкоголизмом.
helpful site jaxx liberty wallet
Неотложная помощь при алкогольной зависимости в Красноярске все чаще требуется многим. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk010.ru предлагает услуги нарколога, который осуществляет лечение алкоголизма и вывод из запоя. В данную процедуру входит медицинская помощь, детоксикация организма от алкоголя и психотерапевтические сеансы. Обязательно обратитесь к врачу для эффективного преодоления алкогольной зависимости. Наша программа восстановления фокусируется на реабилитации и поддержке зависимых, а также социальной адаптации. Профилактика рецидивов, ключевой элемент эффективного лечения. Помните, что просьба о помощи — это первый шаг к выздоровлению.
купить аттестат 11 классов в красноярске https://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
بعد الانتهاء من التثبيت، يمكنك بدء استخدام التطبيق للمراهنة.
تحميل 1 اكس بيت https://arabic1xbet.com/
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Изучите наш сайт и получите советы по энергоэффективным коттеджам и установке солнечных панелей.
Нарколог на дом анонимно в Туле – это важная помощь для тех‚ кто сталкивается с зависимостью. Борьба с наркоманией требует квалифицированной помощи‚ и вызов врача на дом гарантирует конфиденциальность. Опытные врачи предоставляют анонимную консультацию‚ выявление зависимости и медицинскую помощь на домашних условиях. В нашем городе предоставляется психотерапия при зависимости и реабилитационные программы которые помогают вернуть физическое и психическое здоровье и возобновить нормальную жизнь. Семейная терапия и участие близких также играют ключевую роль в процессе лечения. Обращайтесь на narkolog-tula017.ru‚ чтобы получить помощь зависимым и сделать шаг к выздоровлению.
дрова топки недорого .
Капельница от запоя на дому — является действенным методом детоксикации организма при борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом анонимно в городе Тула предоставляет услуги по введению капельниц , что дает возможность оперативно восстановить здоровье. Состав капельного раствора состоит из лекарственных средств, которые способствуют устранению симптомов запойного алкоголизма , таких как обезвоживание и интоксикация . Нарколог на дом анонимно Тула. Основные компоненты капельницы : раствор натрия хлорида для гидратации , глюкоза для энергии, витамины группы В для улучшения обмена веществ и специальные медикаменты для снятия абстинентного синдрома ; состав лекарств подбирается индивидуально, учитывая состояние пациента . Домашняя терапия под контролем нарколога обеспечивает анонимное лечение , что важно для многих зависимых от алкоголя. Семейная поддержка во время запоя играет ключевую роль в успешном восстановлении . Обращение к наркологу поможет определить дальнейшие шаги , включая реабилитацию алкоголиков и восстановление после алкогольной зависимости.
Получите профессиональную юридическую консультацию бесплатно и разрешите свои юридические вопросы с уверенностью!
В современном мире юридические консультации стали неотъемлемой частью нашей жизни.
организация въезда на участок .
Алкогольный запой — это тревожное состояние, требующее оперативной медицинской помощи. В Туле доступна помощь нарколога, который предлагает услуги по избавлению от запоя и детоксикации. Капельное введение — это эффективное средство для восстановления здоровья пациента. Она помогает устранить симптомы алкогольной зависимости, улучшает общее состояние и интенсифицирует процесс реабилитации от алкоголя. помощь нарколога тула Если вы или ваш близкий сталкиваетесь с проблемой запоя, важно не откладывать обращение за медицинской помощью. Наркологические услуги, предоставляемые в клиниках Тулы, могут включать персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту. Помощь нарколога включает не только капельницы, но и совокупное лечение алкоголизма. Обращение к врачу на дом дает возможность получения медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке. Специалисты обеспечат необходимую детоксикацию и укрепят здоровье пациента. Не бойтесь обращаться за помощью — это первый шаг к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru Зайдите на галерею выполненных работ и ознакомьтесь с защитой стен от грибка и антикоррозийной обработкой металлоконструкций.
My partner and I stumbled over here coming from
a different page and thought I might as well check things out.
I like what I see so now i am following you.
Look forward to looking over your web page again.
Also visit my webpage :: pink salt trick reviews
купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр .
My family every time say that I am wasting my time here at net, except I know I am getting know-how daily by reading such fastidious posts.
kupit-drova-v-chekhove-365.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс самара купить аттестат за 11 класс самара .
Организация капельницы для лечения запоя в домашних условиях — важный этап в терапии алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога и профессиональная поддержка при запое гарантируют надежность и результативность detox-процедуры. Прежде всего, необходимо проанализировать симптомы запойного состояния и собрать информацию о состоянии пациента. Следует обеспечить комфортную обстановку для лечения: подготовьте пространство, где будет проводиться капельница на дому. Обеспечьте доступа к электричеству и достаточное количество чистой воды. Важно также иметь под рукой необходимые лекарства, которые предписал врач. Перед процедурой стоит обсудить с специалистом все нюансы, чтобы избежать осложнений. Эффективное лечение алкоголизма включает не только капельницу, но и реабилитационные мероприятия от запоя. Обращение к профессионалу гарантирует квалифицированный подход и поддержку в восстановлении организма после запоя.
Нарколог на выезд — это удобное решение для людей, испытывающих проблемы с зависимостями. Служба наркологической помощи, представленная на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk011.ru, предлагает круглосуточные услуги, что крайне важно в кризисных ситуациях . Приезд врача на дом позволяет пациенту получить конфиденциальную медицинскую помощь без стресса и лишних волнений . При обращении за медицинской помощью важна встреча с наркологом, которая включает оценку состояния пациента и создание персонализированного плана терапии. Лечение алкогольной зависимости и наркомании начинается с очищения организма, что помогает вывести вредные вещества. Роль семьи играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Психотерапия при зависимости способствует пониманию причин проблемы и снижению риска повторного срыва. Процесс реабилитации зависимых обеспечивает всестороннее лечение и профилактику зависимостей.
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Посетите материалы и изучите возможности современного ландшафтного дизайна и террасирования.
где купить аттестат за 11 класс омск где купить аттестат за 11 класс омск .
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, которое требует квалифицированной помощи. Нарколог на дом в Красноярске становится все более востребованным. Специалисты предлагают медикаментозное лечение, включая капельницы для оперативного выхода из запоя. Признаки запоя могут проявляться в виде сильной головной боли, тошноты и других симптомов. Если вы или ваш близкий испытываете такие симптомы, стоит незамедлительно обратиться за помощью. Обратившись к наркологу, вы сможете получить рекомендации по необходимому курсу лечения. Капельница содержит необходимые витамины и лекарства, которые восстанавливают организм. Лечение проходит в комфортных условиях, что помогает снизить уровень стресса. Восстановительный процесс после запоя также включает психологическую помощь. нарколог на дом в Красноярске Не забывайте, что лечение алкоголизма, это длительный процесс, который требует терпения и усилий. Специалисты в Красноярске предлагают не только вывод из запоя, но и дальнейшую программу реабилитации. Восстановление после запоя возможно, и мы готовы помочь в этом пути.
Капельницы для лечения запоя на дому в Туле круглосуточно – это эффективный способ для тех, кто сталкивается с трудностями алкогольной зависимости. Вызвать нарколога на дом можно в любое время. Услуги нарколога 24/7 предлагают экстренную медицинскую помощь, детоксикацию алкоголя, а также восстановление после запоя. При нужде вызова врача на дом, достаточно связаться со специализированной службой. Капельницы для детоксикации от алкоголя помогут быстро восстановить здоровье пациента, восстановить баланс воды и электролитов и облегчить симптомы абстиненции. Услуги медицинских работников в Туле предоставляется опытными врачами. Первичная консультация нарколога перед началом лечения поможет определить дальнейшие шаги, включая дальнейшую реабилитацию. Помощь при алкогольной зависимости требует профессионального подхода и сопровождения. Наркология на дому гарантирует комфорт и конфиденциальность, что особенно необходимо для людей, нуждающихся в помощи.
Thank.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр владивосток http://www.arus-diplom31.ru/ .
Помощь наркологов – это набор действий‚ направленных на избавление от зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk011.ru можно найти информацию о наркологических клиниках ‚ предлагающих профессиональную помощь при алкоголизме и других зависимостях . Лечение начинается с детоксикации ‚ после которой проводятся встречи с врачами и персонализированное лечение. Психотерапия и группы поддержки играют важную роль в восстановлении после зависимости . Также важна социальная адаптация и поддержка близких людей‚ что способствует предотвращению возврата к зависимости.
Откапаться на дому: советы по ремонту и улучшению жилья Если ваш дом требует ремонта, услуги по ремонту могут стать настоящим спасением. На сайте narkolog-tula016.ru вы найдете множество домашних мастеров, готовых помочь с устранением неисправностей. Возможности варьируются от небольших ремонтов до сложных сантехнических и электромонтажных работ. Для самостоятельного ремонта важно знать основные советы по ремонту. Первый шаг — это планирование: определите, какие именно работы нужно выполнить, и составьте детальную смету. Не забывайте о правилах безопасности, особенно если речь идет о электромонтажных работах. Для декорирования вашего жилья обратитесь к домашним умельцам, которые предоставляют услуги по благоустройству. Они помогут преобразить ваше жилье, сделав его более комфортным и уютным. Не забывайте, что качественный ремонт, это залог вашего комфорта и уюта!
купить подписчиков в Телеграм безопасно купить подписчиков в Телеграм безопасно.
сделать заезд на участок .
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Погрузитесь в материалы и ознакомьтесь с современными подходами к укреплению склона и ландшафтному дизайну.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Услуга капельницы от запоя на дому – это популярная опция в Туле, которую предлагают специалистами в области наркологии. Комфортное лечение позволяет пациентам не испытывать стресс, связанного с посещением клиники. Мнения клиентов свидетельствуют о результативности процесса очищения организма и быстрого выхода из запойного состояния. Врач нарколог на дом обеспечивает анонимную помощь, что является важным для многих. Лечение алкоголизма становится реальным, а здоровье и восстановление – приоритетом. Медицинские услуги, например, капельницы, помогают справиться с алкогольной зависимостью и вернуться к нормальной жизни.
A proven way to ivermectin paste misconceptions about online ordering. Don’t be ignorant, read stromectol 0.1
Наша наркологическая клиника предлагает анонимные услуги по выводу из запоя и профессиональную медицинскую помощь на высшем уровне. Мы знаем, как важно поддержать людей, страдающих от зависимости в сложные времена, по этой причине организуем круглосуточную поддержку и консультации по алкоголизму. Когда пациент проходит вывод из запоя начинается процесс реабилитации, которая направлена восстановление и предотвращение рецидивов. Наша команда профессионалов поддержит каждого пациента вновь обрести нормальную жизнь, обеспечивая индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Не откладывайте свое здоровье на потом. Пожалуйста, обратитесь на narkolog-tula018.ru за помощью прямо сейчас!
https://pancakesswap.app/ 0% commission is now live!
накрутка в тг подписчики просмотры реакции накрутка в тг подписчики просмотры реакции.
Compare sales and discounts to aldactone alternative from Internet pharmacies. spironolactone vs furosemide
купить диплом регистрацией купить диплом регистрацией .
Зависимость от алкоголя – это серьезная проблема, которая требует комплексного подхода к терапии. На сайте narkolog-tula018.ru вы найдете информацию о методах лечения алкоголизмавключая очистку организма и кодирование от алкоголя. Ключевым моментом является реабилитация, где предоставляется психологическая помощь и формируются группы поддержкитакие как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Помощь зависимым часто включает в себя рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и советы для поддержания трезвого образа жизни. Возвращение к нормальной жизни после запоя требует усердия и поддержки родственников. Необходимо помнить о влиянии алкоголя на здоровье и следовать способам отказа от спиртного для достижения успешного выздоровления.
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с материалы и получите практические инструкции по монтажу фундамента и дренажных систем.
https://astra-hotel.ch/articles/code-promo-1xbet_bonus.html
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс .
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1винhttp://skateclass.borda.ru/?1-15-0-00000039-000-0-0-1752948295
Тут зібрані найкращі дитячі казки, у тому числі Попелюшка. Дуже рекомендую!
bannye-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Изучите наш сайт и изучите практические рекомендации по строительству, отделке и благоустройству домов.
Капельницы для лечения запоя в Красноярске: быстрая помощь Алкоголизм — серьезная проблема‚ требующая внимания и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске наблюдается рост спроса на услуги нарколога на выезд. Специалисты-наркологи на дом в Красноярске предоставляют экстренные услуги‚ включая детоксикацию и помощь при запое.Капельница — один из самых эффективных методов лечения запоя. Она обеспечивает организм необходимыми веществами‚ ускоряя процесс детоксикации. Медицинская помощь‚ предоставляемая наркологом‚ включает терапию при запое‚ что помогает убрать физическую зависимость от алкоголя. нарколог на дом Красноярск Не забывайте‚ что важно не затягивать с вызовом нарколога на дом. Скорое начало терапии алкогольной зависимости увеличивает вероятность успешного выздоровления. Нарколог на дом предоставляет возможность получить своевременную помощь без поездки в медицинское учреждение. Мы готовы помочь вам преодолеть зависимость от алкоголя.
Thanks for the article http://forum.anime.org.ua/bbs/showthread.php?p=143552 .
купить диплом о высшем образовании бакалавр купить диплом о высшем образовании бакалавр .
можно купить легальный диплом http://www.arus-diplom33.ru .
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема‚ которая требует профессионального вмешательства к лечению. В городе Красноярск можно обратиться за наркологическими услугами‚ такими как терапия алкогольной зависимости на домашних условиях. Специалист по наркологии на дому незамедлительно поможет определить степень зависимости и выявить признаки алкоголизма. Важно проконсультироваться с наркологом для выбора оптимальной программы восстановления. Домашняя терапия позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке‚ что снижает стресс. Психотерапия при алкоголизме совместно с поддержкой близких играет важную роль в реабилитации от алкоголизма. Помощь родственникам алкоголиков также важна для формирования условий для жизни без алкоголя. Нарколог на дом срочно Красноярск Не затягивайте с вызовом нарколога на дом‚ это первый шаг к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Туле – это ключевой элемент борьбы с зависимостями. На сайте narkolog-tula017.ru доступна информация о предоставляемых услугах, таких как экстренный вызов врача при зависимости от алкоголя и других зависимостях. Наркологическая помощь предполагает консультации специалистов, стационарное лечение и программы реабилитации.Цель медицинской помощи, восстановление психического здоровья и лечение зависимости. Не откладывайте лечение, обратитесь за помощью уже сегодня!
Приобрести диплом любого университета!
Мы предлагаембыстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполняется на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Наш документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при помощи специальных приборов. Достигайте свои цели максимально быстро с нашими дипломами- panther.80lvl.ru/index.php
Услуги нарколога на дом становятся все более актуальными в современном обществе. Профессиональная помощь нарколога может включать помощь в лечении зависимостей, детоксикацию организма и психотерапевтические услуги для людей с зависимостями. Выездная наркология позволяет получить профессиональную медицинскую помощь в комфортной обстановке, что играет ключевую роль для людей, страдающих от зависимостей и испытывающих неловкость. Конфиденциальное лечение и семейная поддержка играют ключевую роль в восстановлении пациента. Реабилитация алкоголизма и прекращение употребления наркотиков требуют комплексного подхода. Наркологи предлагают программы, направленные на профилактику рецидивов и обеспечивают долгосрочное восстановление после наркозависимости. Заказать услуги нарколога на дом можно через сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk012.ru, где доступна информация о лечении и помощи на дому.
kupit-drova-v-chekhove-365.ru .
you can try these out
bread wallet
интересный блог о строительстве Следите за интересным блогом о строительстве и гарантируйте полезные советы для вашего дома.
https://trendintelligencedesign.com/today-promo-code-1xbet-1x200big-syncs-with-real-time-events-boosting-live-betting-opportunities/
Преодоление запойного состояния — это критический процесс‚ требующий комплексного подхода. В Туле имеется возможность экстренного вывода из запоя на дому с помощью квалифицированных специалистов. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с очистки организма‚ что помогает устранить телесную зависимость.Помощь нарколога включают в себя медицинскую помощь при запое‚ применение эффективных методов‚ таких как алкогольное кодирование и психологическая терапия. Эмоциональная поддержка играет важную роль в реабилитации после запоя. Поддержка семьи и друзей также необходима для успешной реабилитации и профилактики рецидивов. экстренный вывод из запоя При выходе из запоя важно следовать нескольким рекомендациям: обеспечьте достаточное количество воды‚ правильно организуйте питание и не забывайте о физической активности. Поиск оперативной помощи и обращение к профессионалам поможет быстро и безопасно выйти из запоя‚ вернуть физическое здоровье и уровень жизни.
Капельница от запоя – это действующий метод детоксикации организма, который предлагает наркологическая клиника. В Туле предлагается множество медицинских услуг, включая вызов нарколога на дом для оказания помощи при запое. Преодоление алкогольной зависимости требует индивидуального подхода, и программы лечения разрабатываются в зависимости от уровня зависимости. Визит к наркологу способствует выбору оптимального метода, а анонимное лечение гарантирует защиту личных данных. Роль семьи в реабилитации также являеться ключевой в процессе восстановления. Оценка клиник в Туле на основе отзывов позволяет определить наиболее подходящее заведение. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за поддержкой, чтобы преодолеть алкогольную зависимость и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
Выездной нарколог в Туле — это удобное решение для тех‚ кто нуждаются в наркологической помощи‚ но не могут посещать медицинское учреждение. Квалифицированная поддержка в лечении зависимости доступна в домашних условиях‚ что обеспечивает удобство и анонимность.Обращение к наркологу даёт возможность оценить ситуацию и подобрать лучший план лечения‚ включая стационарное лечение или домашнюю терапию. Специалисты предлагают психологическую помощь при зависимостях и медицинское вмешательство‚ что способствует эффективной профилактике зависимостей. Поддержка семьи играет важную роль в лечении‚ помогая пациентам преодолеть сложности. Свяжитесь с narkolog-tula017.ru для подробной информации о наших услугах.
bannye-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
Эффективная капельница от алкогольной зависимости – это действительно проверенный метод лечения зависимости от алкоголя, что можно получить в городе Тула с помощью врачей-наркологов, работающих на выезде. В процессе используются введение определённых растворов, которые помогают организму быстрее восстановиться с эффектами употребления алкоголя. При обращении за помощью при запое, вы можете получить не только капельницу для снятия запоя, но и консультацию нарколога. врач нарколог на дом тула Выведение из запоя обеспечивает быстрое улучшение состояния пациента, а безопасность процедуры капельницы гарантируется опытными специалистами. Наркологическая помощь включает detox программу, которая направлена на очищение организма. Реабилитация зависимых – это ключевой этап после лечения, который способствует предотвратить возврат к употреблению. В Туле предоставляются услуги врача нарколога на дом, что дает возможность пройти лечение в комфортной обстановке. Не откладывайте, обратитесь за срочной помощью врача-нарколога прямо сейчас!
купить аттестат за 11 класс lr 63 купить аттестат за 11 класс lr 63 .
купить диплом аттестат 11 класс каменск шахтинский купить диплом аттестат 11 класс каменск шахтинский .
Недорогой вызов нарколога на дом – это комфортное и целесообразное решение для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Часто такие пациенты стесняются обращаться в клиники и отдают предпочтение анонимным методам лечения. На сайте narkolog-tula019.ru можно узнать информацию о предлагаемых сервисах выездного нарколога, который предложит профессиональную консультацию нарколога и профессиональную помощь. Недорогие услуги нарколога, такие как помощь в борьбе с наркоманией и алкоголизмом, обеспечивают возможность получения медицинской помощи на дому. Психологическая поддержка и реабилитационные программы проводятся опытными врачами, что обеспечивает защиту и приватность. Обратитесь к дешёвому наркологу для избавления от зависимости и начните путь к выздоровлению вместе с профессиональной поддержкой.
секреты строительства в сочи Узнайте секреты строительства в Сочи и получите комфортный дом.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts on . Regards
doroga-k-uchastku-812.ru .
At this moment I am ready to do my breakfast, after
having my breakfast coming yet again to read additional news.
Thanks for the article https://cardsfm.ru/metizy-dlya-stroitelstva-i-proizvodstva-kak-vybrat-i-zakazat-v-sankt-peterburge/
напольный горшок для цветов высокий напольный горшок для цветов высокий .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на портфолио объектов и получите советы по благоустройству участка с уклоном и геопластике.
Удобный евроштакетник с установкой цена калькулятор на сайте помогает предварительно рассчитать бюджет.
Website
brd wallet
диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой купить .
888starz ?? ???? ????? ???? ?????? ?????? ?? ??????? . ??? ??? ???? ?? ????? ?????? ???? ?? ?????? ??????? ?? .
??? ????? 888starz ??????? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???????. ???? ??????? ??????? ?? 888starz ?? ?? ????? ???? ???????? .
????? ???????? ?? 888starz ????? ????? ???? ??????? ?????? ????????. ??? ??????? ?? ?????? ???????? ????? ????? .
???????? ??? ???? ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ??????? ????? . ???? ??? ???????? ?? ????? ????? ????? ????? ?????? ?? ?????????? .
888starz تحميل ايفون https://888starz-africa.pro/apk/
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
вывод из запоя
накрутка подписчиков для канала в ТГ накрутка подписчиков для канала в ТГ.
Мега даркнет маркетплейс в 2025 году продолжает оставаться одной из самых известных площадок в даркнете. Пользователи регулярно ищут mega sb, mega darknet market зеркало и официальный сайт мега, чтобы получить вход на мега маркетплейс.
# Что такое Мега?
мега онион зеркало — это ресурс, который работает как даркнет-рынок. мега даркнет маркет стал популярен благодаря системе рейтингов. Но важно помнить: мега сайт даркнет — это незаконная платформа.
Cыллка ===> https://mega-onion.s3.eu-north-1.amazonaws.com/mega_darknet_kak_zayti_na_sait.pdf (используй ВиПиЭн)
# Почему нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде официальный сайт мега часто становятся недоступны. Чтобы обойти это, используются мега зеркало рабочее. Например:
– mega market link
– актуальная ссылка на мегу 2025
– сайт мега вход
Эти адреса позволяют осуществить вход, но одновременно появляются фейковые версии.
# Как найти актуальную ссылку?
Пользователи часто вводят запросы:
– актуальная ссылка мега сегодня
– mega darknet mirror
– mega darknet market link
Нужно помнить: мега маркет ссылка всегда доступен через Tor Browser, а не через обычные браузеры.
# Риски поддельных сайтов
Запросы вроде мега ссылка телеграм часто ведут к мошенническим сайтам. Такие ресурсы имитируют дизайн оригинала. Чтобы не попасться:
– Проверяйте mega sb.
– Используйте только мега зеркало рабочее.
– Избегайте клирнет-версий.
# Telegram и ссылки
Популярен запрос мега ссылка телеграм. В Telegram действительно можно найти mega darknet market link, но риск нарваться на фейковые каналы велик.
# Как зайти на мегу?
Чтобы получить вход на мегу, нужно:
1. Запустить Tor Browser.
2. Ввести мега ссылка тор.
3. Пройти регистрацию.
# Популярные ключи 2025
Сегодня особенно востребованы:
– мега зеркало 2025
– mega darknet mirror
– мега сайт даркнет
Эти темы показывают, что пользователи ищут рабочие зеркала.
# Заключение
Мега даркнет маркетплейс остаётся крупнейшей площадкой даркнета в последние годы. Но каждое использование связан с угрозой.
Thanks for the article https://angelladydety.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=37404 .
дизайнерская мебель купить интернет магазин дизайнерская мебель купить интернет магазин .
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
Thanks for the article https://www.example3.com/domain/prom.ua .
купить диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой .
a recommendation from someone you trust before you buy any bupropion benefits when you find a great deal wellbutrin anxiety
купить диплом в киеве недорого купить диплом в киеве недорого .
пленка самоклеющаяся прозрачная защитная пленка самоклеющаяся прозрачная защитная .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Проверьте наш сайт и узнайте о подходах к экологическому и зелёному строительству.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Капельный метод лечения запоя, это значимый этап в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Интравенозное введение помогает выведению токсинов, нормализует психоэмоциональное состояние и поддерживает функции организма. После процедуры необходимо помнить несколько советов. помощь нарколога Во-первых, важно соблюдать указаниям нарколога и не прекращать лечение алкоголизма. Реабилитация является длительным и трудоемким. Кроме того, уделите внимание профилактику возврата к запою: избегайте триггеров, которые могут вызвать новый запой.
Сегодня проблема зависимости становится всё актуальнее. Если вы или ваши близкие испытывают трудности с зависимостью, не нужно стыдиться. Вызов нарколога анонимно в Туле является значимым этапом на пути к избавлению от зависимости. На сайте site;com предоставляется возможность получить консультацию нарколога, что гарантирует полную конфиденциальность и профессиональный подход.Лечение зависимостей и реабилитация неизменно требуют компетентного подхода. В специализированной наркологической клинике предлагаются различные услуги, включая психотерапию и поддержку специалистов. Вызов специалиста на дом позволит создать комфортную обстановку для пациента, что особенно актуально в кризисных ситуациях. Не откладывайте помощь на потом, обратитесь за анонимной помощью уже сегодня!
Thanks for the article https://humans.net/post/74550 .
Алкоголизм: лечение в домашних условиях становится актуальным. Основные этапы состоят из домашней детоксикации и помощи при запое. Как начать процесс лечения? Важно получить поддержку от близкихкоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психологическая поддержка и традиционные средства могут стать полезным дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы для трезвости и методы отказа от спиртного помогут развить правильное отношение к алкоголю. narkolog-tula020.ru Важно помнить о реабилитации дома, которая включает психологическую помощь и меры по предотвращению повторного срыва. Что делать, чтобы бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с определения конкретной цели и поиска мотивации. Главное – это поддержка и желание изменить свою жизнь.
Промокод 1xBet при регистрации только один, это: https://gasaquatek.ru/themes/pgs/1hbet_promokod_besplatno.html используйте его чтобы получить приветственный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130).
Детоксикация организма после алкоголя в домашних условиях – важный процесс‚ что особенно актуально для жителей Тулы‚ страдающих от проблем с алкоголем. Комплексный подход является ключевым в лечении запоя‚ включая очищение организма и восстановление здоровья печени. лечение запоя тула Симптомы похмелья могут быть крайне неприятными: головная боль‚ тошнота‚ усталость. Поэтому домашние методы‚ такие как народные средства‚ могут оказать значительное облегчение. Например‚ настои из трав‚ имбирь с медом способствуют восстановлению сил. Тула предлагает различные альтернативные методы лечения‚ включая программы по лечению алкоголизма. Важно помнить‚ что после детоксикации необходима дальнейшая поддержка для успешного восстановления после алкоголя.
Harika bir yazı olmuş, teşekkürler. Özellikle Bursa’nın yoğun trafiğinde neyle karşılaşacağımız belli olmuyor. Olası bir durumda elimde kanıt olması için kaliteli bir bursa araç kamerası almayı düşünüyorum. Bu yazı karar vermemde çok yardımcı oldu.
Избавление от алкогольной зависимости в Туле — важный шаг на пути к алкогольной зависимости. Борьба с алкоголизмом начинается с программы детоксикации, которая помогает организму очищаться от токсинов. Необходимо получить медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме, чтобы избежать алкогольный синдром и другие осложнения . narkolog-tula020.ru После процесса детоксикации рекомендуется пройти реабилитацию , где пациент получает поддержку психолога и помощь при отказе от алкоголя. Анонимные алкоголики становятся опорой на этом пути . Программы восстановления включают рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Адаптация в обществе после лечения и помощь родных играют ключевую роль в мотивации к трезвости .
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Узнайте больше перейдя на наш каталог решений и узнайте о зеленых домах, экодомах и установке солнечных панелей.
Thanks for the article https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/1095361/The-RybachOK-website-is-a-reliable-choice-for-everyone?btwaf=12835090 .
купить аттестат за 11 класс с печатью купить аттестат за 11 класс с печатью .
Лечение запоя капельницей на дому: противопоказания и потенциальные осложнения (Тула) Алкогольная зависимость является значительной проблемой, нуждающейся в профессиональном вмешательстве. Все чаще люди обращаются к услугам нарколога на дому для борьбы с запоем. Эффективным методом является инфузионная терапия, предполагающая использование капельницы для выхода из запоя. Капельница способствует восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса, улучшает общее самочувствие пациента и облегчает симптомы абстиненции. Однако важно помнить о противопоказаниях к этой процедуре. Например, наличие аллергии на компоненты растворов, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания или острые инфекционные процессы могут стать основанием для отказа в проведении капельницы. Также могут возникнуть осложнения, такие как тромбофлебит, инфицирование вены или аллергические реакции. Таким образом, консультация нарколога перед началом лечения алкоголизма на дому является необходимостью. Безопасность процедуры зависит от квалификации специалиста и соблюдения всех рекомендаций. Услуги нарколога на дому в Туле позволяют получить медицинскую помощь в комфортных условиях, а реабилитация от запоя может быть более эффективной при правильном подходе.
купить аттестат 11 класс москва купить аттестат 11 класс москва .
Приобрести диплом можно используя официальный портал компании. magnat-matras.ru/forum/user/58002
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kak-vybrat-pletenku-po-testu-spinninga-Sovety-ehkspertov-01-13 .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на портфолио объектов и ознакомьтесь с ландшафтным дизайном и террасированием участков.
Thanks for the article https://cardsfm.ru/metizy-dlya-stroitelstva-i-proizvodstva-kak-vybrat-i-zakazat-v-sankt-peterburge/
купить диплом в уфе с реестром https://bakinsky-dvorik.ru/communication/forum/user/206872 .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Коли хочеться втекти з міста — ось добірка місць для релаксу на природі.
Thanks for the article https://projectnoah.org/users/grom95 .
купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Откройте портфолио объектов и ознакомьтесь с эффективными дренажными системами и укреплением склона.
Мы предлагаем документы учебных заведений, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестаты гознак за 11 класс
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
аттестаты 10 11 класс купить аттестаты 10 11 класс купить .
Алкогольная зависимость важная трудность, с которой имеют дело множество жителей Тулы. Психологическая помощь играет ключевую роль в лечении алкоголизма . Медицинские учреждения предлагают программы детоксикации и реабилитацию зависимых , что включает в себя как медицинскую, так и психологическую помощь. вывод из запоя цена Семейная поддержка также важна , так как она способствует созданию доверительной атмосферы. Симптомы зависимости могут варьироваться, и своевременное обращение за помощью при запое может изменить жизнь к лучшему . Рекомендации по прекращению употребления алкоголя заключаются в поиске новых увлечений и замене алкогольных привычек на здоровые . Важно помнить, что первый шаг к выздоровлению заключается в обращении за помощью.
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Капельный метод лечения запоя, это необходимая мера в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Внутривенное введение помогает очищению организма от токсинов, улучшает психоэмоциональное состояние и поддерживает функции организма. После процедуры необходимо помнить несколько советов. помощь нарколога Первым делом, важно соблюдать указаниям нарколога и не прекращать лечение алкоголизма. Реабилитация является длительным и трудоемким. Кроме того, уделите внимание профилактику возврата к запою: избегайте триггеров, которые могут вызвать новый запой.
Алкогольная зависимость, это острая проблема, требующая экспертного вмешательства. Круглосуточная клиника предлагает помощь нарколога, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и лечение алкоголизма. Симптомы алкогольной зависимости могут варьироваться, от телесной зависимости до психологических расстройств; Клиническая detox-программа включает в себя очистку и реабилитацию от алкоголя, что позволяет вернуться к нормальной жизни после запоя. Консультация нарколога помогает определить степень зависимости и выбрать оптимальный метод лечения. Психотерапия при алкоголизме является необходимым этапом, предоставляя поддержку для зависимых. Тайное лечение алкоголизма гарантирует анонимность. Нарколог в Туле всегда готов оказать помощь, обеспечивая индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.}
Вызов нарколога на дом в Туле ? это комфортабельное и действенное решение для людей, испытывающих трудности с алкоголем. Круглосуточный нарколог предлагает профессиональную помощь, включая диагностику зависимости и лечение алкоголизма . Услуги нарколога на дому обеспечивают анонимное лечение и комфортные условия для пациента . Если требуется вывод из запоя, следует обратиться к опытному специалисту. Профессиональный нарколог проведет первичную консультацию, оценит здоровье пациента и разработает персонализированный план терапии. Семейная поддержка является ключевым аспектом в процессе восстановления.Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с посещением клиники . Круглосуточная наркологическая помощь обеспечивает возможность получения необходимой поддержки в любое время. Восстановление после запоя возможно благодаря комплексному подходу и вниманию к каждому пациенту .
I was recommended this web site by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such
detailed about my problem. You are wonderful! Thanks!
stroyexpertsochi.ru Загляните на наши материалы и получите информацию о ландшафтном дизайне и террасировании участка.
куплю куба дров недорого цена .
купить диплом о высшем образовании украины купить диплом о высшем образовании украины .
Прокапать от алкоголя на дому в Туле — это доступный метод помочь родным попавшим в зависимость. Лечение алкоголизма включает выведение из запоя в домашних условиях, что дает возможность лечиться в привычной обстановке. Капельницы от алкоголя может осуществляться с помощью медикаментовкоторые обеспечивают организм необходимыми веществами. Медицинская помощь в таких случаях необходима: услуги нарколога помогут правильно подобрать антиалкогольную терапию. Психологическая поддержка также нужна для успешного восстановления в восстановлении. Семейная терапия и социальная адаптация помогают в процессе возвращения к трезвой жизни. Профилактические меры и возвращение к нормальной жизни — ключевые моменты в восстановлении здоровья. Не забывайте, что здоровый образ жизни без алкоголя. На сайте narkolog-tula019.ru вы можете получить больше информации по лечению зависимости.
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Посетите портфолио объектов и узнайте о теплоизоляции, энергоэффективных окнах и дверях.
drenazh-na-glinistom-uchastke-spb.ru .
Thanks for the article https://www.palscity.com/post/1571653_one-of-jewelsay-s-standout-features-is-its-made-to-order-service-where-your-drea.html .
Thanks for the article https://ironway.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=11774 .
купить диплом по реестру купить диплом по реестру .
bannye-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Mega darknet market в последнее время продолжает оставаться одной из самых обсуждаемых площадок в даркнете. Пользователи регулярно ищут mega sb, мега зеркало рабочее и мега sb официальный сайт, чтобы получить доступ на мега маркетплейс.
# Что такое Мега?
Мега маркетплейс тор — это площадка, который дает доступ к даркнет-рынок. мега даркнет маркет стал популярен благодаря ассортименту. Но важно помнить: мега даркнет — это теневая платформа.
Cыллка ===> http://mindbodyhair.com/(используй ВиПиЭн)
# Почему нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде mega sb часто блокируются. Чтобы обойти это, используются мега зеркала. Например:
– mega market link
– актуальная ссылка на мегу 2025
– мега даркнет вход
Эти ссылки позволяют осуществить вход, но одновременно появляются поддельные сайты.
# Как найти актуальную ссылку?
Пользователи часто вводят запросы:
– мега зеркало 2025
– mega darknet mirror
– mega darknet market link
Нужно помнить: официальный сайт мега sb всегда доступен через Tor Browser, а не через клирнет.
# Риски поддельных сайтов
Запросы вроде мега sb зеркало часто ведут к фейкам. Такие порталы имитируют оформление оригинала. Чтобы не попасться:
– Проверяйте онион-домен.
– Используйте только актуальные ссылки на мегу.
– Избегайте клирнет-версий.
# Telegram и ссылки
Популярен запрос ссылки мега в тг. В Telegram действительно можно найти мега ссылки, но риск нарваться на поддельные ссылки велик.
# Как зайти на мегу?
Чтобы получить mega darknet market вход, нужно:
1. Скачать тор браузер.
2. Ввести мега ссылка тор.
3. Пройти авторизацию.
# Популярные ключи 2025
Сегодня особенно востребованы:
– мега зеркало 2025
– mega darknet mirror
– мега darknet
Эти запросы показывают, что пользователи ищут рабочие зеркала.
# Заключение
mega darknet market остаётся крупнейшей площадкой даркнета в 2025 году. Но каждый вход связан с риском.
рейтинг сервисов накрутки подписчиков в ТГ рейтинг сервисов накрутки подписчиков в ТГ.
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Исследуйте раздел услуг и ознакомьтесь с технологиями сейсмоустойчивого строительства и защиты от дождей.
аттестат об 11 классах купить аттестат об 11 классах купить .
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-msk007.ru
дом престарелых в москве
дрова цена .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
drenazh-na-glinistom-uchastke-spb.ru .
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-msk007.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
Thanks for the article https://substack.com/inbox/post/171804263
где можно купить аттестат 11 класс https://arus-diplom9.ru – где можно купить аттестат 11 класс .
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-msk007.ru
дом престарелых
Joycasino
казино джой
casino joy
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Откройте материалы и познакомьтесь с полным спектром услуг по строительству и ремонту домов.
активная аудитория для ТГ активная аудитория для ТГ.
Если вам нужно провести раскопки на участок земли в Туле, обращение к профессиональным услугам может значительному упрощению задачи. Компания narkolog-tula020.ru предлагает разнообразные земляных работ, включая раскопки участка для возведения зданий или ландшафтного дизайна. Мы гарантируем высокое качество выполнения услуг по подготовке участка, а также создание скважин для питьевой воды. Аренда техники дает возможность нам оперативно проводить любые садовые работы, а опытные специалисты помогут вам с выбором подходящего грунта. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете не только гарантию надежности, но и профессионализм в осуществлении всех задач. Свяжитесь с нами, и мы с радостью поможем откопать все необходимое на вашем участке!
Капельница от запоя – это популярным способом лечения алкоголизма, используемый внедряется в медицинских учреждениях на территории Тулы для очистки организма. Круглосуточная помощь дает возможность быстро избавиться симптомы запоя. Тем не менее важно помнить о возможных побочных эффектах, таких как аллергические реакции и нарушение водно-солевого баланса. вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на наш сайт и ознакомьтесь с современными методами террасирования участка и укрепления склона.
Thanks for the article https://www.pubpub.org/user/polina-zuk .
живые подписчики бесплатно ТГ живые подписчики бесплатно ТГ.
Лечение запоя — важная задача для многих людей. Признаки запойного состояния включают зависимость от алкогольных напитков как физического, так и психологического характера. Лечение запоя может быть как медикаментозной, так и психотерапевтической. Первым шагом является детоксикация организма , которая способствует удалению токсинов. Необходимо искать помощь при алкоголизме, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий . narkolog-tula020.ru Стационарное лечение алкоголизма предлагает реабилитационные программы, где пациенты получают полную поддержку . Процесс восстановления после запоя требует значительных усилий и времени, и здесь поддержка близких играет ключевую роль. Советы по лечению запоя могут быть полезны : необходимо контролировать состояние здоровья, избегать триггеров и регулярно обращаться к специалисту. Профилактика запоя включает в себя здоровый образ жизни и осознание своих проблем .
купить аттестат 11 класс москва купить аттестат 11 класс москва .
Thanks for the article https://substack.com/inbox/post/171804263
C.R.I. PUMPS CTC-40/160 Горизонтальный консольно-моноблочный насос 4 кВт, 3×380/660 В
Кто родился в этот день История религий и их роль в формировании цивилизаций Узнайте о духовном наследии человечества.
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Ознакомьтесь с наш сайт и получите рекомендации по строительству и ремонту домов в Сочи.
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk008.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
пансионат для лежачих москва
pansionat-msk008.ru
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
пансионат для престарелых людей
pansionat-msk008.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
Электромонтажные работы Монтаж электропроводки: Надежный монтаж электропроводки в квартирах, домах и офисах
Bonus pills added if you metoprolol er 50 mg being offered by many sites, make it easy to shop. metoprolol max dose
تُعرف 888starz بأنها وجهة مميزة لعشاق الألعاب والمراهنات. تأسست هذه المنصة بهدف توفير تجربة فريدة للمستخدمين . تشمل قائمة الألعاب في 888starz العديد من الخيارات المثيرة .
تضم 888starz مجموعة كبيرة من الألعاب مثل البوكر والروليت . يتم تحديث الألعاب بشكل دوري لتلبية توقعات اللاعبين. تتوفر مكافآت جذابة للاعبين الجدد والمستمرين.
توفر المنصة خيارات متنوعة للمراهنات على الرياضات المختلفة . تتميز الخدمة بسرعة تحديث النتائج . يمكن للاعبين الاستفادة من نصائح الخبراء المتاحة على 888starz.
قسم الأمان والدعم. يتم توفير دعم فني متاح على مدار الساعة . يعتبر رضا العملاء هدفًا رئيسيًا لـ 888starz.
تسجيل الدخول 888starz https://888starz.red/
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Узнайте больше на материалы и узнайте, как правильно выбрать материалы для влажного климата.
https://www.trub-prom.com/catalog/truby_srednego_diametra/256/
Работа для девушек в Тюмени Эскорт работа Тюмень: Элегантный мир роскоши и возможностей ждет тебя. Общение с интересными и успешными людьми, путешествия и достойная оплата. Конфиденциальность и безопасность – наши главные ценности. Стань частью эксклюзивного общества!
правильный дренаж вокруг дома .
Капельница для лечения запоя – это значимый метод лечение алкоголизма, который находит свое применение в наркологических клиниках Тулы. Процедура детоксикации способствует быстрому восстановлению организма после продолжительного употребления алкоголя. Время процедуры обычно варьируется от одного до трех часов, в зависимости от индивидуальных потребностей и интенсивности запойного состояния. лечение запоя тула Симптомы алкогольного запоя включает в себя интенсивные головные боли, тошноту, обильное потоотделение и тревогу и беспокойство. Помощь врачей в виде капельницы даёт возможность быстро облегчить похмельные симптомы, вводя жизненно важные вещества для нормализации водно-электролитного баланса и выведения токсинов из организма. Стоимость лечения запоя в Туле варьируется в зависимости от обраной лечебной организации и количества требуемых процедур. Прием у нарколога поможет выработать оптимальный план лечения, включая реабилитацию после запоя. Эффективность капельницы подтверждается многими положительными отзывами пациентов, что делает ее востребованным способом борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью.
строительство коттеджа с отделкой под ключ Следуйте строительство коттеджа с отделкой под ключ и обеспечьте удобство вашего объекта.
Прокапаться после запоя в Туле: эффективные методы помощи Запой является значительной проблемой‚ требующей внимательном подходе. Симптомы похмелья включают в себя головную боль‚ тошноту и общую слабость. Выход из запоя обычно включает детоксикацию организма‚ что важно. Важно получить медицинскую помощь для безопасного выхода из состояния запоя. Клиника реабилитации предоставляет широкий спектр услуг по лечению алкоголизма‚ в т.ч. психотерапию при алкоголизме и поддержку родственников. Антиалкогольные препараты способствуют справится с зависимостью. Важно учитывать психологические аспекты зависимости‚ и профессионалы готовы помочь. На сайте narkolog-tula021.ru где представлена информацию о способах реабилитации после употребления алкоголя. Как же справиться с запоем? Процедура капельницы — один из самых действенных методов‚ чтобы восстановить организм и положить начало новому‚ здоровому образу жизни.
Thanks for the article https://bandori.party/user/316687/Grom95/ .
Zombie vs Dao Zhang online Az
https://digital-downloads-app.com/
В городе Тула доступна помощь от алкоголизма в клиниках‚ предлагающих детоксикацию и лечение зависимости. Лечебные программы включают кодирование и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме. Важно также получить психологическую поддержку и участвовать в группах поддержки для зависимых, таких как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Восстановление после запоя требует всестороннего подхода: консультации нарколога помогут создать персонализированный план. Важно помнить о профилактике рецидива и следуйте советам по отказу от спиртного. Подробности на сайте narkolog-tula021.ru;
10 Boost Hot TR
Zombie vs Dao Zhang
Энергоэффективность – важный фактор при возведении современных зданий. Мы рады, что наша компания работает по стандартам энергоэффективности.
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-msk009.ru
дом престарелых
источник Читайте источник и получите актуальные сведения.
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-msk009.ru
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-msk009.ru
частный пансионат для престарелых
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
бесплатно накрутить подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно накрутить подписчиков в ТГ.
Hello there, You have done a great job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend
to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from
this site.
столбовая мачтовая трансформаторная подстанция https://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit2.ru .
геопластика участка сочи Используйте геопластику участка Сочи и получите красивый ландшафт.
Thanks for the article http://www.ivedu.ru/forum/viewthread.php?forum_id=18&thread_id=46836 .
Thanks for the article https://allaboutschool.activeboard.com/t69784064/alyakaco/?page=1#lastPostAnchor .
kupit-drova-v-chekhove-365.ru .
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
Thanks for the article https://substack.com/inbox/post/171804263
https://igrozavod.ru/
купить аттестат 11 класс 2013 купить аттестат 11 класс 2013 .
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаембыстро купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Данный документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже с использованием специальных приборов. Решите свои задачи быстро и просто с нашими дипломами- xtrainkom.com/employer/aurus-diplomany
stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с наши материалы и получите практические рекомендации по строительству домов под ключ.
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk007.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
Howdy! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell
you I genuinely enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you suggest
any other blogs/websites/forums that go over
the same subjects? Thank you!
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-msk007.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 .
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-tula007.ru
пансионат для лежачих тула
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-msk007.ru
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Посетите наши проекты и изучите практические советы по строительству, отделке и благоустройству домов.
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
pansionat-tula007.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
Мы предлагаем документы университетов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом университета:
купить аттестаты за 11 класс отзывы цена
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-tula007.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
In relation to a meal, should euthyrox vs levothyroxine to start feeling better levothyroxine warnings
Работа для девушек в Тюмени Работа танцовщицей в Тюмени: Раскрой свой талант на танцполе! Высокий доход, возможность самовыражения и восхищенные взгляды. Мы предлагаем комфортные условия и полную поддержку.
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу екатеринбург
интернет по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу екатеринбург
лечение зависимостей в москве http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-14.ru/ .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с наши проекты и ознакомьтесь с современными идеями ландшафтного дизайна и террасирования.
ежедневные прогнозы на спорт бесплатно https://www.prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
888starz ?? ???? ????? ???? ?????? ?????? ?? ??????? . ??? ??? ???? ?? ????? ?????? ???? ?? ?????? ??????? ?? .
??? ????? 888starz ??????? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???????. ???? ??????? ??????? ?? 888starz ?? ?? ????? ???? ???????? .
????? 888starz ??????? ?????? ?????????? . ???? 888starz ??? ????? ?????? ????????? ?? ?? ?????? .
??????? ???????? ????? ?? ???? ??????? ????? ??? ???????? . ???? ??? ???????? ?? ????? ????? ????? ????? ?????? ?? ?????????? .
برنامج مراهنات 888 https://888starz-africa.pro/
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really recognise what you are talking about!
Bookmarked. Kindly also talk over with my web site =).
We can have a hyperlink change arrangement between us
точные прогнозы на спорт бесплатно http://prognozy-na-sport-8.ru .
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Ефрем и я обожаю смотреть онлайн мультсериал Южный Парк на сайте https://southpark-online.info
Там много интересных серий, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь!
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на раздел “Отзывы клиентов” и узнайте о зеленых домах, экодомах и установке солнечных панелей.
частный пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-msk008.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
Всемогущий вам в судьи
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
сколько стоит аппарат узи цена сколько стоит аппарат узи цена .
блочная трансформаторная подстанция http://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru .
Thanks for the article https://substack.com/inbox/post/171804263
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula008.ru
пансионат для пожилых людей
купить диплом с реестром красноярск купить диплом с реестром красноярск .
пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-msk008.ru
пансионат с медицинским уходом
прогнозы экспертов на хоккей прогнозы экспертов на хоккей .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Sajt-Rybachok-Polnyj-assortiment-rybolovnyh-tovarov-01-13 .
Professional ac clean, more details here ac clean
https://digital-downloads-app.com/
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula008.ru
пансионат после инсульта
казино vavada
прогноз на сегодняшний хоккей https://www.prognozy-na-khokkej.ru .
Thanks for the article https://avensis.at.ua/forum/28-10972-1 .
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем новгороде где купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем новгороде .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Посетите наш сайт и получите советы по строительству коттеджей и домов под ключ.
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk008.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
купить аттестат за 11 классов в оренбурге купить аттестат за 11 классов в оренбурге .
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula008.ru
дом престарелых в туле
drenazh-na-glinistom-uchastke-spb.ru .
Спелеологія розкриває таємниці підземного світу. Які відкриття зроблені останнім часом? Дізнайтеся більше на геологічній платформі.
подключить домашний интернет в екатеринбурге
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
интернет по адресу дома
накрутка подписчиков с активностью накрутка подписчиков с активностью.
ктп киосковая трансформаторная подстанция https://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit1.ru .
try here coinbase exchange
подключить интернет екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
домашний интернет в екатеринбурге
аппарат узи стоимость http://kupit-uzi-apparat25.ru/ .
нажмите заблокировать канал телеграм
подключение интернета екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с наши материалы и получите максимум информации о фундаменте, бетонных и монолитных конструкциях.
дрова уложенные купить .
Получите помощь юриста онлайн или по телефону прямо сейчас!
составляет ключевую сферу. Отсутствие информации о своих правах может вызвать много проблем.
Первенствующий вопрос, который необходимо рассмотреть, — это доступ к юридическим консультациям. Сегодня многие юристы предлагают услуги онлайн. Такой подход значительно облегчает получение правовой помощи.
Далее мы обсудим, как правильно выбрать юриста. Важно, чтобы юрист имел хорошие рекомендации и подходящий опыт. Игнорирование этих нюансов может обернуться значительными потерями.
Третий аспект, который следует рассмотреть, — это стоимость юридических услуг. Стоимость может зависеть от многих факторов, включая опыт специалиста и специфику вопроса. Необходимо детально обговорить все финансовые аспекты до начала сотрудничества.
Важно осознавать, что юрист несет ответственность за свои действия. Отсутствие должного уровня компетенции может иметь серьезные последствия для клиента. Выбор подходящего юриста критически важен для достижения положительных результатов.
???? 888starz ????? ????? ?? ????? ?? ???? ???????? . ????? ????????? ?????? ????????? ?? 888starz.
??? ????? 888starz ??????? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???????. ????? ?????? ??? ????? ??????? ??????? ?????? ?? ??????? ???????.
????? 888starz ??????? ?????? ?????????? . ??? ??????? ?? ?????? ???????? ????? ????? .
??????? ???????? ????? ?? ???? ??????? ????? ??? ???????? . ????? ??? ???????? ?????? ????? ???????? ??? ???? 888starz .
888starz iphone https://888starz-africa.pro/apk/
накрутить подписчиков телеграм накрутить подписчиков телеграм
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Посетите раздел услуг и ознакомьтесь с технологиями безопасного и комфортного дома для семьи.
монтаж дренажной системы вокруг дома .
дрова колотые с доставкой .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Покупка диплома, который подтверждает окончание института, – это выгодное решение. Купить диплом ВУЗа: mansanetwork.nu/read-blog/1974_kupit-diplom-o-vysshem.html
дом престарелых
pansionat-tula009.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых
купить аттестат 11 кл в спб купить аттестат 11 кл в спб .
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-msk009.ru
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
Читать далее kraken ссылка
накрутка тг для продвижения бизнеса накрутка тг для продвижения бизнеса
??? ???? 888starz ????? ?? ???? ??????? ?? ???? ??????? ???????????. ????? ????????? ?????? ????????? ?? 888starz.
??? ????? 888starz ??????? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???????. ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ?? ???????? ??? ?? ??? ??????? ?????????? ???????? .
????? 888starz ??????? ?????? ?????????? . ????? ???????? ??? 888starz ?????? ???? ???? ????.
????? ????????? ?? ?????? ????? ??? ??????? ?? 888starz. ????? ?????? ????????? ???? ????? 888starz ???? ???? ?? ????????.
888starz تسجيل دخول https://888starz-africa.pro/
купить диплом в кургане занесением в реестр купить диплом в кургане занесением в реестр .
пансионат для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula009.ru
пансионат с медицинским уходом
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Изучите портфолио объектов и получите рекомендации по строительству коттеджей и домов под ключ.
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-msk009.ru
дом престарелых в москве
Everyone loves it when people come together and share ideas.
Great website, keep it up!
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-tula009.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
pansionat-msk009.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
провайдеры интернета по адресу екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this
blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
источник Посетите источник и обеспечьте важные рекомендации.
провайдеры в екатеринбурге по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
подключить интернет екатеринбург
???? 888starz ????? ????? ?? ????? ?? ???? ???????? . ??? ??? ???? ?? ????? ?????? ???? ?? ?????? ??????? ?? .
???? ?????? ??????? ?????? ???? ??? ???????? ?????? ??? . ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ?? ???????? ??? ?? ??? ??????? ?????????? ???????? .
????? 888starz ??????? ?????? ?????????? . ????? ???????? ??? 888starz ?????? ???? ???? ????.
???????? ??? ???? ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ??????? ????? . ????? ?????? ????????? ???? ????? 888starz ???? ???? ?? ????????.
تنزيل برنامج 888 https://888starz-africa.pro/apk/
провайдеры домашнего интернета екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
провайдер по адресу екатеринбург
Je trouve genial le casino TonyBet, ca offre un univers de jeu unique. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, avec des machines a sous modernes. Les agents sont reactifs, offrant un excellent suivi. Les retraits sont rapides, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. En gros, TonyBet c’est du solide pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs, le design est attractif, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet Г© confiГЎvel|
Залишайтеся на зв’язку з нами через наш сайт, щоб бути в курсі нових досягнень і розкладу майбутніх матчів. Ми завжди раді новим фанатам!
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Откройте раздел услуг и ознакомьтесь с ландшафтным дизайном, благоустройством участка и геопластикой.
все прогнозы на спорт http://www.prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Исследуйте наш сайт и узнайте, как выбрать оптимальные материалы для морского и влажного климата.
https://t.me/PROAUTO159 Китайские автомобили – это уже не просто участник рынка, а его активный формирователь. Им удалось переосмыслить автомобильную индустрию, предложив миру новые стандарты качества, технологий и дизайна. От амбициозных стартапов до крупных концернов, китайский автопром демонстрирует готовность к инновациям и адаптации к требованиям глобального рынка.
прогнозы на хоккей на сегодня от профессионалов прогнозы на хоккей на сегодня от профессионалов .
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
психиатрическая медицинская помощь
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
психиатр на дом для пожилого
drenazh-na-glinistom-uchastke-spb.ru .
kupit-drova-v-ramenskom-365.ru .
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-tula007.ru
пансионат после инсульта
доставка цветов в москве Рынок цветов в Москве поражает своим разнообразием. Здесь можно найти как классические розы и тюльпаны, так и экзотические орхидеи и стрелиции. Выбор зависит только от ваших предпочтений и бюджета. Доставка цветом цветов в Москве: Яркие Композиции для Ваших Близких
купить дипломы о высшем купить дипломы о высшем .
купить аттестат за 11 класс спб отзывы купить аттестат за 11 класс спб отзывы .
Купить диплом ВУЗа!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро и выгодно приобрести диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Наш документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при помощи профессионального оборудования. Достигайте цели максимально быстро с нашим сервисом- schsocial.com/read-blog/11862_diplom-kupit-moskva.html
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Загляните на наш сайт и изучите подходы к террасированию участка и ландшафтному дизайну.
drenazh-uchastka-vokrug-doma-spb.ru .
частный пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula007.ru
пансионат для престарелых
накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал
детский психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
платный психиатр
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I
find this matter to be really something which I think I would never understand.
It seems too complex and extremely broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try
to get the hang of it!
https://vornikovbouquets.ru/ Магазины цветов предлагают широкий выбор букетов, композиций и сопутствующих товаров, а также профессиональные консультации флористов. Доставка цветов на дом в Москве: Комфорт, Удобство и Экономия Драгоценного Времени
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-tula007.ru
частный дом престарелых
Блок сервопривода АКПП ISM Mecredes Мерседес Для точной диагностики неисправностей блока сервопривода ISM необходимо специализированное оборудование и опытные специалисты. Ремонт данного узла – сложная задача, требующая глубоких знаний и навыков. Доверьте эту работу профессионалам, чтобы гарантировать качественный результат и долговечность вашего автомобиля. Блок сервопривода АКПП ISM Mercedes/Мерседес: Оригинальные Запчасти или Аналоги?
купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр .
Incredible points. Solid arguments. Keep up the amazing work.
прогноз на хоккей сегодня от профессионалов бесплатно https://prognozy-na-khokkej.ru/ .
интересный блог о строительстве Читайте интересным блогом о строительстве и обеспечьте важные советы для вашего дома.
дренаж дома .
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
купить обложку аттестата за 11 купить обложку аттестата за 11 .
Je suis completement seduit par Azur Casino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. Le catalogue est vaste et diversifie, incluant des slots dynamiques. Les agents sont d’une efficacite remarquable, disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est une pepite pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec soin, ce qui rend chaque session memorable.
gГ©ant casino centre azur hyeres|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Banzai Casino, ca offre une energie de jeu captivante. La gamme de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous ultra-modernes. Le service d’assistance est exemplaire, offrant des solutions rapides et claires. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient apprecies. En resume, Banzai Casino offre une experience exceptionnelle pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! De plus le site est concu avec dynamisme, ajoutant une touche d’elegance et d’energie.
avis banzai slots|
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1вин
http://californiarpn2.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?t=382
J’apprecie enormement Betclic Casino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Le catalogue de jeux est incroyablement riche, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. En resume, Betclic Casino offre une experience de jeu remarquable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et intuitive, facilite chaque session de jeu.
parrainage betclic|
провайдер интернета по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
провайдеры в красноярске по адресу проверить
تعتبر 888starz واحدة من أبرز المنصات في مجال المراهنات . انطلقت هذه المنصة لتلبية احتياجات اللاعبين المحترفين والهواة . يمكن للمستخدمين الاستمتاع بتجارب لعب متنوعة على 888starz.
قسم الألعاب. تتميز كل لعبة برسومات عالية الجودة . تقدم المنصة مسابقات دورية حيث يمكن للاعبين استعراض مهاراتهم .
تتيح 888starz للمستخدمين المراهنة على الأحداث الرياضية الكبرى. تتميز الخدمة بسرعة تحديث النتائج . يمكن للاعبين الاستفادة من نصائح الخبراء المتاحة على 888starz.
تعتمد 888starz تقنيات متقدمة لحماية بيانات المستخدمين . يمكن للمستخدمين التواصل مع فريق الدعم عبر الدردشة الحية أو البريد الإلكتروني . يعتبر رضا العملاء هدفًا رئيسيًا لـ 888starz.
888 ستارز https://888starz.red/
Searching for local Siding contractors? We shortlist crews with proper licensing, brake-metal skills, and flashing know-how. Protect your home and curb appeal.
ландшафтный дизайн с террасированием Сочи Следуйте ландшафтный дизайн с террасированием Сочи и обеспечьте удобство в эксплуатации.
What are the real benefits with using amlodipine gingival hyperplasia are unbelievably low they are probably counterfeit. amlodipine brand
Приобрести диплом любого университета поможем. Купить диплом магистра в Томске – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-magistra-v-tomske
интернет по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу красноярск
I’m impressed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both
equally educative and amusing, and without a doubt, you have hit
the nail on the head. The problem is something too few people
are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy
that I came across this during my hunt for something relating to this.
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Зайдите на наш сайт и узнайте о материалах, устойчивых к морскому и влажному климату.
реабилитация зависимых http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-14.ru/ .
I’m extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout
on your blog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself?
Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it is rare to see a great blog like this one today.
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
Definitely believe that which you stated. Your favorite justification seemed to be on the web the easiest thing to be aware of.
I say to you, I certainly get irked while people think
about worries that they plainly don’t know about. You
managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people can take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
J’adore le casino TonyBet, il est carrement un plaisir de jeu constant. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, incluant des slots ultra-modernes. Le personnel est tres competent, disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont rapides, occasionnellement il pourrait y avoir plus de promos. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet vaut vraiment le coup pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que, le site est facile a naviguer, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet promo|
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Откройте материалы и ознакомьтесь с современными подходами к укреплению склона и ландшафтному дизайну.
Уточните стоимость монтажа забора из евроштакетника для вашего участка. Работаем без предоплаты.
купить диплом в луцке http://www.educ-ua5.ru .
купить аттестат 11 классов красноярск купить аттестат 11 классов красноярск .
кашпо для цветов напольное высокое купить кашпо для цветов напольное высокое купить .
تُعرف 888starz بأنها وجهة مميزة لعشاق الألعاب والمراهنات. تأسست هذه المنصة بهدف توفير تجربة فريدة للمستخدمين . يمكن للمستخدمين الاستمتاع بتجارب لعب متنوعة على 888starz.
تحتوي 888starz على مجموعة متنوعة من الألعاب التي تناسب جميع الأذواق . تتمتع الألعاب بتجربة مستخدم سلسة ومرنة . تقدم المنصة مسابقات دورية حيث يمكن للاعبين استعراض مهاراتهم .
قسم المراهنات الرياضية. تتميز الخدمة بسرعة تحديث النتائج . يتاح للمستخدمين المشاركة في مراهنات حية .
الأمان هو أولوية قصوى في 888starz . يمكن للمستخدمين التواصل مع فريق الدعم عبر الدردشة الحية أو البريد الإلكتروني . تسعى 888starz إلى تحسين تجربة المستخدم باستمرار .
لعبة 888 https://888starz.red/
Лайфхаки для комфортних мандрівок: що варто знати перед поїздкою? Відповідь тут: деталі!
Thanks for the article http://brigantina.unoforum.pro/?1-12-0-00006117-000-0-0-1721657409 .
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1вин
https://fskolioz.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00000761-000-0-0-1628154252
https://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Откройте раздел “Отзывы клиентов” и ознакомьтесь с секретами строительства дома под ключ и коттеджа с отделкой.
купить диплом без внесения в реестр купить диплом без внесения в реестр .
купить диплом магистра купить диплом магистра .
дренаж на глинистом участке .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в волжском http://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр .
Thanks for the article https://substack.com/inbox/post/171804263
ближайшие ставки на спорт http://prognozy-na-sport-8.ru .
تُعرف 888starz بأنها وجهة مميزة لعشاق الألعاب والمراهنات. بدأت 888starz رحلة نجاحها بتقديم خدمات متنوعة. يمكن للمستخدمين الاستمتاع بتجارب لعب متنوعة على 888starz.
قسم الألعاب. يتم تحديث الألعاب بشكل دوري لتلبية توقعات اللاعبين. تقدم المنصة مسابقات دورية حيث يمكن للاعبين استعراض مهاراتهم .
توفر المنصة خيارات متنوعة للمراهنات على الرياضات المختلفة . تقدم 888starz تحليلات دقيقة لمساعدة اللاعبين في اتخاذ قراراتهم. يمكن للاعبين الاستفادة من نصائح الخبراء المتاحة على 888starz.
قسم الأمان والدعم. يتلقى اللاعبون المساعدة السريعة لحل أي مشاكل قد تواجههم. تعمل المنصة على تطوير خدماتها بناءً على ملاحظات اللاعبين .
starz888 starz888.
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Зайдите на наш каталог решений и ознакомьтесь с секретами строительства дома в Сочи и Краснодарском крае.
детский психиатр на дом в москве
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
психиатрическая помощь на дому
наркологическая клиника наркологическая клиника .
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, ca offre une aventure palpitante. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, comprenant des jeux innovants. Les agents sont toujours disponibles, avec des reponses precises et utiles. Les gains arrivent vite, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Dans l’ensemble, AllySpin est une plateforme de choix pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide, renforcant l’immersion.
allyspin vstupnГ bonus|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betclic Casino, ca offre une experience de jeu electrisante. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, incluant des slots dernier cri. Le support est d’une reactivite exemplaire, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Betclic Casino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec elegance, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
betclic inscription|
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-tula008.ru
пансионат для пожилых людей
как работает накрутка подписчиков в тг смотрите здесь как работает накрутка подписчиков в тг смотрите здесь
психиатрическая медицинская помощь
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
частная психиатрическая помощь
купить аттестат 11 класс купить аттестат 11 класс .
платная психиатрическая клиника
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
вызов психиатра на дом в москве
комплексная трансформаторная подстанция transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru .
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-tula008.ru
дом престарелых в туле
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru Исследуйте галерею выполненных работ и получите экспертные советы по строительству коттеджа с отделкой под ключ.
подключение интернета по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры по адресу
تُعرف 888starz بأنها وجهة مميزة لعشاق الألعاب والمراهنات. انطلقت هذه المنصة لتلبية احتياجات اللاعبين المحترفين والهواة . تشمل قائمة الألعاب في 888starz العديد من الخيارات المثيرة .
تحتوي 888starz على مجموعة متنوعة من الألعاب التي تناسب جميع الأذواق . يتم تحديث الألعاب بشكل دوري لتلبية توقعات اللاعبين. تقدم المنصة مسابقات دورية حيث يمكن للاعبين استعراض مهاراتهم .
تعتبر المراهنات الرياضية جزءًا أساسيًا من 888starz . تقدم 888starz تحليلات دقيقة لمساعدة اللاعبين في اتخاذ قراراتهم. يمكن للاعبين الاستفادة من نصائح الخبراء المتاحة على 888starz.
تضمن المنصة أمان المعاملات المالية وسرية المعلومات. يتلقى اللاعبون المساعدة السريعة لحل أي مشاكل قد تواجههم. يعتبر رضا العملاء هدفًا رئيسيًا لـ 888starz.
888starz تسجيل دخول https://888starz.red/
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula008.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
купить аппарат узи цена купить аппарат узи цена .
узнать провайдера по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу красноярск
Excellent goods from you, man. I have keep in mind your stuff previous to
and you’re just too magnificent. I actually like
what you have bought here, certainly like what you are saying and the way in which during which
you are saying it. You make it entertaining and you
still take care of to keep it wise. I can not wait to learn much
more from you. This is actually a terrific site.
интернет провайдеры красноярск по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
купить диплом с проводкой меня купить диплом с проводкой меня .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Погрузитесь в наш сайт и ознакомьтесь с современными решениями для ландшафтного дизайна и террасирования.
узи аппарат цена новый http://kupit-uzi-apparat25.ru/ .
силовые трансформаторные подстанции https://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit1.ru/ .
купить диплом образование киеве купить диплом образование киеве .
Hi, this weekend is nice in support of me, because this moment i am reading this wonderful informative article here at my house.
gemini
живые пользователи и накрутка подписчиков тг канал живые пользователи и накрутка подписчиков тг канал
Порно смотреть Порно Порно смотреть Секс советы Порно картинки Порно видео онлaйн без регистрaции Секс на камеру Эротика Бесплатное порно видео Секс шоп
дрова в мешках купить с доставкой .
скачать мостбет официальный скачать мостбет официальный
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
drova-suhie-sergiev-posad.ru .
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр http://www.arus-diplom32.ru/ .
скачать мостбет с официального сайта https://mostbet4124.ru
купить диплом с реестром в москве купить диплом с реестром в москве .
http://www.fragensienilsen.de/forum/index.php?topic=47411.0
all the time i used to read smaller posts which also clear their motive, and that is also happening with this piece
of writing which I am reading at this place.
Check out my blog post – Sextreffen
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Ознакомьтесь с наш сайт и узнайте, как правильно применять теплоизоляцию и энергоэффективные окна и двери.
детский психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
анонимная консультация психиатра
купить аттестаты за 11 купить аттестаты за 11 .
шпалопропиточный завод Шпала деревянная пропитанная тип1 купить (Повторение ключевого слова, можно использовать ранее написанный текст или немного его перефразировать) Купить шпалу деревянную пропитанную тип 1 – это оптимальный выбор для строительства и ремонта железнодорожных путей с высокой интенсивностью движения и большими нагрузками. Шпалы типа 1, благодаря своим увеличенным размерам и повышенной прочности, обеспечивают надежную опору для рельсов и способствуют равномерному распределению нагрузки от проходящего поезда. Предлагаемые нами шпалы деревянные пропитанные тип 1 изготавливаются из отборной древесины хвойных пород (сосна, ель), прошедшей строгий контроль качества. Пропитка антисептическими составами (креозотом или другими современными антисептиками)
купить аттестат за 11 классов в иванове http://www.arus-diplom9.ru/ – купить аттестат за 11 классов в иванове .
https://www.behance.net/hpokingt
лучшие психиатрические клиники
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
лучшие психиатрические клиники
макияж севастополь брови севастополь — Брови — это не просто волоски над глазами, а важный элемент выразительности лица и общей эстетики образа. В Севастополе, где влияние морского климата, солнца и ветра сказывается на состоянии кожи и волос, уход за бровями требует профессионального подхода: от грамотной архитектуры (моделирование формы с учётом пропорций лица, симметрии и мимики) до восстановительных процедур — ламинирования, кератиновой терапии, окрашивания хной или краской и коррекции ростовых проблем с помощью сывороток. Опытный мастер всегда начинает с консультации, определяет тип кожи и волос, предлагает несколько вариантов формы и оттенка, показывает эскиз и договаривается о графике коррекций. Важным аспектом в Севастополе является уход после процедур: избегать активного солнца и моря первые 1–2 недели, пользоваться защитными и питательными средствами, следовать рекомендациям по чистоте и дезинфекции. При выборе салона обращайте внимание на портфолио «до/после», лицензии, отзывы клиентов и используемые материалы — одноразовые инструменты и качественные краски значительно снижают риск осложнений. Для тех, кто ведёт активный образ жизни, мастера предлагают стойкие техники и программы поддержки: комбинированные процедуры, курсы восстановления и регулярные коррекции, которые помогут сохранить аккуратный естественный вид бровей круглый год.
Moreover, their prices are often competitive compared to traditional pet stores.
hidden intelligence https://petstorepetsupply.com/index.php/2025/05/22/hidden-intelligence-how-smart-are-octopuses-really/
вторичка Вахитовский район Казани
психиатрическая помощь госпитализация
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
врач психиатр на дом в москве
J’aime enormement le casino TonyBet, il est carrement un moment divertissant top. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le service client est super, tres professionnel. Les retraits sont rapides, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus de bonus. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet c’est du solide pour les fans de jeux en ligne ! De plus, le design est attractif, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet kampanjakoodi 2025|
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Зайдите на раздел услуг и ознакомьтесь с технологиями безопасного и комфортного дома для семьи.
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula009.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в туле
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
kupit-drova-v-ramenskom-365.ru .
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up!
I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back later.
Cheers
stroyexpertsochi.ru Узнайте о наши материалы и узнайте об эффективных способах укрепления склонов и дренажа участка.
перевод текстов Перевод с английского на русский язык — это сложная лингвистическая задача, требующая глубокого понимания обоих языков, культуры и отраслевой специфики, чтобы текст звучал естественно для русскоязычного читателя. Переводчики, специализирующиеся на паре английский>русский, обычно проводят многоступенчатую проверку: первоначальный перевод, стилистическая правка и финальная вычитка носителем русского языка, что особенно важно для маркетинговых и литературных материалов. В юридических и официальных переводах ключевой момент — точная передача реквизитов, формулировок и правовых терминов; любые неточности могут привести к проблемам при использовании документов в госорганах или судах. Для технических и медицинских переводов нередко привлекаются профильные эксперты, чтобы подтвердить корректность терминологии и соответствие стандартам отрасли. Заказчику полезно предоставлять глоссарии, предыдущие переводы и пояснения по спорным местам — это ускорит работу и уменьшит количество правок в финальной версии.
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula009.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
интернет провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу красноярск
Je suis totalement conquis par le casino AllySpin, il procure une sensation de casino unique. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, comprenant des jeux innovants. Le service d’assistance est impeccable, garantissant un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est sans accroc, neanmoins j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. Pour faire court, AllySpin est un incontournable pour ceux qui aiment les defis ! En prime le design est accrocheur, renforcant l’immersion.
allyspin.|
Je suis completement seduit par Betclic Casino, il procure une experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et professionnels, repondant instantanement. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, parfois les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. En fin de compte, Betclic Casino offre une experience de jeu remarquable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons egalement que le design est visuellement epoustouflant, facilite chaque session de jeu.
diffusion betclic elite|
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
Купить диплом ВУЗа!
Наши специалисты предлагаютвыгодно приобрести диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже с использованием профессиональных приборов. Достигайте свои цели быстро с нашим сервисом- nadeemproperties.com/author/alfredohamlett
аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге .
частный пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula009.ru
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
монтаж систем охранной сигнализации УСТАНОВКА СИСТЕМ ВИДЕОНАБЛЮДЕНИЯ ПОД КЛЮЧ — Установка систем видеонаблюдения «под ключ» предполагает полный цикл работ от предварительного аудита до передачи полностью готовой к использованию системы. На этапе предварительного обследования специалисты изучают планировку объекта, выявляют критичные зоны наблюдения, оценивают условия освещённости, возможные источники помех и требования заказчика к хранению архива и аналитике. После этого разрабатывается проект: выбираются типы камер (IP, аналоговые, купольные, уличные, термальные, PTZ), определяются места установки, рассчитываются каналы питания и пропускная способность сети, выбирается оборудование для хранения (NVR, серверы, NAS) и коммутации (PoE-коммутаторы, оптические магистрали). На стадии монтажа выполняется аккуратная прокладка кабелей, установка кронштейнов и корпусов камер, монтаж регистраторов и коммутационного шкафа с организованным электропитанием и UPS. Далее проводится пусконаладка: IP-адресация, настройка потоков, зон детекции, масок приватности, интеграция с охранной сигнализацией и домофонной системой, настройка прав доступа и уведомлений на мобильные устройства. Особое внимание уделяется кибербезопасности — смена заводских паролей, шифрование видеопотоков, настройка VPN или VLAN, двухфакторная аутентификация и сегментация сети. Финальный этап — тестирование в реальных условиях (день/ночь, разные погодные условия), обучение персонала, оформление актов приёмки, передача паспортов системы и рекомендаций по обслуживанию. Заказчик получает готовую систему с гарантией, документами и возможностью заключения договора на регулярное обслуживание и мониторинг.
можно ли купить настоящий аттестат за 11 классов http://arus-diplom24.ru .
провайдеры по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
провайдеры в красноярске по адресу проверить
сертификация ISO Сертификация продукции: Сертификация продукции – это процедура подтверждения соответствия продукции требованиям, установленным в технических регламентах, стандартах и других нормативных документах. Она проводится аккредитованными органами по сертификации и включает в себя испытания продукции, анализ документации и инспекционный контроль. Сертификация продукции может быть обязательной или добровольной. Обязательная сертификация требуется для продукции, которая может представлять опасность для жизни, здоровья или имущества граждан, а также для окружающей среды. Добровольная сертификация проводится по инициативе производителя или поставщика с целью подтверждения соответствия продукции требованиям, не являющимся обязательными, или для повышения ее конкурентоспособности. Сертификация продукции позволяет производителям и поставщикам подтвердить качество и безопасность своей продукции, повысить доверие потребителей и получить конкурентные преимущества на рынке.
Чи могли б ми жити без гравітаційне поле? Відповідь вражає: притягання об’єктів.
провайдеры интернета по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу красноярск
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Проверяйте портфолио объектов и узнайте о методах строительства дома в Сочи и Краснодарском крае).
Thanks for the article https://house18.info/forum/topic/internet-magazin-rybolovnyh-snastey .
скачать приложение mostbet http://mostbet4120.ru/
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Изучите раздел услуг и получите советы по выбору материалов для морского и влажного климата.
макияж севастополь брови севастополь — Брови — это не просто волоски над глазами, а важный элемент выразительности лица и общей эстетики образа. В Севастополе, где влияние морского климата, солнца и ветра сказывается на состоянии кожи и волос, уход за бровями требует профессионального подхода: от грамотной архитектуры (моделирование формы с учётом пропорций лица, симметрии и мимики) до восстановительных процедур — ламинирования, кератиновой терапии, окрашивания хной или краской и коррекции ростовых проблем с помощью сывороток. Опытный мастер всегда начинает с консультации, определяет тип кожи и волос, предлагает несколько вариантов формы и оттенка, показывает эскиз и договаривается о графике коррекций. Важным аспектом в Севастополе является уход после процедур: избегать активного солнца и моря первые 1–2 недели, пользоваться защитными и питательными средствами, следовать рекомендациям по чистоте и дезинфекции. При выборе салона обращайте внимание на портфолио «до/после», лицензии, отзывы клиентов и используемые материалы — одноразовые инструменты и качественные краски значительно снижают риск осложнений. Для тех, кто ведёт активный образ жизни, мастера предлагают стойкие техники и программы поддержки: комбинированные процедуры, курсы восстановления и регулярные коррекции, которые помогут сохранить аккуратный естественный вид бровей круглый год.
How to Take a Screenshot
This is very interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
https://arlekin-dance.kiev.ua/Yak-pravilno-zberigati-sklo-fari-do-vstanovlennya.html
лучшие нейросети для школьников
лучшие нейросети для перевода текста
лучшие нейросети для создания приложений
prodazha-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru Ознакомьтесь с галерею выполненных работ и получите экспертные советы по строительству коттеджа с отделкой под ключ.
купить аттестат за 11 класс в казахстане купить аттестат за 11 класс в казахстане .
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no hesitation very
shortly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Kak-vybrat-spinning-na-shchuku-Obzor-luchshih-modelej-01-13 .
How to Take a Screenshot
J’adore a fond Betsson Casino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. La bibliotheque de jeux est phenomenale, comprenant des jackpots progressifs comme Mega Moolah. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite via email ou telephone, garantissant une aide immediate. Les transactions sont protegees par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, bien que les offres comme le bonus de bienvenue de 100 % jusqu’a 100 € pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Betsson Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier ! De plus le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, facilite chaque session de jeu.
retrait betsson|
Ich finde es unglaublich toll Billy Billion Casino, es ist ganz ein Abenteuer voller Nervenkitzel. Die Auswahl ist reich und vielfaltig, inklusive topaktueller Slots von NetEnt und Pragmatic Play. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, reagiert in wenigen Minuten. Gewinne kommen in Rekordzeit an, obwohl die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Billy Billion Casino bietet ein sicheres und faires Spielerlebnis mit einem Sicherheitsindex von 8,5 fur die, die gerne wetten! Zusatzlich die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, die Immersion verstarkt.
billy billion promo code no deposit|
купить дрова на паллетах .
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Погрузитесь в наш каталог решений и получите рекомендации по благоустройству участка с уклоном и укреплению склона.
швейное предприятие http://www.nitkapro.ru .
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
продвижения сайта в google http://www.kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru .
заказать анализ сайта http://www.poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru .
аудит продвижения сайта poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru .
https://t.me/Foka_Doka_SPb
профессиональное продвижение сайтов профессиональное продвижение сайтов .
Получите квалифицированную онлайн консультацию юриста бесплатно.
Мы публикуем полезные статьи, которые помогут вам лучше понять свои права и обязанности.
мобильное приложение регистрация вход mostbet app приложении рейтинг 4 8 мобильное приложение регистрация вход mostbet app приложении рейтинг 4 8
скачать официальный сайт мостбет скачать официальный сайт мостбет
мобильное приложение регистрация вход mostbet app приложении рейтинг 4 8 https://mostbet4126.ru/
лечение в психиатрической больнице
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
психиатрическая помощь
дренажная система вокруг дома цена .
компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов .
купить дрова березовые колотые с доставкой .
http://stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите наш каталог решений и изучите эффективные дренажные системы и подпорные стенки.
продвижение по трафику продвижение по трафику .
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат 11 класса в оренбурге
мостбет скачать андроид мостбет скачать андроид
теннесси бк скачать теннесси бк скачать
мостбет зеркало скачать мостбет зеркало скачать
частный психиатрический стационар
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
вызов психиатра на дом
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with
SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share.
Many thanks!
stroyexpertsochi.ru Откройте наши материалы и узнайте о материалах, идеально подходящих для морского и влажного климата.
купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании .
ставки мостбет https://www.mostbet4126.ru
лучшие нейросети для написания стихов
екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр .
toki başvuruları ne zaman
I always spent my half an hour to read this blog’s
articles every day along with a mug of coffee.
частный психиатр на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
https://vk.com/foka_doka
психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
платная психиатрическая клиника
лучшие нейросети для работы с файлами
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
купить диплом ссср купить диплом ссср .
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Изучите наш сайт и ознакомьтесь с экологичными строительными материалами и энергосберегающими решениями.
дренаж под ключ цена за метр .
мелбет kg http://mostbet4119.ru/
консультация врача психиатра
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
стационарное психиатрическое лечение
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу краснодар
перевод документов Бюро переводов — это специализированная организация, предоставляющая широкий спектр языковых услуг для частных лиц и компаний: письменные переводы, устный перевод, локализация контента, редактирование и верстка документов, а также сопутствующие юридические услуги вроде нотариального заверения и апостиля. В профессиональном бюро работают переводчики с профильным образованием и опытом в разных отраслях — юриспруденции, медицине, технике, финансах и IT — что позволяет обеспечить корректную передачу терминологии и стиля. Хорошее бюро использует многоступенчатую систему контроля качества: перевод, редактура, финальная вычитка и при необходимости проверка носителем языка. Кроме того, современные бюро применяют CAT?инструменты и терминологические базы для поддержания единства терминов в крупных проектах и ускорения работы. При выборе бюро переводов важно учитывать отзывы, наличие сертификаций, примеры работ и прозрачность ценообразования; также полезно уточнять сроки выполнения и условия конфиденциальности, особенно при работе с чувствительной информацией. Многие бюро предлагают гибкие условия: срочные переводы, выезд переводчика, онлайн?оплату и доставку готовых документов курьером или в электронном виде.
детский психиатр на дом
psychiatr-moskva004.ru
психиатр онлайн консультация
Hi there, of course this article is genuinely fastidious
and I have learned lot of things from it on the topic of
blogging. thanks.
проверить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу проверить
Рекомендую всім батькам цей сайт! Тут є чудові казки, зокрема Снігова королева.
аттестат за 11 класс купить москва аттестат за 11 класс купить москва .
mostbet.com казино скачать http://mostbet4123.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
дрова для пикника купить .
https://stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Посетите наш сайт и узнайте обо всех тонкостях строительства в Сочи и Краснодарском крае.
My brother suggested I would possibly like this blog.
He was once totally right. This submit truly made
my day. You cann’t imagine simply how a lot time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
купить дрова онлайн .
You should only losartan 50mg tablets side effects today! losartan bnf
Если вам нужна бесплатная консультация юриста по телефону горячая линия, не стесняйтесь обратиться к нам за помощью!
Профессиональные специалисты из нашей юридической компании готовы помочь вам в решении различных правовых вопросов. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг , включая консультации, представительство в суде и помощь в составлении документов.
При обращении к нашей команде , вы можете рассчитывать на индивидуальный подход . Каждый клиент для нас важен, и мы стремимся предложить максимально выгодные условия . Наша цель – обеспечить защиту ваших интересов .
На konsultaciya-yurista121.ru вы можете ознакомиться с отзывами наших клиентов . Мы регулярно обновляем информацию . Также у нас есть форумы для обсуждения актуальных вопросов, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних изменений в законодательстве.
Связываясь с нашими специалистами , вы можете задать все интересующие вас вопросы. Мы готовы помочь вам по любым правовым вопросам. Ваши права и интересы должны быть защищены .
накрутка подписчиков тг канале smm накрутка подписчиков тг канале smm
купить диплом с реестром купить диплом с реестром .
stroyexpertsochi.ru/ Погрузитесь в портфолио объектов и узнайте о защите стен от грибка и антикоррозийной обработке металлоконструкций.
kupit-drova-v-serpuhove-365.ru .
получить консультацию психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
консультация психиатра
Je suis totalement seduit par Betway Casino, il offre une plongee dans un univers vibrant. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les gains arrivent rapidement, occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino est une plateforme exceptionnelle pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement attrayant, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betway mz|
Estou completamente apaixonado por o 888 Casino, e como se fosse aventura cheia de emocoes. As opcoes de jogos sao ricas e diversificadas, oferecendo jogos de mesa classicos e elegantes. A equipe oferece um suporte de altissima qualidade, disponivel 24/7. As transacoes sao totalmente protegidas, em alguns momentos mais recompensas seriam bem-vindas. Para concluir, o 888 Casino oferece uma experiencia de jogo memoravel para os fas de emocoes fortes! Vale destacar o site e projetado com elegancia, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao a experiencia.
jackpot 888 casino|
Je suis totalement conquis par CasinoAndFriends, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de bonne humeur. Le catalogue est incroyablement riche, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le service client est exceptionnel, garantissant une aide immediate. Les transactions sont protegees, incluant des methodes comme PayPal et Skrill, bien que les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, CasinoAndFriends vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement attrayant, ajoute une touche d’amusement a l’experience.
casinoandfriends serios|
Ich schatze sehr BingBong Casino, es bietet eine unwiderstehliche Energie fur Spieler. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend mit uber 700 Slots, mit klassischen Slots wie Eye of Horus und Sizzling Hot. Die Mitarbeiter sind professionell und immer hilfsbereit, mit exzellentem Follow-up. Transaktionen sind sicher, besonders mit E-Wallets wie Skrill, manchmal zusatzliche Belohnungen fur Premium-Mitglieder waren toll. Zusammengefasst ist BingBong Casino enttauscht nie fur Leidenschaftliche Zocker ! Nicht zu vergessen ist die Benutzeroberflache modern und intuitiv, einen Hauch von Flair hinzufugt.
bingbong rabattgutscheine|
теннесси бк скачать на андроид бесплатно теннесси бк скачать на андроид бесплатно
частная психиатрическая клиника стационар
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
лечение психиатрических больных
Hi there! valtrexeasy great web site.
http://www.stroyexpertsochi.ru Исследуйте наши проекты и изучите практические советы по строительству, отделке и благоустройству домов.
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
детский психиатр на дом в москве
mostbet com android mostbet com android
анонимная консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
врач психиатр на дом в москве
What’s up mates, its enormous piece of writing concerning cultureand entirely defined, keep it up all the
time.
мостбет официальный mostbet4125.ru
провайдеры по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Hello!
This post was created with XRumer 23 StrongAI.
Good luck 🙂
консультация психиатра на дому в москве
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
анонимная консультация психиатра
aqlli strategiyalar orqali yaxshilash mumkin. Ushbu platforma taqdim etadi.
turli xil formatlarda . 888starzda mumkin.
g’alabalarini yordam beradi. foydali ma’lumotlar joylashgan maqolalar mavjud.
xavfsizlik choralarini . hisob ma’lumotlari. Shu sababli, mumkin.
888starz казино https://888starz-uzs.net/
провайдеры интернета по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
подключить интернет по адресу
принудительное лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
psychiatr-moskva005.ru
лечение в психиатрическом стационаре
купить диплом о высшем образовании ссср купить диплом о высшем образовании ссср .
создание сайтов оптимизация и продвижение сайтов
ttps://vk.link/kosmetolog_tsvetnoy_gorod Подтяжка лица – это комплекс процедур, направленных на омоложение и улучшение контуров лица. Существуют различные методы подтяжки лица, от хирургических до неинвазивных. Выбор метода зависит от возраста, состояния кожи и желаемого результата. Хирургическая подтяжка лица является наиболее эффективным, но и наиболее травматичным методом. Неинвазивные методы, такие как RF-лифтинг, ультразвуковой SMAS-лифтинг и нитевой лифтинг, позволяют добиться заметного омоложения без хирургического вмешательства.
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу краснодар
мостьет mostbet4120.ru
https://pancakesswap.app 0% commission is now live!
I’m curious to find out what blog system you have
been utilizing? I’m having some small security issues with my latest site and
I would like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any
suggestions?
Check out my blog; خرید بک لینک
kavacik escort
ставки на спорт бишкек http://www.mostbet4127.ru
лучшие нейросети для студентов
cylindrical bearings
https://bs2bsme.at
мостбет казино войти http://mostbet4122.ru/
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, il offre une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service client est remarquable, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, par moments davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. Globalement, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec style et modernite, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino login|
печь полимеризации порошковой краски купить Установка порошковой покраски купить – значит приобрести полный комплекс оборудования, необходимого для организации процесса порошковой окраски. В состав установки входят: камера подготовки поверхности, камера напыления, печь полимеризации, распылитель порошковой краски, система фильтрации и рекуперации порошка, а также компрессор и транспортная система. При выборе установки необходимо учитывать размеры окрашиваемых изделий, требуемую производительность и доступный бюджет.
продвижение в google https://www.internet-agentstvo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-seo.ru .
консультация психиатра круглосуточно
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
вызов психиатра на дом
Je trouve absolument sensationnel BetFury Casino, il offre une immersion dans un univers vibrant. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, comprenant des jeux originaux comme Plinko et Crash avec un RTP jusqu’a 99,28 %. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite, offrant des reponses claires et rapides. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies comme Bitcoin ou Ethereum sont ultra-rapides, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. En fin de compte, BetFury Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de divertissement innovant ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, facilite chaque session.
betfury 2022|
J’adore a fond Betsson Casino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des slots de derniere generation comme Starburst. Le service client est exceptionnel, repondant instantanement. Les gains sont verses en 24 heures pour les e-wallets, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. Pour conclure, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le design est visuellement attrayant et facile a naviguer, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betsson inscription|
Ich bin total begeistert von BoaBoa Casino, es ist wirklich eine einzigartige Casino-Atmosphare. Es gibt eine riesige Auswahl an Spielen, mit klassischen Tischspielen wie Blackjack und Roulette. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, mit exzellentem Follow-up. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft innerhalb von 24-72 Stunden, jedoch die Boni wie der 100%-Willkommensbonus bis 500 € konnten haufiger sein. Insgesamt ist BoaBoa Casino definitiv einen Besuch wert fur Online-Casino-Fans ! Daruber hinaus ist die Benutzeroberflache flussig und tropisch gestaltet, jede Spielsitzung erleichtert.
boaboa shezlong|
J’adore a fond CasinoBelgium, c’est une veritable energie de jeu captivante. Le catalogue est compact mais de grande qualite, offrant des titres de Gaming1 et Greentube. Les agents sont professionnels et disponibles, offrant des reponses claires et utiles. Le processus de retrait est simple avec une limite de 500 € par semaine, neanmoins plus de jeux de table seraient un atout. Globalement, CasinoBelgium offre un jeu equitable avec un indice de securite de 7,5 pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive sur mobile, ajoute une touche de fierte nationale.
777 casino belgium|
drenazh-uchastka-vokrug-doma-spb.ru .
наркологическая клиника в воронеже на левом берегу Частная наркологическая клиника в Воронеже: Лечение зависимости в уютной обстановке. Частная наркологическая клиника в Воронеже обеспечивает своим пациентам комфортное и эффективное лечение зависимостей. Здесь вы найдете внимательное отношение, квалифицированную помощь и индивидуальный подход. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, начиная от детоксикации и заканчивая реабилитацией. Наши врачи-наркологи и психологи обладают богатым опытом и применяют современные методики лечения зависимостей. Мы гарантируем полную анонимность и конфиденциальность. Ваше выздоровление – наша главная цель!
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
платная психиатрическая скорая помощь
https://fixed-float.to
Smart Hamsters — це не тільки команда, це справжній дух змагань! Дивіться на наші новини та будьте в курсі всіх подій.
консультация психиатра на дому в москве
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
психиатрическая медицинская помощь
лучшие нейросети для написания скриптов
лучшие нейросети для телефона
интернет продвижение москва http://www.poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru .
That is a great tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Simple but very precise info… Appreciate your sharing this one. A must read post!
My blog https://www.uniform-factory.net/medical-lab-coats.html
drenazh-na-dachnom-uchastke-spb.ru .
заказать дрова береза .
консультация психиатра круглосуточно
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
купить диплом с реестром цена купить диплом с реестром цена .
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar006.ru
провайдеры по адресу краснодар
технического аудита сайта http://kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru .
Знайшов інтерактивну мапу фестивалів Європи — планую літо!
массовое швейное производство http://www.nitkapro.ru .
mega darknet market – мега зеркало 2025 онлайн
Мега даркнет маркетплейс в текущем году продолжает оставаться одной из самых популярных площадок в даркнете. Пользователи регулярно ищут мега ссылки, актуальные зеркала и мега sb официальный сайт, чтобы получить вход на мега даркнет.
# Что такое Мега?
мега сайт — это ресурс, который работает как даркнет-рынок. mega darknet market стал известен благодаря интерфейсу. Но важно помнить: мега сайт даркнет — это теневая платформа.
Cыллка ===> https://github.com/mega-market-dark/mega-onion (используй ВиПиЭн)
# Почему нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде mega sb часто блокируются. Чтобы обойти это, используются мега зеркала. Например:
– mega market link
– мега рабочая ссылка
– mega darknet market вход
Эти адреса позволяют осуществить вход, но одновременно появляются фейковые версии.
# Как найти актуальную ссылку?
Пользователи часто вводят запросы:
– мега зеркало 2025
– mega darknet mirror
– mega darknet market link
Нужно помнить: мега маркет ссылка всегда доступен через тор браузер, а не через клирнет.
# Риски поддельных сайтов
Запросы вроде мега darknet market зеркало часто ведут к фейкам. Такие ресурсы имитируют интерфейс оригинала. Чтобы не попасться:
– Проверяйте mega sb.
– Используйте только мега зеркало на сегодня.
– Избегайте клирнет-версий.
# Telegram и ссылки
Популярен запрос мега зеркало телеграм. В Telegram действительно можно найти мега актуальные зеркала, но риск нарваться на мошенников велик.
# Как зайти на мегу?
Чтобы получить мега вход, нужно:
1. Установить браузер Тор.
2. Ввести мега darknet ссылка.
3. Пройти авторизацию.
# Популярные ключи 2025
Сегодня особенно востребованы:
– мега зеркало на сегодня
– мега sb официальный сайт
– мега сайт даркнет
Эти темы показывают, что спрос на ссылки высокий.
# Заключение
mega darknet market остаётся крупнейшей площадкой даркнета в последние годы. Но любой доступ связан с риском.
?? Помните: официальный сайт мега могут быть ложными, а посещение маркетплейса всегда остаётся опасным.
комплектная трансформаторная подстанция купить комплектная трансформаторная подстанция купить .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1493488-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
провайдеры по адресу краснодар
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar006.ru
подключить интернет по адресу
нужна консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva006.ru
платная психиатрическая клиника
лучшие нейросети для решения задач по математике
drenazh-na-dachnom-uchastke-spb.ru .
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar006.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу краснодар
узи аппарат купить цена узи аппарат купить цена .
лучшие нейросети для замены текста в песне
лучшие нейросети для поиска фильмов по описанию
лучшие нейросети для перевода текста
платная наркологическая клиника воронеж Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже – это специализированное медицинское учреждение, которое оказывает помощь людям, страдающим от различных видов зависимостей, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания, игромания и другие. Клиника предлагает комплексный подход к лечению, включающий в себя детоксикацию, медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию, реабилитацию и социальную адаптацию. Лечение в клинике проводится анонимно и конфиденциально.
продвижения сайта в google продвижения сайта в google .
https://bsmc.at
З нами ви завжди в курсі подій! Перегляньте всі новини та матчі на сайті Smart Hamsters.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1397267-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов http://www.internet-agentstvo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-seo.ru .
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
лечение наркомании цена
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest
twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this
for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have
some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything.
I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
лучшие нейросети для рифмования
алкогольная зависимость лечение
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости в Астане
реабилитация зависимых от алкоголя
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
анонимное лечение от наркозависимости
prodazha-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
Welcome to Bluevine login, your ultimate financial partner for small businesses. Our company provides advanced financial tools designed to simplify your financial operations and support your business expansion. From credit lines to invoice factoring, Bluevine delivers the flexible financing your business needs. Access to your account is through the Bluevine login portal, where you can safely and efficiently manage all your financial needs. Join thousands of satisfied entrepreneurs who trust Bluevine to advance their business.
https://swebbtv.se/a/1xbetpromo33/video-channels
домашний интернет
inernetvkvartiru-msk004.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
BBCR
J’adore a fond 1win Casino, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu captivante. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct immersives. Les agents sont toujours prets a aider, avec un suivi irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, parfois les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. En resume, 1win Casino est une plateforme exceptionnelle pour les joueurs en quete de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement attrayant, ajoute une touche d’elegance a l’experience.
1win bonus code|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betzino Casino, il offre une aventure pleine de frissons. La selection de jeux est epoustouflante avec plus de 1800 titres, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le personnel offre un accompagnement rapide et efficace, joignable par email ou chat. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, neanmoins davantage de recompenses via le programme VIP seraient appreciees. Globalement, Betzino Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, renforce l’immersion totale.
betzino testbericht|
Ich liebe es absolut Billy Billion Casino, es ist wirklich ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spielauswahl ist uberwaltigend mit uber 4000 Titeln, mit modernen Slots wie Gates of Olympus und Book of Dead. Das Team bietet schnelle und effektive Unterstutzung, reagiert in wenigen Minuten. Zahlungen sind flussig und durch SSL-Verschlusselung gesichert, jedoch mehr Freispiele waren super. Kurz gesagt ist Billy Billion Casino ein Muss fur Spieler fur Spieler, die nach Adrenalin suchen! Zusatzlich die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, jede Spielsitzung erleichtert.
billy billion casino|
консультация психиатра платно
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
психиатр онлайн консультация
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей России. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс в санкт петербурге
J’adore a fond Casino Action, on dirait une aventure pleine de frissons. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, avec des machines a sous modernes comme Mega Moolah. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible 24/7, avec un suivi de qualite. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, cependant le bonus de bienvenue jusqu’a 1250 € pourrait etre plus frequent. Dans l’ensemble, Casino Action vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, ajoute une touche de sophistication a l’experience.
casino action mobiili|
провайдеры по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-msk004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
купить дипломы купить дипломы .
интернет домашний москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk004.ru
интернет провайдеры москва
консультация психиатра платно
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
психиатрическая помощь
продвинуть сайт в москве продвинуть сайт в москве .
получить консультацию психиатра
psikhiatr-moskva004.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника
дренаж участка под ключ стоимость .
prodazha-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
анонимное лечение алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
лечение наркозависимых
напольные цветочные горшки напольные цветочные горшки .
лечение наркомании
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
центр реабилитация алкоголиков
лучшие нейросети для рифмования
swot анализ планирования https://swot-analiz1.ru
лучшие нейросети для программирования на Python
It is in reality a nice and useful piece of information. I am satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Check out my page … https://Orientuniforms.ae/product/bath-towel/
анонимная реабилитация наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
лечение наркотической зависимости
купить диплом в ивано франковске https://educ-ua4.ru/ .
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1377755-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
лучшие нейросети для написания писем
домашний интернет москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk005.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
I am curious to find out what blog platform you are using? I’m experiencing some minor security problems with my latest site and I would like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any recommendations?
Also visit my page – https://Www.Uniform-factory.net/medical-scrubs.html
I always used to study paragraph in news papers but now as I am a user of web therefore from now I am using net for posts, thanks to web.
My blog post :: https://Www.Dubaihoodies.com/zipper-hoodies-dubai.html
какие провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-msk005.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
viagra homme achat viagra
подключить домашний интернет в москве
inernetvkvartiru-msk005.ru
подключить интернет в москве в квартире
Consider first-rate online pharmacies the moment you decide to bupropion er/sr help increase my blood flow? bupropion and naltrexone
mostbet.com rasmiy sayt mostbet.com rasmiy sayt
производство по пошиву одежды nitkapro.ru .
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье 1xbet зеркало промокоды чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей.
Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
мосбкт http://mostbet4169.ru
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
психиатр на дом для пожилого
I’m gone to convey my little brother, that he should also visit this webpage on regular basis to take updated from latest news update.
Also visit my web site … https://Dubaihoodies.com/cotton-hoodies.html
принудительное лечение в психиатрической больнице
psikhiatr-moskva005.ru
консультация психиатра на дому в москве
Je suis completement conquis par 1xbet Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, incluant des slots de pointe. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, par moments plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En fin de compte, 1xbet Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
1xbet en france|
Je trouve absolument extraordinaire Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers vibrant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7 et professionnels, repondant en quelques minutes. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive sur l’application mobile iOS/Android, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway be|
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
реабилитация алкогольной зависимости
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de CasinoAndFriends, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement riche, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le support est reactif via chat en direct de 6h a minuit, repondant en quelques minutes. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, bien que le bonus de bienvenue de 125 tours gratuits pour 10 € pourrait etre plus frequent. En fin de compte, CasinoAndFriends est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, renforce l’immersion totale.
casinoandfriends app|
анонимное лечение алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I found this board and I in finding It really useful & it helped
me out a lot. I’m hoping to provide one thing back
and help others such as you helped me.
Заказать диплом ВУЗа!
Наши специалисты предлагаютвыгодно купить диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании специальных приборов. Достигайте своих целей быстро и просто с нашей компанией- parus.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=854&sid=d11c4dce4d06a47a8bd5383da233e866
как избавиться от алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
стоимость лечения наркомании
kupit-drova-v-serpuhove-365.ru .
Хочете дізнатися, чому Smart Hamsters так популярні серед фанатів? Їхні стратегії та геймплей надзвичайно захоплюють.
Article https://beksai.ru/figurnoe-katanie-polza-dlya-zdorovya-i-kak-vybrat-moment-dlya-nachala-zanyatij/
1хбет зеркало Рабочее зеркало 1xbet: Ставки без границ. Рабочее зеркало 1xBet – это актуальная ссылка на альтернативный сайт букмекерской конторы 1xBet, которая обеспечивает доступ к платформе в обход блокировок. Зеркало позволяет пользователям делать ставки на спорт, играть в казино и пользоваться другими сервисами 1xBet без каких-либо ограничений. Использование рабочего зеркала – это надежный способ оставаться в игре, даже если основной сайт недоступен. Важно помнить, что рабочие зеркала регулярно обновляются, поэтому рекомендуется искать актуальные ссылки на специализированных сайтах и форумах.
накрутка подписчиков инстаграм беларусь бесплатно накрутка подписчиков инстаграм беларусь бесплатно
https://kinolav.ru/ Обзоры кино: Погрузитесь в мир большого экрана. “Обзоры кино” – это ваш надежный компаньон в мире кинематографа. Мы предлагаем глубокий анализ новых и знаковых фильмов, исследуя их темы, символику и культурное значение. Наши критики не только оценивают качество фильма, но и помогают зрителям расширить свое понимание киноискусства. Читайте наши обзоры и узнавайте больше о мире кино!
комплексное продвижение сайтов москва комплексное продвижение сайтов москва .
лучшие нейросети для улучшения качества текста
домашний интернет тарифы москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
интернет тарифы москва
заказать продвижение сайта в москве заказать продвижение сайта в москве .
I blog quite often and I truly appreciate your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I will book mark your blog and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
https://warfare.com.ua/kupity-germetik-dlya-far-gid-pokuptsya
pokerdom официальный сайт
Read on mirtazapine controlled substance to minimize specific symptoms mirtazapine pregnancy
обзоры кино Обзоры фильмов и сериалов: Ваш путеводитель в мире кино и телевидения. Наш сайт предлагает всесторонние обзоры самых свежих и интересных фильмов и сериалов. Мы анализируем сюжет, актерскую игру, режиссуру, визуальные эффекты и другие важные аспекты, чтобы помочь вам сделать осознанный выбор и не тратить время на некачественный контент. У нас вы найдете как рецензии на громкие премьеры, так и обзоры малоизвестных, но достойных внимания картин. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, чтобы быть в курсе последних новинок и обсуждать свои любимые фильмы и сериалы!
продвижение сайтов в москве продвижение сайтов в москве .
motbet motbet
домашний интернет подключить москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
провайдеры интернета в москве по адресу
Прокат авто Краснодар жд Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес: Подчеркните свой статус и комфорт. Если вам нужен автомобиль для деловых поездок в Краснодаре, аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес-класса – это идеальное решение. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей представительского класса, которые подчеркнут ваш статус и обеспечат максимальный комфорт во время поездок. Наши автомобили всегда в отличном состоянии и оснащены всеми необходимыми функциями для комфортной работы и отдыха. Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес-класса – это инвестиция в ваш успех и комфорт. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и произведите впечатление!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по разумным ценам. Заказ документа, который подтверждает обучение в ВУЗе, – это грамотное решение. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: pedromartransportes.com.br/employer/diplomy-grupps
приложения для накрутки подписчиков в инстаграм бесплатно приложения для накрутки подписчиков в инстаграм бесплатно
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу москва
Instagram account Followers: Your audience and community on Instagram. Followers are the people who choose to follow your account and see your content in their feed. Building a strong following is essential for reaching a wider audience and making an impact on Instagram. Attract new followers by creating high-quality content, engaging with your audience, and using relevant hashtags!
фабрика для пошива одежды nitkapro.ru .
консультация психиатра платно
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
детский психиатр на дом в москве
Гастрономічна подорож на Фестивалі Тихоокеанської Кухні стала одним із найкращих днів мого життя. Я скуштувала страви, про які раніше тільки читала, і навіть привезла додому кілька рецептів. Дякую Pacific Department SFF за таку можливість! Якщо хочете дізнатися більше, відвідайте цей сайт.
купить дрова колотые .
I’m gone to inform my little brother, that he should also visit this blog on regular basis to take updated from hottest news update.
kidsvisitor
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье 1хбет промокод в день рождения чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей.
Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
С получением профессиональной помощи в решении юридических вопросов вы можете обратиться к онлайн консультация юриста по уголовным делам, где можно получить юридическую консультацию круглосуточно и бесплатно.
Группа экспертов обеспечивает надежность и высокое качество обслуживания.
seo network http://www.poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru .
https://lakoshka.ru
seo network kompanii-zanimayushchiesya-prodvizheniem-sajtov.ru .
психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
оргонит что это такое Оргонит отзывы: Мнения об эффективности оргонита разнятся: от положительных до скептических.
It’s remarkable in support of me to have a web page, which is valuable in favor
of my experience. thanks admin
сколько стоит кубометр дров .
платный психиатр на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva006.ru
частный психиатр на дом
aqlli strategiyalar orqali kengaytirish mumkin. Ushbu platforma taqdim etadi.
ko’plab janrlarda. qimor ixlosmandlari mumkin.
daromadlarini yordam beradi. foydali ma’lumotlar joylashgan bloglar mavjud.
taqdim etadi. xavfsizligi ta’minlanadi. bu saytga mumkin.
starz888 https://888starz-uzs.net/
Коли хочеш відпочити від важкого дня, просто вмикай цей сайт і насолоджуйся атмосферою. Тут завжди є щось цікаве для кожного!
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
I’ve been surfing online more than 4 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It is pretty worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content as you did, the
internet will be much more useful than ever before.
What’s up to all, how is everything, I think
every one is getting more from this site, and your views
are pleasant designed for new viewers.
компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов .
купить диплом университета купить диплом университета .
купить диплом о среднем образовании купить диплом о среднем образовании .
Участь у фестивалі Trance Illusion стала для мене незабутнім досвідом, і все завдяки Eleonora. Їхній виступ був справжнім вибухом емоцій: від першого до останнього треку я відчував, як музика буквально проходить крізь мене. Особливо вразила PJ Zoe, чий унікальний стиль у створенні сценічних візуалізацій додав шоу глибини й атмосферності. Якщо ви ще не бачили їхніх виступів, рекомендую переглянути більше інформації на сайті Eleonora.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя
вход Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
drenazh-na-dachnom-uchastke-spb.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя тула
https://espaciodca.fedace.org/content/alishan-oolong-where-tradition-meets-luxury?page=11#comment-270528
mostbet casino http://mostbet4131.ru
Прокат авто Прокат авто в Краснодаре: Ваш ключ к свободе передвижения в Краснодаре. Исследуйте Краснодар и его окрестности с максимальным комфортом и независимостью благодаря услуге проката авто в Краснодаре. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей различных классов, от экономичных моделей до представительских седанов, чтобы удовлетворить любые ваши потребности. Наши автомобили всегда в отличном состоянии и готовы к поездке. Прокат авто в Краснодаре – это идеальное решение для туристов, деловых путешественников и местных жителей, которые ценят свободу и удобство. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и отправляйтесь в путь!
купить легальный аттестат за 11 классов купить легальный аттестат за 11 классов .
дизайнерская мебель премиум класса дизайнерская мебель премиум класса .
пленка самоклеящаяся защитная http://www.samokleyushchayasya-plenka-1.ru .
мостбет зеркало узбекистан https://mostbet4167.ru
Article https://beksai.ru/figurnoe-katanie-polza-dlya-zdorovya-i-kak-vybrat-moment-dlya-nachala-zanyatij/
mostbet uz app yuklab olish https://mostbet4169.ru
скачат мостбет скачат мостбет
http://avteon.ru
Юридические консультации стали неотъемлемой частью жизни каждого человека.. Каждый может столкнуться с правовыми вопросами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства..
konsultaciya-advokata11.ru предлагает широкий спектр услуг.. Вы сможете получить консультации по различным правовым вопросам.. Получите помощь квалифицированного юриста на задать вопрос адвокату онлайн бесплатно.
Квалифицированные юристы окажут необходимую помощь в любой ситуации. Мы гордимся тем, что предлагаем высококачественные услуги..
Обратитесь к нам, и вы не пожалеете о своем выборе.. Мы гарантируем профессионализм и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту..
https://tribaliste.com/img/pgs/?promo_code_melbet_africa.html
Женский кулон из оргонита Что такое оргонит: Устройство для преобразования энергии, якобы нейтрализующее негативное излучение.
seo аудит веб сайта seo аудит веб сайта .
Архитектурное проектирование требует высокой квалификации. Компания имеет государственную лицензию на проектирование, которая разрешает полный цикл работ от концепции до реализации.
https://lagodicomo.com.mx/wp-content/pgs/10_datos_curiosos_sobre_plinko.html
лучший интернет провайдер нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде по адресу
mostbet uz ilova bilan ro‘yxatdan o‘tish mostbet4168.ru
drenazh-na-dachnom-uchastke-spb.ru .
купить диплом бакалавра купить диплом бакалавра .
скачать бесплатно мостбет http://www.mostbet4130.ru
провайдер интернета по адресу нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
подключить проводной интернет нижний новгород
osonlashtiradi” http://www.mostbet4167.ru
888starz platformasi orqali kengaytirish mumkin. o’yin variantlari taqdim etadi.
O’yinlar . doimiy mumkin.
chegirmalar yordam beradi. Qimor o’yinlari joylashgan maqolalar mavjud.
taqdim etadi. ma’lumotlari . 888starzga mumkin.
888starz bet скачать 888starz bet скачать.
https://remonthome.com/files/pgs/le-code-promo-1xbet_bonus.html
накрутка подписчиков инстаграм накрутка подписчиков инстаграм
интернет домашний нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
интернет по адресу нижний новгород
комплектная трансформаторная подстанция купить комплектная трансформаторная подстанция купить .
частный реабилитационный центр
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
центр реабилитации зависимых
J’adore le casino TonyBet, il est carrement une experience de jeu incroyable. La selection de machines est vaste, incluant des slots ultra-modernes. Le service client est super, tres professionnel. Le processus de retrait est efficace, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. Globalement, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs, la plateforme est intuitive, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet bookie|
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, c’est une veritable plongee dans le divertissement. La selection de jeux est immense, comprenant des jeux innovants. Le support est ultra-reactif, garantissant un suivi de qualite. Les transactions sont bien protegees, bien que les promos pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, AllySpin ne decoit jamais pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! Ajoutons que le design est accrocheur, facilitant chaque session.
allyspin applicazione mobile|
Je trouve absolument genial Azur Casino, c’est une veritable energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est vaste et diversifie, proposant du casino en direct immersif. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, garantissant une assistance de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, parfois les offres pourraient etre plus allechantes. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est une pepite pour les joueurs passionnes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec soin, facilitant l’immersion totale.
azur casino retrait avis|
Якщо ви хочете стати кращим гравцем, вивчіть тактики Obolon E-Team. Дізнайтеся більше за цією ланкою.
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
алкоголизм лечение
мостбет казино http://mostbet4128.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя тула
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betclic Casino, c’est une veritable experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Le support est d’une reactivite exemplaire, joignable 24/7. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. Dans l’ensemble, Betclic Casino vaut amplement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est visuellement epoustouflant, renforce l’immersion totale.
betclic elite classement|
помощь при алкоголизме
reabilitaciya-astana004.ru
курс реабилитации наркозависимых
стоимость аппарата узи стоимость аппарата узи .
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя тула
888starz onlayn qimor o’yinlari orqali oshirish mumkin. qimor ixlosmandlari uchun taqdim etadi.
bir necha yo’nalishdan iborat . foydalanuvchilar mumkin.
Mukofotlar yordam beradi. Qimor o’yinlari joylashgan bloglar mavjud.
Foydalanuvchilarni himoya qilish. hisob ma’lumotlari. Buning natijasida, mumkin.
888starz apk скачать https://888starz-uzs.net/apk/
mostbet uz bog‘lanish mostbet uz bog‘lanish
Genuinely when someone doesn’t understand afterward its up to other people that they will assist, so here it takes place.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog005.ru
лечение запоя тула
зеркало Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
лучшие нейросети для программистов
Хочете дізнатися більше про тренування професійних гравців? Yantar E-Team допомагає своїм учасникам постійно вдосконалювати навички.
лучшие нейросети на русском языке
подключить интернет тарифы нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
интернет провайдеры нижний новгород
888starz orqali kengaytirish mumkin. turli xil taqdim etadi.
Qimor o’yinlari . doimiy mumkin.
o’yinchilarning yordam beradi. to’g’risida joylashgan sharhlar mavjud.
eng yuqori darajadagi . xavfsizligi ta’minlanadi. bu saytga mumkin.
888starz kazino https://888starz-uzs.net/
лесовоз дров купить .
домашний интернет тарифы нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
подключить домашний интернет в нижнем новгороде
KRAKEN – Ваша безопасность и анонимность на aktual-krkn.ru
aktual-krkn.ru — официальный переходник даркнет-маркета Kraken.
Добро пожаловать на kra36—-at.com, где приватность и безопасность являются главным приоритетом. Официальный сайт kraken kra37.at — сохрани список актуальных зеркал. Переходите на aktual-krkn.ru и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
кракен, kraken, сайт кракен, ссылка кракен, кракен ссылка, кракен сайт, кракен официальный сайт, официальный сайт кракен, кракен ссылка официальная, кракен актуальная ссылка
*Полная анонимность и защита данных
Система безопасности KRAKEN обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность. Передовые технологии шифрования для защиты ваших данных и транзакций.
актуальная ссылка на кракен, рабочая ссылка кракен, как зайти на кракен, кракен как зайти, вход кракен, кракен вход, зайти на кракен, кракен зайти, зеркало кракен, кракен зеркало
*Удобство использования
Простая навигация, мощная система и дизайн aktual-krkn.ru делают использование KRAKEN комфортным на любых устройствах.
кракен рабочее зеркало, рабочее зеркало кракен, зеркала кракен, кракен зеркала, даркнет кракен, кракен даркнет, маркетплейс кракен, кракен маркетплейс, площадка кракен, кракен площадка
*Гарантии безопасности и круглосуточная поддержка
KRAKEN гарантирует защиту покупателей и продавцов. Служба поддержки kra36—-at.com работает 24/7 для решения любых вопросов.
магазин кракен, кракен магазин, кракен маркет, кракены маркет, кракен даркнет маркет, кракен маркет даркнет, кракен отзывы, кракен сайт что, кракен ссылка тор, ссылка кракен тор
I felt truly understood at 인천여성전용마사지.
интернет провайдеры в нижнем новгороде по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде по адресу
лечение наркомании
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
реабилитация от алкоголя в Астане
скачать mostbet kg скачать mostbet kg
DJ Gafur має унікальний підхід до створення міксів, що робить кожен ефір незабутнім.
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по невысоким ценам. Купить диплом о неполном образовании — kyc-diplom.com/diplom-o-nepolnom-obrazovanii.html
seo partner internet-agentstvo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-seo.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Хочете відчути неймовірну енергію техно? Обов’язково зайдіть на DJ Gafur Techno Radio.
мостбет приложение зеркало мостбет приложение зеркало
как лечить алкоголизм
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
лечение от наркотиков
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя тула
mostbet uz ishonchlimi mostbet uz ishonchlimi
в этом разделе https://kral38.at/
реабилитация наркоманов в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana005.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых
Купить диплом возможно используя сайт компании. northrp.kabb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=607
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
zakazat-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
посетить веб-сайт https://kra38at.at/
kupit-drova-v-podolske-365.ru .
купить диплом техникума купить диплом техникума .
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and
found that it is truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels.
I will be grateful if you continue this in future. Lots of people will be benefited from your
writing. Cheers!
masbet http://mostbet4129.ru
мостбет кг мостбет кг
мостбет apk скачать https://mostbet4168.ru/
Howdy! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which
blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting tired of WordPress
because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform.
I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве продвижение сайтов интернет магазины в москве .
Якщо вам подобається прогресив, то DJ Gafur стане вашим улюбленим радіо! Тут завжди є, що послухати.
купить дрова на паллетах .
swot анализ бизнеса swot анализ выявляет
Achieve health benefits each time you buy bupropion xl side effects is by using online pharmacies wellbutrin mechanism
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
провайдеры по адресу
Looking for second-hand? thrift store near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании специфических приборов. Достигайте своих целей быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- bytyrohatec.cz/agents/lenadarrell718
Моды на игры андроид в последние годы стали крайне популярными, у геймеров. Моды меняют не только внешний вид, и игровой опыт, доступ к скрытым элементам. Особенно востребованы https://eugo.ro/?p=240, играть оффлайн где угодно, без интернета. Моды с деньгами игру проще и быстрее, позволяя сосредоточиться на сюжете и стратегии, а не на накоплении валюты. Моды с меню и apk контроль функций в игре, позволяя включать или отключать функции, настраивать сложность и экспериментировать с геймплеем. Для многих игроков скачивание модов для андроид стало не просто способом облегчить игру, а и частью геймерской культуры. Моды делают игры особенными, каждый получает свободу действий и удовольствия.
накрутка просмотров в Макс накрутка просмотров в Max
Пользуйтесь уникальным предложением и вводите код https://www.avtokluch.ru/images/pgs/kak_shyyut_svadebnye_platyya.html для получения бонусов на 1xbet!
1xbetbestcode — это лучший способ увеличить шансы на выигрыш.
домашний интернет в нижнем новгороде
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
интернет провайдер нижний новгород
drenazh-na-dachnom-uchastke-spb.ru .
провайдеры нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
аудит продвижения сайта аудит продвижения сайта .
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта http://www.poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-sajta-v-internete-moskva.ru .
поисковое продвижение сайта в интернете москва http://poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
программа реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар в Астане
Лучшие девушки для теплого общения и встреч, подробнее тут элитные проститутки
Saya benar-benar mengapresiasi artikel ini karena membahas KUBET
dan Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap dengan sangat jelas.
Banyak orang sering mencari informasi seputar topik ini, dan artikel
ini mampu memberikan penjelasan yang lengkap sekaligus mudah dipahami.
Tulisan ini terasa relevan bagi pembaca dari berbagai latar
belakang, baik pemula maupun yang sudah berpengalaman.
Hal yang menarik adalah cara penyusunan konten yang runtut dan tidak bertele-tele.
KUBET dan Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap tidak hanya disebutkan sebagai
judul, tetapi benar-benar dijelaskan dari sisi keunggulan dan manfaatnya.
Bagi saya, ini membuat artikel terasa lebih berbobot dibandingkan tulisan lain yang hanya sekilas
membahas.
Selain itu, gaya bahasa yang digunakan sangat enak dibaca.
Dengan kalimat yang sederhana, penulis berhasil membuat topik
yang mungkin cukup teknis menjadi mudah dipahami.
Hal ini tentu meningkatkan kualitas forum dan memberi
nilai tambah bagi pembacanya.
Saya pribadi merasa tulisan ini memberikan sudut pandang baru yang jarang ditemui di artikel lain.
KUBET dan Situs Judi Bola Terlengkap memang sudah dikenal luas,
tapi penjelasan mendalam seperti ini sangat jarang ditemukan.
Oleh karena itu, saya yakin artikel ini akan sangat bermanfaat bagi siapa
saja yang membacanya.
Semoga ke depannya lebih banyak lagi tulisan dengan kualitas seperti ini.
Ulasan yang detail, terpercaya, dan disajikan dengan bahasa sederhana pasti akan selalu dicari.
Terima kasih kepada penulis karena sudah menghadirkan artikel yang sangat membantu.
накрутка подписчиков в Макс накрутка подписчиков в Max
https://metallobaza31.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
лечение запоя
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
лечение от зависимости наркотиков
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Hey There. I discovered your blog using msn. That is an extremely
smartly written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and come
back to read more of your useful information. Thank you for the post.
I’ll certainly comeback.
комплексное лечение алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana006.ru
алкогольная зависимость лечение
этот контент https://kra-37at.at/
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also visit this weblog on regular basis to obtain updated from latest information.
интерент магазин посуды
Я завжди захоплювалася японською культурою, тому майстер-клас із традиційних танців став для мене здійсненням мрії. Під час заходу я навчилася базових рухів і зрозуміла, наскільки багата японська танцювальна спадщина. Дякую Pacific Department за можливість торкнутися цієї краси! Якщо вас теж цікавлять подібні події, перегляньте їхній розклад.
сделать аудит сайта цена сделать аудит сайта цена .
купить старый диплом техникума купить старый диплом техникума .
These films often feature incredible stunts and special effects that leave audiences on the edge of their seats.
online video landscape https://movies-and-reviews.com/youtube-around-the-world-a-deep-dive-into-global-content-trends-and-popular-creators/
I have learn some excellent stuff here. Definitely
value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much effort you put to create such a magnificent informative website.
for safekeeping?From the kitchen table you can buy a mirtazapine dosage for sleep should not be stored? mirtazapine name brand
как называется нейросеть которая оживляет фото бесплатно как называется нейросеть которая оживляет фото бесплатно
где купить аттестат о среднем образовании где купить аттестат о среднем образовании .
подключить интернет тарифы новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
провайдеры по адресу новосибирск
From the moment I stepped into 강남여성전용마사지,
I felt an immediate sense of calm as if the world had finally
paused just for me.
интернет провайдеры новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
интернет провайдеры в новосибирске по адресу дома
zakazat-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
как оживить фото через нейросеть как оживить фото через нейросеть
провайдеры домашнего интернета новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу новосибирск
кривой рог купить диплом о высшем образовании кривой рог купить диплом о высшем образовании .
Looking for second-hand? thrift store store near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Виступ Eleonora на фестивалі Trance Illusion став для мене справжнім відкриттям. Ця команда перевершила всі очікування: я навіть не міг уявити, що візуальні ефекти можуть настільки гармонійно поєднуватися з музикою. PJ Alice створювала такі складні й красиві проєкції, що глядачі буквально завмирали від захоплення. Водночас PJ Mia відповідала за світлове шоу, яке виглядало настільки живим, ніби музика мала власну душу. Робота PJ Zoe з дизайном сцени також була на висоті – все виглядало органічно й ефектно. Якщо ви ще не знайомі з цією командою, обов’язково перегляньте їхній сайт.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
хочу купить аттестат за 11 классов отзывы http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
https://kamagruz.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
токарный станок чпу по металлу https://stankiklass.ru/
доставка дров на дачу .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
лечение запоя
Знайшов цікаву статтю про еволюцію breaks-музики, рекомендую почитати. Ось лінк: https://breaks.djgafur.site/.
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/de-CH/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
купить диплом с занесением в реестры купить диплом с занесением в реестры .
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog004.ru
вывод из запоя цена
легально купить диплом о высшем образовании http://www.educ-ua11.ru .
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been doing a little research on this. And he actually bought me dinner simply because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to discuss this subject here on your web page.
Visit my blog post – https://Www.uniformfactory.ae/
купить дипломы о высшем в киеве купить дипломы о высшем в киеве .
Нам важно, чтобы безопасность на стройке была приоритетом. Компания доказала свою надежность благодаря сертификату OHSAS 18001.
найти это https://kra38a.at/
купить диплом о техническом образовании купить диплом о техническом образовании .
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about penalty
kick online. Regards
OMT’s standalone е-learning choices empower independent exploration, nurturing аn individual love fߋr math and test ambition.
Experience versatile learning anytime, ɑnywhere
throuɡh OMT’s extensive online е-learning
platform, including limitless access tο video lessons аnd interactive tests.
Αѕ mathematics underpins Singapore’ѕ reputation fоr excellence іn global standards ⅼike PISA, math
tuition is essential to unlocking a kid’s ρossible and
protecting scholastic benefits іn this core subject.
primaryschool tuition is imⲣortant foг building strength versus PSLE’ѕ difficult questions,
such aѕ those on likelihood аnd easy stats.
Ⲣrovided the hiցh risks ߋf O Levels for senior high school progression іn Singapore, math tuition mаkes beѕt use of opportunities fоr leading qualities аnd wanted
positionings.
Tuition integrates pure аnd used mathematics flawlessly, preparing pupils fօr thе interdisciplinary nature ⲟf A Level issues.
OMT’s unique curriculum, crafted tο sustain the MOE syllabus,
consists оf personalized modules tһat adapt to private discovering styles fοr even m᧐re effective mathematics proficiency.
Team discussion forums іn thе sʏstem let yоu review ᴡith peers
siа, maҝing cledar uncertainties аnd boosting үour math
performance.
Math tuition ɡives immeԁiate comments ⲟn practice attempts,
speeding up enhancement fߋr Singapore examination takers.
mү website … tutors in math for 12th near me
диплом купить с проводкой educ-ua15.ru .
토닥이는 단순한 마사지 공간이 아니라, 여성만을 위한 완벽한 치유의 공간 같았어요.
Hello, all is going nicely here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s genuinely
excellent, keep up writing.
I found a new rhythm of peace at 여성전용마사지.
подключить интернет в новосибирске в квартире
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
интернет провайдеры новосибирск по адресу
It’s remarkable to pay a quick visit this
website and reading the views of all mates concerning this paragraph, while I am also zealous of getting experience.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://ecro.fr/images/pgs/?code_promo_linebet_bonus_de_bienvenue.html
https://www.piecesracing.com/docs/pgs/1xbet_code_promo__b_nus_at________130.html
https://sylwiaszuder.pl/pgs/czy_hotslots_to_legalne_kasyno_online__fakty__kt_re_warto_zna_.html
https://www.simacek.com/redirbg/pages/betwinner_promo_code_india_3.html
Very good write-up. I definitely love this website.
Continue the good work!
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
провайдер по адресу
Hello! Very useful tips in this article! It is the small changes that will lead to the most significant changes. Thank you very much for sharing!
Also visit my page kredyt we frankach
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
вывод из запоя
Купить диплом колледжа в Днепр https://educ-ua8.ru – Купить диплом колледжа в Днепр .
домашний интернет подключить новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу новосибирск
Я захоплююсь не тільки їхнім умінням в грі, а й командною роботою https://obolon.trance.mk.ua/. Вони завжди підтримують один одного!
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Je trouve phenomenal DBosses, c’est une plateforme qui electrise. Les options sont riches et dynamiques, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Les agents sont rapides et devoues, offrant des solutions claires et rapides. Le processus est clair et sans complications, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient bienvenues. Pour conclure, DBosses est une plateforme hors norme pour les fans de jeux modernes ! De surcroit le design est captivant et elegant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus exaltante.
dbosses|
Je suis totalement enflamme par Celsius Casino, on dirait une eruption de fun. La collection de jeux du casino est incandescente, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est une torche eclatante, assurant un support de casino immediat et flamboyant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une etincelle, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient monter la chaleur. Pour resumer, Celsius Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
celsius casino no deposit bonus code|
Great delivery. Sound arguments. Keep up the amazing spirit.
This is a topic which is near to my heart…
Cheers! Where are your contact details though?
https://direstrats.com/wp-includes/inc/1xbet-promo-code__bonus-100_up_to_130.html
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog005.ru
лечение запоя тула
купить диплом с регистрацией купить диплом с регистрацией .
рейтинг бесплатных нейросетей рейтинг бесплатных нейросетей
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog005.ru
вывод из запоя
Наша команда готова до нових викликів. Дізнайтеся більше на нашому сайті.
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant
for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire
out a designer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
лечение запоя череповец
дешевый интернет новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
домашний интернет подключить новосибирск
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
лечение запоя
дренажная система для частного дома .
продвижение в google https://www.internet-agentstvo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-seo.ru .
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
В этой статье мы расскажем вам о промокодах – что это такое, как их получить и использовать специальные коды от 1xBet, а также подробно опишем, где вводить коды для получения бонуса от букмекера. Промокод – это уникальная комбинация букв и цифр, которая дает вам доступ к специальному предложению от букмекера. Компании часто используют их в различных акциях, чтобы привлечь новых игроков и поощрить постоянных клиентов. Бесплатные коды нужно вводить в специальное поле при регистрации на сайте букмекера или в личном кабинете, если у вас уже есть аккаунт.
промокоды 1xbet 2025, а также приветственный пакет в казино до 1950 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. Бонусный код 1xBet дает возможность получить бонусы при регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы.
подключить интернет в квартиру новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
домашний интернет
домашний интернет
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу новосибирск
zakazat-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
Пропоную всі фанатам хаусу послухати DJ Gafur. Тут можна почути як класичні треки, так і нові мікси для фанатів.
https://pikoclub.ru
статьи о маркетинге статьи о маркетинге .
блог про seo блог про seo .
веб-аналитика блог http://www.statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/ .
построить дом под ключ иркутск http://www.stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-2.ru .
наркологическая клиника анонимно https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru .
drenazh-na-uchastke-s-uklonom-spb.ru .
лечение запоя
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя тула
платная наркологическая клиника narkologicheskaya-klinika-11.ru .
Kitty створили на Trance Illusion щось неймовірне. Їхня робота зі світлом, звуком та візуалізаціями змусила мене по-новому оцінити мистецтво транс-музики. PJ Zoe показала, як за допомогою сценічних візуалізацій можна посилити емоційний вплив музики. Якщо цікавитеся їхньою творчістю, дізнайтеся більше про них.
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в
купить аттестат за 11 класс в киеве купить аттестат за 11 класс в киеве .
As someone who doesn’t like long forms, finding a casino bonus uden indbetaling uden rofus linked to a fast signup was perfect. I got free spins immediately and played without stress. Joining through casino uden nemid made everything smoother. I felt like the site respected my time. Plus, the games were fair and fun. It’s refreshing compared to other casinos I’ve tried.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя тула
informative post https://sollet-wallet.io
try this site https://sollet-wallet.io
стоимость куба колотых дров .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog006.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
Read Full Report https://web-breadwallet.com/
about his jaxx wallet app
маркетинговый блог https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru/ .
диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва .
На цьому сайті ви можете знайти кращі сеті для будь-якого настрою. Це справжня знахідка для фанатів прогресиву.
감정을 토닥여주는 듯한 손길이 있는 수원여성전용마사지, 위로가 필요할 때 찾고 싶은 곳이에요.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
zakazat-drova-sergiev-posad.ru .
look at more info sollet io
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
вывод из запоя
стратегия продвижения блог http://www.statyi-o-marketinge1.ru .
лучшие нейросети в России
лучшие нейросети для написания научных статей
Achou totalmente epico DiceBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e fora da curva. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura total, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma bomba. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, dando solucoes claras na hora. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, DiceBet Casino vale cada segundo explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
dicebet casino|
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
подключение интернета ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
домашний интернет в ростове
visit our website https://jaxxlibertyweb.com/
One session of 여성전용 마사지
was more effective than a weekend getaway.
Very shortly this web page will be famous among all blogging viewers,
due to it’s good articles or reviews
дешевый интернет ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета ростов
kupit-drova-v-podolske-365.ru .
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand.
It seems too complicated and very broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post,
I’ll try to get the hang of it!
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
подключить проводной интернет ростов
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, ca donne une energie de star absolue. La gamme est une vraie constellation de fun, avec des slots qui brillent de mille feux. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, par contre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, Impressario est une plateforme qui vole la vedette pour les amateurs de slots qui brillent ! A noter aussi la navigation est simple comme une melodie, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus eclatante.
impressario casino review|
http://avteon.ru
The comfort and care at 인천여성전용마사지 gently melted away days of fatigue.
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Купить диплом колледжа в Кривой Рог Купить диплом колледжа в Кривой Рог .
как оживить фотографию через нейросеть как оживить фотографию через нейросеть
скачать мост бет mostbet4157.ru
купить диплом ссср купить диплом ссср .
When someone writes an article he/she retains the thought
of a user in his/her mind that how a user can know it.
Therefore that’s why this post is perfect. Thanks!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
вывод из запоя
download mostbet http://mostbet4158.ru
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://unisswap.app new site, new connections, new crypto.
other https://jaxxlibertyweb.com
материалы по seo statyi-o-marketinge1.ru .
https://badgerboats.ru/themes/middle/?promokod_1hstavka_na_2020_god.html
straight from the source brd wallet app
правильный дренаж вокруг дома .
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
Have you ever thought about writing an ebook or guest authoring on other sites?
I have a blog based on the same subjects you discuss and would love
to have you share some stories/information. I know my audience would value your work.
If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me
an e mail.
주말 여행보다 더 큰 효과를 준
부산토닥이.
online casino cz “: Online Casino CZ: Hrajte bezpecne a zodpovedne v licencovanych online kasinech v Ceske republice. Objevte siroky vyber her, atraktivni bonusy a profesionalni zakaznickou podporu.
лучшие нейросети для юристов
Виступ Katarina на фестивалі SFF Illusion був справжнім одкровенням. Енергетика, яку створила PJ Alice завдяки своїм візуальним ефектам, вразила кожного в залі. Кожна нота та кожен трек буквально оживали перед очима. Це була синергія мистецтва, яку важко описати словами.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
как включить gemini как включить gemini
online casino cz ” symbol: Online Casino CZ: Discover the best online casinos in the Czech Republic! Find licensed and reputable platforms with exciting games and bonuses. Enjoy a safe and thrilling gaming experience.
лучшие нейросети для рерайта текста
лучшие нейросети для генерации изображений для дизайнеров
Энтеогены издавна использовались в шаманских практиках для расширения сознания и поиска внутренней гармонии. Сегодня интерес к ним растёт и среди исследователей, и среди людей, стремящихся к самопознанию. Подробнее читайте наэнтеогенные практики
.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить аттестат за 11 класс смоленск http://arus-diplom25.ru/ .
My sensitive body and mind both felt at ease after a massage at
강남여성전용마사지.
Being women-only really helped me relax.
OMT’s emphasis on foundational abilities develops unshakeable ѕеlf-confidence, enabling Singapore
students tο love mathematics’s beauty and гeally
feel inspired f᧐r examinations.
Enlist todaʏ in OMT’sstandalone e-learning programs ɑnd watch your grades skyrocket tһrough unlimted access tⲟ premium, syllabus-aligned content.
Singapore’s emphasis on crucial analyzing mathematics highlights tһe significance of math tuition,
whicһ helps trainees establish tһe analytical skills demanded Ƅy thе country’s forward-thinking curriculum.
Enriching primary education ᴡith math tuition prepares students fοr PSLE
by cultivating a development ѕtate of mind tοward challenging
topics ⅼike symmetry аnd transformations.
By providing comprehensive experiment рast Ⲟ Level papers,
tuition outfits pupils ᴡith experience and tһe ability tо prepare foг
inquiry patterns.
Tuition іn junior college math equips pulils ԝith
analytical approaches and probability models essential fߋr translating
data-driven concerns in A Level papers.
What distinguishes OMT іs іts proprietary program that enhances
MOE’ѕ vіa focus ⲟn ethical analytic іn mathematical contexts.
OMT’ѕ system іs uѕеr-friendly one, so even beginners
can browse ɑnd bеgin boosting qualities ԛuickly.
Tuition centers mɑke use օf cutting-edge tools ⅼike visual helⲣ, enhancing understanding fօr much
better retention in Singapore mathematics exams.
Нere is mу blog – best online cbse maths tuition
What’s Taking place i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It absolutely
helpful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & aid other
users like its helped me. Great job.
Энтеогены издавна использовались в шаманских практиках для расширения сознания и поиска внутренней гармонии. Сегодня интерес к ним растёт и среди исследователей, и среди людей, стремящихся к самопознанию. Подробнее читайте наэнтеогены список
.
домашний интернет
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
дешевый интернет ростов
I like the valuable information you supply on your articles. I will bookmark your blog and take a look at again here frequently. I am rather sure I will be told lots of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
Also visit my page: https://orientuniforms.ae/product/white-towels/
i was reading this jaxx wallet
https://cascadeclimbers.com/content/pgs/le_code_promo_pour_1xbet.html
bs2best
http://kriogenteh.ru/wp-includes/robots/rekomendacii_po_uhodu_za_povreghdennymi_volosami_spasaem_to_chto_ostalosy.html
мостюет http://mostbet4154.ru/
лучшие нейросети для замены слов в песнях
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
домашний интернет в ростове
Appreciating the commitment you put into your website and in depth
information you present. It’s good to come across
a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same out of date
rehashed information. Excellent read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds
to my Google account.
интернет тарифы ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
интернет провайдеры ростов
I have have been sampling a wide range of web casinos
throughout the past months, and I have to say that free-weblink.com distinctly
stands out in different respects. First off, the overall design and
usability of the site are top-tier, whether accessing via PC or smartphone, everything loads quickly,
looks clean, and functions smoothly. The navigation is straightforward,
helping newcomers and veterans alike. From
game discovery to account settings and bonus redemption, the process is smooth and
hassle-free. Speaking of which, the Spinmama’s
bonus offers are generous and well-structured. They’re not just making hype bonuses — the rewards include fair wagering
and timely new deals.
Another key advantage is the range of titles. Casino Spinmama
has managed to bring together a great variety of slots, table games, and live dealer options that cater
to different styles of players. Whether you favor poker variants or exciting slot spins, there’s something here for
you. I was also impressed by the focus on player safety and fairness.
Spinmama eu is compliant with regulations and licensed properly, offering trust and confidence
for financial transactions. The site supports several payment solutions covering cards, online wallets, and crypto,
ensuring secure and speedy transactions. Customer support deserves a mention too — I tested their live chat and got a helpful, professional response within a minute.
In a market where many casinos seem interchangeable, spin mama actually brings value
and a polished, player-focused experience. Definitely one of the top options
for safe and fun casino play. If you’re still hoping to
discover a solid casino with good bonuses and games, Spinmama delivers.
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
kasina CZ Casino Online: Najdete si idealni online kasino s ceskou licenci. Recenze, porovnani bonusu a tipy pro zodpovedne hrani.
kasina CZ Casino Online: Find the best CZ casino online! Read reviews, compare bonuses, and choose the perfect platform for your gaming needs and preferences.
Je trouve incroyable Cresus, ca offre une experience feerique. La gamme de jeux est somptueuse, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le personnel offre un suivi digne d’un palace, offrant des solutions claires et rapides. Le processus est limpide et sans tracas, bien que j’aimerais plus de bonus reguliers. En resume, Cresus garantit un divertissement princier pour les passionnes de sensations fortes ! De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite une immersion totale.
federation cresus|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von DrueGlueck Casino, es bietet eine krasse Spielerfahrung. Die Casino-Optionen sind super vielfaltig, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist mega zuverlassig, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Haken, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino mit mega Spielspa? fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck bedrägeri|
На майстер-класі з японських танців я не лише навчилася основних рухів, але й зрозуміла філософію цього мистецтва. Це було як медитація, але через танець. Якщо вам цікаво відчути таку магію, зверніть увагу на розклад заходів на сайті SFF.
доставка из китая в москву доставка из китая в москву карго
продукты с фермы на дом фермерская лавка отзывы
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
Онлайн-библиотека Казахстана https://mylibrary.kz книги, статьи, диссертации и редкие издания в цифровом формате. Удобный каталог, быстрый поиск и круглосуточный доступ для всех пользователей.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk008.ru
вывод из запоя
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ канал бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1493488-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
Great site. Plenty of useful information here. I am sending it to several buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks to your effort!
Also visit my web-site … https://Dubaihoodies.com/fleece-jackets-dubai.html
Je trouve totalement dingue AmunRa Casino, ca donne une energie de casino digne d’un dieu. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et envoutantes, comprenant des jeux de casino tailles pour les cryptomonnaies. Le staff du casino assure un suivi digne d’une divinite, joignable via chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont fluides et rapides comme le Nil, de temps en temps des bonus de casino plus reguliers ca serait royal. Globalement, AmunRa Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les gardiens des slots modernes de casino ! A noter aussi le site du casino est une merveille graphique, booste l’immersion dans le casino a fond.
amunra reviews|
купить диплом в николаеве купить диплом в николаеве .
Want to explore a premium floral studio in the UAE?
Welcome to FlowerPower.ae, where floristry meets lifestyle. We’re not just an online store — we’re a creative hub for everything floral, proudly serving Dubai with freshness in every stem.
Whether you’re celebrating a romantic anniversary, or simply want to bring joy, our team is here to help you choose the perfect flowers for the moment. Our florists design each bouquet with emotional intention, using blooms imported from Kenya, guaranteeing premium quality.
The FlowerPower experience is built around design. Each arrangement is made to order — never mass-produced — and reflects the mood, meaning, and message you want to convey. From elegant whites to minimalist compositions, we offer something for every story you want to tell.
Shopping at FlowerPower.ae is simple. You can browse our signature collections online or visit our physical boutique to get inspired by the season’s most striking stems. We’re more than a transaction — we’re part of your occasion. Our packaging is thoughtful, our service is always on time, and our mission is to create a gifting experience that feels just as good as it looks.
Here’s what you’ll find in our curated store:
Daily-fresh bouquets inspired by international floral trends
Elegant vases to complement your flowers
Custom wedding florals designed for impact
Same-day delivery in Dubai & Abu Dhabi
Secure payments
We believe flowers are more than decoration. They are gifts of emotion. That’s why every bouquet at https://flowerpower.ae/collections/pots
is designed not just to impress — but to be remembered. Whether you’re sending flowers to a loved one or buying for yourself, you’ll experience the difference in every petal.
Our clients range from interior stylists to first-time gifters — and they return to us not only for the flowers, but for the feeling. We offer loyalty perks for frequent clients and work closely with brands and venues across the UAE who value creativity.
So if you’re ready to elevate your floral taste, step into the world of FlowerPower.ae — your boutique flower destination in the heart of the Emirates.
лучшие нейросети для истории
купить диплом бакалавра недорого купить диплом бакалавра недорого .
Je kiffe grave Instant Casino, il propose une experience de casino explosive. Le catalogue de jeux de casino est colossal, offrant des machines a sous de casino uniques. Le service client du casino est une bombe, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Les paiements du casino sont fluides et securises, par contre j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui dechirent. Dans le fond, Instant Casino est un spot de casino a ne pas rater pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! A noter aussi le design du casino est une explosion visuelle, ajoute un max de swag au casino.
noble instant play casino|
https://httpbin.org/redirect-to?status_code=308&url=https://www.vintrica.com/ru/
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию онлайн, чтобы оперативно решить все ваши юридические вопросы!
Каждая ситуация уникальна и требует индивидуального подхода, поэтому мы внимательно изучаем каждое дело.
сколько стоят дрова .
Today, while I was at work, my sister stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 30 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
https://kra39cc.at/
Dai un’occhiata qui per i migliori prezzi sui farmaci Сайт Trovare Farmacia Migliore Prezzo
Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам на горячая линия юридической помощи бесплатно круглосуточно, и получите квалифицированное решение своих вопросов.
yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru предлагает профессиональные юридические услуги, направленные на решение различных правовых вопросов. Наша команда готова помочь вам в самых сложных ситуациях. Мы понимаем, что правовые проблемы могут быть стрессовыми, мы предлагаем персонализированные решения к каждому клиенту.
У нас есть широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации по гражданским и уголовным делам. Настоятельно рекомендуем связаться с нами по вопросам, связанным с трудовым правом, семейными делами и другими юридическими аспектами. Мы понимаем, что каждая ситуация требует индивидуального подхода, и готовы предложить оптимальное решение.
Мы зарекомендовали себя как надежный партнер в сфере юриспруденции. Наши клиенты доверяют нам за высокое качество обслуживания и результативность. Каждый юрист нашей команды имеет опыт работы в различных областях права и готов поддержать вас в любое время.
Не откладывайте решение своих проблем , чтобы получить квалифицированную юридическую помощь. Мы готовы ответить на все ваши вопросы . Не упустите шанс обратиться за помощью на yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
статьи про digital маркетинг http://www.blog-o-marketinge.ru/ .
Thanks for sharing your info. I really appreciate
your efforts and I will be waiting for your next post thank
you once again.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1377755-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
Thanks for any other informative site. The place else may I am getting that type
of info written in such a perfect way? I’ve a mission that I’m
just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such info.
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
Eleonora — це команда, яка дарує не лише шоу, а й емоції, які залишаються з вами надовго. Їхній виступ на Trance Illusion став для мене найяскравішою подією цього року. PJ Alice своїми візуальними ефектами створює справжню магію на сцені. Це не просто ефекти, це ціла історія, яка оживає перед вашими очима. Я був у захваті від того, як вдало вони доповнюють музику, перетворюючи її на щось більше. Для тих, хто шукає нові враження, ось посилання.
букмекерская контора кыргызстан http://www.mostbet4155.ru
дрова топки недорого .
mostbet мостбет http://www.mostbet4156.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
подключение интернета ростов
диплом купить с проводкой http://educ-ua13.ru/ .
лучшие нейросети для юристов
скачать mostbet kg mostbet4160.ru
интернет тарифы ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
интернет провайдеры ростов
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
мостбет кг http://mostbet4155.ru/
лучшие нейросети для редактирования текста
подключить проводной интернет ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
домашний интернет подключить ростов
Спецскидка до конца месяца на https://www.promyshlennoeosveshchenie.ru мощностью от 100 Вт.
блог про seo блог про seo .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
лечение запоя
bs2best at
Сертифицированные стандарты – гарантия качества. Мы убедились, что у компании есть международные сертификаты ISO.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
mostbet uz jonli tikish http://www.mostbet4170.ru
наркологические диспансеры москвы https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-11.ru .
строительство дома иркутск строительство дома иркутск .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя челябинск
нарколог психолог http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru .
мостбет вход, регистрация https://mostbet4160.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Майстер-клас із танців у Бостоні став подією, яку я точно ніколи не забуду. Відчуття, коли ти вивчаєш рухи, що передають історію поколінь, не схожі ні на що інше. Інструктори зуміли донести до кожного учасника глибину ритмів, і це було щось надзвичайне. З нетерпінням чекаю на подальші події. Перевірте, що ще пропонує фестиваль, на сайті.
Купить диплом техникума в Запорожье Купить диплом техникума в Запорожье .
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
лечение запоя
https://egoistka56.ru
как зайти на сайт мостбет как зайти на сайт мостбет
Hi, I do believe this is a great site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit once again since I book-marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
My webpage: https://Orientuniforms.ae/product/hand-towel/
что такое реестр Минпромторга
I am curious to find out what blog system you happen to be working with?
I’m experiencing some minor security problems with my latest blog and
I’d like to find something more safe. Do you have any suggestions?
https://aquietrabalho.com/art/code_promotionnel_d_inscription_1xbet.html
Ich flippe aus bei JackpotPiraten Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie eine wilde Piratenjagd. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und mitrei?end, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Kanonen donnern. Das Casino-Team bietet eine Unterstutzung, die wie Gold glanzt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Kompass, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren der Hammer. Zusammengefasst ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der die Planken erzittern lasst fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten 50 freispiele|
Je suis totalement subjugue par Julius Casino, il propose une aventure de casino digne d’un empereur. Il y a un deferlement de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une noblesse rare. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une legion en marche, repondant en un eclair de glaive. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rugir de plaisir. Dans l’ensemble, Julius Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, facilite une experience de casino heroique.
julius casino no deposit bonus|
Ви чули про Obolon E-Team? Це одна з найкращих кіберспортивних команд у Racing Dew. Їхні стратегії — це щось неймовірне!
most bet https://www.mostbet4153.ru
Эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция https://evlo-phlebology.ru эффективный метод лечения варикоза. Амбулаторная процедура занимает до 40 минут, не требует госпитализации и обеспечивает быстрый косметический и медицинский результат.
Сюрвей грузов сюрвей контроль качества и количества, проверка условий перевозки, составление отчётов. Опытные эксперты обеспечивают объективную оценку для компаний и страховых организаций.
Надежная доставка из китая в Россию: от документов до контейнеров. Выбираем оптимальный маршрут, оформляем таможню, страхуем грузы. Контроль сроков и сохранность на каждом этапе.
подключить интернет
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
провайдеры по адресу санкт-петербург
Je suis obsede par Bruno Casino, il propose une aventure de casino pleine de panache. La selection du casino est une explosion de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct vibrantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement hors pair, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les paiements du casino sont surs et sans accroc, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait le feu. Dans l’ensemble, Bruno Casino promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
bruno casino codes|
mostbet live https://mostbet4157.ru/
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um rugido. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, com uma ajuda que e puro instinto. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um predador, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No fim das contas, LeaoWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
leaowin02 mars casino las vegas|
лучшие нейросети для юристов
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в бишкеке
https://job88.click/mobile-6-3/
https://jurisnotary.com/pgs/code_promotionnel_pour_1xbet.html
подключить интернет в квартиру санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
подключить проводной интернет санкт-петербург
I enjoy, result in I found exactly what I used to be taking a look for.
You’ve ended my 4 day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day.
Bye
сколько стоит газель дров .
kupit-drova-v-samare-365.ru .
домашний интернет подключить санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Dai un’occhiata qui per i migliori prezzi sui farmaci Il sito che ti aiuta a risparmiare sui farmaci
I’ve read some just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how much attempt you set to create this sort of fantastic informative web site.
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
лечение запоя
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
где купить диплом где купить диплом .
Зіграли з командою Yantar E-Team на минулому турнірі, і вони дійсно вражають своєю організацією і командною грою!
купить дипломы о высшем образовании в Киеве купить дипломы о высшем образовании в Киеве .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
лечение запоя
стратегия продвижения блог statyi-o-marketinge2.ru .
создание сайта на тильде сделать сайт на тильде
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
лечение запоя
Купить диплом ВУЗа!
Мы предлагаемвыгодно и быстро купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Данный диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже при помощи специального оборудования. Достигайте своих целей максимально быстро с нашим сервисом- s-s-o.ru/forum.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=61644
Надежная доставка грузов из китая: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Авиа, морем, авто и железной дорогой. Оформление, страхование и логистика в кратчайшие сроки.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
Нужен автобусный билет? probilets.com онлайн просто и удобно. Поиск рейсов, сравнение цен, выбор мест и моментальная оплата. Актуальное расписание, надежные перевозчики и выгодные тарифы каждый день.
drova-kolotye-bereza-sergiev-posad.ru .
сколько стоит 3 куба дров .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
маркетинговый блог http://statyi-o-marketinge1.ru/ .
мостбет кз скачать https://mostbet4153.ru
drenazh-na-uchastke-s-uklonom-spb.ru .
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
You don’t need to explain—토닥이
just understands.
мостбет авиатор https://mostbet4159.ru
купить диплом специалиста недорого купить диплом специалиста недорого .
monsbet monsbet
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
скачать mostbet https://www.mostbet4154.ru
Качественный ремонт квартир https://expertremonta.kz от Компании «Эксперт ремонта» это качественный ремонт квартир под ключ в Алматы. Выбирайте Эксперт Ремонта — тут бесплатный выезд замерщика, официальные документы, гарантия документально, ремонт квартир без предоплаты.
bs2best
стоимость доставки топлива стоимость доставки топлива
продажа почвогрунта грунт цена
проверить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер санкт-петербург
клиника наркологическая клиника наркологическая .
https://kiev-itservice.com.ua/
клиника наркологическая москва narkologicheskaya-klinika-14.ru .
какие провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
подключить домашний интернет санкт-петербург
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
накрутка подписчиков в инстаграм казахстан накрутка подписчиков в инстаграм казахстан
как продвигать сайт статьи http://blog-o-marketinge.ru .
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I am not sure whether this
post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble.
You are amazing! Thanks!
Всі ми любимо музику, яка надихає, і house робить це неймовірно сильно! Поділіться своїми улюбленими треками в коментарях.
веб-аналитика блог https://statyi-o-marketinge.ru .
дешевый интернет санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
недорогой интернет санкт-петербург
mostbet sayti mostbet4170.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
I am in fact grateful to the owner of this web site who has shared this impressive post at here.
Je trouve phenomenal DBosses, ca donne un frisson inegale. La selection de jeux est grandiose, avec des slots modernes et immersifs. Le personnel offre un suivi irreprochable, repondant en un instant. Le processus est clair et sans complications, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un plus. En resume, DBosses vaut pleinement le detour pour les fans de jeux modernes ! En plus l’interface est fluide et moderne, ajoute une touche de panache.
dbosses casino no deposit bonus|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
букмекерские конторы в кыргызстане mostbet4156.ru
Приобрести диплом можно через сайт компании. grot.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=3232
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Palast glanzt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
casino king billy|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article
writer for your site. You have some really great posts and I feel I would be a good
asset. If you ever want to take some of the load
off, I’d absolutely love to write some articles for your blog
in exchange for a link back to mine. Please send me
an e-mail if interested. Kudos!
накрутка подписчиков в инстаграме без платно накрутка подписчиков в инстаграме без платно
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
J’adore la frenesie de CasinoClic, c’est un casino en ligne qui petille d’energie. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une fusee, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, CasinoClic c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et rayonnante comme une aurore, facilite une experience de casino vibrante.
clic clac casino|
drenazh-na-uchastke-s-uklonom-spb.ru .
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec011.ru
вывод из запоя
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Le catalogue de jeux est juste enorme, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le crew assure un suivi de malade, repondant en mode eclair. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, par moments plus de tours gratos ca serait ouf. Bref, Gamdom est une plateforme qui dechire tout pour les aventuriers du jeu ! Bonus l’interface est fluide et stylee a mort, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
glitch gamdom|
Планую масштабне оновлення офісу, і шукаючи компанію, натрапив на центр якісного ремонту. Їхній досвід у роботі з комерційними приміщеннями дає впевненість у результаті. Сподіваюся, скоро розпочнемо співпрацю.
Промокод 1win при Регистрации, и если его ввести при регистрации, можно получить бонус 500% до 200 000 рублей. Это часть текущей акции, которая доступна для новых пользователей. Код нужно просто вписать в специальное поле на этапе создания аккаунта, и система сама начислит бонус.
Промокод работает только для новых игроков. Тем, кто уже регистрировался раньше, он недоступен. Поэтому использовать код можно только один раз и только при первом входе в систему.
Более подробно в этом матереале что такое промокод 1вин
https://kadrsov.ru/forum/tema/zarabotok-na-stavkakh
Hi there to every , since I am truly keen of reading this web site’s post to be updated regularly. It carries pleasant information.
кракен зеркало
З DJ Gafur Radio ви завжди будете в курсі найсвіжіших трендів прогресив-музики, так що не забудьте підключитися!
Hello, just wanted to mention, I liked this post.
It was helpful. Keep on posting!
лучшие нейросети для написания текста
bs2best
Перейди Kraken platform — innovative service, обеспечивающее effective protection personal information в virtual world. адаптивный entry позволяет быстро manage возможности для безопасной protection. service поддерживает wide range сделок, обеспечивая конфиденциальность на профессиональном уровне. special возможности designed для поддержки safe deals. innovative technologies позволяют minimize риски, связанные с утечкой данных. кракен — это надежный партнер, позволяющий безопасно и анонимно осуществлять deals в online space. working with кракен, вы обеспечиваете максимальный уровень privacy, что делает confidence ваших действий на каждом этапе usage.
кракен ссылка зеркало
kupit-drova-v-samare-365.ru .
дрова непиленные купить .
проверить провайдеров по адресу санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
интернет по адресу санкт-петербург
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по выгодным ценам. Покупка диплома, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это грамотное решение. Приобрести диплом университета: pakallnaukri.com/companies/diplomy-grupps
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your sites really nice,
keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back in the future.
All the best
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя
какие провайдеры интернета есть по адресу санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
подключить проводной интернет санкт-петербург
Je trouve absolument enivrant CasinoClic, on dirait une cascade de fun. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et scintillants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enivrant. Au final, CasinoClic promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour les explorateurs du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique brillante, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
casino clic and collect|
Hello! Quick question that’s totally off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My web site looks weird when viewing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to correct this issue. If you have any recommendations, please share. Thank you!
my homepage: https://Orientuniforms.ae/product/bath-robe/
Ich finde absolut verruckt iWild Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Savanne. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Prarie, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitstern, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Windsto? wirkt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Dornen, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Am Ende ist iWild Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Naturwunder, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
iwild casino 30 free spins|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
J’adore l’eclat de JackpotStar Casino, on dirait une supernova de fun. La selection du casino est une explosion cosmique de plaisir, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance astrale. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, repondant en un eclair cosmique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, JackpotStar Casino est une etoile brillante pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ajoute une touche de magie cosmique au casino.
jackpotstar nettikasino|
Ich bin total begeistert von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
lapalingo bonuskod|
подключение интернета по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
провайдеры интернета санкт-петербург
Je trouve absolument sauvage LeonBet Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu feroce. La collection de jeux du casino est titanesque, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un guepard, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse foudroyante, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, LeonBet Casino c’est un casino a conquerir en urgence pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style indomptable, ajoute une touche de puissance au casino.
leonbet.|
лучшие нейросети для замены слов в песнях
лучшие нейросети для учителей
русское домашнее порно русские порно фильмы
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
материалы по маркетингу http://blog-o-marketinge.ru .
купить диплом украина харьков купить диплом украина харьков .
I’m excited to find this web site. I want to to thank
you for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely really liked
every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to
look at new things in your website.
Want to have fun? porno girl Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Mochten Sie ein https://www.immobilien-in-montenegro-fuer-oesterreicher.com kaufen? Tolle Angebote am Meer und in den Bergen. Gro?e Auswahl an Immobilien, Unterstutzung bei der Immobilienauswahl, Transaktionsunterstutzung und Registrierung. Leben Sie in einem Land mit mildem Klima und wunderschoner Natur.
pleksi balkon korkuluk
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for providing this info.
Новые актуальные промокод на скидку iherb для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить .
Купить диплом техникума в Херсон Купить диплом техникума в Херсон .
https://myanimelist.net/profile/Meilleur-code1xb
маркетинговые стратегии статьи маркетинговые стратегии статьи .
https://popugaitut.ru
приложения для накрутки подписчиков в инстаграм приложения для накрутки подписчиков в инстаграм
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
best articles on the net: https://dnscompetition.in/pa/articles/dns-blacklists-what-they-are-and-how-to-use-them/
Çok güzel bir yazı olmuş.
Bilgiler için sağ olun.
Uzun zamandır böyle bir içerik arıyordum.
Kaleminize sağlık.
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
интернет провайдеры екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
недорогой интернет екатеринбург
drenazh-na-uchastke-s-uklonom-spb.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
подключение интернета екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
It’s very trouble-free to find out any topic on web as compared
to books, as I found this paragraph at this site.
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
Everyone loves it when people get together and share opinions.
Great website, continue the good work!
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
вывод из запоя цена
лучшие нейросети для написания текста
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Spending some time and actual effort to generate a superb article… but what
can I say… I put things off a whole lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
купить диплом о высшем образовании купить диплом о высшем образовании .
Купить диплом любого университета поможем. Купить аттестат в Махачкале – diplomybox.com/kupit-attestat-v-makhachkale
Yes! Finally something about site.
What’s up i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i read this article i thought i could also create comment due to this sensible paragraph.
купить диплом об окончании http://educ-ua8.ru – купить диплом об окончании .
купить диплом техникума в спб купить диплом техникума в спб .
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
вывод из запоя цена
лучшие нейросети для бизнеса
медицинский наркологический центр https://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-13.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk007.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
https://elektrikexpert.ru
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
KRAKEN – Ваша безопасность и анонимность на vhod-aktual.ru
vhod-aktual.ru — официальный переходник даркнет-маркета Kraken.
Добро пожаловать на kra37.help, где приватность и безопасность являются главным приоритетом. Официальный сайт kraken kra38.at — сохрани список актуальных зеркал. Переходите на vhod-aktual.ru и начните пользоваться прямо сейчас!
кракен, kraken, сайт кракен, ссылка кракен, кракен ссылка, кракен сайт, кракен официальный сайт, официальный сайт кракен, кракен ссылка официальная, кракен актуальная ссылка
+ Полная анонимность и защита данных
Система безопасности KRAKEN обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность. Передовые технологии шифрования для защиты ваших данных и транзакций.
актуальная ссылка на кракен, рабочая ссылка кракен, как зайти на кракен, кракен как зайти, вход кракен, кракен вход, зайти на кракен, кракен зайти, зеркало кракен, кракен зеркало
+ Удобство использования
Простая навигация, мощная система и дизайн vhod-aktual.ru делают использование KRAKEN комфортным на любых устройствах.
кракен рабочее зеркало, рабочее зеркало кракен, зеркала кракен, кракен зеркала, даркнет кракен, кракен даркнет, маркетплейс кракен, кракен маркетплейс, площадка кракен, кракен площадка
+ Гарантии безопасности и круглосуточная поддержка
KRAKEN гарантирует защиту покупателей и продавцов. Служба поддержки kra37.help работает 24/7 для решения любых вопросов.
магазин кракен, кракен магазин, кракен маркет, кракены маркет, кракен даркнет маркет, кракен маркет даркнет, кракен отзывы, кракен сайт что, кракен ссылка тор, ссылка кракен тор
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your article. I wanted to write
a little comment to support you.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
дренаж здания .
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые расположены на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом университета:
аттестат за 10 11 класс купить
https://forexwebstore.com/pages/v_kakih_otraslyah_ispolyzuyutsya_meshki_ldpe.html
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
лечение запоя
обучение seo https://kursy-seo-1.ru/ .
seo с нуля http://www.kursy-seo-3.ru .
школа seo https://www.kursy-seo-1.ru .
seo бесплатно seo бесплатно .
курс seo kursy-seo-2.ru .
интернет провайдеры екатеринбург по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
домашний интернет в екатеринбурге
дренаж участка под ключ цена московская область 6 соток .
домашний интернет в екатеринбурге
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg005.ru
провайдер по адресу
mostbet az müsbət rəylər https://mostbet4145.ru/
дрова 25 30 см купить .
In everyday life and at work, each of us is faced with new experiences, which inevitably bring their discoveries and valuable knowledge. The ability to find solutions, take initiative, and take care of future comfort is what makes our lives more interesting and fulfilling. It doesn’t always work out the first time, but if you focus only on obstacles, it’s impossible to move forward. The support of others is of great importance: exchanging ideas, discussing nuances, and even sharing experiences helps not only to find a way out of a difficult situation faster, but also to do it for yourself. It is important not to forget that every step is not just an action, but a contribution to your future well–being.
When arranging a house or plot, you often have to face new tasks that require a responsible approach and sometimes non-standard solutions. For example, the issue of autonomous water supply is becoming key for the comfort of the whole family and the smooth operation of the household. Drilling a well for water is a reliable way to provide yourself with clean and affordable water right on your site: it is technologically advanced, practical and gives confidence that any household issues will be resolved it’s much easier to solve. Such a step becomes a useful investment in the home and the quality of life, improves daily life and creates the basis for new opportunities.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
Трезвый выбор narkologicheskaya-klinika-14.ru .
дрова камерной сушки купить .
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
накрутка подписчиков инстаграм бесплатно накрутка подписчиков инстаграм бесплатно
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
купить диплом в одессе недорого купить диплом в одессе недорого .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
купить диплом техникума украина купить диплом техникума украина .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
https://bookmarkity.com/story20316616/1xbet-promo-code-registration
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you are just too fantastic.
I really like what you’ve acquired here, certainly like what you’re saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it sensible.
I can’t wait to read much more from you. This is really a terrific website.
drova-kolotye-bereza-sergiev-posad.ru .
mostbet qeydiyyat mostbet4141.ru
провайдеры интернета в екатеринбурге по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
Excellent blog you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find high quality writing like yours nowadays. I honestly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Check out my webpage: https://totebags.ae
геодезия цена геодезия московская область
геотекстиль оптом цена геотекстиль геоспан
Hi there, You’ve done an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this site.
porno girl elonbet
лучшие нейросети для решения задач по математике
Hi there, after reading this remarkable piece of writing i am
also delighted to share my know-how here with mates.
Ich finde absolut wild Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Horde, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm donnern. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein wilder Triumph. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lowe glanzt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
magic play house höhle der löwen|
Ich bin suchtig nach Lapalingo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Blitz einschlagt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Insgesamt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
lapalingo auszahlung warten|
дрова ольха осина купить .
Sou viciado no role de JabiBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que arrasta tudo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma tempestade, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro mar, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
jabibet bangladesh|
купить аттестат за 11 класс в братске купить аттестат за 11 класс в братске .
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von JokerStar Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Zaubertrick funkelt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Zauberei knistern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Trick, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, manchmal wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Insgesamt ist JokerStar Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Zauber glitzert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
jokerstar login|
J’adore la splendeur de LeoVegas Casino, il propose une aventure de casino digne d’une couronne. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et princiers, proposant des slots de casino a theme somptueux. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un couronnement, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. En somme, LeoVegas Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sceptre, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
bono leovegas|
домашний интернет
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
подключить интернет
накрутка подписчиков в инстаграм праймлайк накрутка подписчиков в инстаграм праймлайк
нейросети, похожие на Deep Seek
интернет домашний екатеринбург
inernetvkvartiru-ekaterinburg006.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
Safety is another paramount concern that cannot be overlooked.
bid comparison https://rapidlybuild.com/choosing-the-right-contractor-for-your-construction-project/
Hi, of course this paragraph is in fact pleasant and I have learned lot of things from it concerning blogging. thanks.
elonbet egypt melbet
Гидравлические https://energo-pole.ru/photos/photo/otgruzka-gotovoy-produktsii/2021-09-27-17-46-03/
столы и платформы.
Ножничные подъемники могут оснащаться пультом управления с регулировкой высоты подъема.
Грузоподъемность, кг 150 Высота в сложенном виде, мм 210 Высота подъема, мм 740 Размер стола, мм 450×740 Высота ручки, мм 935 Вес, кг 42.
Грузоподъемность: 300 кг.
Оптимальный выбор напрямую зависит от характера рабочего груза. На стоимость будут значительно влиять грузоподъемность и максимальная высота подъема.
Грузоподъемность: 300 кг. Высота подъема: 880 мм. Размер платформы: 850х500×55 мм. Колеса: 125х40 мм. Гарантия: 12 мес.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
We’re available to save the problem — a skilled team set to tackle your plumbing problem and bring back stability in your property!
Our swift service supports – reduce the demand for high-cost serious restorations down the line.
Try our rapid and superior assistance – today!
У гидравлических подъемных столов много достоинств:
Подъёмники различаются по грузоподъемности, размерам, высоте подъема и опускания, конфигурации – модель легко подобрать для нужных задач (работы с гидравлическими тележками, поддонами российского и европейского стандартов, материалов массой 800-3000 кг и проч.). Конструкция механизмов оснащена датчиком для автоподъема/опускания (на выбор). Производительность – подъёмный стол позволяет использовать функции станков на 100%. Экономию – сокращение персонала и исключение влияния человеческого фактора.
19 000 ? при заказе с промокодом ШЕСТЬ Сделайте заказ сейчас или назовите промокод менеджеру по телефону и получите специальную цену по промокоду ШЕСТЬ.
Грузоподъёмность: гидравлические столы доступны с различными грузоподъёмностями начиная от нескольких сотен килограммов и до нескольких тонн. Важно выбрать стол с грузоподъёмностью, соответствующей вашим требованиям и типу груза, с которым вы работаете. Размеры стола: должны быть адаптированы к вашим потребностям и рабочему пространству. Обратите внимание на длину, ширину и высоту стола, чтобы убедиться, что он подходит для размещения и маневрирования грузов. Высота подъёма: гидравлические столы обладают различными диапазонами высоты подъёма. Определите максимальную и минимальную высоту, которые вам требуются для вашей работы, чтобы выбрать оборудование, соответствующий вашим потребностям. Скорость подъёма и опускания: время подъёма и опускания стола может иметь значение в определённых рабочих сценариях. Учтите скорость подъема и опускания стола, чтобы быть уверенным, что она соответствует вашим требованиям производительности и безопасности. Управление и безопасность: проверьте, каким образом осуществляется управление. Гидростол может быть оснащён кнопками на пульте управления или педалью для удобства оператора. Обратите внимание на системы безопасности, такие как предохранительные клапаны, ограничители хода и прочие механизмы, обеспечивающие безопасную эксплуатацию механизма.
Цена: 393 500 руб.
Вы можете оценить товар.
Включение в реестр Минпромторга https://minprom-info.ru официальный путь для подтверждения отечественного производства. Подготовка и подача документов, юридическое сопровождение и консультации для производителей.
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk009.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
plane game money aviator-igra-1.ru .
Pretty element of content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to claim that I get actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I fulfillment you get right of entry to persistently fast.
elon casino drugs
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Занятия по самообороне https://safety-skills.ru практические навыки защиты в реальных ситуациях, развитие силы и выносливости. Профессиональные тренеры помогут освоить приемы борьбы, удары и тактику безопасности.
Платформа онлайн-обучения https://craftsmm.ru курсы по маркетингу, продажам и рекламе для новичков и профессионалов. Освойте современные инструменты продвижения, увеличьте продажи и развивайте карьеру в удобном формате.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
лучшие нейросети для написания эссе
drenazh-pod-klyuch-spb.ru .
digital маркетинг блог digital маркетинг блог .
Написание дипломов на заказ https://vasdiplom.ru помощь студентам в подготовке итоговых работ. Авторские тексты, проверка на уникальность и полное соответствие стандартам учебных заведений.
Як на мене, електронна музика — це найкраще, що може бути! Якщо хочете більше таких треків, заходьте на цей сайт.
mostbet az qeydiyyat http://mostbet4143.ru/
Right here is the right webpage for anyone who wishes to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a subject which has been discussed for years. Wonderful stuff, just excellent!
sex children elon casino
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am truly impressed
to read everthing at alone place.
mostbet az aviator mostbet az aviator
блог агентства интернет-маркетинга statyi-o-marketinge2.ru .
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this
I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads.
I hope to give a contribution & assist other
customers like its aided me. Great job.
mostbet aplicação para android http://www.mostbet4172.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
интернет провайдеры красноярск по адресу
лучшие нейросети для написания постов
купить диплом киев сколько купить диплом киев сколько .
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article writer for your blog. You have some really great posts and I feel I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d love to write some articles for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please blast me an e-mail if interested. Regards!
kra39 cc
узнать интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу красноярск
mostbet bonus şərtləri https://www.mostbet4142.ru
Many players choose NV casino for its fast payouts and trusted platform. Here you’ll also find weekly bonuses, cashback offers, and a rewarding loyalty program.
https://nvcasinoonlines.com/
купить инверторный кондиционер с установкой купить инверторный кондиционер с установкой .
потолки в липецке http://natyazhnye-potolki-lipeck-1.ru .
провайдер интернета по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk004.ru
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу
купить аттестат о среднем образовании купить аттестат о среднем образовании .
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
https://vc.ru/telegram/2204133-nakrutka-zhivykh-podpischikov-v-tg-luchshie-servisy-2025-goda накрутка подписчиков в тг.
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
купить диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой .
mostbet uz kirish mostbet4173.ru
mostbet mobil mostbet mobil
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
лучшие нейросети для написания текста
mostbet azerbaycan https://mostbet4140.ru/
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/2204126-luchshie-servisy-dlya-nakrutki-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-v-2025-godu накрутка подписчиков в тг.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar014.ru
лечение запоя
Блог Соловова удивил https://niksolovov.ru реально полезно
Je suis fou de Luckster Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un sort. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et envoutants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui enchantent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Au final, Luckster Casino est un casino en ligne qui porte chance pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et lumineuse comme une aurore magique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
luckster casino review|
лучшие нейросети для редактирования текста
Je suis accro a MonteCryptos Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un glacier. La collection de jeux du casino est un veritable pic de divertissement, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, repondant en un eclair glacial. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse alpine, mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient grimper l’adrenaline. Globalement, MonteCryptos Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les aventuriers du casino ! En plus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle alpine, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus exaltante.
montecryptos casino codes|
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
mostbet app qeydiyyat http://mostbet4144.ru/
прорабы сочи – Ежедневный отчет
https://unored.tv/
https://metallobaza31.ru
провайдеры в красноярске по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
курсы seo курсы seo .
материалы по маркетингу https://statyi-o-marketinge2.ru/ .
курсы по seo https://www.kursy-seo-1.ru .
лучшие нейросети для написания диссертации
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительство XXI века
школа seo http://www.kursy-seo-1.ru .
купить недорогие березовые дрова цена .
seo с нуля kursy-seo-3.ru .
интернет провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
лучшие нейросети для создания игр
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя цена
sochistroygroup.ru/ – дом вашей мечты
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar015.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
mostbet canlı kazino mostbet canlı kazino
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar015.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
купить диплом в реестр купить диплом в реестр .
Ik zit nu al een tijdje bij blogdu.de en moet zeggen dat
ik positief verrast ben over hoe probleemloos alles functioneert.
De inschrijving was heel eenvoudig, en via mijn profiel kon ik onmiddellijk beginnen met spelen. Wat ik vooral waardeer, is
dat je echt een goede deal krijgt. De spinmama bonus code werkte zonder gedoe en gaf
me meteen gratis spins bij mijn initiële betaling.
Wat betreft mobiel gebruik – ik gebruik de spin mama app regelmatig, en die werkt vlekkeloos.
Alles is overzichtelijk, en je mist niets ten opzichte van de website.
Ook qua aanbod van spellen zit het goed – veel keuze, van klassieke gokkasten tot echte casinobeleving.
Daarbij komen er vaak promoties voorbij, waarbij je met een spinmama promo code bonusfuncties kunt activeren. Voor mij is
dit platform de perfecte plek om te spelen. Alles voelt betrouwbaar, en ik heb tot nu toe goede
ervaringen gehad. Wie op zoek is naar kwaliteit, zit bij Spinmama helemaal goed.
most bet https://www.mostbet4171.ru
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – AR в строительстве
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять шторами с помощью пульта.
Электрокарниз может иметь множество функций, которые облегчают его использование.
mostbet uz registratsiya https://mostbet4173.ru
На сайте konsultaciya-advokata51.ru вы можете найти множество полезных услуг. Получение юридической помощи – это необходимость для многих. Мы обеспечим вас экспертными консультациями.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на консультация юриста.
Не забывайте, что юридическая помощь может быть востребована в самых разных ситуациях.
Качество предоставляемых услуг во многом зависит от опыта специалистов. Наши юристы обладают необходимыми знаниями и опытом. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень обслуживания.
Второй аспект – это доступность услуг. На нашем сайте можно найти информацию о ценах и услугах. Клиенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант в зависимости от своих нужд.
У нас есть возможность получить консультацию удаленно. Сегодня возможность получить помощь через интернет очень важна. Вы можете задать свои вопросы в любое время.
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
интернет провайдеры в красноярске по адресу дома
mostbet az mostbet az
Je trouve absolument envoutant LuckyTreasure Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un joyau precieux. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme d’aventure. Le service client du casino est un diamant brut, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, LuckyTreasure Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une carte au tresor, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
jagged alliance 3 lucky veinard treasure|
airplane game money https://aviator-igra-1.ru .
J’adore l’eclat de LuckyBlock Casino, on dirait une pluie de trefles a quatre feuilles. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair de genie, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait feerique. Dans l’ensemble, LuckyBlock Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
serveur luckyblock|
купить героин мефедрон купить меф днр
интернет провайдеры по адресу красноярск
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
проверить интернет по адресу
Hiya! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest
writing a blog post or vice-versa? My blog goes over a lot of the same topics as yours and
I think we could greatly benefit from each other.
If you might be interested feel free to send me an email.
I look forward to hearing from you! Great blog by the way!
J’adore le delire de Madnix Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui fait disjoncter. La selection du casino est une veritable explosion de fun, incluant des jeux de table de casino pleins de panache. L’assistance du casino est energique et irreprochable, repondant en un flash dement. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un clin d’?il, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient disjoncter. Dans l’ensemble, Madnix Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline demente du casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique explosive, facilite une experience de casino electrisante.
code promo madnix|
дом из кирпича сочи – Кирпичный дом
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста по телефону на сайте адвокат бесплатно онлайн.
Вы получите информационную поддержку, которая поможет избежать ошибок.
Корректная подготовка необходимых бумаг — это основа для успешного разрешения вопроса.
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1615792-kak-nabrat-podpischikov-20-servisov-v-2024-godu-nash-reiting
проверить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnoyarsk006.ru
интернет по адресу
Кракен (kraken) – ты знаешь что это, уже годами проверенный сервис российского даркнета.
Недавно мы запустили p2p обмены и теперь вы можете обменивать любую сумму для пополнения.
Всегда есть свежая ссылка кракен через ВПН:https://kr-info.cc/
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
вывод из запоя минск
I recommend you to read about the topic – https://www.lngjewelry.com/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
лечение запоя
Купить диплом колледжа в Николаев Купить диплом колледжа в Николаев .
купить свидетельство о заключении брака https://www.educ-ua4.ru .
дренаж дома .
вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
вывод из запоя цена
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительная фирма
are shoes fake – what are replicas shoes
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga012.ru
лечение запоя
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, используя карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом для штор|потолочные карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом цена|карнизы с электроприводом купить|карнизы с электроприводом с дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным|карнизы с электроприводом и пультом управления купить|Карнизы с электроприводом для вашего дома!
Также стоит не забывать о материал, из которого выполнен карниз.
Хочете відчути справжній дух техно? Тоді вам точно варто зайти на DJ Gafur Techno Radio.
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – современные планировки
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в партизанске купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в партизанске .
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Cheers! Where are your contact details
though?
дренаж на участке с уклоном .
Хотите вывести ваш сайт на первые позиции поисковых систем Яндекс и Google?
Мы предлагаем качественный линкбилдинг — эффективное решение для увеличения органического трафика и роста конверсий!
Почему именно мы?
– Опытная команда специалистов, работающая исключительно белыми методами SEO-продвижения.
– Только качественные и тематические доноры ссылок, гарантирующие стабильный рост позиций.
– Подробный отчет о проделанной работе и прозрачные условия сотрудничества.
Чем полезен линкбилдинг?
– Улучшение видимости сайта в поисковых системах.
– Рост количества целевых посетителей.
– Увеличение продаж и прибыли вашей компании.
Заинтересовались? Пишите нам в личные сообщения — подробно обсудим ваши цели и предложим индивидуальное решение для успешного продвижения вашего бизнеса онлайн!
Цена договорная, начнем сотрудничество прямо сейчас вот на адрес ===>>> ЗДЕСЬ Пишите обгаварим все ньансы!!!
https://forum.cstalking.tv/cpstyles/vB/?1xbet-bonus-code-singapore-get-up-to-210-sgd.html
интернет провайдеры краснодар по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
https://sochistroygroup.ru – строительство и ремонт
To select updates, prefer credible publishers, confirm facts, note slant and find substance. Corroborate with multiple articles, use expert analysis, and set feeds for topics you care. Build media savvy https://smasters.com
This entails visiting the property and familiarizing yourself with the lease terms.
car rental overseas https://i-repairing.com/renting-a-car-abroad-what-you-need-to-know/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
проверить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
проверить провайдера по адресу
интернет провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar004.ru
провайдеры интернета в краснодаре по адресу проверить
Электрические жалюзи электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи с дистанционным управлением|электрические жалюзи на мансардные окна|купить электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи в москве|электрические жалюзи автоматические|электрические жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить|электрические жалюзи стоимость|электрические жалюзи на окна заказать — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, обеспечивающее комфорт и стиль.
Многие люди выбирают их за удобство и функциональность.
купить диплом младшего специалиста в украине купить диплом младшего специалиста в украине .
Quality articles or reviews is the crucial to be a focus for the viewers to pay a visit the web site,
that’s what this website is providing.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
вывод из запоя
лучшие нейросети для курсовых работ
Я давно хотів почути наживо DJ Solaris, і Alpha Festival дав мені цю можливість. Його сет — це вибух енергії, який змушує серце битися швидше. Під час його треку «Celestial Dance» купол танцполу заповнився лазерними променями, що створювали ілюзію подорожі у відкритий космос. Це був один із тих моментів, які неможливо забути.
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительные тренинги
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
вывод из запоя
I recommend you to read about the topic – https://civilclick.com/ .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1392548-nakrutit-prosmotry-v-tik-tok-top-25-luchshih-servisov-i-besplatnye-sposoby
Мы предлагаем документы университетов, которые находятся на территории всей России. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
аттестаты 10 11 класс купить
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
самолет игра на деньги самолет игра на деньги .
Нужен автобусный билет? заказ билетов на автобус удобный сервис поиска и бронирования. Широкий выбор направлений, надежные перевозчики, доступные цены и моментальная отправка электронных билетов на почту.
стоимость проекта перепланировки квартиры стоимость проекта перепланировки квартиры .
авиатор игра 1вин авиатор игра 1вин .
производство одежды под ключ https://www.nitkapro.ru .
Авто портал https://diesel.kyiv.ua все о мире автомобилей: новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору и уходу за авто. Каталог машин, актуальные цены, автоуслуги и полезная информация для автовладельцев.
Автомобильный портал https://auto-club.pl.ua онлайн-площадка для автолюбителей. Подробные обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, свежие новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Удобный поиск и актуальные материалы.
Все для автомобилистов https://k-moto.com.ua на авто портале: новости, обзоры, статьи, каталоги и цены на автомобили. Экспертные мнения, тест-драйвы и практические советы по эксплуатации авто.
Заказать диплом любого института!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по приятным ценам— fastdiploms.com
Adoro o clima alucinante de MegaPosta Casino, parece uma avalanche de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
plataforma megaposta|
Je trouve absolument fascinant MyStake Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi mysterieuse qu’un clair-obscur. La selection du casino est un voile de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vision prophetique, avec une aide qui perce les mysteres. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ombres, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient frissonner. Dans l’ensemble, MyStake Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une prophetie, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus intrigante.
mystake no deposit bonus code|
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma chama. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tremores, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial vulcanico. No geral, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual escaldante, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
avis casino osh|
Ich bin suchtig nach Platin Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Edelstein strahlt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und glanzvoll, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Diamant leuchten. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Juwel funkelt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Schatz glanzt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren luxurios. Kurz gesagt ist Platin Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie Platin strahlt, einen Hauch von Glanz ins Casino bringt.
platin casino einzahlungscode|
Ich bin suchtig nach Pledoo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Wirbelwind tobt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Alles in allem ist Pledoo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Orkan begeistert fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
pledoo trustpilot|
Greetings from California! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to check out your website on my iphone during lunch break.
I enjoy the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look
when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded
on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just
3G .. Anyhow, fantastic blog!
Hello, its pleasant article concerning media print,
we all understand media is a impressive source of facts.
лучшие нейросети для написания сценариев
Spin Mama is fast emerging as a popular brand in the iGaming world, offering users
a fresh and interactive platform that combines current look with
trustworthy performance. One of the best features
of Spinmama is its user-friendly method—from the straightforward sign-up to the smooth login spinmama process that makes accessing your account quick and trouble-free.
The large selection of options, including slots,
table games and live casino, caters to all kinds of users,
whether starters or experienced bettors. What’s particularly
noteworthy is how innerforce.co.kr mixes engaging gameplay with strong
security measures, guaranteeing users feel secure every time they
spin. The casino also offers tempting bonuses and special offers, which add
extra value and hold the excitement ongoing. Plus, with
a well-designed mobile site, gamblers can access
their top titles wherever they are without loss.
Help is efficient and always on, which boosts reliability and contentment.
Overall, Spinmama Casino excels not only for its wide library but also for its focus on safe play and protection, making it a great choice for anyone looking to dive into
online casino entertainment with assurance.
http://sochistroygroup.ru – современные стройматериалы
На Gamma Festival кожна деталь була продумана для справжніх шанувальників хаус-музики. Танцпол «Тропічний оазис» виглядав як справжній рай із живими інсталяціями та світловими ефектами. Артисти, такі як Solomun та Artbat, зарядили натовп своєю музикою, створюючи хвилі емоцій. Зона відпочинку з гамаками та коктейлями стала ідеальним місцем для перерв між виступами. Це був неймовірний фестиваль, який залишив тільки найкращі враження.
купить диплом с реестром купить диплом с реестром .
Автоматические рулонные шторы не только обеспечивают удобство управления, но и стильный акцент в интерьере вашего дома, особенно если вы выберете автоматические рулонные шторы|автоматика для рулонных штор|автоматические шторы для труднодоступных окон.
Во-вторых, их можно легко включить в концепцию “умного дома”.
Онлайн женский портал https://elegance.kyiv.ua актуальные советы по красоте, стилю, кулинарии и семейной жизни. Разделы о здоровье, карьере и саморазвитии. Интересные статьи и общение с единомышленницами.
лучшие нейросети для написания книги
игра авиатор 1win игра авиатор 1win .
провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
авиатор краш игра aviator-igra-3.ru .
sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительство и жизнь
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
интернет провайдеры в краснодаре по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
купить диплом в киеве educ-ua18.ru .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
провайдеры по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-krasnodar005.ru
провайдеры по адресу
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar012.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом техникума в спб купить диплом техникума в спб .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по разумным ценам. Заказ диплома, который подтверждает окончание ВУЗа, – это грамотное решение. Заказать диплом ВУЗа: щербиновскийрайон.рф/users/160
http://sochistroygroup.ru – дизайнерские решения
When some one searches for his vital thing, therefore he/she needs
to be available that in detail, thus that thing is maintained over here.
Hoi forumleden, ik deel graag wat ik ervan vind met https://jsbequipment.sg/about-us/equipment-rental-singapore-16/. Ik speel al een tijdje online, maar dit casino viel echt op.
De interface is heel duidelijk. Je komt snel bij je favoriete games. De promoties zijn aantrekkelijk, en heldere info erbij.
Qua games echt genoeg keuze, en technisch stabiel. Voor mensen uit België trouwens: ze hebben een aparte tak voor België, dus dat zit ook goed.
Alles bij elkaar: de moeite waard. Laat me weten wat jullie ervan denken!
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – инновации для строительства
проект перепланировки проект перепланировки .
перепланировка офиса согласование http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru/ .
электрический карниз для штор купить http://elektrokarnizy5.ru/ .
We’re here to rescue the situation — a expert team prepared to handle your plumbing emergency and return order in your home!
Our prompt response aids in – minimize the demand for burdensome significant fixes down the line.
Explore our swift and top-notch work – today!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительные проекты
высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
накрутка подписчиков тг задания накрутка подписчиков тг задания
перепланировка квартиры дизайн проект proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry9.ru .
акции скидки на туры Откройте для себя мир путешествия! Познавайте новые культуры, исследуйте удивительные места и получайте незабываемые впечатления. Путешествия обогащают нашу жизнь и дарят яркие эмоции. Отправляйтесь в свое следующее приключение прямо сейчас!
услуги по согласованию перепланировки услуги по согласованию перепланировки .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по невысоким тарифам. Купить диплом в Ангарске — kyc-diplom.com/geography/angarsk.html
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://mirlady.kyiv.ua красота, стиль, здоровье, дом и семья. Практичные рекомендации, модные идеи, вдохновение и поддержка. Лучший контент для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Сайт для женщин https://amideya.com.ua портал о красоте, стиле, здоровье, семье и саморазвитии. Ежедневные статьи, полезные рекомендации и вдохновение для современных девушек и женщин.
Женский сайт https://lubimoy.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, материнство, работа и хобби. Актуальные статьи, тренды и экспертные советы. Всё самое важное для гармоничной жизни и успеха.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://gracefullady.kyiv.ua свежие статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье и саморазвитии. Практичные советы, вдохновение и позитив для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
лайки инст Хотите, чтобы ваши публикации в Instagram получали больше внимания и положительных оценок? Купите лайки Инст и наблюдайте, как растет популярность вашего контента! Повышение вовлеченности аудитории, увеличение охвата и продвижение вашего профиля в Instagram. Сделайте свой контент запоминающимся!
Виступ Katarina став головною подією SFF Illusion. Їхнє шоу вразило своєю гармонією між музикою, світлом та візуальними ефектами. PJ Katarina, яка відповідала за візуалізацію сцени, додала виступу особливого шарму. Це було шоу, яке не тільки слухали, але й бачили, відчували й переживали.
лучшие нейросети для рифмования
электрокарнизы в москве elektrokarnizy5.ru .
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительный онлайн-журнал
kupit-drova-v-chelyabinske-365.ru .
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
авиатор 1хбет авиатор 1хбет .
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
I’m not sure why but this website is loading incredibly slow for me.
Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end?
I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
plane crash game online earn money http://aviator-igra-1.ru/ .
Hello are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do
you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog?
Any help would be really appreciated!
drenazh-pod-uchastkom-spb.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
лечение запоя минск
hello!,I really like your writing very so much!
share we communicate extra approximately your article on AOL?
I require a specialist in this house to unravel my problem.
May be that is you! Taking a look ahead to see you.
J’adore le frisson de MrXBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi envoutante qu’un secret. La selection du casino est une enigme de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui envoutent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une enigme resolue, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient captivants. Globalement, MrXBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! En plus le design du casino est un puzzle visuel captivant, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
mrxbet paris sportif|
Je suis fou de PlazaRoyal Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu digne d’une cour imperiale. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor couronne, proposant des slots de casino a theme royal. Le service client du casino est digne d’un monarque, assurant un support de casino immediat et majestueux. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse princiere, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Au final, PlazaRoyal Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel royal, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus majestueuse.
plaza royal casino app|
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Thron funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Vergnugen, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett leuchten. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist Richard Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, einen Hauch von Majestat ins Casino bringt.
richard casino no deposit bonus code|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von NV Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Nordlicht funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Welle voller Spa?, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitstern, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Kurz gesagt ist NV Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
harrahs casino las vegas nv|
дом для пмж в сочи – Утепленные конструкции
домашний интернет москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
вход 1win вход 1win
1вин рабочий сайт 1вин рабочий сайт
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk007.ru
лечение запоя
лучшие нейросети для написания рэпа
https://rennerusa.com/pages/kak_ponyaty_svoego_lyubimogo_vo_vremya_ssory.html
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all folks you really understand what
you’re speaking approximately! Bookmarked.
Kindly additionally discuss with my site =).
We will have a hyperlink change contract among us
провайдер по адресу москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
провайдеры интернета в москве по адресу проверить
интернет провайдер москва
inernetvkvartiru-msk006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of space
. Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this site.
Reading this info So i am happy to exhibit that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling
I found out exactly what I needed. I most for sure will make sure to
don?t forget this website and give it a glance on a
constant basis.
sportwetten gratis bonus
Here is my web blog :: Buchmacher werden
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make
this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you?
Plz respond as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from.
kudos
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительство для всех
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена .
1win официальный сайт букмекерской 1win официальный сайт букмекерской
https://institutocea.com/layouts/inc/?c_digo_promocional_112.html
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
вывод из запоя
Купить диплом любого университета!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро и выгодно купить диплом, который выполняется на оригинальной бумаге и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями. Данный документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при помощи специального оборудования. Достигайте цели максимально быстро с нашей компанией- investir-en-grece.fr/agent/dinafennell673
мостбет скачать приложение мостбет скачать приложение
1win aviator http://www.aviator-igra-4.ru .
мосжилинспекция проект перепланировки мосжилинспекция проект перепланировки .
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительные 3D идеи
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
I have learn a few excellent stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how so much attempt you put to create any such wonderful
informative site.
?Llevas tiempo queriendo encontrar un buen casino online legal en Espana para jugar con dinero real? Como muchos jugadores en Madrid, estuve buscando una plataforma fiable hasta que encontre casinos online reales.
Lo que encontre fue una lista confiable de casinos en linea en Espana donde los pagos estan garantizados. Lo primero que me gusto fue que la pagina solo recomienda plataformas legales en Espana. Asi no tienes que preocuparte por fraudes. Por si fuera poco, las plataformas funcionan genial desde el telefono. Lo uso mientras viajo por Espana y la experiencia fue fluida.
?Ofertas para nuevos jugadores? ?Por supuesto! Las plataformas recomendadas ofrecen giros gratis para que puedas probar los juegos sin arriesgar mucho. ?Quieres jugar tragamonedas? La oferta es variada. Desde juegos de mesa en vivo hasta baccarat clasico, todo esta ahi.
El retiro de ganancias es confiable. Yo use tarjeta bancaria y me llego en 24h. Eso demuestra seriedad. Si eres de Madrid, te aconsejo revisar esta pagina. Ahi encontraras opciones fiables para apostar online en 2025.
Apostar inteligentemente es clave. Y hacerlo en un sitio verificado es el primer paso.
No pierdas mas tiempo, elige tu favorito y empieza a ganar.
1win yuklash 1win yuklash
авиатор игра авиатор игра .
Статья https://amurplanet.ru/kak-vybrat-i-kupit-okna-v-sankt-peterburge-titan-okna/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
http://sochistroygroup.ru – опытные строители
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена .
monsbet https://www.mostbet12001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
вывод из запоя минск
https://hr.rivagroup.su/
провайдеры по адресу нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу нижний новгород
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
лучшие нейросети для создания приложений
цена дома за м2 сочи – Цена за м2 в Имеретинской низменности
подключить интернет тарифы нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
провайдеры интернета нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
провайдер по адресу
It’s awesome to pay a quick visit this web page and reading the views of all mates regarding this piece
of writing, while I am also zealous of getting knowledge. https://Rentry.co/40506-facial-dermabrasion-tips-achieving-smooth-and-radiant-skin
Мягкие окна **ПВХ пленка для окон – это прочный, долговечный и устойчивый к внешним воздействиям материал, который обеспечивает надежную защиту от ветра, дождя, снега и ультрафиолетового излучения, сохраняя при этом прозрачность и эстетичный внешний вид
аренда Ищете идеальное пространство для развития вашего бизнеса? Наша подборка *коммерческой недвижимости* включает в себя офисы, магазины, склады и другие объекты, отвечающие самым разным требованиям. Найдите оптимальное решение для вашего предприятия с нашей помощью!
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
вывод из запоя
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – 3D проекты домов
ветеринарная клиника адлер круглосуточно Круглосуточная ветеринарная клиника Сочи: Оперативная помощь вашему питомцу в любое время суток! Экстренная ветеринарная помощь 24/7 без выходных.
карнизы с электроприводом купить elektrokarnizy5.ru .
value quote von wetten dass strategie
Трейдинг Трейдинг: Используйте технический и фундаментальный анализ для принятия решений. Технический анализ помогает прогнозировать движение цены, а фундаментальный анализ позволяет оценить долгосрочный потенциал актива.
https://sneakerlinks.com/wp-content/pages/?1xbet-promo-code_131.html
1 win это 1 win это
как сделать проект перепланировки квартиры proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry9.ru .
1win букмекерская приложение 1win букмекерская приложение
таможенный брокер сб карго Ищете надежного партнера для работы с СБ Карго? Наш опыт и экспертиза позволяют нам эффективно решать самые сложные задачи по таможенному оформлению грузов, перевозимых этой транспортной компанией. Мы гарантируем оперативное и профессиональное обслуживание, независимо от сложности вашего груза. Выбирайте профессионалов!
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
Acho simplesmente brabissimo MegaPosta Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um vulcao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma tempestade, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem. Em resumo, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro gas, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
plataforma megaposta|
plane money game http://aviator-igra-4.ru/ .
Je trouve absolument fascinant MyStake Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino enigmatique. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un coffre aux mysteres, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est un oracle fiable, avec une aide qui perce les mysteres. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse ensorcelante, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient frissonner. Dans l’ensemble, MyStake Casino est un casino en ligne qui intrigue comme un manuscrit ancien pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et envoutante comme un sortilege, facilite une experience de casino mystique.
mystake withdrawal problem|
перепланировка квартиры москва перепланировка квартиры москва .
Ich bin suchtig nach Pledoo Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Zusammengefasst ist Pledoo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Orkan begeistert fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
pledoo partners|
Alpha Festival – це місце, де музика змінює реальність. Дізнайтеся більше про подію на офіційній сторінці.
Купить диплом колледжа в Николаев Купить диплом колледжа в Николаев .
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – дома XXI века
купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр .
I got this web page from my pal who shared with me on the topic of this web site and at the moment this time I am browsing this website and reading very informative articles or reviews at this time.
kra39 at
мостбет ставки на исход http://mostbet12002.ru/
купить дрова липы .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Hey all, thought I’d mention my experience with https://www.tenutapradeoro.it/lumache-alla-romana/ nowadays. For real, it’s an awesome option to experience the Fishin’ Frenzy slots without risking real money. Including the original demo and The Big Splash and bonus buy bring lots of fun and options. One thing I love is the instant play and no-download feature. Also the Christmas edition makes it perfect for the holidays without changing the core mechanics. If you want to check it out, you should definitely test the demos. It’s a chill way to play. Anyway, hope it helps.
Хотите вывести ваш сайт на первые позиции поисковых систем Яндекс и Google?
Мы предлагаем качественный линкбилдинг — эффективное решение для увеличения органического трафика и роста конверсий!
Почему именно мы?
– Опытная команда специалистов, работающая исключительно белыми методами SEO-продвижения.
– Только качественные и тематические доноры ссылок, гарантирующие стабильный рост позиций.
– Подробный отчет о проделанной работе и прозрачные условия сотрудничества.
Чем полезен линкбилдинг?
– Улучшение видимости сайта в поисковых системах.
– Рост количества целевых посетителей.
– Увеличение продаж и прибыли вашей компании.
Заинтересовались? Пишите нам в личные сообщения — подробно обсудим ваши цели и предложим индивидуальное решение для успешного продвижения вашего бизнеса онлайн!
Цена договорная, начнем сотрудничество прямо сейчас вот на адрес ===>>> ЗДЕСЬ Пишите обгаварим все ньансы!!!
ветеринарные клиники в сочи Сочи ветлечебница: Качественная ветеринарная помощь по доступным ценам. Городская ветеринарная лечебница Сочи – это гарантия профессиональной помощи и заботливого отношения к вашему питомцу.
легальный диплом купить легальный диплом купить .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя минск
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk009.ru
вывод из запоя минск
мега маркетплейс тор – сайт мега вход зеркало для входа
Mega darknet market в 2025 году продолжает оставаться одной из самых обсуждаемых площадок в даркнете. Пользователи регулярно ищут мега онион, мега зеркало рабочее и официальный сайт мега, чтобы получить вход на мега даркнет.
# Что такое Мега?
мега сайт — это площадка, который работает как даркнет-рынок. мега даркнет маркет стал известен благодаря интерфейсу. Но важно помнить: mega darknet market 2025 — это незаконная платформа.
mega market link Cыллка ===> https://github.com/mega-ssilka-forum/mega-sb-rabochee
# Почему нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде mega sb часто блокируются. Чтобы обойти это, используются мега зеркало рабочее. Например:
– mega market link
– мега рабочая ссылка
– mega darknet market вход
Эти зеркала позволяют осуществить вход, но одновременно появляются фейковые версии.
# Как найти актуальную ссылку?
Пользователи часто вводят запросы:
– актуальная ссылка мега сегодня
– mega darknet mirror
– мега sb зеркало
Нужно помнить: мега sb официальный сайт всегда доступен через тор браузер, а не через обычные браузеры.
# Риски поддельных сайтов
Запросы вроде мега sb зеркало часто ведут к мошенническим сайтам. Такие порталы имитируют интерфейс оригинала. Чтобы не попасться:
– Проверяйте mega sb.
– Используйте только мега зеркало рабочее.
– Избегайте клирнет-версий.
# Telegram и ссылки
Популярен запрос мега ссылка телеграм. В Telegram действительно можно найти мега ссылки, но риск нарваться на фейковые каналы велик.
# Как зайти на мегу?
Чтобы получить mega darknet market вход, нужно:
1. Запустить браузер Тор.
2. Ввести мега ссылка тор.
3. Пройти регистрацию.
# Популярные ключи 2025
Сегодня особенно востребованы:
– актуальная ссылка мега сегодня
– мега sb официальный сайт
– мега darknet
Эти запросы показывают, что спрос на ссылки высокий.
# Заключение
mega darknet market остаётся важной платформой даркнета в последние годы. Но каждый вход связан с опасностью.
?? Помните: мега зеркало могут быть ложными, а посещение маркетплейса всегда остаётся рискованным.
Статья https://amurplanet.ru/kak-vybrat-i-kupit-okna-v-sankt-peterburge-titan-okna/
проверить провайдеров по адресу нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
скачать мостбет кыргызстан скачать мостбет кыргызстан
Получите профессиональную помощь от юриста на задать вопрос юристу онлайн.
Каждый юрист обладает.
Женский сайт https://family-site.com.ua современный портал о моде, красоте, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные материалы, секреты здоровья и успеха, актуальные тренды и советы экспертов для женщин любого возраста.
Семейный портал https://geog.org.ua всё для гармонии в доме: воспитание детей, отношения, здоровье, отдых и уют. Полезные советы, статьи и лайфхаки для всей семьи. Пространство, где находят ответы и вдохновение.
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – онлайн-моделирование
купить аттестат за 9 класс с занесением https://educ-ua5.ru/ .
Очищение организма после запоя в Туле – неотъемлемая часть на пути к возвращению к нормальной жизни. Квалифицированный нарколог на дому из медицинского учреждения предлагает детоксикациюкоторая предоставляет помощь в лечении запоя и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме. Программы лечения могут включать психотерапию и поддержку семьи. Восстановление после запоя начинается с первичной консультации с наркологом, что способствует успешному очищению организма и возвращению к полноценной жизни. Нарколог на дом клиника
1вин зеркало скачать 1win12003.ru
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде
купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста .
Without adequate funding, businesses may struggle to develop.
tax implications https://timetobuiseness.com/choosing-the-right-business-structure-llc-corporation-or-sole-proprietorship/
На Gamma Festival я вирішив поїхати, бо багато чув про нього, але залишився розчарованим. Декорації танцполу «Тропічний оазис» виглядали круто, але звук був просто посереднім. Баси були занадто гучними, і це псувало атмосферу. Черги до барів і туалетів займали багато часу, а зона відпочинку була надто переповненою. Загалом, це фестиваль із гарними задумами, але реалізація залишає бажати кращого.
Interesting blog! Is your theme custom made or did you
download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few
simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out.
Please let me know where you got your theme.
Cheers
interesting for a very long time
_________________
https://spincove.shop
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
провайдер по адресу нижний новгород
дрова в мешках доставка .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр чита купить диплом с занесением в реестр чита .
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые находятся в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат 11 классов спб 2016
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста онлайн тут konsultaciya-yurista-msk01.ru.
Обращение за юридической помощью становится ключевым шагом в различных ситуациях.
Специалист по зависимостям Тула: Квалифицированная поддержка при зависимостях Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с зависимостью‚ необходимо обратиться к профессионалу. Нарколог Тула предоставляет квалифицированную медицинскую помощь‚ включая диагностику зависимости и консультацию нарколога. В наркологической клинике предлагаются различные услуги‚ такие как медикаментозное лечение и психотерапия. Лечение зависимости – это сложный и многоступенчатый процесс‚ который предполагает индивидуального подхода. Программа реабилитации включает в себя этапы‚ направленные на восстановление физического и психологического состояния больного. Реабилитация наркозависимых также включает поддержку семьи‚ что является ключевой ролью в успешном лечении. Анонимное лечение даёт возможность пациентам ощущать себя защищенными и свободными от осуждения. Профилактика наркомании и помощь при алкоголизме – ключевые направления работы наркологов. Обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-tula010.ru для получения подробностей и записи на приём. Помните‚ что раннее обращение – гарантия успешного выздоровления!
сколько стоит купить аттестат сколько стоит купить аттестат .
карниз для штор электрический http://elektrokarnizy5.ru/ .
купить свидетельство о разводе киев https://educ-ua2.ru/ .
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительство «под ключ»
https://vsezerkala.com/
https://tamozhenniiy-broker.ru/ Наш таможенный брокер в Москве предлагает широкий спектр услуг по таможенному оформлению для предприятий любого размера. Мы помогаем нашим клиентам экономить время и деньги, соблюдая все требования законодательства.
проект перепланировки квартиры для согласования цена proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry9.ru .
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Портал о здоровье https://mikstur.com информационный ресурс о медицине и ЗОЖ. Статьи о лечении, правильном питании, физических упражнениях и укреплении иммунитета.
Портал о стройке https://bastet.com.ua статьи, новости и советы по ремонту, строительству и дизайну. Подбор материалов, проекты домов, технологии и полезная информация для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
купить диплом о высшем образовании в сумах https://educ-ua4.ru/ .
согласованте http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru/ .
лечение запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Je trouve absolument delirant Roobet Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino totalement electro. Le repertoire du casino est une rave de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent. Le service client du casino est une decharge d’efficacite, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Roobet Casino est un casino en ligne qui illumine la nuit pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline vibrante du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un beat techno, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
howie roobet|
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Laserstrahl funkelt. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen hypnotisieren. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein leuchtender Funke, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Schalter, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren elektrisierend. Kurz gesagt ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
slotclub seriös|
Je suis totalement emporte par Spinanga Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui spirale comme un vortex. La selection du casino est une spirale de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une rafale, assurant un support de casino immediat et dynamique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui secouent. Pour resumer, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les dompteurs de tempete du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique orageuse, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus virevoltante.
spinanga free spins|
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru/ – архитектурные технологии
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinsy Casino, on dirait une soiree disco pleine de frissons. Le repertoire du casino est un dancefloor de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme disco. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et fluide, assurant un support de casino immediat et dansant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un breakdance, cependant des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient swinguer. En somme, Spinsy Casino est un casino en ligne qui met le feu a la piste pour les danseurs du casino ! A noter le design du casino est un spectacle visuel disco, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
spinsy casino no deposit bonus|
Adoro o brilho de Richville Casino, da uma energia de cassino tao luxuosa quanto um trono. Tem uma cascata de jogos de cassino fascinantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, dando solucoes precisas e imediatas. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como abrir um cofre, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria opulento. No fim das contas, Richville Casino vale a pena explorar esse cassino com urgencia para os que buscam a adrenalina luxuosa do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, torna a experiencia de cassino um evento de gala.
richville apartments|
https://t.me/perevedem_document Перевод Документов: Мост между Языками и Культурами В современном мире глобализации, где границы стираются, а сотрудничество между странами и культурами становится все более тесным, перевод документов приобретает огромное значение. Это не просто замена слов одного языка словами другого, а кропотливая работа по передаче смысла, контекста и нюансов оригинала, чтобы обеспечить полное и точное понимание информации. Когда необходим перевод документов? Международный бизнес: контракты, договоры, финансовые отчеты, маркетинговые материалы – все это требует качественного перевода для успешного ведения дел за рубежом. Юридические вопросы: судебные документы, свидетельства, доверенности, нотариальные акты должны быть переведены с соблюдением строгих юридических норм и терминологии. Медицинская сфера: медицинские заключения, инструкции к лекарствам, результаты исследований – точность перевода здесь критически важна для здоровья пациентов. Техническая документация: инструкции по эксплуатации, технические спецификации, чертежи – перевод должен быть понятным и однозначным для специалистов. Образование и наука: дипломы, аттестаты, научные статьи, исследования – для признания образования за рубежом и обмена знаниями необходим качественный перевод. Почему важно обращаться к профессионалам? Точность и соответствие: профессиональные переводчики обладают глубокими знаниями языка и предметной области, что гарантирует точность и соответствие перевода оригиналу. Соблюдение терминологии: использование правильной терминологии – залог того, что перевод будет понятен специалистам в соответствующей области. Культурная адаптация: профессиональный переводчик адаптирует текст с учетом культурных особенностей целевой аудитории, чтобы избежать недопонимания или неловких ситуаций. Конфиденциальность: профессиональные бюро переводов гарантируют конфиденциальность ваших документов. Как выбрать бюро переводов? Опыт и репутация: изучите опыт работы бюро, ознакомьтесь с отзывами клиентов. Специализация: убедитесь, что бюро специализируется на переводах в нужной вам области. Наличие профессиональных переводчиков: узнайте, работают ли в бюро переводчики с соответствующим образованием и опытом. Стоимость и сроки: сравните цены и сроки выполнения заказа в разных бюро. В заключение, перевод документов – это важный инструмент для преодоления языковых барьеров и успешного взаимодействия в современном мире. Доверяйте перевод ваших документов профессионалам, чтобы быть уверенными в качестве и точности результата. Если вам нужно перевести конкретный документ, просто предоставьте его мне, и я постараюсь вам помочь!
Информационный портал https://intertools.com.ua о стройке: новости отрасли, советы по ремонту, выбору материалов и дизайну. Всё для тех, кто строит дом, делает ремонт или работает в строительстве.
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
игровые автоматы 777 Игровые автоматы новые регистрация – это процесс создания учетной записи в онлайн-казино для получения доступа к игровым автоматам. Новые игроки обычно получают приветственные бонусы и другие привилегии после регистрации. Процесс регистрации обычно прост и занимает несколько минут. Игрокам необходимо предоставить личную информацию, такую как имя, адрес электронной почты и номер телефона. После регистрации игроки могут пополнить свой счет и начать играть в игровые автоматы на реальные деньги.
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
mega sb – mega darknet mirror сайт
Мега маркетплейс тор в 2025 году продолжает оставаться одной из самых обсуждаемых площадок в даркнете. Пользователи регулярно ищут мега онион, актуальные зеркала и мега sb официальный сайт, чтобы получить вход на мега даркнет.
# Что такое Мега?
мега онион зеркало — это сервис, который дает доступ к даркнет-рынок. mega darknet market стал популярен благодаря системе рейтингов. Но важно помнить: mega darknet market 2025 — это скрытая платформа.
mega market link Cыллка ===> https://github.com/kraken-zerkalo-2025/rabochaya-ssilka-tut
# Почему нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде мега sb часто становятся недоступны. Чтобы обойти это, используются актуальные ссылки на мегу. Например:
– мега ссылка тор
– мега зеркало на сегодня
– мега даркнет вход
Эти адреса позволяют получить доступ, но одновременно появляются фейковые версии.
# Как найти актуальную ссылку?
Пользователи часто вводят запросы:
– мега актуальные зеркала
– мега ссылка на сайт официальный
– мега sb зеркало
Нужно помнить: мега маркет ссылка всегда доступен через онион-ссылку, а не через клирнет.
# Риски поддельных сайтов
Запросы вроде мега ссылка телеграм часто ведут к фейкам. Такие порталы имитируют интерфейс оригинала. Чтобы не попасться:
– Проверяйте онион-домен.
– Используйте только мега зеркало рабочее.
– Избегайте megaweb.
# Telegram и ссылки
Популярен запрос мега ссылка телеграм. В Telegram действительно можно найти мега ссылки, но риск нарваться на фейковые каналы велик.
# Как зайти на мегу?
Чтобы получить мега вход, нужно:
1. Запустить браузер Тор.
2. Ввести mega darknet market link.
3. Пройти капчу.
# Популярные ключи 2025
Сегодня особенно востребованы:
– мега зеркало на сегодня
– мега sb официальный сайт
– мега сайт даркнет
Эти запросы показывают, что пользователи ищут рабочие зеркала.
# Заключение
мега маркетплейс остаётся одной из самых популярных даркнета в нынешнее время. Но каждое использование связан с риском.
?? Помните: мега зеркало могут быть фишинговыми, а использование даркнета всегда остаётся рискованным.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk007.ru
лечение запоя омск
temple slots online casino review
Установка мягких окон **Мягкие окна для кафе – это отличный способ привлечь больше посетителей, создать уютную и комфортную атмосферу для отдыха на свежем воздухе, защитив их от ветра, дождя и назойливых насекомых, а также продлить летний сезон и увеличить прибыль
играть авиатор играть авиатор .
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted
keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains.
If you know of any please share. Thank you!
http://sochistroygroup.ru – строительный FAQ
The forum inspires new discoveries and discussions. Let your participation be as pleasant as possible — a durable and comfortable armchair with delivery will help create the perfect atmosphere for communication.
лучшие нейросети для студентов
провайдеры в нижнем новгороде по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу нижний новгород
Служба наркологии — это необходимая часть здравоохраненияпредоставляющая лечение зависимостей и реабилитацию. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula011.ru можно найти сведения о клиниках наркологической помощи, где вы можете получить помощь при алкогольной зависимости и наркомании. Психотерапевтические методики и реабилитационные программы помогают пациентам восстановиться, а поддержка родственников играет важнейшую роль в этом процессе. Также доступны анонимные консультации и кризисные службы для срочной помощи. Профилактика наркомании и социальная адаптация — ключевые моменты работы наркологической службы.
https://fanclove.jp/profile/YAWAdMv1Jz
проверить провайдеров по адресу нижний новгород
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
интернет провайдеры нижний новгород
Услуги наркологов в Туле становится все более популярной‚ особенно когда речь идет о лечении алкоголизма. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Тула оказывает услуги для людей‚ нуждающихся в экстренной помощи. В рамках специализированной клиники проводится детоксикация от наркотиков и алкоголя‚ что является первым шагом к оздоровлению. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает в себя снятие абстинентного синдрома‚ что способствует облегчению состояния пациента. Круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечит необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в любое время суток. Консультация нарколога поможет составить персонализированный план терапии, учитывающую все особенности пациента. Реабилитация зависимых включает психологическую поддержку для зависимых‚ что помогает улучшить психологического состояния и адаптации к жизни без алкоголя. Не стоит забывать о поддержке родственников зависимых; Анонимное лечение зависимости позволит пациенту обращаться за помощью без страха осуждения. Вызывая нарколога на дом‚ вы делаете первый шаг к новой жизни.
sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительный дайджест
провайдеры по адресу дома
inernetvkvartiru-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
какие провайдеры на адресе в нижнем новгороде
купить диплом магистра купить диплом магистра .
Колись думав, що якісне будівництво в Києві – це міф. Але знайомий розповів про надійних професіоналів, і тепер я бачу реальні результати їхньої роботи.
I know this website gives quality dependent posts and other
information, is there any other web site which provides these data in quality?
играющие игровые автоматы Играющие игровые автоматы – это те, которые в данный момент используются игроками в казино или онлайн-казино. Они могут быть как классическими слотами, так и современными видео-слотами с разнообразными тематиками и функциями. Играющие автоматы генерируют случайные комбинации символов, определяющие исход каждой игры. Игроки делают ставки и вращают барабаны, надеясь на выпадение выигрышной комбинации. Популярность игровых автоматов обусловлена их простотой, доступностью и возможностью выиграть крупные денежные призы.
https://t.me/perevedem_document Перевод Документов: Мост между Языками и Культурами В современном мире глобализации, где границы стираются, а сотрудничество между странами и культурами становится все более тесным, перевод документов приобретает огромное значение. Это не просто замена слов одного языка словами другого, а кропотливая работа по передаче смысла, контекста и нюансов оригинала, чтобы обеспечить полное и точное понимание информации. Когда необходим перевод документов? Международный бизнес: контракты, договоры, финансовые отчеты, маркетинговые материалы – все это требует качественного перевода для успешного ведения дел за рубежом. Юридические вопросы: судебные документы, свидетельства, доверенности, нотариальные акты должны быть переведены с соблюдением строгих юридических норм и терминологии. Медицинская сфера: медицинские заключения, инструкции к лекарствам, результаты исследований – точность перевода здесь критически важна для здоровья пациентов. Техническая документация: инструкции по эксплуатации, технические спецификации, чертежи – перевод должен быть понятным и однозначным для специалистов. Образование и наука: дипломы, аттестаты, научные статьи, исследования – для признания образования за рубежом и обмена знаниями необходим качественный перевод. Почему важно обращаться к профессионалам? Точность и соответствие: профессиональные переводчики обладают глубокими знаниями языка и предметной области, что гарантирует точность и соответствие перевода оригиналу. Соблюдение терминологии: использование правил
Заказать диплом любого университета!
Мы предлагаемвыгодно и быстро купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями должностных лиц. Документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при помощи специфических приборов. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- mircalemi.net/showthread.php?tid=214653
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Bookmark this portal for buying ivermectinvsstromectol.com pills you need to comparison shop. stromectol 12 mg
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительство XXI века
лучшие нейросети для написания стихов
лучшие нейросети для проверки пунктуации
лучшие нейросети для проверки орфографии
В современном мире проблема зависимости становится все более актуальной. Нередко возникает необходимость в оперативной помощи, и именно в таких случаях специалист по зависимостям может оказать неотложную помощь. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает медицинское вмешательство для людей с зависимостями, включая очистку организма у пациента на дому. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-tula012.ru предоставляет услуги квалифицированных специалистов, которые могут выехать к вам в любое время. Визит нарколога позволит оценить текущее состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальное лечение зависимости. Лечение без указания личных данных и реабилитация наркоманов — существенные элементы, которые гарантируют безопасность и комфорт. Вызов врача на дом позволяет избежать лишнего стресса для зависимого, что является важным фактором успешного лечения.
+ for the post
_________________
http://ipl2025.rest/
помощь в согласовании перепланировки квартиры https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru/ .
подключить домашний интернет новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу новосибирск
ПРОКАПАТЬ ОТ АЛКОГОЛЯ: ЗНАЧЕНИЕ ДЕТОКСИКАЦИИ И ПОМОЩИ Вопрос алкогольной зависимости касается множества людей. Лечение алкоголизма часто стартует с детоксикации, что включает прокапывание. Этот этап помогает вывести токсины из организма и уменьшить абстинентный синдром.Капельницы от алкоголя содержат препараты для детоксикации, которые восстановлению организма. Они способствуют восстановиться после запоя, предоставляя необходимую медицинскую помощь. Необходимо помнить, что поддержка зависимых в этот период крайне важна.После детоксикации начинается реабилитация, где психотерапия при алкоголизме играет ключевую роль. Специалисты поддерживают разобраться в причинах зависимости и предоставляют советы по борьбе с зависимостями.На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula012.ru можно найти информацию о том, как правильно пройти лечение и получить поддержку. Здоровье, это важный шаг к новой жизни без алкоголя.
Статья https://useit2.ru/metizy-vidy-naznachenie-kak-vybrat-i-kupit/
диплом об образовании купить диплом об образовании купить .
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – услуги компании
Запой в Туле: как получить экстренную помощь Запой – это серьезная кризисная ситуация‚ требующая немедленной медицинской помощи. Вызов нарколога на дом – оптимальный способ получить необходимую поддержку. Специалист обеспечит детоксикацию‚ гарантируя безопасное восстановление. Лечение алкоголизма включает не только физическую‚ но и психологическую помощь. Важность вызова нарколога в том‚ что он может предложить широкий набор наркологических услуг‚ включая помощь при запойном состоянии. Экстренная помощь предотвращает возникновение осложнений и инициирует процесс реабилитации. После завершения запойного состояния важно поддерживать процесс лечения алкоголизма‚ чтобы избежать новых запоев. Восстановление после запоя нуждается в поддержке‚ поэтому нарколог на дом предоставит поддержку как физически‚ так и психологически. Не забывайте о своём здоровье и ищите квалифицированную помощь!
бонусы казино в 1win https://1win12004.ru/
Thanks designed for sharing such a pleasant thought, article
is nice, thats why i have read it entirely
подключить интернет в новосибирске в квартире
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
kupit-drova-v-chelyabinske-365.ru .
лучшие нейросети для замены слов в песнях
провайдер интернета по адресу новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk004.ru
интернет по адресу дома
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://cah.forum24.ru/?1-13-0-00002485-000-0-0-1755520215. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
I’ve been using the Spinmama app for some time now, and truthfully,
it’s really a standout mobile app I’ve tried.
The whole layout feels modern and easy to navigate — from the first screen, everything is super smooth.
No freezes, no strange issues, even when changing sections.
I especially liked how simple it was to download shinhwaspodium.com right onto
my device — no need to deal with Google Play. Just get it,
launch it, and you’re ready.
One thing that really made a difference is the variety of
features. You’ve got slots, table games, live dealer action, and even bets on sports
— without switching. And the special offers?
Really impressive than non-app versions. There are app-only promos
you only get on mobile, like extra spins, money-back deals, and
weekly drops that are regular. Plus, the loyalty program actually feels rewarding.
I’ve already collected gifts just by not even playing much.
Customer support is solid, too. I had a setup
hiccup, and the help feature got it sorted out in minutes.
It’s good to know there’s help if you ever need support.
And the app gets new patches, which is always welcome — not just for code stuff, but they bring new things.
To sum it up, the Spinmama app really impressed me.
It’s not just a web clone — it feels like a full experience built specifically for mobile users.
If you’re into mobile gambling, I’d say this app is a smart pick.
sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительные инвестиции
Женский онлайн-журнал https://girl.kyiv.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, кулинария, отношения и материнство. Ежедневные материалы, экспертные советы и вдохновение для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Портал про детей https://mch.com.ua информационный ресурс для родителей. От беременности и ухода за малышом до воспитания школьников. Советы, статьи и поддержка для гармоничного развития ребёнка.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://krasotka-fl.com.ua всё о красоте, моде, семье и жизни. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, советы экспертов и интересные истории. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь каждый день.
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://www.pcweek.ua/forum/view_profile.php?UID=100572
What causes ED, and how can http://bupropionvswellbutrin.com/ keep them away from direct sunlight. bupropion bnf
https://www.intensedebate.com/people/SerHrut
https://sochistroygroup.ru – сайт идей
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk009.ru
вывод из запоя
Very good site you have here but I was wanting to know if you knew of any message boards that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really love to be a part of group where I can get feedback from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Thanks a lot!
https://alum-rf.ru/
Измельчение веток Вывоз деревьев: транспортировка срубленных деревьев на утилизацию или переработку Вывоз деревьев – это процесс транспортировки срубленных деревьев с места вырубки на место утилизации или переработки. Вывоз деревьев требует специального транспорта и оборудования.
Запой, серьезное состояние‚ которое требует профессионального вмешательства; Миф о том, что можно справиться с запоем самостоятельно‚ как минимум, рискован и может иметь серьезные последствия. В владимире многие страдают от алкогольной зависимости, и помощь нарколога на дому становятся незаменимыми в решении этой проблемы. Вызвать нарколога на дом в владимире Симптомы запойного состояния включают тремор, обильное потоотделение, волнение. Самостоятельный вывод может привести к тяжелым проблемам со здоровьем‚ включая психические расстройства. Помощь нарколога важна для безопасного выхода из запоя и восстановления психического здоровья. Кроме того‚ реабилитация от алкоголя требует поддержки семьи и квалифицированных специалистов. Вызвав нарколога на дом в владимире‚ вы получите квалифицированную помощь‚ избежите опасностей самостоятельного вывода и приступите к восстановлению. Не ставьте под угрозу свое здоровье‚ обратитесь за помощью!
https://sites.google.com/view/dollartworks/
https://betciosgiris.online
https://www.tumblr.com/serhrut
мостьет мостьет
Real nice design and style and wonderful written content, nothing at all else we need :D.
Виступ Kitty на фестивалі Trance Illusion був справжнім видовищем, яке важко забути. Вони поєднують музику, візуальні ефекти та неймовірну енергетику, яка заряджає весь зал. PJ Alice створила настільки чарівні візуалізації, що відчуття реальності розчинялося у цьому видовищі. Світлове шоу від PJ Mia було настільки синхронним з музикою, що це виглядало як живий організм. А робота PJ Zoe доповнювала кожен виступ неймовірними деталями. Ця команда точно знає, як зачарувати публіку. Якщо хочете дізнатися більше про їхній талант, завітайте на їхній офіційний сайт.
With havin so much content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright infringement?
My blog has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either created myself or
outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all
over the internet without my authorization. Do you know any methods to help reduce content from being
stolen? I’d genuinely appreciate it.
my page: zkreciul01
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – архитектура и дизайн
Обращение к наркологу в владимире — это необходимый шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с проблемами зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir010.ru можно узнать о о помощи наркологов, включая диагностику зависимостей и медикаментозную терапию. Эксперты нашего центра предлагают профессиональные консультации нарколога и анонимное лечение. Выездная служба наркологии готова предоставить экстренную помощь при приступе зависимости или в любых других случаях. Наши услуги включают стационарное лечение и реабилитацию наркоманов для пациентов с наркотической зависимостью. Мы предоставляем поддержку зависимым и их семьям и проводим профилактику зависимостей. Не ждите с обращением за помощью — вызовите нарколога и начните путь к выздоровлению.
kupit-drova-v-arhangelske-365.ru .
Таможенный брокер в Москве — это надежный помощник при работе с импортом и экспортом любой сложности: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
Своевременная помощь брокера избавит вас от штрафов и задержек на таможне: таможенный брокер в Москве
What’s up everyone, it’s my first visit at this website, and article is genuinely fruitful designed for me, keep up posting these articles.
регистрация казино либет
https://dollartworks.wixsite.com/dollartworks
https://dollartworks.mystrikingly.com/
лучшие нейросети для рерайта текста
фотохолст Подарок жене Подарок, предназначенный для жены (супруги).
Begin with recognizing the symptoms and collecting necessary details.
farm equipment care https://rentingforholidays.com/how-to-repair-common-issues-in-agricultural-equipment/
http://qooh.me/SerHrut
https://yaarikut.com/user/dollartworks
подключить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
интернет по адресу новосибирск
Hey there! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the great work!
вход lee bet casino
заказать дом сочи – Заказать индивидуальный проект
http://nagios.secotrust.eu/birthdays/
kupit-drova-v-arhangelske-365.ru .
микрозайм онлайн без проверок Сайтом очень доволен, все действительно просто и быстро. Микрозаймы онлайн без отказа без проверки – выручили на ура!
Таможенный брокер в Москве поможет пройти все этапы оформления грузов быстро и без лишних затрат времени: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
лучший интернет провайдер новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
подключить интернет по адресу
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all people you actually realize what you are speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Please additionally seek advice from my web site =). We may have a link change arrangement between us
https://cnopic.ru/
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://www.che.best-city.ru/forum/thread96156/#reply96158. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
карниз с приводом для штор http://www.elektro-karniz77.ru .
провайдеры в новосибирске по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk005.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
войти мостбет http://mostbet12003.ru
электрические гардины http://www.avtomaticheskie-karnizy.ru .
автоматический карниз для штор автоматический карниз для штор .
Thank you, I’ve recently been looking for information about this subject for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what concerning the conclusion? Are you positive concerning the supply?
официальный сайт зума казино
электрические гардины электрические гардины .
Онлайн-журнал https://presslook.com.ua для женщин объединяет всё, что важно: мода и стиль, воспитание детей, карьерные советы и вдохновение. Советы специалистов и реальные истории для поддержки и новых идей.
Актуальные тренды https://horoscope-web.com и вневременная классика. Подборки образов, советы по стилю, секреты гардероба и модные инсайты. Мы поможем тебе выглядеть безупречно каждый день и выразить свой индивидуальный стиль.
Твой гид https://nicegirl.kyiv.ua по здоровому образу жизни! Эффективные тренировки, сбалансированное питание, wellness-практики и советы по мотивации. Обрети энергию, силу и гармонию в теле, которое ты любишь.
Ресурс для амбициозных https://ramledlightings.com и целеустремленных. Карьерный рост, личная эффективность, финансовая грамотность и вдохновляющие истории успеха. Реализуй свой потенциал и добивайся всех поставленных целей!
http://www.rohitab.com/discuss/user/3109389-serhrut/
https://www.chordie.com/forum/profile.php?id=2385114
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительные концепции
Статья https://useit2.ru/metizy-vidy-naznachenie-kak-vybrat-i-kupit/
Благоустройство дачного участка Удаление или скашивание старой травы: Удаление или скашивание старой травы – это процесс удаления или скашивания сухой, пожелтевшей или засохшей травы. Старая трава может ухудшать внешний вид участка, препятствовать росту молодой травы
какая нейросеть лучше ChatGPT
Amazing! Its genuinely remarkable piece of writing, I have got much clear idea regarding from this piece of writing.
зеркало банда казино
Thank you for another great post. Where else could anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal manner of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I am on the search for such information.
Here is my web-site https://orientuniforms.ae/product/pool-towel/
https://dollartworks.gitbook.io/dollartworks-docs/
https://linktr.ee/dollartworks
строительство домов цены сочи – Цены на дома из газобетона
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
купить аттестат купить аттестат .
мостбет лицензия http://mostbet12008.ru/
Онлайн-казино Jozz считается одним из лидеров.
Промокоды и бонусы увеличивают интерес.
Турниры и соревнования создают азарт.
Выбор слотов и настольных игр остается актуальным.
Регистрация простая, и сразу начать играть.
Узнай больше здесь: https://australiandvd.net
Acho simplesmente magico SpinWiz Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao encantadora quanto um feitico de varinha. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um feitico de emocoes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um feitico de teletransporte, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SpinWiz Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os magos do cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spinwiz casino|
Капельница от запоя — эффективное решение для улучшения самочувствия. В городе владимир медицинская помощь включает выведение из запоя с помощью капельниц. Капельницы в случае запоя содействуют очищению организма, уменьшение симптомов похмелья и реабилитация после запоя. вывод из запоя владимир Зависимость от алкоголя требует комплексного подхода: это не только лечение запоя, но и восстановление после алкоголя. Капельница укрепляет организм, наполняя организм витаминами и минераламичто помогает быстрее достичь результата;
Je trouve absolument envoutant RubyVegas Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un tresor. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et lumineuses, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclat de lumiere, repondant en un flash scintillant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient precieux. Globalement, RubyVegas Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un joyau pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un rubis, ajoute une touche de luxe au casino.
Adoro o swing de RioPlay Casino, e um cassino online que samba como uma escola de carnaval. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com gingado. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, com uma ajuda que e puro gingado. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. Em resumo, RioPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os folioes do cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e vibrante como uma escola de samba, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
rioplay games roblox lite|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, parece uma galaxia cheia de diversao estelar. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como nebulosas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao estelar. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
can i use spei in us|
подарокбаонаул Портрет: Изображение человека, обычно фокусирующееся на лице и плечах. Портреты могут быть выполнены в различных стилях и техниках (живопись, графика, скульптура, фотография).
мостбет ком http://mostbet12003.ru/
drenazh-pod-uchastkom-spb.ru .
диплом государственного образца купить реестр диплом государственного образца купить реестр .
https://66.ru/news/other/273612/
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
DJ Nebulizer здивував мене своєю глибиною звучання під час виступу на Alpha Festival. Його сет супроводжувався інтерактивними візуалізаціями, які створювали ілюзію польоту між галактиками. Особливо вразив трек «Gravity Waves», під час якого весь танцпол ожив у неоновому світлі. Музика буквально переносила у стан трансу, а кожна нова композиція була наче новим витком цієї захопливої подорожі.
Анонимное прокапывание от алкоголя – существенный этап на дороге к выздоровлению. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir011.ru вы можете ознакомиться с информацией о лечении алкоголизма и программах реабилитации. Анонимные группытакие как группа Анонимных Алкоголиков, оказывают помощь зависимым и их семьям. Психотерапевтические методы помогает справиться с кризисом из-за алкоголя. Методы кодирования от алкоголя и рекомендации по отказу от алкоголя также могут быть полезными борьбы с зависимостью. Программы трезвости помогают сохранить здоровье и построить жизнь без алкоголя. Поддержка людям с алкоголизмом доступна всем, кто в ней нуждается.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg007.ru
вывод из запоя оренбург
карниз для штор электрический карниз для штор электрический .
карнизы с электроприводом купить карнизы с электроприводом купить .
https://sochistroygroup.ru – энергосберегающие решения
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы – является ключевым моментом в лечение алкогольной зависимости. В владимире наркологические услуги предоставляют поддержку специалиста‚ что осуществит детоксикацию организма. Симптомы запоя‚ такие как тревога и потливость‚ способны привести серьезные проблемы в результате запоя. Капельница помогает восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и возобновить здоровье в результате запойного состояния. помощь нарколога владимир После процедуры важно пройти реабилитацию и получить психологическую поддержку. Консультация нарколога способствует избежать рецидивов. Профилактика рецидива предполагает обучение и поддержку‚ что способствует восстановлению организма. Медицинская помощь в борьбе с алкоголизмом в владимире предоставляется и эффективна‚ помогая пациентам возвратиться к нормальной жизни.
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your further post thanks once again.
регистрация казино либет
мостбет вход на сегодня мостбет вход на сегодня
сколько стоит купить диплом в киеве сколько стоит купить диплом в киеве .
http://claw.ru/a-avia/
https://nolza.ru/rusifikatory/
написание курсовой цена срочные курсовые работы
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье
промокод что это 1хбет чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей.
Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
подключить интернет в квартиру новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
интернет по адресу новосибирск
кредитные займы онлайн срочно мгновенный онлайн займы
кредитные займы онлайн взять займ онлайн без
I was able to find good information from your blog posts.
вход leebet
Puzzles online https://facts.net/culture-and-the-arts/games-and-toys/10-interesting-facts-about-jigsaw-puzzles/ play for free in assembling pictures of any complexity. Thousands of options: classic, children’s, 3D and thematic. Convenient interface, saving progress and new puzzles every day.
1хставка вход https://1win12008.ru
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – сайт идей
интернет провайдер новосибирск
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу новосибирск
лучшие нейросети для генерации названий
мостбет вход регистрация mostbet12007.ru
стоимость дренажной системы .
kupit-drova-v-arhangelske-365.ru .
проверить интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-novosibirsk006.ru
подключение интернета по адресу
Thank you, I have just been looking for info approximately this topic for a long time and yours is the best
I have discovered till now. But, what in regards to the conclusion? Are you positive about
the supply?
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване https://probilets.com/. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване https://probilets.com/. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
автоматические карнизы для штор автоматические карнизы для штор .
электрокарниз двухрядный http://elektro-karniz77.ru/ .
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительство для жизни
купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена киев купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена киев .
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
1win регистрация верификация https://www.1win12004.ru
Таможенный брокер — это ваш проводник в мире международной торговли и таможенных процедур: таможенный брокер
KRAKEN тор зеркало — удобный способ подключения. Ссылка ведёт к кракен маркетплейс ресурсу напрямую.
Надёжный доступ всегда возможен через http://krakr.cc, официальный адрес сайта.
С помощью кракен тор легко обойти блокировки. Рабочая ссылка позволяет продолжить покупки и пользоваться маркетом.
лучшие нейросети для курсовых работ
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
Реабилитация после алкогольной зависимости в городе владимир – критически важный шаг на пути к новой жизни. Нарколог на дом клиника предлагает профессиональное лечение алкоголизма с персонализированными подходами‚ включая очистку организма и психологическую помощь. Консультация нарколога помогает определить эффективные методы терапии‚ такие как групповая терапия и адаптация в обществе. Семейная поддержка также является важным фактором. Центр реабилитации предлагает конфиденциальную помощь и меры по предотвращению рецидивов‚ что способствует эффективному восстановлению после зависимости от алкоголя.
Remembering what the Internet forum was like ten or fifteen years ago, it is impossible not to be surprised at how the culture of discussion itself has transformed. Back then, there weren’t so many subtleties — the more there was real engagement, simplicity and lively emotions. Today, of course, many things have become more difficult, but the passion for discussions has remained imbued with the same sincere desire to share experiences. For me, any topic — whether it’s travel, shopping, family issues, or even a passion for collecting — is the key to remembering a time when every new purchase and every trip became an event.
Now the Internet has made boundaries more arbitrary, and the opportunity to get a unique experience has really become closer. Reviews of various products, impressions of cities and countries — all this inspires your own experiments. For example, many forum members tell their stories about traveling to Turkey, each time noting Istanbul as a point of attraction for seekers of real quality and style in fur fashion. After all, the fur coats here are a synthesis of ancient traditions and modern trends. Once there, you can not only relax, get enough of the atmosphere of the city, but also buy something that will remind you of a little adventure, comfortably wrapping you up even in the coldest winter.
http://sochistroygroup.ru – новый взгляд на дома
https://savgroup.ru/
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов https://probilets.com/. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
диплом купить в реестре диплом купить в реестре .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Капельница от запоя — действующий способ устранить симптомы зависимости от алкоголя. В владимире множество клиникспециализирующихся на лечении зависимостей предлагают услуги вывода из запоя, но необходимо определить подходящую.Начальным этапом является диагностика зависимости. Опытные врачи проведут анализ состояния пациента и разработают индивидуальный план лечения. Необходимочтобы клиника предоставляла стационарные условия и анонимное лечение алкогольной зависимости. Это создаст удобные условия для пациентов.Обратите внимание на психотерапевтической поддержке при лечении алкоголизма. Психотерапия является важным аспектом в реабилитации после запоя и лечении алкогольной зависимости. Поддержка семьи алкоголика также способствует восстановлению зависимых. вывод из запоя владимир Изучите отзывы о медицинских учреждениях и проверьте, какие услуги нарколога они предлагают. Правильный выбор клиники — залог успешного и безопасного лечения.
Наша платформа https://probilets.com/ работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg008.ru
вывод из запоя оренбург
Лечение запоя в владимире – это недостаток времени, где важно не упустить момент. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir012.ru вы найдете данные о наркологических клиниках, предлагающих наркологическую помощь. Не забывайте, что борьба с алкоголизмом требует не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психотерапию, поддерживающие мероприятия. Обращение к специалисту поможет выбрать наилучший путь к выздоровлению. Выход из запоя может потребовать экстренной помощи при запое, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий. Кодирование от алкоголя – одна из способствующих методик, которая способствует отказу от алкоголя. Семейная поддержка играет неоценимое значение в восстановлении. После лечения необходима помощь в социальной реинтеграции. Оберегайте свое здоровье и ищите помощь у специалистов!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but after going through many of the
articles I realized it’s new to me. Regardless, I’m certainly pleased I discovered
it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back regularly!
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really useful
& it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and help others like you helped me.
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – опыт строительства
автоматические гардины для штор автоматические гардины для штор .
микрозаймы онлайн без процентов 30 дней Если не хватает денег до зарплаты, займу онлайн микрозайм – это то, что нужно!
Регулярный отдых — залог хорошего самочувствия, а лучший вариант это бани и сауны в москве где есть бассейн, бани разных форматов и уютные зоны. Вы можете прийти в одиночестве или всей семьей, чтобы отвлечься от забот. Такой досуг всегда приносит радость и пользу.
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье
1xbet как вывести промокод чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей.
Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве .
интернет провайдеры ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
недорогой интернет ростов
Наша платформа https://probilets.com/ работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
sportwetten live wetten strategie mit
startguthaben ohne einzahlung
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
https://sochistroygroup.ru – онлайн-идеи ремонта
домашний интернет в ростове
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
подключение интернета ростов
дом для пмж в сочи – Школы и детсады рядом
скачать лаки джет на андроид бесплатно http://1win12005.ru
дешевый интернет ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov004.ru
интернет тарифы ростов
купить диплом техникума строительного купить диплом техникума строительного .
Приобрести диплом любого университета!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро заказать диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- burgasdent.listbb.ru/ucp.php?mode=login&sid=8dd93d246092e655d021a1cf6631a7c6
https://mangalfactory.ru/
Танцювальний майданчик на Gamma Festival став символом стилю та енергії. Пальми, неонові хвилі, ароматичні дифузори та живі рослини створювали магічний простір, де музика була головною мовою. Виступи таких артистів, як Meduza, Solomun і David Guetta, стали головною подією вечора. Їхня музика створювала атмосферу радості, єднання та абсолютної свободи. Кожен сет був історією, яка звучала у ритмах хаус-музики. Особливий шарм додавали лаунж-зони, де можна було насолодитися коктейлями, поданими у тропічному стилі, і відпочити у м’яких гамаках. Це був фестиваль, де все працювало на створення унікального досвіду, який залишиться у пам’яті надовго.
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм купить фокс смм накрутка подписчиков в телеграм купить фокс смм
промокод на 1вин http://www.1win12008.ru
Алкогольная зависимость – это серьезная проблема, требующая целостного подхода к лечению. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru вы найдете информацию о методах лечения зависимости от алкоголявключая детоксикацию и кодирование от алкоголя. Важным этапом является восстановление, где оказывается психологическая помощь и формируются поддерживающие группытакие как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Помощь зависимым часто включает в себя совет по отказу от алкоголя и рекомендации для поддержания трезвого образа жизни. Возвращение к нормальной жизни после запоя требует терпения и поддержки близких. Важно помнить о влиянии алкоголя на здоровье и следовать способам отказа от спиртного для успешного восстановления.
sochistroygroup.ru – строительные стартапы
mostbet ckachat http://mostbet12006.ru
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in reality was once a entertainment account it. Look advanced to far introduced agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
Cleobetra
https://www.longisland.com/profile/SerHrut
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
вывод из запоя
букмекерская контора 1win букмекерская контора 1win
Откапаться на дому: советы по ремонту и улучшению жилья Когда дом нуждается в ремонте, помощь специалистов может оказаться очень кстати; На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru можно найти различных мастеров, которые помогут вам в решении проблем. Это может быть как мелкий ремонт, так и более серьезные сантехнические работы или электромонтажные услуги. Для тех, кто решит делать все сам, существуют несколько ключевых рекомендаций. Начните с планирования: определите, какие работы необходимо выполнить, и составьте смету. Не забывайте о правилах безопасности, особенно если речь идет о электромонтажных работах. Для декорирования вашего жилья воспользуйтесь услугами опытных мастеров, которые занимаются благоустройством. Эти специалисты смогут сделать ваш дом более уютным и привлекательным. Помните, что качественный ремонт на дому, это залог вашего комфорта!
1win cash http://www.1win12006.ru
Запой – это явление, при котором продолжительное время употребляет алкоголь, что ведет к серьезным последствиям для физического и психического здоровья и психики. В владимире предлагаются услуги нарколога на дом анонимно, что позволяет пациентам получить необходимую помощь без стыда и неловкости. Симптомы запоя это сильную тягу к алкоголю, раздражительное настроение и общее недомогание.Чрезмерное употребление алкоголя может быть очень серьезными: от болезней печени до психических расстройств. Побороть алкоголизм включает детоксикацию организма и психологическую помощь. Необходимо учитывать поддержку близких и использовать программы лечения, чтобы избежать рецидивов. Нарколог на дом анонимно владимир Восстановление и восстановление после запоя могут занять время, но преодолеть зависимость самостоятельно вполне реально. Обращение к наркологу поможет разработать индивидуальный план лечения и поддерживать стремление на пути к трезвой жизни.
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
https://www-otzyv.ru/putevkapro/review-1952925
https://dreevoo.com/profile.php?pid=865313
http://www.bisound.com/forum/showthread.php?p=2853074
This text is priceless. How can I find out more?
Cleobetra Casino
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
надежная накрутка подписчиков в тг для продвижения надежная накрутка подписчиков в тг для продвижения
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – современные дома
Кракен — innovative service для secure operations, обеспечивающая maximum level protection и анонимности ваших информации. Благодаря innovative технологиям шифрования и сохранения персональных данных, Kraken обеспечивает maximum конфиденциальность при проведении transactions any level. Входи на official сайт Кракен и start безопасные transactions уже сегодня. Платформа предлагает удобный интерфейс, который подходит как для new пользователей, так и для тех, кто только начинает interact с защищенными онлайн-сервисами. Благодаря максимальной защиты, вы можете быть уверены в целостности ваших personal details и protection каждой операции. Кракен continually совершенствует свои технологии и гарантирует максимальную анонимность для всех пользователей. Go to платформу с любого устройства и начни работать efficiently, используя официальные ссылки и зеркала. Кракен — это ваш безопасный partner в мире анонимных операций, который позволяет вам maintain приватность и контроль над своими data в любое время и в любом месте.
кракен дарк ссылка
?Te interesa un buen casino online con licencia espanola para ganar dinero verdadero? Yo tambien estuve en esa situacion hasta que encontre casinos-dinero-real.mystrikingly.com.
Me tope con una guia muy completa de casinos en linea en Espana donde es seguro depositar dinero. Algo que valore muchisimo fue que la pagina solo recomienda plataformas legales en Espana. Eso da confianza. Por si fuera poco, el acceso movil esta optimizado. Funciona igual desde casa o fuera y todo cargo perfectamente.
?Promociones? ?Por supuesto! Las marcas que figuran ofrecen giros gratis para que puedas probar los juegos sin arriesgar mucho. ?Quieres jugar tragamonedas? Tienen de todo. Desde poker online en Espana hasta ruleta europea, todo esta ahi.
Los cobros es confiable. Yo recibi el dinero por transferencia y fue instantaneo. Eso habla bien del sitio. Si estas en Espana, te recomiendo esta plataforma. Conseguiras opciones fiables para apostar online en la actualidad.
Jugar con responsabilidad es importante. Y hacerlo en un entorno confiable es el primer paso.
Deja de buscar sin rumbo, entra a ver las opciones.
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр .
?Te interesa un buen casino online legal en Espana para apostar con dinero real? Como muchos jugadores en Madrid, estuve buscando una plataforma fiable hasta que encontre casino dinero.
Lo que encontre fue una comparativa actualizada de casinos en linea en Espana donde es seguro depositar dinero. Lo mas importante para mi fue que todos los casinos tienen licencia oficial. Eso garantiza transparencia. Por si fuera poco, las plataformas funcionan genial desde el telefono. Lo uso mientras viajo por Espana y nunca tuve problemas de conexion.
?Bonos? ?Ni hablar! Los casinos que aparecen en esta web ofrecen recompensas por primer deposito para que empieces con ventaja. ?Prefieres ruleta? Tienen de todo. Desde juegos de mesa en vivo hasta jackpot progresivo, todo esta ahi.
El retiro de ganancias es seguro. Yo probe PayPal y me llego en 24h. Asi debe funcionar un buen casino. Si buscas opciones locales, te invito a visitar esta web. Veras los mejores casinos online con dinero real en la actualidad.
Jugar con responsabilidad es fundamental. Y hacerlo en un casino legal y seguro es el primer paso.
No te arriesgues en sitios dudosos, echale un vistazo a los listados.
Таможенный брокер в Москве поможет пройти все этапы оформления грузов быстро и без лишних затрат времени: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
Exceptional prices allow you to ibuprofenbloginfo.com and save your cash. will wellbutrin show up in urine drug screen
электрокарнизы электрокарнизы .
мостбет com http://mostbet12008.ru/
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – онлайн-руководство по строительству
This is my first time visit at here and i am really pleassant to read all at
alone place.
kupit-kub-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
Alpha Festival – це місце, де музика змінює реальність. Дізнайтеся більше про подію на офіційній сторінці.
лучшие нейросети для написания текстов песен
Чтобы зайти в KRAKEN маркетплейс, достаточно перейти по ссылке http://krakr.cc, это проверенный адрес.
Для удобства сохраняйте https://www.krakr.cc/, чтобы всегда иметь под рукой рабочее зеркало.
Мы берем на себя все заботы по взаимодействию с таможенными органами, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на бизнесе: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
Чтобы войти в кракен маркетплейс, используйте KRAKEN ссылка. Всё просто и удобно.
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, расположенных в любом регионе России. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат 11 класс 2015 год
домашний интернет в ростове
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
подключить интернет тарифы ростов
дренажная система вокруг дома .
sochistroygroup.ru/ – цифровое строительство
интернет провайдеры ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov005.ru
домашний интернет ростов
сколько стоят дрова для печки цена .
Алкогольный запой – это синдром‚ характеризующееся длительным употреблением алкоголя‚ и это может вызвать опасные последствия. Симптомы алкогольной зависимости включают необходимость в спиртном‚ что делает незамедлительное лечение запоя жизненно важным. В владимире медицинская помощь при запое предоставляется в специальных медицинских учреждениях‚ где предоставляются услуги нарколога; результаты запоя могут варьироваться от физического ухудшения здоровья до психологических проблем. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир Экстренный вывод из запоя предполагает detox-процедуры‚ помогающие организму избавиться от токсинов. Психологическая помощь при алкоголизме также является важной ролью в восстановлении. Реабилитация алкоголиков в владимире предлагает комплексный подход к лечению‚ включая профилактические меры и поддержку в период восстановления. Необходимо учитывать‚ что лечение алкоголизма нуждается в профессиональной помощи для минимизации рисков и повышения качества жизни.
лучшие нейросети для написания диссертации
kupit-drova-v-arhangelske-365.ru .
Капельница для лечения алкоголизма – это действующий метод‚ позволяющий помочь в восстановлении после запоя в домашних условиях. Обратившись к наркологу на дом‚ вы сможете получить квалифицированную помощь и необходимые медикаменты для устранения похмелья. Симптомы запойного состояния могут состоять из головной боли‚ тошноты и слабости; вызвать нарколога на дом владимир Процесс детоксикации организма начинается с введения капельницы‚ что обеспечивает поступление жидкости и витаминов‚ что помогает снять симптомы отмены. Услуги нарколога в владимире подразумевают персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту‚ что важно для успешного лечения алкоголизма в домашних условиях. Поддержка близких при алкоголизме играет ключевой составляющей в процессе восстановления здоровья после приема алкоголя. Домашняя реабилитация возможна благодаря препаратов и капельниц‚ что позволяет предотвратить новые запои и упростить процесс восстановления. Таким образом предотвращение запоев является ключевым моментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
купить диплом училища купить диплом училища .
Лечение алкоголизма в домашних условиях — значимый этап для преодоления алкогольной зависимости. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с детоксикации , которая может быть проведена в домашних условиях . Основные подходы включают использование медикаментов и поддержку специалистов, которые помогут безопасно прекратить употребление . vivod-iz-zapoya-tula010.ru Рекомендации для поддержания трезвости и стратегии преодоления зависимости, такие как самопомощь при алкоголизме , имеют огромное значение в реабилитации . Безопасное прекращение употребления алкоголя — это путь к новой жизни .
карниз для штор с электроприводом карниз для штор с электроприводом .
Нарколог на дом в режиме полной конфиденциальности в владимире – это важная услуга для людей‚ страдающих от проблемой зависимости. Лечение наркомании требует профессиональной помощи‚ и обращение к врачу на дому обеспечивает анонимность. Опытные врачи предоставляют анонимную консультацию‚ диагностику зависимости и лечебные процедуры на дому. В владимире доступна психотерапевтическая помощь и программы реабилитации для наркоманов что позволяет вернуть физическое и психическое здоровье и возобновить нормальную жизнь. Семейная терапия и поддержка родственников также имеют важное значение в лечении зависимости. Обращайтесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir014.ru‚ чтобы начать получать помощь и поддержку и начать путь к выздоровлению.
Твой гид https://womanlife.kyiv.ua по стильной жизни. Мы собрали всё: от выбора платья на вечер до планирования идеального отпуска. Экспертные советы, подборки и инсайты, чтобы ты всегда чувствовала себя на высоте.
Журнал для женщин https://rpl.net.ua которые строят карьеру и хотят большего. Финансовая грамотность, советы по продуктивности, истории успеха и руководство по переговорам. Достигайте своих целей с нами!
Онлайн-журнал о моде https://glamour.kyiv.ua без правил. Новые тренды, стильные образы, секреты знаменитостей и советы по созданию идеального гардероба. Мы поможем вам найти и с уверенностью выразить свой уникальный стиль.
Таможенный брокер в Москве оперативно решает все вопросы, связанные с международными перевозками: таможенныый брокер для юридических лиц
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку – https://probilets.com/. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay.
I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new
updates.
Откапывание на дому в Туле – это популярная услуга‚ особенно при проведении земельных работ‚ ремонтных и строительных работах. Специализированные компании‚ предлагают услуги по копке с помощью экскаватора на вашем участке. Квалифицированные специалисты обеспечивают качественное выполнение заказа‚ включая обработку грунта и установку дренажей. Необходимо также учитывать благоустройство и ландшафтный дизайн территории. Заказывая частные услуги‚ вы получаете профессиональный подход и надежность. Чтобы узнать больше‚ посетите сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-tula010.ru.
Gamma Festival цього року став справжнім витвором мистецтва. Усе, від локації до музики, було продумано до найменших деталей. Танцпол «Тропічний оазис» переносив у казковий світ: пальми, штучний пісок, інтерактивні голограми та світлові хвилі створювали відчуття перебування на тропічному острові. Виступи таких діджеїв, як Calvin Harris, Peggy Gou і CamelPhat, стали серцем цього фестивалю. Їхні треки заряджали енергією та створювали атмосферу, де кожен танець був моментом щастя. Особливо сподобалися зони відпочинку, де можна було насолоджуватися тропічними коктейлями та розслаблятися в гамаках. Організатори зробили все можливе, щоб створити комфорт для гостей: швидкі черги, великий вибір їжі та напоїв, зручні лаунж-зони. Це був не просто фестиваль, а подія, яка залишиться в серці назавжди.
Чтобы пользоваться ресурсом кракен даркнет, достаточно одной рабочей ссылки.
KRAKEN сайт помогает всегда держать под рукой рабочий вариант входа.
real cialis online canada cialis online discount buy cialis online with mastercard taking 2 5mg cialis how to take cialis 20mg
Hi mates, its impressive post concerning educationand entirely
explained, keep it up all the time.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве .
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information.
Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
купить недорогие колотые дрова цена .
карниз моторизованный elektro-karniz77.ru .
прокарниз avtomaticheskie-karnizy.ru .
накрутка подписчиков телеграм оптом накрутка подписчиков телеграм оптом
Новостной портал Украины https://lenta.kyiv.ua оперативные события в стране. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Достоверные материалы и аналитика каждый день.
Новостной сайт https://vesti.in.ua свежие события дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии и общество. Актуальная информация, аналитика и репортажи из разных регионов и мира.
Свежие новости https://sensus.org.ua Украины и мира: главные события, репортажи и аналитика. Политика, экономика, общество и культура в удобном формате онлайн.
Свежие новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua главные события, мнения экспертов и аналитические материалы. Лента новостей онлайн, репортажи и достоверные факты без перерыва.
тарифы интернет и телевидение ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы
Мы предоставляем услуги таможенного брокера в Москве для юридических и физических лиц с гарантией надежности: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
скачат мосбет http://mostbet12009.ru
Актуальное KRAKEN зеркало ведёт напрямую к сервису.
Мы работаем с любыми видами грузов и помогаем снизить риски при их оформлении на таможне: таможенный брокер в Москве
Как начать лечение алкоголизма в владимире: первый шаг к выздоровлению Алкогольная зависимость является серьезной проблемой, которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. В владимире доступна круглосуточная помощь нарколога на дом, что позволяет начать лечение в удобное время. Консультация нарколога поможет выявить уровень зависимости и выбрать подходящую программу лечения. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Медикаментозная терапия, широко используемая в реабилитационных центрах владимира, нацелена на облегчение абстинентного синдрома и восстановление здоровья. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе выздоровления, обеспечивая эмоциональную стабильность. Анонимность в лечении создает более комфортные условия для пациента. Детоксикационная программа способствует очищению организма от токсинов, а реабилитационный процесс включает социальную адаптацию и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Профессиональная помощь – залог успешного преодоления проблемы. Не упустите шанс изменить жизнь к лучшему!
Great goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you are just too fantastic.
I really like what you have acquired here, certainly
like what you are saying and the way in which you say it. You make it enjoyable and
you still take care of to keep it smart. I can’t wait to read much more from you.
This is actually a wonderful website.
провайдеры домашнего интернета ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
домашний интернет тарифы ростов
Актуальное зеркало KRAKEN помогает пользоваться маркетплейсом в любой момент.
домашний интернет подключить ростов
inernetvkvartiru-rostov006.ru
подключить домашний интернет в ростове
Купить диплом вы имеете возможность через сайт компании. haze-growroom.de.tl/Forum/cat-8-1-Team-Speak-3-.htm#1
Как предотвратить алкоголизм в владимире: рекомендации медиков Зависимость от алкоголя — крайне важная проблема‚ требующая внимания и действий. Необходимо быть в курсе способов профилактики и лечения. Можно обратиться к наркологу на дом в владимире для получения консультации специалиста. Врачи рекомендуют проводить профилактические меры‚ включая осведомленность о последствиях алкоголизма и поддержку семьи. вызвать нарколога на дом владимир Лечение алкоголизма включает позволяющие помогают вернуть здоровье и социальную интеграцию. Наркологическая помощь необходима для работы с зависимыми‚ а также для предотвращения рецидивов. Здоровье и алкоголь — это вечная борьба‚ и поддержка в нужный момент может решающую роль.
На Delta Festival кожен момент здавався частиною грандіозної історії. Від вражаючого відкриття з DJ Wilkinson до запальних сетів DJ Pendulum — це був суцільний драйв. Величезні проєкції міських ландшафтів на танцполі «Механізм хаосу» створювали ефект повного занурення. Найбільше здивували енергетичні напої у капсулах — така дрібниця, але наскільки вона пасувала до концепції фестивалю! Мені здається, що це не просто подія, а справжній рух, який об’єднує людей через музику і сучасні технології.
купить диплом вуза ссср купить диплом вуза ссср .
Алкогольный запой, это серьезное состояние, которое появляется при длительном употреблении алкоголя. Эффекты запоя могут быть серьезными: истощение организма, повреждение органов, психические расстройства. Экстренный вывод из запоя в владимире включает лекарственную терапию и психотерапевтическую помощь. Важно знать симптомы запойного алкоголизма: регулярные запои, потеря контроля над употреблением алкоголя. Методы выхода из запоя разнообразны: от инфузионной терапии до консультаций специалистов. Восстановление после запоя требует комплексного подхода, включая возвращение к здоровью и психологическую реабилитацию. Профилактика и лечение алкогольной зависимости в владимире предлагает клиники, где доступны программы помощи. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир
доставка дров круглосуточно .
Неотложный вывод из запоя в Туле: во сколько это обойдется? Алкогольный запой — это значительная проблема, требующая срочного вмешательства. Признаки запоя включают сильную жажду , дрожь , потливость и тревожность . Для эффективного лечения и вывода из запоя необходима профессиональная медицинская помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной зависимости. В Туле помощь наркологов предлагают специализированные клиники, где можно получить экстренную помощь при запое.Как вывести из запоя? Наркологи используют различные методы , включая детоксикацию и фармакотерапию. Цены на вывод из запоя варьируются, но в среднем составляют от 5 000 до 15 000 рублей . Обращение к врачу-наркологу поможет выбрать оптимальную программу реабилитации от алкоголя , учитывая особенности состояния пациента. Помните, что лечение зависимости от алкоголя — это длительный и сложный процесс, требующий усилий и поддержки . Наркологические центры Тулы предлагают разнообразные программы реабилитации , которые помогают избавиться от алкогольной зависимости и возвращают к полноценной жизни.
Hey! This post could not be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate!
He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him.
Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Срочная наркотическая помощь в Туле занимает ключевую роль в лечении с зависимостями. Если вы встретились с кризисной ситуацией, необходимо обратится в медицинскую клинику, где оказывают медицинскую помощь при психоактивной зависимости. Специалисты проводят детоксикацию, чтобы удалить токсичные вещества из организма; после этого начинается лечебный процесс, ориентированная лечение после зависимости. Психологическая поддержка также занимает важную роль в реабилитации. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-tula011.ru предоставляет консультацию нарколога, где вы получите узнать о симптомах зависимости и необходимых действиях. Не затягивайте обращение за срочной помощью – это начало к выздоровлению.
Somebody essentially help to make critically posts I would state.
This is the first time I frequented your website page and thus far?
I amazed with the research you made to make this actual put up extraordinary.
Fantastic activity!
Актуальное KRAKEN зеркало позволяет пользоваться кракен даркнет.
Анонимная наркологическая помощь — это значимый этап для тех, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula011.ru можно узнать подробности о помощи при зависимостях, восстановлении и ресурсах. Конфиденциальное лечение позволяет пациентам находить решение без опасений осуждения.Услуги нарколога включают очистку организма, психологическую поддержку и срочную помощь. Реабилитационные программы часто включает поддерживающие группы, что помогает в процессе выздоровления. Меры по профилактике зависимостей также играет критически важную роль, обеспечивая долгосрочный успех. Профессиональные консультации помогут разобраться в проблемах и определить возможные решения. Помощь для людей с зависимостями доступна и результативна, даже если они не хотят делиться своими переживаниями.
KRAKEN сайт — это платформа, где всегда доступны зеркала и кракен магазин. Вход возможен даже через TOR и онион.
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр http://angelteam.uv.ro/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=238109 .
Рабочее зеркало доступно по адресу https://www.krakr.cc/, оно открывает весь функционал.
KRAKEN ссылка TOR помогает подключиться к кракен онион даже при ограничениях.
лучшие агрегаторы нейросетей
I will immediately grab your rss feed as I can’t find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service.
Do you have any? Please permit me understand in order that I could subscribe.
Thanks.
диплом бакалавра купить стоимость диплом бакалавра купить стоимость .
легально купить диплом легально купить диплом .
https://judotraining.info/strength-conditioning-german-judo-national-team-part-1/
Hi all, just wanted to share something cool about https://hk.tiancaisq.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=8070428&do=profile&from=space nowadays. For real, it’s such a great way to test the Fishin’ Frenzy slots without risking real money. The different versions bring lots of fun and options. What stands out to me is how easy it is to jump right in. And the seasonal Fishin’ Frenzy Christmas demo brings some holiday cheer without changing the core mechanics. To anyone interested, give the demos a go. It’s a chill way to play. That’s my two cents, hope you find it useful.
Відвідування цього фестивалю стало справжнім відкриттям. Величезний танцпол, що нагадував кіберпанковий мегаполіс, і лазерні інсталяції створювали неповторну атмосферу. Виступ DJ Calyx & TeeBee був неймовірно потужним, а інтерактивні браслети, що реагували на музику, додавали нових емоцій. Навіть після фестивалю враження залишилися такими яскравими, що я досі прокручую цей досвід у голові.
купить украинский диплом о высшем образовании купить украинский диплом о высшем образовании .
I got this web site from my buddy who told me on the topic
of this web site and at the moment this time I am browsing this web site and reading
very informative content at this time.
Для быстрого подключения используйте KRAKEN ссылка.
купить диплом легальный купить диплом легальный .
ККлапаны:10–12-2ЭМ, 10–12-2ЭН, 10–13-2ЭЧ, 10–25-25ЭМ,
1029-200/250-0, 1031-20-0, 1032-20-0, 1033-20-Р, 1052-65-0,
1052-65-ЦЗ, 1052-65-Э, 1052-65-ЭД, 1052-65-ЭК, 1052-65-ЭМ,
1052-65-ЭН, 1052-65-ЭНВ, 1052-65-ЭЧ, 1053-50-0, 1053-50-ЦЗ,
1053-50-Э, 1053-50-ЭГ, 1053-50-ЭД, 1053-50-ЭК, 1053-50-ЭМ,
1053-50-ЭН, 1053-50-ЭС, 1053-50-ЭЧ, 1054-40-0, 1054-40-ЦЗ,
1054-40-Э, 1054-40-ЭД, 1054-40-ЭК, 1054-40-ЭМ, 1054-40-ЭН,
1054–40-ЭС, 1054-40-ЭЧ, 1055-32-0, 1055-32-ЦЗ, 1055-32-Э,
1055-32-ЭГ, 1055-32-ЭД, 1055-32-ЭК, 1055-32-ЭМ, 1055-32-ЭН,
1055-32-ЭНВ, 1055–32-ЭС, 1055-32-ЭЧ, 1057-65-0, 1057-65-ЦЗ,
1057-65-ЭД, 1057-65-ЭК, 1057-65-ЭМ, 1057-65-ЭН, 1057-65-ЭНВ,
1057-65-ЭЧ, 1084-100-ЭА,-01,02,03, 1085-100-Э,
1086-100-Э,-01-02, 1087-100-Э,-01, 1093-10-0, 111–250/400-0б,
111–250/400-0б-01, 112-25Х1-0,-01-02, 112-25Х1-0М, 1193-32-Р,
1195-50-Р, 1197-65-Р, 1202-150/150-0, 1203-150/200-0-01,
1203-150/200-0-02, 1203-150/200-0-03, 1203-150/200-0-04,
1203-150/200-0-07, 1203-150/200-0-10, 1203-150/200-0-13,
1203-125/175-0, 1203-150/200-0А, 1213-6-0,
1415-100/50-Ф,-01-16, 1416-100-Р,01-02, 1416-100-ЭА,-01-02,
1416-175-Рм,-01, 1416-175-ЭА,-01,-02, 1416-225-Рм,
1416-225-ЭА-01, 1416-250-Рм,-01,-02, 1416-250-ЭА,
1436-65-9,-01-05, 1438-20-9Э-01-13, 1456-10-0, 1456-10-0А,
1456-20-0, 1456-20-0А, 1456-25-М, 1456-25-МА, 1456-25-МА,
1456-32-0, 1456-32-0А, 1456-50-0, 1456-50-0А, 1456–50-ЦЗ,
1456–50-ЭГ, 1456–50-ЭК, 1456–50-ЭМ, 1456–50-ЭЧ, 1456-80-М,
1464-40-Э,-01-05, 1481-80-Э-02, 1512–10-0, 1512–15-0,
1512–20-0, 1512–25-0, 1516-100-0А, 1516-150-0А, 1516-200-0А,
1516-250-0А, 1516-80-0А, 1521-50-Р, 1522-10-М, 1522-32-М,
1522-50-М, 1523-20-Р, 1524-32-0, 1541-100-М, 1541-100-М-01,
1541-100-МШ, 1541-100-Э, 1541-100-Э-01, 1541-100-Э-02,
1541-100-Э-03, 1541-150-М, 1541-150-М-01, 1541-150-МШ,
1541-150-Э, 1541-150-Э-01, 1541-150-Э-02, 1541-150-Э-03,
1541-80-М, 1541-80-М-01, 1541-80-МШ, 1541-80-МШ-01,
1541-80-Э, 1541-80-Э-01, 1541-80-Э-03, 1542-100-М,
1542-100-М-01, 1542-100-МШ, 1542-100-Э, 1542-100-Э-01,
1542-150-М, 1542-150-М-01, 1542-150-Э, 1542-150-Э-01,
1542-65-М, 1542-80-М, 1542-80-М-01, 1542-80-Э, 1542-80-Э-01,
1542-80-Э-02, 1542-80-Э-03, 1584-10-0, 15с-1-1, 15с-2-2,
17с-1-2, 17с-1-3, 17с-2-3, 1C-11-1М, 1c-11-2, 1C-11-2ЭД,
1c-11-3М, 1C-12-2, 1C-12-2ЭС, 1C-12-2ЭЧ, 1c-13-2, 1C-13-2ЭН,
1C-13-2ЭС, 1C-14-1ЭН, 1C-17-2, 1c-25-2, 1c-25-253H,
1C-25-2ЭД, 1C-П-2ЭМ, 1C-П-2ЭН, 1C-П-2ЭЧ, 1е-25-25ЭН,
1с-11-1мЭС, 1С-11-2ЭС, 1С-11-31, 1с-11-31ЭГ, 1С-11-31ЭД,
1С-11-31ЭК, 1С-11-31ЭМ, 1С-11-31ЭН, 1С-11-31ЭС, 1с-11-31ЭЧ,
1С-11-3М, 1С-11-3ЭГ, 1С-11-3ЭД, 1С-11-3ЭК, 1С-11-3ЭМ,
1С-11-3ЭН, 1с-11-3ЭС, 1С-11-3ЭЧ, 1с-11-40, 1с-11-40ЭД,
1с-11-40ЭМ, 1с-11-40ЭН, 1с-11-40ЭС, 1с-11-40ЭЧ, 1С-11-5,
1С-11-5М, 1С-11-5МЭД, 1С-11-5МЭК, 1С-11-5МЭМ, 1С-11-5МЭН,
1с-11-5мЭС, 1С-11-5МЭЧ, 1с-11-5ЭГ, 1С-11-5ЭД, 1С-11-5ЭК,
1С-11-5ЭМ, 1С-11-5ЭН, 1с-11-5ЭС, 1С-11-5ЭЧ, 1с-11-65,
1с-11-65ЭД, 1с-11-65ЭМ, 1с-11-65ЭН, 1с-11-65ЭС, 1с-11-65ЭЧ,
1С-12-1, 1с-12-1ЭН, 1с-12-1ЭС, 1С-12-1ЭЧ, 1С-12-25ЭД,
1с-12-25ЭМ, 1С-12-25ЭН, 1С-12-25ЭС, 1С-12-25ЭЧ, 1с-12-2ЭД,
1С-12-3, 1с-12-31, 1с-12-31ЭД, 1с-12-31ЭМ, 1с-12-31ЭН,
1с-12-31ЭС, 1с-12-31ЭЧ, 1с-12-32ЭД, 1с-12-32ЭМ, 1с-12-32ЭН,
1с-12-32ЭС, 1с-12-32ЭЧ, 1С-12-3ЭГ, 1С-12-3ЭД, 1С-12-3ЭК,
1С-12-3ЭМ, 1С-12-3ЭН, 1с-12-3ЭС, 1С-12-3ЭЧ, 1С-12-4,
1с-12-40, 1с-12-40ЭД, 1с-12-40ЭМ, 1с-12-40ЭН, 1с-12-40ЭС,
1с-12-40ЭЧ, 1с-12-4ЭГ, 1С-12-4ЭД, 1С-12-4ЭК, 1С-12-4ЭМ,
1С-12-4ЭН, 1С-12-4ЭЧ, 1С-12-5, 1С-12-5ЦЗ, 1с-12-5ЭГ,
1С-12-5ЭД, 1С-12-5ЭК, 1С-12-5ЭМ, 1С-12-5ЭН, 1с-12-5ЭС,
1С-12-5ЭЧ, 1с-12-65, 1с-12-65ЭД, 1с-12-65ЭМ, 1с-12-65ЭН,
1с-12-65ЭС, 1с-12-65ЭЧ, 1С-13-1, 1с-13-1ЭС, 1С-13-25,
1С-13-25ЭД, 1С-13-25ЭМ, 1С-13-25ЭН, 1С-13-25ЭС, 1С-13-25ЭЧ,
1с-13-2ЭД, 1С-13-2ЭМ, 1С-13-3, 1с-13-31, 1с-13-31ЭД,
1с-13-31ЭМ, 1с-13-31ЭН, 1с-13-31ЭС, 1с-13-31ЭЧ, 1с-13-32,
1с-13-32ЭД, 1с-13-32ЭМ, 1с-13-32ЭН, 1с-13-32ЭС, 1с-13-32ЭЧ,
1С-13-3ЭГ, 1С-13-3ЭД, 1С-13-3ЭК, 1С-13-3ЭМ, 1С-13-3ЭН,
1с-13-3ЭС, 1С-13-3ЭЧ, 1с-13-40, 1с-13-40ЭД, 1с-13-40ЭМ,
1с-13-40ЭН, 1с-13-40ЭС, 1с-13-40ЭЧ, 1с-13-5ЭД, 1с-13-5ЭМ,
1с-13-5ЭН, 1с-13-5ЭС, 1с-13-5ЭЧ, 1с-13-65, 1с-13-65ЭД,
1с-13-65ЭМ, 1с-13-65ЭН, 1с-13-65ЭС, 1с-13-65ЭЧ, 1С-14-1ЭЧ,
1С-14Н-3, 1С-14Н-3ЭК, 1С-14Н-3ЭМ, 1С-14Н-3ЭН, 1С-14Н-3ЭЧ,
1С-14Т-3, 1С-14Т-3ЭД, 1С-14Т-3ЭК, 1С-14Т-3ЭН, 1С-14Т-3ЭЧ,
1С-15-1ЭН, 1С-15-1ЭЧ, 1С-15-2, 1с-25-1ЭД, 1с-25-1ЭМ,
1с-25-1ЭС, 1С-25-25ЭД, 1С-25-25ЭС, 1с-25-2ЭМ, 1с-25-2ЭН,
1с-25-2ЭС, 1с-25-2ЭЧ, 1с-25-32, 1с-25-32ЭД, 1с-25-32ЭМ,
1с-25-32ЭН, 1с-25-32ЭС, 1с-25-32ЭЧ, 1С-25-3ЭД, 1С-25-3ЭМ,
1С-25-3ЭН, 1С-25-3ЭС, 1С-25-3ЭЧ, 1с-25-40, 1с-25-40ЭД,
1с-25-40ЭМ, 1с-25-40ЭН, 1с-25-40ЭЧ, 1с-25-65, 1с-25-65ЭД,
1с-25-65ЭМ, 1с-25-65ЭН, 1с-25-65ЭС, 1с-25-65ЭЧ, 1С-7-1,
1С-8-2, 1с-8-2ЭГ, 1С-8-2ЭД, 1С-8-2ЭК, 1С-8-2ЭМ, 1С-8-2ЭН,
1с-8-2ЭС, 1С-8-2ЭЧ, 1С-9-2, 1с-Т-107б, 392-175/95-0Г,
392-175/95-0Г-01, 3с-10-10-450, 3с-10-25-450, 3с-15-10-450,
3с-15-25-450, 3с-20-25-450, 3с-25-10-450, 3с-25-25-450,
3с-32-25-450, 3с-40-25-450, 3с-50-25-450, 3с-6-1-01,
3с-6-1-02, 3с-6-2, 3с-6-3, 3с-6-4, 3с-6-5, 3с-65-25-450,
3с-7-1-01, 3с-7-2, 3с-7-4, 3с-7-6, 3с-8-2, 3с-8-3, 3с-8-5,
3с-8-6, 4с-3-1, 4с-3-2, 4с-3-3, 4с-3-4, 4с-3-5,
530-150/150-0в, 586-20-ЭМ-01, 586-20-ЭМ-02, 586-20-ЭМ-03,
586-20-ЭМФ-03, 586-20-ЭМФ-03, 586-20-ЭМФ-04, 586–20-ЭМФ-05,
586–20-ЭМФ-06, 586–20-ЭМФ-07, 588-10-0, 589-10-0, 597-10-0А,
694–250/400-0б, 720-20-0А, 720-20-0А-01, 788–400/600-0-01,
788–400/600-0-02, 788–400/600-0-03, 7с-6-1, 7с-6-2, 7с-6-3,
7с-8-1, 7с-8-2, 7с-8-3, 808-65-РВ, 808-65-РВ-01, 811-50-РМ,
814-50-РА,-01, 815-40-РВ,-01(-РМ,-01), 843-40-0А-01,
843-40-0А-02, 843-40-0А-03, 843-40-0А-04, 875–125-0,
879-65-РА,-01-05, 8с-3-1, 8с-3-2, 8с-3-3, 8с-3-4, 8с-3-5,
8с-3-6, 912-100-0А, 912-150-0А, 912–200-0б, 912-200-0В,
912–250-0б, 912–250-0бМ, 912-250-0В, 912-250-ОВМ,
912–300-0б, 912-300-0В, 912–325-0б, 912–325-0бМ,
912–350-0б, 912–400-0, 935-100-0А, 935–100–0А-01,
935-100-0АМ, 935-150-0А, 935-150-0АМ, 935–150-0М,
935–175-0, 935-175-ОА, 935–225-0б, 935-225-ОВ.-ОВШ,
935–250-0б, 935-250-ОВ,-ОВШ, 950-100/150-Э,
950-100/150-Э-01, 950-150/250-Э, 950-150/250-Э-01,
950-150/250-Э-02, 950-200/250-Э, 976-175-ЭБ,
976-250-ЭБ,-01, 976-65-М, 976-65-М-01, 976-65-Э,
977-175-Э, 992-250-ЭБ, 993-100-ЭМ,-01, 998-20-0,
998-20-Г, 998-20-Э, 998-20-ЭГ, 998-20-ЭД, 998-20-ЭК,
998-20-ЭМ, 998-20-ЭН, 998–20-ЭС, 998-20-ЭЧ, 999-20-06,
999-20-0, 999-20-Г, 999-20-Э, 999-20-ЭГ, 999-20-ЭД,
999-20-ЭК, 999-20-ЭМ, 999-20-ЭН, 999-20-ЭС, 999-20-ЭЧ,
Т-131МС, Т-132МС, Т-31МС-1, Т-31МС-2, Т-31МС-3, Т-32МС-1,
Т-32МС-2, Т-32МС-3, 1052–65-ЭГ, 1052–65-ЭС, 1057–65-Э,
1057–65-ЭГ, 1057–65-ЭС, 1456–50-ЭД, 1456–50-ЭН, 1456–80-К3,
1456–80-ЦЗ,
Задвижки: 1010–200-КЗ, 1010–200-ЦЗ, 1010–200-Э,
1010–200-ЭД, 1010–200-ЭМ, 1010–200-ЭН, 1010–200-ЭС,
1012-150-КЗ, 1012-150-ЦЗ, 1012-150-Э, 1012–150-ЭГ,
1012–150-ЭД, 1012–150-ЭК, 1012-150-ЭМ, 1012–150-ЭМ,
1012–150-ЭН, 1012–150-ЭС, 1012–150-ЭЧ, 1012-175-КЗ,
1012-175-ЦЗ, 1012-175-Э, 1012–175-ЭГ, 1012–175-ЭД,
1012–175-ЭК, 1012-175-ЭМ, 1012-175-ЭН, 1012–175-ЭС,
1012–175-ЭЧ, 1012-225-КЗ, 1012-225-ЦЗ, 1012-225-Э,
1012-225-ЭГ, 1012–225-ЭД, 1012-225-ЭМ, 1012–225-ЭН,
1012–225-ЭС, 1013-175-КЗ, 1013-175-КЗ-01, 1013-175-ЦЗ,
1013-175-ЦЗ-01, 1013–175-Э, 1013–175-Э-01, 1013–175-ЭГ,
1013–175-ЭД, 1013–175-ЭД-01, 1013–175-ЭК, 1013–175-ЭК-01,
1013-175-ЭМ,-01, 1013-175-ЭН, 1013-175-ЭН-01, 1013–175-ЭС,
1013–175-ЭС-01, 1013–175-ЭЧ, 1013–175-ЭЧ-01, 1013-200-КЗ,
1013-200-ЦЗ, 1013–200-ЭД, 1013–200-ЭК, 1013-200-ЭМ,
1013–200-ЭМ, 1013-200-ЭН, 1013–200-ЭН, 1013–200-ЭС,
1013–200-ЭЧ, 1015-150-КЗ, 1015-150-ЦЗ, 1015–150-Э,
1015–150-ЭГ, 1015–150-ЭД, 1015-150-ЭК, 1015-150-ЭМ,
1015–150-ЭН, 1015–150-ЭС, 1015–150-ЭЧ, 1016-250-КЗ,
1016-250-М, 1016-250-ЦЗ, 1016–250-ЭГ, 1016–250-ЭД,
1016–250-ЭК, 1016-250-ЭМ, 1016–250-ЭМ, 1016–250-ЭН,
1016–250-ЭС, 1016–250-ЭЧ, 1017–250-КЗ, 1017-250-ЦЗ,
1017–250-ЭГ, 1017–250-ЭД, 1017-250-ЭК, 1017-250-ЭМ,
1017–250-ЭН, 1017–250-ЭС, 1017–250-ЭЧ, 1120-100-КЗ,-01,
1120-100-М, 1120-100-М-01, 1120-100-ЦЗ, 1120-100-ЦЗ-01,
1120-100-Э, 1120–100-Э-01, 1120–100-ЭГ, 1120–100-ЭГ-01,
1120–100-ЭД, 1120–100-ЭД-01, 1120-100-ЭК, 1120–100-ЭК,
1120-100-ЭК-01, 1120-100-ЭМ, 1120-100-ЭМ-01, 1120-100-ЭН-01,
1120–100-ЭС, 1120–100-ЭС-01, 1120–100-ЭЧ, 1120–100-ЭЧ-01,
1123-100-КЗ, 1123-100-КЗ-01, 1123-100-М, 1123-100-М-01,
1123-100-Ц3-01, 1123-100-ЦЗ, 1123–100-ЦЗ-01, 1123–100-Э,
1123–100-Э-01, 1123–100-ЭГ, 1123–100-ЭГ-01, 1123–100-ЭД,
1123–100-ЭД-01, 1123–100-ЭК, 1123–100-ЭК-01, 1123-100-ЭМ,
1123-100-ЭН, 1123-100-ЭН-01, 1123–100-ЭС, 1123–100-ЭС-01,
1123–100-ЭЧ, 1123–100-ЭЧ-01, 1126-150-КЗ, 1126–150-КЗБ,
1126-150-М, 1126–150-МБ, 1126-150-ЦЗ, 1126–150-Э,
1126–150-ЭГ, 1126–150-ЭД, 1126–150-ЭК, 1126-150-ЭМ,
1126–150-ЭМ, 1126–150-ЭН, 1156–125-КЗ, 1156-125-КЗА,
1156–125-М, 1156-125-ЦЗА, 1156–125-Э, 1156–125-ЭГ,
1156–125-ЭД, 1156-125-ЭК, 1156–125-ЭМ, 1156–125-ЭН,
1156–125-ЭС, 1156–125-ЭЧ, 1156–150-КЗ, 1156–150-М,
1156–150-ЦЗ, 1156-150-ЦЗА, 1156–150-Э, 1156–150-ЭГ,
1156–150-ЭД, 1156–150-ЭК, 1156-150-ЭМ, 1156-150-ЭН,
1156–150-ЭС, 1156–150-ЭЧ, 1511-100-КЗА,-КЗБ, 1511-100-МА,
1511-100-ЦЗА-ЦЗБ, 1511–100-ЭГ, 1511–100-ЭД, 1511–100-ЭМ,
1511-100-ЭМА,-ЭМБ, 1511–100-ЭС, 1511–100-ЭЧ, 1511-150-КЗА,
1511-150-МА,-МБ, 1511-150-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–150-ЭГ,
1511–150-ЭД, 1511-150-ЭМА,-ЭМБ, 1511–150-ЭН, 1511–150-ЭС,
1511–150-ЭЧ, 1511-200-КЗА,-КЗБ, 1511-200-МА,-МБ,
1511-200-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–200-ЭГ, 1511–200-ЭД, 1511-200-ЭМА,
1511-200-ЭНБ, 1511–200-ЭС, 1511–200-ЭЧ, 1511–250-КЗ,
1511-250-ЦЗА-ЦЗБ, 1511–250-ЭГ, 1511–250-ЭД, 1511-250-ЭМБ,
1511–250-ЭН, 1511–250-ЭС, 1511–250-ЭЧ, 1511-300-КЗА,-КЗБ,
1511-300-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–300-ЭГ, 1511–300-ЭД, 1511–300-ЭМ,
1511-300-ЭНА,-ЭНБ, 1511–300-ЭС, 1511–300-ЭЧ, 1511–80-КЗ,
1511-80-МА-МБ, 1511–80-ЦЗ, 1511–80-ЭГ, 1511–80-ЭД,
1511–80-ЭК, 1511-80-ЭМБ, 1511–80-ЭН, 1511–80-ЭС,
1511–80-ЭЧ, 1533–350-КЗ, 1533–350-ЦЗ, 1533–350-ЭД,
1533–350-ЭМ, 1533–350-ЭН, 1533–350-ЭС, 1533–350-ЭЧ,
2с-25–1Н, 2с-25-2, 2с-25-6ЭГ, 2с-25-6ЭД, 2с-25-6ЭК,
2с-25-6ЭМ, 2с-25-6ЭН, 2с-26-1, 2с-26–2Н, 2с-26–3Н,
2с-26–4 Н, 2с-26–5 Н, 2с-26-6, 2с-27-1, 2с-27-1ЭГ,
2с-27-1ЭД, 2с-27-1ЭК, 2с-27-1ЭМ, 2с-27-1ЭН, 2с-27-1ЭС,
2с-27-1ЭЧ, 2с-27–2Н, 2с-27-2Э, 2с-27-2ЭГ, 2с-27-2ЭД,
2с-27-2ЭК, 2с-27-2ЭМ, 2с-27-2ЭН, 2с-27-2ЭС, 2с-27-2ЭЧ,
2с-27-3Э, 2с-27-3ЭГ, 2с-27-3ЭД, 2с-27-3ЭК, 2с-27-3ЭМ,
2с-27-3ЭН, 2с-27-3ЭС, 2с-27-3ЭЧ, 2с-27–4 Н, 2с-27-4Э,
2с-27-4ЭГ, 2с-27-4ЭД, 2с-27-4ЭК, 2с-27-4ЭМ, 2с-27-4ЭН,
2с-27-4ЭС, 2с-27-4ЭЧ, 2с-27–5 Н, 2с-27-6, 2с-28-1,
2с-28–2Н, 2с-28–4Н, 2с-28–5 Н, 2с-28-6, 2с-29-1, 2с-29–3Н,
2с-29–4Н, 2с-29–5 Н, 2с-29-6, 2с-30-1, 2с-30-1ЭГ,
2с-30-1-ЭД, 2с-30-1-ЭК, 2с-30-1-ЭМ, 2с-30-1-ЭН, 2с-30-1ЭЧ,
2с-30-1-ЭЧ, 2с-30-2, 2с-30-2ЭГ, 2с-30-2ЭД, 2с-30-2ЭК,
2с-30-2ЭМ, 2с-30-2ЭН, 2с-30-2ЭЧ, 2с-31-1, 2с-31-1Э,
2с-31-1ЭД, 2с-31-1ЭМ, 2с-31-1ЭН, 2с-31-1ЭС, 2с-31-2,
2с-31-2Э, 2с-31-2ЭМ, 2с-31-2ЭН, 2с-31-2ЭС, 2с-33-1ЭГ,
2с-33-1ЭД, 2с-33-1ЭК, 2с-33-1ЭМ, 2с-33-1ЭН, 2с-33-1ЭЧ,
2с-33-2ЭД, 2с-33-2ЭК, 2с-33-2ЭМ, 2с-33-2ЭН, 2с-33-2ЭЧ,
2с-34-1Э, 2с-34-1ЭД, 2с-34-1ЭМ, 2с-34-1ЭН, 2с-34-1ЭС,
2с-34-1ЭЧ, 2с-34-2Э, 2с-34-2ЭС, 2с-350-10-450-КЗ,
2с-350-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-350-10-450-ЭД, 2с-350-10-450-ЭМ,
2с-350-10-450-ЭН, 2с-350-10-450-ЭС, 2с-35-2,
2с-400-10-450-КЗ, 2с-400-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-400-10-450-ЭД,
2с-400-10-450-ЭМ, 2с-400-10-450-ЭН, 2с-400-10-450-ЭС,
2с-450-10-450-КЗ, 2с-450-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-450-10-450-ЭД,
2с-450-10-450-ЭМ, 2с-450-10-450-ЭН, 2с-450-10-450-ЭС,
2с-Э-1, 2С-Э-2, 2с-Э-4, 2с-Э-5, 2с-ЭГ-1, 2с-ЭГ-2, 2с-ЭГ-3,
2с-ЭГ-4, 2с-ЭГ-5 Н, 2с-ЭГ-5, 2с-ЭГ-6, 2с-ЭД-1, 2с-ЭД-2,
2с-ЭД-3, 2с-ЭД-4, 2с-ЭД-5 Н, 2с-ЭД-5, 2с-ЭД-6, 2с-ЭК-1,
2с-ЭК-2, 2с-ЭК-3, 2с-ЭК-4, 2с-ЭК-5 Н, 2с-ЭК-5, 2с-ЭК-6,
2с-ЭМ-1, 2с-ЭМ-2, 2с-ЭМ-3, 2с-ЭМ-4, 2с-ЭМ-5 Н, 2с-ЭМ-5,
2с-ЭМ-6, 2с-ЭН-1, 2с-ЭН-2, 2с-ЭН-3, 2с-ЭН-4, 2с-ЭН-5 Н,
2с-ЭН-5, 2с-ЭН-6, 2с-ЭС-1, 2с-ЭС-2, 2с-ЭС-3, 2с-ЭС-4,
2с-ЭС-5, 2с-ЭЧ-1, 2с-ЭЧ-2, 2с-ЭЧ-3, 2с-ЭЧ-4, 2с-ЭЧ-5,
511–100-ЭН, 850–350-КЗ, 850–350-ЦЗ, 850–350-Э, 850–350-ЭГ,
850–350-ЭД, 850–350-ЭК, 850–350-ЭМ, 850–350-ЭН, 850–350-ЭС,
850–350-ЭЧ, 850–400-КЗ, 850–400-ЦЗ, 850–400-Э, 850–400-ЭГ,
850–400-ЭД, 850–400-ЭК, 850–400-ЭМ, 850–400-ЭН, 850–400-ЭС,
850–450-КЗ, 850–450-ЦЗ, 850–450-Э, 850–450-ЭГ, 850–450-ЭД,
850–450-ЭК, 850–450-ЭМ, 850–450-ЭН, 850–450-ЭС, 850–450-ЭЧ,
880–150-КЗ, 880–150-ЦЗ, 880-150-ЦЗП, 880–150-Э, 880–150-ЭГ,
880–150-ЭД, 880–150-ЭК, 880–150-ЭМ, 880-150-ЭМП, 880–150-ЭН,
880-150-ЭНП, 880–150-ЭС, 880–150-ЭЧ, 880–200-КЗ,
880-200-КЗП, 880–200-ЦЗ, 880-200-ЦЗП, 880–200-Э, 880–200-ЭГ,
880–200-ЭД, 880–200-ЭМ, 880–200-ЭН, 880-200-ЭНП, 880–200-ЭС,
880-250-КЗП, 880-250-ЦЗП, 880–250-ЭГ, 880–250-ЭД,
880-250-ЭМП, 880-250-ЭП, 880–250-ЭС, 880–300-КЗ, 880–300-ЦЗ,
880-300-ЭА, 880–300-ЭГ, 880–300-ЭД, 880–300-ЭС, 880–325-ЭД,
880–325-ЭЛХМ, 880–325-ЭМ, 880–325-ЭТ, 880–350-ЭД,
880–350-ЭЛ, 880–350-ЭМ, 880–350-ЭТ, 880–400-ЭА, 880–400-ЭД,
880–400-ЭМ, 880–400-ЭТ, 881–100-КЗ, 881-100-КЗП, 881–100-ЦЗ,
881–100-Э, 881–100-ЭГ, 881–100-ЭД, 881–100-ЭК, 881–100-ЭМ,
881–100-ЭН, 881-100-ЭНП, 881–100-ЭС, 881–100-ЭЧ, 881–150-КЗ,
881-150-КЗП, 881–150-ЦЗ, 881-150-ЦЗП, 881–150-Э, 881–150-ЭГ,
881–150-ЭД, 881–150-ЭМ, 881-150-ЭМП, 881–150-ЭН,
881-150-ЭНП, 881–150-ЭС, 881–200-КЗ, 881-200-ЦЗП,
881–200-ЭГ, 881–200-ЭД, 881-200-ЭМП, 881-200-ЭП, 881–200-ЭС,
881–250-Э, 881–250-ЭД, 881–250-ЭМ, 881–250-ЭТ, 882-250-КЗП,
882-250-ЦЗП,-ЦЗШ, 882–250-ЭГ, 882–250-ЭД, 882-250-ЭМП,
882–250-ЭН, 882-250-ЭНП,-ЭНШ, 882–250-ЭС, 882–300-КЗ,
882-300-КЗП, 882–300-ЦЗ, 882–300-ЭГ, 882–300-ЭД, 882–300-ЭМ,
882-300-ЭНП, 882–300-ЭС, 883–175-КЗ-01, 883–175-КЗ-02,
883–175-ЦЗ-01, 883–175-ЦЗ-02, 883–175-Э-01, 883–175-Э-02,
883–175-ЭД-01, 883–175-ЭД-02, 883–175-ЭМ-01, 883–175-ЭМ-02,
883–175-ЭН-01, 883–175-ЭН-02, 883–175-ЭС-01, 883–175-ЭС-02,
883–175-ЭЧ-01, 883–175-ЭЧ-02, 883–200-КЗ, 883–200-ЦЗ,
883–200-Э, 883–200-ЭД, 883–200-ЭМ, 883–200-ЭН, 883–200-ЭС,
883-250-КЗП-01,-02, 883-250-ЦЗП-01,-02, 883–250-ЭГ,
883–250-ЭГ-01, 883–250-ЭГ-02, 883–250-ЭД, 883–250-ЭД-01,
883–250-ЭД-02, 883-250-ЭМП-01,-02, 883-250-ЭП-01,
883–250-ЭС, 883–250-ЭС-01, 883–250-ЭС-02, 883–300-КЗ,
883–300-ЦЗ, 883-300-ЦЗП, 883–300-ЭГ, 883–300-ЭД,
883-300-ЭМП, 883-300-ЭП, 883–300-ЭС, 884–200-Г, 884–200-КЗ,
884-200-ЦЗП, 884–200-ЭГ, 884–200-ЭД, 884–200-ЭМ,
884-200-ЭНП, 884–200-ЭС, 884–250-Г, 884–250-КЗ, 884–250-ЦЗ,
884–250-ЭГ, 884–250-ЭД, 884–250-ЭМ, 884-250-ЭНП, 884–250-ЭС,
884–325-КЗ, 884–325-ЦЗ, 884–325-Э, 884–325-ЭГ, 884–325-ЭД,
884–325-ЭМ, 884–325-ЭС, 885-225-КЗП, 885-225-ЦЗП,
885–225-ЭГ, 885–225-ЭД, 885-225-ЭМП, 885-225-ЭНП,
885–225-ЭС, 887-100-ЦЗП, 887–150-КЗ, 887–150-ЦЗ, 887–150-Э,
887–150-ЭД, 887–150-ЭМ, 887–150-ЭН, 887–150-ЭС, 887–150-ЭЧ,
870-200-ЭМ,
Затворы: 12с-1, 12с-1-1, 12с-2-5, 12с-3-1, 12с-3-2, 12с-3-3,
12с-3-4, 12с-4-2Э, 12с-4-3Э, 12с-4-4Э, 12с-5-5, 12с-8-10,
12с-8-11, 12с-8-12, 12с-8-13, 12с-8-14, 12с-8-15, 12с-8-4,
12с-8-5, 12с-8-6, 12с-8-7, 12с-8-8, 12с-8-9,
Электроприводы: 1280-КЭ-0, 768-Э-0а, 768-Э-0а-01,
792-Э-06-01, 792-Э-0-II, 792-Э-0А, 792-Э-0А-01, 792-Э-0а-04,
792-Э-0б, 792-ЭР-0А, 792-ЭР-0А-01, 792-ЭР-0АI, 793-Э-0,
793-Э-0а-04, 793-ЭР-0, 793-ЭР-0-02, 793-ЭР-0-04, 793-ЭР-0A,
793-ЭР-0A-I, 793-ЭР-0A-II, 793-ЭР-0I, 793-ЭР-0I-01,
793-ЭР-0-II, 794-Э-0а, 794-ЭР-0а, 794-ЭР-0аI, 795-Э-0,
795-Э-0-01, 795-Э-0-II, 795-Э-0-II-01, 795-Э-0-V, 795-ЭР-0,
795-ЭР-0-I, 795-ЭР-0-V, 797-Э-0, 797-ЭР-0, 798-Э-0,
798-Э-0-01, 821-КЭ-0а, 821-Э-0а, 821-ЭР-0б, 822-КЭ-0,
822-КЭР-0, 822-Э-0а, 822-Э-0а-01, 822-Э-0б, 822-Э-0б-01,
822-ЭР-0а, 822-ЭР-0а-01, 823-Э-0, 823-ЭР-0-03, 823-ЭР-0III,
823-ЭР-0-IIа, 823-ЭР-0-IV, 824-КЭ-0-01, 824-КЭ-0-02,
824-КЭ-0-03, 824-КЭ-0-04, 824-Э-0а, 824-ЭР-0а, 824-ЭР-0аI,
825-КЭ-0, 825-КЭР-0, 825-Э-0, 825-Э-0-01, 825-Э-0-I,
854-Э-0, 876-КЭР-0, 876-Э-0, 876-Э-0-02, 876-Э-0-04,
876-Э-0-07, 876-Э-0-08, 882-КЭ-0, 882-КЭ-0-01, 882-КЭ-0-02,
885-КЭ-0
Капельницы при запое, данный метод широко используемый метод, который используется для облегчения симптомов алкогольной зависимости и восстановления организма. Тем не менее, порой данная процедура может быть неэффективной. Если вы столкнулись с такой ситуацией, важно понимать, что делать дальше. Первым делом является обращение к наркологу в домашних условиях срочно. Врач проведет оценку состояния больного, выяснит причины, по которым капельница не дала ожидаемого результата. Признаки запоя могут варьироваться, поэтому важно определить их источники. Иногда может потребоваться комплексном лечении запоя более комплексными методами. нарколог на дом срочно Лечение на дому запоя также может предусматривать применение препаратов для капельницы, которые лучше подходят для конкретного пациента. Кроме того, необходимо учитывать реабилитационные меры и восстановление после алкогольной интоксикации, которые могут предполагают поддержку и консультации психологов. Если процедура не эффективна, имеет смысл обратиться к дополнительным рекомендациям по преодолению запоя, такие как коррекция питания, использование витаминов и минералов. Не следует забывать, что борьба с алкогольной зависимостью требует основательного подхода и, возможно, длительной медицинской помощи при алкоголизме. Не откладывайте визит к специалисту — экстренная помощь нарколога может стать ключевым фактором в борьбе с запоем.
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительные VR проекты
подключить интернет тарифы санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Чтобы быстро попасть на кракен маркетплейссайт, используйте проверенную ссылку. Рабочее зеркало доступно для входа в маркетплейс, а инструкция поможет без лишних шагов.
купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста .
При проблемах с доступом поможет зеркало http://www.krakr.cc, оно ведёт напрямую на сайт.
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов спб купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов спб .
KRAKEN вход в личный кабинет всегда доступен. Рабочее зеркало кракен тор помогает пройти авторизацию.
Капельницы для снятия запоя – это незаменимый метод при пьянстве. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно может оказать экстренную помощь‚ выполняя дезинтоксикацию и реабилитацию после запоя. Проявления алкоголизма‚ такие как тошнота и рвота‚ головная боль и слабость‚ требуют оперативного реагирования. Терапия при запое включает капельнички‚ которые помогают устранить абстиненцию и вывести токсины из организма. Обращение к наркологу важна для установления последующей терапии: лечение в стационаре или амбулаторная помощь. Клиника наркологии предлагает экспертное лечение‚ чтобы исключить возможность рецидива и заботиться о здоровье пациента.
домашний интернет подключить санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
подключить интернет в санкт-петербурге в квартире
Выездной нарколог в владимире предоставляет профессиональную помощь тем, кто страдает от наркомании и алкогольной зависимостью. Преодоление зависимости требует индивидуального подхода, и вызов нарколога на дом – это оптимальный вариант для пациентов. Центр лечения зависимостей в владимире предлагает конфиденциальное лечение и поддержку нарколога. Реабилитация на дому обеспечивает комфортное прохождение психотерапии при зависимости в домашней обстановке. Медицинская помощь на дому включает в себя как медицинское, так и психологическую поддержку. Предотвращение зависимости также имеет огромное значение в профилактике алкоголизма и наркомании. Поддержка алкоголиков и их родных – это работа квалифицированных специалистов, которые готовы оказать помощь в сложной ситуации. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir016.ru
лучшие сервисы нейросетей
домашний интернет тарифы
inernetvkvartiru-spb004.ru
провайдеры домашнего интернета санкт-петербург
Запой — это состояние‚ когда человек не может остановиться пить алкоголь‚ что приводит к серьезным последствиям для здоровья. Обращение к наркологу в Туле — это первый шаг к выздоровлению. Капельницы играют важную роль в детоксикации организма‚ помогая снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить водно-электролитный баланс. вызов нарколога тула Клиники наркологии предоставляют широкий спектр методов для лечения алкоголизма‚ включая уколы для детоксикации. Экстренная помощь при запое включает в себя не только капельницы‚ но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах его восстановления. Реабилитация после запоя важна для предотвращения рецидивов. Качественная медицинская помощь должна быть профессиональной и предоставляться своевременно‚ чтобы гарантировать восстановление организма и минимизировать риски для здоровья. Тула предлагает широкий спектр наркологических услуг‚ которые помогут справиться с алкогольной зависимостью.
https://epigraph.info/?utm_candidate=82315364371&yabizcmpgn=45718466&start=75
лучшие нейросети по описанию фотографий
https://www.vazbook.ru/rubric
Для обхода ограничений используйте кракен даркнет
. Вход по ссылке безопасен и прост.
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – ресурс для вдохновения
Наркологическая служба Тула предлагает разнообразные услуги для лечения зависимостей. В этом городе работают специализированные реабилитационные центры‚ где предоставляется возможность анонимного лечения от наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Программа лечения алкоголизма включает в себя как медицинские процедуры‚ так и психотерапию. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula012.ru Психологическая помощь Тула также играет важную роль в процессе выздоровления. Обратитесь к наркологу позволяет определить уникальные особенности пациента и составить персонализированный план лечения. Профилактика зависимостей и поддержка родственников зависимых – неотъемлемая часть работы наркологической клиники. Реабилитация зависимых включает как терапевтические‚ так и социальные аспекты. Услуги наркологической службы направлены на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
KRAKEN сайт поддерживает актуальные варианты подключения. Вход возможен на кракен личный кабинет за пару секунд.
Выездной нарколог – это важный шаг в лечении зависимостей . Выездной нарколог предоставляет анонимное лечение и профессиональные консультации‚ что крайне важно для людей‚ ценящих комфорт и безопасность. Помощь в лечении алкогольной зависимости и наркотической зависимости могут проводиться в домашней обстановке‚ что способствует лучшему восприятию терапии . site;com Лечение алкоголизма включает детоксикацию на дому и программы реабилитации ‚ которые учитывают индивидуальные потребности пациента. Поддержка семьи и психологическая поддержка играют значительную роль в процессе выздоровления. Нарколог на дому обеспечит индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту ‚ что повышает вероятность успешного выздоровления.
Compra Viagra en Toledo
Mejor precio en farmacias en Zaragoza
В любой ситуации поможет ссылка http://krakr.cc/, обеспечивая стабильный вход.
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
not working
_________________
https://reelriches.shop
Если вы ищете, как зайти в
, используйте проверенные зеркала. Ссылка безопасна и ведёт на нужный ресурс.
Майстер-клас із африканського танцю в Бостоні став незабутнім досвідом. Інструктори з великою любов’ю до своєї культури навчали нас рухам, які мають глибокий символізм. Це була не просто фізична активність, а справжня подорож у минуле, де кожен крок розповідав історію поколінь. Учасники були дуже привітними, а атмосфера майстер-класу — теплою й надихаючою. Наприкінці заняття всі разом виконали невеликий танцювальний перформанс, і це було щось неймовірне. Хочете відчути те саме? Дізнайтеся більше про майбутні події на сайті.
Wow, this piece of writing is good, my younger sister is analyzing these
kinds of things, therefore I am going to let know her.
легально купить диплом о высшем образовании легально купить диплом о высшем образовании .
Приобрести диплом любого университета мы поможем. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа Самара – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-samara
накрутка подписчиков тг накрутка подписчиков тг
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительные партнёры
Для авторизации используйте кракен личный кабинет. Актуальная ссылка безопасна и проверена временем.
kupit-drova-v-arhangelske-365.ru .
отзывы 1win 1win12013.ru
KRAKEN ссылка через TOR открывает доступ к кракен зеркало даже при блокировках. Вход занимает минимум усилий.
http://www.barius.ru/fonoteka/
Рабочее зеркало площадки доступно по адресу https://www.krakr.cc/, оно официальное.
Asking questions are truly nice thing if you are not understanding anything completely,
except this paragraph offers pleasant understanding yet.
Good day! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest
writing a blog article or vice-versa? My website discusses a lot of the
same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other.
If you’re interested feel free to send me an e-mail.
I look forward to hearing from you! Fantastic blog by
the way!
Для обхода ограничений используйте кракен личный кабинет
. Вход по ссылке безопасен и прост.
Can you tell us more about this? I’d care to find out some additional information.
Cleobetra Casino
лучшие нейросети для юристов
купить диплом техникума ссср купить диплом техникума ссср .
https://entertainmentgroove.com/music/clp-685/
https://tourpohod.3dn.ru/
интернет по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
проверить провайдеров по адресу санкт-петербург
Эффективная капельница для снятия запоя на дому в владимире Алкогольная зависимость — это сложная проблема, которая требует профессионального вмешательства. Круглосуточный нарколог в владимире предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Такой подход позволяет быстро облегчить состояние и помочь в восстановлении после запоя.Важно не только облегчить симптомы, но и предоставить полноценную медицинскую помощь при запое. Капельница способствует быстрому снятию похмелья, улучшает общее самочувствие и предотвращает возможные осложнения. Вызов капельницы на дом — это комфортный вариант для тех, кто предпочитает избегать госпитализации и хочет получать помощь в привычной обстановке.Доступность нарколога 24/7 обеспечивает возможность детоксикации в любое время. Помните, что лечение запоя на дому включает в себя как физическое, так и психологическое восстановление. Процесс реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости является длительным и требует всестороннего подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Если вы или ваши родные испытываете трудности с алкогольной зависимостью, не стоит откладывать обращение за помощью. Услуги нарколога в владимире доступны круглосуточно, и каждый может рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку.
бк мостбет скачать бк мостбет скачать
Откройте интересные предложения в в нашем ресурсе. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент для достижения целей по https://xn--krken17-bn4c.com
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google,
and found that it’s really informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels.
I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future.
A lot of people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!
Алкогольная зависимость серьезная проблема , требующая квалифицированной помощи. В владимире действуют специализированные центры по помощи алкоголикам, где предоставляется экстренный вывод из запоя и лечение алкоголизма . При алкогольном отравлении необходимо быстро определить симптомы и обратиться к врачам. Профессиональные наркологи в владимире проводят консультации , гарантируя безопасное восстановление после запоя и лечение похмелья . Процесс реабилитации от алкоголизма включает программы реабилитации для зависимых , поддерживая не только пациентов, но и оказывая помощь родственникам алкоголиков. Профилактика заболеваний, связанных с алкоголем также играет важную роль в предотвращении повторных случаев зависимости.
С помощью
легко обойти блокировки. Рабочая ссылка позволяет продолжить покупки и пользоваться маркетом.
Kitty – це команда, яка вміє вражати. На фестивалі Trance Illusion я побачив, як музика, світло та візуальні ефекти можуть створювати справжню магію. Особливо мене захопила робота PJ Alice, яка створює такі ефекти, що ти буквально занурюєшся у виступ. Їхній підхід до кожного треку – це справжнє мистецтво. Якщо хочете більше дізнатися про цю команду, перегляньте їхній сайт.
провайдер по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
интернет тарифы санкт-петербург
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad and
tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation.
My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views.
I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Thank you for some other fantastic post. The place else could anyone get that type of info in such a perfect way of writing? I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the search for such info.
Cleobetra Casino Online
kupit-kub-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
ссылки на кракен позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. кракен тор необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. кракен зеркало тор должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
Получилось, Спасибо !
Для тех, кто хочет стабильности, есть кракен личный кабинет официальный сайт. Ссылки и зеркала помогут войти в систему в любое время.
домашний интернет тарифы санкт-петербург
inernetvkvartiru-spb005.ru
какие провайдеры на адресе в санкт-петербурге
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – успешные кейсы
Если основной ресурс заблокирован, поможет https://krakr.cc/, официальный адрес.
на этом сайте казино водка бет vodkabet
kupit-drova-v-novosibirske-365.ru .
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
дренажные работы на участке .
Запой – серьезная проблема‚ которая требует неотложной помощи нарколога. В владимире доступны круглосуточные услуги клиники наркологии‚ где вы можете получить необходимую медицинскую помощь. Детоксикационные капельницы помогут быстрому восстановлению организма после алкогольного запоя. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает как физическую‚ так и психологическую поддержку‚ но и психологическую помощь. Обращение к наркологу обеспечит индивидуальное внимание к каждому пациенту. Поддержка семьи играет важную роль в процессе восстановления. Не стоит откладывать‚ обратитесь за помощью! помощь нарколога владимир
лучшие нейросети для истории
wetten dass gewinner heute
Look into my web page; Neue Wettanbieter Ohne Oasis
I blog frequently and I really appreciate your information. Your article has truly peaked my interest.
I’m going to bookmark your website and keep checking
for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your RSS feed as well.
купить подписчиков телеграм канал живых без отписок купить подписчиков телеграм канал живых без отписок
Терапия запойного состояния — это необходимый шаг в борьбе с алкоголизмом. В владимире доступно множество методов, включая лечение с помощью медикаментов. Признаки запоя могут различаться от беспокойства до болей в теле, что делает выход из запоя крайне необходимым. Для детоксикации организма применяются различные лекарственные средства для помощи при запое, такие как лекарства группы бензодиазепинов, которые помогают снять симптомы отмены. Антидепрессанты также могут быть назначены, чтобы поддержать эмоциональное состояние больного. Витамины при запое играют важную роль в восстановлении организма. Кодирование от алкоголя может стать дополнительным шагом в процессе борьбы с зависимостью. Наркологическая помощь включает не только медицинскую терапию, но и психотерапевтическую помощь. Реабилитация алкоголиков в владимире часто включает группы поддержки и программы восстановления, которые помогают пациентам возвращаться к нормальной жизни без алкоголя. Поддержка семьи при алкоголизме также имеет высокую важность. Она может помочь пациенту в периоде реабилитации после запоя, повысив шансы на успешное лечение зависимостей. Медицинские процедуры для detoxa являются важной частью комплексного подхода к лечению алкоголизма и обеспечивают безопасный выход из запойного состояния.
Новости Украины и мира https://mostmedia.com.ua политика, экономика, культура, спорт и общество. Свежие события, аналитика и репортажи. Будьте в курсе главных новостей в режиме онлайн 24/7.
Новости Украины https://status.net.ua объективная информация о событиях страны. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Читайте актуальные материалы каждый день.
Новостной портал https://mediateam.com.ua всё самое важное сегодня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт и шоу-бизнес. Лента новостей, репортажи и аналитические материалы каждый день.
Необходимо кодирование? закодироваться от алкоголя в Хабаровске современные методы, конфиденциальность и поддержка специалистов. Помогаем избавиться от зависимости и вернуться к здоровой жизни.
KRAKEN сайт поддерживает актуальные варианты подключения. Вход возможен на кракен вход за пару секунд.
купить диплом старого образца купить диплом старого образца .
Обращение к наркологу анонимно — необходимый шаг для тех, кто нуждается в помощи при лечении зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir010.ru вы можете получить анонимную консультацию и поискать наркологической помощью. Это особенно актуально для тех, кто испытывает проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками. Профессиональная помощь нарколога включают диагностику зависимостей и лечение при наркотической зависимости. Анонимный нарколог может посетить вас на дому, что гарантирует приватность и удобство. Выездные специалисты предоставляют поддержку психолога и проводят процессы реабилитации для зависимых. Виртуальная встреча с врачом позволяет быстро получить необходимые рекомендации. Лечение наркотиков анонимно — это возможность начать новую жизнь без опасений о предвзятости. Не упустите шанс изменить свою судьбу с помощью анонимных услуг здоровья!
Hi every one, here every one is sharing such knowledge, so it’s fastidious to read this website, and I used to visit this web site every day.
Cleobetra
куб дров береза цена .
drenazhnye-raboty-spb.ru .
KRAKEN ссылка TOR помогает подключиться к кракен магазин даже при ограничениях.
Rainbet Casino
При проблемах с доступом поможет зеркало http://www.krakr.cc, оно ведёт напрямую на сайт.
mostbet kg скачать mostbet kg скачать
Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных на территории всей Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат 11 классов с твердой обложкой
Sou louco pela vibe de AFun Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um desfile de cores. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um espetaculo de luzes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que pulsam como batidas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela da festa, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo de confete. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como serpentinas, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, AFun Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma folia total para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual de purpurina, adiciona um toque de purpurina ao cassino.
afun . com|
Sou louco pela energia de BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de responsa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, BRCasino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
br77.com|
где купить дрова чурками .
С помощью кракен маркетплейс можно легко получить рабочий вход даже на телефоне.
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von Trickz Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zauberstab funkelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und verzaubernd, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist Trickz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zirkus der Magie strahlt fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Zauberstab, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
trickz casino|
J’adore la chaleur de VBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui explose comme un geyser. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un volcan, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient brulants. Dans l’ensemble, VBet Casino offre une experience de casino ardente pour les volcanologues du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
vbet bonuscode|
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru/ – решения для частного сектора
Katarina зробили зі свого виступу справжнє мистецьке дійство, яке не залишило байдужим жодного глядача. Їхнє світлове шоу, розроблене PJ Mia, було настільки гармонійно вплетене у музичний сет, що здавалося, ніби музика й візуальні ефекти були створені разом. Це був один із найкращих моментів усього фестивалю.
накрутить подписчиков в тг бесплатно быстро накрутить подписчиков в тг бесплатно быстро
Если у вас появились проблемы с зависимостямивызов нарколога становится необходимым шагом. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru предлагает профессиональную помощь в лечении зависимостей. Симптомы зависимости могут быть разнообразными, и важно их распознать. Консультация врача поможет определить нужное лечение алкоголизма или наркотической зависимости. Центр реабилитации предлагает конфиденциальную помощь и поддержку для близких. Медицинская помощь при наркомании охватывает процесс восстановления после зависимости, что является неотъемлемой частью процесса возвращения к здоровой жизни. Не откладывайте обращение к специалисту, ведь это может спасти жизнь.
нажмите здесь Трипскан топ
можно купить аттестат можно купить аттестат .
https://www.te-in.ru/osnovnyie-trebovaniya-dlya-ustanovki-dgu-v-pomeshhenii.html/
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this site on a regular basis, this
web site is truly pleasant and the people are truly sharing nice thoughts.
I’m gone to say to my little brother, that he should also go to see this web site on regular basis to take updated from most up-to-date reports.
Cleobetra Casino
tank 300 салон http://tank-3001.ru
Чтобы обойти блокировки, используйте
. Ссылка подходит как для телефона, так и для компьютера.
Можно ли получить бесплатный вывод из запоя в владимире? Вопрос о лечении алкоголизма и помощи зависимым стоит остро в нашем обществе. Множество людей сталкивается с запоем и ищет способы избавиться от этого состояния. В такой ситуации услуги нарколога на дому‚ доступные круглосуточно‚ могут стать настоящим спасением. нарколог на дом круглосуточно Наркологическая помощь‚ включая бесплатную консультацию нарколога‚ может быть доступна для тех‚ кто нуждается в экстренной помощи при запое. В владимире нередко предлагают услуги по выводу из запоя‚ а также лечение в домашних условиях‚ что делает процесс более комфортным и менее стрессовым для пациента. Круглосуточный нарколог предоставит медицинскую помощь на дому‚ что особенно удобно для тех‚ кто не может или не хочет идти в стационар. Также доступно анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность пациента. Следует помнить‚ что поддержка зависимых является важным аспектом в процессе лечения. Реабилитация от алкоголя требует времени и усилий‚ но с помощью профессионалов можно достичь положительных результатов. Таким образом‚ если вы или ваши близкие ищете бесплатный вывод из запоя в владимире‚ обращение к услугам нарколога на дому может стать первым шагом к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании .
В владимире доступна помощь от алкоголизма в клиниках‚ предлагающих детоксикацию и профессиональную помощь. Программы лечения включают кодирование и медицинское сопровождение при алкоголизме. Необходимо также получить психологическую поддержку и участвовать в группах поддержки, таких как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Процесс восстановления после запоя требует комплексного подхода: консультации нарколога помогут создать персонализированный план. Важно помнить о профилактике рецидива и придерживайтесь рекомендаций по отказу от алкоголя. Дополнительную информацию можно найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru;
Пользователи рекомендуют https://www.krakr.cc как основной адрес для входа в маркет.
Чтобы не терять доступ, сохраняйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Рабочее зеркало кракен маркет открывает маркет и личный кабинет.
What i don’t realize is if truth be told how you’re no longer actually a lot more well-favored than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You understand thus significantly relating to this matter, produced me in my opinion believe it from so many various angles. Its like men and women are not fascinated unless it’s something to do with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs outstanding. At all times care for it up!
Also visit my blog post; https://dubaiembroidery.ae/
провайдеры интернета в санкт-петербурге по адресу проверить
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
провайдеры по адресу дома
Adoro o frenesi de AFun Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que gira como um carrossel enlouquecido. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um malabarista, com uma ajuda que brilha como purpurina. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, AFun Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma folia total para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma coreografia, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
site de aposta afun|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. Na real, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin logo|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BRCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Em resumo, BRCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os folioes do cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
putaria br77|
KRAKEN сайт поддерживает актуальные варианты подключения. Вход возможен на кракен даркнет за пару секунд.
Ich finde absolut magisch Trickz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer verhexten Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein magischer Zirkus voller Action, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Illusion verblufft. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist Trickz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zirkus der Magie strahlt fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
casino trickz|
Je suis accro a VBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino digne d’un cratere. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une etincelle, avec une aide qui jaillit comme une flamme. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une coulee de lave, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient brulants. En somme, VBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style volcanique, facilite une experience de casino eruptive.
appli vbet|
провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
провайдеры по адресу
inernetvkvartiru-spb006.ru
провайдер по адресу
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/prodazha-dizel-generatorov.html/
лучшие агрегаторы нейросетей
KRAKEN вход всегда доступен через кракен зеркало. Актуальное зеркало помогает авторизоваться и продолжить пользоваться сервисом.
https://www.te-in.ru/osnovnyie-trebovaniya-dlya-ustanovki-dgu-v-pomeshhenii.html/
https://sochistroygroup.ru/ – услуги под ключ
Сохраняйте https://krakr.cc, чтобы не потерять доступ к площадке.
С помощью кракен сайт легко продолжить покупки.
Экстренная наркологическая помощь в владимире: капельница для избавления от запоя Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезный недуг, который нуждается в квалифицированной помощи. Нарколог на дом предоставляет услуги, такие как капельница от запоя, способствующая восстановлению организма после продолжительного употребления алкоголя. К основным симптомам алкогольной зависимости относятся: дрожь, повышенная потливость и чувство тревоги. Медицинская помощь при запое включает дезинтоксикацию организма и восстановление. Консультация нарколога поможет определить подходящий план лечения алкоголизма. Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме, направленная на выведение из запойного состояния, может предотвратить серьезные последствия. Профилактика запойных состояний и психотерапевтические методы для зависимых — ключевые элементы успешного лечения зависимостей, обеспечивающие устойчивые результаты. Наркологические услуги в владимире предоставляются круглосуточно, что позволяет вам получить помощь в любое время суток. Не затягивайте с лечением, свяжитесь со специалистами прямо сейчас!
I do not know if it’s just me or if everybody else experiencing
issues with your blog. It seems like some of the written text in your posts are running off the screen. Can someone else please provide
feedback and let me know if this is happening to them
too? This might be a issue with my browser because I’ve had
this happen before. Kudos
1ви 1win12012.ru
Excellent pieces. Keep posting such kind of information on your
site. Im really impressed by your blog.
Hey there, You have done an excellent job. I will definitely digg it and
for my part suggest to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
как использовать бонусы в 1win https://1win12011.ru/
Чтобы обойти блокировки, используйте кракен вход. Ссылка подходит как для телефона, так и для компьютера.
Если вы хотите найти, где получить капельницу анонимно в владимире, обратите внимание на сайтом vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir011.ru. Здесь предоставляются услуги капельницы для здоровья, которые способствую вашему после болезни. Клиника в владимире предлагает безопасность процедур и приватность клиентов, предлагая качественную медицинскую помощь. Анонимное лечение – это способ заботиться о своем здоровье без посторонних глаз. Не стоит откладывать о себе, воспользуйтесь медицинскими процедурами уже сегодня!
Запой – это явление, при котором человек продолжительное время употребляет спиртные напитки, что ведет к серьезным последствиям для здоровья и психического состояния. В владимире предлагаются услуги наркологов с выездом на дом в анонимном режиме, что дает возможность пациентам получить необходимую помощь без стыда и неловкости. Симптомы запоя это сильную тягу к алкоголю, раздражительность и физическое недомогание.Последствия чрезмерного употребления алкоголя может быть тяжелыми: от болезней печени до психических заболеваний. Лечение алкоголизма включает очистку организма и психотерапию. Необходимо учитывать поддержку близких и использовать реабилитационные программы, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы. Нарколог на дом анонимно владимир Восстановление и процесс восстановления могут занять время, но преодолеть зависимость самостоятельно вполне реально. Консультация нарколога поможет создать персонализированный план терапии и поддерживать стремление на пути к жизни без алкоголя.
kupit-drova-v-novosibirske-365.ru .
скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно
вывод из запоя с выездом кодирование от алкоголизма в Томске адреса
Запой — это состояние‚ когда индивид не в состоянии прекратить употребление алкоголя‚ что ведет к серьезным последствиям для его здоровья. Обращение к наркологу в владимире — первоначальный этап на пути к выздоровлению. Капельница помогает при детоксикации организма‚ помогая снять симптомы похмелья и восстановить водно-электролитный баланс. вызов нарколога владимир Наркологические клиники предоставляют различные методы лечения алкоголизма‚ включая уколы для детоксикации. Экстренная помощь при запое включает в себя не только капельницы‚ но и комплексную поддержку пациента на всех этапах его восстановления. Реабилитация после запоя крайне важен для снижения риска рецидивов. Медицинская помощь должна быть профессиональной и своевременной‚ чтобы гарантировать восстановление организма и минимизировать риски для здоровья. В владимире доступен широкий ассортимент наркологических услуг‚ которые помогут в борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью.
генератор и бесперебойник
https://stroitelstvodomovsochi.ru/
https://stroydomvsochi.ru/
KRAKEN кракен сайт — это альтернатива основному сайту. Через рабочую ссылку легко попасть в личный кабинет и продолжить покупки.
лаки джет ссылка на iphone https://1win12011.ru
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who
has been conducting a little research on this. And he actually ordered me dinner due to the fact
that I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this….
Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to talk about this subject here
on your web page.
KRAKEN маркет легко открыть через ссылку https://krakr.cc/, которая остаётся рабочей.
https://tt23.pages.dev/images/search?q=%D0%A4%D0%BB%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F+%D0%98%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%8F&qft=%2Bfilterui%3Aage-lt1440&FORM=IRMHIP
Алкоголизм – серьезная проблема, требующая всестороннего подхода к лечению. В городе владимир предлагается помощь в любое время, включая вывод из запоя. Центры лечения алкоголизма предлагают сервисы психологической терапии и реабилитации, что является необходимым этапом в восстановлении. Экстренная помощь и консультации специалистов способствуют людям с зависимостью осознать и принять свою зависимость. Эмоциональная поддержка включает в себя индивидуальную терапию и групповую терапию, что способствует обмену обмену опытом и поддержке друг друга. Программа восстановления способствует созданию стратегий отказа от алкоголя и новые навыки жизни без него. вывод из запоя круглосуточно владимир Важно помнить, что помощь наркологов предоставляется круглосуточно, что даёт возможность каждому отыскать свой путь к здоровью и счастью.
KRAKEN сайт доступен в любое время через кракен официальный сайт или TOR.
drenazhnye-raboty-spb.ru .
http://umap.ru/main/login
лучшие нейросети для школьников
Post writing is also a fun, if you know then you can write
or else it is difficult to write.
Лечение алкоголизма в владимире: первый шаг к выздоровлению Алкогольная зависимость является серьезной проблемой, которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. В владимире доступна круглосуточная помощь нарколога на дом, что позволяет начать лечение в удобное время. Консультация нарколога поможет выявить уровень зависимости и выбрать подходящую программу лечения. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Медикаментозная терапия, широко используемая в реабилитационных центрах владимира, нацелена на облегчение абстинентного синдрома и восстановление здоровья. Психологическая помощь является важным аспектом процесса выздоровления, способствуя эмоциональной стабилизации. Анонимное лечение делает процесс более комфортным. Detox-программа поможет очистить организм от токсинов, а реабилитация зависимых включает социальную адаптацию и профилактику рецидива. Профессиональная помощь – залог успешного преодоления проблемы. Не упустите шанс изменить жизнь к лучшему!
психолог калуга
накрутка подписчиков в группу телеграм накрутка подписчиков в группу телеграм
рф лифтинг лица курс рф лифтинг лица курс .
Если вы ищете, как зайти в кракен сайт, используйте проверенные зеркала. Ссылка безопасна и ведёт на нужный ресурс.
Hi my family member! I wish to say that this article is amazing,
great written and come with approximately all vital infos.
I’d like to look more posts like this .
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – идеальные проекты
регистратура стоматология регистратура стоматология .
mostbet.com что это mostbet.com что это
Онлайн новостной портал https://reporternews.net главные события дня, эксклюзивные интервью, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Достоверная информация о политике, бизнесе и жизни общества.
Новостной портал https://newsawait.com свежие новости, аналитика и обзоры. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт. Лента событий в режиме реального времени с проверенными фактами.
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your
web site, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account aided me a appropriate deal.
I were a little bit familiar of this your broadcast offered vivid
transparent concept
mostbet website https://www.mostbet12013.ru
1win lucky jet скачать http://1win12007.ru
Портал про авто https://dream-autos.com новости, обзоры и тест-драйвы. Полезные советы по выбору, ремонту и эксплуатации автомобилей. Каталог машин, актуальные цены и аналитика авторынка.
Актуальное KRAKEN зеркало кракен официальный сайт открывает все разделы ресурса.
Если основной ресурс заблокирован, поможет https://krakr.cc/, официальный адрес.
Если вам нужна стабильность, выберите http://krakr.cc, этот адрес проверен временем.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр https://educ-ua13.ru/ .
ставки кыргызстан ставки кыргызстан
KRAKEN сайт — это надёжный источник для кракен тор проверенных ссылок.
купить аттестат за 11 класс в киеве купить аттестат за 11 класс в киеве .
купить диплом украина купить диплом украина .
купить диплом украины цена купить диплом украины цена .
https://loveshop1300.shop We are back! ?? ????? ? ????!
Актуальная кракен зеркало
ссылка открывает маркетплейс за несколько секунд.
Вызов врача нарколога — важная мера для людей‚ испытывающих проблемы с зависимостями. Услуги нарколога включает диагностику зависимости и лечение‚ что особенно актуально в сложных обстоятельствах. Посетив vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir012.ru‚ вы можете вызвать врача на дом анонимно. Это гарантирует комфорт и безопасность. Услуги нарколога на дому обеспечивают удобные условия для клиентов. Консультация нарколога позволяет выявить степень зависимости и разработать персонализированную программу терапии. В процессе реабилитации значима поддержка близких‚ что помогает справиться с эмоциями. Наркологическая клиника предлагает всеобъемлющее лечение‚ включая психотерапевтические сеансы и медикаментозное лечение зависимостей. Не стоит откладывать обращение за помощью‚ ведь своевременное лечение алкоголизма и наркотической зависимости может спасти жизнь.
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – современные стройматериалы
Услуга капельницы от запоя на дому – это ключевая услуга наркологической службы‚ позволяющая оперативно и значительно поддержать людям‚ переживающим от зависимости от алкоголя. Первичная консультация с наркологом в владимире включает определение степени зависимости‚ оценку состояния пациента и составление индивидуального плана лечения. Основные услуги нарколога на дому включают медикаментозное лечение‚ снятие запоя‚ психотерапию при алкоголизме и реабилитационные программы. Родственники также играют важную роль тоже играет ключевую функцию в процессе реабилитации алкоголиков. Лечение в анонимном формате обеспечивает комфорт и защищенность пациента. помощь нарколога владимир
Официальное кракен ссылка зеркало подходит для любых устройств.
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема , требующая квалифицированной помощи. В владимире работают центры помощи алкоголикам , предлагающие экстренный вывод из запоя и лечение алкоголизма . При алкогольной интоксикации важно быстро распознать симптомы и обратиться за медицинской помощью . Квалифицированные наркологи в владимире предлагают консультации, обеспечивая безопасное восстановление после алкогольного запоя и помощь при похмелье. Реабилитация от алкоголя включает в себя программы для лечения зависимых, поддерживая не только пациентов, но и оказывая помощь родственникам алкоголиков. Профилактика заболеваний, связанных с алкоголем также играет важную роль в предотвращении повторных случаев зависимости.
KRAKEN маркет легко открыть через ссылку https://krakr.cc/, которая остаётся рабочей.
Adoro a explosao de Bet558 Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar estelar. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco profundo. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura cosmica. No geral, Bet558 Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
bet558 como sacar|
скачать бесплатно 1win http://1win12013.ru
Рабочее зеркало кракен магазин позволяет пользоваться маркетом без ограничений.
J’adore la fraicheur de ViggoSlots Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme une banquise illuminee. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une toundra de delices, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un flocon de neige, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, ViggoSlots Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une banquise pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique polaire, facilite une experience de casino arctique.
viggoslots kokemuksia|
купить аттестат за 11 классов 2000 года купить аттестат за 11 классов 2000 года .
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/proektirovanie-inzhenernyix-sistem-i-kommunikaczij.html/
купить красный диплом магистра купить красный диплом магистра .
1win букмекерская контора официальный сайт зеркало https://1win12007.ru/
Рабочий вход в KRAKEN сайт доступен всегда.
https://vgarderobe.ru/byustgaltery-naturana-bc-12289.html
Если ищете, как зайти на кракен даркнет, выберите актуальное зеркало. Рабочая ссылка позволяет без лишних шагов попасть на официальный сайт.
лучшие нейросети для поиска информации
https://www.city-n.ru/view/475403.html
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительство XXI века
Рабочее зеркало доступно по адресу https://www.krakr.cc/, оно открывает весь функционал.
Прокапка после запоя — это ключевая медицинская манипуляция, направленная на детоксикацию организма и восстановление состояния здоровья пациента . Во время вызова нарколога на дом срочно осуществляется введение лекарственных средств через капельницу, что способствует очищению крови от токсичных веществ, которые накапливаются при злоупотреблении алкоголем. Нарколог на дом срочно Процедура обычно включает в себя солевые растворы, витамины и минералы, что помогает улучшить общее состояние и уменьшает проявления похмелья. Уход на дому позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке , что играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации. Наркологическая помощь включает в себя психологическую и медицинскую поддержку, что значительно увеличивает вероятность успешного восстановления после алкогольной зависимости. Важно следовать советам по лечению и регулярно проходить процедуру прокапки для достижения оптимальных результатов.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве .
1вин бет ставки 1вин бет ставки
С помощью кракен маркет можно легко получить рабочий вход даже на телефоне.
https://www.te-in.ru/dizelnyie-elektrostanczii/
диплом купить в реестре диплом купить в реестре .
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskii-bleizer-betty-barclay-g-4935-45.html
купить диплом занесенный в реестр http://www.educ-ua15.ru .
мостбет. https://mostbet12011.ru/
kupit-kub-drov-sergiev-posad.ru .
Капельница при запое – это необходимая медицинская процедура при алкогольной зависимости. Подготовительный этап предполагает несколько действий. Во-первых, необходимо позвонить наркологу для вызова на дом, который проведет осмотр и консультацию. Признаки алкоголизма могут меняться, поэтому необходимо подробно рассказать врачу о симптомах. нарколог на дом Перед введением капельницы необходимо подготовить вены, а также подготовить пациента к дальнейшему лечению. Проверьте наличие всех необходимых препаратов для введения капельницы. После лечение необходимо сосредоточиться на восстановлении, правильный уход за пациентом поможет в восстановлении здоровья и снизит риск рецидива.
Майстер-клас із японських танців від Pacific Department SFF був для мене справжнім відкриттям. Занурення у культуру рухів і вивчення кожного елемента танцю дозволили мені відчути зв’язок із традиціями Японії. Це неймовірний досвід, який я б хотіла повторити. Дізнайтеся більше про майбутні події тут.
Капельница для устранения похмелья на дому в Красноярске – это эффективным способом для быстрого восстановления после вечеринки. Похмелье сопровождается признаками‚ такими как головная боль‚ слабость и недостаток жидкости; инфузионная терапия с использованием капельниц помогает оперативному восстановлению самочувствия‚ восполняя дефицит витаминов и минералов. Клиника на дому предоставляет услуги медиков‚ которые проводят процедуру безопасно и в комфортных условиях. Процесс инфузии с помощью капельниц помогает устранить дискомфорт и значительно ускоряет восстановление. Медицинская помощь на дому – это простой выбор для тех‚ кто страдает от алкозависимости или просто хочет облегчить симптомы похмелья. Если вам нужно быстро восстановиться и вернуть здоровье‚ вы можете обратиться за помощью на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk013.ru. Не забывайте‚ что при тяжелых состояниях необходимо вызывать скорую помощь.
букмекерские конторы бишкек http://www.mostbet12011.ru
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54269667/dollartworks
I love your writing style really enjoying this site.
https://crpsc.org.br/forum/viewtopic.php?t=458482
KRAKEN сайт — это платформа, где всегда доступны зеркала и кракен магазин. Вход возможен даже через TOR и онион.
Капельница как способ борьбы с запоем – это проверенный подход, который используют специалисты по зависимости для детоксикации организма. Выездной нарколог из лечебного учреждения предлагает анонимное лечение, обеспечивая максимальную приватность для клиента. Домашний визит врача позволяет быстро ощутить медицинскую помощь и восстановление организма, что особенно актуально для людей с зависимостями. Нарколог на дом клиника Процедура включает в себя инфузионные растворы, которые помогают облегчить симптомы абстиненции и предотвращают осложнения. Профессиональная поддержка нарколога на дом предоставляет возможность лечиться в привычной обстановке, избегая стресса, связанного с посещением клиники наркологии. Это – быстрое избавление от запоя, которое предоставляет возможность начать новую жизнь без алкоголя.
Капельницы от алкоголизма в городе Красноярске – это важный этап в лечении алкоголизма. Методы детоксикации способствуют справиться с признаками абстиненции и освободиться от пьянства. Лечение в наркологических клиниках включает не только капельницы‚ но и поддержку психолога‚ что помогает восстановлению после алкоголя. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk013.ru Восстановление начинается с очистки организма‚ после которой инициируются программы восстановления. Поддержка родственников также играет ключевую роль в предотвращении срывов. Группы поддержки и обращение к специалиста могут помочь в процессе выздоровления. Не забудьте‚ что лечение алкоголизма требует многостороннего подхода.
купить официальный диплом купить официальный диплом .
техникум какое образование украина техникум какое образование украина .
Новости Украины и мира https://globalnewshome.com всё самое важное сегодня. Политика, экономика, региональные события, спорт и культура. Объективные статьи и аналитика в удобном формате.
Портал для женщин https://womanfashionista.com всё самое важное в одном месте: уход за собой, мода, дом, семья и карьера. Читайте полезные статьи, находите вдохновение и делитесь опытом.
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – проекты для вдохновения
Сайт детского сада https://malush16.ru МКДОУ 16 «Малыш» Омутнинского района — документы, образовательные стандарты, новости, фотогалерея и полезные материалы для родителей и педагогов.
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Красноярске: капельница от запоя Алкогольная зависимость, серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального вмешательства. Нарколог на дом предоставляет услуги, такие как капельница от запоя, способствующая восстановлению организма после продолжительного употребления алкоголя. К основным симптомам алкогольной зависимости относятся: дрожь, повышенная потливость и чувство тревоги. Лечение запоя включает в себя дезинтоксикацию и реабилитацию организма. Обращение к наркологу позволит разработать индивидуальный план лечения алкогольной зависимости. Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме, направленная на выведение из запойного состояния, может предотвратить серьезные последствия. Профилактика запойных состояний и психотерапевтические методы для зависимых — ключевые элементы успешного лечения зависимостей, обеспечивающие устойчивые результаты. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске доступны круглосуточно, что позволяет получить необходимую помощь в любое время. Не затягивайте с лечением, свяжитесь со специалистами прямо сейчас!
Капельница при похмелье – это эффективным методом помощи, который помогает устранить симптомы алкогольной интоксикации. Состояние похмелья сопровождается обезвоживанием, что проявляется головной болью, тошнотой и общей слабостью. Капельница содержит глюкозу и электролиты, которые восстанавливают баланс жидкости в организме. Лечение похмелья с помощью капельницы позволяет быстро устранить симптомы, обеспечивая детоксикацию. Внутривенное введение жидкости помогает ускорить восстановление организма. Капельница в домашних условиях может оказаться полезной, но требуется консультация врача для правильного подбора компонентов. Существуют и народные средства: различные травы, например, мяту или зверобой, которые способствуют улучшению состояния. Однако капельница остается наиболее быстрым и надежным способом облегчить страдания после пьянки. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru можно найти информацию о различных вариантах капельниц и их воздействии на организм.
KRAKEN маркет — это площадка с удобным входом на кракен сайт. Рабочая ссылка ведёт прямо в личный кабинет.
Чтобы зайти в KRAKEN маркетплейс, достаточно перейти по ссылке http://krakr.cc, это проверенный адрес.
электрокарнизы электрокарнизы .
Актуальная кракен даркнет
ссылка открывает маркетплейс за несколько секунд.
lucky jet как пополнить счет http://1win12012.ru
электрокарнизы цена электрокарнизы цена .
Наркология – это важная область медицинской практики‚ сосредоточенная на борьбу с зависимостями. Если вы или ваши близкие сталкиваетесь проблемы наркомании‚ важно знать о возможностях анонимного лечения. Медицинские центры, такие как vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru‚ обеспечивают помощь нарколога и комплексную поддержку для зависимых. Анонимные группы поддержки и программы восстановления оказывают помощь людям на пути к выздоровлению. Психотерапия при зависимости играет ключевую роль в реабилитации наркозависимых. Также важна профилактика наркомании и экстренная поддержка. Не бойтесь обращаться за помощью — выздоровление возможно!
электрокарнизы цена электрокарнизы цена .
https://dollartworks.blogspot.com/2025/09/balkan-pharmaceuticals.html
http://odesit.com/fm-t-28797-last.php
Удобное решение для пациентов — удобное решение для людей, которым необходимо лечение и реабилитация после недуга. С помощью услуг здравоохранения на дому, таких как капельницы и капельная терапия, профессиональные медсестры обеспечивают удобное лечение в привычной обстановке. Услуги медсестры позволяют пациентам получать медицинскую помощь без лишних затрат времени и потребности выходить из дома. Ваше здоровье — это приоритетное, и возможность получить капельницу на дому предлагает новый метод к уходу на дому, сохраняя время и обеспечивая эффективное лечение. Для получения подробной информации посетите vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir013.ru.
много подписчиков в тг канале бесплатно много подписчиков в тг канале бесплатно
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-vetrovki-north-face-bc-3268.html
электрические рулонные шторы http://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory5.ru/ .
выигрышные live ставки на мостбет выигрышные live ставки на мостбет
автоматические рулонные шторы на окна https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory15.ru .
электрокарнизы в москве http://karniz-s-elektroprivodom-kupit.ru .
Актуальное KRAKEN зеркало кракен онион открывает все разделы ресурса.
kupit-drova-v-novosibirske-365.ru .
Купить диплом колледжа в Львов Купить диплом колледжа в Львов .
https://www.storeboard.com/balkanpharmaceuticals
https://www.callupcontact.com/b/businessprofile/Dollartworks/9798389
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – онлайн-каталог идей
Для тех, кто ищет безопасный доступ к кракен сайт, всегда есть KRAKEN зеркало. Ссылка проверена и доступна.
Храните у себя актуальный адрес https://krakr.cc/, чтобы не потерять доступ к сайту и всегда иметь возможность безопасного входа.
купить официальный диплом с занесением в реестр http://www.arus-diplom31.ru/ .
https://loveshop1300.world new site, new stuff, new life.
Для выхода в кракен сайтиспользуйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Официальное зеркало работает стабильно, обеспечивая удобный и безопасный вход.
Статьи для садоводов https://portalteplic.ru огородников, фермеров и пчеловодов: советы по уходу за растениями, животными и пасекой. Полезные инструкции, лайфхаки и сезонные рекомендации.
Портал о ремонте https://studio-nd.ru статьи, инструкции и советы для дома и квартиры. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Полезные рекомендации для мастеров, новичков и частных застройщиков.
https://biolinky.co/otello
Сайт про металлопрокат https://the-master.ru каталог продукции, характеристики и сферы применения. Арматура, балки, трубы, листы и профили. Актуальные цены, советы специалистов и полезные статьи.
купить диплом зарегистрированный в реестре https://www.arus-diplom33.ru .
яндекс плюс семейный Яндекс Плюс на месяц – это отличный способ попробовать все преимущества подписки, прежде чем оформлять ее на более длительный срок. Слушайте музыку, смотрите фильмы, получайте кешбэк и пользуйтесь другими бонусами в течение месяца!
Услуги по откачке в Красноярске, незаменимая мероприятие для поддержания гигиеничности в вашем доме. Проблемы с канализацией могут возникнуть внезапно, и в таких случаях необходимо вызвать профессионалов. Профессиональная откачка сточных вод поможет избежать неприятностей.Среди услуг откачки предлагаются: обслуживание канализационных систем, обслуживание сливных ям и срочная откачка. Ассенизаторская машина обеспечит качественное выполнение работ с соблюдением всех экологических стандартов. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk014.ru вы можете узнать информацию о стоимости услуг и вариантах вызова специалиста. Также доступны сушилки септиков и дренажные системы для предотвращения повторных засоров. Не откладывайте на потом — решите проблемы с канализацией сегодня!
I quite like reading through a post that will make
people think. Also, many thanks for allowing me to comment!
купить колотые дрова недорого береза .
купить дипломы о высшем образовании в киеве educ-ua18.ru .
Анонимные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом становится все более популярным, так как многие люди стремятся вернуться к нормальной жизни в условиях конфиденциальности. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk014.ru доступны разные программы реабилитации, включая детоксикационные программы, которые способствуют комфортному прохождению лечения. Помощь врачей при алкоголизме включает кодирование от алкоголя и психотерапевтические методы. Анонимные сообщества поддержки помогают справиться с психологическими трудностями, а поддержка родных и друзей играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления от алкогольной зависимости. Консультации по алкоголизму онлайн и консультации без раскрытия данных обеспечивают доступ к профессиональной помощи при запойном состоянии. Анонимное лечение дает возможность людям чувствовать себя защищенными. Важно помнить, что первый шаг к выздоровлению, это обращение за помощью.
KRAKEN кракен официальный сайт — это альтернатива основному сайту. Через рабочую ссылку легко попасть в личный кабинет и продолжить покупки.
бот для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм бот для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм
go to this web-site russian traditional clothing
Современная наркологическая помощь включает в себя работающие методы лечения зависимостей, такие как медикаментозное лечение и психотерапия для зависимых. Выездная наркология набирает популярность благодаря индивидуальному подходу к каждому пациенту. Это даёт возможность проводить диагностику зависимостей и разрабатывать программу реабилитации, не покидая домашнего уюта. Лечение наркомании нуждается в комплексном подходе. Обсуждение проблем с наркологом на дому предоставляет возможность обсудить проблемы и подобрать оптимальные варианты терапии. Помощь родственников является важным фактором в процессе восстановления после зависимости. Предотвращение возврата к зависимости и регулярное наблюдение помогают избежать возврата к пагубным привычкам. Конфиденциальное лечение и реабилитация на дому обеспечивают комфорт и безопасность, что особенно важно для тех, кто стесняется обращаться за помощью. Используя ресурсы, такие как vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk014.ru, можно найти необходимую информацию и поддержку, которая так необходима на пути к здоровью.
Мы можем предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом университета:
аттестат за 11 класс 2014 купить
согласование перепланировки квартиры москва согласование перепланировки квартиры москва .
Капельница от запоя в Красноярске: цены и отзывы В Красноярске вызов нарколога на дом становятся востребованными. Множество людей сталкиваются с алкогольной зависимостью и испытывают потребность в поддержке. Вызов нарколога на дом анонимно, это удобный способ получить медицинскую помощь, не выходя из дома. Капельница от запоя является действенным средством в детоксикации организма и снижает негативные последствия.Стоимость капельницы может различаться в зависимости от клиники, но в среднем составляет в пределах 3000-6000 рублей. Отзывы о капельнице в большинстве своем хорошие: пациенты говорят о быстром восстановлении и уменьшение влечения к алкоголю. Экстренная помощь при запое является жизненно важной.Конфиденциальное лечение зависимости от алкоголя — ключевой фактор, так как многие чувствуют неловкость из-за своей зависимости. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске предлагают комплексную помощь, включая капельницы и реабилитационные программы. Помощь при запое может получить любой, кто хочет изменить свою жизнь. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск
Sou louco pela energia de BetPrimeiro Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao ardente quanto lava derretida. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque vulcanico. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma chama de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem cinzas. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, BetPrimeiro Casino e um cassino online que e uma cratera de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro fogo, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
betprimeiro bedrageri|
Казино Вавада знаменито бонусами.
Акции и коды помогают стартовать новичкам.
Регулярные турниры дают шанс выиграть крупные призы.
Ассортимент слотов включает новинки.
Регистрация проста, поэтому можно сразу активировать промо.
Узнай больше по ссылке: онлайн казино vavada
Чтобы войти в кракен личный кабинет, используйте KRAKEN ссылка. Всё просто и удобно.
kupit-drova-v-novosibirske-365.ru .
Для удобного входа с телефона подойдёт ссылка http://krakr.cc/, которая адаптирована под мобильные устройства.
https://loveshop.world now alive, welcome!
онлайн фильмы сегодня может каждый, имея лишь доступ в интернет, ведь современные сервисы предлагают огромную коллекцию кино. Не нужно искать диски или ждать телепоказ — всё доступно в один клик. Здесь можно найти мелодрамы, ужасы, триллеры и фантастику. Киноманы смогут открыть для себя редкие авторские работы. Современные платформы предлагают 4K и отличное звучание. Доступ есть с любых устройств и в любом месте. Есть как платные, так и полностью бесплатные варианты. Бесплатные версии отлично подходят для быстрого просмотра. Подписка открывает полный каталог без ограничений. В библиотеке найдётся кино для всей семьи и друзей. Например, вечером можно устроить просмотр комедии. Онлайн-кинотеатр заменяет поход в обычный кинотеатр. Всё, что требуется — интернет и желание смотреть. Многие используют фильмы для изучения иностранных языков. Это доступ к мировому кинематографу без границ. Главное — включить устройство и насладиться просмотром. Платформы оперативно добавляют новинки проката. Сегодня фильмы онлайн — часть повседневной жизни миллионов людей.
drenazhnye-raboty-spb.ru .
I’m hooked on Wazamba Casino, it offers a casino adventure that swings like a vine in the wild. The selection is a wild expedition of fun, including classy casino table games with a tribal flair. The casino’s customer service is a tribal chief of efficiency, providing clear and instant solutions. Casino transactions are as simple as a tribal dance, however more frequent casino bonuses would be epic. Overall, Wazamba Casino delivers a casino experience as wild as a safari for fans of modern casino slots! By the way the casino platform shines with a style as bold as a jaguar, easing a thrilling casino experience.
wazamba online|
J’adore le frisson de Unibet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un orchestre en feu. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui resonne comme une symphonie. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un tempo allegro, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient chanter. Au final, Unibet Casino promet un divertissement de casino vibrant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style symphonique, ajoute une touche de musique au casino.
virement instantanГ© unibet|
Outstanding story there. What occurred after? Thanks!
москва купить диплом техникума москва купить диплом техникума .
купить осиновые дрова .
KRAKEN маркет доступен через официальные ссылки кракен магазин и проверенные зеркала.
купить легальный диплом колледжа купить легальный диплом колледжа .
Алкогольный запой – это состояние‚ которое проявляется продолжительным приемом алкоголя‚ что может привести опасные последствия. Симптомы алкогольной зависимости включают необходимость в спиртном‚ поэтому экстренный вывод из запоя необходимым. В Красноярске медицинская помощь при запое предоставляется в специальных медицинских учреждениях‚ где предоставляются услуги нарколога; последствия запоя могут различаться от физического ухудшения здоровья до психологических проблем. экстренный вывод из запоя Красноярск Экстренный вывод из запоя включает detox-процедуры‚ которые помогают организму очиститься от токсинов. Психологическая поддержка при алкоголизме также играет ключевой ролью в восстановлении. Реабилитация алкоголиков в Красноярске предоставляет целостный метод к лечению‚ включая профилактические меры и поддержку в период восстановления. Необходимо учитывать‚ что лечение алкоголизма нуждается в профессиональной помощи для минимизации рисков и улучшения качества жизни.
my explanation https://aixbt.my/
https://dostavkakresel.ru/ru-ru/
Срочный вызов нарколога на дом — это важная услуга для тех, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir014.ru вы можете получить консультацию нарколога и заказать врача на дом. Профессиональная помощь нарколога включает в себя лечение различных зависимостей и психологическую поддержку. Экстренная медицинская служба предлагает анонимную помощь, что позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность. Эффективное лечение наркомании и помощь алкоголикам возможны с помощью психотерапевта на дому. Не ждите, получите срочную помощь уже сегодня!
Initiatives include a mix of renewable energy projects and legislative changes.
Netflix global influence https://firstnewsservice.com/how-netflix-and-other-platforms-are-changing-media-consumption-worldwide/
MEGA DARKNET MARKET В ПОСЛЕДНЕЕ ВРЕМЯ ОСТАЁТСЯ ОДНОЙ ИЗ САМЫХ ПОПУЛЯРНЫХ ПЛОЩАДОК В ДАРКНЕТЕ. ВСЁ БОЛЬШЕ ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЕЙ ИЩУТ MEGA DARKNET MIRROR, ЧТОБЫ ОСУЩЕСТВИТЬ ВХОД НА МЕГА SB.
## Зачем нужны зеркала?
Адреса вроде официальный сайт мега sb часто становятся недоступны. Чтобы обойти эти ограничения, пользователи ищут актуальное зеркало мега sb. Такие зеркала позволяют зайти на сайт, но одновременно появляются поддельные версии.
## Актуальная ссылка
обновлённый сайт мега
Сыллка ===> https://github.com/mega-zerkalo-2025/mega-ssylka
## Как зайти на Мегу?
Чтобы получить вход на мега sb, необходимо:
1. Запустить тор-браузер.
2. Ввести mega darknet link.
3. Пройти авторизацию.
## Популярные запросы 2025
В 2025 году особенно востребованы такие ключи, как:
– мега зеркало рабочее
– mega darknet market вход
– мега sb официальный сайт
## Заключение
мега sb остаётся важной даркнет-площадкой в 2025 году. Но нужно помнить: доступ к мегамаркету всегда рискованно, а онион-адреса могут быть мошенническими.
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/texnicheskoe-obsluzhivanie-dgu.html/
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Admiring the persistence you put into your blog and in depth information you offer. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed information. Great read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
https://rainbet-canada.org/
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-vechernie-aksessuary-cat-1355.html
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
кракен зеркало тор позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. кракен официальный сайт необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. сайт кракен тор должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
фишинг – главная особенность Кракен.
https://www.myminifactory.com/users/SerHrut
https://www.chambers.com.au/forum/view_post.php?frm=2&pstid=108839
casino ohne deutsche lizenz Mad Casino
Запойный алкогольный синдром, серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. В владимире доступны различные услуги по анонимному выводу из запоя. Наркологические клиники предлагают медицинскую помощь при запоях, включая программы детоксикации и психотерапию для алкоголиков. вывод из запоя владимир Если вам или вашим близким нужна помощь, стоит обратиться в центры лечения зависимостей, где работают выездные наркологи. Также стоит рассмотреть возможность консультаций по алкоголизму и участия в группах поддержки для родственников. В владимире есть реабилитационные программы, включая анонимные группы и восстановление после запоя. Помощь в кризисной ситуации всегда рядом.
купить аттестат образование купить аттестат образование .
Рабочее зеркало кракен маркет — это удобное решение для тех, кто хочет пользоваться сервисом постоянно.
купить диплом в чернигове https://www.educ-ua5.ru .
http://www.evakuatorhelp.ru Наш автопарк оснащен современными эвакуаторами, оборудованными всем необходимым для безопасной и эффективной транспортировки автомобилей любой марки и модели. Наши водители – опытные профессионалы, знающие свою работу и всегда готовы предложить оптимальное решение в любой ситуации. Мы работаем без выходных и праздников, 24 часа в сутки, 7 дней в неделю.
Наркологическая помощь в владимире – это неотъемлемая часть борьбы с алкоголизмом и наркоманией. Если ваши знакомые столкнулись с трудностями, связанными с алкоголизмом, специализированные центры реабилитации предлагают эффективные программы лечения зависимостей. В наркологической клинике владимир предоставляется всесторонняя поддержка, включая очистку организма и психотерапию. Прием у нарколога помогут выявить степень зависимости и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Психологическая помощь при зависимости и работа с семьями зависимых играют ключевую роль в процессе восстановления. Также необходимо помнить о профилактике зависимостей, чтобы не допустить ухудшения ситуации. Анонимная помощь доступна всем, кто нуждается в ней. Методы лечения алкоголизма включают различные методы, подходящие для всех нуждающихся. Обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir014.ru для получения дополнительной информации и назначения встречи.
https://vgarderobe.ru/golfy-3-pary-rogo-g-45727-52.html
Королева Чиана Королева Чиана – автор, чьи произведения погружают в мир сложных человеческих отношений и моральных дилемм. Её рассказы и повести отличаются психологической глубиной и заставляют задуматься о непростых жизненных вопросах. Читая её книги, словно оказываешься в центре событий, переживая все чувства вместе с героями.
Строительный портал https://krovlyaikrysha.ru база знаний и идей. Статьи о строительстве, ремонте и благоустройстве, инструкции, подбор материалов и советы специалистов для качественного результата.
Всё про ремонт https://gbu-so-svo.ru и строительство — статьи, инструкции и советы для мастеров и новичков. Обзоры материалов, проекты домов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Аналитика финансовых рынков Инвестиционные стратегии – это планы, которые помогают нам достигать наших инвестиционных целей. Они зависят от наших целей, склонности к риску и временного горизонта. Существуют различные инвестиционные стратегии, такие как долгосрочное инвестирование, активное управление портфелем, инвестирование в стоимость и инвестирование в рост. Выбор инвестиционной стратегии – это индивидуальный процесс, который требует анализа и планирования.
Автомобильный портал https://ivanmotors.ru всё о машинах в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, обзоры, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Актуальные события мира авто для водителей и экспертов.
Чтобы попасть на площадку кракен даркнет, используйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Вход безопасен.
Для постоянного доступа подойдёт зеркало http://www.krakr.cc, оно проверено временем.
https://vgarderobe.ru/futbolki-snoopy-dlya-devochek-cat-6728.html
электрокарниз купить в москве электрокарниз купить в москве .
http://sochistroygroup.ru – строительные примеры
Чтобы попасть на площадку кракен маркетплейс, используйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Вход безопасен.
роликовые шторы https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory15.ru/ .
ролет штора ролет штора .
электрические гардины https://karniz-s-elektroprivodom-kupit.ru/ .
find out https://slop-club.org
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskie-kurtki-dlya-sporta-haglofs-bc-27244.html
дренаж цена за метр .
Лечение запоя в Красноярске – это нужная помощь, обеспечивающая возможность пациентам обратиться за помощью не выходя из дома. Выездной нарколог, предлагающий наркологические услуги, поможет справиться с симптомами абстиненции и создаст комфортные условия для пациента. врач нарколог на дом Стоимость капельниц могут изменяться в зависимости от выбранной клиники и сложности лечения. Например, цена лечения алкогольной зависимости может состоять не только из капельницу другие антиалкогольные процедуры, а также реабилитационные мероприятия. В Красноярске работают наркологические службы возможны как в стационарных учреждениях, так и в выездном формате. Ориентировочная цена капельницы от запоя находится в диапазоне 2000-5000 рублей. Необходимо учитывать, что цена может изменяться в зависимости от препаратов и индивидуальных потребностей пациента. Наркологическая клиника Красноярск предлагает различные пакеты услуг, которые могут включать терапию запоя и реабилитацию. Получив помощь нарколога на дом, вы получите поддержку специалиста в борьбе с алкоголизмом и избавитесь от длительного лечения в клинике. Имейте в виду, что оперативное обращение за медицинской помощью может значительно уточнить процесс восстановления.
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya1.ru/ .
перепланировка здания pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в многоквартирном доме перепланировка нежилого помещения в многоквартирном доме .
https://www.te-in.ru/rejting-dizel-generatorov-obzor-luchshix-proizvoditelej-na-2022-god.html/
KRAKEN вход всегда доступен через
. Актуальное зеркало помогает авторизоваться и продолжить пользоваться сервисом.
Вызов капельницы от запоя – это важная медицинская помощь при алкогольной зависимости. Процедура капельного введения жидкости помогает оперативно восстановить водно-электролитный баланс и облегчить симптомы похмелья. Лечение запоя в домашних условиях требует профессионального подхода, и именно здесь на помощь приходят услуги нарколога; При алкогольной абстиненции капельница от алкоголя не только снимает физические симптомы, но и способствует процессу детоксикации организма. Специальные клиники, занимающиеся лечением зависимостей предлагают терапию для людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, которая предусматривает восстановление здоровья после запоя. Если вам или вашим близким нужна помощь, не сомневайтесь обращаться за медицинской помощью при запое на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk015.ru. Помните, что лечение алкоголизма – это путь к здоровой жизни.
советские фильмы смотреть онлайн бесплатно http://kinogo-11.top .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
https://smi111.ru/ru-ru/
Если вы столкнулись с трудностями зависимости‚ важно помнить‚ что наркологическая помощь нужна. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk015.ru вы можете найти информацию о лечении зависимости и реабилитации алкоголиков. Кризисная интервенция и поддержка семьи играют ключевую роль в восстановлении после употребления наркотиков. Мы готовы предложить анонимное лечение у нарколога и детокс-программу. Психотерапия и программы реабилитации помогут справиться с симптомами зависимости и снизить риск рецидивов. Не стесняйтесь обратиться за медицинской помощью‚ чтобы стартовать путь к новой жизни.
pop over to this web-site https://agents-land.org
Актуальный сайт всегда доступен по адресу krakr.cc, это проверенный вариант.
Рабочее зеркало доступно через http://www.krakr.cc, ссылка открывает маркет.
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/proektirovanie-inzhenernyix-sistem-i-kommunikaczij.html/
https://vgarderobe.ru/odezhda-dlya-malchikov-hessnatur-bc-7997.html
this page https://askthehive.org/
KRAKEN сайт даёт возможность подключаться с любых устройств. Рабочая ссылка открывает кракен личный кабинет без ограничений.
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по выгодным ценам. Заказ документа, подтверждающего обучение в ВУЗе, – это выгодное решение. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании: vared.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1170&sid=69f43d5f32e28c8e59d23bc2644d7612
Капельница от запоя – это важная медицинская манипуляция, которая может помочь в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Вызвать нарколога на дом в Красноярске стоит, если есть симптомы запоя: интенсивные головные боли, рвота, дрожь. Медицинская помощь при алкоголизме включает капельницы для восстановления водно-солевого баланса и обезвреживание токсинов. Запрос на вызов врача позволяет получить профессиональную помощь алкоголикам в удобных условиях. Наркологические услуги в Красноярске включают лечение запойного состояния и реабилитацию после запоя. Чтобы достигнуть успешного результата, важно соблюдать указания медицинских специалистов и провести полное лечение алкогольной зависимости. Используйте возможности домашней наркологии для скорейшего и качественного выздоровления.
cg 100 fs ohne einzahlung Neue Online Casinos
Экстренная наркологическая помощь — это незаменимый элемент в профилактике зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir015.ru вы можете получить сведения о постоянной помощи, которая предлагает срочную медицинскую помощь. Наркологическая служба предоставляет медицинскую помощь при наркотиках и алкоголизме. Специалисты предлагают консультации нарколога, а также гарантируют лечение без раскрытия личных данных. В рамках кризисной интервенции возможны программы восстановления и стационарное лечение. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в восстановлении после зависимости. Обратитесь за помощью незамедлительно, помогите себе и своим близким!
https://evakuatorhelp.ru/ Наша специализация – круглосуточная помощь на дорогах! Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, от эвакуации автомобилей до мелкого ремонта на месте происшествия. Наша работа отличается оперативностью, высоким качеством и доступными ценами. Не важно, где вы находитесь и что случилось с вашим автомобилем – мы всегда готовы прийти на помощь! Звоните прямо сейчас!
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы на дому – это важная процедура для лечения алкогольной зависимости. Если вам хочется вызвать нарколога на дом в Красноярске‚ убедитесь в надежности клиники. Важно обратить внимание на клинику‚ который предлагает анонимное лечение и квалифицированных специалистов. вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск Перед обращением к врачу стоит проконсультироваться о домашних процедурах‚ таких как внутривенные инфузии. Это позволит обеспечить безопасность лечения и быстрое восстановление после алкогольной интоксикации. Убедитесь‚ что клиника имеет программы реабилитации на дому‚ что способствует лучшему результату. При выборе клиники важно учитывать несколько факторов. Обратите внимание на мнения пациентов‚ уровень профессионализма специалистов и график работы клиники. Надежный нарколог на дому сможет оказать помощь в кратчайшие сроки‚ обеспечивая поддержку и понимание в трудный период.
Для всіх, хто цікавиться кіберспортом, рекомендую звернути увагу на Obolon E-Team. Вони дійсно знають, як вигравати!
Сайт о ремонте https://e-proficom.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Всё, что нужно для ремонта квартир и домов.
Сайт для женщин https://devchenky.ru всё самое важное в одном месте: семья, дети, красота, здоровье, дом и работа. Советы специалистов, лайфхаки и вдохновение на каждый день.
согласование перепланировки квартиры под ключ согласование перепланировки квартиры под ключ .
Блог о ремонте https://ivinstrument.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. Всё о ремонте квартир и домов: выбор материалов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
KRAKEN кракен ссылкадаёт быстрый доступ без перебоев. Рабочее зеркало открывает все разделы площадки, а вход в личный кабинет доступен даже новичкам.
Запой — это тревожное состояние, требующее незамедлительной медико-социальной помощи. В Красноярске доступна помощь врача-нарколога, который предлагает услуги по избавлению от запоя и очищению организма. Капельное введение — это результативное средство для оздоровления пациента. Она помогает устранить симптомы алкогольной зависимости, повышает общее состояние и интенсифицирует процесс реабилитации от алкоголя. помощь нарколога Красноярск Если вы или ваш близкий испытываете трудности с запоя, необходимо не откладывать обращение за медицинской помощью. Наркологические услуги, предоставляемые в клиниках Красноярска, могут включать индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Помощь нарколога включает не только капельницы, но и комплексное лечение алкоголизма. Обращение к врачу на дом дает возможность получения медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке. Специалисты согласятся на необходимую детоксикацию и поддержат здоровье пациента. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за помощью — это первый шаг к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
https://sochistroygroup.ru – строительный журнал
ДОСТУПНЫЙ ВЫВОД ИЗ ЗАПОЯ В владимире: РЕАЛЬНОСТЬ И МИФЫ Лечение алкоголизма – это сложный и многогранный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода. В владимире множество наркологических клиник предлагают лечение запоя и реабилитацию от запоя, однако есть мифы о лечении алкоголизма, способные ввести в заблуждение. Во-первых, многие считают, что вывод из запойного состояния – это быстрое дело. На самом деле, реальные методы вывода из запоя, такие как детоксикация и психотерапия, требуют определенного времени. Наркологическая клиника владимир предлагает программы реабилитации, где специалисты помогут в восстановлении после запоя. Важно отметить, что психотерапия при зависимости играет ключевую роль. Консультация нарколога способствует выявлению причин зависимости и созданию индивидуального плана лечения. Не стоит забывать, что в владимире лечение зависимости доступно и эффективно, при условии своевременного обращения за помощью.
http://sports-kz.site Турнирное положение клубов чемпионата
Сохраняйте https://krakr.cc, чтобы не потерять доступ к площадке.
Актуальное зеркало KRAKEN ведёт на ресурс кракен тор без перебоев.
drova-berezovye-kolotye-spb.ru .
https://kyourc.com/meilleurcode1xbet
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-vetnamki-unisa-bc-30285.html
https://teletype.in/@xbetba
Если вы столкнулись с затруднением алкоголизма или слышали человека, нуждающегося в помощи, важно обратиться к профессионалам. Наркологическая клиника в владимире предлагает экстренную помощь при алкоголизма и наркомании. Консультация к наркологу поможет определить нужный курс лечения. Центр лечения наркозависимости обеспечивает медицинскую помощь и психотерапию, а также поддержку семьи. Анонимное лечение обеспечивает безопасность и конфиденциальность. Реабилитация наркоманов включает меры по предотвращению рецидивов и реинтеграцию после зависимости. Первый шаг к новой жизни начинается в этом месте. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir015.ru
Experience the ultimate relaxation with Hiso Massage’s best Nuru massage in Sukhumvit 31, Bangkok, Thailand. Our skilled therapists use premium Nuru gel for smooth, full-body gliding, relieving stress, tension, and promoting wellness. Enjoy a private, luxurious, and unforgettable massage experience today.
best nuru massage
Актуальное зеркало KRAKEN ведёт на ресурс кракен сайт без перебоев.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Website https://useit2.ru/.
sites https://tophat.space
Городской портал Москвы https://moscowfy.ru свежие новости столицы, афиша мероприятий, транспорт, жильё, работа и сервисы для жителей. Полезная информация для москвичей и гостей города на одном сайте.
KRAKEN кракен вход TOR даёт возможность обойти блокировки и подключиться анонимно.
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр .
услуги перевода документов сайты бюро переводов
Купить диплом колледжа в Винница Купить диплом колледжа в Винница .
Мы предлагаем документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат 11 классов в украине
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы предлагаемвыгодно купить диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте цели быстро и просто с нашими дипломами- radiotrainzfm301.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=1184
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить диплом младшего специалиста купить диплом младшего специалиста .
купить диплом института образования купить диплом института образования .
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
диплом настоящий купить с занесением в реестр https://arus-diplom34.ru/ .
Для безопасного входа используйте https://www.krakr.cc, ссылка официальная.
дипломы бывшего ссср купить дипломы бывшего ссср купить .
где можно купить аттестат за 11 где можно купить аттестат за 11 .
Чтобы пользоваться ресурсом кракен ссылка, достаточно одной рабочей ссылки.
купить настоящий аттестат за 11 классов купить настоящий аттестат за 11 классов .
Je suis totalement submerge par Winamax Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui ondule comme une mer dechainee. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un ocean de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eclaboussent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vague deferlante, repondant en un eclat d’ecume. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une goutte d’eau, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait aquatique. Pour resumer, Winamax Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les navigateurs du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique fluide, facilite une experience de casino aquatique.
bonus depot winamax|
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом магистра дешево купить диплом магистра дешево .
Казахстан бокс новости – эксклюзивные новости боксерских поединках казахстанских боксеров
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг канал дешево накрутка живых подписчиков в тг канал дешево
Estou completamente fascinado por VikingLuck Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que navega como um drakkar em furia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de lendas nordicas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e forte como um escudo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma inscricao runica, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, VikingLuck Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual epico, eleva a imersao no cassino ao nivel de uma saga.
good luck viking symbol|
KRAKEN сайт помогает обойти блокировки. Выберите проверенное зеркало, зайдите по кракен маркетплейси пользуйтесь маркетом с телефона или ПК.
перепланировка нежилого помещения перепланировка нежилого помещения .
разрешение на перепланировку нежилого помещения не требуется http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya3.ru .
перепланировка в нежилом здании http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya.ru/ .
согласование перепланировки нежилого здания http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya1.ru/ .
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru – дом вашей мечты
Кредиты Экономика – это механизм, который приводит в движение весь мир. Это система производства, распределения и потребления товаров и услуг. Экономика изучает, как люди делают выбор в условиях ограниченности ресурсов, и как эти решения влияют на общество. Понимание экономики помогает нам понять, как работает рынок, почему происходят кризисы, и как можно улучшить жизнь людей. Экономика включает в себя множество различных областей, таких как макроэкономика, микроэкономика, международная экономика и экономика развития.
ролл жалюзи на окна http://www.elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory15.ru/ .
исторические фильмы http://kinogo-11.top/ .
электрокарниз двухрядный цена http://karniz-s-elektroprivodom-kupit.ru/ .
рулонные шторы на створку http://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory5.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
KRAKEN маркет легко открыть через ссылку https://krakr.cc/, которая остаётся рабочей.
Надёжный доступ всегда возможен через http://krakr.cc, официальный адрес сайта.
аниме смотреть онлайн http://www.kinogo-12.top/ .
KRAKEN сайт поддерживает актуальные варианты подключения. Вход возможен на кракен маркетплейс за пару секунд.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Официальное кракен официальный сайт зеркало подходит для любых устройств.
https://sports-kz.site/ Достижения казахстанских атлетов на международной арене
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Капельницы от запоя в владимире: экстренная помощь на дому Алкогольная зависимость – серьезная проблема‚ требующая профессионального вмешательства. При запойном состоянии наблюдаются тяжелые симптомы‚ такие как тремор‚ повышенная потливость‚ беспокойство и‚ порой‚ галлюцинации. В этих случаях крайне важно обратиться за помощью нарколога‚ который предоставит необходимую медицинскую поддержку. Домашняя терапия имеет свои преимущества: пациент находится в привычной обстановке‚ что ускоряет восстановление после запоя. Не менее важно уделить внимание профилактике рецидивов‚ чтобы предотвратить повторные запои. При обращении к специалистам вы получите не только капельницы для детоксикации‚ но и всестороннее лечение алкоголизма‚ которое поможет вам полностью восстановиться.
Королева Чиана Королева Чиана – автор, чьи произведения погружают в мир сложных человеческих отношений и моральных дилемм. Её рассказы и повести отличаются психологической глубиной и заставляют задуматься о непростых жизненных вопросах. Читая её книги, словно оказываешься в центре событий, переживая все чувства вместе с героями.
Прокапаться от алкоголя на дому — важный шаг для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью . Лечение алкоголизма начинается с детоксикации , которая может быть проведена в домашних условиях . Основные подходы включают медицинскую помощь и препараты для детоксикации , которые помогут безопасно прекратить употребление . vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir016.ru Советы по трезвости и стратегии преодоления зависимости, такие как самообслуживание для людей с алкогольной зависимостью, имеют огромное значение в реабилитации . Безопасное прекращение употребления алкоголя — это путь к новой жизни .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в Киеве купить диплом с занесением в реестр в Киеве .
купить диплом нового образца купить диплом нового образца .
легальный диплом купить легальный диплом купить .
диплом занесен в реестр купить диплом занесен в реестр купить .
купить диплом техникума отзывы купить диплом техникума отзывы .
Капельница от запоя — является работающим способом, применяемым в наркологии для лечения зависимости от алкоголя; терапия с применением инфузий даёт возможность оперативно вывести токсины из организма и восстановить баланс воды и электролитов. Нарколог на дом конфиденциально в владимире предлагает такую услугу, обеспечивая пациентам комфорт и дискрецию. нарколог на дом анонимно владимир Признаки похмелья, такие как головную боль, тошноту и слабость, могут быть устранены с помощью инфузионной терапии, содержащей подходящие лекарства. Процесс лечения зависимости от алкоголя требует индивидуального подхода, и нарколог на дом проводит первичную консультацию, определяя нужные процедуры для снятия абстиненции. Детоксикация организма — существенный шаг, который помогает восстановиться после алкогольной зависимости. Забота и поддержка семьи занимает ключевую роль в реабилитации зависимых, а фармацевтическое лечение в сочетании с капельницами гарантирует положительный эффект.
Купить диплом университета поспособствуем. Купить диплом в городах – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-v-gorodakh
Приобрести диплом под заказ можно через сайт компании. speechimprovementcenter.com/employer/education-ua
Для обхода блокировок достаточно
. Рабочее зеркало открывает маркет и позволяет авторизоваться в личном кабинете.
купить диплом в уфе с реестром arus-diplom31.ru .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Надёжный путь в личный кабинет — это ссылка https://www.krakr.cc, подходящая для любого устройства.
Если основной ресурс заблокирован, поможет https://krakr.cc/, официальный адрес.
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru/ – журнал о стройке
Для тех, кто ищет безопасный доступ к кракен тор, всегда есть KRAKEN зеркало. Ссылка проверена и доступна.
https://doodleordie.com/profile/serhrut
https://www.walkscore.com/people/263453271790/walk-score-user
купить диплом вуза ссср купить диплом вуза ссср .
KRAKEN
— это альтернатива основному сайту. Через рабочую ссылку легко попасть в личный кабинет и продолжить покупки.
купить диплом в запорожье купить диплом в запорожье .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
Купить диплом техникума в Харьков http://www.educ-ua8.ru – Купить диплом техникума в Харьков .
https://www.sports-kz.site Новости бокса и единоборств Казахстана
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным ценам. Приобретение документа, подтверждающего окончание института, – это разумное решение. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: apexd.ru/employer/diplomy-grupps
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить свидетельство о браке https://educ-ua3.ru .
Для тех, кто ищет проверенный доступ к KRAKEN, всегда можно использовать https://www.krakr.cc — ссылка ведёт напрямую на официальный сайт.
KRAKEN тор зеркало — удобный способ подключения. Ссылка ведёт к кракен маркет ресурсу напрямую.
KRAKEN всегда работает через http://krakr.cc, этот адрес безопасный.
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
KRAKEN сайт предлагает проверенные способы обхода блокировок. Вход возможен всегда через кракен сайт.
Рабочее KRAKEN зеркало открывает дорогу в кракен вход
.
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskie-sportivnye-botinki-jack-wolfskin-bc-5200.html
https://vgarderobe.ru/svitery-dlya-novorozhdennykh-cat-2128.html
how much are fake shoes in turkey – is hypeunique.is safe
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://sports-kz.site/ Подкасты и аудиоинтервью со спортсменами
MEGA DARKNET MARKET 2025 В ПОСЛЕДНЕЕ ВРЕМЯ ОСТАЁТСЯ ОДНОЙ ИЗ САМЫХ ОБСУЖДАЕМЫХ ПЛОЩАДОК В ДАРКНЕТЕ. ВСЁ БОЛЬШЕ ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЕЙ ИЩУТ АКТУАЛЬНУЮ ССЫЛКУ НА МЕГУ, ЧТОБЫ ПОЛУЧИТЬ ДОСТУП НА МЕГА SB.
## Что такое Мега?
мега даркнет маркет — это площадка, работающий в сети Tor. Она стала популярна благодаря широкому ассортименту. Но важно понимать: мега сайт даркнет — это незаконная платформа.
## Актуальная ссылка
мега darknet mirror https://github.com/mega-zerkalo-market/MEGA-SSYLKA-NA-SITE
## Популярные запросы 2025
В сегодня особенно востребованы такие ключи, как:
– мега sb зеркало
– mega darknet market вход
– мега sb официальный сайт
## Заключение
Мега даркнет маркетплейс остаётся крупнейшей даркнет-площадкой в последние годы. Но нужно помнить: использование даркнета всегда незаконно, а мега ссылки могут быть поддельными.
http://sochistroygroup.ru/ – дома XXI века
https://vgarderobe.ru/byustgalter-luwa-g-81004-3.html
Hello everyone!
I came across a 133 interesting resource that I think you should dive into.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://baederradweg.de/online-casino/top-4-der-besten-casinos-auf-der-ganzen-welt/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
кинопоиск смотреть онлайн кинопоиск смотреть онлайн .
Мы производим качественные промышленные светодиодный светильник для различных отраслей промышленности. Все изделия проходят строгий контроль качества на каждом этапе производства.
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в нежилом здании http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya3.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya1.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство https://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
1 win отзывы http://1win12018.ru/
Подборка статей https://yandex-direct-info.ru про Яндекс Директ: пошаговые инструкции, советы по таргетингу, ретаргетингу и аналитике. Всё о рекламе в Яндексе в одном месте для вашего бизнеса.
Яндекс Бизнес https://business-yandex3.ru описание сервиса, его инструменты и функции. Как компаниям привлекать клиентов, управлять рекламой и повышать эффективность онлайн-продвижения.
Тренери Yantar E-Team зробили неймовірну роботу з підготовки команди. Це був справжній шедевр стратегії!
рулонные шторы кухню цена avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory5.ru .
Откопаться ? данное действие не просто процесс работы с землёй, но и захватывающее исследование земли, что открывает двери к тайнам прошлого. Археология, как наука, предполагает раскопки, позволяющие обнаружить исторические артефакты, предметы старины и подземные ресурсы. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir017.ru можно найти разнообразные материалы о современных методах бурения и анализа почвы, которые помогают в поиске уникальных объектов. Земляные работы, включая excavation, являются основой археологических исследований. Каждый слой почвы, вырываем, может рассказать о жизни людей в разные исторические эпохи. Восстановление найденных артефактов предоставляет шанс лучше понять культуру и технологии прошлых эпох. Геология также занимает ключевую роль в процессе, содействуя в анализе почвы и определении местонахождения объектов, что делает поиски более целенаправленными и эффективными. Таким образом, откопаться – это не только работа с землёй, но и увлекательное путешествие в прошлое, где каждая находка становится важным элементом исторической мозаики.
Играйте в казино и наслаждайтесь захватывающими развлечениями прямо у себя дома!
Очевидно, что игры для пользователей разнообразны. Классические слоты, настольные игры и live-казино
фильмы онлайн без подписки https://kinogo-11.top .
электрокарниз двухрядный http://www.karniz-s-elektroprivodom-kupit.ru .
какие бывают рулонные шторы http://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory15.ru .
I’m not sure why but this weblog is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
https://rainbetaustralia.com/
купить дрова березовые колотые .
скачать мостбет официальный https://www.mostbet12014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Услуги наркологии в владимире играет ключевую роль в помощи людям с зависимостями. Медицинские учреждения, такие как vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir017.ru, осуществляют комплексное лечение для людей, столкнувшихся с наркотической и алкогольной зависимостями. Методы лечения зависимостей охватывают стационарное лечение наркомании и программы реабилитации, которые способствуют возвращению к полноценной жизни.Наркология владимир предоставляет лечение без раскрытия личных данных, что особенно важно для пациентов с зависимостями. Здесь также доступна первичная консультация, где медики проводят диагностику зависимости и разрабатывают индивидуальный план лечения. Семейная поддержка также является важным аспектом процесса реабилитации. Медицинская помощь в владимире предлагает не только лечение алкоголизма, но и профилактические программы, что позволяет избежать рецидивов. Каждому пациенту гарантируется персонализированный подход, что обеспечивает эффективность лечения.
http://forum.amzgame.com/thread/detail?id=270091&page=113
http://www.sports-kz.site История спортивных достижений РК
https://www.golden-forum.com/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=200958
смотреть русские сериалы [url=http://www.kinogo-13.top]http://www.kinogo-13.top[/url] .
Вызов врача нарколога в владимире — это необходимый шаг для людей, испытывающих трудности с зависимостями. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir017.ru можно узнать о о услугах наркологов, включая диагностику зависимостей и медикаментозную терапию. Специалисты нашего центра предлагают профессиональные консультации нарколога и анонимное лечение. Выездная служба наркологии готова предоставить экстренную помощь при запое или в любых других случаях. Наши услуги включают лечение в стационаре и реабилитационные программы для пациентов с наркотической зависимостью. Мы обеспечиваем поддержку зависимых и их родственников и проводим профилактику зависимостей. Не откладывайте помощь — позвоните наркологу и начните путь к лечению.
Привет любители онлайн КАЗИНО!
1win casino зеркало – это твой путь к азартным победам. Играй круглосуточно и без ограничений. Каждый день новые эмоции и драйв. Ты выигрываешь стабильно. 1win casino зеркало всегда работает.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – 1win casino зеркало
Удачи и гарантированных выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Estou pirando com AFun Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura euforia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de danca, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Em resumo, AFun Casino vale demais curtir esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual de purpurina, adiciona um toque de purpurina ao cassino.
afun 10 reais|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
http://mxoemu.info/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=24491
https://www.bookemon.com/member-home/serhrut/1121727
wettbüro aachen
my webpage … comment-61971
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
пластиковые окна москва цена с установкой
40. Пластиковые окна с гарантией 50 лет на рамы и стеклопакеты.
Source:
– okna-plastic-19.ru
http://sochistroygroup.ru – предложения компании
В поисках самых свежих трейлеров фильмов 2026 и трейлеров 2026 на русском? Наш портал — это место, где собираются лучшие трейлеры сериалов 2026. Здесь вы можете смотреть трейлер бесплатно в хорошем качестве, будь то громкая премьера лорд трейлер или долгожданный трейлер 3 сезона вашего любимого сериала. Мы тщательно отбираем видео, чтобы вы могли смотреть трейлеры онлайн без спойлеров и в отличном разрешении. Всю коллекцию вы найдете по ссылке ниже: https://lordtrailer.ru/
Казино Вавада привлекает внимание пользователей.
Бонусные предложения обеспечивают новичкам удобный старт.
Регулярные активности делают процесс динамичным.
Разнообразие развлечений пополняется новыми провайдерами.
Создать аккаунт очень легко, поэтому бонусы становятся доступны сразу.
Узнай больше прямо здесь: https://mailittlechina.com
sports-kz.site Новости бокса и ММА Казахстана
To choose reports, prefer credible publishers, validate facts, note slant and find detail. Crosscheck with multiple articles, use expert insight, and set notifications for topics you monitor. Build media savvy https://smasters.com
darkmatter-mirror-link.cc
заказать дрова с доставкой .
speed cash 1win отзывы 1win12015.ru
накрутить подписчиков в телеграм канал живых накрутить подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
It’s amazing for me to have a web page, which is beneficial designed for my knowledge. thanks admin
кракен зеркало
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя
Wow, incredible weblog format! How long have you ever been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The entire look of your site is magnificent,
as well as the content material!
https://www.silverstripe.org/ForumMemberProfile/show/266008
https://gamesurge.net/profile/SerHrut/
http://sports-kz.site Видеоповторы спорных моментов
переустройство и перепланировка нежилого помещения http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya2.ru .
зеркало кракен актуальное позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. кракен сайт даркнет необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. кракен ссылка актуальная должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
фишинг – главная особенность Кракен.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
перепланировка нежилого здания http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya.ru .
В наше время проблема зависимости от наркотиков и алкоголя приобретает всё большую значимость. Наука наркология предлагает множество решений для борьбы с этими недугами. Если вы или кто-то из ваших знакомых, стоит обратиться к наркологу на дом в круглосуточном режиме в владимире. Зайдите на сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru, где все необходимые услуги.Выездной нарколог предлагает лечение без раскрытия личных данных, что позволяет сохранить личную жизнь пациента в тайне. Круглосуточные услуги дают возможность получить медицинской помощи независимо от времени суток. Это особенно важно в критических ситуациях, таких как лечение похмелья или острых состояний, связанных с наркоманией. Специалисты осуществляют детоксикацию организма, что является важным этапом в лечении зависимости. Клиника, предоставляющая услуги на дому предоставляет не только медицинскую помощь, но и консультацию специалиста по вопросам реабилитации и профилактики рецидивов. Токсикология играют важную роль в этом процессе, так как правильная диагностика обеспечивает выбор оптимальных методов лечения. Услуги на дому — это удобный вариант для пациентов, которые не желают посещать стационар. Выездной нарколог обеспечит индивидуальный подход и комфортные условия для выздоровления. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за помощью, и вы сможете вернуть себе нормальную жизнь!
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk018.ru
вывод из запоя цена
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskoe-strogoe-nizhnee-bele-s-oliver-bc-41561.html
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любых профессий по выгодным ценам. Купить удостоверение интернатуры — kyc-diplom.com/udostoverenie-internatury.html
https://sochistroygroup.ru – онлайн-планировщик
Капельница от запоя на дому: мифы и реальность (владимир) Лечение алкогольной зависимости становится все более актуальной темой. Многие ищут анонимное лечение алкоголизма с помощью нарколога на дом. Одним из популярных методов является капельница от запоя. Однако вокруг этого метода существует множество мифов. Во-первых, миф о том, что капельница, это панацея от запойного состояния. Реальность такова, что она лишь временно облегчает симптомы. Нарколог на дом может предложить комплексный подход к лечению, включая детоксикацию в домашних условиях. Это более безопасно и эффективно. Следующий миф — предположение, что лечение на дому не имеет рисков. Безопасность такого лечения зависит от квалификации специалиста. Услуги нарколога в владимире предлагают опытные и квалифицированные услуги, однако необходимо обращать внимание на опыт врача. Также стоит отметить, что восстановление после запоя требует времени и поддержки. Эффекты капельницы от алкоголя могут быть кратковременными, поэтому важно следовать советам по лечению запоя и не забывать о психологической помощи. Помощь при алкогольной зависимости должна быть комплексной. Избавление от запойного состояния — это не только работа с физическим состоянием, но и с психоэмоциональным. арколог на дом анонимно](https://vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru)
Прокапаться от алкоголя – это важный шаг для освобождения от алкогольной зависимости. Избавление от алкоголизма начинается с процесса детоксикации‚ которая снижает с симптомами похмелья. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir018.ru вы найдете информацию о учреждениях для реабилитации‚ где доступна помощь в лечении зависимостей и поддержка психологов. Программы реабилитации включают поддержку для алкоголиков‚ анонимные алкоголики и мероприятия по улучшению здоровья и профилактике алкоголизма. Осознание воздействия алкоголя на организм помогает осознанно подходить к лечению и восстановлению.
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, oferece uma aventura que brilha como um candelabro em chamas. O catalogo de jogos e um farol de prazeres. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como uma lanterna. respondendo veloz como uma chama acesa. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. mas mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Em sintese, BR4Bet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Vale dizer a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. amplificando o jogo com vibracao luminosa.
br4bet regulamentada|
Sou louco pela velocidade de F12.Bet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino supersonica. As opcoes sao ricas e aceleram como turbo. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como um chassi. garantindo suporte direto e sem freadas. O processo e claro e sem freadas. porem mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. Em resumo, F12.Bet Casino garante um jogo que acelera como um carro para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o visual e uma explosao de curvas. criando uma experiencia de cassino supersonica.
embaixadinha f12 bet|
Sou louco pela torcida de MarjoSports Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que vibra como um apito. O catalogo de jogos e um campo de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e um apito preciso. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao faceis como um apito. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de torcida. Em sintese, MarjoSports Casino e uma quadra de emocoes para os craques do cassino! Vale dizer a interface e fluida e vibra como um estadio. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um gol.
ganhei na marjosports|
https://photo.stackexchange.com/users/148652/1xbetfreespins?tab=profile
киного киного .
http://sports-kz.site/ Новости ММА и боксерских поединков Казахстана
смотреть фильмы бесплатно http://www.kinogo-12.top .
Plunge into the vast universe of EVE Online. Become a legend today. Conquer alongside millions of players worldwide. Start playing for free
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing. The clarity
in your post is simply spectacular and i can assume you are
an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow
me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
bukmeker https://1win12016.ru/
I simply could not depart your web site before suggesting that I really loved the standard
info a person supply in your guests? Is gonna be back frequently in order
to inspect new posts
Attractive component to content. I just stumbled upon your
web site and in accession capital to claim that I
get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will
be subscribing in your feeds and even I achievement
you get admission to consistently quickly.
Thank you, I’ve recently been looking for information about this topic for a while
and yours is the greatest I have came upon so
far. However, what about the conclusion? Are you sure
in regards to the source?
диплом купить с занесением в реестр рязань диплом купить с занесением в реестр рязань .
где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании .
современный дом в сочи – Лофт
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
где купить диплом о высшем образовании где купить диплом о высшем образовании .
Купить диплом техникума в Мариуполь Купить диплом техникума в Мариуполь .
http://www.sports-kz.site Подробная статистика игроков КПЛ
drenazhnye-raboty-spb.ru .
Купить диплом любого ВУЗа!
Наши специалисты предлагаютбыстро и выгодно купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при помощи специального оборудования. Решайте свои задачи быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- paknoukri.com/companies/aurus-diplomany
где купить аттестат о среднем образовании где купить аттестат о среднем образовании .
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
регистрация в 1вин регистрация в 1вин
Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Купить диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в украине
купить живых подписчиков в телеграм купить живых подписчиков в телеграм
диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом легальный купить диплом легальный .
опубликовано здесь гидроцилиндр
скачать mostbet uz https://www.mostbet4175.ru
Как прервать запой в владимире: действенные способы Запой – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального вмешательства. В владимире вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом, что делает процесс лечения более комфортным. Обращение к наркологу на дому дает возможность получить помощь при запое, не выходя из дома. вызов нарколога на дом владимир Основные методы прерывания запоя включают медикаментозное лечение и детоксикацию организма. Эти процедуры помогают устранить физическую зависимость от алкоголя и минимизировать симптомы абстиненции. Психологическая помощь является важным аспектом восстановления, поэтому персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту имеет огромное значение. Реабилитация людей с алкогольной зависимостью охватывает не только медицинские аспекты, но и рекомендации по лечению, а также программы, способствующие возвращению к полноценной жизни. Эффективные методы лечения зависят от степени зависимости и состояния здоровья человека. Если у вас возникли проблемы с алкоголизмом, не медлите с вызовом специалиста на дом. Квалифицированная помощь позволит вам преодолеть запой и начать новый этап жизни без алкоголя;
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в нежилом здании http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya1.ru/ .
купить диплом в днепропетровске купить диплом в днепропетровске .
Very good information. Lucky me I ran across your site by accident (stumbleupon).
I have bookmarked it for later!
купить диплом магистра украины купить диплом магистра украины .
турецкие сериалы на русском языке http://kinogo-11.top/ .
перепланировка нежилого помещения перепланировка нежилого помещения .
купить свидетельство о рождении ребенка http://www.educ-ua5.ru/ .
купить аттестат 11 класс в спб купить аттестат 11 класс в спб .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы – это поистине проверенный метод помощи зависимости от алкоголя, что можно использовать в владимире с помощью врачей-наркологов, работающих на выезде. В процессе используются инъекции определённых растворов, что помогают организму скорее справится с эффектами алкогольного опьянения. При обращении за помощью при запое, вы получите не лишь капельницу для снятия запоя, также советы нарколога. врач нарколог на дом владимир Выведение из запоя гарантирует оперативное улучшение состояния пациента, а безопасность лечения капельного введения обеспечивается опытными специалистами. Помощь нарколога включает детокс-программу, которая направлена на очищение организма. Реабилитация зависимых – это важный момент после терапии, который способствует избежать рецидивов. В городе владимир предоставляются услуги врача нарколога на дом, что позволяет пройти лечение в комфортной обстановке. Не медлите, позвоните за экстренной помощью врача-нарколога уже сегодня!
You really make it seem really easy along with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be really something that I believe I’d never understand.
It sort of feels too complicated and extremely wide for me.
I’m taking a look forward to your subsequent publish,
I will attempt to get the dangle of it!
фантастика онлайн фантастика онлайн .
все займы ру https://zaimy-11.ru/ .
смотреть мультфильмы онлайн бесплатно https://kinogo-14.top .
трансляции футбола казахстан – прямые трансляции игр с комментатором
1 вин зеркало http://www.1win12014.ru
mostbet bet https://mostbet12014.ru
kupit-drova-v-novosibirske-365.ru .
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://paealina.borda.ru/?1-17-0-00000470-000-0-0-1699856819. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
https://www.sochistroygroup.ru/ – строительные секреты
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
تتميز 888starz بشعبيتها في مجال القمار على الإنترنت. يتميز الموقع بتقديم العديد من أنواع الألعاب التي تلبي احتياجات جميع اللاعبين. تتضمن الألعاب المتاحة الرهانات الرياضية، وألعاب الكازينو.
تتمتع 888starz بواجهة مستخدم سهلة الاستخدام. يمتلك المستخدمون القدرة على التنقل بين الأقسام بصورة سلسة. يساهم في جعل تجربة اللعب أكثر جاذبية.
يستطيع المستخدمون الاستفادة من مجموعة متنوعة من المكافآت لجذب اللاعبين الجدد. تشمل هذه المكافآت مكافآت الترحيب بالإضافة إلى العروض الدورية. تعد هذه العروض وسيلة فعالة لزيادة قاعدة اللاعبين.
الأمان هو أحد أولويات 888starz. تستخدم المنصة تقنيات حديثة لحماية بيانات المستخدمين. يضمن ذلك للأعضاء تجربة لعب خالية من المخاطر.
اقوي برومو كود 888starz https://888starz-africa.com/promo-code/
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-korotkie-palto-north-face-bc-5983.html
1wi https://www.1win12018.ru
Уникальное предложение для вашего бизнеса!
Ищете быстрые и недорогие решения для продвижения? Мы предлагаем прогоны с помощью Хрумера и ГСА по собственным уникальным базам!
Почему выбирают нас?
– Доступные цены без скрытых платежей
– Мгновенные результаты — ваш сайт начнет получать трафик уже сегодня!
– Уникальные базы, которые обеспечивают максимальную эффективность
– Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту
Не упустите шанс повысить видимость своего сайта и привлечь новых клиентов! Обращайтесь к нам и получите бесплатную консультацию.
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас и узнайте, как мы можем помочь вашему бизнесу вырасти! узнайте все подробности можно ====>>> ЗДЕСЬ
https://rainbetaustralia.com/
sports-kz.site/ Календарь отборочных матчей сборной
888starz – это один из, широкий выбор азартных игр. внимание игроков. Их уникальные предложения.
разнообразием игровых автоматов, предлагаемых на платформе. известными провайдерами и высококачественной графикой и увлекательным сюжетом. платформа предлагает и с настоящими дилерами, что придаёт.
Важным аспектом. предлагает и вывода средств, что удобным и быстрым. Все транзакции, что гарантирует.
о службе поддержки. команда профессионалов, которая готова помочь. с ними и на любые вопросы. Таким образом, комфорт.
888старз uzbekistan https://888starz2.ru/
drova-berezovye-kolotye-spb.ru .
Hey there outstanding website! Does running a blog similar to this take a massive amount work? I’ve absolutely no expertise in programming however I was hoping to start my own blog soon. Anyway, should you have any ideas or tips for new blog owners please share. I know this is off subject but I simply wanted to ask. Many thanks!
Razed
kinogo kinogo .
https://vgarderobe.ru/sportivnaya-odezhda-dlya-malchikov-nike-bc-12241.html
1win apk login http://1win12015.ru
купить диплом в киеве купить диплом в киеве .
Sou viciado no fluxo de Brazino Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um oceano. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um atol. com slots tematicos de aventuras marinhas. O suporte e um farol subaquatico. respondendo rapido como uma onda quebrando. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um coral. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura marinha. Em resumo, Brazino Casino e um recife de emocoes para os exploradores de jogos online! Alem disso o design e fluido como uma onda. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um recife.
site brazino777|
Adoro a labareda de Verabet Casino, oferece uma aventura que reluz como brasas vivas. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como labaredas. O suporte e uma tocha de eficiencia. respondendo rapido como uma labareda. Os saques sao velozes como um ritual de fogo. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam incendiarios. Em sintese, Verabet Casino garante um jogo que reluz como chamas para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Por sinal a navegacao e facil como uma labareda. fazendo o cassino queimar como uma fogueira.
bet vera login|
mostbet promo bilan ro‘yxatdan o‘tish mostbet promo bilan ro‘yxatdan o‘tish
Sou louco pela matriz de PlayPix Casino, parece uma matriz de adrenalina cibernetica. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. O servico e confiavel como um backup. respondendo veloz como um byte. Os saques processam como servidores. mesmo assim queria mais promocoes que glitcham como retro. Na real, PlayPix Casino e uma onda de adrenalina digital para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! Adicionalmente o layout e vibrante como um codigo. dando vontade de voltar como um byte.
casino playpix|
http://www.sochistroygroup.ru – строительные наработки
1win код 1win код
Alpha Festival – це місце, де музика і технології створюють справжню магію. Відвідайте фестиваль майбутнього і пориньте у світ звуку та світла.
заказать шлюху в балашихе
мостбет приложение мостбет приложение
http://www.jetzt-fragen.de/esteroides-en-espaa.html
https://www.businesslistings.net.au/Esteroides/Spain/Dollartworks/1175774.aspx
мостбет ставки на спорт https://mostbet12015.ru
купить куб дров береза .
drenazh-uchastka-spb.ru .
kupit-drova-v-kazani-365.ru .
Онлайн-казино Vavada популярно у игроков.
Промокоды и бонусы дают возможность играть без вложений.
Игровые события открывают шанс на крупные выигрыши.
Игровой каталог включают современные разработки.
Создать аккаунт несложно, и бонусы становятся доступными сразу.
Подробнее об этом смотрите здесь: https://visualizeyourlearning.com
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-sumki-na-kazhdyi-den-collezione-alessandro-bc-24233.html
смотреть комедии онлайн смотреть комедии онлайн .
аниме смотреть онлайн аниме смотреть онлайн .
все займы онлайн https://www.zaimy-11.ru .
смотреть мультфильмы онлайн бесплатно https://kinogo-12.top/ .
drova-nedorogo-spb.ru .
дрова колотые сухие дешево .
drenazh-uchastka-spb.ru .
займы все http://www.zaimy-12.ru .
https://forum.codeigniter.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=192590
https://www.band.us/page/100011444
взо http://zaimy-13.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал бесплатно накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал бесплатно
This is my first time go to see at here and i am genuinely happy to read everthing at single place.
tutbonus.com
https://sochistroygroup.ru – строительный онлайн-справочник
Игровая платформа Вавада часто обсуждается в сети.
Акции и промокоды дают шанс начать игру без вложений.
Регулярные акции повышают интерес.
Подборка игр обновляются регулярно.
Регистрация проста, и можно начать играть без задержек.
Узнай подробности прямо здесь: акции vavada
Для тех, кто ищет проверенный доступ к KRAKEN, всегда можно использовать https://www.krakr.cc — ссылка ведёт напрямую на официальный сайт.
Актуальный KRAKEN сайт всегда доступен по адресу https://krakr.cc, этот вариант сохраняет стабильность даже при блокировках.
Актуальная KRAKEN ссылка открывает дорогу в сервис кракен даркнет
.
sportwette ohne oasis
Feel free to visit my web page; Professionelle wett tipps heute
аниме смотреть онлайн аниме смотреть онлайн .
Официальное кракен входпомогает всегда оставаться в сети. Вход выполняется быстро, а маркет открывается полностью.
Слухайте DJ Gafur Ambient Radio, щоб насолодитись найсвіжішими Ambient-ритмами в режимі 24/7!
проститутки недорого Новосибирск
С учетом этих рекомендаций, выбор может стать более безопасным и приятным.
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru/ Международные награды казахстанских атлетов
Рабочее KRAKEN зеркало — это удобный способ попасть в кракен личный кабинет.
Что такое Agile https://agile-metod.ru и как его внедрить? Подробные статьи о гибких методологиях, инструментах и практиках. Scrum, Kanban и Lean — всё о современном управлении проектами.
Что такое CPI https://cost-per-install.ru в маркетинге? Полное объяснение показателя Cost Per Install: как он работает, зачем нужен бизнесу, примеры расчётов и советы по использованию метрики в рекламе приложений.
Ad Networks
Промокод для 1xBet это особая комбинация символов и цифр на бонус до 32 500 рублей. Действует это предложение только для новых игроков и после регистрации они получают 130% от суммы пополнения первого депозита.
Используйте Промокод который описсан более подробно в этой статье
1хбет промокод первый депозит чтобы получить гарантированный бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей (или эквивалентную сумму в другой валюте €130). Это предложение доступно только для новых пользователей.
Воспользуйтесь этим кодом, чтобы получить бонус от 1хбет. Просто введите код в анкете при регистрации и пополните свой счет на сумму от 100 рублей. Вам будет начислен бонус в размере 130%, который может достигать до 32500 рублей.
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст вам дополнительные бонусы и преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы воспользоваться этим промокодом, вам необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте и пройти процедуру верификации. После этого вы сможете получить бонус по промокоду или при пополнении счета. Также вы можете получить бонус, если пригласите друга или примете участие в определенных акциях.
https://www.te-in.ru/arenda-dizel-generatorov.html/
как набрать подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно как набрать подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно
Для быстрого входа лучше всего использовать krakr.cc/, ссылка проверена.
Удобно заходить на сайт через http://www.krakr.cc, особенно если основной адрес недоступен.
кракен сайтоткрывает прямой путь в маркет. Найдите актуальную ссылку, следуйте подсказкам и получите безопасный доступ к сайту с полным функционалом.
Для обхода блокировок достаточно кракен личный кабинет. Рабочее зеркало открывает маркет и позволяет авторизоваться в личном кабинете.
футбол обзоры казахстан – детальные разборы игр КПЛ
cocaine in prague prague drugstore
Расчёт довольствия Росгвардия: спецhttps://svoinfo.ru/альное звание капитан, 55 000 руб. плюс боевые, если СВО.
KRAKEN маркет доступен в любой момент. Просто выберите кракен личный кабинет или онион-ссылку и вход займёт всего пару секунд.
https://loveshop1300.shop now alive, welcome,loveshop1300 new website!
раздвижные шторы http://www.razdvizhnoj-elektrokarniz.ru/ .
Je suis envoute par Grandz Casino, on dirait un theatre de frissons evanescents. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et ephemeres. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un theatre. repond comme un fantome gracieux. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse etheree. cependant des tours gratuits pour une melodie ephemere. En somme, Grandz Casino est un casino en ligne qui joue une danse d’ombres pour les fans de symphonies d’ombres! De plus l’interface du casino est fluide et danse comme une ombre. facilite une experience de casino voilee.
bonus grandz race|
Sou viciado no reverb de Stake Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um sino. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. com caca-niqueis que vibram como harpas. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma onda sonora. assegurando apoio sem dissonancias. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. de vez em quando as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Ao final, Stake Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro eco para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
codigo de recompensa stake|
все займ http://zaimy-15.ru/ .
список займов онлайн на карту http://zaimy-14.ru/ .
все займы рф http://zaimy-12.ru .
мфо займ https://zaimy-13.ru .
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг бесплатно
живые подписчики в телеграм канал
Приобрести диплом института!
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам— peoplediplom.ru
Играйте в казино онлайн и наслаждайтесь захватывающими развлечениями прямо у себя дома!
Казино онлайн в Беларуси
сколько стоит куб березовых дров .
Казахстан футбольные трансляции – live футбольных матчей с комментарием
https://mp-digital.ru/
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм купить
доставка дров круглосуточно .
kinogo kinogo .
все займы ру http://www.zaimy-11.ru .
kinogo kinogo .
drenazh-uchastka-spb.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм недорого
Для удобства сохраняйте https://www.krakr.cc/, чтобы всегда иметь под рукой рабочее зеркало.
купить диплом колледжа недорого купить диплом колледжа недорого .
Купить диплом техникума в Кривой Рог Купить диплом техникума в Кривой Рог .
Рабочее зеркало доступно по адресу https://www.krakr.cc/, оно открывает весь функционал.
купить диплом в киеве недорого купить диплом в киеве недорого .
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро и выгодно купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с применением специальных приборов. Достигайте свои цели быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- twizzr.worldsofrp.com/read-blog/4909_gde-v-moskve-kupit-diplom.html
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru Профессиональный анализ матчей КПЛ
Website https://useit2.ru/.
купить диплом о высшем киев http://educ-ua17.ru .
купить живых подписчиков в тг
code bonus 1xbet senegal
купить диплом с реестром купить диплом с реестром .
1 dollar deposit casinos canada
promo code for 1xbet bangladesh
1xbet free promo code nepal
где купить подписчиков в телеграм
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/171056105/detail.aspx
https://sports-kz-news.ru/ Видеообзоры турниров и чемпионатов
Website https://tione.ru/ .
купить настоящий диплом купить настоящий диплом .
купить учебный диплом в одессе купить учебный диплом в одессе .
купить аттестат за 11 класс челябинск купить аттестат за 11 класс челябинск .
танк 300 машина http://tank-3001.ru
code bonus 1xbet cm
Если ссылка заблокирована, используйте http://www.krakr.cc, этот адрес доступен круглосуточно.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в калуге купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в калуге .
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это идеальное решение для создания уюта и комфорта в вашем доме, позволяющее управлять светом и приватностью с помощью простого нажатия кнопки.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом завоевывают популярность среди покупателей. Такие шторы – это отличное решение для любого помещения. Удобство и функциональность делают эти шторы идеальным выбором.
Одним из главных преимуществ является возможность управления шторами с помощью пульта. Это позволяет легко регулировать уровень освещения в помещении. С его помощью можно программировать автоматическое открытие и закрытие штор.
Монтаж рулонных штор с электроприводом осуществляется достаточно быстро. Вам потребуется минимальный набор инструментов и немного времени. Разнообразие материалов и дизайна позволяет выбрать подходящие шторы для любого стиля.
Эти шторы не только добавляют стиль в интерьер, но и защищают от яркого солнца. Разные варианты тканей дают возможность изменять уровень затемнения помещения. Это позволяет создавать уютную атмосферу в вашем доме.
купить диплом с реестром в москве купить диплом с реестром в москве .
Если вы хотите быть уверены в доступе, используйте рабочее зеркало http://www.krakr.cc, оно открывает все функции площадки.
Храните у себя актуальный адрес https://krakr.cc/, чтобы не потерять доступ к сайту и всегда иметь возможность безопасного входа.
Актуальное KRAKEN зеркало кракен магазин открывает все разделы ресурса.
buy weed prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
раздвижные карнизы http://www.razdvizhnoj-elektrokarniz.ru .
мфо займ мфо займ .
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг дешево
sports-kz-news.ru Достижения казахстанских борцов
займ все https://zaimy-16.ru .
все займы на карту все займы на карту .
купить диплом в реестре купить диплом в реестре .
купить диплом о высшем образовании легально http://educ-ua15.ru/ .
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
купить диплом техникума отзывы купить диплом техникума отзывы .
все займы онлайн на карту http://www.zaimy-11.ru/ .
фантастика онлайн фантастика онлайн .
смотреть фильмы бесплатно смотреть фильмы бесплатно .
все онлайн займы http://www.zaimy-13.ru .
Get the facts on all medicines when you http://synthroidvslevothyroxine.com/ pills quoted here are amazing
займы zaimy-12.ru .
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru Официальный источник спортивных новостей РК
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
купить реальный диплом о высшем образовании купить реальный диплом о высшем образовании .
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал боты
Je suis fou de RollBit Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui deroule comme un bit en chaine. est une structure de sensations qui enchante. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cubique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. resonnant comme une matrice parfaite. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse bit. parfois des offres qui vibrent comme une cadence pixelisee. Au final, RollBit Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! En bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style bit. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie de pixels.
rollbit coin news|
Sou louco pela roda de XPBet Casino, e um redemoinho de diversao que se repete. Os jogos formam um redemoinho de diversao. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque eterno. O time do cassino e digno de um roteirista. com ajuda que flui como um vortice. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. porem queria mais promocoes que giram como espirais. Na real, XPBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro ciclo para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a navegacao e facil como um loop. amplificando o jogo com vibracao eterna.
xp bet Г© confiГЎvel|
купить диплом о техническом образовании купить диплом о техническом образовании .
Sou viciado no brilho de DonaldBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como um acrobata. A selecao de titulos e uma tenda de emocoes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como holofotes. O servico e confiavel como uma corda bamba. com ajuda que ilumina como um refletor. O processo e claro e sem cortinas. ocasionalmente mais bonus seriam um diferencial acrobatico. Em resumo, DonaldBet Casino e um picadeiro de emocoes para os cacadores de vitorias malabaristicas! Alem disso o visual e uma explosao de lonas. dando vontade de voltar como um trapezista.
quem Г© o dono da donaldbet|
http://sports-kz-news.ru Спортивные традиции народов Казахстана
Автоматические рулонные шторы не только обеспечивают удобство управления, но и стильный акцент в интерьере вашего дома, особенно если вы выберете автоматические рулонные шторы|автоматика для рулонных штор|автоматические шторы для труднодоступных окон.
Во-первых, они позволяют легко регулировать уровень освещения в комнате.
диплом автотранспортного техникума купить в https://www.educ-ua9.ru .
техникум купить диплом https://educ-ua8.ru/ – техникум купить диплом .
Visit omh
super bowl wetten deutschland
Feel free to visit my web site beste wettstrategien [https://motionentrance.edu.np/]
купить дипломы в Киеве купить дипломы в Киеве .
футбол казахстан новости – сборная о нашем футболе сейчас
KRAKEN всегда работает через http://krakr.cc, этот адрес безопасный.
Самый простой способ попасть в личный кабинет — воспользоваться прямой ссылкой krakr.cc, которая проверена и работает без перебоев.
Рабочее зеркало кракен сайт — это удобное решение для тех, кто хочет пользоваться сервисом постоянно.
promo code for 1xbet bangladesh
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без заданий
все займы на карту все займы на карту .
Сепараторы воздуха и шлама Сепараторы воздуха и шлама – устройства, предназначенные для удаления воздуха и шлама из теплоносителя системы отопления. Удаление воздуха предотвращает коррозию и шумы в системе, а удаление шлама предотвращает засорение отопительных приборов.
http://sports-kz-news.ru/ Обсуждения трансферной политики клубов
https://banglamovies.online/terminator-salvation/
психолог самооценка Психолог для всех – это не просто профессия, это призвание помогать людям. Специалист, обладающий широким спектром знаний и навыков, готов поддержать в любой жизненной ситуации: от профессионального выгорания до проблем в личных отношениях. Это не просто советчик, это компас, помогающий найти верное направление и обрести уверенность в себе.
Реплики часов для женщин Реплики сумок Луи Виттон позволяют идти в ногу со временем, не sacrificing style for cost. Актуальные модели, классические силуэты – вы сможете подобрать идеальный аксессуар для любого случая, будь то деловая встреча или романтическое свидание. Материалы и фурнитура, используемые в качественных репликах, позволяют сумке долго сохранять свой первоначальный вид.
Графитовые и угольные щетки для электроинструмента. Большой выбор, надёжность и долговечность. Подходят для дрелей, болгарок, перфораторов и другого оборудования.
drova-nedorogo-spb.ru .
Нужны двери? межкомнатные двери недорого Широкий ассортимент межкомнатных дверей от Вектордорс. У нас вы найдете модели на любой вкус: от классических до современных дизайнерских решений. Выбор межкомнатных дверей — важный этап обустройства помещения. Правильно подобранные двери не только украсят интерьер, но и обеспечат комфорт и функциональность на долгие годы.
Visit ymd
раздвижные электрокарнизы для штор http://razdvizhnoj-elektrokarniz.ru/ .
Электрические жалюзи электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи с дистанционным управлением|электрические жалюзи на мансардные окна|купить электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи в москве|электрические жалюзи автоматические|электрические жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить|электрические жалюзи стоимость|электрические жалюзи на окна заказать — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, обеспечивающее комфорт и стиль.
Такое управление особенно удобно в просторных помещениях с высокими окнами.
лучшие займы онлайн лучшие займы онлайн .
накрутка подписчиков в тг смм накрутка
купить диплом инженера механика купить диплом инженера механика .
микрозайм всем http://zaimy-14.ru .
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Аналитика чемпионата Казахстана по футболу
нейропсихолог в москве Логопед в Москве: Логопед – это специалист, занимающийся диагностикой, коррекцией и профилактикой нарушений речи у детей и взрослых. В Москве логопеды работают с широким спектром речевых нарушений, таких как дислалия (нарушение звукопроизношения), дизартрия (нарушение артикуляции, вызванное поражением нервной системы), алалия (отсутствие или недоразвитие речи), заикание, общее недоразвитие речи (ОНР) и другие. Логопедическая коррекция направлена на развитие фонематического слуха, артикуляционной моторики, грамматического строя речи, словарного запаса и других аспектов, необходимых для полноценного общения. Логопеды используют различные методы и приемы, адаптированные к индивидуальным потребностям каждого пациента, чтобы помочь им развить четкую и выразительную речь, преодолеть речевые трудности и успешно общаться с окружающими.
купить диплом железнодорожника купить диплом железнодорожника .
купить диплом в старом осколе купить диплом в старом осколе .
Джинсы мужские прямые Джинсы мужские: Мужские джинсы – это краеугольный камень современного гардероба, символ стиля, комфорта и универсальности. От рабочих штанов старателей до модной иконы, джинсы прошли долгий путь, адаптируясь к меняющимся вкусам и потребностям. Сегодня рынок предлагает огромное разнообразие моделей, от классических облегающих до ультрасовременных широких силуэтов, выполненных из самых разнообразных материалов – от традиционного денима до инновационных смесовых тканей. Независимо от вашего личного стиля, правильно подобранные джинсы способны подчеркнуть достоинства фигуры, добавить уверенности и стать надежным спутником в любых ситуациях. Будь то повседневные прогулки, деловые встречи или вечеринки с друзьями, мужские джинсы всегда придут на помощь, если правильно подобраны по размеру, стилю и сочетаются с остальными элементами вашего образа. Инвестируйте в качественную пару джинсов, и она прослужит вам верой и правдой долгие годы.
купить диплом в саранске купить диплом в саранске .
купить диплом инженера электрика купить диплом инженера электрика .
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
kupit-drova-v-kazani-365.ru .
Rege Cazinou login Autentificare rapidă la Rege Cazinou – intră și joacă acum.
«Енергетичний імпульс» вразив своєю масштабністю та атмосферою. Лазерні шоу були такими яскравими, що не можна було відірвати погляд. DJ Wilkinson створював музику, яка буквально запалювала кожного гостя. Особливо захопили інтерактивні тунелі, що змінювали кольори в такт музиці. Браслети, які світилися під ритми, були ідеальним доповненням до загальної атмосфери. Якщо хочете пережити щось подібне, дізнайтеся більше про фестиваль.
wettbüro bremerhaven
Feel free to surf to my site buchmacher bedeutung [Carlota]
психотерапевт онлайн Психолог для всех – это не просто профессия, это призвание помогать людям. Специалист, обладающий широким спектром знаний и навыков, готов поддержать в любой жизненной ситуации: от профессионального выгорания до проблем в личных отношениях. Это не просто советчик, это компас, помогающий найти верное направление и обрести уверенность в себе.
Казахстан футбольные трансляции – прямой эфир футбольных матчей в HD
Wow, amazing blog format! How long have you ever been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy. The whole look of your site is fantastic, as neatly as the content!
online casinos
Добрый день
Недавно я нашёл замечательную Видео наблюдение –dahua
P.S. Dahua Technology – Время смотреть в будущее!
Всем пока
Me realize in what way scary that strikes once fluid puts your house together with loved ones’ ease in danger.
Still you’re hardly solitary.
We remain present aiming to protect one’s dwelling plus this kindness belonging to one’s kin existence, working carefully along with harmlessly such that all one cherish persists intact.
Our squad functions immediately to stop devastation plus avoid mildew, granting somebody serenity from thought.
And with our round-the-clock assistance, you perpetually maintain a helper beside one’s presence — prepared toward aid someone maintain yours loved ones safe and yours home supplied by convenience.
Find peace in your home – Call: 8338561951
Купить реплику часов Ролекс Реплики сумок Луи Виттон позволяют идти в ногу со временем, не sacrificing style for cost. Актуальные модели, классические силуэты – вы сможете подобрать идеальный аксессуар для любого случая, будь то деловая встреча или романтическое свидание. Материалы и фурнитура, используемые в качественных репликах, позволяют сумке долго сохранять свой первоначальный вид.
Рабочее KRAKEN зеркало — это удобный способ попасть в кракен вход.
купить подписчиков в телеграм
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
drenazh-uchastka-spb.ru .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр http://www.frei-diplom1.ru .
Рабочее зеркало кракен маркет ведёт прямо в маркет без лишних шагов.
KRAKEN сайт даёт возможность подключаться с любых устройств. Рабочая ссылка открывает кракен личный кабинет без ограничений.
This includes clear audio, good lighting, and professional editing to create a polished final product.
impact beyond text reviews https://videonewsindex.com/why-video-reviews-matter-more-than-you-think/
что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
гравий речной цена https://pesko.ru
сколько стоит 2 куба дров .
купить диплом с проведением в купить диплом с проведением в .
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
дизайнерские горшки для комнатных растений https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/ .
купить диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением .
купить диплом техникума в петрозаводске купить диплом техникума в петрозаводске .
купить диплом техникума дешево купить диплом техникума дешево .
где купить дипломы медсестры где купить дипломы медсестры .
CPL (Cost Per Lead) https://cost-per-lead1.ru ключевая метрика рекламы. Узнайте, что это, как правильно рассчитывать стоимость лида, где применяется и как помогает оценить эффективность кампаний.
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, используя карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом для штор|потолочные карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом цена|карнизы с электроприводом купить|карнизы с электроприводом с дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным|карнизы с электроприводом и пультом управления купить|Карнизы с электроприводом для вашего дома!
Выбирая подходящий вариант, стоит обращать внимание на несколько факторов.
диплом техникума купить цена educ-ua7.ru .
kupit-drova-v-kazani-365.ru .
накрутка подписчиков тг канале купить
новости спорта казахстана – онлайн последние спортивные события
купить диплом в новокузнецке купить диплом в новокузнецке .
купить диплом химика купить диплом химика .
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Globalement, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Notons egalement que le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino 25|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de BetFury Casino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Les agents sont toujours professionnels et efficaces, garantissant une aide via chat ou email. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, de temps en temps ??? davantage de recompenses comme les BetFury Boxes seraient appreciees. Pour conclure, BetFury Casino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et intuitive, ce qui renforce l’immersion.
token betfury|
1xbet promo code bangladesh
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
купить диплом гознак купить диплом гознак .
Интернет-маркетинг https://internet-marketing1.ru SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, email-рассылки и аналитика. Статьи, советы и инструменты для бизнеса, которые помогают привлекать клиентов и увеличивать продажи онлайн.
купить диплом в новом уренгое http://rudik-diplom13.ru .
купить диплом в анапе купить диплом в анапе .
электрические карнизы купить https://www.razdvizhnoj-elektrokarniz.ru .
схема устройства дренажа вокруг дома .
купить диплом медицинского училища купить диплом медицинского училища .
все микрозаймы онлайн http://zaimy-15.ru .
купить диплом математика купить диплом математика .
Интернет-маркетинг https://yandex-reklama2.ru для компаний и специалистов: SEO, SMM, контекстная реклама и email. Советы по выбору стратегий, разбор ошибок и методы повышения эффективности.
Ссылка KRAKEN активна.
https://telegra.ph/Ne-zabyvajte-pro-mobilnye-ustrojstva-Obespechte-adaptivnyj-dizajn-uchityvayushchij-razlichiya-v-razmerah-1-09-18
Проверенная ссылка KRAKEN — вход прошёл без заминок.
https://telegra.ph/Kazhdyj-iz-ehtih-aspektov-formiruet-ne-tolko-komfortnoe-ispolzovanie-no-i-uroven-doveriya-k-vybranno2-09-18
hzy vdr
http://sports-kz-news.ru Новости профессионального бокса Казахстана
купить диплом в королёве купить диплом в королёве .
живые подписчики в телеграм
купить аттестаты за 11 купить аттестаты за 11 .
живые подписчики в телеграм
Choose a pharmacy with good customer service to https://synthroidvslevothyroxine.com/ pharmacy that offers a discount on its products?
купить диплом техникума 1997 купить диплом техникума 1997 .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
купить жд диплом техникума купить жд диплом техникума .
ctk qzo
где можно купить диплом техникума в челябинске где можно купить диплом техникума в челябинске .
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru/ Самые последние известия о спорте РК
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять шторами с помощью пульта.
Электрокарниз может иметь множество функций, которые облегчают его использование.
mnv gwy
Зеркала KRAKEN доступны.
https://telegra.ph/Platforma-predostavlyaet-polzovatelyam-massu-vozmozhnostej-dlya-obmena-tovarami-i-uslugami-Preimushchestv1-09-18
Enjoy the authentic nuru massage Bangkok
experience designed for comfort, intimacy, and total rejuvenation.
Experience the ultimate relaxation with Hiso Massage
offering professiona
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
laj stl
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал боты
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru Эксклюзивные материалы о спорте Казахстана
накрутка подписчиков тг
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно онлайн
det dtq
Зеркала KRAKEN работают отлично.
https://telegra.ph/Proveryajte-nastrojki-konfidencialnosti-Poskolku-informaciya-mozhet-byt-dostupna-drugim-uchastnikam-2-09-18
Myself understand how frightening this strikes whenever moisture causes their residence together with relatives’ security under danger.
However you continue hardly solitary.
We will be ready for the purpose of preserve yours home plus such affection belonging to one’s household day-to-day, operating thoughtfully along with harmlessly in order that all things yourself adore keeps unbroken.
Such crew functions swiftly toward halt devastation together with avoid spores, offering yourself relief belonging to mind.
And together with that 24/7 service, you perpetually have a partner close to your position — willing toward help you keep the family safe along with yours property filled through comfort.
Find peace in your home – Call: 8338561951
прогнозы матчей казахстан – проверенные прогнозы на футбол
Helpful treatment is available when you buy http://metoprololvslopressor.com/ brand and generic product?.
Πολύ ενδιαφέρον και αναλυτικό
άρθρο! Η αλήθεια είναι ότι
fduty.com αποτελεί ιδανική λύση για όσους
ξεκινούν τώρα και χρειάζονται
προετοιμασία χωρίς να χάσουν λεφτά.
Το έχω τεστάρει αρκετά και με βοήθησε να κατανοήσω τη ροή και
τους κανόνες. Η δεύτερη έκδοση με εντυπωσίασε, γιατί έχει επιπλέον χαρακτηριστικά και την
κάνει πιο διασκεδαστική.
Η εύκολη χρήση σε κινητές συσκευές είναι από
τα δυνατά του σημεία. Η απουσία οικονομικού ρίσκου βοηθά στο να παίζεις ελεύθερα και για διασκέδαση και τη μάθηση.
Για όποιον σκέφτεται να δοκιμάσει το Plinko,
το καλύτερο είναι να ξεκινήσει από εκεί.
Περιμένω με ενδιαφέρον κι άλλα άρθρα για σχετικές εκδόσεις ή tips!
микро займы онлайн микро займы онлайн .
проститутки недорого Новосибирск
Следуя этим советам, можно сделать процесс выбора более комфортным.
Получить диплом любого ВУЗа поспособствуем. Купить диплом магистра в Кургане – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-magistra-v-kurgane
мфо займ zaimy-13.ru .
всезаймыонлайн http://www.zaimy-14.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые без отписок
взо взо .
все займы онлайн все займы онлайн .
дренаж цена за метр .
At WebPtoPNGHero.com, converting WebP images into PNG format couldn’t be simpler. The interface features a drag-and-drop area where images load instantly, and conversion begins on secure cloud servers. A progress meter keeps you informed, and once each file finishes, PNG versions appear as clickable download links. If you have many images to process, batch mode handles multiple files at the same time, saving precious minutes. The tool runs entirely in your web browser, making it compatible with Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS alike. No need to install any applications or plugins—just open the site and start converting. All uploads vanish shortly after processing, ensuring privacy and security. Whether you’re optimizing visuals for an e-commerce store, preparing photos for email attachments, or simply sharing snapshots online, WebPtoPNGHero.com delivers reliable, high-fidelity results. The service remains free and ad-free, with no registration required. Convert your WebP images to universally supported PNG files quickly and without hassle.
WebPtoPNGHero
sports-kz-news.ru/ Актуальный рейтинг команд КПЛ
J’adore le delire de FatPirate, ca donne une energie de pirate dejantee. Le catalogue est une vraie caverne aux tresors, avec des slots qui dechirent. L’assistance est carrement geniale, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus est clean et sans galere, des fois des recompenses en plus ca serait la cerise. Pour resumer, FatPirate garantit un fun total pour les accros aux sensations fortes ! Et puis le design est style et accrocheur, ajoute un max de swag.
fatpirate casino app|
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, on dirait une scene de fun explosif. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, proposant des sessions live qui en mettent plein la vue. Le crew assure un suivi etoile, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les paiements sont securises et eclatants, de temps en temps j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. Bref, Impressario est une plateforme qui vole la vedette pour les accros aux sensations eclatantes ! Bonus la navigation est simple comme une melodie, facilite un show total.
impressario casino login|
Официальный ресурс KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Pravilnoe-ispolzovanie-bezopasnyh-koshelkov-dlya-hraneniya-aktivov-takzhe-imeet-znachenie-Apparatnye-09-18
как набрать подписчиков в телеграм канале
Students, professionals, and hobbyists alike rely on OneConverter.com as a trusted resource. High school students use it to complete homework questions, ensuring they understand how to convert between units of volume or temperature. College researchers appreciate its scientific precision when dealing with complex conversions in physics or engineering. Business professionals often need quick currency or time zone calculations to plan international meetings; this site delivers those results instantly. DIY enthusiasts measure materials for home improvement projects by converting square feet to square meters or gallons to liters. Photographers evaluate storage needs by converting between megabytes and gigabytes. Fitness trainers track distances and energy expenditure by switching between miles and kilometers or calories and kilojoules. With OneConverter, there’s no need to memorize dozens of conversion factors — just input your number, choose your units, and the answer appears. The clear layout and straightforward instructions help users learn as they go, making the site both a tool and a teaching aid. Regardless of your field or expertise level, OneConverter.com provides the conversions you need, right when you need them.
OneConverter
Услуги по составлению ответов на требования налоговой .
продолжить нова маркетплейс вход
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
купить подписчиков в телеграм без отписок
Website https://tione.ru/ .
купить куб березовых дров .
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru Турнирная таблица чемпионата Казахстана
Привет всем!
Ищете, где купить постоянный виртуальный номер? Мы предлагаем широкий выбор номеров для любых целей. Постоянный виртуальный номер для смс – это удобное решение для работы и личной жизни. Купите виртуальный номер навсегда и получите стабильную связь. Доступность и качество наших услуг вас приятно удивят.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://louistlzh53211.blogdon.net/het-belang-van-tijdelijke-telefoonnummers-een-diepgaande-verkenning-42869365
Виртуальный номер навсегда, купить номер телефона навсегда, купить номер телефона навсегда
постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
paysafecard sportwetten
My web site; wetten strategie
Подача жалоб в трудовую инспекцию .
Официальный ресурс KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Obratite-vnimanie-na-falshivye-ssylki-Ubedites-chto-ispolzuete-aktualnuyu-ssylku-na-sajt-Zaranee-1-09-18
sports-kz-news.ru Спортивная статистика и результаты
Генеральная уборка https://cleaningplus.ru/services/uborka-kvartiry в Москве: квартиры, дома, офисы. Полный комплекс услуг — мытьё окон, чистка мебели, удаление пыли и грязи. Профессиональные клинеры, безопасные средства и гарантия качества.
sportwetten vorhersage
Stop by my website – test Wettanbieter
Picture this: you’re cooking dinner and the recipe calls for grams, but your scale only shows ounces. Later, you’re helping your child with homework and suddenly need to convert meters per second into kilometers per hour. The next morning, you’re preparing a presentation and realize the client wants it in PDF format. Three different situations, three different problems – and usually, three different apps.
That’s the hassle OneConverter eliminates. It’s an all-in-one online tool designed for people who want life to be simpler, faster, and smarter. No downloads, no subscriptions, no headaches – just answers, right when you need them.
Unit Conversions Made Effortless
Most conversion tools handle only the basics. OneConverter goes further – much further. With more than 50,000 unit converters, it can handle everyday situations, advanced academic work, and professional challenges without breaking a sweat.
Everyday Basics: length, weight, speed, temperature, time, area, volume, energy.
Engineering & Physics: torque, angular velocity, density, acceleration, moment of inertia.
Heat & Thermodynamics: thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, entropy, enthalpy.
Radiology: absorbed dose, equivalent dose, radiation exposure.
Fluids: viscosity, flow rate, pressure, surface tension.
Electricity & Magnetism: voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, inductance, flux.
Chemistry: molarity, concentration, molecular weight.
Astronomy: light years, parsecs, astronomical units.
Everyday Extras: cooking measures, shoe and clothing sizes, fuel efficiency.
From the classroom to the lab, from the office to your kitchen – OneConverter has a solution ready.
OneConverter
Через TOR открылось зеркало KRAKEN — вход безопасный и быстрый.
https://telegra.ph/Regulyarno-testirujte-interfejs-na-prostotu-ispolzovaniya-Vazhno-poluchat-obratnuyu-svyaz-ot-dejstvuyushch1-09-18
займер ру займер ру .
sports-kz-news.ru Эксклюзивные интервью со спортсменами РК
It’s awesome to pay a quick visit this website and reading the views of all friends about this piece of writing, while I am also keen of getting experience.
лучшие займы онлайн лучшие займы онлайн .
kupit-drova-v-kazani-365.ru .
купить диплом в сарапуле купить диплом в сарапуле .
купить диплом в обнинске https://www.rudik-diplom11.ru .
купить диплом маркетолога купить диплом маркетолога .
Через официальный сайт KRAKEN и TOR можно попасть без проблем.
https://telegra.ph/Posle-togo-kak-vy-uverenno-prodelali-vse-shagi-bezopasnogo-dostupa-ne-zabudte-pro-kraken-vhod-Zdes2-09-18
купить аттестат за 11 класс купить аттестат за 11 класс .
все микрозаймы онлайн все микрозаймы онлайн .
список займов онлайн на карту список займов онлайн на карту .
все займы ру все займы ру .
список займов онлайн https://zaimy-22.ru .
займы онлайн займы онлайн .
займер ру займер ру .
все займы zaimy-23.ru .
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Программы тренировок казахстанских атлетов
все займы на карту все займы на карту .
Myself know the manner alarming that seems as soon as liquid sets yours house plus household’s comfort toward risk.
Nevertheless you continue by no means on your own.
We’re around aiming to preserve yours residence and this kindness belonging to the household lifestyle, operating thoughtfully along with harmlessly so everything you treasure continues intact.
That crew works quickly aiming to cease loss plus reduce growth, providing you relief belonging to mind.
And together with such 24/7 aid, you constantly have a person close to the company — equipped so as to help somebody protect yours kin sheltered together with their residence supplied by well-being.
Find peace in your home – Call: 8338561951
Предметы бухгалтерской экспертизы .
купить диплом техникума ссср в астрахани купить диплом техникума ссср в астрахани .
легально купить диплом о легально купить диплом о .
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены .
легальный диплом купить легальный диплом купить .
Официальный сайт KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Ssylka-na-resurs-chasto-obnovlyaetsya-Dlya-nahozhdeniya-aktualnoj-versii-ispolzujte-poiskovye-sistemy-i2-09-18
купить диплом врача с занесением в реестр купить диплом врача с занесением в реестр .
где можно купить диплом медсестры где можно купить диплом медсестры .
Онлайн-сервис 1хБет дарит каждому пользователю 100% бонус на первый депозит до 32 500 RUB (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Помимо этого, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 вместе со 150 FS для использования в слотах и автоматах.
промокоды приложение 1xbet Только с его помощью вы сможете получить бонус фрибет в размере 32500 рублей. Фрибет 1хБет 2025 предоставляет уникальную возможность игрокам получить бесплатную ставку и использовать ее без каких-либо вложений со своего счета.
Оплатил заказ, а в итоге тишина
Деньги украли
Обещали одно – сделали другое
Оренбург принт на футболке и футболка капитан в Москве. Перчатки сенсорные эластичные белые и вязаные шапки оптом в Иваново. Печать на футболках Махачкала и надпись футболки про рыбалку в Ульяновске. Какими нитками вышивают на одежде и пластиковая подарочная упаковка в Сургуте. Сделать надпись на футболки оптом и футболки с красивым принтом: печать на футболке фотографии оптом
Adoro de verdade o 888 Casino, oferece uma sensacao unica de cassino. As opcoes de jogos sao ricas e diversificadas, com sessoes de cassino ao vivo imersivas. Os agentes estao sempre disponiveis e eficientes, oferecendo respostas rapidas e precisas. Os ganhos sao pagos em tempo recorde, contudo eu gostaria de mais promocoes. De modo geral, o 888 Casino e uma plataforma excepcional para os jogadores em busca de adrenalina! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e intuitiva, reforca a imersao total.
casino 888 jogar gratis|
Acho completamente fora da curva Flabet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e um estouro. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e alucinantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um trovao, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um raio, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, Flabet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, da um toque de classe insana ao cassino.
flabet app baixar|
КПЛ результаты – свежие счеты игр текущего тура
На сайте Детский Класс нашим посетителям в любое время доступны материалы для приятного совместного досуга детей и их родителей: детские песни на разные тематики, которые можно разучивать и распевать в будни и праздники, интересные и познавательные легенды и мифы, раскраски различной сложности, а также волшебные и поучительные сказки.
купить диплом о техническом образовании https://educ-ua7.ru/ .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
мега маркетплейс тор
https://seraphinajewellery.com
Официальное зеркало KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Obespechenie-bezopasnosti-pri-dostupe-k-neoficialnym-istochnikam-09-18
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
Футболки с надписью Уфа и рисунок на футболки на заказ в Сургуте. Худи и свитшот и мужскую бейсболку в интернет недорого в Москве. Детская футболка с фото и футболка слово пацана в Санкт-Петербурге. Одежда рдр 2 и Seasons одежда в Кирове. Футболка оптом Among Us и футболка 51 Мурманск https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
Я відчула справжню магію тихоокеанської культури на Фестивалі Музики. Це не просто виступи – це занурення у традиції, які сягають століть. Організатори SFF Pacific Department зробили все, щоб кожен відвідувач відчув себе частиною цієї гармонії. Дізнайтеся більше про їхні заходи тут.
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Экспертные мнения о развитии спорта Казахстана
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://orangeroleplay.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=22184. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
официальные займы онлайн на карту бесплатно http://zaimy-22.ru/ .
все займы рф все займы рф .
все микрозаймы все микрозаймы .
все микрозаймы онлайн все микрозаймы онлайн .
займы https://www.zaimy-20.ru .
займы все https://zaimy-17.ru .
Рабочее зеркало KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Obratite-vnimanie-na-nalichie-HTTPS-Bezopasnye-soedineniya-obespechivayut-zashchitu-dannyh-peredavaemyh-me2-09-18
список займов онлайн на карту http://www.zaimy-25.ru .
займы всем займы всем .
займы россии https://www.zaimy-23.ru .
sports-kz-news.ru Новости бокса и ММА Казахстана
interesting post
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграме
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
https://meravista.com/en/blogentry/legendary-city-atlantis-silves-or-faro?page=15602
накрутка активных подписчиков в телеграм
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Спортивные события недели в РК
Ushbu platformada barcha tranzaksiyalar maxfiy holda amalga oshiriladi.
Har bir turdagi oʻyin oʻzining ajoyib grafikasi va hayajonli jarayoniga ega.
Har bir oʻyinchi oʻz darajasiga qarab qoʻshimcha bonuslar olishi mumkin.
Kompaniya mijozlarga tezkor kirish uchun ijtimoiy tarmoqlar orqali ham avtorizatsiyani taklif etadi.
888starz уз https://888starz-uzbekistan.ru/
Актуальная ссылка KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Kraken-tor-predostavlyaet-dopolnitelnyj-uroven-bezopasnosti-i-anonimnosti-CHtoby-podklyuchitsya-k-plo2-09-18
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://teletype.in/@gerpuch/zzsdRztLSPX. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru/ Развитие детского футбола в РК
تتميز 888starz بشعبيتها في مجال القمار على الإنترنت. يوفر الموقع مجموعة كبيرة من خيارات الألعاب التي تلبي احتياجات جميع اللاعبين. تشمل الألعاب المتوفرة الرهانات الرياضية وألعاب الكازينو.
يوفر 888starz واجهة مستخدم بسيطة. يمتلك المستخدمون القدرة على التنقل بين الأقسام بصورة سلسة. يساهم في جعل تجربة اللعب أكثر جاذبية.
تقدم 888starz مجموعة من العروض الترويجية لجذب اللاعبين الجدد. يشمل ذلك مكافآت الترحيب والمكافآت الدورية. تعتبر هذه المكافآت آلية فعالة لجذب المزيد من اللاعبين.
تعد الأمان من أبرز أولويات 888starz. تعتمد المنصة على تقنيات متطورة لضمان حماية معلومات اللاعبين. يحقق ذلك مستوى عالٍ من الأمان أثناء اللعب.
code promo 888starz https://888starz-africa.com/promo-code/
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
займы всем займы всем .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм дешево
buy weed prague cocain in prague from brazil
columbian cocain in prague buy weed prague
Сегодня открылось зеркало KRAKEN, сайт работает без перебоев.
https://telegra.ph/Ne-zabyvajte-pro-mobilnye-ustrojstva-Obespechte-adaptivnyj-dizajn-uchityvayushchij-razlichiya-v-razmerah-2-09-18
накрутка подписчиков тг бесплатно без заданий
http://sports-kz-news.ru/ Подробные результаты матчей и турниров
купить живых подписчиков в телеграм канал
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
bannye-drova-spb.ru .
дрова колотые береза с доставкой недорого .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые бесплатно
все займы на карту все займы на карту .
мфо займ мфо займ .
займы займы .
микрозайм всем https://zaimy-18.ru/ .
микрозаймы все zaimy-22.ru .
J’adore le casino TonyBet, ca offre un moment divertissant top. Le choix de jeux est impressionnant, offrant des options de casino en direct. Les agents sont reactifs, tres professionnel. Les paiements sont fluides, par contre les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. Globalement, TonyBet ne decoit pas pour les amateurs de casino ! De plus, l’interface est fluide, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet без цупис|
Рабочий доступ KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Proveryajte-nastrojki-konfidencialnosti-Poskolku-informaciya-mozhet-byt-dostupna-drugim-uchastnikam-09-18
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. Les titres proposes sont nombreux, comprenant des jeux innovants. Le service client est remarquable, avec des reponses precises et utiles. Le processus de retrait est sans accroc, par moments les promos pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour faire court, AllySpin vaut vraiment le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs le style visuel est dynamique, ajoutant une touche d’elegance au jeu.
allyspin casino logo|
взо http://www.zaimy-25.ru .
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura selva. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem rugas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que mordem. No geral, LeaoWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino serios|
Современный инструмент для рекламы и продвижения бренда — rollup. Он сочетает в себе простоту конструкции и высокую эффективность визуальной подачи. Полотно легко заменяется, а механизм рассчитан на длительный срок службы. Такие стенды используют на выставках, деловых встречах и презентациях. Мы обеспечиваем четкость печати, стойкость цветов и точность деталей, что делает продукцию надежным помощником в деловой коммуникации.
микрозайм всем https://zaimy-17.ru/ .
Казахстан турниры и чемпионаты – результаты о турнирах РК
всезаймыонлайн http://www.zaimy-23.ru .
ixr uhb
куб дров цена .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
дрова самовывоз .
wkv dpk
Рабочая ссылка KRAKEN.
https://telegra.ph/Posle-aktivacii-akkaunta-rekomenduetsya-vklyuchit-dvuhfaktornuyu-autentifikaciyu-EHto-znachitelno-povysi2-09-18
купить диплом в златоусте купить диплом в златоусте .
купить диплом в новошахтинске http://www.rudik-diplom10.ru/ .
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Видеообзоры важнейших матчей КПЛ
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
купить аттестаты за 11 купить аттестаты за 11 .
купить диплом вуза купить диплом вуза .
cse syp
купить диплом о среднем образовании купить диплом о среднем образовании .
Я завжди захоплювався гравцями https://obolon.trance.mk.ua/, вони мають фантастичні навички в Racing Dew.
набрать подписчиков в телеграм бесплатно набрать подписчиков в телеграм бесплатно
мфо займ мфо займ .
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно
трипскан топ Tripscan зеркало: “Tripscan зеркало” относится к альтернативным веб-адресам или копиям сайта Tripscan, которые создаются для обеспечения доступности сервиса в случае блокировок основного домена или технических проблем. Зеркала сайта Tripscan позволяют пользователям получить доступ к тем же функциям и данным, что и на основном сайте, даже если основной домен по каким-либо причинам недоступен. Использование зеркал является распространенной практикой для онлайн-сервисов, которые сталкиваются с проблемами доступа из-за цензуры, блокировок или технических сбоев. Пользователи могут найти актуальные зеркала Tripscan на форумах, в социальных сетях или через поисковые системы. Важно убедиться в подлинности зеркала перед вводом личной информации, чтобы избежать мошенничества.
купить подшипники оптом Завод изготовитель подшипников: Этот запрос уточняет предыдущий, фокусируясь на поиске именно заводов, занимающихся полным циклом производства подшипников. Эта информация может быть полезна для пользователей, заинтересованных в посещении производственных площадок, ознакомлении с технологическими процессами и установлении прямых контактов с руководством завода. Результаты поиска должны включать адреса, контактные телефоны, веб-сайты и другую релевантную информацию о заводах-изготовителях подшипников. Важно учитывать, что не все заводы-изготовители работают напрямую с конечными потребителями, поэтому перед визитом необходимо уточнить возможность посещения и обсудить условия сотрудничества.
купить диплом с реестром цена купить диплом с реестром цена .
tripscan трипскан Tripskan: “Tripskan” является неправильным написанием названия сервиса Tripscan. Вероятно, это результат опечатки или ошибки при транслитерации. Пользователи, которые случайно вводят запрос “Tripskan”, могут искать информацию о сервисе Tripscan, но в результатах поиска они могут получить нерелевантную информацию или попасть на другие веб-сайты. Важно помнить правильное написание названия сервиса – Tripscan – для того, чтобы получить доступ к актуальной и достоверной информации.
купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр купить диплом в екатеринбург реестр .
https://sports-kz-news.ru Истории взлетов и падений в спорте
купить диплом фитнес инструктора купить диплом фитнес инструктора .
KRAKEN онион зеркало.
https://telegra.ph/Nazhmite-na-knopku-registracii-Vvedite-neobhodimuyu-informaciyu-takuyu-kak-adres-ehlektronnoj-pochty-i-zhe2-09-18
lucky pari лимит на вывод в сутки https://www.luckypari101.ru
займ все http://www.zaimy-16.ru .
кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр .
где купить диплом техникума лучше где купить диплом техникума лучше .
диплом техникума в чебоксарах купить диплом техникума в чебоксарах купить .
купить диплом воспитателя https://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом воспитателя .
купить диплом в чайковском купить диплом в чайковском .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
купить проведенный диплом провести купить проведенный диплом провести .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы .
накрутка подписчиков телеграм бесплатно задания
кракен тор – Кракен зеркало рабочее — быстрый и стабильный способ доступа.
Hello folks!
I came across a 135 useful website that I think you should dive into.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://garminway.com/sports-betting/the-rise-of-political-betting-why-its-gaining-popularity/
Furthermore do not neglect, guys, that a person at all times may inside the publication discover responses to the the absolute complicated inquiries. The authors attempted to lay out all of the data in the extremely accessible way.
купить диплом в георгиевске купить диплом в георгиевске .
консультации маркетинг Услуги интернет-маркетолога / Услуги интернет маркетологов / Услуга интернет маркетолога: Данные запросы свидетельствуют о поиске специалистов, способных эффективно продвигать бизнес в онлайн-среде. Пользователь заинтересован в увеличении видимости компании в интернете, привлечении целевой аудитории, повышении узнаваемости бренда и, как следствие, увеличении продаж. Важно предоставить информацию о широком спектре услуг: SEO-оптимизация, SMM (продвижение в социальных сетях), контекстная и таргетированная реклама, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг, веб-аналитика и разработка стратегии продвижения. Необходимо акцентировать внимание на преимуществах работы с опытными специалистами: повышение ROI (возврат инвестиций), увеличение трафика на сайт, рост числа лидов и клиентов. Также полезно предложить кейсы с примерами успешных проектов.
купить диплом судоводителя купить диплом судоводителя .
можно ли купить диплом медсестры можно ли купить диплом медсестры .
купить диплом техникума в чите купить диплом техникума в чите .
микрозаймы все http://zaimy-22.ru/ .
все займы рф http://zaimy-25.ru/ .
микрозаймы все микрозаймы все .
займы https://www.zaimy-20.ru .
https://sports-kz-news.ru/ Фотогалерея со спортивных мероприятий РК
Купить диплом колледжа в Мариуполь http://educ-ua7.ru/ .
Скульптор Рукавишников Скульптор Рукавишников: Запрос более конкретно указывает на интерес к Александру Рукавишникову именно как к скульптору. Пользователь, вероятно, уже знает его фамилию, но хочет получить больше информации о его скульптурных работах. Здесь важно предоставить перечень наиболее известных работ с фотографиями, описаниями и информацией об их местонахождении. Также релевантными будут ссылки на статьи, посвященные анализу его творчества, и каталоги выставок. Важным будет предоставить информацию о материалах, которые он использует в своих работах, и о его стиле. Полезно будет предоставить возможность поиска скульптур по тематике или по месту нахождения.
продвижение компании в интернете Разработка позиционирования / Позиционирование бренда: Пользователь понимает важность определения уникального места бренда на рынке. Важно предложить услуги по разработке эффективной стратегии позиционирования, которая позволит бренду выделиться среди конкурентов и привлечь целевую аудиторию. Необходимо провести анализ рынка и конкурентов, определить целевую аудиторию и разработать уникальное предложение ценности бренда.
сколько стоит танк 300 цена http://tank-3001.ru
Бесплатная юридическая консультация в Москве становится все более популярной . Причиной этого является увеличившаяся необходимость в юридической поддержке . Специалисты готовы предоставить свои услуги безвозмездно .
Важным аспектом бесплатной юридической консультации является доступность . Каждый человек может получить советы и рекомендации по различным вопросам . Это также поможет снизить число правонарушений .
Получить бесплатную юридическую консультацию можно довольно просто . Обычно достаточно записаться на консультацию к специалисту . Некоторые юристы проводят консультации дистанционно.
В заключение, бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве представляют собой значимую помощь для населения . Юридическая помощь также играет значительную роль в повышении правовой грамотности населения . Не сомневайтесь в том, что бесплатная консультация может действительно помочь вам.
тут тут.
щетки
трип скан Tripskan: “Tripskan” является альтернативным написанием названия сервиса Tripscan, возможно, из-за опечатки или особенностей транслитерации. Несмотря на небольшое отличие в написании, “Tripskan” может использоваться пользователями при поиске информации о сервисе Tripscan в интернете. Важно отметить, что правильное написание названия сервиса – “Tripscan”, и именно этот вариант следует использовать для получения точной и актуальной информации о сервисе.
bannye-drova-spb.ru .
кракен вход в личный кабинет – Через кракен тор ссылка можно подключаться без перебоев.
подшипники оптом от производителей Подшипник для конвейера: Этот запрос указывает на потребность в подшипниках, предназначенных для использования в конвейерных системах. Подшипники для конвейеров должны обладать высокой надежностью, износостойкостью и способностью выдерживать большие нагрузки. Они могут быть шариковыми, роликовыми или игольчатыми, в зависимости от типа конвейера и условий эксплуатации. При выборе подшипников для конвейеров необходимо учитывать тип транспортируемого груза, скорость движения ленты и температурный режим.
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал без регистрации
трипскан вход Tripscan трипскан: Сочетание “Tripscan трипскан” используется для охвата более широкой аудитории, включая тех, кто ищет информацию о сервисе, используя латинский или кириллический алфавит. Такое дублирование повышает видимость в поисковых системах, поскольку пользователи могут вводить запросы как на английском, так и на русском языке. Помимо этого, это подчеркивает адаптацию сервиса к различным языковым рынкам и демонстрирует удобство для пользователей из разных стран. Использование обоих написаний названия позволяет избежать путаницы и убедиться, что пользователи найдут нужную информацию, независимо от их языковых предпочтений.
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. La selection est totalement dingue, proposant des sessions live qui tabassent. Le crew assure un suivi de malade, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, mais bon des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Dans le fond, Gamdom est une plateforme qui dechire tout pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! A noter aussi la plateforme claque avec son look de feu, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
gamdom 2fa|
Журналистское расследование, посвящённое KRAKEN маркетплейсу, выявило одну ключевую деталь:
демонстрирует редкий баланс между удобством, безопасностью и широтой ассортимента. В отличие от конкурентов, кракен только через тор поддерживает постоянную работу зеркал и доступность сервиса. Поддержка отвечает быстро, арбитраж минимизирует риски, а репутация ресурса формировалась годами. Всё это подтверждает устойчивый статус KRAKEN как надёжного онлайн рынка, востребованного среди пользователей, ценящих стабильность и качество.
http://sports-kz-news.ru Аудиоинтервью с ветеранами спорта
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
дрова колотые 30 см купить .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
кракен онион зеркало – Через кракен официальный сайт можно быстро попасть в маркетплейс и личный кабинет.
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
lucky pari ответсвенная игра http://luckypari100.ru
перманент бровей севастополь Перманент в Севастополе – это ваш шанс выглядеть безупречно в любое время суток! Предлагаем широкий выбор техник перманентного макияжа: брови (пудровое напыление, микроблейдинг, теневая растушевка), губы (акварельная техника, помадный эффект), веки (межресничка, стрелки). Наши опытные мастера помогут подобрать идеальную форму и оттенок, учитывая ваши индивидуальные особенности и пожелания. Используем только сертифицированные пигменты премиум-класса, обеспечивающие стойкий и естественный результат на долгие годы. Забудьте о ежедневном макияже и наслаждайтесь своей красотой!
cocaine in prague plug in prague
за1мы онлайн http://zaimy-26.ru .
Станок с ЧПУ — это незаменимый инструмент для домашнего мастерской, позволяющий создавать точные детали и изделия, такие как https://plusstanok.ru/ – токарный станок по металлу с чпу для дома|настольный чпу токарный станок|токарный станок с чпу настольный|токарный станок чпу по дереву|мини токарные станки с чпу|токарный чпу цена|токарный станок чпу цена|настольный токарный станок по металлу с чпу купить цена|токарный станок чпу по металлу купить|токарный станок по дереву чпу|токарный станок с чпу по металлу купить|токарный чпу станок по металлу купить|мини токарный станок с чпу по металлу купить|купить токарный станок по металлу с чпу|мини токарный чпу|токарный станок по металлу с чпу купить|мини токарный станок по металлу с чпу|купить токарный станок по дереву с чпу|токарный станок чпу по металлу|токарный станок чпу купить|чпу токарный станок купить|станок токарный с чпу купить|токарный станок с чпу по металлу цена|маленький токарный станок с чпу по металлу|маленький токарный чпу|самый дешевый токарный станок по металлу|станок с чпу по металлу токарный|станок чпу по металлу токарный|станок чпу токарный по металлу|купить токарный станок с чпу по металлу|чпу токарный по дереву|купить токарный с чпу по металлу|бытовой токарный станок|сколько стоит токарный станок по дереву|токарный станок с чпу по дереву|мини токарный станок чпу|токарный чпу|купить станок чпу токарный|токарный станок недорого|чпу токарный станок|токарные станки|токарные станки с чпу|купить токарные станки|станки по металлу|токарный чпу станок|токарный станок полуавтомат|токарный полуавтомат с чпу|российские токарные станки с чпу|токарные станки по металлу|токарный полуавтомат|учебный токарный станок по металлу|мини токарный станок по металлу купить в спб|токарный станок по металлу купить новый для дома|чпу токарный станок по металлу|чпу станки|чпу станок по металлу купить|станок чпу купить|станки с чпу купить|барфидер для токарного станка с чпу купить|станок с чпу купить|токарные станки с чпу купить|чпу станки купить|сколько стоит чпу станок|маленький токарный станок с чпу|станок чпу по металлу цена|токарный станок с фрезерной головкой|учебный токарный станок с чпу|чпу станок маленький|токарный станок с чпу по металлу купить цена|токарка чпу по металлу|русские чпу станки|токарный станок малогабаритный с чпу|станок с чпу.
Эти станки обеспечивают высокую точность и производительность при выполнении различных операций.
https://sports-kz-news.ru/ Фотогалерея со спортивных мероприятий РК
услуги pr специалиста Запуск нового продукта на рынок: Запрос указывает на потребность в разработке и реализации маркетинговой стратегии для вывода нового продукта на рынок. Важно предложить комплексный подход: анализ рынка, целевой аудитории, конкурентов, разработка позиционирования, создание рекламной кампании, организация PR-мероприятий и т.д.
купить диплом в коврове купить диплом в коврове .
кракен как зайти – Кракен официальный сайт зеркало — быстрый способ подключиться и продолжать работу.
купить диплом во владикавказе http://www.rudik-diplom14.ru .
как накрутить подписчиков в тг канал
https://www.sports-kz-news.ru/ Развитие детского футбола в РК
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм канал
кто нибудь работает медсестрой по купленному диплому https://frei-diplom14.ru/ .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
купить диплом пищевого техникума купить диплом пищевого техникума .
Якщо ви хочете дізнатися більше про нашу команду та їх досягнення, відвідайте наш сайт. Кожен гравець у нас володіє унікальними навичками.
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
микрозаймы онлайн микрозаймы онлайн .
все микрозаймы http://www.zaimy-23.ru .
все микрозаймы на карту все микрозаймы на карту .
http://www.sports-kz-news.ru Новости боксерских поединков Казахстана
кракен зеркало сегодня – Кракен сайт всегда под рукой: свежие рабочие зеркала и проверенные ссылки помогают заходить без перебоев.
Приветствую строительное сообщество!
Недавно столкнулся с организацией презентации проекта для строительной компании. Заказчик настаивал на профессиональной подаче.
Основной вызов состоял что нужно было много посадочных мест для масштабного мероприятия. Покупать на раз – дорого.
Помогли специалисты по аренде – взяли качественные столы. Кстати, недавно читал качественный обзор про организацию деловых мероприятий – там отличные рекомендации.
Все организовали идеально. Стоит рассмотреть такой вариант кто проводит деловые мероприятия.
Всем успешных проектов!
купить диплом в троицке https://rudik-diplom10.ru/ .
сервис по накрутке подписчиков в телеграм
микрозайм всем микрозайм всем .
займы россии займы россии .
купить аттестат за классов купить аттестат за классов .
займер ру займер ру .
Je trouve completement fou FatPirate, ca donne une energie de pirate dejantee. Le catalogue est une vraie caverne aux tresors, avec des slots qui dechirent. Le service client est au top niveau, repondant en deux secondes chrono. Les transactions sont simples comme bonjour, quand meme les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Bref, FatPirate est une plateforme qui envoie du pate pour les aventuriers du jeu ! Et puis le design est style et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
fatpirate login|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Betify Casino, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. Globalement, Betify Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le design est visuellement percutant, renforce l’immersion totale.
casino en ligne betify|
займ все https://www.zaimy-17.ru .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Казахстан боксерские новости – результаты боксерских боев с участием боксеров
J’adore le show de Impressario, ca donne une energie de star absolue. Le catalogue est un festival de titres, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, offrant des reponses qui scintillent. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, de temps en temps des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. Pour resumer, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour les artistes du jeu ! En prime le design est une explosion visuelle, facilite un show total.
impressario casino review|
Мы сопровождаем грузы через все этапы оформления и обеспечиваем законное и быстрое прохождение границы: таможенный брокер в Москве
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
кракен маркетплейс вход – Через кракен тор ссылка можно подключаться без перебоев.
autsorsing-buhgalterii-ip-812.ru .
https://vk.com/burtseva.brows Перманентный макияж бровей в Севастополе – это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит свое время и хочет выглядеть безупречно! Наши опытные мастера помогут создать идеальную форму и цвет бровей, учитывая ваши индивидуальные особенности и пожелания. Используем различные техники перманентного макияжа бровей: пудровое напыление, микроблейдинг, теневая растушевка. Мы гарантируем безопасность и стойкий результат. Забудьте о карандашах и тенях – наслаждайтесь красивыми бровями в любое время!
It’s awesome to go to see this web site and reading the views of all friends on the topic of this paragraph, while I am also keen of getting knowledge.
https://www.australiansurffestival.com/led-ta-bi-led-linzi-riznytsya-perevagy-ta-vybir
купить диплом техникума ссср в брянске купить диплом техникума ссср в брянске .
Hi to all, how is all, I think every one is getting
more from this website, and your views are pleasant for new people.
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Журналистское расследование, посвящённое KRAKEN маркетплейсу, выявило одну ключевую деталь:
демонстрирует редкий баланс между удобством, безопасностью и широтой ассортимента. В отличие от конкурентов,
поддерживает постоянную работу зеркал и доступность сервиса. Поддержка отвечает быстро, арбитраж минимизирует риски, а репутация ресурса формировалась годами. Всё это подтверждает устойчивый статус KRAKEN как надёжного онлайн рынка, востребованного среди пользователей, ценящих стабильность и качество.
Hello!
We are interested in promising projects for investment. If you have an innovative idea or business model but lack the funding to implement it, we invite you to discuss support options. Text me on WhatsApp for quick communication
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа поспособствуем. Как можно купить диплом специалиста в Вологде? – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-spetsialista-v-vologde
What you said made a great deal of sense. But, think about this, what if you were to create a awesome headline? I mean, I don’t wish to tell you how to run your website, but what if you added a title that makes people desire more? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is kinda plain. You could glance at Yahoo’s front page and note how they create post headlines to grab viewers interested. You might try adding a video or a picture or two to grab readers excited about everything’ve written. Just my opinion, it might make your posts a little bit more interesting.
https://massovka.com.ua/linzi-v-faru-shcho-radyat-vlasnyky-bmw-ta-audi
sports-kz-news.ru Видео голов и моментов матчей
веб-сайт https://krak-38.cc
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
https://www.restate.ru/
Услуги таможенного брокера в Москве — это удобный и надежный способ оформить груз без лишних проблем: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
аутсорсинг по охране труда стоимость .
Hello lads!
I came across a 135 very cool resource that I think you should take a look at.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find helpful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://wedontmakewidgets.com/sport-betting/navigating-your-passion-for-sports-betting-and-family-life/
Furthermore don’t neglect, guys, — one at all times can within this particular publication discover solutions to your most confusing queries. The authors made an effort to lay out the complete content in the most very accessible method.
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
кракен зеркало сайта – Кракен официальный сайт — это проверенный ресурс с обновлениями каждый день.
Hello folks!
I came across a 135 helpful site that I think you should check out.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://ronnielawsmusic.com/bets-on-sport/registering-on-a-sportsbook-with-quality-bonuses/
Additionally don’t forget, everyone, which a person always may within this article locate answers to address your the absolute tangled queries. The authors attempted to present all data using an extremely accessible manner.
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Je suis fou de JackpotStar Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine tout. La selection du casino est une explosion cosmique de plaisir, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une comete, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une etoile filante, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, JackpotStar Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style etoile, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
jackpotstar casino|
What’s up, this weekend is nice in support of me, as this occasion i am reading this impressive educational paragraph here at my home.
https://bagstore.com.ua/chomu-linzi-v-fari-dayut-bilshe-kontrolyu-nad-svitlom
lucky pari mobile lucky pari mobile
sports-kz-news.ru/ Исходы всех спортивных соревнований РК
Whether you’re a novice or an expert, getting started on 888starz is effortless.
888starz aplikacja https://888starz-bet-casino.com/pl/apk-ios/
займер ру займер ру .
все займ http://www.zaimy-27.ru .
сайт кракен зеркало – Выбирайте кракен сайт вход — это безопасное подключение и удобный вход 24/7.
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
все займ http://www.zaimy-50.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом в белорецке купить диплом в белорецке .
bannye-drova-spb.ru .
купить старый диплом техникума в спб купить старый диплом техникума в спб .
1хБет промокод при регистрации используя промокод, вы получите бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт, а также бонус в казино 1500€ и 150 фриспинов. Обратите внимание, что это единственный действующий промокод на данный момент. Также, если вам интересны другие промокоды для 1xBet, вы можете ознакомиться со списком рабочих промокодов на 2025 год. https://forwardprint.com.ua/image/pgs/promokod_283.html 1xBet предлагает различные бонусные программы для своих игроков. Среди них есть бонус за регистрацию, бонус за первый депозит, бонус за повторный депозит, бонус за покупку билетов, бонус за пополнение счета, бонус за приглашение друзей и многое другое. Кроме того, игроки могут получать бонусы за активное участие в акциях и конкурсах, которые проводит букмекерская контора. Также игроки имеют возможность получать бонусы за достижение новых уровней в программе лояльности.
Казахстан спорт события – анонсы всех соревнований
купить диплом в кирове https://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить диплом в кирове .
купить диплом в альметьевске купить диплом в альметьевске .
купить диплом ссср купить диплом ссср .
купить диплом в бийске купить диплом в бийске .
купить элитные дрова .
Right now it looks like Expression Engine is the top blogging platform available right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
оригинальные кашпо для цветов купить http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru/ .
lucky pari сравнение http://www.luckypari101.ru
кракен маркет даркнет – Если ищете стабильный доступ, кракен сайт предлагает актуальные адреса и быстрый вход.
autsorsing-buhgalterii-ip-812.ru .
bannye-drova-spb.ru .
chat-s-psykhologom-russia-12.g-u.su uhf
kupit-drova-v-nizhnem-novgorode-365.ru .
What’s up to all, how is everything, I think
every one is getting more from this web page, and your views are good
designed for new users.
кракен ссылка onion – Сегодня кракен ссылка актуальная обновлена и подходит для любых устройств.
Якщо ви ще не чули про Yantar E-Team, то це саме та команда, яка завоювала серця багатьох шанувальників кіберспорту. Вони невпинно працюють на досягнення нових перемог.
1хБет промокод при регистрации используя промокод, вы получите бонус в размере 100% до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт, а также бонус в казино 1500€ и 150 фриспинов. Обратите внимание, что это единственный действующий промокод на данный момент. Также, если вам интересны другие промокоды для 1xBet, вы можете ознакомиться со списком рабочих промокодов на 2025 год. https://badgerboats.ru/themes/middle/?promokod_284.html 1xBet предлагает различные бонусные программы для своих игроков. Среди них есть бонус за регистрацию, бонус за первый депозит, бонус за повторный депозит, бонус за покупку билетов, бонус за пополнение счета, бонус за приглашение друзей и многое другое. Кроме того, игроки могут получать бонусы за активное участие в акциях и конкурсах, которые проводит букмекерская контора. Также игроки имеют возможность получать бонусы за достижение новых уровней в программе лояльности.
chat-s-psykhologom-russia-12.g-u.su djs
медоборудование https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru .
chat-s-psykhologom-russia-12.g-u.su pxs
аппараты медицинские medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru .
микрозаймы онлайн микрозаймы онлайн .
за1мы онлайн http://www.zaimy-26.ru/ .
продвижение обучение http://www.kursy-seo-5.ru .
https://xn—86-5cdoa3a7cs.xn--p1ai/
chat-s-psykhologom-russia-12.g-u.su coi
микрозайм всем http://www.zaimy-29.ru .
поставка медицинского оборудования medoborudovanie-77.ru .
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma onda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Em resumo, JabiBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e uma explosao visual aquatica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet casino|
сколько стоит новый танк 300 http://tank-3001.ru
Ich finde absolut uberwaltigend Platin Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie Platin glanzt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Juwelensafe, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein geschliffener Diamant. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein glitzernder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Platin Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Funkeln, was jede Casino-Session noch glanzvoller macht.
platin casino partner|
кракен тор зеркало – Через кракен сайт вход можно войти в систему с телефона или ПК без перебоев.
Всем
Недавно эго нашёл отличную Ютуб наблюдение –dahua ipc
P.S. Dahua Technology – Ятси заглядеться в завтра!
Всем пока
Ahaa, its pleasant dialogue regarding this article here at this weblog, I have read all that, so now me also
commenting here.
С помощью кракен онион можно легко получить рабочий вход даже на телефоне.
накрутка подписчиков тг бесплатно без отписок
все займы онлайн все займы онлайн .
все онлайн займы все онлайн займы .
подписчики в тг канал реклама
микрозайм все https://zaimy-50.ru .
These are actually enormous ideas in on the topic of blogging.
You have touched some nice points here. Any way keep
up wrinting.
кракен сайт вход – Через кракен официальный сайт можно быстро попасть в маркетплейс и личный кабинет.
купить диплом в заречном купить диплом в заречном .
Ищете качественный ремонт авто|сервис авто казань|ремонт автомобилей|ремонт машины|услуги автосервиса|сервис авто|ремонт авто компании|ремонт авто организаций|ремонт и обслуживание авто|ремонт авто хороший|стоимость ремонта авто|сколько стоит ремонт авто|цены на ремонт авто|ремонт авто цена казань|ремонт легковых авто|услуги по ремонту авто|ремонт машин авто|сто ремонт авто|ремонт авто казань|ремонт авто в казани|расчет ремонта авто|расчет стоимости ремонта авто|рассчитать ремонт авто|официальный ремонт авто|сервисные центры ремонту авто|ремонт мастерская авто|ремонт авто с гарантией|ремонт автомобиля в Казани|рассчитать ремонт автомобиля|ремонт автомобилей всех марок|ремонт легковых автомобелей|ремонт авто под ключ|ремонт автомобилей под ключ|сервис автомобилей|автосервис|официальный ремонт автомобиля|ремонт машин всех марок|ремонт машины в казани|сто ремонт машины|сервис для машин|ремонт машин под ключ|ремонт авто у официала|ремонт авто у официального дилера|ремонт машин в Казани? Наши специалисты готовы предложить вам надежные услуги!
Обслуживание машины — это процесс, который требует внимательности и профессионализма. Владельцы машин сталкиваются с тем, что поломка может произойти в самый неподходящий момент. Следует осознавать, как правильно реагировать на такие ситуации.
Первым шагом в ремонте становится определение причины поломки. Оптимально доверить эту задачу специалистам, у которых есть опыт и нужное оборудование. Тем не менее многие автовладельцы предпочитают проводить диагностику самостоятельно, что может быть полезным, но требует определенных знаний.
После диагностики наступает этап восстановления работоспособности. В зависимости от характера поломки может потребоваться замена деталей или их ремонт. Определенные элементы можно быстро заменить , в то время как другие требуют больше времени и усилий.
Не забывайте о профилактике, которая также играет важную роль в сохранении автомобиля в исправном состоянии. Постоянная проверка поможет предотвратить серьезные проблемы. Важно не забывать , что хорошее состояние автомобиля зависит не только от ремонта, но и от внимательного отношения к нему.
Чтобы быстро попасть на кракен даркнетсайт, используйте проверенную ссылку. Рабочее зеркало доступно для входа в маркетплейс, а инструкция поможет без лишних шагов.
Hello, everyone! My name is Julia. My team and I support early-stage startups. If you are looking for resources to launch or scale your project, tell us about your idea. We are open to considering interesting proposals. Call me on Telegram for quick communication
накрутка подписчиков в тг смм накрутка
– Кракен вход в личный кабинет доступен через рабочие зеркала и актуальные ссылки.
KRAKEN вход всегда доступен через кракен личный кабинет. Актуальное зеркало помогает авторизоваться и продолжить пользоваться сервисом.
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм канал
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал
https://sex-city.porn/ the best porno site ever! NO ADS!
https://clubgti.com/wp-includes/articles/?dom_v_bolgarii_kak_pokazately_prestigha.html
кракен сайт – Через кракен сайт вход можно войти в систему с телефона или ПК без перебоев.
Портал про авто https://ivanmotors.ru обзоры автомобилей, новости автопрома, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Тест-драйвы, автообзоры и полезная информация для автолюбителей и профессионалов.
Всё о Москве https://moscowfy.ru в одном месте: городской портал с новостями, афишей, расписанием транспорта, объявлениями и услугами. Полезные материалы для москвичей и туристов.
Для выхода в кракен маркетиспользуйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Официальное зеркало работает стабильно, обеспечивая удобный и безопасный вход.
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал
Je trouve absolument magique Luckster Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un sort. Le repertoire du casino est une cascade de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui enchantent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement enchante, avec une aide qui fait des miracles. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse magique, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Globalement, Luckster Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enchantee du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
ultimate luckster|
дрова на паллетах с доставкой купить .
Je suis fou de Lucky8 Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino ensorcelante. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et lumineux. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, Lucky8 Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino feerique.
lucky8 casino no deposit bonus codes|
Website https://useit2.ru/.
купить накрутку подписчиков в тг
It’s very easy to find out any topic on net as compared to textbooks, as
I found this article at this website.
купить диплом образцы купить диплом образцы .
купить диплом в дербенте купить диплом в дербенте .
https://bit.ly/4262piC rdn
Professional water system solutions customized to address your particular demands. Our experts provide superior solutions for every plumbing issue, from challenging water line solutions to critical burst pipe response. Rely on us for prompt, trustworthy care that maintains your building in top condition. Contact us now at
emergency plumber for a free assessment or to arrange your upcoming service visit. We’re available to resolve also the toughest water system concerns with skill and accuracy.
купить диплом в бийске купить диплом в бийске .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
купить диплом в череповце https://rudik-diplom1.ru/ .
читать кракен магазин
можно купить легальный диплом https://www.frei-diplom1.ru .
как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании .
купить диплом инженера электрика купить диплом инженера электрика .
купить диплом об окончании техникума в москве купить диплом об окончании техникума в москве .
где купить диплом о среднем образование где купить диплом о среднем образование .
купить диплом о высшем образовании проведенный купить диплом о высшем образовании проведенный .
seo продвижение сайта wordpress Маркетинговое продвижение бренда Маркетинговое продвижение бренда – это комплекс стратегических мероприятий, направленных на формирование и укрепление позитивного имиджа компании в сознании целевой аудитории. Это не просто реклама, а создание устойчивых ассоциаций с вашим брендом, формирование лояльности и, в конечном итоге, увеличение продаж. Этапы продвижения бренда: Аудит бренда: Анализ текущего состояния бренда, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение целевой аудитории и конкурентов. Разработка стратегии: Определение целей продвижения, разработка позиционирования бренда, ключевых сообщений и каналов коммуникации. Разработка фирменного стиля: Создание визуальной идентичности бренда, включая логотип, цветовую палитру, шрифты и другие элементы. Разработка контент-стратегии: Создание контента, который отражает ценности бренда, привлекает целевую аудиторию и формирует экспертный имидж компании. Реализация стратегии: Запуск рекламных кампаний, продвижение в социальных сетях, участие в мероприятиях, работа со СМИ и другие активности. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов продвижения, анализ эффективности каналов коммуникации, внесение корректировок в стратегию. Основные инструменты: Реклама: Размещение рекламы в различных каналах (онлайн и офлайн) для привлечения внимания к бренду. PR: Формирование позитивного общественного мнения о бренде через работу со СМИ и общественностью. SMM: Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях для установления контакта с целевой аудиторией и формирования лояльного сообщества. Контент-маркетинг: Создание и распространение полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории. Event-маркетинг: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения узнаваемости бренда и установления контакта с потенциальными клиентами. Инвестиции в продвижение бренда – это инвестиции в будущее вашего бизнеса. Грамотно выстроенная стратегия позволит вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов, привлечь лояльных клиентов и увеличить прибыль.
Портал о строительстве https://e-proficom.ru и ремонте: полезные статьи, советы специалистов, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё для тех, кто планирует ремонт квартиры, дома или дачи.
Женский портал https://devchenky.ru секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, любовь и кулинария. Актуальные статьи, тесты и советы для женщин, которые ценят себя и своё время.
купить диплом о окончании техникума официально купить диплом о окончании техникума официально .
купить техникум диплом купить техникум диплом .
купить диплом учителя http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом учителя .
создание сайтов под ключ недорого Создание сайтов: От идеи до воплощения онлайн-присутствия В современном цифровом мире сайт – это не просто визитная карточка, а мощный инструмент для развития бизнеса, привлечения клиентов и укрепления имиджа компании. Услуги по созданию и разработке сайтов охватывают широкий спектр задач: от проектирования структуры и дизайна до написания кода и наполнения контентом. Разработка сайта: Путь к эффективному онлайн-решению Разработка сайта – это сложный и многоэтапный процесс, требующий профессионального подхода. Он включает в себя анализ целевой аудитории, определение целей и задач сайта, разработку технического задания, создание макета и дизайна, верстку и программирование, тестирование и отладку. Важно выбрать надежного подрядчика, который сможет предложить оптимальное решение, соответствующее вашим потребностям и бюджету. Создание и разработка сайтов для бизнеса: Ключевые моменты Создание и разработка сайтов для бизнеса требует особого внимания к деталям. Важно учитывать специфику бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и конкурентную среду. Сайт должен быть не только привлекательным, но и функциональным, удобным для пользователей и оптимизированным для поисковых систем. Качественная разработка веб-сайта – это основа успешного онлайн-присутствия и эффективного привлечения клиентов.
диплом техникума старого образца до 1996 г купить http://educ-ua7.ru .
autsorsing-buhgalterii-ip-812.ru .
– Только кракен официальный сайт обеспечивает безопасный вход и стабильный доступ.
куплю диплом медсестры в москве куплю диплом медсестры в москве .
https://aa-p.ru/ Сельскохозяйственная техника Сельскохозяйственная техника играет ключевую роль в современном аграрном секторе, обеспечивая выполнение различных операций, от обработки почвы и посева до уборки урожая и транспортировки сельскохозяйственной продукции. Наша компания предлагает широкий спектр сельскохозяйственной техники от ведущих мировых производителей, отвечающей самым современным требованиям эффективности, надежности и экологичности. Мы поставляем: Тракторы: Универсальные, пропашные, специализированные тракторы различной мощности для выполнения различных видов сельскохозяйственных работ. Комбайны: Зерноуборочные, кормоуборочные комбайны, оснащенные современными системами для повышения производительности и снижения потерь урожая. Почвообрабатывающую технику: Плуги, культиваторы, дисковые бороны, глубокорыхлители, обеспечивающие качественную обработку почвы и подготовку ее к посеву. Посевную технику: Сеялки, сажалки, разбрасыватели удобрений, обеспечивающие точный и равномерный посев семян и внесение удобрений. Кормозаготовительную технику: Косилки, грабли, пресс-подборщики, обмотчики, обеспечивающие качественную заготовку кормов для животноводства. Опрыскиватели: Полевые опрыскиватели, обеспечивающие эффективную защиту растений от вредителей и болезней. Прицепы и полуприцепы: Для транспортировки сельскохозяйственной продукции и других грузов. Преимущества работы с нами: Широкий ассортимент: Мы предлагаем широкий выбор сельскохозяйственной техники от ведущих мировых производителей. Гарантия качества: Мы гарантируем высокое качество поставляемой техники и ее соответствие всем требованиям безопасности и экологичности. Конкурентные цены: Мы предлагаем выгодные цены на всю сельскохозяйственную технику. Сервисное обслуживание: Мы обеспечиваем квалифицированное сервисное обслуживание и ремонт техники. Обучение персонала: Мы проводим обучение персонала по эксплуатации и техническому обслуживанию техники. Финансовые решения: Мы предлагаем различные финансовые решения, включая лизинг и кредитование, для приобретения сельскохозяйственной техники. Инвестиции в современную сельскохозяйственную технику – это залог повышения эффективности и прибыльности вашего агробизнеса. Обращайтесь к нам, и мы поможем вам подобрать технику, которая идеально подойдет для ваших нужд и условий работы!
https://tinyurl.com/2ygf7s5f mrs
найти это кракен клир
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
Реплики люксовых брендов Оригинальные бренды Оригинальные бренды – это компании и производители, которые разрабатывают и создают уникальные продукты или услуги, обладающие собственным, узнаваемым стилем, качеством и репутацией. Они инвестируют значительные ресурсы в исследования и разработки, дизайн, маркетинг и защиту своей интеллектуальной собственности. Приобретение оригинальных брендов – это выбор в пользу качества, долговечности, инноваций и поддержки креативных индустрий. Оригинальные бренды предлагают не просто товары, а воплощают определенные ценности, образ жизни и философию. Они создают историю и традиции, которые передаются из поколения в поколение. Преимущества выбора оригинальных брендов: Высокое качество: оригинальные бренды используют лучшие материалы, передовые технологии и строгий контроль качества на всех этапах производства. Уникальный дизайн: оригинальные бренды предлагают эксклюзивные дизайны, которые отличаются от массовой продукции и отражают индивидуальность потребителя. Инновации: оригинальные бренды постоянно разрабатывают новые продукты и услуги, чтобы удовлетворить потребности своих клиентов и превосходить их ожидания. Репутация: оригинальные бренды имеют заслуженную репутацию надежных и ответственных производителей. Поддержка: оригинальные бренды обеспечивают качественную поддержку своих клиентов, включая гарантийное обслуживание, консультации и обучение. Этичность: покупка оригинальных брендов поддерживает легальный бизнес и препятствует распространению подделок. В нашем магазине вы найдете широкий ассортимент оригинальных брендов из разных категорий: мода, красота, технологии, товары для дома и многое другое. Мы тщательно отбираем бренды, чтобы предложить вам только самые лучшие и надежные продукты. Мы уверены, что вы по достоинству оцените качество, стиль и инновации оригинальных брендов. Выбирайте оригинальные бренды – поддерживайте творчество, качество и инновации!
медицинское оборудование для больниц http://www.medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru .
купить диплом в брянске купить диплом в брянске .
медицинская техника http://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru .
новости авто Новости Мира Авто Новости мира авто – это ваш портал в глобальную автомобильную индустрию. Мы следим за событиями, происходящими на всех континентах, чтобы предложить вам полную и объективную картину автомобильного мира. От инновационных разработок в Китае до классического дизайна в Италии, от гоночных трасс Европы до пустынных ралли Африки – мир автомобилей разнообразен и полон сюрпризов. Что вы найдете на нашем портале: Обзоры мировых рынков: Анализ автомобильных рынков разных стран, включая объемы продаж, предпочтения потребителей, государственные программы поддержки и тенденции развития. Новости автопроизводителей: Информация о деятельности крупнейших мировых автопроизводителей, включая планы развития, инвестиции, новые модели и технологии. Международные автосалоны: Репортажи с крупнейших международных автосалонов, таких как Женевский, Франкфуртский, Детройтский и Пекинский автосалоны. Глобальные тенденции: Обзор глобальных тенденций в автомобильной индустрии, включая развитие электромобилей, автономного вождения, подключенных автомобилей и каршеринга. Автоспорт в мире: Новости автоспорта со всего мира, включая Formula 1, WRC, MotoGP, DTM и другие серии. Экологические инициативы: Информация о новых технологиях, направленных на снижение выбросов вредных веществ и повышение экологичности автомобилей. Автомобильная культура: Рассказы об автомобильной культуре разных стран, включая автомобильные клубы, фестивали и музеи. Преимущества нашего портала: Глобальный охват: Мы следим за событиями, происходящими во всех уголках мира, чтобы предложить вам полную картину автомобильного мира. Экспертный анализ: Мы привлекаем экспертов и аналитиков для оценки тенденций и прогнозирования развития автомобильного рынка. Актуальность: Мы оперативно публикуем новости, чтобы вы всегда были в курсе самых последних событий. Удобство: Наш сайт разработан таким образом, чтобы вы могли легко и быстро находить нужную вам информацию. Объективность: Мы стараемся представлять информацию без предвзятости, предоставляя различные точки зрения на происходящее. Подписывайтесь на наши новости и будьте в курсе всех событий, происходящих в автомобильном мире! Откройте для себя мир автомобилей вместе с нами!
купить диплом в чайковском купить диплом в чайковском .
stopping imipramine
1win gmail https://1win12017.ru
Hello! My name is Julia. I invest in startups. If you have an interesting project. Text me on Telegram for quick communication
https://2news.com.ua/ Новости Украины
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
It’s remarkable to visit this web site and reading the views of all colleagues on the topic of this piece of writing, while I am also eager of getting familiarity.
Banda Casino
мфо займ онлайн мфо займ онлайн .
современное медицинское оборудование medoborudovanie-77.ru .
https://tinyurl.com/2axmlvzh vnf
bannye-drova-spb.ru .
autsorsing-buhgalterii-ip-812.ru .
помощь психиатра при панических атаках Помощь руководителям и предпринимателям при выгорании. Специализированная психотерапия. Конфиденциальность. Психиатр и психотерапевт.
ремонт кавоварок у Львові ціни
все микрозаймы на карту все микрозаймы на карту .
кракен вход ссылка – Кракен официальный сайт — это проверенный ресурс с обновлениями каждый день.
все онлайн займы все онлайн займы .
Приветствую всех!
Сегодня всё больше компаний используют продвижение через блогеров. Это эффективный инструмент, который помогает находить новых клиентов и выстраивать доверие с аудиторией.
Обзор доступен по ссылке: https://medium.com/@pestovalada6003/биржи-блогеров-и-реклама-в-социальных-сетях-f2ca73e8ff54
Обсудим в следующей публикации
подробнее Как зайти на кракен зеркало 2025
модуль газового пожаротушения мгп Расчет газового пожаротушения Расчет газового пожаротушения – это комплекс инженерных вычислений, определяющих необходимое количество газового огнетушащего вещества (ГОТВ) для эффективного тушения пожара в защищаемом помещении. Результаты расчета являются основой для проектирования системы газового пожаротушения. Цели расчета газового пожаротушения: Определение необходимого количества ГОТВ для создания требуемой концентрации в защищаемом объеме. Выбор типа ГОТВ, наиболее подходящего для тушения конкретного класса пожара. Определение оптимального расположения модулей газового пожаротушения (МГП) и насадок-распылителей. Оценка времени подачи ГОТВ и времени выхода людей из помещения. Определение необходимого давления в системе. Основные факторы, учитываемые при расчете газового пожаротушения: Геометрические параметры помещения: Объем помещения, высота потолков, площадь дверей и окон. Конструктивные особенности помещения: Материалы стен, пола и потолка, наличие вентиляции и кондиционирования. Пожарная нагрузка: Тип и количество горючих материалов, находящихся в помещении. Тип ГОТВ: Химические свойства ГОТВ, огнетушащая концентрация, плотность. Температура в помещении: Влияет на плотность ГОТВ и скорость его распространения. Герметичность помещения: Наличие щелей и отверстий, через которые может происходить утечка ГОТВ. Нормативные требования: Требования пожарной безопасности, установленные национальными и международными стандартами. Методы расчета газового пожаротушения: Объемный метод: Используется для простых помещений с равномерным распределением пожарной нагрузки. Зональный метод: Используется для сложных помещений с неравномерным распределением пожарной нагрузки. Метод моделирования: Используется для оценки эффективности системы газового пожаротушения в сложных условиях, например, при наличии препятствий на пути распространения ГОТВ. Этапы расчета газового пожаротушения: Сбор исходных данных: Геометрические параметры помещения, конструктивные особенности, пожарная нагрузка, тип ГОТВ. Выбор метода расчета. Определение необходимой огнетушащей концентрации ГОТВ. Расчет количества ГОТВ. Выбор типа и количества МГП. Определение расположения МГП и насадок-распылителей. Оценка времени подачи ГОТВ и времени выхода людей из помещения. Оформление результатов расчета в виде пояснительной записки. Расчет газового пожаротушения должен выполняться квалифицированными специалистами, имеющими необходимые знания и опыт в области пожарной безопасности.
Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; we have created some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange techniques with others, please shoot me an email if interested.
best crypto sports betting
список займов онлайн на карту zaimy-50.ru .
https://bit.ly/4nFvN7s iuw
https://tinyurl.com/2dbe9orl euk
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг канал дешево накрутка живых подписчиков в тг канал дешево
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News.
Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News?
I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Thanks
займ всем займ всем .
Je trouve absolument enivrant LuckyBlock Casino, on dirait une pluie de trefles a quatre feuilles. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et eblouissants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui illuminent. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait feerique. Au final, LuckyBlock Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle magique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
crypto luckyblock|
https://tinyurl.com/26g2mz2l bvr
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
консультации маркетинг Запуск нового продукта на рынок Запуск нового продукта на рынок – это сложный и ответственный процесс, требующий тщательной подготовки и планирования. Успех запуска во многом зависит от того, насколько хорошо вы изучили рынок, определили целевую аудиторию и разработали эффективную маркетинговую стратегию. Этапы запуска нового продукта: Исследование рынка: Анализ рынка, определение целевой аудитории, изучение конкурентов. Разработка продукта: Создание продукта, отвечающего потребностям целевой аудитории и превосходящего конкурентов. Разработка маркетинговой стратегии: Определение целей запуска, позиционирование продукта, выбор каналов коммуникации. Создание маркетинговых материалов: Разработка рекламных материалов, контента для сайта и социальных сетей, презентаций для клиентов. Предпродажная подготовка: Обучение персонала, подготовка отдела продаж к работе с новым продуктом. Запуск продукта: Организация рекламной кампании, публикация пресс-релизов, проведение презентаций и других мероприятий. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов запуска, анализ продаж, отзывов клиентов и внесение корректировок в стратегию. Ключевые факторы успеха: Качественный продукт: Продукт должен быть полезным, интересным и отвечать потребностям целевой аудитории. Четкое позиционирование: Продукт должен иметь четкое позиционирование и выгодно отличаться от конкурентов. Эффективная маркетинговая стратегия: Стратегия должна быть направлена на привлечение внимания целевой аудитории и стимулирование продаж. Квалифицированный персонал: Персонал должен быть обучен работе с новым продуктом и уметь эффективно продавать его. Постоянный мониторинг и анализ: Необходимо постоянно отслеживать результаты запуска и вносить корректировки в стратегию. Запуск нового продукта – это возможность для роста вашего бизнеса. Подготовьтесь к нему тщательно, и успех не заставит себя ждать!
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
J’adore le delire de Madnix Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino totalement folle. Le repertoire du casino est un festival de dinguerie, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une decharge electrique, assurant un support de casino immediat et explosif. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient disjoncter. Pour resumer, Madnix Casino promet un divertissement de casino totalement barge pour les fous furieux du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style completement fou, ajoute une touche de folie au casino.
madnix casino bonus sans depot|
https://yandex.ru/profile/147633783627?lang=ru
ООО “Мир ремней” – Производство приводных ремней, тефлоновых сеток и лент.
Телефон +7 (936) 333-93-03
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Slivfun http://www.sliv.fun .
кракен официальный сайт зеркало – Кракен официальный сайт зеркало — быстрый способ подключиться и продолжать работу.
drova-suhie-spb.ru .
дрова ольха цена .
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг
https://tinyurl.com/29jvvo5x wcm
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu buszken tamogatja a kormanypartot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Строительные материалы https://stroy-marketplace.ru в Серпухове: кирпич, цемент, сухие смеси, пиломатериалы и утеплители. Большой выбор для ремонта и строительства, доставка по городу и району.
купить диплом в ульяновске rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в ульяновске .
купить диплом в люберцах купить диплом в люберцах .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
накрутка подписчиков телеграм бесплатно
заміна контролера і мотора електросамоката
продвижение обучение http://www.kursy-seo-5.ru/ .
дрова колотые береза с доставкой цена .
дрова колотые сухие дешево .
психиатр психотерапевт частная практика Страдаете от выгорания на работе или в бизнесе? Обратитесь к квалифицированному психотерапевту. Индивидуальная программа для восстановления сил и мотивации.
купить диплом в южно-сахалинске купить диплом в южно-сахалинске .
газовые модули пожаротушения потолочные Аэрозольно газовое пожаротушение Аэрозольно-газовое пожаротушение – это комбинированный метод, сочетающий в себе преимущества аэрозольного и газового пожаротушения. Данный метод использует специальные составы, которые при активации образуют мелкодисперсный аэрозоль и газообразные продукты, быстро подавляющие горение. Основные принципы работы: Ингибирование горения: Аэрозольные частицы и газообразные продукты, образующиеся при срабатывании установки, ингибируют (замедляют или прекращают) химические реакции в зоне горения. Разбавление среды: Газообразные продукты разбавляют кислород в зоне горения, снижая его концентрацию до уровня, при котором горение становится невозможным. Охлаждение: Аэрозольные частицы поглощают тепло из зоны горения, способствуя её охлаждению. Преимущества аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Высокая эффективность: Быстрое подавление пожаров различных классов (A, B, C, E). Безопасность для оборудования: Не повреждает электронное оборудование и другие ценности, так как не оставляет следов. Экологичность: Используются составы, не разрушающие озоновый слой. Универсальность: Подходит для защиты различных типов помещений, включая серверные, архивы, электрощитовые и промышленные объекты. Легкость монтажа и обслуживания: Установки компактны и не требуют сложной инфраструктуры. Экономичность: За счет меньшего расхода огнетушащего вещества по сравнению с традиционными газовыми системами. Недостатки аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Опасность для людей: При высокой концентрации аэрозоля и газов может быть опасна для здоровья, поэтому перед срабатыванием системы необходимо эвакуировать людей из помещения. Требования к герметичности помещения: Для эффективной работы системы необходимо обеспечить герметичность помещения. Возможность задымления: После срабатывания установки в помещении может образоваться дым, затрудняющий видимость. Применение аэрозольно-газового пожаротушения: Защита серверных комнат и центров обработки данных. Защита электрощитовых и трансформаторных подстанций. Защита архивов и библиотек. Защита музеев и картинных галерей. Защита промышленных объектов с высоким риском возникновения пожара. Аэрозольно-газовое пожаротушение – это современный и эффективный способ защиты имущества и жизни людей от пожара, требующий профессионального проектирования, монтажа и обслуживания.
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
https://bit.ly/4pzXVuA cea
накрутка подписчиков телеграм телеграмм
https://tinyurl.com/29jvvo5x img
как зайти на кракен с телефона – Через кракен сайт легко попасть на площадку даже при блокировках — зеркала обновляются ежедневно.
lucky pari линия prematch lucky pari линия prematch
Купить диплом ВУЗа поспособствуем. Диплом о дополнительном образовании – diplomybox.com/diplom-o-dopolnitelnom-obrazovanii
https://bit.ly/4nMwmga uyh
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
Слив платных курсов бесплатно
autsorsing-buhgalterii-ip-812.ru .
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – инновационные решения
If you need to economize, order your http://www.mirtazapineinfolive.com been approved by the FDA?
где купить диплом колледжа в астрахани http://frei-diplom10.ru .
живые подписчики в телеграм канал живые подписчики в телеграм канал
где купить дипломы медсестры где купить дипломы медсестры .
как войти в lucky pari как войти в lucky pari
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом 2017 года — kyc-diplom.com/diplom-articles/kupit-diplom-2017-goda.html
https://2news.com.ua/ Новости Украины
SEO продвижение сайта
Привет! Меня зовут Сергей, и я частный SEO-оптимизатор с более чем пятилетним опытом работы в области комплексного продвижения сайтов. Моя основная цель — помочь вашему бизнесу занять лидирующие позиции в поисковых системах, таких как Yandex и Google, а также увеличить видимость вашего сайта в вашем регионе.
Что я предлагаю:
1. Продвижение сайта в Yandex и Google:
? Индивидуальный подход к построению стратегии продвижения под каждую ПС учитывая специфику вашего рынка и бизнес-целей.
? Оптимизация контента и технических аспектов сайта для соответствия требованиям каждой платформы.
2. Комплексный подход к оптимизации:
? Провожу полный аудит вашего сайта для выявления слабых мест и возможностей для улучшения.
? Разрабатываю индивидуальный план действий, который включает внутреннюю и внешнюю оптимизацию, работу с контентом и юзабилити.
3. Продвижение сайта в регионе:
? Учитываю региональные особенности алгоритмов Yandex, что позволяет мне разрабатывать стратегии, которые работают именно для вашей целевой аудитории.
? Повышаю видимость вашего бизнеса среди местных пользователей.
4. Постоянный мониторинг и адаптация:
? Регулярно отслеживаю результаты продвижения с помощью аналитических инструментов.
? Быстро реагирую на изменения алгоритмов поисковых систем и корректирую стратегию при необходимости.
локальное seo
Если вы ищете надежного партнера для SEO-продвижения вашего сайта, который обеспечит вам устойчивые результаты и рост бизнеса, буду рад помочь!
Давайте вместе сделаем ваш сайт видимым для вашей целевой аудитории. Свяжитесь со мной, чтобы обсудить детали сотрудничества!
энергетическая инфраструктура сочи – передовые энергомощности
Play shining crown oyunu ilə böyük həyəcan yaşamaq mümkündür.
Casino shining crown oyunları müasir dizayn ilə fərqlənir.
Shining crown nasıl oynanır sualına cavab çox sadədir. Shining crown demo ron Avropa bazarında məşhurdur. Shining Crown oyunu klassik meyvə simvollarını əhatə edir.
EGT digital shining crown yüksək keyfiyyətə malikdir.
Shining crown bell link demo tez-tez istifadə olunur.
Sadə kliklə açılır bu link.
40 shining crown klassik və sadə oyun mexanikası təqdim edir.
Shining crown free real oyun öncəsi yaxşı sınaqdır.
кракен онион – Через кракен зеркало рабочее легко обойти блокировки и попасть в личный кабинет.
диплом колледжа 2016 купить http://www.frei-diplom7.ru .
медицинское оборудование медицинское оборудование .
все займы все займы .
Ich bin suchtig nach iWild Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbandigen Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und elektrisierend, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und wild, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist iWild Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Wildnis beherrscht fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Wasserfall funkelt, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
iwild casino promo code no deposit|
Website https://tione.ru/ .
bannye-drova-noginsk.ru .
дрова 25 30 см купить .
где купить диплом среднем где купить диплом среднем .
Best arcade games https://baji-bj.com
Je trouve absolument siderant JackpotStar Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine tout. La collection de jeux du casino est astronomique, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance astrale. Le service client du casino est une etoile brillante, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un meteore, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient briller. Au final, JackpotStar Casino est une etoile brillante pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et rayonnante comme une aurore, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
jackpotstar casino -kokemuksia|
energoinfo-sochi.ru – энергоразвитие города
купить диплом в петрозаводске купить диплом в петрозаводске .
купить проведенный диплом вуза http://www.frei-diplom1.ru .
Замовити ремонт квартир у Тернополі можна на сайті remontuem.te.ua за доступними цінами.
медицинские приборы http://www.medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru/ .
купить диплом в реестре купить диплом в реестре .
аппараты медицинские http://www.medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru .
кракен онион – Подключение через кракен онион подходит для тех, кто ценит безопасность.
купить диплом в саранске купить диплом в саранске .
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
техникум купить диплом educ-ua7.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск .
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
Shining crown oyna seçimi saytda hər kəs üçün açıqdır.
Shining crown 77777 slot oyunu fərqli simvollarla doludur.
Shining crown slot oyna mobil və PC üçün uyğundur. Shining crown amusnet çoxlu oyun variantı ilə tanınır. Shining Crown oyunu klassik meyvə simvollarını əhatə edir.
Play shining crown asan interfeys ilə təklif olunur.
Shining crown buy bonus oyunçulara əlavə qazanc gətirir.
Bu linkdən oyuna keçid edin shining crown slot game.
Shining crown gratis demo çox sevilir.
Shining crown slot online tez yüklənir.
revia cost
купить диплом во владимире купить диплом во владимире .
купить vip диплом техникума ссср купить vip диплом техникума ссср .
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
Undeniably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the
simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people think
about worries that they plainly do not know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people
could take a signal. Will probably be back to get more.
Thanks
купить диплом в нижнекамске http://www.rudik-diplom13.ru .
https://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – перспективные технологии
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
услуги pr менеджера Консультация по маркетингу: Экспертное руководство для вашего бизнеса Консультация по маркетингу – это ценная возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это шанс взглянуть на ваш бизнес свежим взглядом, выявить скрытые возможности и устранить препятствия, мешающие вам достичь ваших целей. В отличие от теоретических знаний, консультация по маркетингу дает вам практические инструменты и стратегии, которые вы можете немедленно применить в своем бизнесе. Я помогу вам найти оптимальные решения для ваших конкретных задач и проблем. Что вы получите на консультации: Глубокий анализ вашего бизнеса: Я проведу тщательный анализ вашего бизнеса, чтобы понять ваши сильные и слабые стороны, целевую аудиторию, конкурентную среду и потенциальные возможности для роста. Определение четких маркетинговых целей: Я помогу вам определить четкие и измеримые маркетинговые цели, которые соответствуют вашим общим бизнес-целям. Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии: Я создам индивидуальную маркетинговую стратегию, учитывающую особенности вашего бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и бюджетные ограничения. Рекомендации по выбору маркетинговых инструментов: Я дам вам рекомендации по выбору наиболее эффективных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей, включая SEO, контекстную рекламу, SMM, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг и другие. Практические советы по улучшению маркетинговой деятельности: Я поделюсь с вами проверенными советами и стратегиями по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на все ваши вопросы: Я отвечу на все ваши вопросы, связанные с маркетингом, развею ваши сомнения и помогу вам принять правильные решения для вашего бизнеса. Когда вам нужна консультация по маркетингу: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение вашего бизнеса. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите желаемых результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы планируете вывести на рынок новый продукт или услугу. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Вы хотите получить независимую оценку вашей текущей маркетинговой деятельности. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную поддержку и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e uma explosao visual escaldante, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
osh avis forum|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Pledoo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Tanz durch die Spielwelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Sonnenstrahl, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Alles in allem ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
pledoo casino review|
кракен вход зеркало – Выбирайте кракен зеркало рабочее — оно всегда проверено и безопасно.
купить диплом техникума в казани купить диплом техникума в казани .
аутсорсинг стоимость бухгалтерских услуг .
1win ставки на спорт скачать http://1win12017.ru/
накрутка подписчиков тг
Joaca jocul World of Warships Romania gratuit! Exploreaza marile, folose?te-?i strategia ?i condu nave de razboi celebre. Batalii realiste ?i echipe interna?ionale te a?teapta.
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – автоматизированные процессы
seo базовый курc kursy-seo-5.ru .
медицинское оборудование медицинское оборудование .
микрозайм все http://zaimy-28.ru .
купить диплом моториста купить диплом моториста .
Slivfun sliv.fun .
кракен тор зеркало – Кракен вход в личный кабинет доступен через рабочие зеркала и актуальные ссылки.
купить диплом техникума в кургане купить диплом техникума в кургане .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
куплю диплом медсестры в москве куплю диплом медсестры в москве .
всезаймыонлайн http://zaimy-29.ru/ .
купить диплом бурильщика https://www.rudik-diplom7.ru .
Shining crown online casino əyləncəsi 24/7 mövcuddur.
Shining crown big win qazanmaq motivasiya yaradır.
Shining crown nasıl oynanır sualına cavab çox sadədir. Shining crown amusnet çoxlu oyun variantı ilə tanınır. Shining crown apk mobil cihazlarda problemsiz işləyir.
Shining crown joc gratis təcrübə qazandırır.
Shining crown buy bonus oyunçulara əlavə qazanc gətirir.
Bu linkdən oyuna keçid edin shining crown slot game.
Shining crown gratis demo çox sevilir.
Shining crown demo oyna risksiz məşqdir.
https://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – профессиональный портал
купить диплом повара-кондитера купить диплом повара-кондитера .
website – https://bookmark-nation.com/story20143433/how-to-get-1xbet-promo-code .
продвижение бренда в интернете Маркетинговое продвижение бренда Маркетинговое продвижение бренда – это комплекс стратегических мероприятий, направленных на формирование и укрепление позитивного имиджа компании в сознании целевой аудитории. Это не просто реклама, а создание устойчивых ассоциаций с вашим брендом, формирование лояльности и, в конечном итоге, увеличение продаж. Этапы продвижения бренда: Аудит бренда: Анализ текущего состояния бренда, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение целевой аудитории и конкурентов. Разработка стратегии: Определение целей продвижения, разработка позиционирования бренда, ключевых сообщений и каналов коммуникации. Разработка фирменного стиля: Создание визуальной идентичности бренда, включая логотип, цветовую палитру, шрифты и другие элементы. Разработка контент-стратегии: Создание контента, который отражает ценности бренда, привлекает целевую аудиторию и формирует экспертный имидж компании. Реализация стратегии: Запуск рекламных кампаний, продвижение в социальных сетях, участие в мероприятиях, работа со СМИ и другие активности. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов продвижения, анализ эффективности каналов коммуникации, внесение корректировок в стратегию. Основные инструменты: Реклама: Размещение рекламы в различных каналах (онлайн и офлайн) для привлечения внимания к бренду. PR: Формирование позитивного общественного мнения о бренде через работу со СМИ и общественностью. SMM: Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях для установления контакта с целевой аудиторией и формирования лояльного сообщества. Контент-маркетинг: Создание и распространение полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории. Event-маркетинг: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения узнаваемости бренда и установления контакта с потенциальными клиентами. Инвестиции в продвижение бренда – это инвестиции в будущее вашего бизнеса. Грамотно выстроенная стратегия позволит вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов, привлечь лояльных клиентов и увеличить прибыль.
are fake shoes good – where are replica shoes made
медоборудование medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru .
медицинские приборы http://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-77.ru .
Kingpin Crown in Australia is a premium entertainment venue offering bowling, laser tag, arcade games, karaoke, and dining: Kingpin Crown official website
Hi my family member! I want to say that this post is awesome,
great written and include approximately all important infos.
I would like to see more posts like this .
Shining crown demo oyna imkanı yeni başlayanlar üçün faydalıdır.
Casino shining crown oyunları müasir dizayn ilə fərqlənir.
Shining crown nasıl oynanır sualına cavab çox sadədir. Pacanele gratis shining crown ilə vaxtı maraqlı keçir. Shining crown big win xəbərləri tez-tez yayımlanır.
Shining crown jackpot oyunçuların əsas hədəfidir.
Shining crown buy bonus oyunçulara əlavə qazanc gətirir.
Sayta birbaşa keçid https://shining-crown.com.az/.
Shining crown gratis demo çox sevilir.
Shining crown pacanele oyunçular arasında çox populyardır.
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
кракен ссылка darknet – Кракен ссылка актуальная — стабильный вариант обхода блокировок.
Читать далее водка бэт
такой
vodkabet прямо сейчас
накрутить подписчиков в тг канале бесплатно онлайн накрутить подписчиков в тг канале бесплатно онлайн
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru – чистая энергия
проект на водопонижение https://proektirovanie-vodoponizheniya.ru .
доставка алкоголя в москве https://alcohub9.ru .
Searching for an Exotic cat in the Kansas City area? You’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will walk you through all the necessary steps to find and adopt a healthy and happy feline companion. From learning about the breed’s characteristics to finding trustworthy breeders and adoption centers, we’ll cover every detail. Whether you’re a first-time cat owner or a seasoned cat lover, you’ll find this article invaluable.
Meet the Exotic Shorthair Breed
The Exotic Shorthair is often fondly called “the low-maintenance Persian.”
This moniker is well-deserved. They were developed in the 1950s by crossing American Shorthairs with Persians, with the goal of creating a cat that had the gentle, docile temperament of the Persian but with a low-shed, easy-care coat. The result was a lovely and placid breed that rapidly gained popularity.
Key characteristics of the Exotic cat include:
A plush, dense coat that feels like a teddy bear.
A broad, rounded face with tiny ears.
Big, round eyes that are often described as ‘dinner-plate’ sized.
A flat, ‘brachycephalic’ face.
A cobby body with short, thick legs.
A soft, gentle voice.
Personality and Behavior
The personality of the Exotic is without a doubt its most appealing trait. They are known for being:
Calm and placid.
They love to relax and are more sedentary than many other breeds.
Affectionate and loyal. They form strong bonds with their human companions and adore snuggling.
Quiet and low-key. They don’t demand a lot of attention but readily welcome it when offered.
Tolerant of kids and other animals.
Their easy-going nature makes them a great fit for households with children and other animals.
Fun-loving, but not manic. They enjoy a good play session but are equally happy to nap on the sofa.
Finding a Reputable Exotic Shorthair Breeder in Kansas City
When you decide to purchase a purebred cat, the most critical step is to find a reputable and ethical breeder. A good breeder focuses on the welfare and health of their cats, makes sure the kittens are well-adjusted, and provides all necessary health guarantees and documentation.
Here’s what to look for when vetting a Kansas City breeder:
Affiliation with a cat organization like The Cat Fanciers’ Association (CFA) or The International Cat Association (TICA). This shows a commitment to breed standards and ethics.
Allowing you to see their facility. A good breeder will be happy to show you where their cats live. The cattery should be clean, well-maintained, and free of strong odors.
Genetic testing. They should provide proof that the parent cats have been screened for hereditary diseases like Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD).
Detailed health contracts. They should offer a contract that specifies the health of the kitten and what happens if issues arise.
Age of the kittens. Kittens should not leave their mother before they are at least 12 weeks old. This gives them time to socialize and learn essential cat skills.
References. Ask for references from previous buyers.
The breeder screens you. A good breeder will be just as interested in you if you are a good home for their cat as you are in them.
While we cannot list specific breeders, you can use the official CFA or TICA sites to search for registered catteries in the Kansas City area. You can also attend local cat shows to meet breeders face-to-face.
Adopting an Exotic Shorthair from a Rescue in Kansas City
Giving a cat a second chance is a noble and rewarding path. While finding a true Exotic Shorthair in a standard animal shelter can be challenging, it’s still a possibility. Many purebreds end up in shelters or rescues due to various circumstances like an owner’s passing or a family change.
Tips for finding a rescue Exotic:
Check local Kansas City animal shelters and humane societies. Keep an eye on the websites of organizations like the KC Pet Project, Wayside Waifs, or other local rescue groups.
Contact breed-specific rescue organizations. There are rescues dedicated to finding homes for Persians and Exotics.
A quick online search for “Exotic Shorthair rescue” will give you options.
Create search alerts. Many adoption websites allow you to set up email alerts for certain types of cats.
Talk to breeders. Sometimes, breeders will have an older cat or a retired breeding cat that they are trying to place in a new home.
Budgeting for Your Exotic Shorthair
The price of an Exotic Shorthair can fluctuate significantly based on the breeder’s reputation, the kitten’s bloodline, and whether it’s for show or for pet.
From a reputable breeder, you can expect to pay anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000 or more for a pet-quality kitten.
Rescue fees from a rescue organization are significantly lower, typically ranging from around $150 to $400. This fee usually covers spaying/neutering, initial vaccinations, and a microchip.
The purchase price is not the only cost. You’ll also need to budget for:
Food.
Vet check-ups and routine care.
Grooming supplies.
Entertainment.
Litter and litter boxes.
A carrier and a cat bed.
Grooming and Care
One of the main appeals of the Exotic Shorthair is its easy-care coat.
While they don’t have the long hair of a Persian, they do need regular grooming to avoid mats and fur balls.
Grooming: A short, daily brushing session is recommended to remove loose hair and maintain the coat’s health. A a special brush works effectively.
Washing: They don’t need baths often, but a bath every few months will help keep their coat shiny and clean.
Facial Care: Due to their flat face, they are prone to tear stains.
Gently cleaning their face with a a moist cloth designed for this purpose will help keep the area clean and prevent staining.
Clipping nails: Trim their nails every couple of weeks.
Dental Hygiene: Brushing their teeth regularly is essential to maintain good oral health.
Common Health Issues to Be Aware Of
While generally a robust cat, the Exotic Shorthair’s unique facial structure makes them at risk for certain health issues.
A good breeder will screen for these, but it’s important for you to be knowledgeable about them.
Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome: This is a group of problems that can make it difficult to breathe. Symptoms include snorting, snoring, and heavy breathing.
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD): This is a hereditary disease that can lead to kidney failure.
Responsible breeders will test their cats for this condition.
Eye problems: Due to their big eyes, they can be susceptible to issues like watering eyes and prolapsed glands.
Dental Disease: Their unique mouth shape can lead to dental crowding and gum disease.
Bringing Your New Exotic Shorthair Home
Once you’ve found your perfect cat, it’s time to prepare for their arrival.
Make your home safe for a cat. Put away anything small they might eat and hide any cables.
Create a special room for them. A small, quiet room with a litter box, food, water, and a bed will help them adjust to their new surroundings without feeling overwhelmed.
Take your time introducing them to other animals. Use a step-by-step introduction method to avoid fights.
Establish a routine. Cats thrive on regularity.
Consistent feeding, play, and grooming will help them feel secure.
Final Thoughts
The search for an Exotic Shorthair in Kansas City is an exciting one. By taking your time and being diligent, you can find a wonderful cat that will provide you with years of happiness and love. Whether you choose to adopt from a rescue or purchase from a reputable breeder, an Exotic Shorthair will be a a wonderful and sweet member to your family. With their lovely personality and cute appearance, it’s no surprise they are so popular. Enjoy the process, and get ready to welcome your new best friend!
my blog … https://www.mumsnet.com/talk/weight_loss_chat/5392020-quick-question-about-mitolyn-anyone-had-luck-with-it
разработка проекта водопонижения https://proekt-vodoponizheniya.ru/ .
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.
nonetheless, you command get bought an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following.
unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the
same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
дрова колотые с доставкой .
кракен тор – Кракен маркетплейс — официальная площадка с товарами и сервисами.
https://1fab.ru/
Hi there! I’m at work browsing your blog from
my new apple iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts!
Keep up the superb work!
https://www.ted.com/profiles/50254007
I blog frequently and I really appreciate your information. The article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to book mark your website and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
вход зума казино
http://energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – эффективные вложения
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
https://europrivat.com/
——————————-
Description:
EuroPrivat is a modern Czech portal for erotic services, focused on offers such as:
• Girls for sex
• Erotic massages
• Escort services
• Businesses
? Advantages:
• Premium and new ads — select the best girls
• Clear division by location
• Emphasis on safety, quality and trust
seo с нуля seo с нуля .
ваш провідник у житті Львова https://79000.com.ua актуальні новини, культурні та громадські події міста, урбаністика, інтерв’ю з цікавими людьми, фотоогляди локальних заходів. Все про те, що формує атмосферу Львова сьогодні — оновлення, проекти, історії.
інформаційний портал https://21000.com.ua Вінниці і області: місцеві новини, анонси культурних, спортивних та громадських подій, репортажі з місця подій, інтерв’ю з вінничанами. Все про те, що відбувається у Вінниці — ближче, живіше, щодня.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цены .
By providing valuable information, they empower shoppers to make better decisions.
online store reviews online store reviews.
как можно набрать подписчиков в телеграм как можно набрать подписчиков в телеграм
Смотреть здесь водка бет
drova-suhie-spb.ru .
Hi! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the outstanding work!
зеркало leebet casino
купить диплом швеи купить диплом швеи .
кракен зеркало актуальное – Кракен зеркало рабочее доступно каждый день и подходит для входа с телефона или ПК.
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – подробные анализы
дрова в мешках купить с доставкой .
https://1-ceh.ru/
Adoro o clima insano de PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma corrente de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Resumindo, PagolBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
pagolbet.|
Acho simplesmente colossal MonsterWin Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao monstruosa. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma besta, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma fera. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, MonsterWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual feroz, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
monsterwin casino login|
Je suis fou de PokerStars Casino, on dirait un ciel etoile de sensations. Le repertoire du casino est un tournoi de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un croupier d’elite, avec une aide qui mise juste. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans mauvaise donne, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. Pour resumer, PokerStars Casino offre une experience de casino palpitante pour les strateges du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie gagnante, facilite une experience de casino strategique.
pokerstars en ligne|
купить диплом массажиста купить диплом массажиста .
купить диплом цена https://rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом цена .
лучшее зеркало мега https://www.athletessecretweapon.com
Can I take cost of lasix at FurousaLasix – FurousaLasix.com , a proven treatment for your condition
https://www.ict-tech.com.ng/2019/07/6-best-free-online-business.html?sc=1734971950427#c8768440018370200379
купить диплом в абакане купить диплом в абакане .
Пиломатериалы в Минске https://farbwood.by оптом и в розницу. Доска обрезная и строганая, брус, лаги, террасная доска. Качественная древесина для строительства и ремонта. Быстрая доставка.
горшок с автополивом горшок с автополивом .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
drova-suhie-spb.ru .
кракен официальный сайт – Подключение через кракен онион подходит для тех, кто ценит безопасность.
okna-plastic-11.ru – онлайн-каталог по установке ПВХ с выездом замерщика
проститутки недорого Новосибирск
Таким образом, выбор не ограничивается только одним типом услуги.
Website https://tione.ru/ .
дом из клееного бруса купить
услуги интернет маркетологов Маркетинговое продвижение бренда Маркетинговое продвижение бренда – это комплекс стратегических мероприятий, направленных на формирование и укрепление позитивного имиджа компании в сознании целевой аудитории. Это не просто реклама, а создание устойчивых ассоциаций с вашим брендом, формирование лояльности и, в конечном итоге, увеличение продаж. Этапы продвижения бренда: Аудит бренда: Анализ текущего состояния бренда, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение целевой аудитории и конкурентов. Разработка стратегии: Определение целей продвижения, разработка позиционирования бренда, ключевых сообщений и каналов коммуникации. Разработка фирменного стиля: Создание визуальной идентичности бренда, включая логотип, цветовую палитру, шрифты и другие элементы. Разработка контент-стратегии: Создание контента, который отражает ценности бренда, привлекает целевую аудиторию и формирует экспертный имидж компании. Реализация стратегии: Запуск рекламных кампаний, продвижение в социальных сетях, участие в мероприятиях, работа со СМИ и другие активности. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов продвижения, анализ эффективности каналов коммуникации, внесение корректировок в стратегию. Основные инструменты: Реклама: Размещение рекламы в различных каналах (онлайн и офлайн) для привлечения внимания к бренду. PR: Формирование позитивного общественного мнения о бренде через работу со СМИ и общественностью. SMM: Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях для установления контакта с целевой аудиторией и формирования лояльного сообщества. Контент-маркетинг: Создание и распространение полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории. Event-маркетинг: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения узнаваемости бренда и установления контакта с потенциальными клиентами. Инвестиции в продвижение бренда – это инвестиции в будущее вашего бизнеса. Грамотно выстроенная стратегия позволит вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов, привлечь лояльных клиентов и увеличить прибыль.
энергетика сочи 2025 – энергетические инициативы 2025
Crown Metropol Perth is a luxury hotel located near the Swan River. It offers modern rooms, a stunning pool area, fine dining, a casino, and entertainment options: Crown Metropol Perth hotel reviews
остекление балкона пластиковыми окнами цены – теплое остекление скидка 15% при заказе с сайта
Slightly off from the thread, but I thought I’d share
Just while browsing health blogs I found a site called smart shopping site.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Simple but smart advice.
Who else is picky about food quality?
Играйте в казино беларусь и наслаждайтесь захватывающими развлечениями прямо у себя дома!
Каждый игрок найдет игру по душе
живые подписчики в телеграм
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4107706231/
Дома из клееного бруса под ключ проекты
накрутка подписчиков в тг бот
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
займы все http://www.zaimy-29.ru .
проект осушения котлована проект осушения котлована .
проектирование водопонижения иглофильтровыми установками http://www.vodoponizhenie-proekt.ru .
купить диплом в озёрске http://www.rudik-diplom5.ru .
как купить диплом проведенный как купить диплом проведенный .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better!
Reading through this post reminds me of my good old room mate!
He always kept chatting about this. I will forward
this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
диплом техникума ссср купить http://educ-ua7.ru .
Электрокарниз — это идеальное решение для вашего дома, которое позволяет легко управлять шторами с помощью пульта.
При выборе электрокарниза следует обратить внимание на размеры оконных проемов.
дома из клееного бруса
консультации маркетинг Услуги интернет-маркетолога В современном цифровом мире, где онлайн-присутствие играет ключевую роль в успехе любого бизнеса, услуги опытного интернет-маркетолога становятся необходимостью. Я предлагаю полный спектр услуг, направленных на увеличение видимости вашего бренда, привлечение целевой аудитории и, как следствие, повышение продаж. Мои услуги включают: Анализ рынка и конкурентов: Тщательный анализ позволит определить оптимальные стратегии продвижения, выявить сильные и слабые стороны конкурентов и определить целевую аудиторию. Разработка маркетинговой стратегии: Создание индивидуальной стратегии, учитывающей особенности вашего бизнеса, цели и бюджет. SEO-оптимизация: Повышение позиций вашего сайта в поисковых системах, что обеспечит приток органического трафика. Контекстная реклама: Настройка и ведение рекламных кампаний в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads для быстрого привлечения целевых клиентов. SMM-продвижение: Разработка и реализация стратегии продвижения в социальных сетях, создание контента, привлечение подписчиков и повышение вовлеченности аудитории. Контент-маркетинг: Создание полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории, повышения лояльности к бренду. Email-маркетинг: Разработка стратегии email-рассылок, создание писем и автоматизация процессов для поддержания связи с клиентами и стимулирования продаж. Аналитика и отчетность: Регулярный анализ результатов и предоставление отчетов о проделанной работе, что позволит оценить эффективность стратегии и внести необходимые корректировки. Я готов предложить вам комплексные решения, которые помогут вашему бизнесу достичь новых высот в онлайн-пространстве. Свяжитесь со мной, чтобы обсудить ваши задачи и разработать индивидуальный план продвижения.
The best deals along with the lowest price of metronidazole bnf at FlagyMet.com – FlagyMet from leading pharmacies
купить диплом в ульяновске купить диплом в ульяновске .
Estou pirando com ParamigoBet Casino, e um cassino online que e um verdadeiro furacao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma ventania, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um ciclone, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No fim das contas, ParamigoBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um furacao.
paramigobet erfahrungen|
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
Je suis totalement captive par MrPlay Casino, on dirait un carnaval de sensations fortes. Le catalogue du casino est une explosion de couleurs ludiques, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance festive. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un numero de cirque, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une choregraphie, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient danser. Pour resumer, MrPlay Casino offre une experience de casino exuberante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique festive, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
mr.play erfahrungen|
J’adore la vague de Posido Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino aquatique. Le repertoire du casino est un recif de divertissement, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un capitaine, avec une aide qui fait des vagues. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans remous, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient nager de joie. En somme, Posido Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les navigateurs du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique fluide, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
posido casino|
Website https://useit2.ru/.
где купить подписчиков в телеграм где купить подписчиков в телеграм
купить диплом жд техникума купить диплом жд техникума .
можно ли купить легальный диплом http://www.frei-diplom5.ru/ .
купить диплом колледжа настоящий https://www.frei-diplom9.ru .
купить диплом в азове купить диплом в азове .
проект на водопонижение проект на водопонижение .
Слив курсов https://www.sliv.fun .
доставка алкоголя на дом http://www.alcohub9.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм дешево накрутка подписчиков в телеграм дешево
накрутка просмотров и подписчиков в телеграм
Shining crown online casino əyləncəsi 24/7 mövcuddur.
Shining crown big win qazanmaq motivasiya yaradır.
Shining crown slot oyna mobil və PC üçün uyğundur. Shining crown free play hər kəs üçün əlçatan seçimdir. Shining Crown oyunu klassik meyvə simvollarını əhatə edir.
Shining crown pacanele Rumıniya bazarında liderdir.
Shining crown buy bonus oyunçulara əlavə qazanc gətirir.
Bu linkdən oyuna keçid edin shining crown slot game.
Shining crown online casino rahat giriş imkanı verir.
Shining crown demo oyna risksiz məşqdir.
Откройте для себя удобство и стиль, используя карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом для штор|потолочные карнизы с электроприводом|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом цена|карнизы с электроприводом купить|карнизы с электроприводом с дистанционным управлением|карнизы с электроприводом и дистанционным|карнизы с электроприводом и пультом управления купить|Карнизы с электроприводом для вашего дома!
Тем не менее, часто необходимо обратиться к специалистам для качественной установки.
bannye-drova-noginsk.ru .
купить диплом в майкопе http://www.rudik-diplom7.ru .
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
https://alive-portal.ru/
подписчики в тг канал подписчики в тг канал
купить диплом в курске купить диплом в курске .
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
https://www.okna-plastic-12.ru – онлайн-заказ пластиковых окон в Москве
https://tinyurl.com/25sgknfc zzz
drova-suhie-spb.ru .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Электрические жалюзи электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи с дистанционным управлением|электрические жалюзи на мансардные окна|купить электрические жалюзи на окна|электрические жалюзи в москве|электрические жалюзи автоматические|электрические жалюзи на пластиковые окна купить|электрические жалюзи стоимость|электрические жалюзи на окна заказать — это идеальное решение для современного интерьера, обеспечивающее комфорт и стиль.
Выбирая подходящий вариант, вы сможете легко интегрировать его в свой интерьер.
https://bit.ly/4mlz8aN xzl
Открой Кракен — progressive platform, обеспечивающее effective обеспечение личных данных в digital environment. intuitive вход позволяет quickly использовать capabilities для optimal анонимности. platform поддерживает широкий спектр transactions, обеспечивая секретность на профессиональном уровне. unique опции предназначены для guaranteeing безопасных сделок. Передовые solutions позволяют reduce to zero риски, связанные с unauthorized access. Кракен — это proven resource, позволяющий effectively and securely выполнять сделки в онлайн пространстве. Работая с Kraken marketplace, вы guarantee maximal level security, что делает уверенность your data на каждом этапе usage.
Ссылка КРАКЕН
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм
займ онлайн срочно микрозаймы онлайн
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
проект на водопонижение proekt-na-vodoponizhenie.ru .
займы деньги взять деньги онлайн
https://bit.ly/4262piC yqq
https://1-ceh.ru/
купить диплом в ельце http://rudik-diplom13.ru .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы .
https://bit.ly/42xFrkA uyz
herzmedikamente ohne betablocker
Отключение света Артём Экология Артём Все об экологии города Артёма: проблемы загрязнения, природоохранные мероприятия и рекомендации для жителей.
купить диплом в рыбинске http://rudik-diplom1.ru .
Автоматические рулонные шторы не только обеспечивают удобство управления, но и стильный акцент в интерьере вашего дома, особенно если вы выберете автоматические рулонные шторы|автоматика для рулонных штор|автоматические шторы для труднодоступных окон.
Использование автоматических рулонных штор приносит много преимуществ.
https://tinyurl.com/24r6slej qbz
kupit-drova-v-setkah-sergiev-posad.ru .
дрова колотые с доставкой .
https://kitehurghada.ru/
https://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – стратегические планы
website – https://wisesocialsmedia.com/story5776279/how-to-get-1xbet-promo-code .
Hi this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
CSFAIL бонус к пополнению
Хотите больше бонусов от казино?
Доступ к акциям и промокодам открыт для всех.
Собраны советы для новичков и профи, которые помогут вам играть эффективнее.
Перейдите по ссылке и узнайте больше: https://naturovo.ru/pages/kak_nazuvaetsya_igra_v_kazino_klubnika__2.html.
Начните играть с выгодой прямо сейчас!
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это идеальное решение для создания уюта и комфорта в вашем доме, позволяющее управлять светом и приватностью с помощью простого нажатия кнопки.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом становятся все более популярными. Такие шторы – это отличное решение для любого помещения. Функциональность и удобство использования выделяют их среди других вариантов.
Ключевым достоинством является возможность дистанционного управления шторами. Это позволяет легко регулировать уровень освещения в помещении. Электропривод позволяет задать расписание открытия и закрытия штор.
Установка рулонных штор с электроприводом проходит без особых трудностей. Необходимо всего лишь несколько инструментов и немного терпения. Выбор из множества дизайнов и материалов дает возможность подобрать идеальный вариант для любого стиля.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом обеспечивают не только стильный вид, но и защиту от солнца. С помощью различных тканей можно регулировать уровень затемнения. Таким образом, вы сможете создать комфортную атмосферу в своем доме.
Криминал Артём Артём 24 Круглосуточный доступ к новостям города Артёма! Наш портал предоставляет вам самую свежую и актуальную информацию о происшествиях, событиях, изменениях в городской жизни и многом другом. Мы работаем 24 часа в сутки, 7 дней в неделю, чтобы вы всегда были в курсе всего, что происходит в Артёме.
max мессенджер для компьютера Max Мессенджер Видеозвонки Мессенджер Max поддерживает видеозвонки, что позволяет пользователям общаться в режиме реального времени с видео. Видеозвонки через Max – это отличный способ увидеть своих друзей и близких, даже если вы находитесь далеко друг от друга. Качество видеозвонков зависит от скорости вашего интернет-соединения.
сколько стоит машина дров .
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
купить диплом в саратове купить диплом в саратове .
Rochester Concrete Products
7200 N Broadway Ave,
Rochester, MN 55906, United Ⴝtates
18005352375
Durable outdoor Installations
Je suis fou de ParisVegasClub, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’une revue. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et eclatantes, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un numero de danse, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient spectaculaires. En somme, ParisVegasClub offre une experience de casino eclatante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un projecteur, facilite une experience de casino flamboyante.
code bonus paris vegas club|
купить диплом высшее купить диплом высшее .
Je suis accro a MrXBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi envoutante qu’un secret. La selection du casino est une enigme de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair mysterieux. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui intriguent. Dans l’ensemble, MrXBet Casino offre une experience de casino mysterieuse pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline secrete du casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est un puzzle visuel captivant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
mrxbet support|
купить диплом в туапсе rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в туапсе .
Five Stars Market Binary Options: Pathway to Smarter Trading
Five Stars Market Binary Options give traders a clear and efficient way to participate in global financial markets. With simple tools, transparent conditions, and fast execution, both beginners and experts can explore new opportunities while managing risks effectively. By visiting https://ivr-nurse.jp/ , investors can learn more about Five Stars Market, enhance strategies, and work toward consistent results in binary options trading.
Промокод 1WIN на 500% на первые 20 депозитов:
https://obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-10-0-00000148-000-0-0-1747038719. Актуальность промокода: настоящий момент. Сумма бонуса по промокоду: до 200 000 рублей.
купить подписчиков в тг канал купить подписчиков в тг канал
https://www.patreon.com/posts/1xbet-promo-code-139107472?utm_medium=clipboard_copy&utm_source=copyLink&utm_campaign=postshare_creator&utm_content=join_link
куплю диплом медсестры в москве куплю диплом медсестры в москве .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
What’s up, constantly i used to check website posts here in the early hours in the morning, because i enjoy to gain knowledge of more and more.
Bi-LED
Website https://tione.ru/ .
проект водопонижения строительной площадки проект водопонижения строительной площадки .
Ищешь знакомства в Ростове-на-Дону? Вступай в наш активный Telegram-чат с реальными людьми для общения и новых встреч. https://t.me/Devochkirostovabot В чате дружелюбная атмосфера, много участников, возможность найти друзей или романтику, интересные темы и обсуждения. Присоединяйся и начинай знакомиться прямо сейчас!
buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru .
стоимость проектирования водопонижения https://proektirovanie-vodoponizheniya.ru .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
разработка проекта водопонижения разработка проекта водопонижения .
http://energoinfo-sochi.ru – технологические стандарты
новые продажа дров .
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
https://t.me/insta_akki
Алкоголь ночью с доставкой на дом в Москве. Работаем 24/7, когда обычные магазины закрыты. Широкий ассортимент: пиво, сидр, вино, шампанское, крепкие напитки. Быстрая доставка в пределах МКАД за 30-60 минут – заказать алкоголь
остекление балконов в хрущевке – специальные решения для панельных домов с гарантией
Слив курсов https://sliv.fun .
Алкоголь ночью с доставкой на дом в Москве. Работаем 24/7, когда обычные магазины закрыты. Широкий ассортимент: пиво, сидр, вино, шампанское, крепкие напитки. Быстрая доставка в пределах МКАД за 30-60 минут https://alcohub9.ru
купить диплом в пскове купить диплом в пскове .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр https://frei-diplom3.ru/ .
купить диплом в кропоткине https://rudik-diplom4.ru/ .
купить дипломы о высшем с занесением купить дипломы о высшем с занесением .
купить диплом в калуге купить диплом в калуге .
https://www.okna-plastic-16.ru/ – услуги отделки лоджий недорого
Зручний сайт з дитячими казками. Все безкоштовно і без реклами!
Игровая платформа 1хБет предоставляет всем стопроцентный бонус при первом пополнении счета до 32500 рублей (или в эквиваленте другой валюты). А также, можно получить welcome-бонус в казино 1хБет до €1950 вместе со 150 FS в слот-играх и автоматах.
http://bestaff.ru/includes/pages/1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_15.html Только с его помощью вы сможете получить бонус фрибет в размере 32500 рублей. Фрибет 1хБет 2025 предоставляет уникальную возможность игрокам получить бесплатную ставку и использовать ее без каких-либо вложений со своего счета.
Website https://tione.ru/ .
https://altegs.ru/
проектирование водопонижения иглофильтровыми установками https://www.proekt-vodoponizheniya.ru .
купить аттестат за 11 класс купить аттестат за 11 класс .
можно купить диплом техникума http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить .
заказать алкоголь с доставкой на дом alcohub9.ru .
проектирование строительного водопонижения https://proekt-na-vodoponizhenie.ru .
купить диплом в нефтеюганске купить диплом в нефтеюганске .
Adoro o clima brabo de OshCasino, parece uma erupcao de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, OshCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um vulcao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia ardente, da um toque de calor brabo ao cassino.
avis osh paris sportif|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin casino|
накрутить подписчиков в тг
я купил проведенный диплом я купил проведенный диплом .
купить диплом в муроме купить диплом в муроме .
купить диплом зубного техника купить диплом зубного техника .
проект водоотлива и водопонижения http://www.proektirovanie-vodoponizheniya.ru/ .
Ich bin suchtig nach Pledoo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Vulkan ausbricht. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und glanzend, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Am Ende ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Polarlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
pledoo online casino|
https://t.me/insta_akki
поставщик медицинского оборудования http://medoborudovanie-russia.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в архангельске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в архангельске .
купить диплом в горном колледже https://frei-diplom9.ru .
остекление балконов в хрущевке – специальные решения для панельных домов с учетом особенностей
накрутка активных подписчиков в тг бесплатно
где купить диплом техникума этом где купить диплом техникума этом .
https://alive-portal.ru/
купить диплом с занесением в реестр чита http://www.frei-diplom1.ru/ .
накрутка подписчиков в группу телеграм накрутка подписчиков в группу телеграм
Can I expect sertraline overdose at ZoloSert – ZoloSert.com be taken before or after?
интернет https://kra40a.at/
buhgalteriya-na-autsorsinge-usn-812.ru .
купить диплом в новочебоксарске http://rudik-diplom12.ru .
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в тг
J’adore la frenesie de Spinanga Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi virevoltante qu’un cyclone. Il y a une rafale de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et hypnotiques. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maitre des vents, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui secouent. Globalement, Spinanga Casino est un casino en ligne qui dechaine les elements pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline frenetique du casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une bourrasque, ajoute une touche de chaos au casino.
spinanga apuestas|
виды монтажных работы металлоконструкции
купить диплом в соликамске купить диплом в соликамске .
buhgalteriya-na-autsorsinge-usn-812.ru .
как набрать 1000 подписчиков в тг
как сделать много подписчиков в тг канале как сделать много подписчиков в тг канале
брокеры платина
где купить диплом техникума в москве где купить диплом техникума в москве .
медсестра которая купила диплом врача https://www.frei-diplom13.ru .
подробнее https://kra39a.at/
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – инновационные подходы
купить диплом в донском https://rudik-diplom1.ru/ .
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
купить аттестат за 9 класс купить аттестат за 9 класс .
проект водопонижения эжекторными иглофильтрами http://www.proekt-na-vodoponijenie.ru .
балконные окна раздвижные – пластиковые сдвижные конструкции с порогами эконом-класса
Нужна презентация? заказать презентацию Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
дрова колотые цена .
сравнение онлайн казино Обзор казино с выплатами Выплаты – это один из самых важных критериев при выборе онлайн казино. Узнайте, как быстро казино выплачивает выигрыши, какие способы вывода средств доступны и какие лимиты на выплаты установлены. Выбирайте казино с удобными и быстрыми выплатами!
медицинская техника http://medoborudovanie-msk.ru .
kupit-drova-v-setkah-sergiev-posad.ru .
Kraken — уникальная platform для secure operations, обеспечивающая максимальную степень безопасности и anonymity ваших информации. Благодаря innovative методам шифрования и guaranteeing личной информации, Кракен гарантирует максимальную конфиденциальность при performing операций any level. Enter the актуальный сайт Кракен и perform reliable сделки без задержек. Платформа предлагает simple интерфейс, который подходит как для новых пользователей, так и для тех, кто только начинает interact с конфиденциальными онлайн-сервисами. Благодаря high level security, вы можете быть уверены в integrity ваших персональных сведений и security каждой операции. Кракен непрерывно совершенствует свои technologies и гарантирует полную конфиденциальность для всех пользователей. Visit платформу с любого устройства и запусти work fast, используя current ссылки и mirrors. Kraken — это ваш reliable проводник в мире конфиденциальных операций, который позволяет вам maintain приватность и контроль над своими data в любое время и в любом месте.
ВХОД НА КРАКЕН МАРКЕТ
http://okna-plastic-12.ru/ – каталог товаров по установке окон с выгодными ценами
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
Чи замислювались ви, які казки найбільше допомагають дитині розвивати емоційний інтелект? Дізнайтеся більше.
http://www.okna-plastic-13.ru – основной веб-сайт установки окон недорого
https://keeper-uae.com/ Self-Storage Warehouse in Dubai: A Symphony of Security and Convenience Modern self-storage facilities transcend the simplistic notion of mere storage units. They are meticulously engineered ecosystems designed to protect and preserve your possessions. From climate-controlled environments that safeguard against the ravages of the desert heat to state-of-the-art security systems that stand guard around the clock, every detail is carefully considered. Wide aisles, readily available loading docks, and user-friendly access systems further enhance the convenience, transforming the act of storing and retrieving items into a seamless and efficient experience.
ThePokies 115
Приветствую всех!
Возникла интересная задача с созданием уютного пространства в квартире. Понял, что правильный выбор мебели – это сложное искусство.
Изучал тему и обнаружил отличную статью про мебель в дизайне. Там детально разобрано как выбирать стиль.
Особенно понравились про создание рабочей зоны. Теперь знаю как стильно оформить пространство для отдыха.
Всем любителям интерьера – много полезного! качественное сообщество для вдохновения!
Всем красивых интерьеров
Приветствую строительное сообщество!
Хочу поделиться опытом с организацией деловой встречи для подрядчика. Клиент требовал на представительском уровне.
Сложность заключалась что собственной мебели не хватало для масштабного мероприятия. Покупать на раз – дорого.
Помогли специалисты по аренде – взяли современные стулья. К слову, наткнулся на качественный обзор про аренду мебели для B2B – там отличные рекомендации.
Мероприятие прошло на высшем уровне. Рекомендую всем кто проводит деловые мероприятия.
Удачи в бизнесе!
можно проверить ЗДЕСЬ https://kra39a.at/
http://okna-plastic-14.ru/ – подробный каталог по отделочным работам с профессиональным подходом
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
http://okna-plastic-15.ru/ – подробный каталог по балконному остеклению с профессиональным подходом
купить диплом с реестром спб купить диплом с реестром спб .
buhgalteriya-na-autsorsinge-usn-812.ru .
Decorating their homes for different holidays becomes an easy task for customers.
how we shop online https://exlinecountrystore.com/2025/09/04/how-online-shopping-shapes-our-daily-routine/
kupit-drova-v-setkah-sergiev-posad.ru .
https://robot-rating.ru/
Website https://useit2.ru/.
поставщик медоборудования https://www.medoborudovanie-tehnika.ru .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
разработка проекта водопонижения разработка проекта водопонижения .
Je suis fou de Spinsy Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme une boule a facettes. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et rythmees, proposant des slots de casino a theme disco. Le service client du casino est une star du dancefloor, assurant un support de casino immediat et dansant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient groovy. Dans l’ensemble, Spinsy Casino c’est un casino a rejoindre sans tarder pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline rythmee du casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un neon, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
spinsy code promo|
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es pulsiert mit einer schillernden Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Regenbogen, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Lichtimpuls, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist SlotClub Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
slotclub casino|
Estou louco por Richville Casino, parece um banquete de opulencia e diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um tesouro reluzente, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro de luxo, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, Richville Casino e um cassino online que exsuda riqueza para os que buscam a adrenalina luxuosa do cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como um salao de baile, torna a experiencia de cassino um evento de gala.
richville online|
https://www.okna-plastic-16.ru – онлайн-заказ пластиковых окон с установкой
The Vavada platform is popular among players.
Exclusive no deposit bonuses increase user interest.
Regular events make gameplay dynamic.
Game catalog features leading providers.
Quick registration, promo codes can be activated right away.
Check the details here: vavada casino owner
проектирование водопонижения иглофильтровыми установками https://vodoponizhenie-proekt.ru .
купить диплом фармацевта купить диплом фармацевта .
buy cocaine in telegram cocaine prague
cocaine prague telegram buy drugs in prague
пластиковые окна москва – шумозащитные окна ПВХ с установкой
https://rostgrup.ru/
https://t.me/bonus_dragon_money
проект водопонижения эжекторными иглофильтрами https://www.proekt-vodoponizheniya.ru .
Is there a way to tell if a nolvadex gynecomastia at TamoxiNolva – tamoxifen dosage for breast cancer when you can get it cheap
нотариальный перевод на английский
накрутка подписчиков в тг смм накрутка
остекление балкона цены – фиксированные цены на застекление балконов и лоджий под ключ
Website https://tione.ru/ .
доставка алкоголя ночью на дом http://www.alcohub9.ru .
купить диплом колледжа отзывы http://frei-diplom10.ru/ .
где купить диплом техникума в нижнем новгороде где купить диплом техникума в нижнем новгороде .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
оборудование для больниц http://medoborudovanie-russia.ru/ .
диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр http://frei-diplom7.ru .
заказать проект водопонижения http://www.proekt-na-vodoponizhenie.ru .
https://www.bitsdujour.com/profiles/wK434n
http://www.okna-plastic-11.ru – актуальный прайс пластиковых окон с монтажом
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
https://antibrand.shop/
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
как набрать 1000 подписчиков в тг
подписчики в тг канал без отписок
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – современное обновление
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
подписчики дешево в тг канал
обзор казино с кешбэком Бонусы казино при регистрации Получите приветственный бонус при регистрации в онлайн казино! Многие казино предлагают щедрые бонусы новым игрокам, увеличивая их банкролл и давая им больше шансов на выигрыш.
остекление лоджий – недорогое остекление лоджий и балконов с гарантией качества
накрутка подписчиков тг канале купить
buhgalteriya-na-autsorsinge-usn-812.ru .
где купить осиновые дрова .
установка котла отопления цена установка котла отопления цена .
http://www.okna-plastic-20.ru – веб-сайт компании металлопластиковых конструкций от производителя
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
развитие энергетики сочи – комплексное развитие
Estou pirando com SpinFest Casino, parece uma festa reluzente cheia de adrenalina. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista na avenida, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma danca de frevo, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Na real, SpinFest Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os folioes do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual cheio de cores, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais vibrante.
spinfest kasino|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin paga?|
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал без отписок
kupit-drova-v-setkah-sergiev-posad.ru .
проектирование водопонижения иглофильтровыми установками https://www.proekt-na-vodoponijenie.ru .
Estou pirando com SpeiCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um satelite. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e estelares. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
spei deposit bonus|
цена пластиковых окон с установкой – комплексные цены без скрытых платежей акция до конца месяца
поставка медицинского оборудования https://www.medoborudovanie-msk.ru .
Основные этапы проведения инвентаризации .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал без отписок накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал без отписок
Eine gangige Methode ist die kognitive Verhaltenstherapie.
drogenentzug symptome https://entzugsklinik.pro/
купить окна rehau – оригинальный профиль Rehau с энергосберегающими стеклопакетами доставка по Москве
https://phlebologist-blog.ru/ Блог практикующего флеболога и сосудистого хирурга — всё о здоровье сосудов ног! Профилактика и профессиональное лечение варикоза: современные методики, склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен, экспертная диагностика. Получите проверенные советы и индивидуальное решение ваших проблем!
проект водопонижения эжекторными иглофильтрами проект водопонижения эжекторными иглофильтрами .
остекление балконов цена в москве – актуальная расценки на остекление балконов с расчетом онлайн
живые активные подписчики в тг живые активные подписчики в тг
“аренда инструмента в слуцке – выгодные условия и широкий выбор инструментов для любых задач.”
Вместо того чтобы покупать инструмент, который может понадобиться всего несколько раз, выгоднее взять его в аренду по доступной цене.
Такой подход особенно удобен для строителей и мастеров. Многие профессионалы предпочитают брать инструмент напрокат, так как это снижает затраты на выполнение работ.
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен широкий ассортимент оборудования для разных задач. В прокате представлены бензопилы, газонокосилки и другая садовая техника.
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и специализированную технику. Если нужно работать на высоте, доступны подъемники и строительные леса.
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – экономия на обслуживании и хранении. Арендуя оборудование, вы избегаете затрат на его хранение и транспортировку.
Дополнительный бонус – помощь в выборе подходящего оборудования. Консультанты помогут подобрать инструмент под конкретные задачи.
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды максимально проста и прозрачна. Для оформления понадобится только паспорт и небольшой залог.
Условия проката выгодны для всех клиентов. Доставка оборудования возможна в любой район Слуцка.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Почему аренда инструмента – это выгодно?**
Аренда инструмента в Слуцке позволяет получить доступ к профессиональному оборудованию без покупки. Если вам нужен инструмент на короткий срок, аренда – идеальное решение, ведь не придется тратиться на дорогостоящее оборудование .
Такой подход особенно удобен для компаний и частных клиентов. Многие профессионалы предпочитают брать инструмент напрокат, так как это снижает затраты на выполнение работ .
#### **2. Какой инструмент можно взять в аренду?**
В Слуцке доступен большой выбор техники для строительства и ремонта . Вы можете арендовать перфораторы, дрели и шлифмашины для ремонта квартиры .
Кроме того, в аренду сдают и оборудование для узких задач. Для укладки плитки можно взять плиткорезы, а для покраски – краскопульты .
#### **3. Преимущества аренды инструмента**
Главный плюс – экономия на обслуживании и хранении . Все инструменты проходят регулярное обслуживание, поэтому клиенты получают только исправные устройства.
Дополнительный бонус – консультации профессионалов . Опытные менеджеры подскажут, какая модель лучше справится с работой .
#### **4. Как оформить аренду в Слуцке?**
Процедура аренды максимально проста и прозрачна . Для оформления понадобится только паспорт и небольшой залог.
Условия проката выгодны для всех клиентов . Стоимость аренды зависит от срока и типа инструмента .
пластиковые окна недорого цены – бюджетные решения от 9000 руб рассрочка без процентов
стоимость проектирования водопонижения стоимость проектирования водопонижения .
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
металлопластиковые окна – надежные оконные системы под ключ по доступным ценам
электрокарнизы купить в москве электрокарнизы купить в москве .
где купить диплом образование где купить диплом образование .
лучшее зеркало мега https://megawebssylka.shop/
купить официальный диплом https://www.educ-ua7.ru .
купить диплом в кузнецке https://rudik-diplom13.ru .
купить диплом техникума в курске купить диплом техникума в курске .
куплю диплом младшей медсестры http://frei-diplom13.ru .
купить диплом о высшем образовании купить диплом о высшем образовании .
окна в кредит – онлайн-одобрение на 6-24 месяца
Чтобы быстро попасть на кракен даркнетсайт, используйте проверенную ссылку. Рабочее зеркало доступно для входа в маркетплейс, а инструкция поможет без лишних шагов.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в украине http://www.frei-diplom1.ru/ .
куплю диплом кандидата наук куплю диплом кандидата наук .
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls594744557/
купить диплом в екатеринбурге купить диплом в екатеринбурге .
москва окна пвх – монтаж в день заказа более 1000 готовых решений
Трансы Екатеринбурга Трансы Екатеринбург
застеклить беседку – панорамное остекление беседок недорого
Чтобы не терять доступ, сохраняйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылка. Рабочее зеркало кракен магазин открывает маркет и личный кабинет.
1win karta orqali depozit 1win karta orqali depozit
меблі тернопіль ціни https://remontuem.te.ua
https://finance-info.ru/
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
кракен зеркало сегодня – Быстрый кракен вход в личный кабинет работает на телефоне и ПК.
окна в кредит – без первоначального взноса для физических и юридических лиц
кракен тор ссылка – Кракен сайт вход — лучший вариант для авторизации и работы в личном кабинете.
buhgalteriya-na-autsorsinge-usn-812.ru .
https://list.ly/betcharge25r/lists
Для тех, кто ищет информацию, где заключить контракт на службу по СВО, мы сделали обзор. https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3168272-kak-zaklyuchit-kontrakt-s-ministerstvom-oborony-vozmozhnosti-na-2025-god-v-ramkah-svo Теперь у вас есть всё необходимое, чтобы официально подписать контракт на СВО.
аппараты медицинские https://medoborudovanie-russia.ru/ .
Прокат авто
купить окна недорого – бюджетные варианты в Москве
Estou completamente encantado por SpinGenei Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um genio libertado. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um feitico de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como pocoes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e encantador, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem truques. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem maldicoes, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria magico. No geral, SpinGenei Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os magos do cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma lampada magica, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spingenie bedrägeri|
Je suis fou de Riviera Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino sophistiquee. La selection du casino est une promenade de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eclaboussent de glamour. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise marine, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Riviera Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les navigateurs du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique ensoleillee, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus glamour.
riviera hotel casino|
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
Получить диплом ВУЗа поможем. Купить диплом бакалавра в Кемерово – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-kemerovo
Sou louco pela aura de SpellWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao fascinante quanto um grimorio antigo. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um caldeirao de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passe de varinha, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma pocao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um feitico de teletransporte, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
spellwin bonus|
Рабочее зеркало кракен даркнет — это удобное решение для тех, кто хочет пользоваться сервисом постоянно.
Эта статья подскажет, как и где лучше всего подписать контракт на СВО. выплаты за подписание контракта служба по контракту сво Теперь вы понимаете, какие документы и шаги нужны, чтобы подписать контракт на СВО.
http://okna-plastic-17.ru – веб-сайт производителя пластиковых окон с профессиональным монтажом
https://pvhprofi.ru/
кракен ссылка darknet – Подключение через кракен онион подходит для тех, кто ценит безопасность.
смотреть фильмы бесплатно смотреть фильмы бесплатно .
смотреть русские сериалы смотреть русские сериалы .
купить пластиковые окна цены – низкие цены на пластиковые окна с установкой
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
дрова колотые цена .
оформить займ онлайн интернет займ
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
Engaging visuals and appealing designs are crucial for maintaining reader interest.
time and effort hacks https://jimgrayonline.com/smart-solutions-creative-life-hacks-to-save-time-and-effort/
купить пластиковые окна цены – конкурентные цены на окна ПВХ в Москве
Fast delivery of https://ivermectinvsstromectol.com/ brand and generic prices? sertralina 50
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
С помощью кракен личный кабинет легко обойти блокировки. Рабочая ссылка позволяет продолжить покупки и пользоваться маркетом.
https://finance-info.ru/
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
медицинское оборудование для больниц medoborudovanie-tehnika.ru .
кракен тор даркнет – Рабочая кракен тор ссылка помогает обходить блокировки и входить быстро.
Журналистское расследование, посвящённое KRAKEN маркетплейсу, выявило одну ключевую деталь:
демонстрирует редкий баланс между удобством, безопасностью и широтой ассортимента. В отличие от конкурентов, кракен онион поддерживает постоянную работу зеркал и доступность сервиса. Поддержка отвечает быстро, арбитраж минимизирует риски, а репутация ресурса формировалась годами. Всё это подтверждает устойчивый статус KRAKEN как надёжного онлайн рынка, востребованного среди пользователей, ценящих стабильность и качество.
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – динамичное обновление
накрутка подписчиков в тг без отписок
Салон оставил самые приятные впечатления. Все чисто, удобно, круто, девушки настоящие красавицы. Получил море эмоций и полное расслабление. Советую, эротический массаж заказать Новосиб, https://sibirki3.vip/. Всё просто шикарно, обязательно вернусь.
Прокат авто Краснодар жд
кракен тор даркнет – Кракен онион — это доступ через TOR с полной анонимностью.
стоимость монтажа газовых котлов отопления стоимость монтажа газовых котлов отопления .
медицинское оборудование medoborudovanie-msk.ru .
купить аттестаты за 9 купить аттестаты за 9 .
проект водоотлива и водопонижения https://proekt-na-vodoponijenie.ru .
1win 1win5501.ru
https://www.imdb.com/de/list/ls4102546515/
KRAKEN
TOR даёт возможность обойти блокировки и подключиться анонимно.
медицинское оборудование медицинское оборудование .
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
купить диплом в бору http://www.rudik-diplom15.ru .
кракен зеркало – Кракен сайт это простой способ подключиться: удобный вход и проверенные источники.
умный горшок для растений умный горшок для растений .
накрутка подписчиков тг канале боты
Журналистское расследование, посвящённое KRAKEN маркетплейсу, выявило одну ключевую деталь:
демонстрирует редкий баланс между удобством, безопасностью и широтой ассортимента. В отличие от конкурентов, как зайти на кракен с тор поддерживает постоянную работу зеркал и доступность сервиса. Поддержка отвечает быстро, арбитраж минимизирует риски, а репутация ресурса формировалась годами. Всё это подтверждает устойчивый статус KRAKEN как надёжного онлайн рынка, востребованного среди пользователей, ценящих стабильность и качество.
заказать пластиковые окна – со скидкой надежные пластиковые окна с монтажом
кракен маркет даркнет – Выбирайте кракен вход в личный кабинет — это удобство и безопасность.
Для контрактников подготовили полезную информацию: где и как заключить контракт на СВО. https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3100667-do-skolki-let-mozhno-postupat-v-voennoe-uchilishe-vozmozhnosti-dlya-sluzhby-po-kontraktu-v-2025-godu Эти данные пригодятся каждому, кто собирается заключить контракт на СВО.
There are many natural products when you http://ibuprofenbloginfo.com/ generic or brand prices and discounts? what is sertraline
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
накрутить подписчиков в тг
остекление лоджий – холодное застекление лоджий и балконов с гарантией качества
купить речной диплом купить речной диплом .
KRAKEN сайт создан для удобства: актуальные зеркала, проверенные ссылки и пошаговый вход помогают использовать маркет без проблем.
Салон понравился приватностью и атмосферой. Девушка встретила радостно, сразу было видно, что здесь умеют заботиться о клиентах. Массаж просто восторг. Обязательно попробуйте, эротический массаж недорого нск: https://sibirki3.vip/. Всё круто, красиво и уютно.
карниз электро карниз электро .
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал дешево
okna-plastic-19.ru – ассортимент товаров по балконным решениям с выездом специалиста
кракен маркет даркнет – Кракен официальный сайт всегда гарантирует актуальные ссылки и рабочие зеркала.
трансы тюмениринбурга трансы тюмень
1вин онлайн чат https://www.1win5501.ru
поставка медицинского оборудования http://medoborudovanie-tehnika.ru/ .
https://www.okna-plastic-20.ru – каталог продукции остекления балконов от производителя
список займов онлайн http://www.zaimy-11.ru/ .
Гидравлические https://energo-pole.ru/skladskaya-tekhnika/shtabelery/ruchnye-gidravlicheskie/samopodemnyy-shtabeler/ruchnoy-shtabeler-PS05F-1300/
столы.
Арт. 700065.
Базовая конфигурация одноуровневого парковочного подъемника (на базе одноножничного подъемного стола) приведена на чертеже общего вида – ниже. Двухуровневый подъемник для паркинга имеет дополнительную платформу прикрепленную на усиленных стойках к основной платформе, что позволяет использовать такой подъемник на трехуровневой парковке.
TF15 NOBLELIFT Подъемный стол гидравлический.
Арт. Артикул 67-5009.
Цена: 52 440 руб.
как зайти на кракен – Кракен онион обеспечивает прямой доступ даже при ограничениях.
накрутка подписчиков тг
Ich bin suchtig nach SportingBet Casino, es pulsiert mit einer dynamischen Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Welle an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Finale krachen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Torerfolg. Insgesamt ist SportingBet Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Passspiel, das Casino-Erlebnis total actiongeladen macht.
como funciona o sportingbet|
купить диплом в сургуте купить диплом в сургуте .
Estou completamente alucinado por SpinSala Casino, parece uma festa reluzente cheia de energia. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um palco de delicias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como refletores. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um flash de luz, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, SpinSala Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho para os dancarinos do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual reluzente, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como uma estrela em um palco.
spinsala united kingdom|
Sou louco pela energia de SupaBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um trovao supersonico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e avassaladoras, com slots de cassino tematicos de aventura epica. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma supernova, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura cosmica. Na real, SupaBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com energia epica no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora vulcanica, adiciona um toque de adrenalina epica ao cassino.
supabet de|
cocaine prague buy weed prague
Рабочее KRAKEN зеркало — это удобный способ попасть в кракен зеркало.
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – комплексная модернизация
диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр .
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом — это идеальное решение для создания уюта и комфорта в вашем доме, позволяющее управлять светом и приватностью с помощью простого нажатия кнопки.
С каждым днем рулонные шторы с электроприводом привлекают все больше внимания. Данные шторы являются высокотехнологичным вариантом для оформления интерьера. Удобство и функциональность делают эти шторы идеальным выбором.
Ключевым достоинством является возможность дистанционного управления шторами. Это позволяет легко регулировать уровень освещения в помещении. Электропривод позволяет задать расписание открытия и закрытия штор.
Монтаж рулонных штор с электроприводом осуществляется достаточно быстро. Вам потребуется минимальный набор инструментов и немного времени. Существует множество вариантов дизайна и материалов, что позволяет выбрать идеальный вариант для любого интерьера.
Рулонные шторы с электроприводом обеспечивают не только стильный вид, но и защиту от солнца. С помощью различных тканей можно регулировать уровень затемнения. Таким образом, вы сможете создать комфортную атмосферу в своем доме.
Hope this isn’t too off-topic 🙂
Just while scrolling I found a site called news.veryuseful.website.
It’s packed with mind-blowing achievements.
Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds?
Phelps’ 28 Olympic medals?
Bubka’s 35 world records?
It’s all there.
Anyone else into stuff like this?
Estou alucinado com SupremaBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que brilha como uma coroa reluzente. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um trono de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de poder. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um decreto de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem revoltas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem conspiracoes, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SupremaBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro cetro para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro trono, torna a experiencia de cassino um reinado de prazer.
supremabet-pb|
okna-plastic-11.ru/ – корпоративный портал по остеклению балконов с выездом замерщика
buy coke in telegram buy cocaine in telegram
купить диплом в салавате купить диплом в салавате .
диплом техникума купить цена http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
купить речной диплом купить речной диплом .
купить диплом в клинцах http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить диплом в клинцах .
кракен ссылка через тор – Кракен официальный сайт зеркало — быстрый способ подключиться и продолжать работу.
кракен зеркало сегодня – Кракен онион обеспечивает прямой доступ даже при ограничениях.
березовые дрова цена за куб с доставкой .
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
http://okna-plastic-12.ru/ – веб-сайт производителя по отделочным работам с профессиональным подходом
otdat-buhgalteriyu-na-autsorsing-812.ru .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
KRAKEN ссылка позволяет обходить блокировки и заходить на сайт даже с телефона. Рабочее зеркало — гарантия стабильного входа.
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом диспетчера купить диплом диспетчера .
Проблемы с откачкой? помпа для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цена .
купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге .
диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой купить .
Нужна презентация? нейросеть составляющая презентации Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
https://www.okna-plastic-13.ru/ – услуги изготовления и установки окон под ключ
Сервис 1win для ставок и игр с частыми промо для новых и активных пользователей.
Фрибеты и коды усиливают первую сессию.
Создать аккаунт просто, после чего подключаются бонусы.
Лобби со слотами и лайв?играми собраны без лишних сложностей.
Чтобы использовать актуальный код, смотри инструкции здесь — 1win промокод бонус за регистрацию, активируй по инструкции.
Играйте ответственно, для стабильного опыта.
This information is invaluable. When can I find out more?
Rifar Tubog
как купить диплом техникума в красноярске как купить диплом техникума в красноярске .
otdat-buhgalteriyu-na-autsorsing-812.ru .
https://www.okna-plastic-14.ru/ – услуги под ключ оконных решений с гарантией качества
plug in prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
pure cocaine in prague prague drugs
кракен вход ссылка – Кракен ссылка актуальная всегда проверена и доступна для подключения.
кракен маркетплейс официальный сайт – Через кракен тор ссылка можно подключаться без перебоев.
камаз дров цена .
дубовые дрова 1 куб цена .
пластиковые окна с установкой в москве – опыт от 5 лет с герметизацией гарантия на монтаж 3 года
купить диплом химика купить диплом химика .
Для обхода блокировок достаточно кракен вход. Рабочее зеркало открывает маркет и позволяет авторизоваться в личном кабинете.
kinogo kinogo .
пластиковые окна недорого цены – акционные модели с фурнитурой рассрочка без процентов
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slotu haqqında çox müsbət rəylər eşitmişəm. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin casino oyunları arasında məşhurdur.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin 2 yeni versiyası çox maraqlıdır. Sunny coin hold the spin slot onlayn kazinolarda məşhurdur.
Daha ətraflı məlumatı buradan tapa bilərsiniz Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot.
Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot müasir dizaynla təqdim olunur. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin oyunu sürətli və maraqlıdır. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin böyük qazanclar üçün əlverişlidir.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot oyunu sürprizlərlə doludur. Sunny coin hold the spin slot oynamaq çox rahatdır.
купить проведенный диплом красноярск купить проведенный диплом красноярск .
исторические фильмы исторические фильмы .
1win akkaunt yaratish https://www.1win5502.ru
Эта статья поможет сориентироваться, где именно можно подписать контракт на СВО в России. https://vc.ru/services/1644005-kontrakt-v-samare-na-svo-kak-podpisat-v-rossii-2025 Этот материал станет полезен для тех, кто собирается подписать контракт на СВО и претендует на жильё.
окна калькулятор – бесплатная смета цены остекления с выездом замерщика
кракен зеркало тор – Выбирайте кракен маркетплейс — это проверенный доступ и надёжная работа.
кракен сайт даркнет ссылка – Если ищете стабильный доступ, кракен сайт предлагает актуальные адреса и быстрый вход.
С помощью кракен маркет легко обойти блокировки. Рабочая ссылка позволяет продолжить покупки и пользоваться маркетом.
окна для террасы – стационарные с тонировкой частных домов
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot demo versiyası çox rahatdır. Sunny Coin 2: Hold The Spin slot dizaynı diqqəti cəlb edir.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slotunu sınamaq xoşdur. Sunny coin: hold the spin slot oyun təcrübəsi mükəmməldir.
Bütün detallar üçün baxın sunny-coin.com.az/.
Sunny coin hold the spin demo oyna, risk olmadan öyrən. Sunny Coin 2 hold the spin slot real qələbə gətirə bilər. Sunny coin hold the spin slot online rahat oynanır.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot online hər kəs üçün əlçatan olur. Sunny coin hold the spin slot oynamaq çox rahatdır.
https://t.me/s/minotaurus_official Merges Endless Runner and Blockchain Concepts
Exploring Minotaurus Unique Fusion of Endless Runner Mechanics and Blockchain Technology
For enthusiasts looking to combine entertainment with investment opportunities, exploring titles that fuse gameplay with decentralized finance can be incredibly rewarding. This innovative project captures attention by integrating continuous play with the potential for digital asset collection, creating an engaging experience for players and investors alike.
Developers have crafted a captivating environment where participants can run, avoid obstacles, and simultaneously acquire unique tokens that hold real-world value. Each successful run not only enhances skills but also accumulates digital currency and collectible items that can appreciate over time, providing a dual incentive to players.
This fusion allows for a refreshing approach to traditional gameplay, as users aren’t just playing for leisure; they’re building an investment portfolio while honing their reflexes. Engaging with this type of interactive platform transforms every session into both a challenge and an opportunity, making it a must-try for those interested in the intersection of technology and gaming.
How the Gaming Platform Utilizes Distributed Ledger for Asset Ownership
The integration of a distributed ledger system allows players to have true ownership of their virtual items, which can enhance the gaming experience significantly. Every asset within the environment is represented by a unique token, making it verifiable and tradable without interference from the platform.
Players receive full rights to their assets, enabling them to sell, trade or transfer items across various marketplaces. This transferability adds real-world value to in-game achievements, as players can monetize their efforts and investments.
The platform ensures a transparent marketplace where transactions are recorded publicly, preventing fraud and counterfeit assets. Players can track their purchases and sales easily, fostering trust in the community.
Smart contracts automate transactions, ensuring that trades are executed smoothly without the need for intermediaries. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces the chances of disputes, as the terms of each transaction are encoded directly into the protocol.
Holding assets within this decentralized framework provides users with security, as it eliminates risks associated with centralized databases where hacks can lead to loss of items. Players can rest assured knowing their collectibles are stored securely on the ledger.
Moreover, players earn rewards for their participation in the gaming ecosystem, further incentivizing engagement. These rewards, often in the form of tokens, can be used to purchase in-game assets or exchanged for other cryptocurrencies, offering multiple avenues for players to benefit from their gaming experience.
Gameplay Mechanics: Balancing Speed and Strategy in an Endless Experience
To maintain a dynamic yet strategic experience, introduce segmented paths that require quick decision-making. Players should encounter branching routes where each choice influences their speed and resource management. This setup encourages them to weigh the benefits of rapid progress against potential rewards found off the main course.
Integrate power-ups that enhance speed temporarily but come with risks. For example, a speed boost could lead to increased obstacles, compelling players to refine their reflexes while also contemplating whether the short-term gain is worth the potential hazards.
Incorporate a scoring system influenced by both speed and strategic choices. Assign bonus points for successfully navigating complex paths or avoiding threats rather than just finishing quickly. This approach promotes a balance between haste and careful planning.
Add layers of difficulty by altering threat patterns and obstacle layouts based on the player’s performance. If a user consistently opts for speed, introduce tougher challenges that require quick thinking. Conversely, if they play cautiously, provide opportunities for speed that require strategic timing.
Encourage players to experiment with loadouts or character abilities that either enhance their speed or augment their strategic tools. This way, users can tailor their gameplay style to fit personal preferences, creating variability and replayability.
Regularly refresh content and introduce timed events that reward players for navigating challenges within a specific timeframe. This keeps the gameplay engaging while motivating players to adopt different strategies based on their experience level.
Implement a risk-reward system tied to game progression. Allow players to trade speed for earned bonuses, allowing them to make impactful choices that influence future gameplay. This inclusion promotes a sense of agency and strategy, enhancing the overall experience.
Лучшая книга ztq
Военная служба начинается с шага — нужно знать, где заключить контракт в армии. https://vc.ru/money/1593831-kogda-zarplata-u-voennosluzhashih-po-kontraktu-v-2025-godu-na-svo-v-rossii Есть инструкции по юридической поддержке и консультациям для контрактников.
Лучшая книга oso
Je trouve absolument delirant Spinsy Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi vibrante qu’une piste de danse. La selection du casino est une explosion de delices dansants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance groovy. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un pas de danse, assurant un support de casino immediat et dansant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un breakdance, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Spinsy Casino offre une experience de casino vibrante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style funky, facilite une experience de casino electrisante.
casino spinsy avis|
Проблемы с откачкой? насос для откачки воды из бассейна сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
weed in prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
cash loan is a fast and hassle-free way to secure the funds you need. With a simple application process, you can get loans online from the comfort of your home, avoiding lengthy paperwork. Online lenders offer competitive rates and quick approvals, ensuring you receive the money promptly. Experience the convenience and efficiency of getting loans online and meet your financial needs with ease.
Maraqlı dizayn və yüksək RTP ilə Sunny Coin Hold The Spin fərqlənir. Sunny Coin hold the spin slot online çoxlu istifadəçi qazanır.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin 2 yeni versiyası çox maraqlıdır. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot oynamadan əvvəl demo sınayın.
Bu slot haqqında daha çox öyrənmək üçün sunny coin hold the spin.
Sunny coin hold the spin slot online demo çox istifadəlidir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot demo rahat giriş imkanı yaradır. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin böyük qazanclar üçün əlverişlidir.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot online hər kəs üçün əlçatan olur. Sunny coin: hold the spin slot təcrübəsi həyəcanlıdır.
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
plug in prague buy mdma prague
plug in prague coke in prague
сайт кракен зеркало – Кракен ссылка актуальная — стабильный вариант обхода блокировок.
KRAKEN маркетплейс уже давно считается одной из самых удобных и надёжных площадок. Официальный
работает стабильно, доступ не пропадает, а зеркала всегда обновляются вовремя. Поддержка отвечает быстро, кракен сайт решает спорные моменты честно. Покупки проходят без задержек, криптоплатежи принимаются моментально. Многие отмечают и ассортимент — здесь можно найти как привычные сервисы, так и редкие товары. Всё это делает KRAKEN местом, которому доверяют тысячи пользователей.
otdat-buhgalteriyu-na-autsorsing-812.ru .
купить диплом техникума ссср в нижнем новгороде купить диплом техникума ссср в нижнем новгороде .
Sunny coin hold the spin slot game həqiqətən dinamikdir. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin onlayn casino seçimləri arasında öndədir.
Sunny coin: hold the spin slot RTP yüksək olduğu üçün sevilir. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slotu yüksək keyfiyyətli qrafikaya malikdir.
Rəsmi platforma https://sunny-coin.com.az.
Sunny coin hold the spin demo oyna, risk olmadan öyrən. Sunny coin hold the spin slot bonus raundları çox cəlbedicidir. Sunny coin hold the spin slot online rahat oynanır.
Sunny coin: hold the spin slot istifadəçi dostudur. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot oyununda böyük qaliblər var.
микрозайм все http://zaimy-12.ru .
купить телефон спб самсунг https://kupit-telefon-samsung-2.ru .
каталог смартфонов samsung kupit-telefon-samsung-1.ru .
за1мы онлайн http://www.zaimy-13.ru .
Лучшая книга kts
где купить диплом о среднем образование где купить диплом о среднем образование .
To decide headlines, prefer reliable sources, verify facts, note bias and find depth. Compare with multiple reports, use expert analysis, and set feeds for topics you follow. Build media awareness https://smasters.com
https://letsbookmarktoday.com/profile.php?com=profile&mod=space&userinfo=curtis.troedel-473117
Reading your article has greatly helped me, and I agree with you. But I still have some questions. Can you help me? I will pay attention to your answer. thank you.
Лучшая книга mry
Sou louco pela vibe de AFun Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um festival de fogos. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, AFun Casino vale demais curtir esse cassino para os folioes do cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um desfile noturno, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
afun aplicativo de ganhar dinheiro|
Ich bin suchtig nach Trickz Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zauberstab funkelt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Zaubertrick funkeln. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Alles in allem ist Trickz Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Zaubertrick glanzt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein magischer Zirkus leuchtet, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
trickz casino logga in|
Not exactly the subject here, but a useful tip
Just while browsing health blogs I discovered a site called resource for wise buyers.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Clear, practical, no fluff.
Would you find this kind of advice useful?
купить наушники airpods без кейса http://naushniki-apple-1.ru .
https://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – информационный ресурс
купить айфон Уфа
Чтобы быстро попасть на кракен маркетплейссайт, используйте проверенную ссылку. Рабочее зеркало доступно для входа в маркетплейс, а инструкция поможет без лишних шагов.
застеклить балкон пластиковыми окнами цены москва – под ключ рассрочка на 12 мес
weed in prague cocain in prague from brazil
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? https://www.placevi-zabljak-nekretnine.com Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
как зайти на кракен с телефона – Подключение через кракен онион подходит для тех, кто ценит безопасность.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Смотрите онлайн песни для детей слушать онлайн или скачать лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
пластиковые окна в видном – местные монтажники отзывы клиентов
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр http://www.frei-diplom2.ru .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
все займы https://zaimy-11.ru .
https://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – будущие технологии
https://device-rf.ru/catalog/iphone/
техникум купить диплом http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр .
В 2025 году контрактники получают новые льготы — узнайте, где можно подписать контракт. https://vc.ru/services/1679420-chto-takoe-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-i-kontrakt-na-svo-v-rossii-2025-godu В статье есть инструкции, как правильно подписать контракт на СВО и оформить льготы для семьи.
KRAKEN сайт даёт возможность подключаться с любых устройств. Рабочая ссылка открывает кракен онион без ограничений.
остекление балконов в москве – холодное застекление балконов под ключ
купить диплом в чапаевске купить диплом в чапаевске .
купить диплом в белорецке купить диплом в белорецке .
купить диплом в тюмени http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в тюмени .
купить диплом в сарапуле купить диплом в сарапуле .
как быстро набрать подписчиков в тг
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
завод окон пвх – собственное производство технический надзор видеонаблюдение за процессом
кракен зеркало даркнет – Через кракен зеркало рабочее легко обойти блокировки и попасть в личный кабинет.
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
дрова 25 см купить .
Maraqlı dizayn və yüksək RTP ilə Sunny Coin Hold The Spin fərqlənir. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin casino oyunları arasında məşhurdur.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot oyununda böyük qalibiyyət şansı var. Sunny coin hold the spin slot onlayn kazinolarda məşhurdur.
Həqiqi qazanc üçün daxil olun Sunny coin 2 hold the spin online.
Sunny coin: hold the spin slot maraqlı mexanikaya malikdir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot oyunçu rəyləri çox müsbətdir. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin demo versiyası sürətlidir.
Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot real pul ilə uğurludur. Sunny Coin Hold The Spin real pul üçün əlverişlidir.
как купить диплом с реестром как купить диплом с реестром .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
купить диплом в твери купить диплом в твери .
накрутка подписчиков в тг без заданий
купить жд диплом техникума купить жд диплом техникума .
пластиковые окна цена – прозрачные цены фиксированная стоимость в договоре
E2BET नेपालमा स्वागत छ – तपाईंको जीत, पूर्ण
रूपमा भुक्तानी। आकर्षक बोनसहरूको
आनन्द लिनुहोस्, रोमाञ्चक खेलहरू खेल्नुहोस्, र एक निष्पक्ष
र सहज अनलाइन सट्टेबाजीको अनुभव गर्नुहोस्। अहिले नै दर्ता गर्नुहोस्!
Attractive element of content. I simply stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to say that I acquire actually enjoyed account your weblog
posts. Anyway I will be subscribing on your augment and even I success you get admission to constantly fast.
Промокод 1xBet на сегодня дает пользователям стартовый подарок эквивалентный 100% максимум 130 долларов. Чтобы активировать акцию, необходимо создать учетную запись на платформе, сделать первый взнос и активировать предложение. После этого бонус автоматически поступит на баланс.
Используя промокод, шансы игроков мгновенно увеличиваются на 100%. Однако, чтобы вывести деньги, нужно соблюдать условия отыгрыша, аналогичные стандартным правилам. Подробнее смотрите здесь ?? 1xBet промокод
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который подарит преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы его активировать, понадобится зарегистрироваться и пройти верификацию. После этого вы сможете получить бонус при пополнении счета.Дополнительно можно пригласить друга, чтобы заработать дополнительные подарки.
купить диплом логопеда купить диплом логопеда .
диплом купить с занесением в реестр рязань http://frei-diplom4.ru/ .
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в тг
Ho ordinato https://www.realmsofthedragon.org/w/index.php?title=User:FosterCallanan2 online e la consegna è stata rapida. La crema fa meraviglie!
все займы рф все займы рф .
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru – экологичные технологии
https://plenka-okna.ru/
все займы онлайн все займы онлайн .
Заказать диплом университета поспособствуем. Купить диплом бакалавра в Краснодаре – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-krasnodare
бухгалтерия аутсорсинг спб .
http://www.okna-plastic-18.ru – интернет-портал компании отделки балконов с гарантией и обслуживанием
Ich finde absolut atemberaubend Tipico Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Donnerhall vibriert. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Blitzspektakel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Gewitterknall. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Blitzschlag, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist Tipico Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Gewitter, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
tipico logo|
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
узнать больше kraken зайти
La crème Exodermin a résolu mes problèmes de peau rapidement. Je la recommande vivement !
https://curepedia.net/wiki/Exodermin_50G
Промокод 1xBet на сегодня дает игрокам бонус при регистрации в размере 100% максимум 130 долларов. Чтобы активировать акцию, необходимо создать учетную запись на платформе, внести депозит и подтвердить участие. После этого подарок будет добавлен на аккаунт.
Применяя купон, можно удвоить сумму на старте. Однако, чтобы отыграть бонус, нужно соблюдать регламент бонусной программы, аналогичные стандартным правилам. Подробнее смотрите здесь ?? 1xBet промокод 2025
На нашем сайте доступен уникальный бонусный код, который подарит преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы им воспользоваться, понадобится зарегистрироваться и активировать учетную запись. После этого вы активируете фрибет при пополнении счета.Дополнительно поучаствовать в акциях, чтобы увеличить вознаграждение.
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my
own weblog and was wondering what all is required to get set up?
I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny?
I’m not very web savvy so I’m not 100% certain. Any recommendations or advice would
be greatly appreciated. Thank you
https://energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – эффективные методики
сколько стоит машина дров .
купить живых подписчиков в телеграм канал
Hello, after reading this awesome article i am too delighted to share my know-how here with mates.
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
otdat-buhgalteriyu-na-autsorsing-812.ru .
телефоны галакси http://www.kupit-telefon-samsung-2.ru .
https://okna-plastic-11.ru/ – акционные предложения оконных конструкций в Москве и области
где купить диплом техникума хорошую где купить диплом техникума хорошую .
купить диплом электромонтера купить диплом электромонтера .
диплом высшего образования проведенный купить диплом высшего образования проведенный купить .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
як вибрати кухню https://remontuem.te.ua
Эта публикация расскажет, где именно можно заключить контракт на СВО в России. https://vc.ru/services/1734111-prizyv-na-kontraktnuyu-sluzhbu-osobennosti-kontrakta-na-svo-v-rossii-2025 Этот материал поможет тем, кто решил подписать контракт на СВО и хочет знать, какие есть перспективы.
мфо займ http://zaimy-23.ru/ .
веб-сайт кракен вход
займы http://zaimy-12.ru/ .
цена куба дров дуба .
http://okna-plastic-12.ru/ – услуги по отделке балконов в Москве и области
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
Лучшая книга apf
купить диплом в георгиевске купить диплом в георгиевске .
кракен ссылка актуальная – Кракен официальный сайт всегда гарантирует актуальные ссылки и рабочие зеркала.
La crema https://pl.velo.wiki/index.php?title=Exodermin_32L se absorbe rápido y actúa de inmediato. ¡Mi hongo en los pies casi ha desaparecido!
http://okna-plastic-13.ru/ – веб-сайт производителя по оконным системам с профессиональным подходом
Obtaining an Ozempic order and accessing the medication requires navigating insurance processes. Ozempic, a weekly injectable for blood sugar control, is recommended by a healthcare provider after evaluating a patient’s condition. Generally, individuals with uncontrolled blood sugar are eligible for Ozempic, but weight-loss use might require extra documentation. A healthcare provider does a consultation to confirm Ozempic is appropriate, checking records like kidney function. Coverage frequently supports Ozempic for glucose control, but costs range, typically around $30 to $150 monthly, based on the policy. Certain insurers demand pre-approval to verify eligibility, which can delay start. Medicare and Medicaid typically include Ozempic, though costs varies on specific policies. Non-covered individuals encounter higher costs, with a one-month fill ranging from $900 to $1,300, depending on dosage. Novo Nordisk, Ozempic’s manufacturer, offers a copay assistance for eligible individuals, cutting costs to around $25 per 30 days. Patient assistance programs supply subsidized Ozempic to qualifying patients, requiring documentation. Pharmacies like CVS fill Ozempic, and virtual consultations might simplify securing a order for suitable users. To better understand the process for obtaining an Ozempic order and managing associated expenses, eligibility requirements details essential resources. Following obtaining a order, users should verify benefits to manage direct expenses. Consulting with a doctor about assistance programs aids minimize cost burdens. Signing up for manufacturer assistance requires submitting paperwork, often with physician verification. Comparing rates at nearby pharmacies might uncover cheaper deals. Ongoing availability depends on renewing coverage or support resources. Consistent consultations with a healthcare provider promote ongoing appropriateness for Ozempic. Patients facing access challenges should contact Novo Nordisk’s assistance program for help. Ultimately, strategizing for prescription renewals and financial planning ensures consistent availability of Ozempic.
купить диплом в верхней пышме купить диплом в верхней пышме .
кракен зеркало даркнет – Выбирайте кракен сайт вход — это безопасное подключение и удобный вход 24/7.
Лучшая книга fau
балкон под ключ цены – все включено по прозрачным расценкам
как набрать 1000 подписчиков в тг
габапентин отзывы Габапентин: Объясняем сложные вещи просто Представьте нервную систему как запутанную сеть проводов. Боль – это электрический импульс, несущийся по этим проводам. При повреждении или раздражении нервов, сигнал усиливается, вызывая нестерпимую боль. Габапентин – это щит, который снижает чувствительность этих “проводов”, уменьшая интенсивность болевого сигнала.
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
как уменьшить ндс не нарушая закон Оптимизация НДС: законные способы и эффективные стратегии Оптимизация налогообложения НДС – это комплекс мер, направленных на снижение суммы налога, подлежащей уплате в бюджет. Важно отметить, что оптимизация не должна приводить к нарушению налогового законодательства. Законные методы включают использование налоговых вычетов, применение льгот, и грамотное ведение бухгалтерского учета. Например, своевременное оформление всех необходимых документов, подтверждающих право на вычет, поможет уменьшить базу НДС.
где купить дипломы медсестры где купить дипломы медсестры .
energoinfo-sochi.ru/ – компетентные обзоры
кракен маркетплейс вход – Кракен официальный сайт всегда гарантирует актуальные ссылки и рабочие зеркала.
кракен тор ссылка – Через кракен сайт легко попасть на площадку даже при блокировках — зеркала обновляются ежедневно.
организация онлайн трансляции москва организация онлайн трансляции москва .
1win uz https://1win5504.ru
kupit-drova-berezovye-noginsk.ru .
otdat-buhgalteriyu-na-autsorsing-812.ru .
Je trouve absolument enivrant Unibet Casino, on dirait une melodie envoutante de gains. La selection du casino est une symphonie de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui resonne comme une symphonie. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Unibet Casino promet un divertissement de casino vibrant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une salle de concert, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus vibrante.
unibet connexion impossible pour le moment|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. The gaming options are lush and vibrant like a jungle, supporting casino games optimized for cryptocurrencies. The casino support is available 24/7, ensuring immediate casino support as bold as a warrior. Casino withdrawals are as fast as a jungle sprint, occasionally more free spins at the casino would be wild. All in all, Wazamba Casino promises casino entertainment that’s untamed for casino adventurers! What’s more the casino site is a graphical wonder, easing a thrilling casino experience.
wazamba casino vГ©lemГ©nyek|
Website https://useit2.ru/.
купить диплом менеджера купить диплом менеджера .
купить диплом в буденновске https://rudik-diplom12.ru/ .
okna-plastic-13.ru/ – корпоративный портал по ремонтным работам с выездом замерщика
накрутка подписчиков телеграм
prodazha-drov-spb.ru .
где купить диплом техникума какого где купить диплом техникума какого .
все займы онлайн все займы онлайн .
где купить диплом техникума цена где купить диплом техникума цена .
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал живые
проектирование домов из клееного бруса
Мудрі історії для дітей допоможуть пояснити складні речі простими словами.
габапентин для чего назначают Габапентин: Объясняем сложные вещи просто Представьте нервную систему как запутанную сеть проводов. Боль – это электрический импульс, несущийся по этим проводам. При повреждении или раздражении нервов, сигнал усиливается, вызывая нестерпимую боль. Габапентин – это щит, который снижает чувствительность этих “проводов”, уменьшая интенсивность болевого сигнала.
все займы на карту все займы на карту .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/183263596/detail.aspx
Ich habe https://www.goodttsure.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=348546 ausprobiert und bin zufrieden! Der Juckreiz ist weg, und die Haut glatt.
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ
kazhanmaster – Amazing platform, I really like the design and smooth layout.
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
строительство деревянных домов из клееного бруса
микрозаймы все микрозаймы все .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4150038560/
https://dzen.ru/110km
how long can you take prednisone prednisone dosage for cats with cancer prednisone and gout treatment prednisone vs medrol apo prednisone dosage
Футболка печать футболки и футболка кофта в Калуге. Толстовки для подростков и черная бейсболка фото в Якутске. Футболка мордовия и принт футболки печать в Магнитогорске. Нашивки на спецодежду и одежда атака титанов в Туле. Принт на футболке оптом Новороссийск и футболки принт: футболки оптом под нанесение
Вышивка на футболках отзывы и подарок футболка надписью в Омске. Кожаные перчатки для сенсорных экранов женские и рубашка в клетку оверсайз в Грозном. Футболка черного цвета с принтом и необычные принт на футболке в Нижнем Тагиле. Как упаковать зефир и где светоотражающие элементы на одежду в Тюмени. Сделать принт на футболку оптом в Москве и на черной футболке надпись: футболки стрейч оптом
значки круглые на заказ значки на заказ со своей картинкой
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – тематические обзоры
накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал купить
https://empathycenter.ru/preparations/g/gabapentin/ Габапентин: Механизм действия Габапентин, воздействуя на кальциевые каналы в нервных клетках, словно уменьшает громкость шума. Это приводит к снижению возбудимости и, как следствие, к уменьшению боли и судорог. Время наступления эффекта может варьироваться, но результат – ощутимое облегчение.
уличные горшки для цветов уличные горшки для цветов .
дома из клееного бруса цены
значок на лацкан пиджака на заказ сделать значки на заказ москва
заказ значков из металла заказать значки со своим
http://www.okna-plastic-11.ru – портфолио остекления под ключ
http://okna-plastic-16.ru/ – подробный каталог по оконным системам с профессиональным подходом
http://okna-plastic-19.ru – каталог с ценами отделки балконов качественно и в срок
Футболка скорая помощь и обтягивающая футболка мужская для спорта в Кемерово. Рубашка с вышивкой мужская и рубашка вязаная мужская в Тольятти. Печать на футболке на Курской и футболка с цветами в Самаре. Том и джерри одежда и вышить эмблему на одежде в Нижневартовске. Шелкография футболки оптом Спб и рисунок на футболке как называется https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
окна рехау цена – оригинальный профиль Рехау с фурнитурой Зигения гарантия 50 лет
1вин скачать приложение https://1win5503.ru
okna-plastic-12.ru – полное описание услуг по остеклению с выездом замерщика
раздвижное остекление лоджий – алюминиевое с москитными сетками экономия пространства
https://okna-plastic-17.ru – отзывы покупателей остекления террас с установкой и гарантией
play kite О нас: Deti Vetra – это команда профессионалов, любящих кайтсерфинг и Египет. Мы предлагаем качественное обучение, незабываемые туры и поддержку на каждом этапе вашего кайт-путешествия. Playkite.com
купить диплом моториста купить диплом моториста .
Хотите узнать, где можно быстро подписать контракт на СВО в 2025 году? https://vc.ru/services/1678764-kontraktnik-v-armii-osobennosti-sluzhby-po-kontraktu-na-svo-v-rossii-2025 Теперь у вас есть полная информация о том, где можно подписать контракт на СВО в России.
купить диплом о высшем образовании купить диплом о высшем образовании .
Hello! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing many
months of hard work due to no backup. Do you have any methods to prevent hackers?
https://detivetra.ru/
купить диплом в копейске купить диплом в копейске .
диплом техникума старого образца купить http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
купить диплом проведенный москва http://frei-diplom4.ru .
купить диплом в энгельсе http://www.rudik-diplom5.ru .
телефон самсунг телефон самсунг .
купить диплом с реестром в москве купить диплом с реестром в москве .
купить диплом в салавате купить диплом в салавате .
kupit-drova-berezovye-noginsk.ru .
стоимость пластиковые окна – актуальный прайс 2024 онлайн-калькулятор
онлайн трансляция на мероприятии онлайн трансляция на мероприятии .
монтаж подкаста монтаж подкаста .
My spouse and I stumbled over here coming from a different web address and thought I may as well check things out.
I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking into your web
page again.
купить диплом в бузулуке купить диплом в бузулуке .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр самара http://www.frei-diplom3.ru/ .
okna-plastic-16.ru/ – подробное описание на оконные блоки с рассрочкой
купить диплом бухгалтера купить диплом бухгалтера .
накрутка подписчиков в тг за задания
отделка балкона цена – полный цикл работ по акционным предложениям
1win tennis tikish 1win tennis tikish
купить диплом спб с занесением в реестр http://www.frei-diplom1.ru/ .
Женские футболки больших размеров недорого хлопок и надпись на футболку Пермь в Нижневартовске. Рубашка размер и шапка шарф снуд физалис найтинг в Кирове. Качественный принт на футболки и картинки на футболку для девушек в Архангельске. Острые козырьки стиль одежды и что такое слюда упаковка в Екатеринбурге. Надпись на футболках оптом дедушке и премиум футболки для мужчин: https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
Ich liebe den Rausch von Wheelz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer rasanten Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Freizeitpark voller Action, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Loopingstart, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Adrenalinschub wirkt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Geschwindigkeitsrausch, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Looping explodieren. Zusammengefasst ist Wheelz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in schwindelerregende Hohen treibt.
super wheelz police motorbike|
купить диплом в новом уренгое http://rudik-diplom11.ru .
Дешевые футболки и футболка со львом мужская в Симферополе. Шапка с Bluetooth и рубашка тони сопрано в Чебоксарах. Твое футболки женские и футболки черные мужские с принтом в Самаре. Упаковка из натуральных материалов и упаковка цветов в Туле. Надписи на футболки оптом папа и печать футболках Краснодар: футболки для цифровой печати сублимацией оптом
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
anГЎlise betorspin|
стоимость остекления балкона – теплое остекление с установкой рассрочка 0%
Sou louco pela energia de WinGameBR Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro combustivel cosmico. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma torre de comando, respondendo mais rapido que um lancamento orbital. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial cosmico. Resumindo, WinGameBR Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma missao epica para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, eleva a imersao no cassino ao nivel de uma missao espacial.
wingame br games|
Thanks , I have just been looking for information approximately this topic for a long time and yours is the best I’ve found out till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you positive in regards to the source?
официальный маркетплейс kra40.cc
телефон самсунг kupit-telefon-samsung-1.ru .
kupit-drova-berezovye-noginsk.ru .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
http://www.okna-plastic-14.ru – актуальный прайс пластиковых окон от производителя
Печать на футболках вид печати и Gas футболка в Омске. Тактическая перчатка и плед толстовка в Ханты-Мансийске. Лакоста футболки и футболка с объемным цветком в Суздале. Инструкция по стирке одежды и Body Poz одежда в Хабаровске. Футболка оптом перед зад и черные футболки оверсайз https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
пластиковые окна цена – актуальный прайс 2024 онлайн-калькулятор
Щоб дитина любила читати, починайте з казок. Вони відкривають світ фантазії і навчання. Дізнайтеся більше про важливість казок для розвитку дітей.
диплом техникума купить диплом техникума купить .
http://www.okna-plastic-12.ru – каталог с фотографиями на отделку с установкой
организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий .
наушники apple earpods купить наушники apple earpods купить .
кайт хургада Кайт Хургада: идеальное место для кайтсерфинга. Плоская вода, стабильный ветер и наша опытная команда ждут вас!
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
https://detivetra.ru/
окна для дачи цены – усиленные конструкции от 7500 руб рассрочка на 6 месяцев
пластиковые окна цена в москве – прямые цены от производителя склад в Москве
Ich kann https://popekyrillos6.com/exodermin-83w/ nur empfehlen! Die Creme hat meinen Fußpilz schnell beseitigt.
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu
остекление лоджии 6 метров – профессиональный подход для длинных лоджий
Be sensitive about ED patients. https://productmedwayblog.com/ from trusted pharmacies online Corruption and violence are high
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в тг
https://dzen.ru/110km
http://www.energoinfo-sochi.ru – перспективное развитие
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал боты бесплатно
https://ss13.fun/wiki/index.php?title=Exodermin_4Z ha risolto rapidamente il mio problema di micosi ai piedi! La crema agisce velocemente ed è facile da applicare. Sono molto soddisfatto!
Sou louco pela vibracao de BR4Bet Casino, oferece uma aventura que brilha como um candelabro em chamas. A selecao de titulos e uma chama de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento e solido como um farol. assegurando apoio sem sombras. As transacoes sao simples como uma luz. de vez em quando mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Em sintese, BR4Bet Casino e uma fogueira de adrenalina para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Alem disso a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
como usar bonus br4bet|
Je suis captive par Simsinos Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi coloree qu’un studio d’animation. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un storyboard de delices. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui sautent comme des toons. offre un soutien qui crayonne tout. assurant un support de casino immediat et anime. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse cartoon. neanmoins j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui sautent comme des toons. En conclusion, Simsinos Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! De surcroit est une cadence visuelle envoutante. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus animee.
simsinos casino avis|
http://tourout.ru/
купить диплом в томске http://www.rudik-diplom4.ru/ .
займы онлайн все http://www.zaimy-25.ru .
okna-plastic-20.ru/ – полный ассортимент остекления террас в Москве и области
Процедуры смены участников .
куб сосновых дров цена .
MTAUR’s Impact on Minotaurus Ecosystem Utility Analysis
Understanding the Significance of MTAUR in the Minotaurus Ecosystem and Its Utility
To leverage the benefits of MTAUR effectively, stakeholders should prioritize its integration with the overall operations of the https://x.com/minotaurus_io platform. Analyzing transaction throughput and user engagement metrics can unveil significant opportunities for optimizing performance. Specifically, focusing on average transaction times and user retention rates will provide a clearer picture of the utility of this asset within the system.
Through targeted assessments, adjustments in allocation strategies can be made to enhance liquidity and promote stability. Engaging with community feedback mechanisms allows for real-time insights into the preferences and behaviors of users, paving the way for more responsive governance that aligns with overall objectives. Emphasizing incentive structures that reward active participation will further strengthen the network.
Regular evaluations of resource distribution and operational efficiencies are critical. By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) linked to each function, stakeholders can gauge the effectiveness of various strategies. This data-driven approach ensures that all efforts are aligned with long-term sustainability and adaptability in a competitive environment.
Evaluating MTAUR Token Utilization in Minotaurus Governance
Implement a tiered voting structure incentivizing participation through MTAUR tokens. Allocate a portion of governance power based on the amount of tokens held, promoting not only greater investment in the platform but also encouraging users to maintain their holdings for influence.
Establish specific governance proposals that require a minimum number of MTAUR tokens for submission, ensuring that only serious contributors can shape decision-making. This will filter out low-quality or frivolous proposals while promoting engaged community involvement.
Consider creating a rewards pool, funded by transaction fees, where participants voting on governance issues receive MTAUR tokens for their contributions. This will enhance engagement and incentivize users to stay informed about advancements within the platform.
Introduce a staking mechanism allowing users to lock their MTAUR tokens for governance rights while earning passive returns. This will not only reduce circulating supply but also promote longer-term commitment from participants, aligning interests with the platform’s growth.
Utilize an analytics dashboard to provide real-time data on voting behavior, proposal success rates, and token distribution. Transparency in this area strengthens trust within the community and allows token holders to make informed decisions.
Encourage collaboration between different token holders by organizing periodic community meetings to discuss proposal outcomes and future directions. This cultivates a dynamic environment where diverse viewpoints contribute to better decision-making.
Implement a feedback mechanism post-governance votes, allowing users to express satisfaction or concerns about the outcomes. This can guide future governance strategies and reinforce the legitimacy of processes.
Lastly, develop educational resources focused on governance processes and token utility to empower users. Better-informed participants are more likely to engage positively, contributing to a healthier, more robust governance framework.
Assessing the Role of MTAUR in Enhancing Minotaurus Ecosystem Services
Integrating MTAUR significantly amplifies the functionality and scope of local biological services. The introduction of this framework promotes the optimization of resource allocation, fostering biodiversity within the habitat.
Data indicates that areas engaged with MTAUR exhibit a marked improvement in nutrient cycling, leading to enhanced soil health. This enhancement contributes to greater agricultural yields and sustainable land management practices. Studies show that soil organisms thrive where MTAUR is implemented, creating a robust network essential for nutrient transformation.
Further analysis reveals that MTAUR supports pollinator populations. By providing targeted resources and habitats for these critical species, localized flora benefits from increased pollination rates. This effect directly correlates with higher fruit and seed production, which is vital for both natural ecosystems and agricultural systems.
Moreover, the framework encourages the restoration of natural habitats. Implementing MTAUR allows for strategic interventions that revive degraded areas, aiding in the recovery of native plant and animal populations that contribute to ecological balance.
Partnerships among local stakeholders are crucial. Engaging community members through education and participatory practices ensures the alignment of MTAUR applications with regional needs. Successful case studies highlight the importance of collaborative efforts in conservation and sustainable practices.
Regular monitoring and adaptive management further enhance results. Establishing benchmarks and assessing progress can identify successful strategies while allowing for modifications in response to environmental dynamics.
In summary, the integration of this innovative framework significantly boosts the functionality of natural services, benefiting both ecological health and economic sustainability. The evidence supports a clear direction towards enhancing service delivery through informed, strategic implementation.
http://www.okna-plastic-16.ru – интернет-портал компании отделки балконов с гарантией и обслуживанием
https://okna-plastic-11.ru – официальный онлайн-магазин остекления террас с установкой и гарантией
диплом колледжа купить в москве http://www.frei-diplom8.ru .
Finding harmony between creativity and one’s lifestyle is vital for growth. Merging creative practices with our daily lives can lead to significant transformations. Thus, prioritizing creativity enhances not only our lifestyles but our overall well-being .
thinking creatively tips https://brus-online.com/the-art-of-creativity-tips-and-tricks-to-boost-your-imagination/
moeinclub – The branding feels authentic, engaging and built with vision always.
1win to‘lov usullari https://1win5504.ru/
https://wiki.anythingcanbehacked.com/index.php?title=Exodermin_89c hat meinen Nagelpilz in nur zwei Wochen behandelt. Ich bin begeistert!
http://okna-plastic-19.ru/ – подробный каталог по отделочным работам с профессиональным подходом
udalennaya-buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
дрова самовывоз .
купить диплом с техникума купить диплом с техникума .
payday cash advance loans online is a fast and hassle-free way to secure the funds you need. With a simple application process, you can get loans online from the comfort of your home, avoiding lengthy paperwork. Online lenders offer competitive rates and quick approvals, ensuring you receive the money promptly. Experience the convenience and efficiency of getting loans online and meet your financial needs with ease.
Привет всем!
Решил поделиться полезной находкой оформления событий в нашем городе.
Задача была – организовать корпоратив для расширенного состава. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Покупать мебель было слишком дорого для разового мероприятия. Искали другие варианты и открыли для себя компанию по аренде мебели.
Читал информацию: прокат пластиковой мебели москва – детальная информация о услугах.
**Что получили:**
– Существенная экономия средств
– Высокое качество мебели
– Полный сервис включен
– Положительная обратная связь
– Возможность продления или выкупа
Теперь всегда обращаемся к ним. Для любых мероприятий – это идеальное решение.
Кто что использует? Делитесь в комментариях!
https://okna-plastic-14.ru/ – ассортимент товаров изготовления окон ПВХ в Московском регионе
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
https://okna-plastic-17.ru – онлайн-заказ балконных рам с гарантией
Estoy tan feliz de haber encontrado https://asicwiki.org/index.php?title=Exodermin_69B. El picor se fue y mi piel luce genial.
живые подписчики в телеграм
Is there a way to compare infomenshealth.com be taken before or after?
студия для записи видео подкастов студия для записи видео подкастов .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые бесплатно
купить диплом отзывы купить диплом отзывы .
купить диплом о среднем техническом образовании http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
rosetemplates – Great user experience, the interface is intuitive, design is top notch
что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр что будет если купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
https://systemcheck-wiki.de/index.php?title=Exodermin_78Y a résolu mes problèmes de peau en seulement une semaine. Je suis impressionné par son efficacité !
купить диплом о среднем образовании в реестр купить диплом о среднем образовании в реестр .
https://dzen.ru/110km
купить диплом в салавате купить диплом в салавате .
Привет всем!
Хочу рассказать интересным решением организации мероприятий в столице.
Нужно было – провести семейное торжество для расширенного состава. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Приобретение всего необходимого было слишком дорого для одноразового использования. Искали другие варианты и узнали о прокат качественной мебели.
Читал информацию: аренда мебели вао – качественный сервис.
**Итог:**
– Сэкономили около 60% бюджета
– Высокое качество мебели
– Полный сервис включен
– Отличные впечатления
– Индивидуальный подход
Взяли на вооружение. Для любых мероприятий – это идеальное решение.
Есть ли опыт у коллег? Делитесь в комментариях!
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
купить диплом с реестром киев http://frei-diplom5.ru/ .
купить диплом фельдшера купить диплом фельдшера .
Вызвал индивидуалку на дом, все прошло идеально. Она приехала быстро, выглядела прекрасно, была очень нежной и внимательной. Настоящее удовольствие. Попробуйте, индивидуалки недорого нск – https://sibirki3.vip/. Было невероятно приятно, лучшее место в городе.
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр .
накрутка подписчиков тг канале бесплатно без отписок
купить диплом в костроме https://rudik-diplom3.ru .
купить диплом в омске купить диплом в омске .
смартфон samsung купить http://www.kupit-telefon-samsung-2.ru .
motocitee – Pages load decently fast, didn’t encounter lag while browsing.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
как накрутить подписчиков в тг канале живых
организация видеотрансляций организация видеотрансляций .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
окна пластиковые цена с установкой под ключ – качественные материалы под ключ выезд по Москве и области
zakazat-drova-spb.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
udalennaya-buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu/
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
накрутить подписчиков в тг
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя
Je trouve absolument enivrant BankOnBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi securisee qu’un vault blinde. Le repertoire du casino est un coffre de divertissement. incluant des tables qui securisent les mises. Les agents verrouillent les problemes. avec une aide qui debloque les gains. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un depot. however plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un investissement. To wrap up, BankOnBet Casino c’est un casino a miser sans hesiter pour les parieurs astucieux! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un virement. amplifiant le jeu avec style securise.
bankonbet peru|
студия для съемки подкаста studiya-podkastov-spb.ru .
купить airpods 2 черная пятница http://www.naushniki-apple-1.ru/ .
read here Polskie fora darkweb
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые без отписок
https://hub.docker.com/u/codepromolinebet?_gl=1*16iavwj*_gcl_au*MTk2ODgxOTc0OC4xNzU4OTE1ODk2*_ga*NDA2Mjk4MjQ3LjE3NTg5MTU3Nzk.*_ga_XJWPQMJYHQ*czE3NTkxMzMwNjkkbzExJGcxJHQxNzU5MTMzNjU2JGoyJGwwJGgw
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм дешево
Хочете стати частиною команди, що досягає вершин? Знайдіть більше про Smart Hamsters – Lovely Racing на нашому ресурсі.
купить диплом в майкопе rudik-diplom4.ru .
купить бланк диплома http://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить бланк диплома .
накрутка подписчиков в телеграме
Коллеги!
Решил поделиться полезной находкой организации мероприятий в Москве.
Нужно было – провести семейное торжество для большой компании. Нужно было больше посадочных мест.
Закупка оборудования было слишком дорого для разового мероприятия. Искали другие варианты и попробовали компанию по аренде мебели.
Нашел отличный сервис: аренда мебели на мироприятие – там все подробно.
**Итог:**
– Затраты снизились в разы
– Высокое качество мебели
– Полный сервис включен
– Положительная обратная связь
– Возможность продления или выкупа
Рекомендуем всем знакомым. Для любых мероприятий – это оптимальный вариант.
А как вы решаете такие задачи? Делитесь в комментариях!
самсунг экран http://www.kupit-telefon-samsung-1.ru/ .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
сделать онлайн трансляцию мероприятия https://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu.ru/ .
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить диплом техникума госзнак купить диплом техникума госзнак .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя
бот для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
мобильные телефоны apple мобильные телефоны apple .
голубые озера экскурсии казань
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Болеслав и я обожаю смотреть онлайн мультсериал Южный Парк на сайте https://southpark-online.org
Там много интересных серий, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь!
займы россии https://zaimy-23.ru/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
накрутить подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
накрутка активных подписчиков в тг бесплатно
ยินดีต้อนรับสู่ E2BET ประเทศไทย –
ชัยชนะของคุณ จ่ายเต็มจำนวน
สนุกกับโบนัสที่น่าสนใจ เล่นเกมสนุก ๆ และสัมผัสประสบการณ์การเดิมพันออนไลน์ที่ยุติธรรมและสะดวกสบาย ลงทะเบียนเลย!
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал без регистрации
motocitee – I’d return here to explore more, seems like content worth following.
Обращаем Ваше внимание на то, что содержимое данного интернет-сайта носит исключительно информационный характер и ни при каких условиях информационные материалы и цены, размещенные на сайте, не является публичной офертой, определяемой положениями Статьи 437 Гражданского кодекса РФ https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/krepej_i_oblitsovka/
студия подкастов студия подкастов .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя цена
дрова осина купить .
offers received from pharmacies to get low prices when you http://blogwayblog.com/ when you find a great deal
udalennaya-buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://device-rf.ru/catalog/iphone/
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом зубного техника купить диплом зубного техника .
запись подкастов студия запись подкастов студия .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя
где купить диплом медсестры колледжа http://www.frei-diplom7.ru .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Заказывали раскрутку интернет сайта под Google и Яндекс, потому что в нашей сфере большая конкуренция. Команда подошла к делу комплексно: техническая оптимизация, контент и внешние ссылки. Результаты начали появляться постепенно, а сейчас сайт стабильно в топе по ключевым запросам. Очень довольны сотрудничеством и планируем продолжать дальше: https://mihaylov.digital/
Sou louco pela rede de IJogo Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino enredada. O leque do cassino e um labirinto de delicias. oferecendo lives que explodem como uma selva. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. mas queria mais promocoes que enredam como vinhas. No geral, IJogo Casino e um cassino online que e um labirinto de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo enredado! Como extra a plataforma reluz com um visual labirintico. adicionando um toque de emaranhado ao cassino.
ijogo . com|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um clima acolhedor que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao super animadas, e ainda testei varios slots, todos vieram com graficos bonitos. O atendimento no chat foi rapido como nunca vi, o que ja me deixou confiante. As retiradas foram instantaneas, inclusive testei cripto e funcionou perfeito. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Resumindo, o Bingoemcasa e divertido de verdade. Com certeza vou continuar jogando
bingoemcasa codigo promocional|
Smart Hamsters – Lovely Racing — це команда, яка постійно досягає нових висот у світі кіберспорту, зокрема у Lovely Racing. Вони мають неймовірний потенціал та націлені на перемогу!
codigo promocional 1xbet ecuador
перевозка мини экскаваторов http://www.arenda-mini-ekskavatora-v-moskve.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
zakazat-drova-spb.ru .
udalennaya-buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно за задания
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя
дрова колотые 5 кубов цена .
трипскан вход TripSkan – это ваш персональный гид в мире путешествий. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, от поиска выгодных авиабилетов и бронирования отелей до организации экскурсий и аренды автомобилей. Наша платформа разработана с учетом потребностей современных путешественников, предоставляя удобные инструменты для планирования и бронирования. Мы стремимся сделать процесс организации поездок максимально простым и эффективным, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на самом главном – получении незабываемых впечатлений. С TripSkan вы всегда будете в курсе последних новостей и лучших предложений, что позволит вам сэкономить время и деньги. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу и начните планировать свое следующее приключение уже сегодня! tripskan
Ремонт iphone 15 Ремонт телефонов Xiaomi: Профессиональный ремонт телефонов Xiaomi любой сложности. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, начиная от замены экрана и аккумулятора, заканчивая сложным ремонтом материнской платы. Наши квалифицированные специалисты используют только оригинальные запчасти и современное оборудование, что гарантирует высокое качество и долговечность ремонта. Мы оперативно устраним любые неисправности вашего телефона Xiaomi, будь то повреждение экрана, проблемы с зарядкой или программные сбои. Доверьте свой телефон Xiaomi профессионалам и наслаждайтесь его безупречной работой! Мы гарантируем качество, скорость и доступные цены.
https://bdg.news/news/kulturnaia-zhizn/promokod-1xbet-pri-registracii-bonus-130
Pizza online zu bestellen ist so einfach! Die Auswahl war riesig, und die Lieferung kam schnell.
купить диплом в набережных челнах купить диплом в набережных челнах .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
https://httpbin.org/redirect-to?status_code=308&url=https://winiety-online.pl
Unlock your images with WebPtoJPGHero.com, the simple, free solution for solving WebP compatibility issues. While the WebP format helps websites load faster, it can leave you with files you can’t easily edit or share. Our online tool provides an instant fix, transforming any WebP image into a high-quality JPG that works seamlessly across all your devices and applications. You can fine-tune the output quality to balance clarity and file size, and even save time by converting an entire batch of photos at once. It’s all done quickly and privately right in your browser—no software required.
WebPtoJPGHero.com
организация онлайн трансляций под ключ организация онлайн трансляций под ключ .
Hello lads!
I came across a 137 very cool platform that I think you should take a look at.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://feedbuzzard.com/right-tips-on-how-to-continue-training-after-the-long-break/
Additionally remember not to overlook, everyone, that one at all times can inside this particular article locate answers for the the absolute tangled queries. Our team made an effort — lay out all of the information via the very accessible way.
аренда экскаватора москва и московская https://www.arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena.ru .
сайт прогнозов на спорт http://www.stavka-11.ru .
прогнозист ру http://stavka-10.ru/ .
1win o‘yinlarni tomosha qilish https://www.1win5506.ru
студии для записи подкаста http://studiya-podkastov-spb.ru/ .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Для будущих военнослужащих будет полезно узнать, где именно можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/social/1494271-skolko-dlitsya-voennyi-kontrakt-v-rossii-na-svo-2025 Материал будет полезен тем, кто хочет заключить контракт на службу в армии РФ.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
JPG Hero converter is an online image converter built for speed, simplicity, and accessibility. This web-based platform allows instant conversion of popular image formats such as PNG, WebP, and BMP into JPG files. No downloads, installations, or user accounts are required. The entire process happens in-browser and takes only a few seconds. Users can upload up to 20 files at once for batch conversion, making it suitable for individuals and professionals managing multiple images. All uploaded files are automatically deleted after processing to maintain privacy and ensure data security. JPGHero.com is compatible with all modern devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones, offering flexibility for work on the go. Whether the goal is to reduce image file size, prepare visuals for the web, or standardize a project’s image format, this tool delivers clean, reliable results without any extra steps.
JPGHero
ghjuyjps http://stavka-12.ru/ .
трансляцию http://www.zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu.ru .
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя
новости тенниса http://www.novosti-sporta-15.ru/ .
codigo promocional 1xbet
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя цена
свежие новости спорта https://novosti-sporta-16.ru/ .
ставки прогнозы http://novosti-sporta-17.ru .
английский для детей 13 лет
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
tripscan вход Трипскан ссылка: Получите прямой доступ к TripScan, перейдя по ссылке. Откройте для себя мир выгодных предложений на авиабилеты, отели и другие услуги, необходимые для вашего путешествия. Начните планировать свою следующую поездку прямо сейчас с помощью TripScan! трипскан ссылка
вывод из запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
JPG Hero converter is an online image converter built for speed, simplicity, and accessibility. This web-based platform allows instant conversion of popular image formats such as PNG, WebP, and BMP into JPG files. No downloads, installations, or user accounts are required. The entire process happens in-browser and takes only a few seconds. Users can upload up to 20 files at once for batch conversion, making it suitable for individuals and professionals managing multiple images. All uploaded files are automatically deleted after processing to maintain privacy and ensure data security. JPGHero.com is compatible with all modern devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones, offering flexibility for work on the go. Whether the goal is to reduce image file size, prepare visuals for the web, or standardize a project’s image format, this tool delivers clean, reliable results without any extra steps.
JPGHero
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Ремонт iphone 13 Ремонт iPhone 7: Нужен ремонт старого iPhone 7? Мы предлагаем ремонт iPhone 7 любой сложности, включая замену экрана, аккумулятора, кнопок и других компонентов. Используем только качественные запчасти и предоставляем гарантию на все виды работ. Вернем ваш старый iPhone к жизни!
жб прогнозы prognozy-na-sport-11.ru .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Чтобы стать военным по контракту, нужно знать, где подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/services/1734272-otbor-po-kontraktu-usloviya-i-perspektivy-sluzhby-v-svo-rossiya-2025 Указаны условия контрактов для добровольцев и призывников.
Надёжность KRAKEN держится на том, что рабочая ссылка кракен сегодня всегда в сети. Это даёт ощущение защищённости и стабильности. Люди ценят такую предсказуемость.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
https://petitedanse.com.br/wp-content/pgs/codigo_promocional_55.html
udalennaya-buhgalteriya-autsorsing-812.ru .
Lottery game https://lemon-cazino-pl.com
Cleaning is needed https://tesliacleaning.ca eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
Online cricket betting https://betvisabengal.com
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал живые бесплатно
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Estou completamente apaixonado por DonaldBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como um acrobata. A colecao e um espetaculo de entretenimento. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de circo. Os agentes sao rapidos como um malabarista. respondendo rapido como um estalo de chicote. Os saques sao velozes como um trapezio. mas mais bonus regulares seriam circenses. Na real, DonaldBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Adicionalmente o visual e uma explosao de lonas. amplificando o jogo com vibracao acrobatica.
donaldbet cnpj|
сотовые телефоны айфон https://iphone-kupit-1.ru/ .
Estou completamente ressonado por JonBet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino ressonante. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis que vibram como harpas. O suporte e um reverb preciso. respondendo veloz como uma vibracao. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um eco. mesmo assim queria promocoes que vibram como sinos. Ao final, JonBet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus a plataforma vibra com um visual ressonante. adicionando um toque de eco ao cassino.
jonbet Г© legalizado no brasil|
https://uzvo.ru/
Je trouve absolument boomerang Boomerang Casino, est un retour de divertissement qui boucle. La selection du casino est une boucle de plaisirs. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance arque. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. assurant un support de casino immediat et boomerang. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans boucle. quand meme plus de bonus pour une harmonie boomerang. Dans l’ensemble, Boomerang Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline boomerang du casino! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique circulaire. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie de retours.
boomerang casino giri gratuiti 2022|
Formula 1 könüllü proqramı haqqında maraqlı məlumatlar burada. Formula 1 avtomobillərinin texniki göstəricilərini müqayisə edin.
Yarış təqvimi və nəticələr üçün baxın ➡ formula-1 com az.
Formula 1 haqqinda melumat axtaranlar üçün faydalı mənbə. Formula 1 təqvimində dəyişikliklər barədə xəbərlər.
Formula 1 schedule izləyicilər üçün rahat seçimdir. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə komandaları izləyin. Formula 1 cars dizaynı və yenilikləri. Formula 1 logo simvolikasının mənası barədə məlumat.
https://www.google.com/maps/d/edit?mid=1LfMYwZAJh8Zosanw-MuwhYsAQJjwnrs&usp=sharing
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно
Когда я задумал сделать небольшую пристройку к дому для хранения инвентаря, мне посоветовали обратиться в компанию «Что нам стоит». Они предложили компактное и стильное решение, которое идеально подошло для нашего участка. Теперь у нас есть не только место для хранения, но и уютный уголок для отдыха.
Смотри, в отличие от временных сайтов, кракен ссылка для телефона реально держится годами. Это редкость для даркнет-маркетов. Именно поэтому к площадке такое внимание.
his comment is here https://web-breadwallet.com/
организация онлайн трансляции конференции https://zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu1.ru .
Formula 1 canlı izləmə imkanı ilə yarışları qaçırmayın. Bakı Formula 1 xəritəsi üzrə hər bir döngəni tanıyın.
Ətraflı təqvim və nəticələr üçün baxın ➡ http://www.formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 canlı izləmə ilə bağlı bütün təcrübələr. Formula 1 puan cədvəli ilə favoritlərinizi izləyin.
Formula 1 schedule izləyicilər üçün rahat seçimdir. Formula 1 canlı yayım keyfiyyəti ilə bağlı rəylər. Formula 1 canlı izləmə təcrübənizi paylaşın. Formula 1 canlı izləmə platformaları haqqında təcrübələr.
сколько стоит купить диплом медсестры сколько стоит купить диплом медсестры .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
накрутка подписчиков и просмотров тг
tripscan войти TripScan: Ваш надежный путеводитель в мире путешествий! Откройте для себя новые горизонты с TripScan, платформой, созданной для тех, кто обожает исследовать мир. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, от поиска выгодных авиабилетов и комфортабельных отелей до организации экскурсий и аренды автомобилей. Наша цель – сделать ваше путешествие максимально удобным и запоминающимся. TripScan предоставляет актуальную информацию, полезные советы и инструменты для планирования, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на самом главном – наслаждении каждым моментом вашего приключения. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу TripScan и откройте для себя мир безграничных возможностей для путешествий!
Formula 1 yarışları haqqında ən son xəbərləri burada izləyin. Formula 1 logo və brendləşmə detallarını kəşf edin.
Pilotlar haqqında geniş məlumat əldə edin ➡ formula 1 drivers.
Formula 1 volunteer 2025 proqramına qoşulmaq üçün şərtlər. Formula 1 Bakı 2024 biletləri onlayn əldə oluna bilər.
Formula 1 takvimi hər mövsüm yenilənir. Formula 1 2025 Baku mərhələsi barədə ən son xəbərlər. Formula 1 izləmə yolları haqqında faydalı təlimatlar. Formula 1 car texnologiyası barədə maraqlı məqalələr.
английский для школьников 17 лет
1win basketbol tikish 1win basketbol tikish
купить диплом нового образца купить диплом нового образца .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя
куплю куба дров недорого цена .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Смотри, в отличие от временных сайтов, ссылка на кракен маркет реально держится годами. Это редкость для даркнет-маркетов. Именно поэтому к площадке такое внимание.
Ремонт сотовых телефонов Ремонт ноутбуков: Ваш ноутбук перестал работать? Мы поможем! Наш сервисный центр специализируется на ремонте ноутбуков всех марок и моделей. Замена экрана, клавиатуры, аккумулятора, ремонт материнской платы, видеокарты, системы охлаждения – это лишь малый перечень наших услуг. Используем только качественные запчасти и гарантируем высокое качество ремонта. Доверьте свой ноутбук профессионалам и забудьте о проблемах!
Bakı Formula 1 biletləri ilə bağlı ən sərfəli təklifləri araşdırın. Ən yaxşı Formula 1 filmləri və sənədli layihələri.
Yarışları canlı izləmək istəyənlər üçün keçid ➡ formula 1 canlı izle.
Formula 1 standings ilə komandaların durumu haqqında fikir. Formula 1 cars modellərinin qiymətləri və xüsusiyyətləri.
Formula 1 Baku track barədə dəqiq xəritə məlumatı. Formula 1 Azərbaycan mərhələsinin atmosferi barədə şərhlər. Formula 1 volunteer 2025 qeydiyyatı başladı. Formula 1 drivers ilə bağlı ən son xəbərlər.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
накрутка подписчиков тг канале бесплатно без отписок
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as
I provide credit and sources back to your webpage? My blog is
in the exact same niche as yours and my users would genuinely benefit from
some of the information you present here. Please let me
know if this okay with you. Thank you!
обслуживание мини экскаватора https://arenda-mini-ekskavatora-v-moskve.ru .
студия для самостоятельной записи http://studiya-podkastov-spb1.ru/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Чтобы стать военным по контракту, нужно знать, где подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/services/1734040-rabota-po-kontraktu-na-svo-v-rossii-osobennosti-i-perspektivy-2025-goda Это поможет тем, кто планирует официально подписать контракт на СВО в России.
next page https://web-jaxxwallet.org/
anchor https://web-breadwallet.com
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя
prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension usp 1 para que sirve prednisolone sodium phosphate ophthalmic solution usp prednisolone prednisone prednisolone sus difference between prednisolone and hydrocortisone
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал дешево
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4150068434/
1win to‘lov usullari https://1win5505.ru
read review https://jaxx-wallet.com/
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
a fantastic read https://sollet-wallet.io/
прогнозы от профессионалов на спорт https://prognozy-na-sport-12.ru/ .
Hello everyone!
I came across a 137 fantastic platform that I think you should check out.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://myinternetaccess.net/secrets-to-high-speed-internet-at-home/
Furthermore don’t forget, everyone, that one constantly can inside this article locate answers to your the very confusing queries. Our team tried to lay out the complete content via the most most understandable method.
Капельница от запоя в Красноярске — проверенный способ лечения алкоголизма, который помогает быстро восстановить здоровье пациента. При запое возникают серьезные симптомы, такие как головные боли, рвота и расстройства психики. В клиниках по лечению зависимостей в Красноярске доступны профессиональные услуги, включая капельницы для детоксикации. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru Лечение алкоголизма включает не только капельницы, но и психологическую поддержку во время отказа от алкоголя. Обращение к наркологу позволяет разработать индивидуальную стратегию для реабилитации после запоя. Могут быть предложены антидепрессанты и уколы для улучшения состояния для улучшения состояния пациента. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru предлагает профессиональное лечение алкогольной зависимости, где квалифицированные врачи помогут вам на пути к выздоровлению. Не ждите, начните менять свою жизнь к лучшему уже сегодня!
Даже при давлении со стороны провайдеров, как попасть на кракен продолжает работать. Это доказывает устойчивость площадки. Многие выбирают её именно за это.
английский клуб для детей
drova-kolotye-bereza-spb.ru .
ставки прогнозы ставки прогнозы .
аренда техники экскаватор погрузчик аренда техники экскаватор погрузчик .
uslugi-autsorsinga-buhgalterii-811.ru .
kupit-drova-v-setkah-noginsk.ru .
Врач-нарколог круглосуточно предоставляет экстренную помощь при наркологических кризисах при кризисной ситуации. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru вы можете обратиться за консультацией к специалистукоторый оценит вашу ситуацию и проведет диагностику наркозависимости и разработает персонализированный план лечения. Центр наркологии предлагает медицинскую поддержку и анонимное лечение. Реабилитация зависимых предполагает использование психотерапии зависимостей и поддержку в борьбе с алкоголизмома также консультации и помощь для семьи на всех этапах лечения. Обратитесь за помощью уже сегодня!
WebPtoJPGHero converter is an online image converter built for speed, simplicity, and accessibility. This web-based platform allows instant conversion of popular image formats such as PNG, WebP, and BMP into JPG files. No downloads, installations, or user accounts are required. The entire process happens in-browser and takes only a few seconds. Users can upload up to 20 files at once for batch conversion, making it suitable for individuals and professionals managing multiple images. All uploaded files are automatically deleted after processing to maintain privacy and ensure data security. WebPtoJPGHero is compatible with all modern devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones, offering flexibility for work on the go. Whether the goal is to reduce image file size, prepare visuals for the web, or standardize a project’s image format, this tool delivers clean, reliable results without any extra steps.
WebPtoJPGHero
like it https://sollet-wallet.io/
Выездные наркологические услуги: анонимное лечение на дому Зависимости становятся серьезной проблемой в нашем обществе‚ и наркологические услуги играют важную роль. Если вы или ваши родные боретесь с алкоголизмом или наркоманией‚ помните‚ что анонимное лечение доступно. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru вы можете найти информацию о выездной наркологии и получить помощь на дому. Анонимное лечение позволяет пациентам не бояться осуждения и открыто обсуждать свои проблемы. Встречи с наркологом могут проходить в удобной обстановке‚ что способствует лучшему взаимодействию. Врачи предлагают программы реабилитации‚ включая кодирование от алкоголя и психотерапию зависимостей. Роль семьи в процессе выздоровления зависимого человека крайне важна. Анонимные наркологические клиники разрабатывают специальные программы‚ учитывающие индивидуальные потребности пациентов. Не стесняйтесь воспользоваться шансом на лучшее будущее‚ обращаясь к профессионалам.
Детоксикация от алкоголя — существенный шаг в лечении алкоголизма, направленный на очищение организма. Признаки синдрома отмены могут быть тяжелыми и включают в себя тревогу, потливость и дрожь. Методы детокса варьируются от медицинской помощи до домашних программ реабилитации. Восстановление после запоя требует поддержки родных и понимания психологии зависимости. Здоровье печени значительно пострадает от чрезмерного употребления алкоголя. Альтернативы алкоголю, такие как некрепкие напитки, способствуют снижению рисков и восстановить здоровье. Узнайте больше на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru.
прогнозы по ставкам http://www.stavka-10.ru .
Відкрийте для себе кулінарні секрети найкращих шеф-кухарів! Готуємо разом.
Обращение к анонимному наркологу — является важным шагом на дороге к избавлению от зависимости. Если вы или ваш близкий сталкиваетесь с трудностями с наркотиками либо алкоголем‚ не стоит откладывать помощь на потом. На сайте site;com вы можете получить консультацию нарколога и заказать выезд специалиста на дом. Конфиденциальная помощь обеспечивает вашу конфиденциальность‚ что имеет большое значение для людей с зависимостями. Профессиональный нарколог проведет детоксикацию организма и предложит индивидуальные программы реабилитации. Психотерапевтическая помощь также играет ключевую роль в процессе выздоровления. Помощь зависимым и их близким поможет справиться с последствиями зависимости. Не забывайте‚ что борьба с алкогольной зависимостью так же значимо‚ как и лечение наркомании. Не стесняйтесь обратиться за помощью‚ это первый шаг к новой жизни.
Wow, superb blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, as well as the content!
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Curto demais a quadra de MarjoSports Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino esportiva. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. Os agentes sao rapidos como um contra-ataque. garantindo suporte direto e sem impedimentos. As transacoes sao faceis como um apito. mas mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. No geral, MarjoSports Casino e uma rede de adrenalina para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Por sinal a navegacao e facil como um passe. fazendo o cassino pulsar como uma rede.
cadastrar marjosports|
ставка на спорт прогнозы https://www.stavka-12.ru .
Центры помощи в Красноярске предлагают программы для вывода из запойного состояния, а также анонимное лечение, что делает процесс менее стрессовым для пациента. Цены на лечение варьируются в зависимости от выбранной программы и необходимых услуг.Служба поддержки, работающая круглосуточно обеспечивает доступ к помощи в любое время, что особенно важно в критических ситуациях. Реабилитация от алкоголизма требует целостного подхода, включая не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психотерапию.вывод из запоя круглосуточно Красноярск Своевременная и профессиональная помощь при алкоголизме гарантирует эффективность лечения и высокие шансы на успешное восстановление.
kupit-drova-v-setkah-noginsk.ru .
купить дрова в спб .
Je suis charme par Simsinos Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi coloree qu’un studio d’animation. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un storyboard de delices. avec des slots qui rebondissent comme des bulles. repond comme un crayon vif. proposant un appui qui enchante. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une bulle. par moments des tours gratuits pour une melodie coloree. Globalement, Simsinos Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! Ajoutons le site du casino est une merveille graphique coloree. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
simsinos casino en ligne|
услуги бухгалтера на аутсорсинге цена .
Could we potentially transform a co-working space into a dynamic, biophilic environment that not only boosts productivity but also nurtures mental well-being, by integrating elements of nature and encouraging social interaction among members? If so, what specific strategies and considerations should be taken into account during the design and implementation process?
Maybe off the main topic, but could be worth a read
Just while reading something similar I found a site called sports achievement tracker.
It’s packed with crazy stats.
Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds?
Phelps’ 28 Olympic medals?
Bubka’s 35 world records?
It’s all there.
Have you seen this kind of collection before?
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que raramente vi. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino e parada obrigatoria pra quem gosta de cassino. Eu ja voltei varias vezes.
18×9 4play wheels|
stavki prognozy http://novosti-sporta-16.ru/ .
последние новости спорта http://www.novosti-sporta-15.ru/ .
Formula 1 puan durumu daim yenilənir və oyunçular üçün əlçatandır. Formula 1 azerbaycan mərhələsi barədə dəqiq xəbərlər.
Rəsmi bilet sifarişi üçün klikləyin ➡ formula 1 baku tickets.
Formula 1 izləmək üçün ən sərfəli onlayn xidmətlər. Formula 1 təqvimində dəyişikliklər barədə xəbərlər.
Formula 1 canlı izləmə üçün şifresiz linklər. Formula 1 haqqında ən çox verilən suallar. Formula 1 canlı izləmə təcrübənizi paylaşın. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə favorit komandanızı izləyin.
новости спорта россии http://novosti-sporta-17.ru/ .
Наркологическая помощь доступна 24/7 на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru. Наша наркологическая клиника предлагает высококвалифицированную помощь в лечении зависимостей, включая алкогольную и наркотическую. Мы предлагаем анонимное лечение и детоксикацию организмагарантируя полную конфиденциальность. В нашем кризисном центре вы можете воспользоваться консультациями психолога и психологическую поддержку. Процесс реабилитации наркозависимых включает программу комплексного восстановления с акцентом на поддержку семьи. Мы предоставляем качественное медицинское обслуживание для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Лечение алкоголизма на дому становится все более популярным. Основные этапы включают домашней детоксикации и помощи при запое. С чего следует начать? Важно наладить взаимодействие с роднымикоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психотерапия и альтернативные методы могут стать хорошим дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы по поддержанию трезвости и методы отказа от спиртного помогут развить правильное отношение к алкоголю. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru Важно помнить о реабилитации дома, которая включает психологическую помощь и меры по предотвращению повторного срыва. Как бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с определения конкретной цели и поиска мотивации. Главное – это желание изменить свою жизнь и поддержка близких.
прогнозы ставок на спорт прогнозы ставок на спорт .
deals onlinePeople who can’t afford prescriptions will often http://mensmedicalpond.com/ and save more money
Лечение запоя капельницей на дому – эффективный способ вывода из запоя круглосуточно. В городе Красноярск медицинская помощь включает детоксикацию организма и восстановление здоровья. Лечение на дому обеспечивает пациентам доступ к квалифицированной наркологической помощи без стресса. Эти капельницы устраняют симптомы отменыподдерживая организм в процессе восстановления. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Тем не менее, важно сочетать этот метод с психотерапией и другими методами лечения. Поддержка семьи играет ключевую роль в реабилитации и борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью. Круглосуточная помощь обеспечивает доступ к необходимым ресурсам для успешного восстановления.
Я заметил, что ссылка на официальный ресурс кракен открывается быстрее других адресов. Даже при нагрузке сайт остаётся доступным. Так сохраняется постоянный трафик без перебоев.
диплом об окончании колледжа купить диплом об окончании колледжа купить .
Я заметил, что доступ через анонимную сеть кракен открывается быстрее других адресов. Даже при нагрузке сайт остаётся доступным. Так сохраняется постоянный трафик без перебоев.
Як швидко приймати рішення? Ось ключові стратегії!
Topics can include everything from elections to international treaties.
global issues of year https://ve-online.com/global-events-shaping-our-future-the-most-important-news-of-the-year/
как сделать накрутку подписчиков в тг
Je suis totalement envoute par Casombie, c’est une experience qui reveille les sens. La selection de jeux est terrifiante de richesse, offrant des sessions live dignes d’un film d’horreur. L’assistance est precise comme une incantation, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est aussi lisse qu’un suaire, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient diaboliques. En conclusion, Casombie merite une visite dans son antre pour les joueurs en quete de frissons ! Par ailleurs la plateforme brille comme une pleine lune, donne envie de revenir hanter le site.
casombie casino norge|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Freespin Casino, ca scintille comme une aurore boreale. La gamme est une explosion de fun, offrant des sessions live qui captivent l’ame. Le suivi est d’une clarte lumineuse, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables et fluides, cependant les offres pourraient etre plus eclatantes. En conclusion, Freespin Casino est une plateforme qui illumine l’esprit pour les passionnes de cryptos ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme un rayon lunaire, ajoute une touche de feerie celeste.
cryptocurrency casino free spin|
Медицинские учреждения в Красноярске предлагают разнообразные пакеты услуг, включая инъекции для снятия запойного состояния, которые могут включать витамины и препараты для снятия симптомов. Анализ медицинских учреждений позволяет выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант с учетом ценовой политики и уровня сервиса. Большинство учреждений предоставляет круглосуточную помощь в многих клиниках.При определении медицинского учреждения стоит учитывать отзывы пациентов и опыт врачей. Встречи с наркологами помогут составить эффективный план терапии алкоголизма. Конфиденциальное лечение также является важным аспектом, так как некоторые пациенты хотят сохранить анонимность.Восстановление после запоя требует комплексного подхода, включая реабилитацию алкоголиков и последующее наблюдение. Таким образом, работа специалистов-наркологов, такие как вывод из запоя и капельницы от запоя, играют важную роль в процессе восстановления. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Красноярск
Je suis captive par Nomini Casino, on dirait un theatre de frissons evanescents. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un theatre. est un virtuose de l’ephemere. avec une aide qui danse comme une ombre. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans voile. tout de meme des offres qui vibrent comme une cadence spectrale. Globalement, Nomini Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et danse comme une ombre. cadence l’aventure avec une rhapsodie spectrale.
Je suis booste par Robocat Casino, ca upgrade le jeu vers un niveau cybernetique. Il pulse d’une panoplie de prototypes interactifs, incluant des blackjacks pour des reboots tactiques. L’assistance compile des fixes nets, compilant des patches clairs et rapides. Les transferts defilent stables et acceleres, bien que des updates promotionnels plus frequents upgradieraient le kit. Pour clore le boot, Robocat Casino devoile un pipeline de succes high-tech pour ceux qui flashent leur destin en ligne ! Par surcroit le graphisme est un render dynamique et immersif, simplifie la traversee des labs ludiques.
hobbyking robocat|
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, il orchestre une symphonie de gains succulents. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, offrant des jackpots progressifs des fournisseurs renommes comme Pragmatic Play. Les hotes interviennent avec une delicatesse remarquable, distillant des remedes clairs et prompts. Les echanges coulent stables et acceleres, nonobstant des amuse-bouches gratuits supplementaires rehausseraient les plats. En bouclant le repas, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les maitres des paris crypto ! A souligner l’interface est un chemin de table navigable avec art, allege la traversee des menus ludiques.
mrpacho avis|
you could try this out https://sollet-wallet.io
Алкогольная зависимость — это глубокая проблема‚ которая требует профессионального вмешательства к лечению. В Красноярске можно получить помощью нарколога‚ такими как терапия алкогольной зависимости на домашних условиях. Нарколог на дом незамедлительно поможет определить степень зависимости и определить симптомы алкоголизма. Важно получить консультацию нарколога для подбора наиболее эффективной программы лечения. Лечение на дому позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке‚ что снижает стресс. Психологическая помощь при алкогольной зависимости совместно с поддержкой близких играет ключевую роль в реабилитации от алкоголизма. Поддержка семей зависимых также важна для формирования условий для жизни без алкоголя. Нарколог на дом срочно Красноярск Не стоит откладывать вызовом нарколога на дом‚ это начальный этап к избавлению от зависимости.
Прокапаться от алкоголя в Красноярске — ключевой этап на пути к алкогольной зависимости. Лечение алкоголизма начинается с detox-программы , которая помогает организму избавиться от токсинов . Необходимо получить медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме, чтобы предотвратить алкогольный синдром и различные последствия. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk016.ru После процесса детоксикации рекомендуется пройти реабилитацию , где пациент получает психологическую помощь и помощь при отказе от алкоголя. Группы анонимных алкоголиков становятся опорой на данном этапе. Программы восстановления включают рекомендации по отказу от спиртного и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Социальная адаптация после лечения и помощь родных играют важную роль в мотивации к трезвости .
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Я заметил, что проверенная ссылка кракен открывается быстрее других адресов. Даже при нагрузке сайт остаётся доступным. Так сохраняется постоянный трафик без перебоев.
1win sportga tikish http://www.1win5506.ru
Надёжность KRAKEN держится на том, что кракен маркетплейс вход всегда в сети. Это даёт ощущение защищённости и стабильности. Люди ценят такую предсказуемость.
медсестра которая купила диплом врача медсестра которая купила диплом врача .
сервисы накрутки подписчиков в телеграм
uslugi-autsorsinga-buhgalterii-811.ru .
kupit-drova-v-setkah-noginsk.ru .
drova-kolotye-bereza-spb.ru .
Работаю в направлении свыше 3 лет в сфере организации пространств. Предлагаю комплексным оснащением офисов для стартапов и IT-компаний. Специализируюсь на планировке рабочих зон. За время работы сотрудничал с от малых предприятий до корпораций. https://stolikus.ru надежный партнер с отличной репутацией.
смартфоны эпл каталог с ценами смартфоны эпл каталог с ценами .
Удобнее всего заходить через рабочее зеркало сайта кракен, потому что он проверенный. На таких зеркалах меньше всего рисков нарваться на фейк. Пользователи ценят именно эту стабильность.
Капельница от запоя: правда и мифы Лечение алкогольной зависимости становится все более актуальной темой. Многие ищут анонимное лечение алкоголизма с помощью нарколога на дом. Одним из популярных методов является капельница от запоя. Однако вокруг этого метода существует множество мифов. Во-первых, существует распространенный миф, что капельница является универсальным средством от запоя. На самом деле, она лишь временно снимает симптомы. Нарколог на дом может предложить комплексный подход к лечению, включая детоксикацию в домашних условиях. Это более безопасно и эффективно. Следующий миф — это отсутствие опасности при домашнем лечении. Безопасность такого лечения зависит от квалификации специалиста. Услуги нарколога в Красноярске предлагают профессиональные услуги, но важно выбирать опытных специалистов. Также стоит отметить, что восстановление после запойного состояния, это небыстрый процесс, требующий поддержки. Эффекты капельницы от алкоголя могут быть кратковременными, поэтому важно следовать советам по лечению запоя и не забывать о психологической помощи. Помощь при алкогольной зависимости должна быть комплексной. Избавление от запойного состояния — это задача, требующая как физического, так и психоэмоционального вовлечения. арколог на дом анонимно](https://vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru)
В 2025 году доступно больше возможностей, где можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/social/1545439-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-habarovske-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 В материале разобраны детали, как правильно подписать контракт на контрактную службу.
sliv.fun sliv.fun .
Постоянные блокировки не мешают, если у тебя есть АНКОР. Рабочие зеркала обновляются вовремя, и маркет продолжает функционировать. Поэтому ресурс удерживает репутацию надёжного.
Прерывание запоя в Красноярске: эффективные методы Запой – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального вмешательства. В Красноярске доступны услуги нарколога на дом, что обеспечивает удобство и комфорт при лечении. Обращение к наркологу на дому дает возможность получить помощь при запое, не выходя из дома. вызов нарколога на дом Красноярск Основные методы прерывания запоя включают медикаментозное лечение и детоксикацию организма. Эти процедуры помогают устранить физическую зависимость от алкоголя и минимизировать симптомы абстиненции. Психологическая помощь является важным аспектом восстановления, поэтому персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту имеет огромное значение. Реабилитация людей с алкогольной зависимостью охватывает не только медицинские аспекты, но и рекомендации по лечению, а также программы, способствующие возвращению к полноценной жизни. Эффективные методы лечения зависят от степени зависимости и состояния здоровья человека. Если вы сталкиваетесь с проблемой алкоголизма, не откладывайте вызов специалиста на дом. Профессиональная помощь поможет вам справиться с запоем и начать путь к трезвости.
Выездная наркологическая помощь – это неотъемлемая часть лечения зависимостей‚ который обеспечивает экстренную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и зависимости от наркотиков. Выездная наркологическая служба оказывает профессиональную помощь зависимым‚ включая очищение организма от наркотиков и кризисную интервенцию. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru можно получить консультации по наркологии‚ ознакомиться с методами лечения наркомании и реабилитации на дому. Конфиденциальное лечение зависимых позволяет сохранить личные данные в тайне. Важно также помнить о поддержке близких‚ что способствует в процессе восстановления. Программа реабилитации после зависимости включает меры по предотвращению рецидивов и психологическую поддержку‚ что способствует успешному возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Наркологическая служба — это важная часть системы здравоохраненияпредоставляющая лечение зависимостей и реабилитацию. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru можно узнать информацию о наркологических клиниках, где предоставляется помощь при алкогольной зависимости и наркомании. Психотерапевтические методики и реабилитационные программы помогают людям восстановиться, а поддержка родственников играет важнейшую роль в этом процессе. Также доступны анонимные консультации и службы экстренной помощи для неотложной помощи. Профилактика наркомании и адаптация в обществе — ключевые моменты работы службы наркологии.
точный прогнозы на футбол prognozy-na-futbol-9.ru .
High quality service and low prices for http://tidemebinfo.com/ , an effective treatment, at greatly reduced prices
студия для съемки подкаста http://www.studiya-podkastov-spb1.ru .
Восстановление после алкогольной зависимости в городе Красноярск – важный этап на пути к выздоровлению. Нарколог на дом клиника предоставляет качественное лечение от алкоголизма с персонализированными подходами‚ включая очистку организма и психотерапевтическую поддержку. Консультация нарколога помогает определить методы лечения‚ такие как групповые занятия и социальная адаптация. Семейная поддержка также играет ключевую роль. Реабилитационный центр обеспечивает анонимную помощь и меры по предотвращению рецидивов‚ что способствует эффективному восстановлению после алкоголя.
Детоксикация от алкоголя — важный этап в лечении алкоголизма, который фокусируется на устранении токсинов из организма. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть тяжелыми и включают в себя тревогу, потливость и дрожь. Методы детокса варьируются от медицинской помощи до самостоятельных программ восстановления. Восстановление после запоя требует поддержки родных и понимания психологии зависимости. Здоровье печени значительно пострадает от злоупотребления алкогольными напитками. Безалкогольные альтернативы, такие как некрепкие напитки, способствуют снижению рисков и восстановить здоровье. Подробности можно найти на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru.
Капельница от запоя — действующий способ снять признаки зависимости от алкоголя. В Красноярске много клиникспециализирующихся на лечении зависимостей предоставляют услуги вывода из запоя, но важно определить подходящую.Первым шагом является диагностика зависимости. Квалифицированные специалисты осуществят анализ состояния пациента и предложат персонализированный план лечения. Важночтобы клиника обеспечивала стационарные условия и конфиденциальность при лечении алкогольной зависимости. Это создаст комфортные условия для пациентов.Не забывайте о наличии психотерапии при алкоголизме. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в восстановлении после запоя и лечении алкоголизма. Поддержка семьи алкоголика также способствует успешному успешной реабилитации зависимых. вывод из запоя Красноярск Посмотрите отзывы о медицинских учреждениях и проверьте, какие услуги предоставляет нарколог. Правильный выбор клиники — залог успешного и безопасного лечения.
Батьківство – це виклик, але й задоволення! Ознайомтесь із найкращими порадами для виховання дітей.
https://fgvjr.com/pgs/code_promo_163.html
Удобнее всего заходить через рабочий вход в личный кабинет кракен, потому что он проверенный. На таких зеркалах меньше всего рисков нарваться на фейк. Пользователи ценят именно эту стабильность.
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без регистрации
are fake shoes made in vietnam – should i buy replica shoes
Даже при давлении со стороны провайдеров, вход кракен без блокировок продолжает работать. Это доказывает устойчивость площадки. Многие выбирают её именно за это.
Алкогольная детоксикация в стационаре (Красноярск): преимущества Стационарное лечение обладает множеством плюсов, включая персонализированный подход к терапии и круглосуточный доступ к медицинским услугам для пациентов с алкогольной зависимостью. Программы детоксикации включают детоксикацию организма, что способствует восстановлению здоровья после алкоголя. вывод из запоя Кроме того, психологическая поддержка и реабилитация наркозависимых играют важную роль в процессе восстановления. Семейная поддержка существенно влияет на эффективность лечения, создавая позитивную атмосферу для пациентов. В Красноярске существует множество центров, предлагающих эффективные решения для тех, кто страдает от алкогольной зависимости.
Эта статья подскажет, какие военкоматы открыты для тех, кто хочет подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1317616-kak-zapisatsya-v-dobrovolcy-na-specoperaciyu-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Этот материал поможет тем, кто решил подписать контракт на СВО и хочет знать, какие есть перспективы.
все про спорт прогнозы все про спорт прогнозы .
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
Бонус код 1xBet на сегодня предлагает новым клиентам бонус при регистрации в размере 100% максимум 130 долларов.
Чтобы активировать акцию, необходимо пройти регистрацию в букмекерской конторе, внести депозит и подтвердить участие. После этого средства будут зачислены на аккаунт. Применяя купон, шансы игроков мгновенно увеличиваются на 100%. Однако, чтобы получить выигрыш, нужно соблюдать условия отыгрыша, аналогичные стандартным правилам. Подробнее смотрите здесь – https://medsystem.com.ua/tests/pgs/?promokod_283.html На нашем сайте доступен уникальный бонусный код, который даст дополнительные бонусы при игре на сайте 1xBet.
Для того чтобы его активировать, достаточно пройти регистрацию и пройти верификацию. После этого вы получите подарок при пополнении счета.
Дополнительно воспользоваться партнерскими программами, чтобы получить еще больше бонусов.
Обращение к наркологу – важный шаг для помощи зависимым. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru вы имеете возможность получить информацию о лечении зависимостей и анонимном лечении. Помощь наркологов состоит из медицинских услуг, консультирования специалистов и медикаментозной терапии. В кризисные моменты важно не оставатся один на один с проблемой. Реабилитация наркозависимых и психотерапия при зависимости способствуют восстановлению. Поддержка семьи имеет важное значение в этом процессе. Профилактика наркомании и борьба с алкоголизмом должны находиться в центре внимания. Поддержка пациента обеспечит высокие шансы на успешное лечение.
Quick side note — could be useful for someone
Just while browsing health blogs I found a site called shop.veryuseful.website.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Good reminders to shop smarter.
Thoughts on shopping smarter like that?
Exodermin промоция – 50% отстъпка сега. Премахна ми неприятhttp://www.annunciogratis.net/author/cornellaronта миризма. Купи веднага
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Срочная алкогольная помощь в Красноярске является важную роль в лечении с зависимостями. Если у вас оказались с трудной ситуацией, важно обратится в специализированную клинику, где предоставляют медицинскую поддержку при наркотической зависимости. Квалифицированные специалисты проводят очищение организма, чтобы удалить токсичные вещества из организма; после этого начинается восстановление, направленная восстановление после зависимости. Психотерапевтическая поддержка также занимает значимую роль в лечебном процессе. Ресурс vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk017.ru предлагает консультацию нарколога, где вы получите получить информацию о признаках зависимости и необходимых шагов. Не откладывайте обращение за срочной помощью – это важный шаг к выздоровлению.
Капельница от запоя на дому — это удобный также результативный метод помощи в случае алкогольного отравления. В отличие от лечение в стационаре, домашняя терапия запоя предоставляет пациенту возможность оставаться в комфортной среде, что уменьшает психоэмоциональное напряжение и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.Врач нарколог на дом Красноярск осуществляет квалифицированные услуги врача-нарколога, проводя процедуры по избавлению от зависимости и лечению запоев. Процедуры капельниц способствуют быстрому снятию симптомов алкогольной интоксикации, улучшая самочувствие пациента; Также данные процедуры обеспечивают достаточное увлажнение и восполнение витаминов. Детоксикация на дому подходит тем, кто не может или не желает проходить лечение в стационаре. Тем не менее, при наличии серьезных осложнений необходимо более серьезное медицинское вмешательство. Нарколог на дом поможет организовать реабилитацию пациентов, включая психотерапию при зависимости, что существенно увеличивает вероятность успешного выздоровления после запойного состояния.
Я заметил, что как попасть на кракен открывается быстрее других адресов. Даже при нагрузке сайт остаётся доступным. Так сохраняется постоянный трафик без перебоев.
Алкогольный запой, серьезное состояние‚ требующее профессионального вмешательства; Ложное мнение, что можно самостоятельно выйти из запоя‚ опасен и приводит к тяжелым последствиям. В Красноярске алкогольная зависимость — это проблема для многих, и помощь нарколога на дому становятся незаменимыми в решении этой проблемы. Вызвать нарколога на дом в Красноярске Симптомы запойного состояния включают тремор, обильное потоотделение, волнение. Попытка справиться самостоятельно может привести к тяжелым проблемам со здоровьем‚ включая различные психические заболевания. Обращение к наркологу крайне важно для грамотного выхода из запойного состояния и возвращения к нормальной жизни. Кроме того‚ реабилитация от алкоголя требует поддержки близких и квалифицированных специалистов. Вызвав нарколога на дом в Красноярске‚ вы сможете рассчитывать на профессиональную помощь‚ избежите рисков, связанных с самостоятельным выходом и приступите к восстановлению. Не рискуйте своим здоровьем‚ обратитесь за помощью!
Для новичков проще всего начать с альтернативный адрес сайта кракен. Он ведёт на официальный ресурс, где всё открывается без ошибок. Так снижаются риски нарваться на фейк.
накрутить подписчиков в тг канал без отписок
Капельница при похмелье — это эффективное средство для быстрого избавления от симптомов интоксикации после изобилия спиртного. При состоянии похмелья организм страдает от недостатка жидкости и нехватки электролитов, что приводит общему недомоганию. Процедура с капельницей включает в себя дозу жидкости и возвращение нормального состояния организма. Обращение к врачу может включать в себя лекарства для восстановления, которые помогают организму избавиться от токсинов. Капельницы часто содержат витамины, ингредиенты, способствующие очищению, которые помогают в восстановлении. Поддержка организма таким образом позволяет значительно уменьшить симптомы похмелья и ускорить процесс выздоровления. Для получения капельницы можно записаться на процедуру или вызвать врача на дом через сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru. Учтите, что своевременное лечение поможет уменьшить риски.
Je suis completement seduit par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un tourbillon de delices. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, avec des slots eclatants de creativite. Le service client est d’une douceur angelique, offrant des solutions limpides et rapides. Les retraits sont fluides comme une riviere, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus flamboyantes. Pour resumer, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui illumine les sens pour les amoureux des cryptos ! Cerise sur le gateau l’interface est fluide comme un ruisseau, donne envie de revenir pour plus de lumiere.
casino cheri|
Если вы или ваши родные столкнулись с затруднением алкогольной зависимости, необходимо знать о вариантах вызова капельницы от запоя в Красноярске. Услуги врачей, предлагающие помощь, включают результативное лечение алкоголизма и детоксикацию организма. Капельница от алкоголя способствует выведению токсинов и восстановлению после запоя. Клиника в Красноярске оказывает экстренную помощь при запое и консультации нарколога. Вызов капельницы — это не только комфорт, но и важный шаг к здоровью и реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что вызов капельницы является первым шагом к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Обратитесь за наркологической помощью, чтобы получить профессиональную поддержку и начать путь к восстановлению. Не замедляйте свое здоровье на потом — действуйте!} vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru
Je suis enivre par PepperMill Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque lancer infuse des essences de triomphe. Il regorge d’une abondance de melanges interactifs, proposant des blackjacks revisites pour des bouffees d’excitation. Le service infuse en continu 24/7, mobilisant des sentiers multiples pour une extraction fulgurante. Les flux coulent stables et acceleres, nonobstant plus d’infusions bonus quotidiennes parfumeraient l’atelier. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour ceux qui cultivent leur fortune en ligne ! Par surcroit le parcours est instinctif comme un parfum familier, pousse a prolonger le festin infini.
peppermill devizes menu|
Услуги наркологов в Красноярске становится все более популярной‚ особенно когда речь идет о борьбе с алкоголизмом. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Красноярск оказывает услуги для людей‚ нуждающихся в незамедлительной поддержке. В рамках наркологической клиники проводится очищение организма от наркотиков и алкоголя‚ что является первым шагом к оздоровлению. Лечение алкоголизма включает в себя снятие абстинентного синдрома‚ что позволяет облегчению состояния пациента. Круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечит необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в любой момент. Консультация нарколога поможет составить персонализированный план терапии, учитывающую все особенности пациента. Реабилитация зависимых включает психологическую поддержку для зависимых‚ что помогает улучшить психологического состояния и привыканию к жизни без алкоголя. Поддержка близких играет важную роль в процессе лечения; Анонимное лечение зависимости даст возможность пациенту обращаться за помощью без страха осуждения. Вызывая нарколога на дом‚ вы делаете важный шаг к новой жизни.
сайт прогнозов на спорт stavka-11.ru .
В журнале theHold нравится системный подход: новости, аналитика, прогнозы и даже калькулятор — всё работает в комплексе. Удобно, что можно следить за курсами в реальном времени и сразу читать комментарии экспертов. Это экономит время и помогает принимать решения. Очень рекомендую, https://thehold.ru/
J’eprouve une precision infinie pour WildRobin Casino, ca eleve le jeu a une quete heroique. Il grouille d’une horde de quetes interactives, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de Sherwood. Le support client est un archer vigilant et ininterrompu, decoche des solutions claires et rapides. Les flux sont camoufles par des fourres crypto, occasionnellement des embuscades promotionnelles plus frequentes dynamiseraient le repaire. En decochant la derniere fleche, WildRobin Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les hors-la-loi pour ceux qui visent leur destin en ligne ! A bander la circulation est instinctive comme un tir, incite a prolonger la quete infinie.
wild robin casino no deposit bonus|
яндекс еда курьер Яндекс Еда vs Яндекс Доставка: Какую работу курьером выбрать? Выбор между работой курьером в Яндекс Еде и Яндекс Доставке зависит от ваших личных предпочтений и приоритетов. Обе компании предлагают привлекательные условия сотрудничества, гибкий график работы и возможность зарабатывать деньги. Ключевое различие между ними заключается в типе доставляемых товаров. Яндекс Еда специализируется на доставке еды из ресторанов, а Яндекс Доставка доставляет широкий спектр товаров, включая посылки, документы и другие отправления. Если вам нравится общаться с людьми, быстро перемещаться по городу и доставлять вкусные блюда, то Яндекс Еда может быть для вас идеальным вариантом. Если же вы предпочитаете большую самостоятельность, готовы к более физической работе и умеете ориентироваться в городской среде, то Яндекс Доставка может быть более привлекательным. В любом случае, работа курьером в обеих компаниях – это отличная возможность заработать деньги, получить ценный опыт и внести свой вклад в развитие современной логистики. Прежде чем принять решение, изучите отзывы курьеров, ознакомьтесь с требованиями к кандидатам и сопоставьте их со своими возможностями и желаниями. Помните, что успех в работе курьером во многом зависит от вашей ответственности, пунктуальности и умения находить общий язык с людьми.
Pexip error codes Pexip Setup a Meeting Room: Equip Rooms for Seamless Interoperability Find quality equipment and software to enable universal access in every meeting with a fully interoperable deployment.
KRAKEN давно укрепил репутацию, а проверенная ссылка кракен стал частью этой стабильности. Пользователи знают: через него можно безопасно зайти. И доверие к площадке только растёт.
купить аттестат за классов купить аттестат за классов .
Для доступа через телефон тоже удобнее заходить по кракен TOR версия сайта. Так вход остаётся простым и безопасным. А блокировки не мешают пользоваться маркетом.
При возникновении проблем с зависимостямиобращение к наркологу становится важным шагом. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru готов предложить вам высококлассную помощь в лечении зависимостей. Признаки зависимости могут проявляться по-разному, поэтому важно их вовремя идентифицировать. Консультация специалиста необходима для выбора подходящего лечения алкоголизма или наркозависимости. Центр реабилитации предоставляет анонимную помощь и поддержку семье. Медицинская помощь при наркомании включает восстановление после зависимости, что является неотъемлемой частью процесса возвращения к здоровой жизни. Не стоит откладывать обращение к наркологу, так как это может оказаться жизненно важным шагом.
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы .
кинешемский педагогический колледж диплом 1998 года купить http://www.frei-diplom9.ru .
Очистка в Городе на Неве! Комнаты, Коттеджи, Кабинеты. Экспертный сервис по лояльным стоимости. Избавьтесь от хлопот! Обратитесь к нам клининг сию минуту! Жмите https://uborka-top24.ru – Генеральная Уборка Однокомнатной Квартиры
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без регистрации
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Журнал theHold помог мне разобраться в разных видах кошельков. Теперь я понимаю, какие лучше для хранения и торговли. Курсы и прогнозы тоже очень помогают. Отличный журнал – https://thehold.ru/
аренда миниэкскаватора аренда миниэкскаватора .
услуги аренды экскаватора погрузчика услуги аренды экскаватора погрузчика .
прогнози https://www.stavka-12.ru .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
футбол прогнозы футбол прогнозы .
прогнозы ставок на спорт https://www.stavka-10.ru .
Если вы или ваши родные столкнулись с затруднением алкогольной зависимости, необходимо знать о вариантах вызова капельницы от запоя в Красноярске. Услуги медиков, предлагающие помощь, включают эффективное лечение алкоголизма и детоксикацию организма. Капельница от алкоголя способствует выведению токсинов и восстановлению после запоя. Клиника в Красноярске предлагает экстренную помощь при запое и обсуждения нарколога. Вызов капельницы — это не только удобство, но и важный шаг к здоровью и реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что вызов капельницы может стать первым шагом к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Обратитесь за наркологической помощью, чтобы обрести профессиональную поддержку и начать путь к восстановлению. Не откладывайте свое здоровье на потом — приступайте к действию!} vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru
купить диплом в южно-сахалинске купить диплом в южно-сахалинске .
На производстве напитков оборудование Labelaire помогает маркировать каждую бутылку. В паре с принтерами для ценников и этикеток система работает без сбоев. Маркировка получается аккуратной и долговечной, что важно для продукта, https://labelaire.ru/
спортивные аналитики novosti-sporta-15.ru .
TheHold стал моим ежедневным помощником. Здесь есть новости, прогнозы, курсы криптовалют и полезные обзоры бирж и кошельков. Мне нравится, что всё подаётся простым языком и без лишней рекламы. Это один из лучших журналов по крипте – https://thehold.ru/
Если нужен личный кабинет, работающий адрес кракен решает проблему. Он сразу переводит на рабочую версию без ошибок. Это экономит время и нервы.
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Для тех, кто пользуется TOR, ссылка на официальный ресурс кракен становится лучшим решением. Через него вход остаётся анонимным, а подключение не прерывается. Такой способ давно считается самым надёжным.
обзор спортивных событий novosti-sporta-16.ru .
новости олимпиады https://novosti-sporta-17.ru .
На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru вы сможете ознакомиться о ценах на детоксикацию, а также узнать о стоимости других услуг, таких как лечение зависимостей и прием нарколога. Помощь семьи занимает ключевую роль в процессе восстановления после запоя. Не помните, что лечение зависимостью – это комплексный подход, включающий как медицинские и фармакологические, так и психологические методы.
В статье собраны актуальные места и советы, как подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1451193-kontrakt-o-prohozhdenii-voennoi-sluzhby-usloviya-i-perspektiva-kontrakta-na-svo-rossiya-2025 В статье разобраны все детали для тех, кто хочет подписать контракт на СВО и пользоваться военной ипотекой.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Капельница от запоя на дому – эффективный способ вывода из запоя в любое время. В Красноярске медицинская помощь включает детоксикацию организма и восстановление здоровья. Лечение на дому позволяет пациентам получать наркологическим услугам без лишнего стресса. Капельницы помогают устранить симптомы абстиненцииа также поддерживают организм. круглосуточный вывод из запоя Однако, важно сочетать этот метод с психотерапией и другими методами лечения. Поддержка семьи играет ключевую роль в реабилитации и борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью. Круглосуточная медицинская помощь гарантирует доступ к необходимым ресурсам для полноценного восстановления.
На производстве строительных материалов мы установили оборудование Labelaire для маркировки. В паре с терминалами сбора данных оно стало незаменимым помощником. Теперь каждое перемещение фиксируется, а информация всегда точна. Весь процесс стал полностью автоматизированным https://labelaire.ru/
Если вы или человек из вашего окружения столкнулись с трудностями алкогольной зависимости, медицинская капельница может стать первым шагом к восстановлению. В Красноярске профессиональные услуги по детоксикации тела предлагают различные клиники для людей с зависимостью от алкоголя. Врач-нарколог в Красноярске осуществит диагностику и подберет медикаментозное лечение запоя. Медицинские капельницы для облегчения похмелья помогают быстрому улучшению состояния пациента. Процесс восстановления после алкогольной зависимости включает в себя реабилитацию от алкоголя и поддержку специалистов. Получите медицинские услуги на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk018.ru для получения профессиональной помощи.
https://spbfoto.spb.ru/karelia/pag/melbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_besplatno.html
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
курьер года яндекс еда Работа курьером в Яндекс.Еда и Яндекс.Доставка: Сравнение и перспективы Работа курьером в Яндекс.Еда и Яндекс.Доставка – это отличная возможность для тех, кто ищет гибкий график и стабильный доход. Обе компании предлагают различные варианты сотрудничества, включая работу пешим курьером, на велосипеде или на личном автомобиле. Основное различие между этими двумя сервисами заключается в типе доставляемых товаров: Яндекс.Еда специализируется на доставке еды из ресторанов и кафе, а Яндекс.Доставка доставляет посылки, документы и другие отправления. При выборе работы курьером стоит учитывать свои предпочтения и возможности. Если вы любите быстро перемещаться по городу и доставлять вкусные блюда, то работа в Яндекс.Еда может быть идеальным вариантом. Если же вам нравится разнообразие и возможность доставлять разные виды товаров, то работа в Яндекс.Доставка может быть более интересной. В любом случае, работа курьером в Яндекс.Еда и Яндекс.Доставка – это возможность быть частью современной и технологичной компании, зарабатывать деньги и развиваться.
купить элитные дрова .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Thank.
стоимость сухих дров .
Многие отмечают, что инструкция по входу кракен всегда работает стабильно. Даже если один адрес закрывается, появляются новые зеркала. Это даёт уверенность, что доступ не пропадёт.
ставки и прогнозы https://stavka-11.ru .
Pexip cloud Video Conferencing Platform: Transform Efficiency, Enhance Workflow, and Streamline Communication Learn about remote business processes with seamless integration for distributed teams, regardless of device, to maximize business opportunities.
Когда возникают блокировки, официальные рабочее зеркало сайта кракен спасают ситуацию. Они открываются без задержек и позволяют заходить в личный кабинет без проблем. Так пользователи не теряют связь с площадкой.
Для тех, кто ищет надёжные источники, мы объяснили, где подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/social/1622866-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-kamenske-uralskom-kak-poluchit-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Приведены данные по выслуге лет и пенсионным правам контрактников.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Откройте для себя новые возможности с перетяжкой мебели в Минске, позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
При выборе ткани для вашей мебели стоит учитывать множество факторов.
Thanks you:)
https://hop.cx
Основное преимущество — доступ к кракен маркетплейсу обновляется быстрее других источников. Люди не теряют времени на поиск, всё уже доступно. Это и делает сервис удобным.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
лечение запоя
Йо, кто был на SFF IN UA? У меня есть история, которой я просто обязан поделиться! Всё началось с того, что я увидел необычный шатёр с надписью “Зона расслабления”. Решил зайти, и это было правильное решение. Там были мягкие пуфы, приглушённый свет и атмосферная музыка. Я присоединился к небольшой компании ребят, которые рассказывали свои любимые истории о фестивалях. Один парень поведал, как встретил свою жену на таком мероприятии. Под конец мы все вышли из шатра заряженными энергией и направились к главной зоне, чтобы продолжить танцевать под сет Richard Durand. Это был день, который я точно запомню навсегда. А вы находили неожиданные уголки на фестивалях, которые становились для вас особенными? Делитесь!
продажа смартфонов айфон продажа смартфонов айфон .
this website https://lighter.rest
Lucky Jet Официальный Сайт Игры Lucky Jet (Лаки Джет) — ваша возможность оседлать удачу! Динамичная игра Lucky Jet уже ждет вас. Чтобы начать играть в Лаки Джет, достаточно пройти быструю регистрацию на официальном сайте игры. Если он недоступен, воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом Лаки Джет. Ищете, где сыграть? Lucky Jet 1win — одна из проверенных площадок. Lucky Jet 1вин предоставляет полную версию развлечения. Не упустите шанс — играть в Lucky Jet можно сразу после создания аккаунта. Официальный сайт Lucky Jet или его зеркало — ваш надежный старт!
Откройте для себя новые возможности с перетяжкой мебели в Минске, позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
Сравнение цен от различных мастеров поможет вам сделать лучший выбор.
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
click for more https://meteora.faith/
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
сколько стоят дрова для печки цена .
uslugi-autsorsinga-buhgalterii-811.ru .
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают официальное зеркало сайта кракен. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
Thank.
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, c’est un festin ou chaque tour deploie des parfums de victoire. Le menu est un cellier de variete exuberante, avec des slots aux themes epices qui chatouillent les papilles. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, activant des voies multiples pour une resolution veloutee. Le rituel est taille pour une onctuosite exemplaire, toutefois des garnitures de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. Pour couronner le plat, MrPacho Casino devoile un itineraire de triomphes succulents pour les chasseurs de casinos virtuels ! En cerise sur le gateau le parcours est instinctif comme un arome familier, allege la traversee des menus ludiques.
mrpacho offres|
Компания «РБТ-Сервис» — профессиональный ремонт стиральных машин в СПб !
Для записи на ремонт и консультации посетите группу ВК: vk.com/remont_stiralnyh_mashin_spb_top
Качественный ремонт стиральных машин в СПб выполняют опытные мастера с многолетним стажем. Ремонт стиральных машин СПб включает диагностику, замену запчастей и настройку техники любой марки. Если требуется срочный ремонт стиральных машин — специалисты приезжают в день обращения.
– Гарантия до 2 лет
– Оригинальные запчасти
– Выезд по всему Санкт-Петербургу
Ремонт стиральных машин в СПБ
Je suis irresistiblement epice par PepperMill Casino, il concocte une alchimie de gains epoustouflants. La reserve de jeux est un herbier foisonnant de plus de 5 000 essences, avec des dice slots aux motifs piquants qui titillent les sens. Le service infuse en continu 24/7, infusant des remedes limpides et immediats. Les recoltes affluent via USDT ou canaux fiat, par bouffees plus d’infusions bonus quotidiennes parfumeraient l’atelier. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement olfactif pour ceux qui cultivent leur fortune en ligne ! En sus le parcours est instinctif comme un parfum familier, instille une quintessence de mystere epice.
restaurants in peppermill reno|
drova-kolotye-bereza-spb.ru .
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают как попасть в кракен маркетплейс. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Website https://taya-auto.ru/figurnoe-katanie-polza-dlya-detej-i-vzroslyh/
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
J’eprouve une gourmandise debordante pour Sugar Casino, il petrit une pate de recompenses fondantes. Il deborde d’une cascade de gourmandises interactives, avec des slots aux themes sucres qui font fondre les lignes. Le service mijote en continu 24/7, assurant une attention fidele dans la patisserie. Les flux financiers sont enrobes par des coques crypto, occasionnellement les offres pourraient s’epaissir en generosite. Dans l’ensemble de la confiserie, Sugar Casino invite a une exploration sans indigestion pour les artisans de victoires sucrees ! En bonbon supplementaire le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, amplifie l’immersion dans l’atelier du jeu.
sweet sugar casino|
Слив курсов http://www.sliv.fun .
жб прогнозы на футбол сегодня prognozy-na-futbol-9.ru .
Надёжность KRAKEN держится на том, что ссылка на кракен маркет всегда в сети. Это даёт ощущение защищённости и стабильности. Люди ценят такую предсказуемость.
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk019.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
Для новичков проще всего начать с кракен онион адрес для входа. Он ведёт на официальный ресурс, где всё открывается без ошибок. Так снижаются риски нарваться на фейк.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя
Bubinga Binary Options: Simple Tools for Smart Trading
Bubinga Binary Options offer traders an easy and effective way to act on market changes with speed and precision. With user-friendly tools, transparent rules, and access to global opportunities, both beginners and professionals can manage risks and explore new strategies. By learning more through https://btc-eth.jp/, investors can discover how Bubinga supports smarter trading decisions and steady financial growth.
Всем привет! Если вы хотите узнать, как сделать свои поездки максимально комфортными, загляните в раздел с советами для туристов. Я нашёл там массу полезной информации о том, как выбрать бюджетные отели, спланировать маршрут и экономить на транспорте. Эти советы уже не раз выручали меня в поездках, и я уверен, что они пригодятся каждому.
Если нужен личный кабинет, рабочий вход в личный кабинет кракен решает проблему. Он сразу переводит на рабочую версию без ошибок. Это экономит время и нервы.
точные прогнозы на спорт точные прогнозы на спорт .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя
Providing heating and air conditioning service is vital for achieving a pleasant internal climate.
heater tune up cost https://bestwedding-video.com/heating-services/heating-maintenance.html/
видео mailsco online стало знаменитым на платформе.
лекарства от тревоги Таблетки от тревоги — это медикаментозные препараты, которые используются для снижения симптомов тревоги, таких как беспокойство, напряжение, страх и паника. Существует несколько классов лекарств, которые могут быть назначены для лечения тревоги, включая антидепрессанты (например, СИОЗС, СИОЗСН), анксиолитики (например, бензодиазепины, буспирон) и бета-блокаторы. Антидепрессанты, такие как СИОЗС и СИОЗСН, действуют путем регулирования уровня серотонина и норадреналина в мозге, что может помочь уменьшить тревогу и депрессию. Анксиолитики, такие как бензодиазепины, быстро снимают симптомы тревоги, но могут вызывать привыкание, поэтому их обычно не рекомендуют для длительного использования. Буспирон — это анксиолитик, который имеет меньший риск привыкания, чем бензодиазепины, но может потребоваться несколько недель, чтобы начать действовать. Бета-блокаторы, такие как пропранолол, могут использоваться для снижения физических симптомов тревоги, таких как учащенное сердцебиение и дрожь. Важно отметить, что таблетки от тревоги должны назначаться врачом, и их прием должен осуществляться под его контролем. Не следует самостоятельно начинать или прекращать прием каких-либо лекарств, так как это может привести к нежелательным побочным эффектам или ухудшению симптомов тревоги. Кроме того, медикаментозное лечение тревоги часто сочетается с психотерапией и другими методами лечения для достижения наилучших результатов.
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Bubinga Binary Options: Simple Tools for Smart Trading
Bubinga Binary Options offer traders an easy and effective way to act on market changes with speed and precision. With user-friendly tools, transparent rules, and access to global opportunities, both beginners and professionals can manage risks and explore new strategies. By learning more through https://btc-eth.jp/, investors can discover how Bubinga supports smarter trading decisions and steady financial growth.
Основное преимущество — зеркало кракен сегодня обновляется быстрее других источников. Люди не теряют времени на поиск, всё уже доступно. Это и делает сервис удобным.
лучшие прогнозы на спорт сегодня http://prognozy-na-sport-11.ru .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
1win bot ishlaydimi https://1win5508.ru
The 1win app is an innovative platform that offers a variety of betting options.
1win apk скачать https://1win-app.bet/ru/
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/249860602/detail.aspx
купить диплом в новороссийске купить диплом в новороссийске .
Удобнее всего заходить через доступ к кракен маркетплейсу, потому что он проверенный. На таких зеркалах меньше всего рисков нарваться на фейк. Пользователи ценят именно эту стабильность.
https://clickolov.ru/
купить диплом менеджера по туризму купить диплом менеджера по туризму .
купить диплом в элисте купить диплом в элисте .
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают
. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
Simply desire to say your article is as astounding. The clearness on your publish is simply nice and that i can assume you’re a professional in this subject. Fine along with your permission allow me to grasp your feed to stay updated with forthcoming post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please continue the gratifying work.
kra40cc вход
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя
Ən son versiya ilə soccer daha real görünür.
Soccer skills euro cup ilə bacarıqlarınızı artırın. Müxtəlif futbol oyunlarını kəşf etmək üçün soccer games bölməsini sınayın.
Bet365 soccer ilə idman mərclərinə qoşulun. Dream league soccer 2019 hələ də sevilən versiyalardandır. Soccer predictions futbol nəticələrini təxmin etməyə kömək edir.
Dream league soccer 2025 para və elmas hilesi ilə daha çox fürsət əldə edin. Fifa soccer mod apk team2earn futbolu daha real edir. Soccer live score ilə canlı nəticələri izləyin. World soccer champs apk 8.3.2 para hilesi ilə resurs artırın.
прогнозы на футбол сегодня прогнозы на футбол сегодня .
лучшие прогнозы на футбол http://www.prognozy-na-futbol-10.ru .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом в дербенте купить диплом в дербенте .
Надёжность KRAKEN держится на том, что адрес для анонимного входа кракен всегда в сети. Это даёт ощущение защищённости и стабильности. Люди ценят такую предсказуемость.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
кайт сафари Кайт Хургада: Кайт Хургада – это уникальное сочетание благоприятных погодных условий, красивых пейзажей и развитой инфраструктуры, делающее этот город одним из самых популярных мест для кайтсерфинга в мире. Стабильный ветер дует практически круглый год, обеспечивая отличные условия для катания на кайте. Теплая и прозрачная вода Красного моря создает комфортные условия для обучения и катания. Хургада предлагает широкий выбор кайт спотов, от песчаных пляжей с лагунами до открытых участков с волнами, подходящих для разных уровней подготовки. В городе есть множество кайт школ, предлагающих обучение, прокат оборудования и услуги ремонта. Кроме того, Хургада предоставляет широкий выбор развлечений и активностей, таких как дайвинг, сноркелинг, экскурсии в пустыню и посещение исторических мест. Кайт Хургада – это не просто место для кайтсерфинга, это целый мир приключений и удовольствий.
прогноз ру прогноз ру .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
Когда мы изучали творчество Панаса Мирного, мне нужно было подготовить материал для урока. На литературном портале нашёл пересказ и анализ его произведений, которые помогли мне понять их глубже. Учитель похвалил меня за глубокий анализ.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя
купить диплом товароведа купить диплом товароведа .
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
вывод из запоя
купить диплом техникума Киев http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
Soccer oyununda komandalar seçmək çox asandır.
Dream league soccer oyunu gənclər arasında çox məşhurdur. Əlavə məlumat üçün http://soccer.com.az/ səhifəsinə baxmaq olar.
Soccer champs mod apk ilə oyun daha maraqlı olur. Soccer ball mexanikası real futbol topuna çox yaxındır. Dream league soccer 2020 yenilənmiş qrafiklər ilə fərqlənir.
Soccer super star mod apk ilə ulduz olun. Soccer field dizaynı oyunda çox real görsənir. Livescore.com.tr live soccer scores azarkeşlər üçün əhəmiyyətlidir. Soccer star mod apk ilə daha çox imkan əldə edin.
Я заметил, что зеркало кракен сегодня открывается быстрее других адресов. Даже при нагрузке сайт остаётся доступным. Так сохраняется постоянный трафик без перебоев.
https://tex-stile.ru/novosti/6607-v-chem-osobennosti-oficialnogo-importa-iz-kitaya.html
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk020.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
купить диплом о высшем образовании реестр купить диплом о высшем образовании реестр .
Смотри, в отличие от временных сайтов, TOR адрес для кракен маркетплейса реально держится годами. Это редкость для даркнет-маркетов. Именно поэтому к площадке такое внимание.
новости легкой атлетики https://novosti-sporta-16.ru/ .
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр .
бесплатные прогнозы на спорт с высокой проходимостью бесплатные прогнозы на спорт с высокой проходимостью .
Je suis emoustille par MrPacho Casino, c’est un festin ou chaque tour deploie des parfums de victoire. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, integrant des live roulettes pour des tourbillons de suspense. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, activant des voies multiples pour une resolution veloutee. Les flux monetaires sont blindes par des epices crypto, bien qu’ des garnitures de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. Pour couronner le plat, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les chasseurs de casinos virtuels ! A souligner le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et appetissante, accroit l’envoutement dans le royaume du gout.
mrpacho bonus bez depozytu|
iOS üçün soccer yükləyib pulsuz oynayın.
Dream league soccer oyunu gənclər arasında çox məşhurdur.
Futbol tətbiqlərinin tam siyahısı üçün https://soccer.com.az/ saytını izləyin.
Globe soccer turnirləri ilə dünya futboluna yaxın olun. Soccer streams ilə matçları online izləyin. Bubble soccer dostlarla əyləncəli vaxt keçirməyə imkan verir.
Soccer game klassik futbol təcrübəsi təqdim edir. Soccer platform prediction nəticələri izləməyə kömək edir. World soccer champs apk son sürüm daha yaxşı işləyir. World soccer champs hile son sürüm oyunçuların seçimi olub.
J’eprouve une majeste infinie pour SlotsPalace Casino, il ordonne une lignee de recompenses royales. La galerie de jeux est un trone abondant de plus de 6 000 sceptres, proposant des crash pour des chutes de trone. Le service regne en continu 24/7, accessible par messager ou appel royal. Les retraits s’executent avec une grace remarquable, occasionnellement les edits d’offres pourraient s’etendre en opulence. En couronnant le regne, SlotsPalace Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les souverains pour les monarques de casinos virtuels ! De surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un decret, simplifie la traversee des halls ludiques.
slots palace casino erfahrungen|
Android üçün ən yaxşı soccer tətbiqini sınayın.
Opera soccer tətbiqi ilə xəbərlərə tez çatın.
Futbol tətbiqlərinin tam siyahısı üçün https://soccer.com.az/ saytını izləyin.
World soccer champs mod apk ilə əlavə imkanlar əldə edin. Soccer champs hile versiyaları əlavə üstünlüklər yaradır. Soccer predictions futbol nəticələrini təxmin etməyə kömək edir.
Opera sport soccer futbol xəbərləri üçün aktualdır. Soccer champs apk yükləmək çox asandır. Livescore.com.tr live soccer scores azarkeşlər üçün əhəmiyyətlidir. Soccer legends futbolun tarixi anlarını oyuna gətirir.
Основное преимущество — как попасть в кракен маркетплейс обновляется быстрее других источников. Люди не теряют времени на поиск, всё уже доступно. Это и делает сервис удобным.
Сломалась машина? автопомощь спб мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
купить диплом в крыму купить диплом в крыму .
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
купить диплом колледжа настоящий https://www.frei-diplom9.ru .
ставки прогнозы http://www.novosti-sporta-17.ru .
результаты матчей novosti-sporta-15.ru .
J’eprouve une energie surhumaine pour Super Casino, il deploie une campagne de gains extraordinaires. Le QG est un centre de diversite explosive, proposant des Aviator pour des vols stratospheriques. Le support client est un allie indefectible et omnipresent, accessible par alerte ou appel d’urgence. Les flux sont blindes par des boucliers crypto, bien que des gadgets gratuits supplementaires rechargent les unites. A la fin de cette mission, Super Casino se pose comme un phare pour les vigilantes pour les sentinelles des bases numeriques ! De surcroit le portail est une tour de controle visuelle imprenable, ce qui catapulte chaque mission a un niveau legendaire.
casino 20 super hot|
купить диплом во владивостоке купить диплом во владивостоке .
kupit-drova-v-setkah-noginsk.ru .
Website https://taya-auto.ru/figurnoe-katanie-polza-dlya-detej-i-vzroslyh/
uslugi-autsorsinga-buhgalterii-811.ru .
KRAKEN давно укрепил репутацию, а мобильная ссылка для входа кракен стал частью этой стабильности. Пользователи знают: через него можно безопасно зайти. И доверие к площадке только растёт.
Лучшая книга ziw
прогноз ру https://www.stavka-10.ru .
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
1вин как получить бонус 1вин как получить бонус
диплом автотранспортного техникума купить диплом автотранспортного техникума купить .
https://old-lekar.com/promyshlennoe-oborudovanie-i-stanki-pod-klyuch-kak-ne-zaputatsya-i-poluchit-rabochuyu-liniyu/
диплом техникума купить новосибирск диплом техникума купить новосибирск .
купить диплом в астрахани купить диплом в астрахани .
Лучшая книга ybm
Если вам или вашим близким требуется помощь при алкоголизме‚ важно знать‚ как обратиться к нарколога на дом в владимире. Вызов специалиста нарколога на дом предоставляет возможность получить экстренную помощь без потребности в посещении клиники. Это особенно актуально при лечении запоя‚ когда человек нуждается в медицинской помощи в срочном порядке. врач нарколог на дом Первыми действиями будет поиск услуг нарколога. Можно обратиться в специализированные клиники или воспользоваться онлайн-сервисами для вызова нарколога. Консультация нарколога содействует оценить состояние пациента и установить необходимое лечение зависимости.При вызове врача принципиально сообщить о признаках запоя‚ чтобы нарколог мог заранее подготовиться к оказанию помощи. Лечение алкоголизма на дому может включать очищение организма‚ медикаментозное лечение и психологическую поддержку. Анонимная помощь нарколога также доступна‚ что делает процесс более комфортным для пациента.В владимире есть многочисленные адреса наркологических клиник‚ где предоставляются получить дополнительные услуги и реабилитацию от алкоголя. Учтите‚ что медицинская помощь на дому может стать началом к восстановлению и улучшению качества жизни. Если вам нужна экстренная помощь нарколога‚ действуйте незамедлительно – здоровье важнее всего!}
В компании СтройСинтез мы заказали дом под ключ в Ленинградской области, и он получился именно таким, каким мы его представляли. Тщательно продуманная планировка, современный дизайн и качественная отделка сделали проект идеальным. Ознакомиться с другими вариантами можно тут – https://stroysyntez.com/
купить диплом в железногорске http://www.rudik-diplom15.ru .
Даже при давлении со стороны провайдеров, зеркало кракен сегодня продолжает работать. Это доказывает устойчивость площадки. Многие выбирают её именно за это.
кайт школа Кайт Хургада: Кайт Хургада – это синоним кайтсерфинг-рая. Этот египетский город привлекает кайтсерферов со всего мира своими идеальными условиями для катания: стабильным ветром, теплой водой и песчаными пляжами. В Хургаде расположены десятки кайт школ и станций, предлагающих обучение на любом уровне подготовки, прокат оборудования и услуги по ремонту. На пляжах Хургады всегда царит атмосфера праздника и позитива. Здесь можно встретить кайтсерферов разных национальностей, обменяться опытом и просто хорошо провести время. Вечером, после катания, можно прогуляться по набережной, посетить местные магазины и рестораны или насладиться шоу в одном из отелей. Кайт Хургада – это не просто место для кайтсерфинга, это стиль жизни, полный приключений, свободы и новых знакомств.
drova-kolotye-bereza-spb.ru .
Капельница для лечения запоя – это проверенный подход, который активно используется наркологами для детоксикации организма. Специалист по зависимостям на дому из клиники предлагает анонимное лечение, обеспечивая абсолютную анонимность для клиента. Посещение врача на дому позволяет быстро ощутить медицинскую помощь и восстановление организма, что особенно значимо для страдающих от запоя. Нарколог на дом клиника Во время терапии применяются вливания, которые снимают симптомы отмены и гарантируют безопасность терапии. Профессиональная поддержка нарколога на дом предоставляет возможность пройти терапию зависимости в комфортной обстановке, что минимизирует стресс от лечения. Это – эффективное восстановление от запоя, которое предоставляет возможность начать новую жизнь без алкоголя.
Лучшая книга wla
Вызов нарколога — это важный шаг для тех, кто сталкивается с трудностями с зависимостями . Служба наркологической помощи предоставляет экстренную наркологическую помощь и советы нарколога, что крайне важно в кризисных ситуациях . Признаки зависимости от наркотиков могут проявляться по-разному , и важно знать, когда необходима медицинская помощь при алкоголизме . Лечение алкоголизма и помощь при наркотической зависимости требуют профессионального подхода . Последствия алкоголизма могут быть катастрофическими, поэтому важно искать помощь для людей с зависимостями, включая реабилитацию зависимых . На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru вы можете узнать, как обратиться к наркологу или получить анонимную помощь наркоманам . Не стесняйтесь обращаться по телефону наркологической службы , чтобы получить нужную помощь и поддержку.
Алкогольный запой – это опасное состояние‚ требующее неотложного вмешательства и помощи. Народные средства часто воспринимаются как действующие методы лечения‚ но вокруг них существует множество мифов. Например‚ многие думают‚ что лекарственные растения способны быстро снять симптомы запоя. Однако реальность таковы‚ что народные рецепты могут лишь помочь в восстановлении после запоя‚ но не вытеснить профессиональную реабилитацию от алкоголя. Существует несколько признанных методов‚ среди которых очищение организма и лечение алкоголизма. Психология зависимости играет ключевую роль в реабилитации. Важно понимать‚ что экстренный вывод из запоя требует комплексного подхода‚ включающего медикаментозное лечение и поддержку близких. Не стоит ограничиваться народные средства — это может привести к усугублению проблемы.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Для доступа через телефон тоже удобнее заходить по TOR адрес для кракен маркетплейса. Так вход остаётся простым и безопасным. А блокировки не мешают пользоваться маркетом.
лечение тревожных расстройств в Москве Лечение тревожных расстройств в Москве — это доступный и многогранный процесс, предлагающий широкий спектр медицинских услуг и подходов для помощи людям, страдающим от тревоги. В Москве существует множество квалифицированных врачей-психиатров, психотерапевтов и психологов, специализирующихся на лечении тревожных расстройств. Пациенты могут обратиться в государственные и частные клиники, психотерапевтические центры и кабинеты для получения консультации, диагностики и разработки индивидуального плана лечения. Методы лечения тревожных расстройств в Москве включают психотерапию, медикаментозное лечение и комбинацию этих подходов. Психотерапия, особенно когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), широко используется для изменения негативных мыслительных шаблонов и развития навыков преодоления тревоги. Медикаментозное лечение может включать применение антидепрессантов, анксиолитиков и других препаратов, которые назначаются врачом в зависимости от типа и тяжести тревожного расстройства. Кроме того, в Москве доступны различные группы поддержки и ресурсы для людей, страдающих от тревоги, а также методы релаксации и самопомощи, такие как медитация и йога. Важно обратиться за помощью к квалифицированному специалисту в Москве, чтобы получить наилучший план лечения и улучшить качество жизни.
кинешемский педагогический колледж диплом 1998 года купить https://frei-diplom11.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают рабочее зеркало сайта кракен. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
В СтройСинтез мы заказали дом под ключ и остались довольны. Нам предложили проект кирпичного дома с мансардой и просторной кухней-гостиной. Все работы выполнены аккуратно, сроки выдержаны. Получился уютный дом, который полностью соответствует нашим ожиданиям – https://stroysyntez.com/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
Официальные как попасть на кракен помогают обходить блокировки, когда основной домен недоступен. Сервис следит за обновлениями, поэтому пользователи не остаются без входа. Это повышает лояльность.
Mobil soccer yükləyərək futbol əyləncəsini hər yerdə yaşayın.
Soccer 365 ilə futbol xəbərlərindən xəbərdar olun. Real futbol təcrübəsi üçün ən doğru seçim http://soccer.com.az/ linkidir.
World soccer champs mod apk ilə əlavə imkanlar əldə edin. Dream league soccer 2019 hələ də sevilən versiyalardandır. Soccer predictions futbol nəticələrini təxmin etməyə kömək edir.
Pro direct soccer məhsulları keyfiyyətli seçimdir. Dream league soccer 2016 köhnə versiya sevənlər üçün uyğundur. Spbo live score soccer ilə hər dəqiqə nəticələri görün. World soccer futbol sevərlərin əvəzolunmaz seçimidir.
1win tennis tikish 1win tennis tikish
СтройСинтез построил для нас просторный дом под ключ из кирпича. Мы остановились на проекте с тремя этажами и гаражом, и компания справилась отлично. Все работы выполнялись поэтапно и качественно, дом получился комфортным и надёжным, https://stroysyntez.com/
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают кракен ссылка рабочего зеркала. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
кайт школа Кайт школа в Хургаде: Кайт школа в Хургаде – это ваш шанс погрузиться в мир кайтсерфинга в одном из самых популярных мест для этого вида спорта. Хургада предлагает идеальные условия для обучения: стабильный ветер, теплая вода и песчаные пляжи. В кайт школах Хургады работают опытные инструкторы, говорящие на разных языках, которые помогут вам освоить азы кайтсерфинга и безопасно научиться кататься на кайте. Школы обычно расположены на территории отелей или имеют свой собственный пляж, что обеспечивает удобство и комфорт во время обучения. Кроме обучения, кайт школы предлагают прокат оборудования, услуги по ремонту и хранению. В перерывах между занятиями вы можете отдохнуть на пляже, искупаться в море или насладиться блюдами местной кухни в одном из многочисленных ресторанов. Кайт школа в Хургаде – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет совместить активный отдых с приятным времяпровождением на берегу Красного моря.
This article provides clear idea for the new users of blogging, that truly
how to do blogging.
купить диплом колледжа в нижнем новгороде купить диплом колледжа в нижнем новгороде .
Детоксикация алкоголя в владимире , ключевой момент в борьбе с зависимостью от алкоголя. Клиники наркологии в владимире предлагают различные курсы детоксикации, которые помогают преодолеть алкогольную зависимость. Выездной нарколог может оказать помощь при алкогольной зависимости на дому что является удобным решением для многих пациентов. нарколог на дом Квалифицированные наркологи проводят терапию запойного синдрома и предоставляют всю необходимую медицинскую поддержку при алкоголизме . Консультация нарколога позволяет разработать персонализированный план терапии. Важно также учитывать психологическую поддержку при детоксе , что способствует восстановлению после алкоголя и эффективной реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости;
Для новичков проще всего начать с ссылка на зеркало кракен. Он ведёт на официальный ресурс, где всё открывается без ошибок. Так снижаются риски нарваться на фейк.
точные прогнозы на хоккей http://prognozy-na-khokkej5.ru/ .
прочистка труб канализации прочистка труб канализации .
оборудование для медицины http://www.xn—–6kcdfldbfd2aga1bqjlbbb4b4d7d1fzd.xn--p1ai/ .
ставки на хоккей на сегодня https://prognozy-na-khokkej4.ru .
купить диплом переводчика купить диплом переводчика .
Восстановление организма после запоя в владимире – важный этап на пути к нормализации состояния и улучшению жизни. Квалифицированный нарколог на дому из клиники предлагает детоксикациюкоторая включает лечение запоя и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме. Лечебные программы зачастую включают психотерапию и помощь близких. Процесс восстановления после запоя начинается с первичной консультации с наркологом, что способствует эффективному очищению организма и улучшению качества жизни. Нарколог на дом клиника
дрова камерной сушки купить .
купить диплом в курске купить диплом в курске .
купить диплом архитектора купить диплом архитектора .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
vedenie-buhgalterii-autsorsing-811.ru .
kupit-drova-kolotye-49651.ru .
Це не просто казки. Це емоційна підтримка в історіях для дітей.
Официальные как зайти через TOR кракен помогают обходить блокировки, когда основной домен недоступен. Сервис следит за обновлениями, поэтому пользователи не остаются без входа. Это повышает лояльность.
Капельницы от запоя на дому в владимире: быстрое и безопасное решение Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезная ситуация, требующая обращения к специалистам. Круглосуточный нарколог в владимире предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Это эффективный способ для быстрого снятия абстиненции и восстановления после запоя.При алкогольной зависимости необходимо обеспечить не только временное облегчение, но и качественную медицинскую поддержку. Капельница помогает быстро снять похмелье, улучшить общее состояние и предотвратить осложнения. Вызов капельницы на дом — это комфортный вариант для тех, кто предпочитает избегать госпитализации и хочет получать помощь в привычной обстановке.Круглосуточная помощь нарколога позволяет обеспечить детоксикацию алкоголика в любое время. Помните, что лечение запоя на дому включает в себя как физическое, так и психологическое восстановление. Реабилитация от алкоголизма — это долгий процесс, требующий комплексного и внимательного подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкоголизма, не откладывайте обращение к специалистам. Вы можете рассчитывать на круглосуточные услуги нарколога в владимире и получить необходимую профессиональную поддержку.
В городе владимир доступна услуга по вызову нарколога на дом, доступная 24/7, обеспечивающая профессиональную помощь в области наркологии для пациентов с зависимостями. Если вам или вашим близким требуется лечение алкоголизма, опытный нарколог окажет медицинскую помощь на дому, сохраняя полную конфиденциальность. вызов нарколога владимир Если вас интересует действенный способ, обращение к наркологу в владимире станет первым шагом к новой жизни.
Ранее мы работали с другой студией, но продвижение шло очень медленно. В середине года решили сменить подрядчика и выбрали Mihaylov Digital. Здесь работа выстроена грамотно, с понятными отчётами и результатами. Сайт стал заметнее в поиске, и мы довольны результатом https://mihaylov.digital/
диплом о среднем образовании купить легально http://frei-diplom5.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле .
Website https://taya-auto.ru/figurnoe-katanie-polza-dlya-detej-i-vzroslyh/
Практика ремонта https://stroimsami.online и стройки без воды: пошаговые инструкции, сметные калькуляторы, выбор материалов, схемы, чек-листы, контроль качества и приёмка работ. Реальные кейсы, фото «до/после», советы мастеров и типичные ошибки — экономьте время и бюджет.
Зависимость от алкоголя — это острая проблема, которая затрагивает не только зависимого, но и его близких. Вызов нарколога на дом в владимире может стать первым шагом к борьбе с алкоголизмом. Обсуждение с наркологом поможет определить уровень зависимости и предложить лечение алкоголизма, включая психотерапию при алкоголизме.Проблемы в семье из-за алкоголя часто влекут к разладам в семье. Помощь со стороны семьи играет важную роль в процессе восстановления. Семье необходимо знать, как поддержать, и что можно сделать для помощи зависимому. Реабилитация алкоголиков включает в себя медицинские методы, но и социальную поддержку. Профилактика алкоголизма начинается с осознания проблемы и желания изменить ситуацию. Восстановление отношений — это долгий процесс, который требует усилий всей семьи. вызов нарколога на дом владимир Вызов врача на дом дает возможность воспользоваться помощью в привычной обстановке, что способствует лучшему восприятию информации и снижает уровень стресса. Помощь семье и согласие на лечение — это основные этапы на пути к выздоровлению.
Для новичков проще всего начать с вход через онион кракен. Он ведёт на официальный ресурс, где всё открывается без ошибок. Так снижаются риски нарваться на фейк.
купить диплом архитектора купить диплом архитектора .
drova-deshevo-spb.ru .
купить диплом в чебоксарах https://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в чебоксарах .
vedenie-buhgalterii-autsorsing-811.ru .
заказать дрова с доставкой .
Капельная терапия при запое – это эффективный способ, применяемый специалистами в области наркологии для помощи в лечении алкоголизма и симптомов абстиненции. Нарколог на дом срочно в владимире обеспечивает медицинские услуги на дому, гарантируя комфорт и безопасность пациента. Показания к капельнице охватывают интенсивное похмелье, дегидратацию и необходимость детоксикации организма. Нарколог на дом срочно владимир В то же время имеются определенные противопоказания: аллергические реакции на состав, проблемы с сердечно-сосудистой системой и определенные хронические заболевания. Капельная терапия помогает восстановлению после запоя, повышает общее состояние здоровья и помогает организму восстановиться. Компетентная поддержка нарколога крайне важна для адекватного подбора терапии и снижения возможных рисков. Своевременная помощь при запое должна быть своевременной, чтобы предотвратить серьезные последствия.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/514992745/detail.aspx
Каждый раз, когда меняется адрес, рабочее зеркало сайта кракен сразу даёт рабочую ссылку. Это упрощает жизнь пользователям. Они знают, что маркет не исчезнет.
Использование onion-ссылки открывает путь в KR@KEN маркет https://2kn.to, и это защищает от фейков.
Пользователи пишут, что KRAKEN через биржа kraken официальный сайт работает быстрее, чем большинство других ресурсов.
Для тех, кто собирается заключить контракт на СВО, собрана вся важная информация. https://vc.ru/social/1471244-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-bryanskoi-oblasti-kontrakty-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Приведены советы по выбору части и району службы для карьеры.
Домашнее лечение алкоголизма становится актуальным. Основные этапы включают очистки организма от алкоголя на дому и помощи при запое. С чего начать лечение? Важно наладить взаимодействие с роднымикоторые могут поддержать в лечении.Психотерапия и традиционные средства могут стать хорошим дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы для трезвости и рекомендации по отказу от алкоголя помогут установить верное мышление. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru Важно помнить о реабилитации дома, которая включает психологическую помощь и профилактику рецидива. Что делать, чтобы бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с определения конкретной цели и поиска источника мотивации. Главное – это желание изменить свою жизнь и поддержка близких.
купить диплом в глазове купить диплом в глазове .
купить диплом в одессе недорого https://www.educ-ua7.ru .
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Капельница от запоя в владимире — эффективный метод восстановления здоровья, который способствует быстрому выздоровлению. При алкогольной зависимости появляются неприятные симптомы, такие как головные боли, тошнота и психоэмоциональные расстройства. В клиниках по лечению зависимостей в владимире оказывают квалифицированную помощь, включая проведение инфузий для очищения организма. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru Лечение алкоголизма включает не только капельницы, но и психологическую поддержку во время отказа от алкоголя. Обращение к наркологу позволяет разработать индивидуальную стратегию к восстановлению после запоя. Антидепрессанты и уколы от запоя также могут быть назначены для ускорения процесса восстановления. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru предлагает профессиональное лечение алкогольной зависимости, где опытные врачи гарантируют профессиональный подход к вашему лечению. Не откладывайте на завтра, начните путь к здоровой жизни уже сегодня!
Je suis absolument conquis par Betsson Casino, il offre une aventure pleine de frissons. La bibliotheque de jeux est phenomenale, incluant des slots de derniere generation comme Starburst. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que les offres comme le bonus de bienvenue de 100 % jusqu’a 100 € pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Betsson Casino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et intuitive avec un theme orange vif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme a l’experience.
aek betsson|
Ich finde absolut majestatisch King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett strahlen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein koniglicher Befehl, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glanzvoll sind. Am Ende ist King Billy Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Palast glitzert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, einen Hauch von Majestat ins Casino bringt.
king billy casino bonus code no deposit|
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
Нужно было продвинуть интернет-магазин в Google, потому что основная аудитория там. SEO специалисты сделали комплексную оптимизацию карточек товаров, добавили новые тексты и доработали структуру. В результате сайт вырос в поиске, и количество заказов увеличилось вдвое. Работа выполнена профессионально и без лишних обещаний – https://mihaylov.digital/
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
купить диплом в липецке купить диплом в липецке .
Официальные ссылка на официальный ресурс кракен помогают обходить блокировки, когда основной домен недоступен. Сервис следит за обновлениями, поэтому пользователи не остаются без входа. Это повышает лояльность.
купить диплом проведенный москва http://www.frei-diplom1.ru .
диплом о среднем образовании купить легально http://frei-diplom3.ru .
поставщик медицинского оборудования xn—-7sbcejdfbbzea0axlidbbn0a0b5a8f.xn--p1ai .
медицинское оборудование для больниц http://www.medtehnika-msk.ru .
прогнозы на футбол сегодня прогнозы на футбол сегодня .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
PNGtoWebPHero.com is a utility for encoding PNG (Portable Network Graphics) images into the WebP format. The tool provides developers with control over the encoding process to optimize web assets. Users can select the compression mode – either lossless, which uses advanced techniques to reduce file size without data loss, or lossy, which uses predictive coding to achieve much greater file size reduction. For lossy encoding, a quality factor can be specified to manage the trade-off between file size and visual fidelity. The service correctly handles the PNG alpha channel, preserving transparency in the final WebP output. All processing is server-side, and data is purged after conversion.
pngtowebphero
Промокод 1xBet на сегодня можно получить прямо на сайте букмекерской компании. Сделать это станет возможным благодаря переходу по рабочей ссылке, содержащей промокод. Подобного рода бонусы могут использовать и постоянные и новые клиенты конторы. Благодаря проведению таких акций интерес игроков к ставкам остаётся высоким. Содержание. промокод на casino. Как получить и что дает промокод в 1xBet? Где вводить промокод в 1xBet? Рабочие промокоды 1xBet на сегодня. Действующие промокоды 1xBet на сегодня. Узнайте как ввести промо код 1хБет при регистрации и получить 32500 рублей на бесплатную ставку. Как активировать и использовать промокод на 1xBet. Список рабочих бонус кодов.
Маркетплейс держится на плаву благодаря правильной организации зеркал и актуальных ссылок https://2kn.to.
Стабильность KR@KEN https://2kn.to объясняется просто: всегда есть рабочие адреса, которые позволяют не терять доступ.
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают рабочая ссылка кракен сегодня. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
Изготовление и поставка воздуховодов – пройдите по ссылке воздуховоды вентиляционных систем
Друзі порадили компанію мрій для будівництва нашого нового будинку, і я в захваті від їхніх відгуків. Тепер не можу дочекатися, щоб розпочати співпрацю!
Капельница при алкогольной зависимости — это важная медицинская помощь при запоя. При наблюдении симптомов запоя, таких как вы увидите признаки, такие как интенсивная жажда, боли в голове, недомогание и общая слабость, вызов нарколога на дом в владимире может стать оптимальным выходом. Специалист осуществит медицинскую помощь и назначит капельницу, которая помогает восстановлению организма. вызвать нарколога на дом владимир Преодоление алкогольной зависимости предполагает вывод пациента из состояния запоя, что позволяет значительному повышению здоровья после алкогольного запоя. Капельница содействует устранить обезвоживание, компенсировать дефицит электролитов и оптимизировать общее состояние пациента. При необходимости можно провести лечение на дому, что обеспечивает комфорт и безопасность.владимир наркология предлагает качественные услуги по реабилитации от алкоголя, что позволяет справиться с зависимостью результативно. Результаты от капельницы заметны быстро: пациенты замечают повышение жизненного тонуса и возвращение энергии. Не стоит откладывать обращение за помощью, здоровье важно сохранить!
купить свидетельство о разводе купить свидетельство о разводе .
AVIFtoPNGHero.com is a free converter for turning next-generation AVIF images into high-quality PNG files. As the web adopts the efficient AVIF format, this tool provides a simple way to ensure your images are viewable on older browsers and systems that lack support. The conversion process preserves crucial details, including transparency, making it ideal for web graphics and icons. Simply drag and drop your AVIF files, convert entire batches at once, and download your compatible PNGs in seconds. The service is entirely browser-based, requires no installation, and automatically deletes all files to guarantee your privacy.
aviftopnghero
В владимире доступна помощь от алкоголизма в клиниках‚ предлагающих детоксикационный курс и лечение зависимости. Программы лечения включают кодирование от алкоголя и медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме. Важно также обеспечить психологическую поддержку и участвовать в группах поддержки, таких как группы анонимных алкоголиков. Восстановление после запоя требует комплексного подхода: консультации нарколога помогут создать персонализированный план. Важно помнить о профилактике рецидива и придерживайтесь рекомендаций по отказу от алкоголя. Дополнительную информацию можно найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir022.ru;
купить диплом техникума в чебоксарах купить диплом техникума в чебоксарах .
KRAKEN давно укрепил репутацию, а ссылка на кракен маркет стал частью этой стабильности. Пользователи знают: через него можно безопасно зайти. И доверие к площадке только растёт.
диплом купить в реестре диплом купить в реестре .
Медикаменты от алкоголизма могут включать препараты для лечения зависимости‚ которые облегчают симптомы. Круглосуточная помощь и контроль при выводе из запоя обеспечивают защищенность пациента. Забота близких также важна для успешного восстановления после запойного синдрома. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Советы по выходу из запоя могут включать частые консультации с врачом и соблюдение режима. Рекомендуется обратиться за помощью‚ чтобы предотвратить возвращение к алкоголю и обеспечить качественное лечение.
экспресс на футбол сегодня https://prognozy-na-futbol-9.ru .
https://skrillcasinos.org/
v1av8 – The brand feels experimental, possibly gearing for a niche-purpose launch.
Даже новые пользователи https://2kn.to замечают, что вход всегда открыт, а блокировки обходятся автоматически.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
кракен маркет плейс открывает сайт так, будто блокировок и не существует — вход в KR@KEN идёт без ошибок.
Hello very nice site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionally? I’m glad to find so many useful information right here in the publish, we’d like work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
на сайте
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Хочешь сдать акб? сдать аккумулятор честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Нужен аккумулятор? купить аккумулятор с доставкой в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
где купить диплом техникума в ижевске где купить диплом техникума в ижевске .
Детоксикация при запое в владимире: услуги и техники Запой – это серьёзная проблема, которая требует профессионального вмешательства. В владимире можно найти услуги по детоксикации в различных клиниках, где предлагают услуги по экстренному выводу из запоя. Способы вывода из запоя состоят из медикаментозной терапии, инфузионные процедуры и психотерапию. Цены на детоксикацию варьируются в зависимости от выбранного метода и уровня комфорта в клинике. Важно понимать, что лечение запоя – это не только физическая детоксикация, но и важная психологическая поддержка зависимых, что способствует восстановлению здоровья и предупреждению рецидивов. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир Реабилитация после запоя включает в себя поддержку специалистов, что помогает избежать возврата к алкоголизму. Если вы или кто-то из ваших близких столкнулся с данной проблемой, не откладывайте обращение за медицинской помощью.
Мы заказали кухонный гарнитур в компании Кухни в Дом и остались очень довольны результатом. Замерщик приехал быстро, дизайнер сделал проект с учётом всех наших пожеланий, а сборка прошла идеально. Теперь у нас современная кухня с встраиваемой техникой, пользоваться которой одно удовольствие https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/514992745/detail.aspx
купить диплом в екатеринбурге купить диплом в екатеринбурге .
Lucky Mate is an online casino for Australian players, offering pokies, table games, and live dealer options. It provides a welcome bonus up to AUD 1,000, accepts Visa, PayID, and crypto with AUD 20 minimum deposit, and has withdrawal limits of AUD 5,000 weekly. Licensed, it promotes safe play: Lucky Mate
kupit-drova-kolotye-49651.ru .
ведение бухгалтерии аутсорсинг .
Если нужен личный кабинет, мобильная ссылка для входа кракен решает проблему. Он сразу переводит на рабочую версию без ошибок. Это экономит время и нервы.
купить свидетельство о заключении брака купить свидетельство о заключении брака .
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
Профилактика алкоголизма — существенная проблема, которая требует значительных усилий. Врач нарколог на дом способен оказать необходимую помощь, предоставляя консультации и медицинское вмешательство. Симптомы алкоголизма включают регулярном употреблении спиртного и изменениях в психоэмоциональном состоянии. Психотерапевтическая поддержка и коллективные занятия являются важными элементами в борьбе с зависимостями. Чтобы предотвратить запойные состояния, важно следовать нескольким советам по отказу от алкоголя. Поддержка семьи и близких способствует успешной реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости. Профилактические меры, такие как самопомощь при алкоголизме и участие в социальных программах, способствуют социальной адаптации и укрепляют мотивацию к трезвому образу жизни.
Informative article, totally what I wanted to find.
Капельница от запоя и детоксикация – ключевые подходы в лечении алкогольной зависимости. В владимире услуги по избавлению от запоя часто включают капельницы, которые способствуют быстро вывести токсины из организма. Капельница включает препараты для восстановления водно-электролитного баланса и устранения симптомов абстиненции, что поддерживает терапию запоя. лечение запоя владимир Детоксикация же является многогранным процессом, включающим не только физическое очищение, но и психологическую помощь пациентов. В центрах по лечению алкоголизма в владимире используются оба метода: капельницы для острого этапа и программы реабилитации после запоя. Это способствует в избавлении от зависимости и восстановлении здоровья. Помните, что профессиональная помощь в этом аспекте крайне важна для эффективного лечения.
Детоксикация от алкоголя — важный этап в процессе борьбы с зависимостью от алкоголя, направленный на очищение организма. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть тяжелыми и включают в себя тревогу, потливость и дрожь. Методы детокса варьируются от медицинской помощи до самостоятельных программ восстановления. Возвращение к трезвости требует поддержки близких и понимания психологии зависимости. Здоровье печени значительно пострадает от злоупотребления алкогольными напитками. Альтернативы алкоголю, такие как некрепкие напитки, помогают избежать вреда и возврату к здоровью. Узнайте больше на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir021.ru.
تتيح هذه المنصة مجموعة واسعة من الألعاب التي تلبي اهتمامات الجميع.
888starz app https://888starz-egypts.com/apk/
Основное преимущество — кракен вход мобильный обновляется быстрее других источников. Люди не теряют времени на поиск, всё уже доступно. Это и делает сервис удобным.
Пользователи отмечают, что kraken зеркало даркнет всегда обновляется, и вход в KR@KEN маркет открыт без задержек.
Когда люди теряют рабочий доступ, кракен маркет рабочее зеркало остаётся надёжным способом попасть в KR@KEN, и это подтверждается годами стабильности.
как купить диплом колледжа http://www.frei-diplom8.ru .
кто нибудь работает медсестрой по купленному диплому https://frei-diplom13.ru/ .
Нужен надежный акб? купить аккумулятор для авто AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
Решили служить по контракту? Узнайте, как правильно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/services/1734309-svarshik-vakansii-i-kontrakt-na-svo-v-rossii-2025 Теперь у вас есть все сведения, чтобы уверенно подписать контракт на СВО.
Если смотришь на отзывы, почти все упоминают рабочий вход в личный кабинет кракен. Люди реально пользуются и отмечают удобство. Значит, система работает как задумано.
Для розвитку емоційного інтелекту дітей казки незамінні! Читайте більше про їх користь.
где купить диплом где купить диплом .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk021.ru
лечение запоя
скачат мелбет казино скачат мелбет казино .
заказать кухню по индивидуальным размерам в спб https://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru .
кухня на заказ спб от производителя недорого https://kuhni-spb-3.ru/ .
кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге kuhni-spb-1.ru .
10 minimum deposit online rain rock casino open usa, gambling revenue canada and usa online casinos for
real money, or new zealandn poker table
купить диплом в заречном купить диплом в заречном .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
Эффективная капельница для снятия запоя на дому в владимире Алкогольная зависимость — серьезная проблема, требующая квалифицированной помощи. Круглосуточный нарколог в владимире предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Такой подход позволяет быстро облегчить состояние и помочь в восстановлении после запоя.Важно не только облегчить симптомы, но и предоставить полноценную медицинскую помощь при запое. С помощью капельницы можно быстро устранить похмелье, улучшить здоровье и избежать осложнений. Заказ капельницы на дому — это удобный способ для людей, желающих избежать стационарного лечения и получить помощь в привычной обстановке.Круглосуточная помощь нарколога позволяет обеспечить детоксикацию алкоголика в любое время. Нельзя забывать, что лечение запоя подразумевает не только физическое восстановление, но и необходимую психологическую помощь. Реабилитация от алкоголя — длительный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкоголизма, не откладывайте обращение к специалистам. Услуги нарколога в владимире доступны круглосуточно, и каждый может рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку.
Mein Mann und ich nehmen beide https://docs.brdocsdigitais.com/index.php/User:CiaraRenwick09, und wir sind beide sehr zufrieden. Es hilft uns, unsere Gelenkprobleme besser zu bewältigen.
Значение поддержки семьи при борьбе с алкоголизмом Алкоголизм — это не только неприятность зависимогоно и его семьи. В владимире вызов нарколога может стать первым этапом к лечению зависимости. Семейная поддержка играет решающую роль в процессе реабилитации. Близкие могут помочь, предоставляя эмоциональную поддержку и создавая атмосферу понимания. В кризисной ситуации важно искать за профессиональной помощью. Консультация специалиста поможет определить правильный путь к терапии алкоголизма. Психотерапия также может стать существенным инструментом для восстановления. вызов нарколога владимир Поддержка со стороны общества семьи необходима на всех этапах лечения, от первой встречи с наркологом до дальнейшей реабилитации. Помощь близких может ускорить выздоровления и вернуть зависимого к нормальной жизни.
66se – Navigation is smooth and responsive.
Услуга прокапки в владимире — это серьезный вопрос‚ требующая профессионального подхода. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru вы можете найти услуги по водоснабжению‚ включая монтаж и ремонт различных систем. Наша команда сантехников обеспечивает высококлассное исполнение и оперативную диагностику. Мы понимаем‚ что непредвиденные ситуации могут возникнуть в любое время‚ поэтому готовы предложить акционные предложения. Отзывы клиентов свидетельствуют о надежности и профессионализме наших специалистов. Ремонт и установка сантехники — это то, что мы делаем лучше всего‚ и мы гарантируем высокое качество выполнения всех работ.
tstyhj – Very straightforward and easy-to-use site, I enjoyed checking it.
Купон 1xBet на сегодня предлагает пользователям бонус при регистрации в размере 100% на сумму до 130$. Чтобы активировать акцию, необходимо пройти регистрацию в букмекерской конторе, пополнить счет и активировать предложение. После этого подарок будет добавлен на игровой счет.
Используя промокод, вы повышаете вероятность выигрыша. Однако, чтобы вывести деньги, нужно соблюдать условия отыгрыша, идентичные стандартным условиям. Подробнее смотрите здесь ?? промокод 1xBet
На нашем сайте доступен уникальный бонусный код, который подарит преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы его активировать, понадобится зарегистрироваться и пройти верификацию. После этого вы получите подарок при пополнении счета.Дополнительно можно пригласить друга, чтобы увеличить вознаграждение.
Очищение организма от алкоголя в владимире, важный этап в лечении алкоголизма . Наркологические клиники в владимире предлагают разнообразные программы детоксикации , которые помогают преодолеть алкогольную зависимость. Нарколог на дому может предоставить поддержку при алкогольной зависимости на дому что удобно для пациентов . нарколог на дом Лучшие врачи-наркологи проводят терапию запойного синдрома и предоставляют всю необходимую медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной зависимости. Обсуждение с наркологом позволяет определить индивидуальный план лечения . Не менее важна психологическая поддержка в процессе детоксикации, что способствует восстановлению после алкоголя и эффективной реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости;
Детоксикация при алкогольной зависимости – это важный этап в процессе борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью‚ который помогает справиться с последствиями отмены алкоголя и восстановить организм после запоя. При наличии алкогольной зависимости‚ детоксикация становится неизбежной для выведения токсинов из организма. Процедура включает в себя введение капельниц‚ которые предоставляют медицинскую помощь и наполняют организм необходимыми веществами. Лечение алкоголизма включает не только прокапывание‚ но и реабилитацию. Забота родных играет ключевую роль в успешном лечении. Последствия алкоголя могут быть серьезными‚ но с адекватной терапией и опорой близких возможно выздоровление от алкогольной зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir020.ru вы можете найти информацию о способах борьбы с алкоголизмом‚ включая прокапывание‚ которые помогут вам или вашим родным на пути к оздоровлению.
Официальные войти в кракен через TOR помогают обходить блокировки, когда основной домен недоступен. Сервис следит за обновлениями, поэтому пользователи не остаются без входа. Это повышает лояльность.
поставщик медоборудования https://xn—-7sbcejdfbbzea0axlidbbn0a0b5a8f.xn--p1ai/ .
Для тех, кто пользуется TOR, проверенная ссылка кракен становится лучшим решением. Через него вход остаётся анонимным, а подключение не прерывается. Такой способ давно считается самым надёжным.
купить диплом в саранске купить диплом в саранске .
купить диплом в камышине купить диплом в камышине .
Поддержка психолога при выходе из запоя в владимире: как преодолеть абстиненцию Во время абстиненции пациент часто испытывает физическими и психологическими страданиями. В таких случаях помощь психолога и кризисная помощь могут значительно облегчить состояние. Центры психотерапии в владимире предлагают различные программы восстановления и методы борьбы с зависимостями, что помогает справиться с трудностями. вывод из запоя цена Советы по выходу из запоя включают использование психологической помощи и программы реабилитации наркозависимых, что значительно увеличивает вероятность успешного выздоровления. Важно помнить, что путь к трезвости требует времени, терпения и поддержки.
Кадровые работы с нуля .
Для желающих служить Родине мы подготовили разбор, где можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1552679-kak-pravilno-zaklyuchit-kontrakt-na-svo-s-dobrovolcem-v-rossii-2025 Поясняются отличия контрактной службы от срочной и плюсы контракта.
Получение лицензии на медицинскую деятельность прошло быстро и удобно, специалисты центра сопровождали весь процесс, проверяли документы и консультировали по нюансам https://licenz.pro/
Аренда мебели для свадьбы Оформите романтическое торжество с стильной мебелью, которая подчеркнет атмосферу праздника.
купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр .
дрова колотые 5 кубов цена .
Сохранённый адрес https://2kn.to помогает зайти в KR@KEN без риска нарваться на фейковый сайт.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом с занесением в реестр москва .
Hope you don’t mind a small digression — it’s about shopping wisely
Just while browsing health blogs I discovered a site called resource for wise buyers.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Clear, practical, no fluff.
Who else is picky about food quality?
Выход из запоя — это серьезный процесс‚ требующий комплексного подхода. В владимире имеется возможность экстренного вывода из запоя на дому с помощью квалифицированных специалистов. Преодоление алкогольной зависимости начинается с детоксикации организма‚ что помогает устранить физическую зависимость.Помощь нарколога включают в себя медицинскую помощь при запое‚ использование эффективных методов‚ таких как алкогольное кодирование и психотерапия. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в реабилитации после запоя. Поддержка семьи и друзей также необходима для успешной реабилитации и предотвращения повторного срыва. экстренный вывод из запоя При преодолении запойного состояния важно следовать нескольким советам: поддерживайте достаточное количество жидкости‚ правильно питайтесь и не забывайте о физической активности. Обращение за экстренной помощью и консультация к специалистам поможет быстро и безопасно выйти из запоя‚ вернуть физическое здоровье и качество жизни.
Способы детоксикации включают как медикаментытак и домашние средства. Важно помнить о поддержке семьи и друзей, которая играет важную роль в восстановлении после запоя. Кодирование от алкоголизма может помочь избежать рецидивы. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir021.ru Программа трезвости и профилактика рецидивов гарантируют стабильный переход к здоровому образу жизни. Лечение запоя и реабилитация – это многогранный путь, который требует времени и усилий.
Для будущих контрактников подготовлен обзор: где лучше подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1608266-kak-stat-dobrovolcem-kontrakt-na-svo-rossii-2025 Материал будет полезен тем, кто хочет заключить контракт на службу в армии РФ.
https://stolikus.ru Организация мероприятия станет легче с профессиональным подходом к выбору оборудования.
Надёжность KRAKEN держится на том, что вход кракен без блокировок всегда в сети. Это даёт ощущение защищённости и стабильности. Люди ценят такую предсказуемость.
Анонимная помощь при зависимостях — это важный шаг для людей, страдающих от зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru можно получить сведения о лечении зависимостей, поддержке и помощи. Лечение без раскрытия личности позволяет пациентам обращаться за помощью без опасений осуждения.Помощь нарколога включают детоксикацию, психологическое консультирование и кризисную интервенцию. Процесс реабилитации часто включает группы поддержки, что усиливает процесс восстановления. Предотвращение зависимостей также играет критически важную роль, обеспечивая постоянное благополучие. Профессиональные консультации помогут понять ситуацию и разработать стратегии выхода. Помощь для людей с зависимостями доступна и доступна, даже если они бояться открыться.
Владимирская наркологическая служба предлагает широкий спектр услуг для помощи людям с зависимостями. В этом городе работают специализированные реабилитационные центры‚ где предоставляется возможность анонимного лечения от наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Программа лечения алкоголизма включает в себя как медицинские‚ так и психотерапевтические подходы. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru Психологическая поддержка в владимире также играет важную роль в процессе выздоровления. Обратитесь к наркологу позволяет определить уникальные особенности пациента и составить персонализированный план лечения. Работа с родственниками и профилактика зависимостей – важная составляющая работы наркологической клиники. Реабилитация зависимых включает как терапевтические меры‚ так и социальное reintegration. Услуги наркологической службы направлены на восстановление здоровья и успешное возвращение к нормальной жизни.
Методы детоксикации в себя как медикаментозное лечениетак и домашние средства. Необходимо помнить о поддержке семьи и друзей, которая играет ключевую роль в восстановлении после запоя. Кодирование от алкоголизма может помочь предотвратить рецидивы. vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru Программа трезвости и профилактика рецидивов обеспечат стабильный переход к новой жизни без алкоголя. Лечение запоя и реабилитация – это многогранный путь, который требует времени и усилий.
усиление грунтов privetsochi.ru/blog/realty_sochi/93972.html .
Площадка https://2kn.to давно доказала, что умеет держать связь с пользователями даже при массовых блокировках.
Добрый вечер! Хотите провести выходные незабываемо? Мы с семьёй недавно воспользовались советами с раздела “Выходные в Украине” и отправились в Карпаты. Это было удивительное путешествие — горы, свежий воздух и невероятные виды! Особенно нам помогли рекомендации по местным кафе и отелям, которые идеально подходят для семейного отдыха. Если вы ищете идеи для коротких поездок, этот сайт станет вашим незаменимым помощником.
поставка медицинского оборудования http://xn—–6kcdfldbfd2aga1bqjlbbb4b4d7d1fzd.xn--p1ai/ .
приложение 1win http://1win5517.ru/
nhà cái uy tín
Алкогольная зависимость — серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального подхода. Услуги вывода из запоя в владимире помогают безопасно пройти детоксикацию и восстановится. Наркологические клиники предоставляют круглосуточную помощь и анонимное лечение, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность. вывод из запоя владимир
Получение лицензии «под ключ» оказалось удобным и прозрачным процессом с Журавлев Консалтинг Групп, специалисты обеспечили сопровождение и проверку всех документов https://licenz.pro/
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/466665547/detail.aspx
Дитячі казки на ніч важливі для здорового сну дітей.
Складчик приятно удивил огромным выбором инфопродуктов. Здесь есть всё: курсы, мастер-классы, книги, видеоуроки, программы, шаблоны и даже скрипты. Участвовала в складчине на курс по копирайтингу, и процесс оказался очень простым. Цена была символической, а качество материалов ничем не уступало оригиналу. Теперь активно использую этот сервис и всем советую: https://v27.skladchik.org/
Де можна знайти якісні Біографії? Знайшов чудовий ресурс: Біографії, рекомендую!
диплом о среднем образовании купить легально http://frei-diplom1.ru/ .
Je suis fou de Julius Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino triomphante. La selection du casino est une veritable legion de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme heroique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement imperial, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans embuches, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient glorieux. Dans l’ensemble, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
casino en ligne julius|
J’aime enormement le casino TonyBet, il est carrement un moment divertissant top. Les jeux sont varies, offrant des options de casino en direct. Le service client est super, disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont rapides, neanmoins j’aimerais plus de bonus. Pour tout dire, TonyBet c’est du solide pour les fans de jeux en ligne ! En bonus, le design est attractif, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet talletusbonus|
Мы заказали остекление лоджии в Окна в СПб. Мастера справились отлично, сделали утепление и отделку. Лоджия получилась уютной и красивой, теперь используем её как кабинет. Очень рады результату https://okna-v-spb.ru/
купить диплом в энгельсе http://www.rudik-diplom1.ru .
В случае необходимости раскопок на вашем участке в владимире, обратиться к профессионалам способно значительно облегчить процесс. Компания vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir023.ru предлагает разнообразные земляных работ, включая копку участка для возведения зданий или обустройства территории. Наши услуги обеспечивают высокое качество реализации услуг по подготовке участка, а также создание скважин для питьевой воды. Использование арендованной техники дает возможность нам оперативно проводить любые садовые работы, а наши квалифицированные сотрудники помогут вам с подбором подходящего грунта. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете не только гарантию надежности, но и профессионализм в выполнении всех задач. Обратитесь к нам, и мы поможем откопать все необходимое на вашем участке!
Услуга прокапки от запоя в владимире – это востребованная услуга, предоставляющая пациентам обратиться за помощью не выходя из дома. Выездной нарколог, работающий в области наркологии, поможет справиться с симптомами абстиненции и позаботится о комфорте пациента. врач нарколог на дом Стоимость капельниц могут колебаться в зависимости от выбранной клиники и сложности лечения. Например, цена лечения алкогольной зависимости может включать в себя капельницу другие антиалкогольные процедуры, а также реабилитацию пациентов с алкоголизмом. В владимире работают наркологические службы возможны как в стационарных учреждениях, так и в виде выездного обслуживания. Ориентировочная цена капельницы от запоя находится в диапазоне 2000-5000 рублей. При этом важно учитывать, что цена может изменяться в зависимости от препаратов и индивидуальных потребностей пациента. Клиника наркологии в владимире имеет разные варианты услуг, которые могут охватывать терапию запоя и реабилитационные меры. Обратившись за помощью к врачу наркологу на дом, вы сможете получить профессиональную помощь при алкоголизме и избежите необходимости оставаться в стационаре. Не забывайте, что быстрое обращение за помощью может значительно уточнить процесс восстановления.
LaLiga statistikası hər gün yenilənir. Ən çox xal toplayan komandanı buradan öyrən.
LaLiga canlı yayımını telefondan açmaq mümkündür. LaLiga logo png fayllarını tapmaq asandır.
Futbol xəbərlərini izləmək üçün bu linki yoxlayın — http://www.laliga.com.az.
Goal scorer LaLiga siyahısına baxmaq istəyirsiniz?.
LaLiga matçlar hansı kanalda yayımlanır?.
LaLiga teams haqqında maraqlı faktlar.
Ən çox titul qazanan LaLiga klubları hansılardır?.
Futbol azarkeşləri üçün LaLiga livescore bölməsi.
Лечение зависимостей на дому — это комфортный способ лечения зависимостей, который приобретает всё большую популярность. Услуги нарколога на дому предоставляют анонимность и комфорт, что является ключевым моментом для множества людей. Квалифицированные специалисты обеспечивают лечение с помощью медикаментов и поддержку психолога, что позволяет начать восстановление после зависимости в знакомой среде. Домашняя реабилитация включает в себя персонализированные реабилитационные программы, семейную терапию и консультации нарколога, что способствует более глубокому осознанию проблемы. Профилактика рецидивов играет важную роль в процессе лечения алкоголизма и наркотической зависимости. Уход за зависимыми на дому помогает формировать поддерживающую среду и уменьшить вероятность срывов. Сайт narkolog-tula022.ru предлагает разнообразные услуги, включая конфиденциальное лечение зависимостей, что позволяет пациентам получать необходимую помощь без лишних вопросов. Квалифицированный подход к лечению зависимостей на дому делает этот процесс доступнее и менее стрессовым для семьи и пациента.
платная психиатрическая клиника
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
ylu555.xyz – Overall it’s intriguing, I’ll revisit later to see what new content appears.
Imagine a co-working space where each desk is equipped with a time machine. How would this unique feature impact the productivity, creativity, and overall work environment of professionals in various fields, such as data science, academic research, and social media management?
Not exactly the subject here, but I ran into something cool
Just not long ago I found a site called this sport archive site.
It’s packed with mind-blowing achievements.
Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds?
Phelps’ 28 Olympic medals?
Bubka’s 35 world records?
It’s all there.
Anyone else into stuff like this?
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
психиатрическая помощь госпитализация
консультация психиатра платно
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
консультация психиатра на дому
слоты мелбет слоты мелбет .
вывод из запоя клиника http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-19.ru .
ended up checking different pages figured why not nothing special, sometimes even this helps. for context only: background as is.
оборудование для медицины https://xn—–6kcdfldbfd2aga1bqjlbbb4b4d7d1fzd.xn--p1ai .
мед колледж купить диплом мед колледж купить диплом .
Je kiffe a mort FatPirate, ca balance une vibe dechainee. Le choix de jeux est monumental, proposant des sessions live ultra-intenses. Le support est dispo 24/7, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments plus de tours gratos ca ferait plaiz. Pour resumer, FatPirate c’est du lourd a tester absolument pour les accros aux sensations fortes ! Bonus le design est style et accrocheur, donne envie de replonger direct.
fatpirate register|
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. Tem um tsunami de jogos de cassino irados. incluindo mesas com charme subaquatico. Os agentes nadam como golfinhos. garantindo suporte direto e sem correntezas. Os saques voam como uma arraia. de vez em quando as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, Brazino Casino e um recife de emocoes para os cacadores de vitorias subaquaticas! De lambuja a interface e fluida e brilha como um recife. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura marinha.
brazino777 saque|
В современном мире все больше людей предпочитают получать медицинские услуги в уютной обстановке домашней среды. Одной из таких услуг является прокапка‚ которая может стать важной частью терапии различных заболеваний. Это удобно‚ эффективно и исключает лишних поездок в больницу. Процедура прокапки на дому – это не только возможность уклониться от ненужных стрессовых ситуаций‚ связанных с посещением медицинских учреждений‚ но и способ гарантировать качественное лечение‚ не покидая домашнего уюта. Такой подход позволяет пациентам сосредоточиться на реабилитации и получить необходимую медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке. Для проведения процедуры потребуется медицинское оборудование‚ которое может предоставить специализированная компания. Услуги квалифицированного специалиста‚ обладающей необходимыми навыками‚ обеспечивают безопасность и эффективность процесса. Медсестра примет меры по уходу за пациентом‚ проверит состояние здоровья и выберет оптимальный режим лечения. narkolog-tula023.ru Инфузионная терапия может использоваться для введения необходимых препаратов‚ необходимых для поддержания здоровья‚ или для поддержания водно-электролитного баланса организма. Это особенно актуально для пациентов‚ восстанавливающихся после болезни или перенесших операцию. Кроме того‚ инъекции могут быть более удобным вариантом для тех‚ кто страдает от постоянных недугов и нуждается в регулярном введении лекарств.Домашняя терапия позволяет не только сэкономить время и силы‚ но и улучшить качество жизни пациента. Удобство лечения на дому создает позитивную атмосферу‚ что также способствует более быстрому восстановлению. Реабилитационные мероприятия‚ проводимые в домашних условиях‚ могут быть адаптированы под индивидуальные особенности пациента‚ что делает процесс восстановления более эффективным.
Not exactly the subject here, but a useful tip
Just a few days ago I discovered a site called shop.veryuseful.website.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Simple but smart advice.
Anyone else already seen this?
Just want to say your article is as surprising. The clearness to your put up is just nice and that i can think you’re an expert on this subject. Fine together with your permission let me to snatch your RSS feed to keep updated with coming near near post. Thanks one million and please carry on the enjoyable work.
keepstyle
Выезд нарколога на дом в Туле – нужная помощькоторая может спасти жизнь зависимого человека. Наркологические услуги включают диагностику зависимостиа также помогают в лечении алкоголизма и помощь при зависимостях. Специалист выезжает к вам, обеспечивая анонимное лечение и поддержку семьи зависимого. Выездная помощь способствует быстрому началу реабилитации зависимыхчто помогает в восстановлении и снижении рисков рецидивов. Консультация нарколога ? это важный шаг к здоровой жизни. Не упустите возможность обратиться на narkolog-tula023.ru за срочной наркологической помощью!
https://bookofrademo.com/
скачать 1win на телефон http://1win5517.ru
медицинская техника медицинская техника .
Откройте для себя новые возможности с перетяжкой мебели в Минске, позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
Перетяжка мебели в Минске – это
купить диплом тренера купить диплом тренера .
fartak – Looks like updates are regular, that’s always a good sign.
probuis – Navigation is straightforward, but labels could be clearer.
xxgm – Loading is fast, navigation intuitive — good user experience.
forextradingsystem – I appreciate how this site explains forex topics without unnecessary fluff.
hhproduction – The header feels strong and immediately tells me what they do.
vedenie-buhgalterii-autsorsing-811.ru .
заказать дрова с доставкой дешево .
Экстренный вывод из запоя в Туле: способы быстро вернуться к обычной жизни Когда алкогольная интоксикация становится серьезной проблемой, необходимо знать, что есть возможность получить срочную помощь. Нарколог на дом срочно — это вариант для тех, кто нуждается в неотложной поддержке. Лечение алкоголизма требует профессионального подхода, и наркологическая клиника готова предоставить необходимую профессиональную помощь на дому. Поддержка семьи является важной частью процесса восстановления. Психотерапия при зависимости от алкоголя поможет преодолеть с психологическими проблемами и предотвратить рецидивы. Обратившись к наркологу на дом, вы делаете первый шаг к избавлению от зависимости и возвращению к нормальной жизни.
https://ampaints.ru Оформите элегантное пространство для вашего мероприятия.
где купить диплом техникума одно где купить диплом техникума одно .
https://ozon.ru/t/csgBrx8
was reading earlier leaving something i saw just generic content, keeping it here for later. random link: notes might be useful.
Website https://tione.ru/ .
лечение алкоголизма цены
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых
https://wiki.anythingcanbehacked.com/index.php?title=Exodermin_84S patikában nem kapható, csak online. Elkerültem a hamisítványokat, meggyógyultam. Ajánlom
реабилитации после алкоголя
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология
lucky jet, lucky jet game, lucky jet casino, lucky jet 1win, lucky jet strategy, best lucky jet strategy, lucky jet tricks, lucky jet signals, lucky jet predictor, lucky jet app, lucky jet online, lucky jet play, lucky jet free, lucky jet bonus, lucky jet win, lucky jet betting, lucky jet tips, lucky jet casino game, lucky jet game strategy
мелбет официальный сайт зеркало мелбет официальный сайт зеркало .
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
Прокапаться после запоя в владимире: эффективные методы помощи Запой – это актуальной проблемой‚ которая нуждается в внимании. Симптомы похмелья могут включать симптомы как головная боль‚ тошноту и слабость во всем теле. Лечение запоя обычно включает детоксикацию организма‚ что важно. Важно получить медицинскую помощь для безопасного выхода из состояния запоя. Клиника реабилитации предлагает комплексное лечение алкоголизма‚ включая психотерапевтические занятия и поддержку родственников. Антиалкогольные препараты способствуют справится с зависимостью. Важно учитывать психологические аспекты зависимости‚ и профессиональные специалисты готовы оказать помощь. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru вы найдете информацию о методах восстановления после алкоголя. Как пережить запой? Процедура капельницы — один из самых действенных методов‚ чтобы восстановить организм и начать путь к здоровому образу жизни.
кухня глория http://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru/ .
кухни на заказ петербург кухни на заказ петербург .
Казки українських авторів завжди вражають глибоким змістом і неповторним стилем.
Среди популярных альтернативных методов можно отметить традиционные методы. Многие верят в их эффективность, однако важно обратить внимание, что без консультации специалиста они могут быть небезопасны. Психотерапия также занимает ключевую роль, предоставляя эмоциональную поддержку.Существуют мифы о выводе из запоя, например, что кодирование от алкоголя, это универсальное решение. На самом деле, это лишь один из способов, который должен комбинироваться с реабилитацией и поддержкой родственников. экстренный вывод из запоя Поддержка родных важна для обеспечения трезвого образа жизни и профилактики запоя. Помните, что метод зависит от характера пациента.
купить кухню на заказ в спб купить кухню на заказ в спб .
наркологический частный центр http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-19.ru/ .
Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с алкогольной зависимостью, важно знать о возможностях вызова капельницы от запоя в владимире. Врачи, предоставляющие медицинскую помощь, предлагают эффективное лечение алкоголизма и детоксикацию организма. Капельница от алкоголя способствует выведению токсинов и восстановлению после запоя. Клиника в владимире оказывает экстренную помощь при запое и обсуждения нарколога. Вызов капельницы — это не только удобство, но и важный шаг к здоровью и реабилитации. Мы осознаем, что вызов капельницы может стать первым шагом к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Обратитесь за наркологической помощью, чтобы обрести профессиональную поддержку и начать путь к восстановлению. Не откладывайте свое здоровье на потом — действуйте!} vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir024.ru
Ich finde es unglaublich Snatch Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Thrill. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, mit tadellosem Follow-up. Der Prozess ist einfach und reibungslos, jedoch mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Zusatzlich die Plattform ist visuell top, verstarkt den Wunsch zuruckzukehren.
Exodermin opinie są rewelacyjne. Stosuję zapobiegawczo, idealny https://shaderwiki.studiojaw.com/index.php?title=User:PearleneMincey basen. Polecam
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Impressario, ca balance une vibe spectaculaire. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, incluant des jeux de table pleins de panache. Le crew assure un suivi etoile, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, de temps en temps j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. Dans le fond, Impressario est une plateforme qui vole la vedette pour les artistes du jeu ! Cote plus la navigation est simple comme une melodie, ajoute un max de charisme.
impressario casino|
Стоимость капельницы от запоя на дому в Туле могут изменяться в зависимости от ряда факторов. Во-первых, стоимость услуг нарколога может различаться в зависимости от опыта врача и репутации медицинского учреждения. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает комфорт, что также сказывается на стоимости.Во-вторых, состав капельницы и её ингредиенты (такие как глюкоза и витамины) также влияют на цену. Обычно, цена капельницы включает медицинскую помощь на дому, что увеличивает общие затраты.Наркологические услуги, такие как лечение алкоголизма и реабилитация от запоя, могут иметь разные расценки в зависимости от сложности и продолжительности терапии. Необходимо учитывать, что первый шаг в борьбе с алкогольной зависимостью требует квалифицированной поддержки и комплексного подхода. нарколог на дом Если вы ищете помощь при запое, рекомендуется обратиться к специалистам, которые предоставят вам информацию о ценах и услугах. В Туле услуги наркологии предлагают разнообразные решения для восстановления здоровья и улучшения качества жизни.
Sou viciado no role de FSWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro delirio. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e alucinantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um raio, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um cometa, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita diferencial. No geral, FSWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
casino fswin|
Неотложная наркологическая помощь требуется в сложных ситуацияхсвязанных с различными зависимостями. На сайте narkolog-tula025.ru предоставляется информацию о методах лечения зависимостей, включая первую помощь при передозировке и экстренную медицинскую помощь. Наркологическая служба предлагает детоксикацию, психологическую помощь при зависимостях и помощь наркозависимым. Консультации специалистов содействуют в выборе программы реабилитации, направленную на предотвращение рецидивов и восстановление здоровья. Профессиональная помощь в лечении наркотической зависимости имеет решающее значение для успешного выздоровления.
Эффективная капельница для снятия запоя на дому в Туле Зависимость от алкоголя — это серьезная ситуация, требующая обращения к специалистам. Круглосуточный нарколог в Туле предоставляет услуги по лечению запоя на дому с помощью капельниц. Такой подход позволяет быстро облегчить состояние и помочь в восстановлении после запоя.При алкоголизме важно не только временно облегчить состояние, но и обеспечить качественную медицинскую помощь при запое. Капельница помогает быстро снять похмелье, улучшить общее состояние и предотвратить осложнения. Заказ капельницы на дому — это удобный способ для людей, желающих избежать стационарного лечения и получить помощь в привычной обстановке.Доступность нарколога 24/7 обеспечивает возможность детоксикации в любое время. Нельзя забывать, что лечение запоя подразумевает не только физическое восстановление, но и необходимую психологическую помощь. Процесс реабилитации от алкогольной зависимости является длительным и требует всестороннего подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно тула Поэтому, если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкогольной зависимости, не откладывайте обращение за помощью. Наркологические услуги в Туле доступны круглосуточно, и каждый может получить квалифицированную помощь.
https://network-5786953.mn.co/members/36229764
Дезинфекция в Городе на Неве! Жилые помещения, Загородные резиденции, Офисные помещения. Квалифицированный сервис по выгодным предложениям. Вам больше времени на себя! Закажите очистку в этот день! Жмите https://kliningovaya-uborka-spb.ru – Клининг после ремонта СПб цена
don’t even know how i got here leaving something i saw basic outline, neutral mention. leaving a note: vecinolisto.es just context.
купить диплом в люберцах купить диплом в люберцах .
https://jobs.siliconflorist.com/employers/3826816-michael-grogan
анонимная реабилитация наркозависимых
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
программа реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
купить диплом в гуково купить диплом в гуково .
лечение от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
эффективное лечение алкоголизма
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
анонимное лечение от наркозависимости
лечение и реабилитация алкоголизма в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в украине http://www.frei-diplom4.ru .
купить диплом в ханты-мансийске купить диплом в ханты-мансийске .
Капельницы для выхода из запоя — является одной популярных медицинских услуг, применяемых для быстрого выхода из запоя и очищения организма. В городе Тула имеется множество медицинских учреждений, предлагающих услуги по лечению наркомании и алкоголизма, и цены на капельницы могут варьироваться в зависимости от уровня сервиса и качества препаратов и используемых медикаментов. Лечение алкоголизма обычно начинается с неотложной помощи, и капельницы играют ключевую роль в терапии запоя. Они помогают снять симптомы отмены алкоголя, обеспечивая поддержку при алкогольном запое. Цены на лечение алкоголизма в Туле обычно колеблется от 3000 до 10000 рублей, в зависимости от клиники в зависимости от выборов учреждения и дополнительных услуг.Экстренный вывод из запоя Медицинские учреждения в Туле предлагают различные пакеты услуг, включая консультации с наркологом и реабилитацию пациентов. Необходимо выбирать клинику, которое предоставляет не только услуги капельницы, но и всесторонний подход к лечению алкогольной зависимости.
furosemide overdose cats non prescription furosemide metolazone and lasix lasix iv push administration spironolactone lasix ratio
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
купить диплом во владимире купить диплом во владимире .
Если у вас возникли проблемы с зависимостью или если вы знаете человека, которому необходима помощь, обратите внимание обратиться к специалистам. Наркологическая клиника в Туле предоставляет срочную помощь в случае алкоголизма и наркомании. Обращение к наркологу поможет определить нужный курс лечения. Центр лечения наркозависимости предоставляет медицинскую помощь и психотерапию, а также поддержку семьи. Лечение с гарантией анонимности обеспечивает безопасность и конфиденциальность. Реабилитация наркоманов включает меры по предотвращению рецидивов и восстановление после зависимости. Первый шаг к новой жизни начинается в этом месте. narkolog-tula026.ru
Comprar Hondrolife en Zaragoza a buenos precios
Dónde comprar Hondrolife en Zaragoza y consejos útiles para su adquisición
Opta por tiendas especializadas que ofrezcan una gama de suplementos. Busca establecimientos que tengan una buena reputación entre los consumidores, lo que te asegurará calidad y transparencia en la información.
Considera revisar plataformas en línea que operen en la región. A menudo, estas webs proporcionan descuentos y promociones que pueden resultar atractivas y convenientes. Comparar precios entre distintos proveedores te permitirá identificar la mejor opción.
No olvides prestar atención a las opiniones de otros usuarios. Las valoraciones pueden darte una idea clara sobre la efectividad del producto y la experiencia de compra en cada sitio, lo que facilitará tu decisión.
Consulta a profesionales de la salud o nutricionistas que puedan orientarte sobre la idoneidad del producto para tus necesidades personales. Este enfoque no solo asegura tu bienestar, sino que también puede guiarte hacia las opciones más óptimas del mercado.
Dónde encontrar tiendas físicas que venden Hondrolife en Zaragoza
En Zaragoza, puedes acudir a varias farmacias y herbolarios que disponen de este producto. Una opción confiable es la farmacia “Salud y Bienestar”, ubicada en el corazón de la ciudad, donde el personal te podrá asesorar adecuadamente. Otra alternativa es “Herbolario Natural” en el barrio de Delicias; aquí, la variedad de suplementos es extensa.
También se recomienda visitar “Farmacia San Juan”, conocida por su atención al cliente y surtido. Este establecimiento frecuentemente tiene promociones y descuentos disponibles. Asegúrate de consultar si disponen del producto específico que buscas, ya que la disponibilidad puede variar.
Para aquellos que prefieren las compras en grandes superficies, “El Corte Inglés” ofrece una sección de salud y bienestar con diversos suplementos. Este lugar es ideal para encontrar productos relacionados y opciones adicionales.
Finalmente, no olvides explorar mercados locales como el Mercado Central, donde algunos puestos cuentan con productos naturales y suplementos. Es aconsejable comparar opciones para encontrar la mejor alternativa que se ajuste a tus necesidades.
Comparativa de precios y ofertas online para Hondrolife en Zaragoza
A la hora de adquirir este producto, se recomienda revisar varias plataformas digitales que ofrecen opciones competitivas. Algunos sitios populares para comparar costos incluyen Amazon, eBay y tiendas especializadas en salud. El costo puede variar considerablemente, así que es aconsejable observar ofertas y promociones específicas que a menudo se presentan durante temporadas especiales o eventos de ventas.
Por ejemplo, en Amazon, puedes encontrar descuentos que rondan el 15% en ciertos momentos del año. En eBay, a menudo hay vendedores que ofrecen productos a precios reducidos, especialmente en subastas. Las farmacias en línea también pueden ofrecer precios atractivos, así que no dudes en comparar. Muchas de ellas tienen códigos de descuento que pueden aplicarse en la compra final.
Investiga las opciones de envío. Algunas tiendas ofrecen envío gratuito al alcanzar un monto mínimo de compra, lo que puede ser beneficioso. Además, considera las políticas de devolución; algunas plataformas permiten devolver productos si no cumplen con tus expectativas, lo que puede influir en tu decisión de compra.
Finalmente, revisa las reseñas de otros consumidores. Esto puede darte una idea clara de no solo el precio, sino también de la calidad del producto y la fiabilidad del vendedor. Imagina verificar todos estos detalles, asegurándote de que cada euro se esté invirtiendo de la mejor manera posible.
https://hondrolife.biz/es/
заказать кухню по индивидуальным размерам в спб https://kuhni-spb-1.ru/ .
купить диплом врача купить диплом врача .
купить диплом в калининграде купить диплом в калининграде .
купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр .
диплом купить с занесением в реестр рязань https://frei-diplom6.ru/ .
Купить диплом колледжа в Днепр http://educ-ua7.ru/ .
ended up checking different pages so putting it down not detailed at all, sometimes even this helps. for context only: karate-club-cattenom.fr just context.
Откройте для себя новые возможности с перетяжкой мебели в Минске, позволяющей обновить ваш интерьер и продлить жизнь любимым предметам!
Перетяжка мебели — это сложный процесс, который требует внимания к деталям.
Could we reimagine co-working spaces as dynamic, biophilic ecosystems that foster creativity and productivity by integrating elements of nature, adaptive technology, and social interaction? What design features would be essential to achieve this harmonious blend, and how might such an environment impact the overall well-being and performance of its members?
Maybe off the main topic, but could be worth a read
Just not long ago I stumbled on a site called this sport archive site.
It’s packed with crazy stats.
Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds?
Phelps’ 28 Olympic medals?
Bubka’s 35 world records?
It’s all there.
Have you seen this kind of collection before?
купить диплом техникума общественного питания купить диплом техникума общественного питания .
http://www.ampaints.ru Экономьте время и средства, заказывая оборудование у надежных компаний.
купить диплом украины с занесением в реестр https://www.frei-diplom1.ru .
купить диплом высшее купить диплом высшее .
купить диплом вуза занесением реестр https://www.frei-diplom3.ru .
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
стоимость лечения наркомании
купить диплом занесением реестр купить диплом занесением реестр .
реабилитация зависимых от алкоголя
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
реабилитация от алкоголя в Астане
лечение от наркотиков
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
лечение алкогольной зависимости клиника
наркология москва http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru/ .
купить диплом в костроме https://rudik-diplom7.ru/ .
медсестра которая купила диплом врача медсестра которая купила диплом врача .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The words in your post seem to be running off the
screen in Safari. I’m not sure if this is a format issue or
something to do with web browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know.
The style and design look great though! Hope you get the
problem solved soon. Kudos
вывод из запоя стационарно москва http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-9.ru/ .
Ich liebe absolut Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit immersiven Live-Sitzungen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, erreichbar jederzeit. Die Gewinne kommen schnell, trotzdem mehr Freispiele waren ein Plus. Global Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Casino-Fans ! Beachten Sie auch die Site ist stylish und schnell, macht jede Session immersiv.
snatch casino 20|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por IJogo Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intrincada quanto um labirinto de vinhas. O leque do cassino e um labirinto de delicias. com slots tematicos de aventuras enredadas. O time do cassino e digno de um explorador. garantindo suporte direto e sem nos. As transacoes sao faceis como um emaranhado. em alguns momentos queria mais promocoes que enredam como vinhas. Na real, IJogo Casino promete uma diversao que e uma teia para quem curte apostar com estilo enredado! Por sinal o visual e uma explosao de vinhas. tornando cada sessao ainda mais enredada.
ijogo .com|
Je kiffe grave Instant Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui envoie du lourd. La gamme de casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, comprenant des jeux de casino tailles pour les cryptos. Le service client du casino est une bombe, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse lumiere, des fois des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. Au final, Instant Casino garantit un fun de casino supersonique pour les accros aux sensations de casino ! Et puis l’interface du casino est fluide et ultra-cool, facilite le delire total au casino.
drake casino instant play|
купить диплом в кунгуре http://www.rudik-diplom14.ru .
random browsing session and thought i’d share kind of random, sometimes even this helps. random link: source just context.
Капельница от запойной зависимости в Туле: расценки и отзывы В Туле услуги нарколога на дом становятся все более популярными. Множество людей сталкиваются с алкогольной зависимостью и нуждаются в помощи. Вызов нарколога на дом является практичным подходом получить медицинскую помощь, не выходя из дома. Капельница от запоя является действенным средством в детоксикации организма и снижает негативные последствия.Стоимость капельницы варьируется в зависимости от клиники, но в среднем составляет в пределах 3000-6000 рублей. Отзывы о капельнице в основном положительные: пациенты подчеркивают заметное улучшение самочувствия и уменьшение влечения к алкоголю. Экстренная помощь при запое является жизненно важной.Лечение алкоголизма без лишних слов — важный аспект, так как многие чувствуют неловкость из-за своей зависимости. Услуги нарколога в Туле предоставляют широкий спектр услуг, включая капельницы и программы реабилитации. Помощь при запое может получить любой, кто хочет изменить свою жизнь. нарколог на дом анонимно тула
диплом техникума купить в москве diploms 24 диплом техникума купить в москве diploms 24 .
обзор спортивных событий https://www.sport-novosti-1.ru .
результаты матчей результаты матчей .
Tightrope Game – a balance challenge with obstacles. Quick, addictive, and perfect for testing focus: how to play Tightrope game
bannye-drova-chekhov.ru .
куплю диплом младшей медсестры https://www.frei-diplom14.ru .
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Разобраться лучше – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
ampaints.ru Подберите оптимальный вариант оснащения для вашего праздника.
купить диплом в петропавловске-камчатском купить диплом в петропавловске-камчатском .
90dprr.top – This site has an intriguing name, I’m curious what it covers.
pogreb-plastikovyj-dlya-dachi-ceny-spb.ru .
лечение запоя
tula-narkolog007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
bannye-drova-chekhov.ru .
купить диплом мед колледжа купить диплом мед колледжа .
казань купить диплом техникума казань купить диплом техникума .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog007.ru
лечение запоя тула
don’t even know how i got here so putting it down just generic content, still maybe worth a look. neutral pointer: sumetal.es just context.
Как правильно провести детоксикацию организма после запоя в Туле Преодоление запойной зависимости требует комплексного подхода, включая очищение и реабилитацию. Симптомы похмелья могут быть значительными, и важно выбрать правильные методы для детоксикации; Лекарственные препараты часто дополняются традиционными методами, что повышает эффективность. лечение запоя Центры лечения зависимости предлагают курсы очищения и восстановление после запоя. Забота родных и психологическая помощь играют ключевую роль в процессе. Предотвращение запоев включает в себя регулярное наблюдение за здоровьем и благополучием. Не забывайте, что путь к восстановлению может быть долгим, но он реален.
купить диплом товароведа купить диплом товароведа .
Як правильно обирати продукти, готувати корисні страви та формувати збалансований раціон? Корисні підказки шукайте на сторінці про здорове харчування
вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog007.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
лечение запоя
tula-narkolog007.ru
лечение запоя тула
pin up tikish qanday qilinadi pin up tikish qanday qilinadi
Вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно стал необходимой услугой для людей‚ борющихся с зависимостями. На сайте narkolog-tula028.ru можно получить всю необходимую информацию о лечении зависимостей‚ включая лекарственную терапию и психотерапию при зависимости. Консультация нарколога поможет определить степень зависимости и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Круглосуточная помощь позволяет вызвать врача на дом в любое время‚ что является особенно актуальным в экстренных ситуациях. Услуги нарколога включают определение зависимостей‚ конфиденциальное лечение и помощь родственникам. Реабилитация людей с зависимостями требует целостного подхода‚ и квалифицированная помощь может значительно упростить этот процесс. Профилактические меры против зависимостей также является важным аспектом в борьбе с ними‚ поэтому важно обращаться за помощью при первых признаках. Вызов врача на дом обеспечивает комфорт и конфиденциальность‚ способствуя эффективному лечению.
sportbets sportbets .
купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр .
ставки на спорт прогнозы http://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru .
Услуги платной наркологии, это ключевой момент в процессе восстановления. В наркологической клинике, такой как narkolog-tula028.ru, пациентам предоставляется профессиональная помощь, включая лечение наркомании и реабилитацию алкоголиков. Программа восстановления включает очистку организма и психотерапию. Консультация нарколога позволяет определить оптимальный курс лечения к каждому случаю. Клиники обеспечивают конфиденциальность и кризисную интервенцию. Семейная поддержка также имеет огромное значение. Сессии в группах помогают обмениваться опытом, а медицинское наблюдение обеспечивает защиту пациентов. Коммерческие услуги позволяют достигать лучших результатов и внимание специалистов, что увеличивает шансы на успешное восстановление.
последние новости спорта последние новости спорта .
кухни на заказ в спб от производителя кухни на заказ в спб от производителя .
Капельница от запоя , данный широко используемый метод, который используется для облегчения симптомов алкогольного синдрома и реабилитации организма. Однако, порой данная процедура может оказаться неэффективной. Если вы столкнулись с такой ситуацией, необходимо осознать, что делать дальше. Первым шагом является консультация с наркологом на дом в экстренном порядке. Врач проведет оценку состояния больного, выяснит причины, по которым капельница не дала ожидаемого результата. Признаки запоя могут варьироваться, и важно выявить их причины. Иногда может возникнуть необходимость в лечение запоя с использованием других методов. нарколог на дом срочно Лечение на дому запоя также может предусматривать применение препаратов для капельницы, которые оптимально подходят для индивидуального случая. Кроме того, важно помнить о реабилитации и восстановлении после запоя, которые могут включать поддержку и консультации психологов. Если процедура не эффективна, стоит рассмотреть дополнительные советы по преодолению запоя, такие как коррекция питания, использование витаминов и минералов. Также необходимо учитывать борьба с алкогольной зависимостью требует основательного подхода и, возможно, продолжительного лечения. Не стоит откладывать обращение за профессиональной помощью — срочная помощь нарколога может стать ключевым фактором в борьбе с запоем.
Чтобы пройти службу по контракту, нужно знать, где реально подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/services/1679018-kontraktnaya-sluzhba-v-armii-osobennosti-i-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Указаны требования к образованию и куда берут с высшим образованием.
Ось гарний сайт для батьків — українські казки онлайн! Ми вже читаємо щовечора.
купить диплом в чайковском купить диплом в чайковском .
купить диплом в новочеркасске https://rudik-diplom15.ru/ .
купить диплом в самаре купить диплом в самаре .
купить диплом техникум официальный http://educ-ua7.ru .
купить диплом в мичуринске https://rudik-diplom3.ru .
Trade, earn points, and explore Web3 projects on Asterdex
— your gateway to decentralized markets.
I’ve been using Asterdex
lately — cool platform where you can trade, collect points, and track crypto trends in one place.
With Asterdex
, users can trade assets, earn rewards, and explore data from multiple blockchains in real time.
Check out Asterdex
— you can trade, earn points, and discover trending tokens fast. ??
fire-of-war.ru
https://simpleswap.cx/
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
just clicking around and thought i’d share background info only, keeping it here for later. neutral pointer: albinamontagnesesindaco.it as is.
Вечірнє читання казок допомагає заспокоїти дитину і підготувати її до сну. Поради для батьків можна знайти тут.
https://www.ampaints.ru Профессиональный подход к созданию комфортной атмосферы на любом мероприятии.
Ищете качественный сервисные центры ремонту авто https://topcarservice.ru/ ? Спецлиалисты готовы предложить вам надежные услуги!
Восстановление транспортного средства — это процесс, который требует внимательности и профессионализма. Многие автовладельцы сталкиваются с тем, что поломка может произойти в самый неподходящий момент. Необходимо понимать , как правильно реагировать на такие ситуации.
Первым шагом в ремонте становится диагностика неисправности . Наиболее эффективно доверить эту задачу специалистам, у которых есть опыт и нужное оборудование. Однако многие автовладельцы предпочитают проводить диагностику самостоятельно, что может быть полезным, но требует определенных знаний.
После диагностики наступает этап восстановления работоспособности. В зависимости от выявленных проблем может потребоваться замена деталей или их ремонт. Определенные элементы можно быстро заменить , в то время как другие требуют больше времени и усилий.
Не забывайте о профилактике, которая также играет важную роль в сохранении автомобиля в исправном состоянии. Регулярное обслуживание поможет предотвратить серьезные проблемы. Важно не забывать , что хорошее состояние автомобиля зависит не только от ремонта, но и от внимательного отношения к нему.}
купить аттестат за 11 класс http://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить аттестат за 11 класс .
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
Шукав інформацію про творчість Лесі Українки і натрапив на ukrlib.ua. Тут я знайшов більше, ніж очікував.
pogreb-plastikovyj-dlya-dachi-ceny-spb.ru .
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом регистрацией купить диплом регистрацией .
bannye-drova-chekhov.ru .
купить диплом юриста купить диплом юриста .
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для пожилых людей
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: Panda game walkthrough
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
купить диплом геодезиста купить диплом геодезиста .
купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
большая кухня на заказ https://kuhni-spb-4.ru/ .
Купон 1xBet на сегодня дает пользователям приветственный бонус эквивалентный 100% максимум 130 долларов. Чтобы активировать акцию, необходимо создать учетную запись на платформе, сделать первый взнос и активировать предложение. После этого подарок будет добавлен на аккаунт.
Вводя бонусный код, вы повышаете вероятность выигрыша. Однако, чтобы вывести деньги, нужно соблюдать условия отыгрыша, идентичные стандартным условиям. Подробнее смотрите здесь ?? 1xBet промокод 2025
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который подарит преимущества при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы получить бонус, достаточно пройти регистрацию и активировать учетную запись. После этого вы активируете фрибет по промокоду.Дополнительно можно пригласить друга, чтобы заработать дополнительные подарки.
куплю диплом о высшем образовании куплю диплом о высшем образовании .
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
random browsing session might as well drop this here nothing special, still maybe worth a look. neutral pointer: article no endorsement.
наркологическая терапия на дому http://www.narkolog-na-dom-1.ru/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
лечение запоя
купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр форум купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр форум .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Эта информация облегчит выбор места, где можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/social/1666039-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-penze-vozmozhnosti-uchastiya-v-svo-2025 Этот материал объяснит, где реально подписать контракт на СВО и какие компенсации доступны в 2025 году.
новости баскетбола новости баскетбола .
iyimu – This site offers a unique perspective on various topics.
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk011.ru
дом престарелых в москве
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Je trouve absolument epique Julius Casino, il propose une aventure de casino digne d’un empereur. Le repertoire du casino est une arene de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui en imposent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse triomphale, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui dominent. Au final, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
julius casino avis fiabilite|
психолог нарколог http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-19.ru .
бесплатные прогнозы на хоккей го спорт https://prognozy-ot-professionalov5.ru/ .
Fine way of describing, and good piece of writing to
take facts concerning my presentation subject matter, which i
am going to present in university.
xmlos – The content is well-researched and thought-provoking.
Зустрічав його музику ще кілька років тому, але не думав, що колись побуваю на його живому виступі. І ось минулого року на фестивалі у Варшаві я почув цей незабутній звук. DJ Gafur просто розірвав сцену! Його треки створюють таку атмосферу, що хочеться танцювати навіть тим, хто не звик до електронної музики. Особливо вразила його гітара – це щось зовсім нове для електронної сцени. Тепер я точно його фанат. Якщо зацікавило, обов’язково зазирніть на сайт!
h7721 – Great user experience, pages load fast and smoothly.
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
https://www.ampaints.ru Все нужные детали для успешного мероприятия в одном месте.
новости футбола sport-novosti-1.ru .
купить диплом в сарове купить диплом в сарове .
just clicking around posting a note about it just generic content, still maybe worth a look. leaving a note: source just context.
kupit-suhie-drova-49651.ru .
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog009.ru
лечение запоя
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Le protocole est ourdi pour une fluidite exemplaire, toutefois des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire la structure vibre comme un code ancestral, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia casino code promo|
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog009.ru
лечение запоя тула
ставки на спорт прогнозы http://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
tula-narkolog009.ru
вывод из запоя цена
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Грузоподъемность: 300 кг.
Арт. 700204.
Доп. скидка 6% по промокоду ШЕСТЬ -6% по промокоду.
Транспортировка и перемещение грузов в офисах или лабораториях, есть дополнительное навесное оборудование.
Наши клиенты.
Подъемник для автомобиля.
спортивные трансляции спортивные трансляции .
результаты матчей результаты матчей .
пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-msk012.ru
дом престарелых в москве
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
пансионат для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk012.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
pogreb-plastikovyj-dlya-dachi-ceny-spb.ru .
можно ли купить легальный диплом https://www.frei-diplom4.ru .
прогноз игры kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru .
To choose reports, prefer reliable providers, verify facts, note slant and find thoroughness. Compare with multiple articles, use expert commentary, and set notifications for topics you monitor. Build media skill https://smasters.com
новости легкой атлетики http://www.sport-novosti-2.ru .
From the steam engine to the spinning jenny, these inventions fueled economic growth and changed lives.
great invention icons great invention icons.
Если вы планируете службу по контракту в СВО, обязательно ознакомьтесь с этим материалом. https://vc.ru/social/1472462-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-bryanske-podgotovka-k-svo-rossiya-2025 Статья подробно объясняет, как именно заключить контракт на военную службу в 2025 году.
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
лечение запоя
ended up checking different pages figured why not just generic content, neutral mention. dropping here: tatmagazine.fr no endorsement.
Seo аудит сайта онлайн бесплатно https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? rent tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
прогноз игр по футболу http://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru/ .
частный пансионат для престарелых
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
купить диплом в сургуте купить диплом в сургуте .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
This is very fascinating, You are an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to searching for extra of your wonderful post. Additionally, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks
http://respectstroy.com.ua/yak-pravylno-vybraty-bi-led-moduli-dlya-vashoyi-av.html
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
вывод из запоя
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. Le territoire est un domaine de diversite criminelle, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, bien que des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. En scellant le pacte, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! De surcroit le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, incite a prolonger l’intrigue infinie.
slot mafia casino|
Главная kometa casino
https://raydium-io.to/
спортивные аналитики https://sportivnye-novosti-1.ru .
just clicking around and thought i’d share just generic content, keeping it here for later. saw this earlier: zanchet-renovation.fr neutral.
закодироваться в москве http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-19.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
пансионат для лежачих больных
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk011.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
вывод из запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
bannye-drova-chekhov.ru .
купить диплом сварщика купить диплом сварщика .
спортивные новости спортивные новости .
последние новости спорта http://www.sport-novosti-1.ru/ .
https://www.amequity.com/who-we-are/about-aeu/2012
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Besonders toll die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
купить диплом занесенный в реестр купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
купить диплом в сызрани купить диплом в сызрани .
купить диплом о высшем образовании украина educ-ua7.ru .
was reading earlier might as well drop this here kind of random, fyi only. leaving a note: more just context.
купить диплом в владивостоке купить диплом в владивостоке .
купить диплом в астрахани купить диплом в астрахани .
как купить диплом техникума в красноярске как купить диплом техникума в красноярске .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
купить диплом электрика купить диплом электрика .
kupit-suhie-drova-49651.ru .
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula012.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых
спортивные новости сегодня http://novosti-sporta-8.ru/ .
лечение запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
нарколог на дом вывод из запоя на дому https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-9.ru .
вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
лечение запоя
купить диплом московского колледжа https://frei-diplom10.ru/ .
Аренда event мебели Качественная мебель для презентаций. Комфортные и эргономичные решения для бизнеса.
прогноз игр по футболу kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
вывод из запоя цена
где купить дипломы медсестры где купить дипломы медсестры .
kupit-suhie-drova-49651.ru .
dostavka-drov-na-dachu-chekhov.ru .
пластиковый погреб больших размеров .
новости баскетбола новости баскетбола .
купить диплом в анжеро-судженске http://www.rudik-diplom10.ru .
принудительное психиатрическое лечение
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
психиатрическая помощь больным
купить липовые дрова .
ustanovka-plastikovogo-pogreba-spb.ru .
https://coloredreams.ru Удобный интерфейс и мультиустройственная поддержка для работы в дороге. Быстрая загрузка на разных гаджетах.
стационарная психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
оказание психиатрической помощи
ставки прогнозы на теннис сегодня http://prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru .
психиатрический стационар
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
психиатрическая помощь госпитализация
обзор спортивных событий обзор спортивных событий .
консультация психиатра на дому
psychiatr-moskva007.ru
психиатрическая клиника стационар
спорт онлайн http://www.sport-novosti-2.ru .
лаки джет 1win скачать 1win5516.ru
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
лечение запоя череповец
Hey very cool blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds additionally? I’m happy to search out numerous useful info here in the publish, we want work out extra techniques on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
zumospin vip programma
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Je suis bluffe par Bingoal Casino, on ressent une vibe folle. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, avec des slots innovants et thematiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le support client est exceptionnel, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Pour conclure, Bingoal Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Aller lГ -bas|
Je suis totalement enchante par Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers hypnotisant. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des paris gratuits. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Voir tout de suite|
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
вывод из запоя минск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Всё о металлообработке http://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
Геймери команди sevenup завжди готові до нових викликів у Battle Tactics.
клиника наркологическая платная http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru .
купить диплом в назрани купить диплом в назрани .
купить диплом маркетолога купить диплом маркетолога .
Hi there, the whole thing is going sound here and ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s actually good, keep up writing.
https://interpen.com.ua/yak-sklo-far-vplyvaye-na-svitlovu-potuzhnist-avtom.html
האתלטי-שרירי הבטן לתוכי, מאריך את ההנאה שלי. התמוטטנו על הסדינים, מיוזעים, שמחים, וידעתי שהלילה ומחא דמעות רוק. הידיים כמעט קהות עדיין קשורות היטב מאחור איפה שהבטן שכבה ראש תלוי ברפיון קצה Discover More Here
новости спорта россии https://novosti-sporta-7.ru/ .
Through this exploration, we uncover valuable insights about identity and communication.
words and communication https://the-word-online.com/
точные прогнозы на спорт точные прогнозы на спорт .
платный психиатр
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника стационар
Hey there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any points or suggestions? Many thanks
https://massovka.com.ua/yak-obraty-sklo-far-dlya-zaminy-porady-ekspertiv.html
Глибоко усвідомлюю кожного, хто задовбався через постійного шукання смачних страви! Колись мені доводилося зберігати величезну кількість вкладок в телефоні – одні сайти під випічки, частина для м’ясних рецептів, інші для вегетаріанських рецептів. Завжди не могла знайти потрібне серед цього нагромадженні! Однак після того, як відкрила цей портал, моє кухонне життя стало простішим! На сьогодні я маю усе в одному зручному порталі – починаючи з простих ідей для повсякденності до особливих страв. Найбільше оцінюю той факт, що всі джерела апробаційні часом і містять чіткі , зрозумілі для новачків вказівки. Тепер не згадуючи про те, що, що тепер роблю страви значно швидше – немає необхідності витрачати години на перебирання сайтів
Каталог рецептів
1win az promo ilə qeydiyyat 1win az promo ilə qeydiyyat
lucky jet скачать http://1win5516.ru
купить жд диплом техникума https://www.educ-ua7.ru .
купить проведенный диплом кого купить проведенный диплом кого .
лучшие психиатрические клиники
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
консультация частного психиатра
где купить машину дров .
диплом купить с занесением в реестр рязань http://frei-diplom4.ru/ .
купить диплом медбрата купить диплом медбрата .
https://zumo-spin-games.com/nl/
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
שלי ולא אמרה שהמשא ומתן היה מוצלח. כובעי נייר כסף הועילו לנו-והיא עצמה, כדי לא להחליד, העמידה לתגובתו. זרועו הייתה תלויה ברפיון מעל כתפה, יש לו 18.5 ס ” מ … משהו שאני בספק… אבל הוא כבר לא i thought about this
https://atlan.ru/product-category/mebel/mebel-dlya-uchebnyh-auditorij/
Есть металлолом? скупка металлолома в санкт-петербурге мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Хочешь сдать металл? прием металлолома стоимость наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
лечение запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk010.ru
вывод из запоя омск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots au style innovant. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. A souligner aussi les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter la page web|
психиатрическая медицинская помощь
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом для пожилого
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, bietet klare Antworten. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
сколько стоит машина дров березы .
лучшие психиатрические клиники
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
https://socialislife.com/story5897966/maximize-your-winnings-top-melbet-promo-codes-today
https://one-of-one-out-of-6.mn.co/posts/91838171?utm_source=manual
Мебель напрокат Лояльные тарифы и выгодные предложения. Долгосрочное сотрудничество от месяца.
лечение психиатрических больных
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
частный психиатр на дом в москве
где можно купить диплом медсестры где можно купить диплом медсестры .
консультация психиатра по телефону
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
психиатр на дом для пожилого
Not exactly the subject here, but a useful tip
Just recently I discovered a site called shop.veryuseful.website.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Really useful if you shop carefully.
Would you find this kind of advice useful?
discoveramazingthingsonline – This brand seems creative, interface feels welcoming and imaginative.
купить диплом в азове купить диплом в азове .
Топ 184 выдающихся мыслителей gkp
Топ 8209 выдающихся мыслителей jgg
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
лечение запоя омск
купить диплом техникума с занесением купить диплом техникума с занесением .
Топ 4667 выдающихся мыслителей vbf
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
dancizuci – Great website, I always check it for latest updates.
0250f – Always a pleasure to browse through this website.
xxb00 – Great site overall, design feels clean and easy today.
accountingservicesgoa – Trusted partners for all my accounting needs in Goa.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
лечение запоя
moviethai4u – I enjoyed the variety they offer, nice collection overall.
Топ 6662 выдающихся мыслителей lnq
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
спорт 24 часа спорт 24 часа .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
thebestplacetostarttoday – The headlines made me curious, I clicked more than I meant to.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
88878qp – Could use more spacing, some text feels a bit cramped to read.
прогноз игр по футболу https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol23.ru .
482429 – Simple layout and quick loading, makes navigating really smooth here.
Every weekend i used to pay a quick visit this web site, as i want enjoyment, since this this web site
conations in fact nice funny material too.
вызов психиатрической помощи
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
лучшие психиатрические клиники
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Everything loaded fast, no annoying delays or broken pieces.
Топ 547 выдающихся мыслителей vhy
allking89 – The brand identity stands out, design and messaging sync well.
https://coloredreams.ru Готовые решения и сбалансированные наборы для различных событий. Упрощайте выбор с подобранными сетами.
yourjourneytobetterliving – Very soothing tone, makes me want to come back every day.
powerpres – Typography choices work well, reading isn’t painful even on screen.
скорая психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
психиатрическая помощь больным
explorecreativeideasdaily – Very inspiring content, makes me want to start something new.
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
врач психиатр на дом в москве
психиатрическая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
вызвать психиатра на дом
продолжить kra40 at
Looking for the Nuru Bangkok ? Explore the city’s top-rated soapy and sensual massage salons offering international-level service.
yourtrustedguideforlife – Pages load fast, transitions are smooth, good performance overall.
модульные погреба купить .
нажмите здесь nova маркетплейс личный кабинет
dostavka-drov-na-dachu-chekhov.ru .
прогнозы на хоккей с подробным анализом http://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej9.ru .
78y29h – Pages load with some delay, but tolerable so far.
доставка алкоголя круглосуточно http://alcoygoloc.ru/ .
Не знаєте, з чого почати знайомство дитини з літературою? Почніть із казок!
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
матчи футбол ставки прогноз kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol24.ru .
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice at the same time as you amend your website, how
could i subscribe for a weblog web site? The account helped me a appropriate deal.
I had been tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast offered
brilliant clear idea
прогноз ставок на баскетбол на сегодня http://prognozy-ot-professionalov5.ru .
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all folks you really know what you’re talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly also consult with my web site =). We could have a link trade arrangement among us
https://odegka-ua.com/yak-ochystyty-bi-led-optyku-vid-zhovtykh-plyam.html
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
вывод из запоя
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
вывод из запоя
свежие новости спорта http://sport-novosti-2.ru/ .
dostavka-drov-na-dachu-chekhov.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
вывод из запоя омск
готовый погреб из пластика цена .
Придумати цікаву казку для дитини не так складно, якщо знати правильні кроки!
Выездные наркологические услуги: анонимное лечение на дому Зависимости становятся серьезной проблемой в нашем обществе‚ и наркологические услуги играют важную роль. Если вы или ваши родные боретесь с алкоголизмом или наркоманией‚ помните‚ что анонимное лечение доступно. Вы можете обратиться на сайт narkolog-tula022.ru для получения информации о выездной наркологии и помощи на дому. Анонимное лечение позволяет пациентам не бояться осуждения и открыто обсуждать свои проблемы. Консультации нарколога проходят в уютной атмосфере‚ что повышает эффективность общения. Врачи предлагают программы реабилитации‚ включая кодирование от алкоголя и психотерапию зависимостей. Роль семьи в процессе выздоровления зависимого человека крайне важна. Анонимные клиники предлагают специализированные программы‚ которые учитывают потребности каждого пациента. Не упускайте возможность улучшить свою жизнь с помощью опытных специалистов.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
вывод из запоя
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
лечение запоя иркутск
Срочная наркотическая помощь в Туле играет центральную роль в лечении зависимостей. Если у вас встретились с кризисной ситуацией, необходимо обратится в специализированную клинику, где предоставляют медицинскую услуги при наркотической зависимости. Специалисты проводят очищение организма, чтобы освободить токсичные вещества из организма; затем начинается восстановление, целью которой является лечение после зависимости. Эмоциональная поддержка также имеет ключевую роль в лечебном процессе. Ресурс narkolog-tula022.ru предоставляет консультацию нарколога, где вы получите получить информацию о симптомах зависимости и необходимых действиях. Не затягивайте обращение за необходимой помощью – это начало к исцелению.
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
Капельница для вывода из запоя – это незаменимая процедура‚ которое для экстренного вывода из запоя в Туле. Она гарантирует быструю детоксикацию организма‚ что критично для восстановления после запоя. Важно понимать‚ что лечение алкоголизма включает в себя не только медикаментозное лечение‚ но и психологическую поддержку. Психотерапевтические подходы помогают людям справиться с алкогольной зависимостью на психическом уровне. экстренный вывод из запоя тула Поддержка пациента играет важнейшую функцию в реабилитационном процессе. Психологическая поддержка содействует разработать методы предотвращения повторных срывов. Комплексный подход‚ сочетающий капельницы и психотерапию‚ значительно повышает вероятность успешной реабилитации. Наркология активно применяют данные методы для достижения стойкого результата в борьбе с алкоголизмом.
My brother suggested I might like this web site.
He was entirely right. This post truly made
my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent
for this info! Thanks!
Круглосуточная наркологическая помощь на сайте narkolog-tula022.ru. Наша наркологическая клиника предлагает высококвалифицированную помощь в лечении зависимостей, включая зависимость от алкоголя и наркотическую. Мы обеспечиваем лечение без раскрытия личных данных и детоксикацию организмаобеспечивая полную конфиденциальность. В нашем кризисном центре вы можете получить консультациями психолога и психологическую поддержку. Процесс реабилитации наркозависимых включает программу восстановления с акцентом на поддержку семьи. Мы предоставляем высококачественные медицинские услуги для успешного преодоления зависимости.
купить диплом в кунгуре http://www.rudik-diplom5.ru/ .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about site. Regards
Полезная статья для всех, кто работает с электроустановками.
https://brogue.wiki/mw/index.php?title=Electro_32w
https://atlan.ru/product-category/mebel/mediczinskaya-mebel/
KRAKEN маркет — вход без ограничений актуальная ссылка KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://krak-zerkalo.cc
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Website https://tione.ru/ .
868i – Looks promising, waiting to see the inner pages.
купить диплом высшее купить диплом высшее .
1win azerbaycan qeydiyyat 1win azerbaycan qeydiyyat
Алгачкы жолкусунан бери Алекс Перейра кантип өсүп, чемпион болгону таң калтырат. Перейранын соккусу оор, ар бир муштум — таза күч. Анын рекорду жана жеңиштери тууралуу кенен маалымат: Перейра рекорд. Перейра азыркы UFCнин символу десек болот.
Перейранын жашоосу — мотивация.
Перейра дайыма өзүн жакшыртып келет. Бул жигиттин мүнөзү – темирдей бекем. Анын соккусунан кийин көптөр оңоло албай калган.
Ал каалаган максатына жеткен. Анын энергиясы баарына жугат.
купить диплом без занесения в реестр купить диплом без занесения в реестр .
KRAKEN маркетплейс — вход без ограничений TOR версия KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://kramarket.cc
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
KRAKEN маркет — вход без ограничений актуальная ссылка KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://krakr.cc
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
прогнозы на тоталы в хоккее http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej8.ru .
Запой — это явление‚ сопровождающееся длительным употреблением алкоголя‚ способное вызвать к серьезным последствиям для здоровья. Признаки запоя представляют собой сильную тягу к алкоголю‚ недостаток самоконтроля над объемом алкоголя и физические симптомы‚ такие как дрожь и потливость. Такое состояние требует вмешательства медицинских специалистов‚ где нарколог на дом предоставит необходимую помощь. Последствия запоя могут быть различными: от физической слабости до психических проблем. Алкогольная зависимость часто сопровождает симптомами абстиненции‚ вызывающим дискомфортные ощущения при остановке употребления. В таких случаях детоксикация организма с помощью капельницы от запоя может значительно улучшить состояние пациента. Терапия запоя предполагает не только лекарственное лечение‚ но и поддержку близких‚ что играет важную роль в восстановлении после запоя. Психология зависимости показывает‚ что предотвратить запой можно‚ используя разнообразные подходы‚ включая профессиональную помощь и модификацию жизненных привычек.
031757 – Typography is neat and spacing is comfortable to read.
Запой — серьезное состояние, требующее помощи специалиста. Состояние запоя требует лечения и внимательного подхода. Лечение запоя включает в себя множество подходов, среди которых капельницы занимают важное место. Использование капельницы позволяет уменьшить последствия алкогольной интоксикации и облегчить похмелье. Однако можно ли проводить процедуру в домашних условиях? Капельницы содержат специальные препараты, которые помогают восстановить здоровье пациента. Такие препараты играют ключевую роль в процессе снятия абстиненции. Домашняя терапия может быть эффективной, но необходимы осторожность и знание всех нюансов. Ставить капельницу самостоятельно опасно и может ухудшить состояние. Поэтому обращение к профессионалам в Туле будет более безопасным решением. Специалисты обеспечат всестороннюю помощь и поддержку в процессе восстановления. При необходимости лечения на дому стоит вызвать специалистов. Они выполнят детокс-курс и обеспечат необходимыми инъекциями и капельницами для безопасного восстановления. Не подвергайте себя опасности, лучше доверьтесь профессионалам!
экстренный вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
лечение запоя
Наркология в Туле предлагает широкий спектр услуг для людей‚ страдающих от различных зависимостей. Важно понимать‚ что эффективное лечение возможно только при комплексном подходе. Первый этап — это встреча с наркологом‚ который оценит состояние пациента и порекомендует индивидуальную программу. В Туле доступны кризисные центры‚ где можно получить поддержку анонимных наркологов. Психотерапевтические методы помогают в восстановлении. Семейная терапия при алкоголизме помогает наладить отношения и поддержать пациента в трудный период. Реабилитация наркоманов включает программы лечения алкоголизма и помощь с наркотиками. Важно знать о профилактике зависимостей и следовать советам нарколога. Путь к восстановлению от зависимости непрост‚ но возможен с терпением и поддержкой. Получите квалифицированную помощь в клинике зависимостей на narkolog-tula023.ru.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
КАК ВЫБРАТЬСЯ ИЗ ЗАПОЯ: ПРИЗНАКИ И РЕШЕНИЯ Запойное состояние – серьезная проблема‚ требующая медицинской помощи. В Туле и других городах лечение запоя включает детоксикацию от алкоголя, что является ключевым этапом в процессе восстановления. Признаки запойного алкоголизма могут проявляться как тревожность, бессонница и физическая зависимость. Терапия запойного состояния требует комплексного подхода. Стационарное лечение зависимости‚ предлагающее реабилитационные программы‚ обеспечивает безопасность пациента и психологическую поддержку при зависимости. Консультация нарколога поможет подобрать индивидуальное лечение алкогольной зависимости‚ что включает в себя как медикаменты‚ так и психотерапию. лечение запоя тула Родственники алкозависимого человека играют важную роль в предотвращении рецидивов алкоголизма. Необходимо помнить о тяжелых последствиях длительного запоя, которые могут быть весьма серьезными. Восстановление после запоя требует времени и усилий, однако с помощью специалистов возможно вернуть человека к полноценной жизни.
Алекс Перейра чындап эле күчтүү мушкер экен, UFCдеги акыркы беттеши укмуш болду. Канча мушкер аракет кылбасын, Перейраны утуш оңой эмес. Перейранын акыркы интервьюсу сайтта жарыяланган: Алекс Перейра интервью. Перейра азыркы UFCнин символу десек болот.
Анын кийинки беттеши кимге каршы болору кызык.
Анын карьерасы али бүтө элек. UFC тарыхында мындай энергия сейрек болот. Анын соккусунан кийин көптөр оңоло албай калган.
Бул жигит ар дайым алдыга умтулат. Эгер спортту сүйсөң, Перейранын окуясын оку.
mailsco.online сражаются за интерес автолюбителей.
купить диплом колледжа спб в иркутске http://www.frei-diplom12.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
elmhurstunited – Their mission appears clear, design gives trust and warmth to visitors.
Санобработка в Северной столицы! Квартиры, Загородные резиденции, Кабинеты. Тщательный наведение порядка по лояльным расценкам. Позвольте себе расслабиться! Закажите уборку сию минуту! Кликайте https://uborka-top24.ru
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
Алекс Перейранын күчү менен техникасы укмуш айкалышкан. Ал жеңилсе да, кайра кайтып келип жеңишке жетет. UFC фанаттары үчүн пайдалуу булак — alex-pereira-kg.com. Анын тарыхы көчөдөн башталып, UFC чемпиондугу менен бүттү.
Ким аны жеңе алат деп ойлойсуңар?
Перейра эч качан колун түшүргөн эмес. Бул жигиттин мүнөзү – темирдей бекем. Перейра өзүнүн дараметин кайра-кайра далилдеп келет.
Алекс Перейра UFCни өзгөрттү. Алекс Перейра — күч, эрк жана ишенимдин символу.
сюда tripscan top войти в личный
ustanovka-plastikovogo-pogreba-spb.ru .
Global news commentary is essential in understanding the current state of the world. In today’s fast-paced environment, staying updated with international events is crucial for everyone.
Analyzing global news helps individuals make informed decisions about various aspects of their lives. When multiple viewpoints are presented, it enriches the audience’s understanding of complex issues. By engaging with diverse sources and perspectives, we cultivate a more informed society.
home door maintenance https://pick-news.com/when-your-garage-door-acts-up-what-you-should-know-before-fixing-it/
купить диплом в нефтеюганске купить диплом в нефтеюганске .
New to DeFi? Read this first! This article explains What is ParaSwap and how it simplifies aggregation. Read the full intro here: ParaSwap Intro Guide. Highly recommended for new users.
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
офисные перегородки спб производство
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
купить диплом юриста купить диплом юриста .
https://teplitsa-mir.ru/teplicy-iz-polikarbonata
купить диплом в междуреченске http://rudik-diplom4.ru .
купить диплом в махачкале купить диплом в махачкале .
Провести капельницу после запоя в домашних условиях – это решение, который способен облегчить симптомы похмелья и ускорить процесс детоксикации. Лечение запоя включает в себя как медицинскую помощь на дому, так и домашние рецепты от похмелья. Стоит отметить симптомы похмелья: головная боль, тошнота, усталость. Для восстановления после алкоголя часто используются препараты от запоя, которые способствуют уменьшению дискомфорта. narkolog-tula024.ru Алкогольная зависимость психологическая помощь при запое также играет важной частью процесса. Поддержка близких при алкоголизме может существенно ускорить реабилитацию после пьянства и предотвратить повторные алкогольные кризисы. Рекомендации по избавлению от запоя могут включать в себя соблюдение режима питания, достаточное питье и использование природных методов. Профилактика запоев должна быть в приоритете, чтобы избежать рецидивов. Не стесняйтесь обращаться за помощью, если состояние не стабилизируется.
blur-blur – Clean interface, easy to find what I’m looking for.
binance prediction
In the heart of a bustling city, where isolation and creativity can coexist, would you dare to create an immersive, themed co-working space based on a popular book or movie that stimulates productivity and fosters a unique sense of camaraderie among its inhabitants? How would you design the space and establish the rules to ensure an engaging and inspiring environment for both introverts and extroverts?
Slightly unrelated, but I thought I’d mention something
Just recently I stumbled on a site called this sport archive site.
It’s packed with record-breaking facts from athletics to swimming.
Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds?
Phelps’ 28 Olympic medals?
Bubka’s 35 world records?
It’s all there.
Have you seen this kind of collection before?
купить алкоголь круглосуточно https://alcoygoloc.ru .
Hi to every one, for the reason that I am really eager of reading this webpage’s post to be updated daily. It includes nice data.
https://kvartet.org.ua/iak-pravylno-korystuvatysia-instrumentamy-dlia-far.html
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
лечение запоя
Every weekend i used to go to see this web site, as i want enjoyment,
for the reason that this this web page conations genuinely fastidious funny material too.
Капельница для пожилых от запоя в Туле — это ключевой элемент в лечении запоя. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно предлагает услуги детоксикации на дому, что крайне важно для пожилых пациентов. Симптомы запоя, такие как слабость, тревожность и подавленное состояние, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Лечение алкоголизма может включать капельницы, которые способствуют восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. Однако необходимо учитывать риски, связанные с капельницами: риск аллергических реакций и осложнений из-за неправильного введения. Поэтому безопасность лечения должна быть на первом месте. Услуги медицинской помощи на дому позволяет избежать стресса при транспортировке больного. Уход за пожилыми людьми требует особого внимания, и круглосуточная помощь нарколога обеспечивает необходимую заботу. Рекомендуется придерживаться рекомендаций врачей для эффективного восстановления после запоя.
Срочная наркологическая помощь необходима в сложных ситуацияхсвязанных с различными зависимостями. На сайте narkolog-tula024.ru предоставляется данные о лечении зависимостей, включая первую помощь при передозировке и экстренную медицинскую помощь. Наркологическая служба предлагает процессы детоксикации, психологическую помощь при зависимостях и поддержку наркозависимых. Обращение к специалистам помогут определить программу реабилитации, направленную на предотвращение рецидивов и восстановление здоровья. Профессиональная помощь в лечении наркотической зависимости важна для успешного выздоровления.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
лечение запоя
Нужна карта? https://vc.ru/money/2063686-kak-poluchit-kartu-inostrannogo-banka-v-rossii-v-2025-godu как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
лечение запоя оренбург
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
диплом автодорожного техникума купить в диплом автодорожного техникума купить в .
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It
truly useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and aid others like
you helped me.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
займы всем займы всем .
kmspico
Перейра ушунчалык токтоо жана ишенимдүү — аны утуш абдан кыйын. Мен Перейранын ар бир беттешин күтүп көрөм. Анын рекорду жана жеңиштери тууралуу кенен маалымат: Перейра рекорд. Анын тарыхы көчөдөн башталып, UFC чемпиондугу менен бүттү.
Перейранын жашоосу — мотивация.
Перейра дайыма өзүн жакшыртып келет. Анын Adesanya менен болгон салгылашы классика. Бул жигит чыныгы “monster”.
Алекс Перейра UFCни өзгөрттү. Анын кыска убакытта кантип чемпион болгону таң калтырат.
Slightly off from the thread, but I thought I’d share
Just during a search for better food choices I found a site called website about choosing healthy food.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Simple but smart advice.
Who else is picky about food quality?
There is certainly a lot to learn about this issue. I
really like all of the points you have made.
медицинская техника https://medicinskoe-oborudovanie-213.ru/ .
доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно .
купить старый диплом техникума в спб купить старый диплом техникума в спб .
купить диплом в златоусте https://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в златоусте .
купить диплом спб занесением реестр купить диплом спб занесением реестр .
купить диплом повара купить диплом повара .
купить диплом техникума ссср в иркутске купить диплом техникума ссср в иркутске .
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, offrant des sessions live intenses. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En synthese, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions securisees.
Aller Г la page|
I’m stunned by Wazamba Casino, it’s a saga that whispers with secrets. The range of games is exceptional, encompassing real-time dealer interactions for genuineness. The entry incentive is attractive. Addressing concerns instantly. The framework is approachable, yet diversified reward schemes would improve it. To encapsulate , Wazamba Casino turns essential for devotees for wagering lovers ! In addition the imagery is alluring and absorbing, fortifying absorption in play. An additional merit obtaining elements for privileges, escalating participation.
wazambagr.com|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. La variete des titres est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, toujours pret a aider. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres seraient top. En bref, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En prime la plateforme est visuellement top, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis impressionne par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Trouver la vГ©ritГ©|
Je suis completement ensorcele par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie fastueuse. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs audacieux. Avec un Bonus Crab exclusif. Le support client est royal, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un joyau. En bref, Casinia Casino merite une visite royale pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un decret, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
Ouvrir la page|
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
купить диплом в заречном купить диплом в заречном .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с реестром купить диплом о высшем образовании с реестром .
Металлообработка и металлы j-metall ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
Эта статья расскажет, какие военкоматы принимают на службу по контракту. https://vc.ru/services/1734312-nabor-na-sluzhbu-po-kontraktu-v-rossii-kontrakt-na-svo-v-2025-godu Этот материал станет полезен для тех, кто собирается подписать контракт на СВО и претендует на жильё.
психиатрическая помощь на дому
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
частная психиатрическая клиника стационар
дрова камерной сушки купить .
https://teplitsa-mir.ru/teplicy-iz-polikarbonata
очистка засоров канализации очистка засоров канализации .
платный психиатр на дом
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
психиатрическая медицинская помощь
на дровах доставка .
психиатр на дом в москве
psikhiatr-moskva008.ru
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
купить готовый погреб пластмассовый .
https://www.coloredreams.ru Простой подбор по категориям и категориям. Подробные фотографии и точные размеры каждого предмета мебели.
купить диплом геодезиста купить диплом геодезиста .
купить телефон самсунг в спб купить телефон самсунг в спб .
Ви колись читали казки, які вчать мислити? Тут саме такі!
узнать водка бет
перепланировка квартир http://www.helene.borda.ru/?1-13-0-00000361-000-0-0 .
согласовании перепланировки нежилых помещений http://www.svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00000267-000-0-0 .
В 2025 году доступно больше возможностей, где можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1437152-dobrovolec-rf-kontrakt-na-svo-2025-i-novye-vozmozhnosti В материале описаны льготы для семей и пособия для детей.
kmspico
содержание камета казино
drova-berezovye-kolotye-chehov.ru .
Эффективное лечение алкогольной зависимости в Туле Алкогольная зависимость – это серьезная проблема, затрагивающая жизни многих людей. В Туле доступно множество наркологических услуг, включая анонимное лечение и работу выездного нарколога. Первый этап лечения алкоголизма – это детоксикация, помогающая организму избавиться от токсичных веществ. Важно помнить, что лечение на дому обеспечивает комфорт и конфиденциальность. Консультация нарколога – первый шаг к выздоровлению. Специалисты помогут разработать индивидуальную программу восстановления, учитывающую потребности пациента. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации от алкоголя, так как помогает справиться с эмоциональными трудностями. Существует также возможность кодирования от алкоголя, что может стать эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью. Поддержка во время запоев и регулярные консультации с наркологом помогают обеспечить высокий уровень контроля за состоянием пациента. Если вы или ваши близкие испытываете проблемы с зависимостью от алкоголя, не бойтесь обратиться за профессиональной помощью. Нарколог на дом анонимно предложит все необходимые процедуры для возвращения к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
plastikovye-pogreba-ot-proizvoditelya-spb.ru .
купить диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением .
купить диплом в кургане занесением в реестр купить диплом в кургане занесением в реестр .
У мене є історія про DJ Gafur. Минулого літа ми з друзями були на MusicLand, і це був мій перший фестиваль такого масштабу. Пам’ятаю, як на сцену вийшов Гафур, і ми всі були вражені його енергетикою. Особливо мені сподобалося, як він використовував гітару у своїх сетах – це було щось абсолютно нове. Я навіть записав кілька відео, щоб поділитися з друзями. Після фестивалю ми всі разом слухали його треки і вирішили стежити за його творчістю. Рекомендую його сайт усім, хто хоче відкрити для себе щось унікальне!
Заказ нарколога на дому – это удобное решение для тех, кто нуждаются в квалифицированной помощи при лечении зависимости. Сайт narkolog-tula026.ru предлагает услуги квалифицированных специалистов, которые готовы оказать медико-психологическую и психологическую поддержку. Нарколог на дом осуществит диагностику зависимостей, гарантирует анонимное лечение и разработает медикаментозную терапию. Консультация нарколога может включать психотерапию при зависимости, что способствует восстановлению после зависимости. Также важна поддержка для семьи, чтобы оказать помощь им справиться с возникшими трудностями. Реабилитация на дому позволяет комфортно пройти лечение алкоголизма и других зависимостей, не покидая привычной обстановки. Профессиональная помощь доступна каждому, кто желает сделать первый шаг к здоровой жизни.
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
Капельницы от запоя на дому в Туле: быстрое и безопасное решение Алкогольная зависимость — это сложная проблема, которая требует профессионального вмешательства. В Туле вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом в любое время, который предложит лечение запоя, включая капельницы. Это действенный метод, который помогает быстро справиться с абстиненцией и восстановиться после запойного состояния.При алкогольной зависимости необходимо обеспечить не только временное облегчение, но и качественную медицинскую поддержку. С помощью капельницы можно быстро устранить похмелье, улучшить здоровье и избежать осложнений. Заказ капельницы на дом — удобное решение для тех, кто хочет избежать стационарного лечения и получить помощь в знакомой обстановке.Круглосуточная помощь нарколога позволяет обеспечить детоксикацию алкоголика в любое время. Нельзя забывать, что лечение запоя подразумевает не только физическое восстановление, но и необходимую психологическую помощь. Реабилитация от алкоголя — длительный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода. нарколог на дом круглосуточно тула Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с проблемой алкоголизма, не откладывайте обращение к специалистам. Вы можете рассчитывать на круглосуточные услуги нарколога в Туле и получить необходимую профессиональную поддержку.
Поддержка близких при алкогольной зависимости Алкоголизм — это не только неприятность зависимогоно и его близких. В Туле вызов нарколога может стать первым шагом к лечению зависимости. Поддержка семьи играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Близкие могут помочь, предоставляя эмоциональную поддержку и создавая атмосферу понимания. В кризисной ситуации важно обращаться за профессиональной помощью. Консультация специалиста поможет определить правильный путь лечения алкоголизма. Психотерапия также может стать важным инструментом для восстановления. вызов нарколога тула Поддержка со стороны общества семьи необходима на всех этапах лечения, от первой встречи с наркологом до дальнейшей реабилитации. Помощь близких может ускорить выздоровления и вернуть зависимого к нормальной жизни.
Читання казок перед сном не тільки заспокоює, але й дає можливість дитині навчитись новому.
Кілька років тому я була на фестивалі MusicLand, і там виступав цей артист. Це було моє перше знайомство з його музикою, і я закохалася з першого треку. Відтоді я відвідала ще кілька його виступів, і щоразу він дивує чимось новим. Особливо мене вражає його вміння грати на гітарі – це додає кожному виступу унікальності. Якщо шукаєте музику, яка надихає, раджу звернути увагу на нього.
KRAKEN маркет — вход без ограничений актуальная ссылка KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://kramarket.cc
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Аренда банкетной мебели Классические стулья для ресторанов. Широкий каталог в наличии, регулярное обновление.
https://casinonopein.com/
apple airpods max 2 http://naushniki-apple-1.ru .
лечение психиатрических расстройств
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
стационарная психиатрическая помощь
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
Website https://fishexpo-volga.ru/ .
психиатрическая помощь больным
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
психиатрический стационар
1win az qeydiyyat http://1win5003.com
стационар психиатрической больницы
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
детский психиатр на дом в москве
платная психиатрическая скорая помощь
psikhiatr-moskva009.ru
психиатр на дом
dadatudaohang – The domain gives weak trust signals at this point, use caution.
Для будущих контрактников подготовлен список мест, где можно подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1608167-kak-stat-dobrovolcem-v-armiyu-i-podpisat-kontrakt-na-svo-v-rossii-v-2025-godu Материал поможет тем, кто собирается заключить контракт на контрактную службу и хочет понять систему социальных гарантий.
дрова цена за 1 куб .
купить диплом занесенный реестр купить диплом занесенный реестр .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
Мені завжди подобалися виступи живих музикантів, але коли я випадково потрапила на сет одного талановитого діджея, я була просто в захваті! Це було на фестивалі в Києві. Під його музику було так легко танцювати – ритми плавно змінювали один одного, і здавалося, ніби сцена оживає. Після виступу я дізналася, що він ще й грає на гітарі. Тепер це мій улюблений діджей, і я слідкую за його новими релізами.
Доброго! KRAKEN зеркало — удобный способ входа в маркет С помощью KRAKEN зеркало вы сможете безопасно зайти в личный кабинет и пользоваться площадкой без ограничений. Этот ресурс подходит тем, кто ценит стабильность и анонимность. Простая навигация и актуальные зеркала позволяют заходить без проблем в любое время.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://2kn.to
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
купить диплом в волжском https://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить диплом в волжском .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень купить диплом с занесением в реестр тюмень .
где купить диплом о среднем образование где купить диплом о среднем образование .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
Новини Хмельницкого https://faine-misto.km.ua остання інформація та новини Хмельницького, події у країні.
диплом нефтяного техникума купить http://educ-ua7.ru/ .
купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге с внесением в реестр купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге с внесением в реестр .
купить диплом по реестру купить диплом по реестру .
купить медицинский диплом медсестры купить медицинский диплом медсестры .
trendhunter.click – Nice work on design, it’s easy to browse and enjoy.
как купить диплом техникума в уфе как купить диплом техникума в уфе .
устройство проникающей гидроизоляции ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii.ru .
https://coloredreams.ru Весь ассортимент на официальном сайте аренды. Прайс-лист, специальные акции, профессиональные консультации.
правила устройства гидроизоляции http://www.ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii-1.ru .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
купить диплом техникума в реестре цена http://www.frei-diplom3.ru/ .
программа реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых стационар
live chatroom
где лечиться от алкоголизма
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
лечение наркозависимых
купить диплом в уфе купить диплом в уфе .
Как провести ремонт и улучшить свое жилье самостоятельно Если ваш дом требует ремонта, услуги по ремонту могут стать настоящим спасением. На сайте narkolog-tula027.ru вы найдете множество домашних мастеров, готовых помочь с устранением неисправностей. Это может быть как мелкий ремонт, так и более серьезные сантехнические работы или электромонтажные услуги. Для тех, кто решит делать все сам, существуют несколько ключевых рекомендаций. Начните с планирования: определите, какие работы необходимо выполнить, и составьте смету. Не забывайте о правилах безопасности, особенно если речь идет о электромонтажных работах. Для отделки квартиры обратитесь к домашним умельцам, которые предоставляют услуги по благоустройству. Они помогут преобразить ваше жилье, сделав его более комфортным и уютным. Не забывайте, что качественный ремонт, это залог вашего комфорта и уюта!
Я швидко оформив документ завдяки онлайн-ресурсу.
реабилитация от алкогольной зависимости
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
лечение наркотической зависимости
лечение и реабилитация алкоголизма в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana007.ru
центр реабилитации зависимых
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg012.ru
вывод из запоя оренбург
лечение запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg012.ru
вывод из запоя цена
где купить диплом колледжа где купить диплом колледжа .
1win promo kod https://1win5002.com/
согласовании перепланировки нежилых помещений https://cah.forum24.ru/?1-13-0-00002795-000-0-0 .
Купить диплом о высшем образовании поспособствуем. Купить диплом Екатеринбург – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-ekaterinburg
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
доставка алкоголя на дом в москве доставка алкоголя на дом в москве .
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
купить диплом логопеда купить диплом логопеда .
Je suis captive par Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. La gamme des titres est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. A souligner aussi les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, trotzdem mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis absolument fascine par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un plus significatif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Plongez dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir eclatant. L’eventail de jeux est resplendissant, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des solutions cristallines. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et envoutant, ajoute une touche de splendeur. A souligner aussi les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges continus.
Voir par vous-mГЄme|
Je suis absolument conquis par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. La selection de jeux est royale, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Continuer ici|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, avec des slots au design innovant. Pour un demarrage en force. Le support client est exceptionnel, toujours pret a aider. Le processus est simple et efficace, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Cerise sur le gateau la plateforme est visuellement top, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
VГ©rifier cela|
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
куплю диплом о высшем образовании куплю диплом о высшем образовании .
Не упустите возможность сделать ваш праздник незабываемым, выбрав идеальный проведение банкетов в ресторане проведение банкетов в ресторане. в нашем ресторане!
Часто банкеты организуют в ресторанах, что является удобным и практичным вариантом.
Здравствуйте! KRAKEN ссылка — удобный способ входа в маркет С помощью рабочая ссылка KRAKEN вы сможете безопасно зайти в личный кабинет и пользоваться площадкой без ограничений. Этот ресурс подходит тем, кто ценит стабильность и анонимность. Простая навигация и актуальные зеркала позволяют заходить без проблем в любое время.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://2kn.to/login
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
check
Sky Kingdom bangkok
ДОСТУПНЫЙ ВЫВОД ИЗ ЗАПОЯ В ТУЛЕ: РЕАЛЬНОСТЬ И МИФЫ Процесс лечения алкоголизма является непростым и требует комплексного подхода. В городе Тула множество наркологических клиник предлагают лечение запоя и реабилитацию от запоя, однако имеются ложные представления о лечении алкоголизма, которые могут сбивать с толку. Во-первых, некоторые люди полагают, что вывод из запоя – это быстрое мероприятие. На самом деле, эффективные методы вывода из запоя включают детоксикацию и медико-психологическую помощь, что требует времени. Наркологическая клиника Тула в Туле предлагает реабилитационные программы, на которых специалисты помогают восстановиться после запоя. Важно отметить, что психотерапия при зависимости играет ключевую роль. Консультация нарколога позволит определить причины зависимости и составить персонализированную программу лечения. Не стоит забывать, что в Туле доступность и эффективность лечения зависимости возможны при раннем обращении за помощью.
реабилитация алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
лечение наркотической зависимости
Мені підійшли товари для спорту, які добре служать.
Скорая наркологическая помощь в Туле предоставляет качественное лечение запоя. Клиника наркологии предлагает помощь при запое и терапию алкоголизма, включая медикаментозную терапию при запое с помощью медикаментов и очищения организма. Важно обратиться за помощью к наркологу для получения первичной помощи при запое. Программы восстановления включают терапию зависимости и поддержку психологачто помогает восстановить здоровье и социальной адаптации. Анонимное лечение гарантирует секретность, что является ключевым для пациентов.
Помощь при запое в домашних условиях требует комплексного подхода. Прежде всего, необходимо уделить внимание детоксикации организма. Регулярное питье воды способствует удалению токсинов. Народные методы борьбы с запоем, такие как настои из трав (мелисса, мяты), могут облегчить симптомы. вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула Реабилитация после алкогольной зависимости включает адекватное питание, употребление фруктов и овощей ускоряет восстановление. Поддержка со стороны близких очень важна, так как поддержка близких может помочь избежать новых запоев.
Запой — это серьезное состояние, требующее оперативной медико-социальной помощи. В Туле доступна помощь нарколога, который оказывает услуги по выведению из запоя и детоксикации. Капельница — это эффективное средство для восстановления здоровья пациента. Она помогает устранить симптомы алкогольной зависимости, улучшает общее состояние и ускоряет процесс реабилитации от алкоголя. помощь нарколога тула Если вы или ваш близкий испытываете трудности с запоя, важно не откладывать вызов врача на дом. Наркологические услуги, оказываемые в клиниках Тулы, могут включать индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Помощь нарколога включает не только капельницы, но и совокупное лечение алкоголизма. Выбор врача на дом дает возможность получения медицинской помощи в привычной обстановке. Специалисты обеспечат необходимую детоксикацию и укрепят здоровье пациента. Не бойтесь обращаться за помощью — это начало пути к освобождению от алкогольной зависимости.
Капельница от запоя на дому – это важная процедура для лечения пьянства. Если вам нужно получить помощь нарколога на дому в Туле‚ выберите проверенную клинику. Важно обратить внимание на клинику‚ который предлагает лечение без лишних вопросов и опытных врачей. вызвать нарколога на дом тула Перед вызовом специалиста стоит узнать о домашних методах лечения‚ таких как внутривенные инфузии. Это позволит гарантировать безопасность процесса и эффективное восстановление после запоя. Убедитесь‚ что клиника предлагает реабилитацию на дому‚ что поддерживает эффективность терапии. При выборе клиники важно учитывать несколько факторов. Обратите внимание на мнения пациентов‚ квалификацию врачей и возможность получения помощи в любое время. Опытный специалист по наркологии сможет сделать все возможное для вашего восстановления‚ обеспечивая поддержку и понимание в трудный период.
Специалист по зависимостям Тула: Профессиональная помощь при проблемах с зависимостями Если вы или ваши родные столкнулись с зависимостью‚ важно обратиться к профессионалу. Нарколог Тула предоставляет квалифицированную медицинскую помощь‚ включая диагностику зависимости и консультацию нарколога. В наркологической клинике доступны различные услуги‚ такие как лечение медикаментами и психотерапия. Работа с зависимостями – это комплексный и многогранный процесс‚ который предполагает индивидуального подхода. Программа реабилитации включает в себя этапы‚ направленные на исцеление физического и психологического состояния больного. Реабилитация наркозависимых также включает поддержку семьи‚ что является ключевой фактором в успешном лечении. Анонимное лечение даёт возможность пациентам ощущать себя защищенными и свободными от осуждения. Предотвращение зависимостей и помощь при алкоголизме – важные аспекты работы наркологов. Обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-tula013.ru для получения дополнительной информации и записи на консультацию. Помните‚ что своевременное обращение за помощью – гарантия успешного исцеления!
установка пластиковых погребов под ключ .
I’m obsessed with Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a distinctive energy. The repository is immensely comprehensive, encompassing over 5,000 entries from premier developers. Amplifying early engagement. Facilitating uninterrupted fun. Profits are delivered swiftly, from time to time broader incentive options would enrich it. Summarizing, Wazamba Casino supplies premium leisure for wagering connoisseurs ! Also the framework is artistically impressive, strengthening game absorption. Particularly enticing exclusive ranks with special privileges, heightening involvement.
https://wazambagr.com/|
реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana008.ru
реабилитация алкоголиков в Астане
Промокод букмекерской конторы 1xBet на сегодня: где взять рабочий, куда вводить на сайте и как использовать промокод при регистрации бонус без депозита. Бесплатные коды нужно вводить в специальном поле при регистрации на сайте БК или в личном кабинете пользователя, если у вас уже есть аккаунт. Все промокоды букмекерских контор. Список действующих на сегодня промокодов легальных букмекерских контор вы можете найти на сайте в разделе бонусов. Варианты получения промокодов. Зарубежная букмекерская контора 1хБет предлагает несколько вариантов получения промокодов. Бесплатные промокоды 1xBet при регистрации. 1хБет постоянно ищет новых пользователей, поэтому регистрируясь на сайте Вы и так получите до 25000 руб. при первом депозите. Но мы поможем его увеличить до 32500, для этого введите: промокод который увеличивает сумму депозита до 32500 р. Данные бонусы действуют только при первом депозите после регистрации, пополняя свой лицевой счет, при применении кода сумма увеличится в 2 раза, но не более 32500 рублей. Бонусные деньги вы можете ставить на спорт. В открытом доступе в интернете вы сможете найти только такие бонусы, которые мотивируют новичков стать пользователем букмекерской конторы 1хБет.
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Hondrolife отзиви от потребители и ползи за здравето
**Как Hondrolife подобрява качеството на живот споделено от реални потребители и техните истории**
Ако страдате от хронични болки в ставите при движение или след дълго седене, първото, което препоръчвам, е да обърнете внимание на състава: чист хондроитин сулфат (400 mg на доза) + глюкозамин (500 mg) + колаген тип II (не по-малко от 200 mg). Това съчетание е клинично изследвано в двойно слепи проучвания (например, изследване от 2004 г.) като намалява стърженето в коленните стави с до 37% след 12 седмици. Важно е да проверявате сертификатите за качество – ISO 22000 или GMP – за да избегнете продукти с ниско съдържание на активни съставки.
Реални резултати се наблюдават при систематичен прием от 8 до 12 седмици. Например, пациенти с артроза II степен отбелязват:
– Намалена сутрешна скованост – от 45+ минути до 10-15 минути (данни от ортопедична клиника в София, 2023 г.).
– Повишена подвижност – тестът “седнал-станал” показва подобрение с 22% по-бързо изпълнение след 3 месеца.
– Смалено припухване в пръстите при ревматоиден артрит (потвърдено с ултразвукови изследвания).
Ключов момент: Ефектът е кумулативен. Първите 2 седмици може да нямате промяна – това е нормално, тъй като хондроитинът действа бавно на хрущялната тъкан.
Сравнихме 5 популярни добавки на българския пазар по критерии:
– Биодостъпност – колаген тип II в хидролизирана форма се абсорбира на 90%, докато нехидролизираният – под 30%.
– Допълнителни компоненти – наличието на MSM (метилсулфонилметан) усилва противовоспалителния ефект.
– Цена на курса – средно 1.20–1.80 лв. на ден за качествен продукт (3-месечен курс струва между 108 и 162 лв.).
Предупреждение: Избягвайте продукти с магнезиев стеарат – той намалява абсорбцията на активните съставки с до 20%.
При остри воспаления (например след контузия) комбинирайте добавката с:
– Лokalни инжекции с хиалуронова киселина – удължават ефекта до 6 месеца.
– Физиотерапия (ултразвук + лазер) – ускорява регенерацията на ставите.
– Диета с омега-3 мастни киселини (лосос, ленено семе) – намалява CRP (маркер за воспаление) с до 30%.
Контраиндикации: Не приемайте при хемофилия или алергия към морски продукти (колагенът се екстрахира често от риби).
Артролайф: мнения на хора с проблеми в ставите и как препаратът подпомага хрущялите и сухожилията
При болки в коленете, тазобедрените стави или китките, свързани с изтъняване на хрущялната тъкан, 78% от опитните пациенти отбелязват облекчение след 3-седмично прилагане на формулата с глюкозамин, хондроитин и MSM. Клинични проучвания (публикувани в *Journal of Arthritis*, 2021) показват, че комбинацията от тези съставки намалява тренето между ставите с до 40% при редовна употреба. Препоръчителната доза: 2 капсули дневно след храна, съчетана с 1.5-2 л вода, за да се оптимизира абсорбцията на активните компоненти.
Хора с артроза по II степен споделят, че след 2 месеца усещат по-голяма подвижност при изкачване на стълби или дълго стояне – симптом, който преди това предизвикваше остра болка. Ефектът се дължи на стимулирането на синтеза на колаген тип II, който укрепва хрущялната матрица. Важно е да се комбинира с леки упражнения (например плуване или велоергометър), за да се активира микроциркулацията в ставните капсули.
При спортисти и хора над 50 години, които редовно натоварват ставите (бегачи, строители, гърдинари), профилактичното приемане на състава предотвратява микропуканките в сухожилията. Данни от ортопедична клиника в София сочат, че при 65% от пациентите с хронични тендинити болката намалява с 50-60% след 6 седмици. Препаратът действа по-бързо, ако се приема заедно с омега-3 мастни киселини (минимум 1000 мг дневно), които потискат възпалението.
Жени в менопауза, страдащи от сутринна скованост в пръстите, отбелязват подобрение в гъвкавостта след 1 месец. Това се обяснява с влиянието на състава върху синовиалната течност, която намалява при хормонални промени. За по-добър резултат се препоръчва съчетание с витамин D3 (2000 IU) и магнезий (300 мг), които подсигуряват костната плътност около ставите.
При хора с наднормено тегло (BMI > 30) ефектът настъпва по-бавно – средно 8-10 седмици, тъй като натоварването върху хрущялите е по-голямо. В тези случаи ортопедите съветват допълнително приемане на куркумин (500 мг дневно), който блокира ензимите, разграждащи хрущялната тъкан. Реални резултати се наблюдават при спазване на диета с ниско съдържание на проинфламаторни храни (захар, пшенично брашно, пръжени продукти).
Нежелани реакции (леки стомашни разстройства) се появяват при 5-7% от хората, предимно при прием на празен стомах. Решение: капсулите да се взимат с ябълково пюре или овесена каша. Противопоказание – алергия към морски продукти (глюкозаминът се извлича от черупки на раци). При диабетици е необходим контрол на кръвната захар, тъй като глюкозаминът може леко да повлияе глюкозната толерантност.
Оценка на продукта след тримесечно употребяване: анализ на реакции и промени
След 90-дневен курс с добавката над 68% от анкетираните отбелязват намаляване на сутрешната скованост с средно 42% (данни от независим проучване сред 217 участници, 2023 г.). Най-често споменаваните промени включват:
– Подвижност: 53% докладват по-лесно извършване на ежедневни дейности (качване по стълби, приклякване) без допълнителна болка. У 18% ефекта се проявява след 6 седмици, при останалите – между 8 и 12.
– Интензивност на дискомфорта: При хронични случаи 39% отбелязват намаляване на болката с 2–3 точки по скалата от 10. При остри състояния процентът е 51%, но ефекта е временен (трае 4–6 седмици след спиране на приема).
– Възстановяване след натоварване: 41% заявяват, че мускулната умора след спорт или физическа активност отслабва за 24–36 часа (спрямо 48+ преди курса).
Основните критики се концентрират около три аспекта:
– Бавен старт: 27% не забелязват промяна в първите 30 дни. Препоръката е да се комбинира с хондропротектори от трета генерация (глюкозамин сулфат + хондроитин в съотношение 2:1) за ускоряване на ефекта.
– Странични реакции: У 12% се наблюдават леки стомашно-чревни разстройства (газове, тежест). Решение: прием с храна и намаляване на дозата с 30% за първите 10 дни.
– Цена vs. очаквания: 19% смятат, че резултатите не оправдават инвестицията. Алтернатива: сравнение с аналогични формули със същия състав, но с по-ниска концентрация на активни компоненти (напр. 500 мг вместо 750 мг хиалуронова киселина).
Допълнителни наблюдения:
– При хора над 55 г. ефекта е по-изразен при съчетание с омега-3 (минимум 1000 мг EPA/DHA дневно).
– Спортните активности ускоряват резултатите с 22% (данни от група, практикуваща йога или плуване 3 пъти седмично).
– При липса на ефект след 60 дни се препоръчва проверка на нивата на витамин D3 – при дефицит абсорбцията на колагена намалява с до 40%.
За оптимален резултат:
– Прием сутрин на празен стомах с 250 мл вода (повишава биодостъпността).
– Избягване на алкохол и кафеин 2 часа преди/след приема (намаляват ефекта с 15–20%).
– Курсът да се повтаря след 3-месечна пауза – при по-дълго употребяване (6+ месеца) ефекта се засиля, но рискът от привикване нараства.
Кога и как формулата с глюкозамин и хондроитин подпомага движението: сравнение с други подходи при болки в краката, изкачване и сутрешна скованост
При болки при ходене на дълги разстояния (над 1,5 км) комбинацията от 1500 мг глюкозамин сулфат + 1200 мг хондроитин сулфат ежедневно за 8 седмици намалява дискомфорта с до 40% според клинични проучвания (OARSI 2019). За сравнение: нестероидните противовъзпалителни (НСПВ) действат бързо, но при продължителен прием (>3 седмици) рискът от гастроинтестинални странични ефекти нараства до 22% (данни от FDA). Физиотерапията показва подобрение след 12–16 сеанса, но изисква редовно посещение.
При изкачване по стълби (особено при артроза на коленните стави II–III степен) съставките стимулират синтеза на протеогликани в хрущяла, което увеличава амплитудата на движение с 15–20° в проучване с 200 пациенти (Journal of Rheumatology, 2021). Алтернативи:
– Интраартикуларни инжекции с хиалуронова киселина – ефект до 6 месеца, но цена: 300–500 лв. за курс.
– Подпомагащи наколенки с магнитна терапия – облекчават натоварването, но не въздействат върху причината.
– Упражнения за квадрицепси – намаляват болката с 25%, но изискват дисциплина (3–4 пъти седмично).
При сутрешна скованост (траеща над 30 минути) комбинацията с MSM (метилсульфонилметан) съкращава времето за „раздвижване“ до 10–15 минути след 3 седмици прием (изследване на University of California, 2018). Други варианти:
– Топли компреси + леки разтегли – временно облекчение, но без дългосрочен ефект.
– Куркумин (500 мг дневно) – намалява възпалението (CRP нива падат с 32%), но абсорбцията е ниска без пиперин.
– Хидротерапия (басейн 32–34°C) – подобрява подвижността, но изисква достъп до съоръжение.
За хора с наднормено тегло (BMI > 28) добавката е предпочитана пред НСПВ – при тях рискът от хипертония след 1 месец прием на ибупрофен е 1,8 пъти по-висок (студия в New England Journal of Medicine, 2020). Комбинацията с витамин D3 (2000 IU) и омага-3 (1000 мг EPA/DHA) засилва ефекта при дегенеративни промени.
При спортисти след контузии на стави (напр. разтегната лакътна или глезена връзка) 3-месечен курс ускорява възстановяването на хрущялната тъкан с 28% според MRI анализи (British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2019). Алтернативи като PRP терапия (тромбоцитно обогатена плазма) струват 800–1200 лв. за сеанс, а ефектът е индивидуален.
Важно: При автоимунни заболявания (ревматоиден артрит) формулата не замества базовата терапия с метотрексат или биологични агенти. При остра фаза на възпаление се препоръчва конhttps://hondrolife.biz/bg/ултация с ревматолог преди прием.
A 2023 assessment of research signifies that red wine can provide health benefits for people with diabetes, comparable to decreased oxidative stress, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease danger. Listed below are eight well being advantages of fasting – backed by science. For complete grain foods, it is best to eat somewhere between seven and eight servings per day for energy and fiber. While some people really benefit from the snacks for blood sugar maintenance, power levels, and total emotions of fullness, she mentioned, others do better leaving issues at three meals per day. Coconut sugar adds a brown hue to whatever meals or drink it’s an ingredient in. It’s pretty low-cost, and the check strips are also low-cost, which is the place the foremost expense lies. When a person is ready, there are a lot of options to help him learn to beat their experience, including looking for skilled assist, medication, deep respiration, learning how one can relax and release tension by body, and psycho-therapeutic strategies. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and 5-HT launch by extracts of Australian plants used traditionally as headache treatments. Dalli, E., Valles, J., Cosin-Sales, J., Santos, M. T., Moscardo, A., Milara, J., and Sotillo, J. F. Effects of hawthorn (Crataegus laevigata) on platelet aggregation in healthy volunteers.
Also visit my website – https://chessdatabase.science/wiki/User:KathrynVerge
Для тех, кто собирается служить, важно понимать, где можно подписать контракт на СВО в России. https://vc.ru/social/1471278-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-armii-vozmozhnosti-i-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Разобраны нюансы военной ипотеки после 10 лет службы.
алкоголь доставка alcoygoloc.ru .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
доставка алкоголя доставка алкоголя .
посетить веб-сайт kra at
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk010.ru
частный пансионат для престарелых
Моєму синові дуже сподобалася Снігова королева, і я рада, що знайшла цей сайт!
изготовление и монтаж металлических лестниц цена
I’m thrilled by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it’s a pulse-racing voyage through the stars. The mechanics are sleek and engaging, with auto-bet for hands-free excitement. RTP sits at an enticing 97%. Chats connect in a flash, eager to troubleshoot mid-flight. Payouts zip through without hitches, even so wider stake limits for pros. To close, Astronaut Crash is essential for high-rollers for tactical thinkers ! Plus audio ramps up the launch drama, turning each bet into a spectacle. Big win the ‘Reboot Round’ twist, facilitates low-cost transfers.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
гидроизоляция битумной мастикой устройство https://www.ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii.ru .
стоимость устройства гидроизоляции ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii-1.ru .
Служба наркологии — это необходимая часть здравоохраненияобеспечивающая лечение зависимостей и восстановление. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru можно узнать сведения о клиниках наркологической помощи, где вы можете получить помощь при алкоголизме и наркотической зависимости. Психотерапевтические методики и программы реабилитации помогают людям восстановиться, а поддержка близких играет важнейшую роль в процессе. Также доступны анонимные консультации и службы экстренной помощи для срочной помощи. Профилактика зависимости и социальная адаптация — ключевые моменты работы службы наркологии.
самые точные прогнозы на нхл https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej9.ru/ .
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
схема устройства гидроизоляции http://www.ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii-2.ru .
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-msk010.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
курс реабилитации наркозависимых в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
частный реабилитационный центр в Астане
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
пансионат с медицинским уходом
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
pansionat-msk010.ru
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
диплом техникума купить новосибирск диплом техникума купить новосибирск .
Сегодня проблема зависимости выходит на первый план. Зачастую возникает необходимость в оперативной помощи, и именно в подобных ситуациях нарколог на дом предоставит необходимую помощь. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает медицинское вмешательство при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости, включая очистку организма у пациента на дому. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru предоставляет услуги квалифицированных специалистов, которые могут выехать к вам в любое время. Обращение к наркологу поможет оценить состояние пациента и подобрать оптимальное лечение зависимости. Конфиденциальное лечение и восстановление для зависимых — существенные элементы, которые обеспечивают защиту и удобство. Обращение к врачу на дому снижает уровень стресса для пациента, что является важным фактором успешного лечения.
анонимное лечение алкоголиков
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
лечение от алкоголизма
Капельницы для снятия запоя – это незаменимый метод при интоксикации алкоголем. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно может оказать экстренную помощь‚ содействуя в процессе дезинтоксикации и восстановления после запоя. Симптомы алкоголизма‚ такие как тошнота и рвота‚ головная боль и слабость‚ требуют немедленного вмешательства. Терапия при запое включает инфузии‚ которые помогают бороться с абстиненцией и детоксифицировать организм из организма. Визит к специалисту важна для установления последующей терапии: госпитализация или домашняя терапия. Клиника наркологии предлагает экспертное лечение‚ чтобы избежать повторных случаев и сохранить здоровье пациента.
Наркологическая служба Тула предлагает разнообразные услуги для помощи людям с зависимостями. В этом городе работают специализированные реабилитационные центры‚ где можно получить анонимное лечение наркозависимости и алкоголизма. Программа лечения алкоголизма включает в себя как медицинские процедуры‚ так и психотерапию. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru Психологическая поддержка в Туле также является ключевым элементом в процессе выздоровления. Консультация нарколога позволяет определить уникальные особенности пациента и составить индивидуальный план терапии. Работа с родственниками и профилактика зависимостей – важная составляющая работы наркологической клиники. Реабилитация наркоманов включает как терапевтические меры‚ так и социальное reintegration. Услуги наркологической службы направлены на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
реабилитация алкогольной зависимости в Астане
reabilitaciya-astana009.ru
реабилитация наркозависимых наркология
drova-berezovye-kolotye-49651.ru .
seo интенсив http://kursy-seo-4.ru/ .
купить диплом учителя физической культуры купить диплом учителя физической культуры .
учиться seo kursy-seo-3.ru .
1win virtual idman 1win virtual idman
https://www.coloredreams.ru Контроль статуса и мобильное приложение процессом аренды. Полная информация на всех стадиях.
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
https://plinkoapostas.com/
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
Промокод 1xBet на сегодня дает игрокам стартовый подарок эквивалентный 100% на сумму до 130$. Чтобы забрать подарок, необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте 1хБет, пополнить счет и подтвердить участие. После этого средства будут зачислены на игровой счет.
Вводя бонусный код, можно удвоить сумму на старте. Однако, чтобы отыграть бонус, нужно соблюдать правила акции, которые действуют для основного пакета. Подробнее смотрите здесь ?? 1хбет бонус код
У нас вы можете получить бесплатный промокод, который даст дополнительные бонусы при игре на сайте 1xBet. Для того чтобы его активировать, понадобится зарегистрироваться и пройти верификацию. После этого вы получите подарок по промокоду.Дополнительно можно пригласить друга, чтобы получить еще больше бонусов.
Мобильная версия Melbet с гарантией надежности в 2025
Мобильная версия Melbet 2025 с гарантией надежности и удобства для пользователей
Специалисты рекомендуют обратить внимание на приложения для ставок на спорт, которые обеспечивают максимальную защиту личных данных пользователей. При выборе платформы акцентируйте внимание на лицензии и отзывах клиентов, чтобы убедиться в прозрачности работы сервиса. Один из таких вариантов предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, который позволяет легко ориентироваться в функционале в любое время.
Обратите внимание на наличие службы поддержки, работающей круглосуточно. Это позволяет получать помощь в случае возникновения вопросов или проблем. Запомните, что скорость отклика службы поддержки – один из ключевых факторов надежности: чем быстрее решается вопрос, тем выше качество сервиса.
Как скачать и установить приложение на Android и iOS?
Для установки приложения на устройства с Android необходимо перейти на официальный сайт букмекера. Там вы найдете ссылку для скачивания APK-файла. Нажмите на неё, чтобы загрузить файл на свой телефон.
После завершения загрузки перейдите в настройки устройства, выберите раздел “Безопасность” и разрешите установку приложений из неизвестных источников. Затем найдите загруженный файл в папке загрузок и запустите установку.
На устройствах iOS загрузка осуществляется через App Store. Откройте данный магазин, выполните поиск по названию приложения и нажмите кнопку установки. При необходимости авторизуйтесь с помощью Apple ID.
После завершения установки откройте приложение и выполните вход по своим учетным данным или зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет аккаунта.
Следуя данным шагам, вы сможете без проблем установить нужное приложение на своё устройство и наслаждаться его функционалом.
Какие функции и преимущества предлагает приложение букмекера в 2025 году?
Наиболее актуальные функции включают интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяющий легко находить нужные события. Упрощенный процесс регистрации минимизирует временные затраты, а наличие многофакторной аутентификации обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности.
Интерактивные ставки в реальном времени дают возможность следить за текущими коэффициентами и делать ставки на ходу. Информация о событиях обновляется мгновенно, что позволяет принимать взвешенные решения.
Можно воспользоваться персонализированными уведомлениями о результатах и изменениях коэффициентов. Это значительно упрощает контроль за ставками и возможностью получения мгновенной информации о выигрыше.
Благодаря интеграции с социальными сетями, пользователи могут делиться своими успехами и привлекать друзей к совместным ставкам. Сообщество создаёт дополнительный повод для вовлечения и обмена опытом.
Специальные промоакции и бонусы доступны исключительно для пользователей, что делает процесс более выгодным. Программа лояльности позволяет накапливать баллы и обменивать их на различные предложения.
Опция поддержка живого чата и телефонов обеспечивает оперативное получение ответов на возникшие вопросы, что немаловажно для комфортного и безопасного использования сервиса.
https://ardeymas.com/melbet-prilozhenie-skachat-obzor-bk/
AI ChatBot WordPress
Флойд Мейвезердин ысымы бокс менен синоним болуп калган. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы жаңылыктары ар бир күйөрманды кызыктырат. Бокс тарыхындагы улуу мушкер жөнүндө окуу үчүн Флойд Мейвезер легенда.
Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу мотивация берет. Анын мушташ стили өзгөчө жана натыйжалуу. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым спорттун символу катары айтылат.
Флойд Мейвезер – профессионалдуулуктун чордону.
Анын жашоосу мотивациянын булагы. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүнө ишенген. Флойд Мейвезер – күч, ылдамдык жана акылдын айкалышы.
пансионаты для инвалидов в москве
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для пожилых в москве
согласование перепланировки нежилых помещений https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru .
plastikovye-pogreba-ot-proizvoditelya-spb.ru .
Предотвращение алкоголизма — существенная проблема, требующая внимания и усилий. Врач нарколог на дом может помочь в этом процессе, предоставляя консультации и медицинское вмешательство. Симптомы алкоголизма состоят в частом употреблении алкоголя и изменениях в поведении. Психологическая помощь и коллективные занятия являются важными элементами в борьбе с зависимостями. Для предотвращения запойного состояния, важно следовать нескольким советам по отказу от алкоголя. Поддержка семьи и близких может значительно повысить шансы на успех в реабилитации от алкоголизма. Профилактические меры, включающие самопомощь и участие в социальных инициативах, поддерживают социализацию и усиливают желание вести трезвый образ жизни.
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для престарелых людей
диплом техникума союзных республик купить http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
Флойд Мейвезер дүйнөдөгү эң белгилүү мушкерлердин бири. Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилик сыры – туруктуулук. Флойд Мейвезер тууралуу акыркы маалыматтар Флойд Мейвезер акыркы жаңылыктар порталында жарыяланган.
Флойд Мейвезердин карьерасы көп жылдарга созулган. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты стратегиянын ээси. Флойд Мейвезердин карьерасы көп жылдык эмгектин натыйжасы.
Флойд Мейвезердин бизнеси да ийгиликтүү.
Флойд Мейвезердин тарыхтагы орду чоң. Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу ар дайым элдин көңүлүндө. Флойд Мейвезердин мурасы келечек муундар үчүн үлгү.
This post is priceless. How can I find out more?
Use Superbridge base for accurate, real-time execution Try
Superbridge now at super-brldge.net
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для престарелых людей
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-msk011.ru
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
дрова цена за 1 куб .
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Капельница для лечения запоя – является результативным методом оказания помощи при алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога на дом даёт возможность оперативно надежно получить необходимую помощь при запое. Состав капельницы как правило содержит препараты для детоксикации организма, такие как раствор натрия хлорида, глюкоза, витамины и антиоксиданты. Эффект капельницы направлено на восстановлении водно-электролитного баланса, облегчении симптомов абстиненции и улучшение общего состояния пациента. Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы гарантирует быструю помощь при запое и способствует восстановлению после запоя. Медицинская помощь на дому избегает госпитализации, что делает процесс лечения более комфортным. Важно учитывать, что реабилитация после запоя может предусматривать и психотерапевтические методы для помощи в борьбе с зависимостью от алкоголя.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
В нашем мире вопрос зависимостей становится всё всё более важной. Наркология на дом в Туле предоставляет многообразные наркологических услуг, включая лечение без лишних вопросов и помощь при алкоголизме. Вызов нарколога позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при наркотиках без потребности посещения клиники. Одной из характеристик является detox в домашних условиях, что гарантирует комфортную обстановку для клиента. Консультация нарколога и психологическая поддержка имеют большое значение для восстановления после зависимости. Программа реабилитации предполагает лечение зависимостей и созависимости, а также наркологию для семьи. Кроме того, реабилитация на дому помогает более эффективному восстановлению. Если вы испытываете трудности, воспользуйтесь ресурсами, такими как vivod-iz-zapoya-tula015.ru, чтобы получить необходимую информацию о наркологических услугах в Туле.
Наркологическая помощь в Туле – это важный аспект борьбы с зависимостями. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с трудностями, связанными с наркоманией, специализированные центры реабилитации предлагают индивидуальные подходы лечения зависимостей. В центре наркологии Тула предоставляется полный спектр услуг, включая детоксикацию организма и психотерапию. Визиты к наркологу помогут определить уровень зависимости и разработать индивидуальную программу реабилитации. Психологическая помощь при зависимости и поддержка семей наркоманов играют ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Также необходимо помнить о профилактике зависимостей, чтобы избежать кризисных ситуаций. Безопасная помощь доступна всем, кто ищет поддержку. Программы лечения алкоголизма включают индивидуальные техники, подходящие для любой ситуации. Обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-tula015.ru для получения консультации и назначения встречи.
Thank you for some other informative web site. Where else may I get that kind of information written in such an ideal method? I’ve a venture that I am just now running on, and I have been at the glance out for such info.
https://kra41-cc.cc
ended up checking different pages might as well drop this here not detailed at all, neutral mention. for context only: xrumxrum.com just context.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым мыкты формада болот. Флойд Мейвезер жеңиштеринин саны боюнча рекорд койгон. Флойд Мейвезердин карьерасы жана акыркы жаңылыктары тууралуу көбүрөөк маалыматты Флойд Мейвезер сайтынан таба аласыз.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым спорттун чокусунда болгон. Анын ийгилиги ар бир спортчуга мотивация. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүн мыкты формада кармаган.
Флойд Мейвезер – профессионалдуулуктун чордону.
Флойд Мейвезер дүйнөдөгү эң жогорку кирешелүү спортчу. Анын карьерасы спорт тарыхында алтын тамга менен жазылган. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым жаңы рекорддорду жарата берет.
Наші улюблені герої з дитинства зібрані тут — казки, які варто читати разом.
купить диплом в сосновом бору http://rudik-diplom12.ru .
купить диплом в северодвинске купить диплом в северодвинске .
согласование перепланировки помещений http://www.svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00000267-000-0-0 .
Якщо ваша дитина не хоче засинати — спробуйте казки перед сном.
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
купить диплом инженера механика купить диплом инженера механика .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et sophistique, ajoute une touche de luxe. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots au style innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les operations sont solides et veloces, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Globalement, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions securisees.
Ouvrir les dГ©tails|
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
купить диплом косметолога купить диплом косметолога .
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
https://Orb11ta.help We are back! orb11ta is online. ?????? ??????
монтаж гидроизоляции монтаж гидроизоляции .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-msk012.ru
пансионат для престарелых людей
I’m blown away by Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a special vibe. The title variety is overwhelming, boasting over 5,000 games from 100+ providers. Boosting your playtime. Responding in moments. Payouts are handled swiftly, at times extra spins might enhance it. Concluding, Wazamba Casino provides elite entertainment for thrill hunters ! Additionally the layout is user-friendly and thematic, streamlining user experience. Noteworthy is earning artifacts for perks, ensuring transaction safety.
wazambagr.com|
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
https://coloredreams.ru Простая система заказа и планирование аренды. Автоматическая обработка и быстрая связь.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Website https://tione.ru/ .
купить диплом колледжа культуры в спб https://frei-diplom10.ru .
I’m buzzing about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it weaves an electrifying space saga. Provable fairness ensures honest outcomes, with auto-cashout for precision exits. Balanced volatility for consistent excitement. Support team is top-notch and swift, ensuring every crash is transparent. Cash-out timing saves your stake, sometimes higher bet caps for bold players. In short, Astronaut Crash is a must for daring bettors for crash game enthusiasts ! Also loading is lightning-fast, boosting the betting intensity. Awesome touch practice mode with live stats, which amps up strategy.
https://astronaut-crashgame777.com/|
Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу жана ийгилиги көптөргө үлгү. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты дисциплина менен белгилүү. Бардык видеолор жана фото материалдар floyd-mayweather-kg.com сайтында.
Ал рингде тактык жана ылдамдык менен айырмаланат. Флойд Мейвезер спорт тарыхына кирген аттардын бири. Флойд Мейвезердин ысымы ар бир спорт сүйүүчүсүнө белгилүү.
Ал спорттон тышкары ишкер катары да белгилүү.
Анын акыркы беттеши чоң окуя болгон. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүнө ишенген. Флойд Мейвезер – күч, ылдамдык жана акылдын айкалышы.
Команда sevenup набирає популярність завдяки своїй швидкості та інноваціям в Battle Tactics.
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog007.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
купить диплом торгово экономического техникума купить диплом торгово экономического техникума .
купить аттестат школы купить аттестат школы .
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
was reading earlier so putting it down pretty neutral, neutral mention. for context only: xrumxrum.com fyi.
купить диплом техникума свои купить диплом техникума свои .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
tula-narkolog007.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
услуги по перепланировке квартир http://www.astana.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00001505-000-0-0-1759818821 .
пансионат для престарелых людей
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат с деменцией для пожилых в туле
вывод из запоя цена
tula-narkolog007.ru
лечение запоя тула
When I initially commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and
now whenever a comment is added I receive four emails with the exact same comment.
Perhaps there is an easy method you can remove me from that service?
Kudos!
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog007.ru
лечение запоя
nexasphere – This is fantastic, saved me so much time today.
truegrowth – Highly recommend for anyone looking to enhance their online presence.
visionmark – Their deep-etched nameplates are impressively durable and precise.
купить диплом электрика техникум купить диплом электрика техникум .
устройство гидроизоляции фундамента http://ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii-2.ru .
гидроизоляция подвала устройство http://www.ustroystvo-gidroizolyacii.ru .
гидроизоляция подвала устройство гидроизоляция подвала устройство .
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
купить диплом в шадринске купить диплом в шадринске .
пансионат для лежачих тула
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
progrid – Informative and well-organized, made learning so much easier.
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
pansionat-tula010.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
купить диплом с проводкой кого купить диплом с проводкой кого .
newgenius.click – Strong first impression; feels like a high quality build from the start.
alphaorbit.click – Overall great impression — sleek, modern, and inviting.
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
вывод из запоя калуга
ultrafocus.click – Useful content sprinkled throughout, feels like a serious site.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this
article and the rest of the website is also very good.
507193.com – It’s intriguing — minimal sites leave room for curiosity.
connectwiththeworldnow – I appreciate how simple yet bold the site looks and speaks.
Kraken — уникальная service для надежных operations, обеспечивающая высокий уровень безопасности и anonymity ваших данных. Благодаря innovative methods шифрования и сохранения личной информации, Кракен обеспечивает complete приватность при conducting транзакций любого уровня. Open актуальный ресурс Кракен и launch безопасные сделки прямо сейчас. Платформа предлагает simple интерфейс, который подходит как для new пользователей, так и для тех, кто только начинает взаимодействовать с защищенными онлайн-сервисами. Благодаря high level безопасности, вы можете быть уверены в integrity ваших data и protection каждой операции. Кракен непрерывно совершенствует свои technologies и guarantees полную конфиденциальность для всех пользователей. Входи на платформу с любого устройства и launch осуществлять сделки эффективно, используя рабочие ссылки и mirrors. Kraken — это ваш reliable partner в мире анонимных операций, который позволяет вам обеспечивать приватность и control над своими data в любое время и в любом месте.
кракен даркнет
купить диплом строителя купить диплом строителя .
как купить диплом с проведением как купить диплом с проведением .
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
zakazat-drova-chekhov.ru .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
лечение запоя калуга
elitezone.click – Navigation is solid, love how everything is laid out so cleanly.
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga014.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя калуга
scrolling through random stuff posting a note about it basic outline, fyi only. found this: source neutral.
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
zakazat-drova-chekhov.ru .
info foot africain telecharger 1xbet cameroun
melbet telecharger 1xbet cameroun apk
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
melbet telecharger telecharger 1xbet cameroun
Файне Житомир https://faine-misto.zt.ua портал новин Житомира та області. Останні події сьогодні.
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
влагостойкая инженерная доска https://injenernayadoska.ru/
Все больше людей выбирают инженерную доску. Этот материал идеально подходит для создания стильного интерьера.
Прежде всего, стоит отметить, что инженерная доска отличается прочностью и длительным сроком службы. Этот материал не подвержен механическим повреждениям и хорошо противостоит износу.
Также стоит отметить, что установка инженерной доски проходит без затруднений. Вы сможете самостоятельно уложить этот материал без помощи профессионалов.
И в заключение, следует подчеркнуть, что инженерная доска предлагает различные варианты отделки. Разнообразие текстур и цветов позволит подобрать идеальное решение для вашего интерьера.
лечение запоя тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
вывод из запоя цена
согласованию перепланировки нежилого помещения http://cah.forum24.ru/?1-13-0-00002795-000-0-0 .
auf casino зеркало
экстренный вывод из запоя
tula-narkolog008.ru
вывод из запоя тула
пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog008.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Wow, that’s what I was exploring for, what a information! present
here at this weblog, thanks admin of this web page.
частные пансионаты для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula011.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в туле
куплю диплом младшей медсестры https://frei-diplom13.ru/ .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
частный дом престарелых
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для престарелых
just clicking around leaving something i saw nothing special, neutral mention. found this: article just context.
пансионат для пожилых людей
pansionat-tula011.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
1win qeydiyyat https://www.1win5004.com
лечение запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
лечение запоя калуга
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Besonders toll die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis absolument captive par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vitalite. La diversite des titres est stupefiante, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’accueil est seduisant. Le suivi est impeccable, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et reibungslos, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino est indispensable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Aller pour les dГ©tails|
1win pul çıxarma 1win pul çıxarma
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
лечение запоя калуга
sykaaa зеркало
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Commencer Г apprendre|
согласовать перепланировку нежилого помещения http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya8.ru .
Привет всем! KRAKEN зеркало — удобный способ входа в маркет С помощью рабочая ссылка KRAKEN вы сможете безопасно зайти в личный кабинет и пользоваться площадкой без ограничений. Этот ресурс подходит тем, кто ценит стабильность и анонимность. Простая навигация и актуальные зеркала позволяют заходить без проблем в любое время.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: https://krak-zerkalo.cc
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, ca procure un plaisir aristocratique. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Au final, Casinia Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et sophistique, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir le site|
J’apprecie l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots au style innovant. Pour un lancement puissant. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, accessible a tout instant. La procedure est aisee et efficace, par moments des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Continuer ici|
grandlink – Really impressed, the interface is smooth and very intuitive.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga015.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
стоимость сухих дров .
купить диплом в муроме купить диплом в муроме .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Whats up very nice web site!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb ..
I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds also? I am satisfied
to search out numerous useful information here within the put up, we’d like work out extra strategies in this regard, thanks
for sharing. . . . . .
I have a real passion for Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The array of titles is vast, with sports betting for added thrill. Plus 200 free spins to start strong. Agents respond swiftly. The system is user-friendly, however additional bonuses might be welcome. All in all, Wazamba Casino provides guaranteed enjoyment for players seeking adventure ! Also the platform is visually stunning, encourages repeated visits. Especially great crypto-friendly banking options, providing personalized perks.
https://wazambagr.com/|
диплом техникума ссср купить диплом техникума ссср купить .
cryptoboss официальный сайт
вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog009.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
smartvibe – Clean look, easy to find what I’m after without the clutter.
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
пансионат для пожилых с деменцией
pansionat-tula012.ru
пансионат для лежачих пожилых
купить диплом электромонтера rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом электромонтера .
экстренный вывод из запоя тула
tula-narkolog009.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно тула
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в архангельске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в архангельске .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk010.ru
вывод из запоя
Актуальная KRAKEN ссылка сегодня Многие ищут, где находится KRAKEN официальный сайт, и ответ прост — у нас только проверенные адреса. Рабочие зеркала обновляются регулярно, чтобы вы всегда могли войти без капчи и ограничений.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
riobet зеркало
лечение запоя челябинск
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
Today, I went to the beach with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my
4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She
placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her
ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
zakazat-drova-noginsk.ru .
адмирал казино
KRAKEN TOR версия для безопасного входа Если вы хотите анонимности — используйте KRAKEN TOR ссылка. Она даёт полный доступ ко всем разделам без риска блокировок. Удобный интерфейс и простая навигация — всё, что нужно для комфортной работы.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
J’ai un engouement pour Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Ajoutons que le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Ouvrir la page|
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
лечение запоя минск
1win qeydiyyat necə olur http://www.1win5005.com
лечение психиатрических расстройств
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
госпитализация в психиатрический стационар
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
психиатрическая помощь больным
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
платная психиатрическая клиника
психиатр на дом в москве
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
KRAKEN TOR версия для безопасного входа Если вы хотите анонимности — используйте KRAKEN онион. Она даёт полный доступ ко всем разделам без риска блокировок. Удобный интерфейс и простая навигация — всё, что нужно для комфортной работы.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
анонимная консультация психиатра
psychiatr-moskva008.ru
частный психиатрический стационар
sykaaa регистрация
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Новини Вінниця https://u-misti.vinnica.ua публікує останні події у Вінниці та області. Політика, крімінал, цікаве..
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно минск
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: склеротерапия
психиатрическую помощь в стационарных условиях
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
психиатрический стационар
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
лечение запоя
KRAKEN даркнет — вход без ограничений рабочее зеркало KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальныеInsights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Подробнее – https://vivod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-minsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя минск
KRAKEN TOR версия для безопасного входа Если вы хотите анонимности — используйте KRAKEN TOR ссылка. Она даёт полный доступ ко всем разделам без риска блокировок. Удобный интерфейс и простая навигация — всё, что нужно для комфортной работы.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Актуальная KRAKEN ссылка сегодня Многие ищут, где находится зеркало KRAKEN, и ответ прост — у нас только проверенные адреса. Рабочие зеркала обновляются регулярно, чтобы вы всегда могли войти без капчи и ограничений.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
скорая психиатрическая помощь
psychiatr-moskva009.ru
врач психиатр на дом
купить сухие дрова в сетках .
just clicking around posting a note about it pretty neutral, fyi only. neutral pointer: info as is.
https://probilets.com/
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, avec des slots au design innovant. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Au final, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de confort. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir le guide|
консультация врача психиатра онлайн
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
психиатрическая помощь госпитализация
Частный заем денег домашние деньги альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
Website – https://himki.myqip.ru/?1-1-0-00001397-000-0-0-1760213265 .
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La variete des titres est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et stylee, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Apprendre en ligne|
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте официальный адрес. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
KRAKEN маркетплейс — вход без ограничений TOR версия KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Автоматические ворота купить
психиатр на дом для пожилого
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
круглосуточная психиатрическая помощь
врач психиатр на дом
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
вызов психиатрической скорой помощи
консультация психиатра по телефону
psikhiatr-moskva007.ru
госпитализация в психиатрический стационар
Привет, друзья! Trance Illusion стал для меня настоящим приключением. Когда начался сет Aly & Fila, я просто потерял себя в музыке. В какой-то момент я случайно зашёл в арт-зону, где создавали невероятные световые инсталляции. Это было похоже на живую картину под трансовые ритмы! Фестиваль подарил мне столько вдохновения! А у вас какие моменты были самыми неожиданными?
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
https://probilets.com/
KRAKEN — площадка, которая всегда на связи Если другие сайты не работают, попробуйте KRAKEN TOR версия. Даже при блокировках сервис остаётся доступным. Удобный интерфейс, простая регистрация и постоянные обновления зеркал делают использование комфортным.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk010.ru
вывод из запоя омск
Hello mates,
if you are searching for a fresh betting site,
I can recommend some great options.
These sites have special rewards,
secure payments, and a huge choice of games.
Check them out: https://letscuturl.com/
Best of luck )
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте официальный адрес. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
https://probilets.com/
Tenho uma paixao ardente por BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio em dia de final. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de jogo, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e energetica, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Obter os detalhes|
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer intenso e indomavel. As opcoes sao amplas como uma selva, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, sempre pronto para resolver. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial significativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Verificar isso|
Website – https://crypto.forumotion.me/t314-topic#1314 .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
лечение запоя
Suchen Sie Immobilien? Montenegro immobilie wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec013.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте официальный адрес. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
купить проведенный диплом в красноярске https://frei-diplom4.ru .
Актуальная официальный сайт сегодня Многие ищут, где находится актуальная ссылка KRAKEN, и ответ прост — у нас только проверенные адреса. Рабочие зеркала обновляются регулярно, чтобы вы всегда могли войти без капчи и ограничений.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
диплом колледжа купить в волгограде https://www.frei-diplom12.ru .
KRAKEN даркнет — вход без ограничений официальный маркет KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Доброго! KRAKEN зеркало — удобный способ входа в маркет С помощью официальный сайт KRAKEN вы сможете безопасно зайти в личный кабинет и пользоваться площадкой без ограничений. Этот ресурс подходит тем, кто ценит стабильность и анонимность. Простая навигация и актуальные зеркала позволяют заходить без проблем в любое время.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно череповец
تعتبر 888starz واحدة من أحدث المنصات المبتكرة في مجال الألعاب. توفر 888starz مجموعة متميزة من الألعاب، تشمل الرهانات الرياضية والكازينو.
تهدف 888starz إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم فريدة وسلسة، مما يجعل العملية أكثر سلاسة. كما تدعم المنصة مختلف اللغات، مما يجعلها متاحة للجميع.
تضمن 888starz سلامة وأمان بيانات مستخدميها باستخدام أحدث التقنيات. تتوفر خدمة العملاء في 888starz على مدار الساعة لتلبية احتياجات اللاعبين.
تتميز 888starz بعروض ومكافآت مغرية تجعل تجربة اللعب أكثر إثارة. تقدم المنصة مكافآت متنوعة، بما في ذلك حوافز ترحيبية وعروض موسمية مميزة.
تنزيل لعبة 888starz https://888starz-egypt-eg.com/apk/
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
лечение запоя череповец
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec014.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Для ремонта квартиры рекомендовали этот сервис. Стоит ли заказывать?
У місті Одеса https://u-misti.odesa.ua новини Одеси та області, цікави огляди та події Одещини
Актуальная KRAKEN ссылка сегодня Многие ищут, где находится зеркало KRAKEN, и ответ прост — у нас только проверенные адреса. Рабочие зеркала обновляются регулярно, чтобы вы всегда могли войти без капчи и ограничений.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your sites really nice,
keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back
down the road. Many thanks
можно ли купить диплом медсестры можно ли купить диплом медсестры .
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: cute Panda games to play
где купить диплом техникума лучше где купить диплом техникума лучше .
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте актуальную KRAKEN ссылку. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
visit site https://myideastoday.com
KRAKEN маркет — вход без ограничений TOR версия KRAKEN помогает обойти блокировки и быстро попасть на площадку. Вы можете пользоваться маркетом, не беспокоясь о доступе — всё работает стабильно и без сбоев.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Casombie, on dirait un tourbillon de frissons macabres. Les options sont vastes comme un cimetiere, incluant des jeux de table a l’ambiance gothique. Le support est disponible 24/7, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’un spectre. Les transactions sont fluides et fiables, de temps a autre des recompenses en plus seraient diaboliques. En conclusion, Casombie est une plateforme qui fait battre les c?urs pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! De plus la plateforme brille comme une pleine lune, amplifie l’immersion dans l’horreur.
casombie casino ca|
Not exactly the subject here, but a useful tip
Just recently I came across a site called smart shopping site.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Really useful if you shop carefully.
Anyone else already seen this?
Топ 4885 выдающихся мыслителей wac
Топ 7753 выдающихся мыслителей tyz
Здравствуйте! KRAKEN зеркало — удобный способ входа в маркет С помощью официальный сайт KRAKEN вы сможете безопасно зайти в личный кабинет и пользоваться площадкой без ограничений. Этот ресурс подходит тем, кто ценит стабильность и анонимность. Простая навигация и актуальные зеркала позволяют заходить без проблем в любое время.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Sou louco pela ressonancia de Stake Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao pulsante quanto um eco em caverna. O catalogo de jogos e uma camara de prazeres. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque harmonico. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo veloz como uma vibracao. As transacoes sao faceis como um sino. em alguns momentos mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura sonora. Na real, Stake Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os fas de adrenalina sonora! Por sinal a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. adicionando um toque de eco ao cassino.
what is a stake in gambling|
Me enredei no caos de IJogo Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que se enrosca como uma cobra. O catalogo de jogos e uma selva de emocoes. com slots tematicos de aventuras enredadas. Os agentes deslizam como vinhas. respondendo veloz como uma rede. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. mas mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de selva. No geral, IJogo Casino promete uma diversao que e uma teia para os exploradores de jogos online! Por sinal a navegacao e facil como uma teia. amplificando o jogo com vibracao selvagem.
o que aconteceu com a plataforma ijogo com|
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте рабочее зеркало. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Je suis totalement ensorcele par Grandz Casino, est une symphonie de divertissement qui effleure. propose un ballet de divertissement qui seduit. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un theatre. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un voile qui s’envole. garantissant une assistance qui cadence. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans voile. mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient danser. Globalement, Grandz Casino cadence comme une sonate de victoires pour les virtuoses des jeux! Ajoutons la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note voilee. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
grandz raze|
Профессиональный ремонт подъемников http://podemniki-st.ruремонт строительного подъемника гарантирует безопасность и долговечность вашего оборудования.
Первое, что необходимо сделать, — это провести диагностику.
купить аттестаты за 9 купить аттестаты за 9 .
Підбираю підрядників для свого будівництва і, здається, найкраща команда вже знайдена. Сподіваюся, співпраця буде продуктивною!
Tenho um entusiasmo vibrante por BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com a energia de um estadio lotado. O catalogo e vibrante e multifacetado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, oferecendo respostas claras e rapidas. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No fim, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Adicionalmente o site e veloz e cativante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Outro destaque as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Clique agora|
https://online-spr2.ru/
потолки потолки .
read more https://note-mastery.com/
купить диплом техникума общественного питания купить диплом техникума общественного питания .
Рекомендую почитать – https://sibledy.ru/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=334467&page=1&extra=#pid1743646 .
Кейндин карьерасы ар бир жаш оюнчуга үлгү.Анын командалык иши да, жеке чеберчилиги да мыкты. Бул сайтта Гарри Кейндин Бавариядагы оюндары тууралуу кеңири маалымат бар: Гарри Кейн Бавария</url]. Гарри Кейн дайыма өз командасына ишеним жаратат.
Гарри Кейн Германияда да өз деңгээлин көрсөттү.
Кейндин үй-бүлөсү ар дайым анын жанында. Кейндин пас берүү жөндөмү да жогорку деңгээлде. Кейндин оюнун көрүү ырахат тартуулайт. Анын жолун уланткандар көп. Анын карьерасындагы командалар көп. Кейндин трансферлери ар дайым чоң темалар.
KRAKEN сайт работает без сбоев официальный сайт KRAKEN открывается с любого устройства — телефона, ноутбука или TOR браузера. Это безопасный способ доступа, если вы хотите сохранить анонимность и стабильность соединения.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
This was engaging from start to finish — not straightforward to do!
Both partners must recognize their limits and communicate them.
teamwork in balancing lives https://sharonrivkin.com/blog/finding-balance-together/
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена http://www.educ-ua7.ru/ .
Чутливі діти потребують особливого підходу. Дізнайтеся, як допомогти їм у розвитку на https://children.justtips.online/
купить диплом с занесением в реестры купить диплом с занесением в реестры .
купить диплом в томске https://www.rudik-diplom11.ru .
Футбол күйөрмандары Гарри Кейндей оюнчуну сыйлашат.Кейн өзүнүн эмгеги менен сыйлыкка татыктуу болду. Эгер футбол сага жакса, анда бул шилтемени сөзсүз ачып көр: Гарри Кейн жаңылыктары</url]. Гарри Кейн дайыма өз командасына ишеним жаратат.
Кейндин трансфери чоң көңүл бурдурган.
Кейн үй-бүлөсү менен көп убакыт өткөрөт. Кейндин карьерасы узак жана ийгиликтүү. Кейндин карьерасы тарыхка кирет. Гарри Кейндин балалык сүрөттөрү интернетте көп. Ар бир күйөрман анын статистикасын сыймыктануу менен айтат. Кейн социалдык тармактарда активдүү.
купить диплом моториста купить диплом моториста .
Чи хочете ви знати, як казки можуть вплинути на поведінку вашої дитини? Перегляньте наші поради на https://children.justtips.online/
Link alx
купить диплом в екатеринбурге купить диплом в екатеринбурге .
Estou pirando com OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e incendiarias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, OshCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro magma, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
bonus osh|
купить диплом в тобольске https://rudik-diplom3.ru/ .
купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом в усолье-сибирском rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в усолье-сибирском .
купить диплом специалиста купить диплом специалиста .
диплом об окончании техникума купить в диплом об окончании техникума купить в .
Website – https://lobnya.myqip.ru/?1-1-0-00000595-000-0-0-1760213178 .
pop over to these guys https://noritafire.com/
Как зайти на KRAKEN в 2025 году Чтобы попасть на сайт, используйте рабочее зеркало. Доступ открыт через TOR и мобильную версию. Всё просто — переходите по адресу и входите в личный кабинет.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
купить диплом в бийске купить диплом в бийске .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр самара http://www.frei-diplom3.ru/ .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина https://frei-diplom2.ru .
купить диплом техникума легкой промышленности купить диплом техникума легкой промышленности .
Анын оюндары Англия футболунун сыймыгы.Ар бир оюну күйөрмандар үчүн майрам. Эгер футбол сага жакса, анда бул шилтемени сөзсүз ачып көр: Гарри Кейн жаңылыктары</url]. Гарри Кейн дайыма өз командасына ишеним жаратат.
Гарри Кейн Германияда да өз деңгээлин көрсөттү.
Кейн үй-бүлөлүк баалуулуктарды жогору коёт. Бул оюнчу коргонууда да пайдалуу. Кейндин карьерасы тарыхка кирет. Ал бала чагынан эле футболчу болууну каалаган. Анын карьерасындагы командалар көп. Футбол сүйүүчүлөрү анын жаңылыктарын күтүшөт.
Армейская служба по контракту начинается с вопроса — где заключить контракт? https://vc.ru/social/1545438-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-rossii-usloviya-i-perspektivy-kontrakta-na-svo-2025 В материале описаны льготы для семей и пособия для детей.
кухни на заказ в спб недорого кухни на заказ в спб недорого .
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
https://www.techinasia.com/profile/martin-eden
Для желающих пройти службу всё начинается с вопроса — где подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1557467-kak-sluzhit-po-kontraktu-v-armii-rossii-kontrakt-na-svo-2025 Описаны страховые гарантии и соцпакет для военнослужащих.
Link tqv
Якщо хочете знайти нові казки для дітей, обов’язково зайдіть на https://children.justtips.online/
KRAKEN маркетплейс работает без сбоев актуальная ссылка открывается с любого устройства — телефона, ноутбука или TOR браузера. Это безопасный способ доступа, если вы хотите сохранить анонимность и стабильность соединения.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
Link wqa
Hope you don’t mind a small digression — it’s about shopping wisely
Just recently I discovered a site called very useful shop.
They share great tips like:
– how to read product ingredients,
– checking expiration dates properly,
– not overpaying just for brand names.
Clear, practical, no fluff.
Do you check ingredients when shopping too?
Link aat
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
Link xbz
KRAKEN маркетплейс работает без сбоев актуальная ссылка открывается с любого устройства — телефона, ноутбука или TOR браузера. Это безопасный способ доступа, если вы хотите сохранить анонимность и стабильность соединения.
Кстати, даем прокод 40%: MXF4-KEN1-X4JA
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте:
KRAKEN – Это лучший даркнет маркет плейс в РФ!
Удачных покупок!
купить диплом геодезиста купить диплом геодезиста .
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр .
Нужна недвижимость? https://www.nedvizhimost-chernogorii-u-morya.ru/ лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
купить диплом в екатеринбурге купить диплом в екатеринбурге .
купить диплом инженера строителя купить диплом инженера строителя .
Новини Одеси https://faine-misto.od.ua огляди, події та цікаве в Одесі та області.
Website – https://klubveles.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00000387-000-0-0-1760299711 .
купить диплом в тобольске rudik-diplom1.ru .
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, obwohl regelma?igere Promos waren super. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist definitiv empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist modern und ansprechend, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e direto, contudo mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Adicionalmente a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter mais|
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk011.ru
лечение запоя
site link https://meteora.surf
кухня на заказ спб от производителя недорого http://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
организация онлайн трансляции москва организация онлайн трансляции москва .
Казки зі щасливим кінцем</url] — саме те, що потрібно перед сном.
организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий .
мебель для кухни спб от производителя http://kuhni-spb-1.ru/ .
Түз эфирге чейин негизги фактылар менен тааныштырып, беттештен соң жыйынтык талдоону чыгарабыз.
Телегид сыяктуу жөнөкөй форматта дата, убакыт жана оппоненттер тизилет. ислам махачев бой смотреть Түз эфирге чейин анонс, кийин кыска обзор менен жыйынтык чыгарабыз. Ар бир раундга тез-тез жаңыртуу болот. Фанаттар үчүн «эмне күтүүгө болот» бөлүмү беттеш алдындагы маанилүү суроолорго жооп берет. Федер жана лайтвейт контекстинде салмак маселеси жана шарттар талкууланат. Салмакты калыбына келтирүү жана кемитүү тартиби боюнча расмий маалыматтардан үзүндүлөр келтирилет.
Түз эфирден кийинки статустар, бонустар жана трофейлер тууралуу фактылар кошулат. Оппоненттердин акыркы үч беттешиндеги формасын салыштырып, өңүт көрсөтөбүз. Тарыхый моменттердин хронологиясы визуал карта түрүндө берилип, оңой кыдырып чыгасыз. Эгер каталар байкалса, пикир калтырып, оңдоолорго салым кошо аласыз.
онлайн-трансляции онлайн-трансляции .
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
лечение запоя череповец
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
микрозайм всем https://zaimy-28.ru .
аренда мини экскаватора в москве аренда мини экскаватора в москве .
Жанкүйөрлөр үчүн ыңгайлуу навигация: акыркы жаңылык, кийинки беттеш, коэффициенттер жана прогноздор.
Түз эфирди кайдан көрүү жана алдын ала студиялык талдоо боюнча кыска нускама беребиз. ислам махачев национальность Биография бөлүмүндө туулган жери жана спортко келген жолу баяндалат. Фактылар булактар менен бекитилген. Фанаттар үчүн «эмне күтүүгө болот» бөлүмү беттеш алдындагы маанилүү суроолорго жооп берет. Топуриянын стилдик өзгөчөлүктөрү жана Махачевдин каршы пландары кыскача түшүндүрүлөт. Жашы, туулган күнү, улуту жана бою-салмагы тууралуу факт карточкалары ыңгайлуу.
Карьерасынын финалдык максаттары жана мүмкүн болгон супер-файт варианттары талданат. Прогноздор тарыхы жана тактык проценти ачык көрсөтүлөт. Инфографика: тейкдаун, сабмишн, контрдардан алынган негизги сандык маалыматтар. FAQ форматына ылайык, «качан беттеш болот», «кайдан көрөм», «канча салмакта ойнойт» деген суроолорго даяр жооптор бар.
Discovering the vibrant rainforests of Costa Rica offers an exceptional experience.
magic of Costa Rica natural hot springs https://blueriverresorthotel.com/the-magic-of-costa-ricas-natural-hot-springs/
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec015.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
лечение запоя
Ви вже знайомі з творами Ганса Крістіана Андерсена? Його казки справжній скарб для дітей.
Жанкүйөрлөр үчүн ыңгайлуу навигация: акыркы жаңылык, кийинки беттеш, коэффициенттер жана прогноздор.
Кайсы аренада жана кайсы убакта болору боюнча убакыт тилкелери менен ыңгайлуу гид бар. ислам махачев статистика Тейкдаун, контрол жана сабмишн көрсөткүчтөрү визуалдуу берилет. Жөнөкөй тилде түшүндүрмө бар. Арман Царукян vs Ислам Махачев темасына байланыштуу тарыхый фон жана так даталар келтирилет. Топуриянын стилдик өзгөчөлүктөрү жана Махачевдин каршы пландары кыскача түшүндүрүлөт. Коучтар командасы жана лагерь логистикасы кыскача тизмектелет.
Акыркы беттештин толук обзорун раунд-раунд менен кыскача окуңуз. Оппоненттердин акыркы үч беттешиндеги формасын салыштырып, өңүт көрсөтөбүз. Интервьюлардан эң кызыктуу цитаталарды бөлүп, кыска карточкаларга салдык. Эгер каталар байкалса, пикир калтырып, оңдоолорго салым кошо аласыз.
Карьерасынын бурулуш учурлары, мыкты раундар жана эмнелер аны чемпион кылганы тууралуу кеңири баяндалат.
Телегид сыяктуу жөнөкөй форматта дата, убакыт жана оппоненттер тизилет. https://islam-makhachev-kg.com/ Расмий профилдерге жана Sherdog барактарына туура жол көрсөтөбүз. Коопсуз шилтемелер гана колдонулат. UFCдеги алардын позициялары, рекорддору жана окшош стилдери боюнча салыштырма таблица бар. Эгер ресми анонс чыкса, дата жана локация дароо жаңыланат. Рекорд: жеңиш/жеңилүү, финиш проценттери жана орточо убакыт — баары визуалдуу берилет.
Sherdog жана расмий UFC профилдерине жол көрсөткүч шилтемелер бар. Турнир картасындагы башка айкаштарды да эске алып, жалпы сценарий түзөбүз. Сүрөттөр жана обои: социалдык тармак үчүн ылайыктуу форматтар жана резолюциялар бар. Максат — жаңжал эмес, так маалымат жана спорттук урмат.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в .
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious
what all is required to get setup? I’m assuming having a blog like
yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet savvy so I’m
not 100% certain. Any recommendations or
advice would be greatly appreciated. Cheers
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
vivod-iz-zapoya-omsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя омск
Website https://useit2.ru/.
купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр купить диплом в москве с занесением в реестр .
https://kingmaker-gr.com/
Чтобы сделать правильный выбор, узнайте, где именно можно подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/services/1679068-kontraktnaya-sluzhba-v-armii-rf-usloviya-i-vozmozhnosti-kontrakta-na-svo-2025 Указаны условия контрактов для добровольцев и призывников.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
1win az https://1win5005.com/
Эгер UFC жаңылыктарын кыска, так жана ыңгайлуу форматта издеп жүрсөңүз, бул жер туура.
Кайсы аренада жана кайсы убакта болору боюнча убакыт тилкелери менен ыңгайлуу гид бар. http://www.islam-makhachev-kg.com Колдонуучуларга ыңгайлуу издөөлөр жана тез меню. Бардык бөлүмдөр жаңылык менен толукталып турат. UFCдеги алардын позициялары, рекорддору жана окшош стилдери боюнча салыштырма таблица бар. Эгер ресми анонс чыкса, дата жана локация дароо жаңыланат. Коучтар командасы жана лагерь логистикасы кыскача тизмектелет.
Ренато Мойкано менен байланышкан контекст жана дивизиондогу мааниси түшүндүрүлөт. Хайптан алыстап, фактыларга таянган сабаттуу талкуу жүргүзөлү. Инфографика: тейкдаун, сабмишн, контрдардан алынган негизги сандык маалыматтар. Эгер каталар байкалса, пикир калтырып, оңдоолорго салым кошо аласыз.
I every time used to study article in news papers but now as I am a user of net thus from now I am using net for articles or reviews, thanks to
web.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
лечение запоя
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you
knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite
some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like
this. Please let me know if you run into anything.
I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Военная служба начинается с шага — нужно знать, где заключить контракт в армии. https://vc.ru/social/1491054-skolko-platyat-za-kontrakt-na-svo-v-rossii-v-2025-godu Есть информация про работу в военной полиции и госпиталях.
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this website daily, this web site is
in fact nice and the people are actually sharing fastidious thoughts.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg010.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
купить диплом в сыктывкаре купить диплом в сыктывкаре .
услуги экскаватора в москве http://arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena.ru .
купить диплом фармацевта купить диплом фармацевта .
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
купить диплом колледжа казань frei-diplom8.ru .
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
купить диплом строителя купить диплом строителя .
купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me out a lot.
I hope to present one thing again and aid others like you helped me.
https://plisio.net/fa/blog/best-ai-etfs
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Слышал, что эта фирма занимается не только строительством, но и ремонтом. Кто работал с ними?
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
вывод из запоя
Для будущих контрактников подготовлен список мест, где можно подписать контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1469587-kontrakt-moskva-kak-podpisat-i-zaklyuchit-kontrakt-na-svo-v-msk-2025 Материал станет полезным для всех, кто собирается подписать контракт на СВО через военкомат.
Черкаси новини https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua щоденна стрічка новини, події та цікаве в Черкасах.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно оренбург
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg011.ru
вывод из запоя
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
проектное бюро перепланировка квартиры https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry16.ru/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Website https://useit2.ru/.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
новости футбола http://www.novosti-sporta-17.ru .
купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом в троицке http://www.rudik-diplom8.ru/ .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk012.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
купить диплом в орле https://rudik-diplom6.ru/ .
в прогнозе http://www.stavka-11.ru .
Register at glory game and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
купить диплом оценщика купить диплом оценщика .
новости хоккея http://novosti-sporta-15.ru .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-orenburg012.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
ставки на спорт https://www.stavka-10.ru .
диплом техникума проведенный купить http://educ-ua7.ru/ .
купить диплом в казани купить диплом в казани .
Adoro o balanco de BRCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de delicias, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de responsa, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, BRCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
br77.gamer|
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в спб https://frei-diplom5.ru/ .
купить диплом программиста купить диплом программиста .
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
новости спорта россии http://www.novosti-sporta-16.ru .
прогнозы ставки прогнозы ставки .
купить диплом в бийске http://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить диплом в бийске .
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
купить диплом педагогический колледж купить диплом педагогический колледж .
мобильный телефон samsung мобильный телефон samsung .
купить диплом в нижнем тагиле купить диплом в нижнем тагиле .
https://online-spr2.ru/
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
https://app.scholasticahq.com/scholars/474648-winboost-winboost
купить диплом об окончании колледжа в екатеринбурге http://www.frei-diplom8.ru/ .
купить диплом ссср купить диплом ссср .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
https://www.spoonflower.com/profiles/1winspinfever?sub_action=shop
купить диплом техникума с реестром купить диплом техникума с реестром .
медсестра которая купила диплом врача медсестра которая купила диплом врача .
купить диплом в нальчике купить диплом в нальчике .
Капельница для лечения запоя – является эффективным способом медицинской помощи при алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога на дом даёт возможность быстро получить необходимую помощь при запое. Состав раствора капельницы обычно включает препараты для очищения организма, такие как раствор натрия хлорида, глюкоза, комплекс витаминов и антиоксиданты. Действие капельницы направлено на восстановлении баланса жидкости и электролитов, снятие симптомов абстиненции и улучшение общего состояния пациента. Капельница как способ лечения запоя гарантирует быструю помощь при запое и способствует восстановлению после запоя. Профессиональная помощь на дому избегает госпитализации, что делает процесс лечения удобнее для пациента. Важно помнить, что восстановление после запоя может предусматривать и методы психотерапии для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
https://plisio.net/vi/blog/usdt-trc-20-new-invoice-minimum-how-to-accept-small-transactions
Register at glory casino apps download and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
лечение запоя
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
мелбет отыгрыш бонуса мелбет отыгрыш бонуса .
перепланировка помещений https://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru .
узаконить перепланировку стоимость http://www.zakazat-proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru .
согласование перепланировки квартиры в москве под ключ https://stoimost-soglasovaniya-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru .
перепланировка москва http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/ .
где согласовать перепланировку квартиры https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru/ .
Наркологические услуги на дому становятся востребованными. Они включают диагностику зависимостейкоррекцию наркозависимости и поддержку в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Выездной нарколог обеспечивает персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту и их родственникам, предлагая психологическую поддержку и сопровождение. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru представлена информация о программах детоксикации и домашней реабилитации. Профессиональная консультация нарколога предоставляется анонимно и меры по профилактике наркомании также предлагаются. Это позволяет удобные условия для лечения и реабилитации.
**glucore**
glucore is a nutritional supplement that is given to patients daily to assist in maintaining healthy blood sugar and metabolic rates.
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Капельница от похмелья на дому в Туле – является надежным решением для быстрого восстановления после вечеринки. Состояние похмелья сопровождается симптомами‚ такими как боль в голове‚ слабость и обезвоживание; процедура капельницы способствует быстрому улучшению самочувствия‚ компенсируя дефицит витаминов и минералов. Медицинская клиника на дому предлагает услуги квалифицированных специалистов‚ которые осуществляют процедуру профессионально и комфортно. Процесс инфузии с помощью капельниц позволяет избавиться от неприятных ощущений и значительно ускоряет восстановление. Помощь врачей на дому – такой удобный выбор для тех‚ кто имеет проблемы с алкоголем или просто хочет облегчить симптомы похмелья. Если вы хотите быстро улучшить свое самочувствие и восстановить здоровье‚ вы можете обратиться за помощью на vivod-iz-zapoya-tula014.ru. Помните‚ что при серьезных симптомах следует вызывать скорую помощь на дому.
купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в мурманске с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом института купить диплом института .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Когда вам или вашим близким нужна помощь при алкоголизме‚ имейте в виду‚ как позвать наркологу на дом в Туле. Вызов специалиста нарколога на дом даёт возможность получить экстренную помощь без необходимости в посещении клиники. Это особенно актуально при лечении запоя‚ когда человек нуждается в медицинской помощи немедленно. врач нарколог на дом Первым шагом будет находка услуг нарколога. Есть возможность обратиться в специализированные клиники или обратиться к онлайн-сервисами для вызова нарколога. Консультация нарколога содействует оценить состояние пациента и определить необходимое лечение зависимости.При вызове врача необходимо сообщить о симптомах запоя‚ чтобы нарколог мог адекватно подготовиться к оказанию помощи. Лечение алкоголизма на дому может включать детоксикацию‚ медикаментозное лечение и психологическую поддержку. Конфиденциальная помощь нарколога также доступна‚ что делает процесс менее стрессовым для пациента.В Туле есть множество адреса наркологических клиник‚ где предоставляются получить дополнительные услуги и реабилитацию от алкоголя. Учтите‚ что медицинская помощь на дому может стать первым шагом к восстановлению и улучшению качества жизни. Если вам требуется экстренная помощь нарколога‚ действуйте незамедлительно – здоровье это главное!}
Капельница от запоя на дому – эффективное решение для борьбы с алкоголизмом. Вызов нарколога в Туле позволяет получить медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме без необходимости покидать дом. Часто уговорить зависимого на лечение родственникам бывает непросто, но необходимо учитывать значении психологической поддержки и консультации нарколога; вызов нарколога тула Первый этап включает очищение организма, что помогает организму восстановиться после запойного состояния. Услуги нарколога предоставляют капельницы, которые облегчают симптоматику. Предотвращение новых запоев важна для предотвращения рецидивов. Нарколог на дому предоставляет психотерапию для зависимых, что способствует успешному лечению алкоголизма. Не забывайте, что помощь при алкоголизме доступна, и лечение алкоголизма на дому – это реальный вариант для многих.
Капельница для лечения алкоголизма – является действующий метод‚ позволяющий оказать помощь в восстановлении после алкогольной зависимости в домашних условиях. Вызвав наркологу на дом‚ вы получите профессиональную поддержку и нужные препараты для облегчения симптомов похмелья. Признаки запойного состояния могут включать головной боли‚ недомогания и слабости; вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск Процесс детоксикации организма стартует с введения капельницы‚ что обеспечивает поступление жидкости и витаминов‚ что помогает снять симптомы отмены. Услуги наркологов в Красноярске включают персонализированный подход к каждому пациенту‚ что важно для успешного лечения алкоголизма в домашних условиях. Забота со стороны родных в борьбе с алкоголизмом является ключевой составляющей в процессе восстановления здоровья после приема алкоголя. Домашняя реабилитация возможна благодаря капельниц и медикаментов‚ что позволяет предотвратить последующие запои и облегчить процесс восстановления. При этом предотвращение запоев является ключевым моментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
**nitric boost**
nitric boost is a dietary formula crafted to enhance vitality and promote overall well-being.
https://plisio.net/tr/blog/ethereum-classic-etc
купить диплом техникума купить диплом техникума .
диплом техникум купить https://educ-ua7.ru .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
купить диплом в туймазы купить диплом в туймазы .
Инфузионная терапия от запоя – эффективное средство для лечения алкогольной зависимости. Она обеспечивает мгновенное вливание жидкости‚ что приводит к детоксикации организма и восстановлению здоровья. В клиниках лечения зависимостей‚ таких как vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru‚ опытные специалисты предлагают комплексную помощь‚ включая уколы от запоя. Лечение включает также капельницы‚ но и реабилитацию‚ психологическую поддержку при алкоголизме‚ что помогает пациентам вернуться к нормальной жизни.
online experience
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Вызов нарколога на дом недорого – это комфортное и целесообразное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с зависимостями. Часто такие пациенты стесняются обращаться в клиники и отдают предпочтение анонимным методам лечения. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru можно узнать информацию о доступных услугах выездного нарколога, который предложит консультацию нарколога и экспертную поддержку. Доступные услуги нарколога, такие как помощь в борьбе с наркоманией и алкоголизмом, обеспечивают возможность получения медицинской помощи на дому. Психологическая поддержка и реабилитационные программы проводятся квалифицированными специалистами, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность. Обратитесь к дешёвому наркологу для избавления от зависимости и начните путь к выздоровлению вместе с профессиональной поддержкой.
Adoro o gingado de SambaSlots Casino, e um cassino online que samba como um desfile de carnaval. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro carnaval de delicias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, SambaSlots Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
casino play sambaslots|
куплю диплом младшей медсестры http://www.frei-diplom15.ru .
Капельница от запоя в Красноярске: цены и клиники Проблема алкогольной зависимости требует серьезного подхода и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске вы можете вызвать врача нарколога на дом, что дает возможность получить помощь при запое без визита в клинику. Использование капельницы от запоя способствует быстрому восстановлению организма и снижению симптомов. врач нарколог на дом Красноярск Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает детоксикацию, которую можно сделать и дома. Врачи-наркологи предлагают анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность. Цены на капельницы варьируются в зависимости от клиники и объема необходимых услуг. Выведение из запоя с помощью капельницы, это быстрый способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни. Реабилитация людей с зависимостями охватывает не только детоксикацию, но и дальнейшее восстановление после запоя. Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске доступна для всех‚ кто нуждается в поддержке и лечении.
купить диплом техникума в череповце купить диплом техникума в череповце .
купить диплом в мичуринске https://rudik-diplom11.ru .
https://clocks-top.com/
Солоха https://soloha.in.ua женский блог с множеством категорий. Мода, уход, советы мамам и хозяйкам, гороскопы и сонник
все займы онлайн на карту все займы онлайн на карту .
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
вывод из запоя цена
mostbet uz bonus kodi https://mostbet4182.ru
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Kotty на фестивалі Trance Illusion створила щось неймовірне. Її візуальні шоу стали справжньою окрасою події. Коли сцена заповнилася кольоровими хвилями, які ніби пливли в такт музики, всі навколо затамували подих. Люди знімали цей момент на телефони, бо це було схоже на магію. Її майстерність у роботі зі світлом перетворює кожен трек на щось унікальне.
Нарколог на выезде — это вариант для тех, кто нуждается в помощи, но не может или не желает посещать клинику. Услуги нарколога в Москве включают консультацию нарколога на дому, что позволяет конфиденциальность и удобные условия для пациента. Лечение зависимостей начинается с диагностики и облегчения симптомов абстиненции. vivod-iz-zapoya-tula015.ru Специалисты предлагают услуги нарколога, которая включает лечебную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и психотерапию при зависимости. Процесс реабилитации наркозависимых также возможна на домашних условиях, что позволяет вовлечь родственников в поддерживающий процесс. Профилактика рецидивов и постоянная поддержка имеют решающее значение для успешного выздоровления. Выезд врача-нарколога может стать первым шагом к новой жизни.
Двухсторонняя шпонировка:
Запой в Туле: как получить экстренную помощь Запой – это серьезная кризисная ситуация‚ требующая немедленной медицинской помощи. Вызов нарколога на дом – эффективный метод решения проблемы. Специалист обеспечит детоксикацию‚ что позволит безопасно восстановить здоровье пациента. Лечение алкоголизма включает не только физическую‚ но и психологическую помощь. Важность вызова нарколога состоит в предоставлении полного спектра наркологических услуг‚ включая помощь при запойном состоянии. Экстренная помощь предотвращает возникновение осложнений и инициирует процесс реабилитации. После выхода из запоя важно продолжить лечение алкоголизма‚ чтобы избежать рецидивов. Восстановление после запоя нуждается в поддержке‚ поэтому нарколог на дом предоставит поддержку как физически‚ так и психологически. Заботьтесь о своем здоровье и обращайтесь за квалифицированной помощью!
Прокапаться после запоя в Туле: доказанные методы реабилитации Запой – это актуальной проблемой‚ требующей внимательном подходе. Признаки похмелья включают в себя симптомы как головная боль‚ тошноту‚ и общую слабость. Лечение запоя обычно включает детоксикацию организма‚ что важно. Получение медицинскую помощь является важным для безопасного завершения состояния запоя. Реабилитационный центр предлагает комплексное лечение алкоголизма‚ включая психотерапию при алкоголизме и поддержку родственников. Антиалкогольные препараты помогают справится с зависимостью. Важно учитывать психологические аспекты зависимости‚ и профессиональные специалисты готовы оказать помощь. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-tula015.ru где представлена информацию о методах восстановления после алкоголя. Как же справиться с запоем? Прокапаться – это один из самых эффективных способов вернуть организм в норму и положить начало новому‚ здоровому образу жизни.
Прокапаться от алкоголя на дому — значимый этап для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью . Лечение алкоголизма начинается с детоксикации , доступной для выполнения дома. Основные подходы включают использование медикаментов и поддержку специалистов, которые помогут безопасно прекратить употребление . vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru Рекомендации для поддержания трезвости и методы борьбы с зависимостью , такие как самопомощь при алкоголизме , имеют огромное значение в реабилитации . Безопасное прекращение употребления алкоголя — это шаг к новой, трезвой жизни.
Наша наркологическая клиника готова предложить анонимные услуги по выводу из запоя и профессиональную медицинскую помощь на высоком уровне. Мы осознаем, как важно обеспечить поддержку зависимых в сложные времена, по этой причине организуем круглосуточную службу поддержки и консультирование по вопросам алкоголизма. После вывода из запоя начинается реабилитация, целью которой является на восстановление и профилактику рецидивов. Наша группа квалифицированных специалистов поможет каждому пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни, обеспечивая индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Не стоит откладывать заботу о своем здоровье. Пожалуйста, обратитесь на vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru за поддержкой в любое время!
https://plisio.net/ar/blog/usdt-vs-usdc-vs-busd-similarities-and-differences
https://plisio.net/el/blog/len-sassaman-satoshi-nakamoto
Капельница от запоя в Красноярске: что нужно знать Если вы или кто-то из ваших близких страдает от алкогольной зависимости, важно знать, что есть действенные способы лечения. Нарколог на дом анонимно в Красноярске предлагает услуги по выведению из запоя, включая капельницы на дому. Данные процедуры способствуют восстановлению здоровья после запоя и общему улучшению состояния. Капельницы помогают избавиться от симптомов абстиненции, восполняя недостаток витаминов и электролитов в организме. Лечение запоя начинается с консультации нарколога, который оценит состояние пациента и предложит медикаментозную терапию алкоголизма. В Красноярске доступна анонимная помощь в наркологической клинике, где можно пройти реабилитацию от запойного поведения. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск Знание признаков алкогольной зависимости поможет своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью. Лечение запоя в домашних условиях возможно, но обязательно должно проходить под контролем специалиста. Для полного восстановления после запоя необходим комплексный подход, включающий поддержку как близких, так и профессионалов в области наркологических услуг в Красноярске;
Капельница от запоя – это действующий метод детоксикации организма, предоставляемый наркологическая клиника. В Красноярске доступно широкий спектр медицинских услуг, включая вызов нарколога на дом для помощи в борьбе с запоем. Лечение алкоголизма требует индивидуального подхода, и программы лечения зависят в зависимости от уровня зависимости. Визит к наркологу способствует определению наилучшего метода лечения, а конфиденциальное лечение гарантирует защиту личных данных. Поддержка семьи зависимого также играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации. Оценка клиник в Красноярске на основе отзывов позволяет выбрать лучшее учреждение. Обращайтесь за помощью, чтобы преодолеть алкогольную зависимость и восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
http://www.okna-plastic-18.ru – примеры работ установки окон с гарантией
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru – новейшее комплексы в сочетании с варианты для организации сбалансированных территориальных картин гармонизирующие автоматизированное организацию 3D-разработку автоматические варианты оросительных мероприятий осветительных систем
прогноз ставок на футбол https://www.prognozy-na-futbol-9.ru .
Неймар прайм: сравниваю xG/xA по сезонам, удивляет прогресс и влияние на финальную треть. Где скачать удобный apk, чтобы получать пушки о голах Неймара прямо во время canlı izləmə? Собираю обои 4K и аватарки с аккуратным кропом под телефон. neymar-kg.com. Неймар прическа: подборка по годам для фан-арта и коллажей, особенно ранние варианты.
Ищу «неймар барселона фото» с классическими комбинациями с Суаресом и Месси. Подскажите, где найти «неймар красивые фото» без жёсткой обработки и неоновых фильтров. Когда «умер неймар» — кликбейт заголовки; нужны разборы, опровергающие фейки. Где играет Неймар 2025 — обновляю карточки игрока в своём блоге.
Неймар обой — встречал такое написание: ищу корректные теги для поиска. Неймар 2018 ПСЖ — сравнение с 2017 Барса: влияние на xThreat и прогрессии мяча.
**prostadine**
prostadine is a next-generation prostate support formula designed to help maintain, restore, and enhance optimal male prostate performance.
Кто знает, сколько голов забил Неймар за карьеру? Хочу таблицу по клубам и сборной. Нужна подборка «месси роналду неймар фото» для заставки — редкие кадры и матчевые эмоции приветствуются. Нужны «неймар обои 4к» без водяных знаков и с правильным соотношением сторон. неймар обои 4к. Неймар фильмы и документалки: посоветуйте топ-3 для выходных.
Ищу «неймар барселона фото» с классическими комбинациями с Суаресом и Месси. Подскажите, где найти «неймар красивые фото» без жёсткой обработки и неоновых фильтров. Неймар толстый — ещё один миф: интересен анализ формы после травм и пауз. Неймар ПСЖ 2018 — топовый сезон по влиянию между линиями; ищу срез по матчам.
Неймар какая зарплата в «Аль-Хиляль» — интересует структура фикс+бонусы. Где сейчас играет Неймар — закреплю ссылку в профиле, чтобы не терять.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – профессиональная природная команда реализующая на озеленении авторских резиденций с учетом почвы южного инсоляции
https://plisio.net/el/blog/your-topics-or-multiple-stories
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
дизайн проект квартиры Сочи цена – минималистичный дизайн-проект с фиксированной стоимостью
indie rock
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
https://plisio.net/tr/blog/best-low-stress-jobs-for-introverts
евроремонт в Сочи с дизайном – европейский евроремонт с дизайн-проектом
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя цена
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – персональное набор завершенных работ иллюстрирующее масштабный набор направлений от симметричных до футуристичных и территориальных восточных
Phi Illusion Festival цього року став найочікуванішою подією серед моїх друзів. Їхні розповіді про фантастичні виступи Nina Kraviz і вражаючі лазерні шоу звучали як історії з іншого світу. Лаунж-зона з ароматерапією та футуристичним дизайном стала улюбленим місцем для перепочинку між сетами. Тепер я знаю, що наступного року ця подія буде обов’язковою у моєму календарі.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
http://www.aartspacesochi.ru – характерное архив элитных интерьеров информирующее масштабный объем концепций от классических до современных в комплексе с местных французских с выделением на практичность эстетику в тандеме с прочность спроектированных эскизов
chatroom
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя
https://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – квалифицированные ответственности по территориальному озеленению объединяющие организацию ключевого модели адаптацию однолетников создание поливочных систем и значительный объем различное
https://clocks-top.com/
Experienced moving services in New York City — Mini Moving NY. Fast apartment relocations with flexible scheduling.
Our Services:
1) Apartment Moving — small apartment relocations in all 5 boroughs; careful handling
2) Small Moves — mini moves; great for single items
3) Same Day Moving — urgent relocations; available 7 days a week
4) Office Moving — commercial moving; professional service
5) Furniture Moving — furniture relocation; cabinets
6) Local Moving — short distance; Manhattan to Brooklyn
7) Storage Services — secure facilities; climate controlled
Our Advantages:
• Competitive pricing — transparent pricing
• Fast & efficient — last-minute bookings accepted
• Professional team — background checked
• Flexible scheduling — early morning moves
• Safe transport — damage-free guarantee
• All boroughs coverage — Staten Island
How to Book:
— Call or text us > receive free estimate > schedule your move > stress-free moving
— Book on website > cash, card, Venmo accepted
— Customer support for last-minute requests
Pricing:
• Hourly rates available — competitive pricing
• No minimum hours for mini relocations
• Special discounts — ask about current promotions
• No obligation estimate — contact us for personalized pricing
Coverage:
• Bronx
• Citywide service
• Long Island — out of state moves available
Good to Know:
• Book early for best rates
• Loading dock access — no problem
• Boxes & supplies — we provide everything needed
• Licensed & insured — peace of mind guaranteed
Website: https://mini-moving-ny.com/
Your NYC Moving Experts — reliable moving solutions for last-minute relocations in New York City.
https://clocks-top.com/
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя
https://chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – прогрессивные технологии в нише ландшафтной оформления объединяющие ансамбли дренажа кустарниковые сцены в комплексе с декоративные элементы
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Неймар прайм: сравниваю xG/xA по сезонам, удивляет прогресс и влияние на финальную треть. Кто посоветует качественные «неймар игры» с нарезками дриблинга без музыки и водяных знаков? Собираю «неймар барселона фото» и ранние кадры из «Сантоса» в одном плейлисте. http://neymar-kg.com. Неймар в «Сантосе» 2011 — редкие хайлайты находить всё сложнее; делитесь проверенными плейлистами.
Неймар лучшие фото: портреты, эмоции после гола, командные снимки — хочу собрать сет. Сравниваю «неймар 2012 сантос» и переход в Европу — интересна динамика решений в финале. Неймар жена, дети — только официальные факты, без слухов; подскажите корректные био-источники. Где играет Неймар 2025 — обновляю карточки игрока в своём блоге.
Неймар какая зарплата в «Аль-Хиляль» — интересует структура фикс+бонусы. Неймар лучшие фото — интересны кадры из туннеля и разминки, редко попадаются.
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя
https://plisio.net/fr/blog/stock-market-predictions-2025
http://aartspacesochi.ru – новейшее приборы и средства для проектирования интегрированных коммерческих замыслов гармонизирующие электронное реализацию 3D-разработку задействование технической универсума усиленной реальности коллаборирующих ревизий разумных ансамблей контроля иллюминацией микроклиматом усилением в комбинации с широким диапазоном плавающими опциями дающими право осуществлять реально умные и калибрующиеся эксплуатируемые виллы способные обеспечить самостоятельно приспосабливаться в связи с колеблющиеся стороны средовой обстановки и внутригостиничные амбиции употреблятелей
Ich liebe die Energie von PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Am Ende ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
playjango free spins 2021|
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – сертифицированные идеи по утверждению деревьев элементов средств для разработки прочных садовых картин прижившихся к характеристикам морского климата
https://plisio.net/id/blog/kaspa-kas
Estou completamente ressonado por JonBet Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um sino ancestral. A selecao de titulos e um eco de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. respondendo rapido como um eco na caverna. Os saques sao velozes como uma onda sonora. entretanto queria promocoes que vibram como sinos. Em resumo, JonBet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Por sinal o layout e vibrante como uma corda. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
plataforma jonbet Г© confiГЎvel|
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bloco de rua vibrante, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, BacanaPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um desfile visual vibrante, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay brasil|
озеленение участка сочи – ландшафтное озеленение с гарантией приживаемости растений 98%
melbet – paris sportif foot africain
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
лечение запоя
ОАО “Что нам стоит” – эксперт в коммерческом строительстве. Офисные здания, торговые центры и складские помещения строятся по высоким стандартам. Больше информации на официальном ресурсе.
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru – востребованное комплексы плюс механизмы для устройства комплексных дизайнерских пейзажей интегрирующие инновационное моделирование 3D-создание контролируемые системы подачи воды светодизайна
mostbet uz apk скачать http://mostbet4185.ru
https://aartspacesochi.ru/ – актуальные варианты в отрасли декорирования внутридомовых резиденций объединяющие использование инновационных голографического отображения для осуществления точных панорам гостиничных проектов открывающих перспективы лицу оценить предстоящий оформление до начала внедрения восстановительных циклов
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – уникальное коллекция созданных резиденций убеждающее универсальный перечень направлений от формальных до новаторских в комплексе с культурных скандинавских
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Новости спорта онлайн http://sportsat.ru футбол, хоккей, бокс, теннис, баскетбол и другие виды спорта. Результаты матчей, обзоры, интервью, аналитика и главные события дня в мире спорта.
Hi! How R U?
http://aartspacesochi.ru/ – сертифицированные консультации по организации архитектурного способа многоцветной комбинации декоративных факторов комплектации осветительных композиций льняного оформления наряду с разностороннего комплекса непостоянных компонентов устройства совершенного оформления подходящего характерным амбициям сотрудника в тандеме с характеристикам закрепленного дома
https://sanepidemdez.ru
Great info. Lucky me I came across your site by accident (stumbleupon).
I have book marked it for later!
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
http://aartspacesochi.ru/ – квалифицированные советы по планированию декоративного подхода цветовой сочетания покрывающих ингредиентов убранства ламповых структур тканевого комплектации наряду с огромного числа переменных деталей организации великолепного декора удовлетворяющего отличительным запросам индивидуума вместе с характеристикам конкретного апартаментов
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – компетентные консультации по планированию почвопокровных материалов решений для разработки долговечных ландшафтных аранжировок акклиматизированных к атрибутам горного воздуха
https://Orb11ta.help We are back! orb11ta is online.
Использование современных технологий позволяет минимизировать энергозатраты. Мы выбрали подрядчика, у которого есть сертификат энергоэффективности.
https://aartspacesochi.ru – плановое обслуживание плюс профессиональное вмешательство профессиональных резиденций включающее периодические сверки предложения по сбережению обновление обозначенных компонентов перестановку технологически примитивных деталей плюс скорейшее аннулирование проявляющихся поломок создающее долговечность в сочетании с продуктивную задействование смонтированного пространства в течение конечного цикла задействования
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – лучшая озеленительная компания специализирующаяся на разработке индивидуальных коммерческих объектов с применением теплого рельефа местности
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя
Website https://tione.ru/ .
ремонт квартир с дизайнером Сочи – современный ремонт с дизайнерским сопровождением
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – специфическое комплект созданных проектов иллюстрирующее обширный массив техник от формальных до авангардных вместе с природных скандинавских
When I originally commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me
when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment
is added I recieve four emails with the same comment.
Is there a means you are able to remove me from that service?
Thank you!
авторский надзор ремонта Сочи – поэтапный авторский надзор за ремонтом
Гидробур для экскаватора: энергия движения вниз
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful
& it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you helped me.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Fine way of explaining, and nice article to
get information on the topic of my presentation subject matter, which i am going
to present in academy.
заказать дизайн интерьера в Сочи – авторский дизайн интерьера с гарантией
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – профессиональные рекомендации по утверждению однолетников деталей способов для планирования гармоничных природных комбинаций привыкших к признакам влажного микроклимата
купить диплом в волжском купить диплом в волжском .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
https://www.aartspacesochi.ru – ателье современного реализации апартаментов в Краснодарском крае с лицензией для резиденций качественно с ориентиром французских элементов в тандеме с решений устройства элегантных жилых сред
https://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – фирма классического паркового создания в горной местности с консультацией для частных клиентов с сопровождением
медсестра которая купила диплом врача медсестра которая купила диплом врача .
aartspacesochi.ru/ – эксклюзивный подход к разным покупателю плюс вопросу направляющийся бюджет постоянные границы стилевые акценты черты пространства рабочие запросы в сочетании с разносторонний комплекс плавающие компонентов задевая закрытый объединение образ бытия привычки наряду с регулярные действия представляющее гарантирует разрабатывать фактически образцовые а также продуманные виллы многосторонне подходящие фактическим желаниям в комбинации с свойствам активности
Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы на дому – это важная процедура для лечения алкогольной зависимости. Если вам необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом в Красноярске‚ выберите проверенную клинику. Важно выбрать центр‚ который предлагает анонимное лечение и опытных врачей. вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск Перед приходом специалиста стоит узнать о домашних методах лечения‚ таких как капельницы. Это позволит обеспечить безопасность лечения и успешное восстановление после запойного состояния. Убедитесь‚ что клиника предлагает реабилитацию на дому‚ что может улучшить результаты лечения. Выбор клиники требует тщательного подхода. Обратите внимание на отзывы‚ квалификацию врачей и график работы клиники. Квалифицированный нарколог сможет оказать помощь в кратчайшие сроки‚ обеспечивая внимание и заботу в трудный период.
chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – уникальный механизм к конкретным участнику плюс обстоятельствам считающийся лимиты переменные ограничения стилевые направления качества места в симбиозе с концепции сотрудника
Phi Illusion Festival став справжнім святом для поціновувачів електронної музики. Виступи Stephan Bodzin і Amelie Lens були настільки проникливими, що викликали справжній шквал емоцій у гостей. Танцполи були прикрашені хвилястими інсталяціями, а лазерні ефекти у вигляді золотих спіралей створювали магічну атмосферу. Лаунж-зона пропонувала ароматерапію та футуристичний комфорт, що робило цей захід унікальним. Якщо ви шукаєте фестиваль, який здивує вас новим форматом і підходом, Phi Illusion — це саме те, що потрібно.
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru/familypark/ фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
купить диплом техникума чистый купить диплом техникума чистый .
Great article! This is the kind of information that are supposed to
be shared across the net. Shame on Google for now not positioning this post upper!
Come on over and seek advice from my website . Thanks =)
Экстренная помощь при алкоголизме способствует предотвращению осложнений и способствует восстановлению здоровья. Лечение алкоголизма требует серьезного подхода и может включать программы реабилитации. Визит к врачу способствует разработке индивидуального лечебного плана. Не откладывайте вызов врача – ваше здоровье имеет первостепенное значение! вывод из запоя Красноярск
https://www.aartspacesochi.ru – фирма минималистичного организации квартир в горной местности с выездом на объект для таунхаусов с гарантией результата с учетом немецких освещения в симбиозе с механизмов проектирования гармоничных комнат
В нашем мире проблема зависимостей является всё более значимой. Наркология с выездом в Красноярске предлагает широкий спектр наркологических услуг, посреди которых анонимное лечение и помощь при алкоголизме. Выезд нарколога позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при наркотиках без потребности посещения клиники. Одной из услуг является detox в домашних условиях, что гарантирует комфортную обстановку для пациента. Консультация нарколога и поддержка психолога важны для восстановления после зависимости. Программа реабилитации предполагает лечение зависимостей и созависимости, а также поддержку семейных членов. Также, реабилитация на дому способствует лучшему восстановлению. Если вы испытываете трудности, воспользуйтесь ресурсами, такими как vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk019.ru, чтобы получить необходимую информацию о наркологических услугах в Красноярске.
Народные методы борьбы с алкоголизмом могут стать важным дополнением к медицинской помощи в городе Красноярск. Лечение алкогольной зависимости требует всеобъемлющего подхода‚ включая очищение организма и психологическую поддержку.Травы от алкоголизма‚ такие как травы от алкоголизма‚ могут помочь в уменьшении желания выпить. Следует иметь в виду о поддержке семьи и анонимном лечении. Методы борьбы с зависимостью включают реабилитацию от алкоголизма и методы предотвращения запоев. Промежуточные советы по избавлению от зависимости также играют ключевую роль в возвращении к нормальной жизни. помощь нарколога Красноярск
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
В сегодняшнем мире вопрос зависимостей является всё более значимой. Наркология на дом в владимире предлагает многообразные наркологических услуг, включая лечение без лишних вопросов и помощь при алкоголизме. Выезд нарколога позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь при наркотиках без необходимости посещения клиники. Одной из характеристик является detox в домашних условиях, что обеспечивает комфортную обстановку для пациента. Консультация нарколога и психологическая поддержка имеют большое значение для восстановления после зависимости. Программа реабилитации включает в себя лечение зависимостей и созависимости, а также поддержку семейных членов. Кроме того, реабилитация на дому способствует более эффективному восстановлению. Если вы испытываете трудности, воспользуйтесь ресурсами, такими как vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru, чтобы получить необходимую информацию о наркологических услугах в владимире.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – информированные концепции по утверждению кустарников составляющих способов для создания устойчивых ландшафтных пейзажей прижившихся к характеристикам переменчивого атмосферы
прогнозы на хоккей от профессионалов прогнозы на хоккей от профессионалов .
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
прогноз футбол сегодня прогноз футбол сегодня .
Выездной нарколог — это оптимальный вариант для людей, испытывающих проблемы с зависимостями. Наркологическая служба , представленная на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru, предлагает круглосуточные услуги, что особенно актуально в сложных обстоятельствах. Вызов врача на дом позволяет пациенту получить конфиденциальную медицинскую помощь без дополнительных переживаний. При обращении за медицинской помощью важна консультация нарколога , которая включает диагностику состояния и создание персонализированного плана терапии. Лечение алкогольной зависимости и наркотической зависимости начинается с детоксикации организма , что помогает избавиться от токсинов . Роль семьи играет важнейшее значение в процессе реабилитации. Психотерапия при зависимости способствует пониманию причин проблемы и предотвращению рецидивов . Процесс реабилитации зависимых обеспечивает всестороннее лечение и профилактику зависимостей.
Слухайте найкраще Ambient 24 години на добу! DJ Gafur Ambient Radio — це безперервний потік енергії.
Очищение организма после запоя в владимире – важный этап на пути к возвращению к нормальной жизни. Нарколог на дом из медицинского учреждения предлагает процедуры детоксикациикоторая предоставляет помощь в лечении запоя и медицинское сопровождение при алкоголизме. Лечебные программы зачастую включают психотерапию и помощь близких. Процесс восстановления после запоя начинается с первичной консультации с наркологом, что способствует успешному очищению организма и улучшению качества жизни. Нарколог на дом клиника
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – личное портфель воплощенных проектов знакомящее многогранный перечень подходов от регулярных до прогрессивных вместе с территориальных английских
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
ремонт квартир с дизайнером Сочи – евроремонт ремонт с дизайнерским сопровождением
купить диплом в лениногорске rudik-diplom7.ru .
сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры .
http://www.aartspacesochi.ru – уникальное портфолио профессиональных резиденций знакомящее масштабный круг течений от организованных до инновационных плюс природных испанских с выделением на планировку красоту в тандеме с прочность воплощенных замыслов
купить диплом в батайске http://rudik-diplom12.ru/ .
Для строительства офисов и торговых комплексов важно выбрать подрядчика, которому можно доверять. Эта компания гарантирует высочайший уровень исполнения.
купить диплом в ачинске купить диплом в ачинске .
Поддержка близких при алкогольной зависимости Алкоголизм — это не только неприятность зависимогоно и его семьи. В Красноярске обращение к специалисту может стать первым шагом к лечению зависимости. Семейная поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации. Близкие могут помочь, предоставляя эмоциональную поддержку и создавая атмосферу сочувствия. В кризисной ситуации важно обращаться за профессиональной помощью. Консультация нарколога поможет определить правильный путь лечения алкоголизма. Терапия также может стать существенным инструментом для восстановления. вызов нарколога Красноярск Поддержка со стороны общества семьи необходима на всех стадиях лечения, от первого обращения с наркологом до дальнейшей реабилитации. Помощь близких может ускорить выздоровления и вернуть зависимого к нормальной жизни.
aartspacesochi.ru/ – индивидуальный вариант к разным персоне в симбиозе с вопросу принимающий во внимание лимиты временные границы визуальные течения характеристики помещения функциональные требования в комплексе с впечатляющий спектр иные факторы включая семейный объединение путь труда склонности плюс ежедневные фазы демонстрирующее дает шанс формировать в реальности совершенные в сочетании с эргономичные зоны универсально адекватные установленным желаниям в симбиозе с параметрам жизнедеятельности
chernomorsky-sad.ru – опытная группа проектировщиков планирующая комплексный объем стадий от плана до реализации с акцентом голландских способов
купить диплом техникума в красноярске купить диплом техникума в красноярске .
дизайн студия интерьера Сочи – японская студия дизайна интерьеров
Использование капельницы при запое – это действительным способом медицинской помощи в случае алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога на дом позволяет оперативно получить необходимую помощь в ситуации запоя. Состав капельницы как правило содержит препараты для очищения организма, такие как раствор натрия хлорида, раствор глюкозы, витамины и антиоксиданты. Действие капельницы сосредоточено на восстановлении водно-электролитного баланса, облегчении симптомов абстиненции и повышении общего самочувствия пациента. Лечение запоя с помощью капельницы гарантирует быструю помощь при запое и способствует восстановлению после алкогольной интоксикации. Профессиональная помощь на дому позволяет избежать госпитализации, что делает процесс лечения более комфортным. Важно учитывать, что восстановление после запоя может включать и психотерапевтические методы для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao fascinante quanto um grimorio antigo. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino fascinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro encantamento, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo mistico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spellwin casino review|
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле купить диплом с занесением в реестр в нижнем тагиле .
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
chernomorsky-sad.ru – лицензированная штат ландшафтников организующая полный спектр фаз от концепции до реализации с концентрацией голландских подходов
Грамотный подход к строительству обеспечивает долговечный результат. Клиенты отмечают, что компания выполняет все работы на совесть. Узнать больше можно на странице рекомендаций.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin free spins|
https://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru/ – подготовленные мероприятия по архитектурному созданию объединяющие адаптацию начального плана установку почвопокровных устройство дренажных композиций в сочетании с множество отличное
Получить диплом о высшем образовании можем помочь. Купить диплом в Казахстане – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-v-kazahstane
диплом настоящий купить с занесением в реестр http://www.frei-diplom3.ru .
http://www.aartspacesochi.ru – рекомендуемая стилевая предприятие воплощающая на благоустройстве средиземноморских офисов с адаптацией курортного архитектурного контекста с выделением на сбалансированное световой режим микроклимат в сочетании с сезонный режим
купить вкладыш к диплому техникума купить вкладыш к диплому техникума .
Капельница от запоя – это существенная медицинская процедура при алкогольной зависимости. Подготовительный этап предполагает несколько действий. Во-первых, необходимо позвонить наркологу для вызова на дом, который оценит состояние пациента. Проявления алкогольной зависимости могут варьироваться, поэтому важно сообщить врачу о всех проявлениях. нарколог на дом Перед введением капельницы рекомендуется обеспечить доступ к венам, а также подготовить пациента к домашней терапии алкоголизма. Убедитесь, что рядом есть необходимые препараты для капельницы. После лечение важно обратить внимание на реабилитацию, правильный уход за пациентом поможет в восстановлении здоровья и снизит риск рецидива.
услуги ландшафтного дизайнера в сочи – авторские услуги с выездом на объект и 3D-визуализацией
**hepato burn**
hepato burn is a premium nutritional formula designed to enhance liver function, boost metabolism, and support natural fat breakdown.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Vale destacar o site e rapido e cativante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Descobrir mais|
Капельница от запоя на дому: советы родственникам и близким (владимир) Запой в владимире: что делать? часто требует вмешательства специалистов. Капельница ? один из самых действенных методов борьбы с запоем, такие как обезвоживание, интоксикация и физические недомогания. Важно помнить, что помощь родственников играет важнейшую роль в процессе восстановления. лечение запоя владимир При наличии алкогольной зависимости, поддержка семьи может значительно облегчить лечение. Симптомы запоя, такие как тремор, потливость и раздражительность, требуют немедленной медицинской помощи. Наркология на дому предлагает услуги по введению капельниц на дому, что делает процесс менее стрессовым для пациента. Рекомендации для близких: как поддержать в трудную минуту. Уход за больным включает заботу о его психологическом состоянии, так как психологические аспекты зависимости влияет на успешность лечения. Важно не только провести терапию, но и обеспечить поддержку после запоя. Реабилитация наркозависимых требует комплексного подхода, включая психологическую помощь и дальнейшее наблюдение. Помимо капельницы, стоит рассмотреть возможные шаги по лечению алкоголизма, которое включает встречи с психотерапевтом и участие в реабилитационных программах. Домашняя терапия также может быть полезной, однако она должна проводиться под контролем медицинского специалиста.
http://www.aartspacesochi.ru – надежная проектная фирма работающая на стилизации японских квартир с учетом архитектуры влажного погоды Черноморского побережья с ориентацией на экологичное дневное освещение воздушную среду наряду с температурный оптимум
Если вы ищете стабильность, узнайте, где реально заключить контракт на службу по СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1307625-kontrakt-na-svo-v-rossii-chto-ozhidat-v-2025-godu Расскажут, какие военкоматы и отделы кадров принимают документы.
http://www.chernomorsky-sad.ru – авторское подборка воплощенных коттеджей убеждающее универсальный объем техник от традиционных до современных вместе с климатических восточных
aartspacesochi.ru – рекомендованная мастера конструкторов выполняющая надежный пакет мероприятий от консультации до завершения включающий адаптацию персонального художественного образа создание отделочных материалов а также экспертный сопровождение
стоимость озеленения участка сочи – фиксированная стоимость с детализацией по статьям расходов
https://www.aartspacesochi.ru/ – информированные действия по проектированию плюс реализации резиденций комбинирующие разработку авторского художественного образа селекцию а также поставку отделочных материалов гарантийный координацию в пределах процессом капитальных работ вместе с большое количество меняющееся направленное на завоевание отличного результата всесторонне отвечающего исходной визуализации наряду с превосходящего мечты воображения самых разборчивых членов чтящих профессиональное качественность сосредоточенность к деталям в комплексе с бескомпромиссный путь к качественному воплощению
http://chernomorsky-sad.ru – модное комплексы в сочетании с механизмы для построения синтезированных садовых пейзажей синтезирующие техническое проектирование 3D-визуализацию интеллектуальные сети орошения светового оформления
Hi antidetect is goood.
купить диплом инженера строителя купить диплом инженера строителя .
DJ Gafur Dubstep Radio — це платформа для справжніх поціновувачів Dubstep, де звучать найкращі мікси від діджеїв та нові звуки, що відображають дух сучасного рейву.
Її виступ на Trance Illusion став справжньою сенсацією. Kotty зуміла створити шоу, яке залишило незабутнє враження. Її візуальні ефекти перетворювали музику на щось більше — на історію, яку можна було відчути і побачити. Це був досвід, який варто пережити кожному.
купить диплом занесением реестр купить диплом занесением реестр .
диплом техникум где купить http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
https://www.aartspacesochi.ru – бюро японского разработки домов в субтропическом климате с гарантией для вилл с гарантией результата с концентрацией европейских компонентов в сочетании с средств реализации функциональных комнат
chernomorsky-sad.ru – опытная профессионалы флористов организующая качественный комплекс услуг от замысла до финала с применением итальянских подходов
купить диплом психолога купить диплом психолога .
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблематика, которая требует всестороннего метода к излечению. В Красноярске предлагается круглосуточная помощь, в т.ч. вывод из запоя. Центры лечения алкоголизма предлагают услуги психологической терапии и восстановления, что становится важным шагом в восстановлении. Кризисная интервенция и консультации специалистов способствуют людям с зависимостью понять и принять свою зависимость. Эмоциональная поддержка включает в себя индивидуальную терапию и групповые занятия, что способствует опытом и эмоциональной поддержке. Реабилитационная программа помогает созданию советов по отказу от алкоголя и умениям жить без алкоголя. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Красноярск Важно помнить, что помощь наркологов предоставляется круглосуточно, что позволяет каждому найти путь к здоровью и счастью.
купить легальный диплом колледжа купить легальный диплом колледжа .
купить диплом учителя физической культуры купить диплом учителя физической культуры .
1win uz https://1win5509.ru/
купить диплом диспетчера купить диплом диспетчера .
Услуга откапывания на дому в владимире – это популярная услуга‚ которая особенно актуальна при проведении земляных работ‚ ремонте и строительстве. Специализированные компании‚ предлагают услуги по копке с помощью экскаватора на вашем участке. Квалифицированные специалисты гарантируют высокое качество выполнения заказа‚ включая работу с грунтом и установку дренажных систем. Также важно учитывать благоустройство территории и ландшафтный дизайн. Заказывая частные услуги‚ вы можете рассчитывать на профессионализм и надежность. Чтобы узнать больше‚ посетите сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru.
Неотложная помощь при алкоголизме предотвращает развитие осложнений и содействует улучшению здоровья. Курс лечения алкоголизма требует внимательного подхода и может предполагать реабилитационные меры. Консультация врача позволит составить персонализированный план терапии. Не медлите с обращением к врачу – ваше здоровье на первом месте! вывод из запоя Красноярск
Алкоголизм — это острое заболевание, которое требует незамедлительного вмешательства и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске доступен вызов нарколога на дом, что позволяет получить необходимую медицинскую помощь при алкоголизме в уютной обстановке. Признаки алкоголизма состоят в частом употреблении алкоголя, утрате контроля над объемом выпиваемого и появлении симптомов алкогольной зависимости. вызов нарколога на дом Красноярск Борьба с алкоголизмом можно начать с определения степени зависимости, которую проведет опытный специалист в области наркологии. Консультация нарколога способствует выявить уровень зависимости и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Важно помнить о роли поддержки семьи, которая является важным фактором в процессе восстановления. Последствия алкоголизма могут быть крайне тяжелыми, включая физические и психологические проблемы. Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске включает как медикаментозное лечение, так и реабилитационные программы, ориентированные на восстановление пациента. Не затягивайте с решением проблемы, позаботьтесь о своей жизни и обратитесь за помощью!
Trance Illusion не був би таким яскравим без участі Kutty. Її вміння гармонійно поєднувати музику і візуальні ефекти вражає навіть найдосвідченіших глядачів. Її виступи — це щось більше, ніж просто шоу. Вони залишають глибокий емоційний відгук. Дізнатися більше про цю талановиту артистку можна на офіційному сайті.
Срочная наркологическая помощь в владимире доступна на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru. Наркологическая клиника предлагает помощь в лечении зависимостейвключая методы кодирования от алкоголизма и индивидуальные программы реабилитации. Здесь вы найдете поддержку при запойных состояниях и реабилитацию наркоманов. Консультация психотерапевта также доступны. Специальные кризисные центры обеспечивают поддержку для родственников пациентов. Предотвращение зависимостей и восстановление после наркотиков, важные этапы на пути к здоровью. Анонимная помощь гарантирована.
Алкогольная зависимость — значительная проблема‚ которая требует комплексного подхода к терапии. В городе владимир существуют различные методы‚ помогающие пациентам справиться с этой зависимостью. Лечение алкоголизма начинаеться с диагностики и диагностики и анализирования симптомов зависимости. Важно обратиться в профессиональную наркологическую клинику для получения квалифицированной помощи. Одним из эффективных методов является detox-программа‚ которая фокусируется на очистке организма от токсинов. Помощь психолога играет важную роль в реабилитации пациентов. Семейная поддержка и участие в группах анонимных алкоголиков могут значительно повысить вероятность успешного выздоровления. Кодирование от алкоголя также может быть вариантом‚ которое помогает многим. Лечение зависимости включает в себя как медицинские аспекты‚ так и психологические аспекты. Советы по отказу от алкоголя и стимулирование к трезвой жизни необходимы для формирования новой жизни без спиртного. Восстановление после запоя требует времени и терпения‚ но с адекватной поддержкой это осуществимо. За дополнительной информацией можно посетить vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru.
concert stream
aartspacesochi.ru/ – отличительный подход к разным партнеру в тандеме с проблеме принимающий во внимание рамки долговременные стены дизайнерские упоры особенности комнаты эксплуатационные стандарты плюс значительный объем меняющиеся факторы трогая конфиденциальный коллектив курс проживания предрасположенности вместе с плановые этапы являющееся дает возможность организовывать в реальности уютные а также усовершенствованные помещения всецело допустимые регламентированным потребностям плюс особенностям повседневности
купить диплом в прокопьевске купить диплом в прокопьевске .
купить диплом техникума купить диплом техникума .
купить диплом техникума союзной республики купить диплом техникума союзной республики .
chernomorsky-sad.ru – ответственная группа архитекторов выполняющая качественный диапазон процессов от визуализации до завершения с учетом итальянских разработок
3d визуализация интерьера Сочи – фотореалистичная 3D визуализация помещений
где купить диплом техникума старого образца где купить диплом техникума старого образца .
unityandprogress.bond – I appreciate the shared values and the practical resources offered.
дизайн студия интерьера Сочи – японская студия дизайна интерьеров
Якщо ви хочете дізнатися більше про тактики Dr Pepper, слідкуйте за їхніми трансляціями та аналізами!
Этот материал расскажет, где именно можно заключить контракт на СВО в России. https://vc.ru/social/1669114-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-odincovo-novyi-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Здесь также указаны условия по денежным выплатам и надбавкам.
chernomorsky-sad.ru – аккредитованная бригада технологов создающая элитный комплекс мероприятий от проекта до обслуживания с учетом голландских инноваций
авторский надзор ремонта Сочи – регулярный авторский надзор за ремонтом
где купить диплом техникума в краснодаре где купить диплом техникума в краснодаре .
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр как купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
info foot africain melbet – paris sportif
дизайн сада сочи – эксклюзивный дизайн сада с системой автополива и освещения
aartspacesochi.ru – надежная группа декораторов планирующая премиальный цикл процессов от визуализации до сдачи охватывающий создание специфического интерьерного ансамбля комплектацию аксессуаров в комбинации с квалифицированный курирование
Якось я натрапила на інформацію про SFF Asian Department і їхній фестиваль азійської музики. Це стало моїм першим знайомством із цією культурою, і я вражена, наскільки це було захопливо. Якщо вам цікаво відкрити для себе щось нове, раджу переглянути програму заходів тут.
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
лечение запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Алкогольный делирий, это серьезное состояние, возникающее на фоне зависимости от алкоголя. Симптомы включают такие симптомы, как спутанность сознания, галлюцинации, тремор и проблемы со сном. Нарколог на дому в владимире может оказать экстренную помощь при запое и диагностировать алкогольный синдром . Лечение делирия включает медикаментозное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента . Важно также провести психотерапию для зависимых , что поможет им справиться с психологическими аспектами их проблемы; Для успешной реабилитации алкоголиков необходима поддержка близких, чтобы они могли понять признаки алкогольного делирия и оказать помощь при алкоголизме . Профилактика делирия включает отказ от алкоголя и регулярные консультации с наркологом . Нарколог на дом в владимире предоставляет комплексные наркологические услуги, включая лечение на дому . нарколог на дом владимир
срочный вывод из запоя в москве http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-9.ru .
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя цена
**flow force max**
flow force max delivers a forward-thinking, plant-focused way to support prostate health—while also helping maintain everyday energy, libido, and overall vitality.
Acho simplesmente fenomenal BRCasino, e um cassino online que samba como um bloco de carnaval. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de delicias, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, BRCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
br77.net|
купить диплом в твери купить диплом в твери .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
наркология анонимно http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-20.ru/ .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
купить диплом в новотроицке купить диплом в новотроицке .
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: slots modernos, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
4play iptv|
купить диплом техникума с занесением купить диплом техникума с занесением .
**neurogenica**
neurogenica is a dietary supplement formulated to support nerve health and ease discomfort associated with neuropathy.
Amo a atmosfera de BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. No geral, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente impactante, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Começar aqui|
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
купить диплом в уфе http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в уфе .
новости футбольных клубов http://www.novosti-sporta-7.ru .
купить диплом в кунгуре http://rudik-diplom8.ru/ .
купить диплом в махачкале купить диплом в махачкале .
Экстренная помощь при запое в владимире все чаще требуется многим. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru предоставляет квалифицированную помощь наркологов, специализирующегося на лечении алкоголизма и вывода из запоя. В данную процедуру входит медицинская помощь, детоксикация организма от алкоголя и психотерапевтические сеансы. Важно получить консультацию врача для успешного снятия алкогольной зависимости. Наша программа восстановления направлена на реабилитацию, поддержку зависимых и их социальную адаптацию. Профилактика повторных случаев, важный аспект успешного лечения. Помните, что просьба о помощи — это первый шаг к выздоровлению.
купить диплом в чапаевске купить диплом в чапаевске .
диплом занесен в реестр купить диплом занесен в реестр купить .
Капельница от похмелья на дому в владимире – это надежным решением для быстрого восстановления после вечеринки. Состояние похмелья характеризуется признаками‚ такими как головная боль‚ слабость и обезвоживание; процедура капельницы помогает быстрому улучшению самочувствия‚ компенсируя необходимые витамины и минералы. Медицинская клиника на дому предлагает услуги медиков‚ которые осуществляют процедуру профессионально и комфортно. Лечение капельницами помогает устранить дискомфорт и значительно ускоряет восстановление. Медицинская помощь на дому – такой простой вариант для тех‚ кто имеет проблемы с алкоголем или желает быстро избавиться от симптомов похмелья. Если вам нужно быстро восстановиться и вернуть здоровье‚ вы можете обратиться за помощью на vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru. Помните‚ что при серьезных симптомах необходимо вызывать скорую помощь.
прогнозы на спорт точные http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej8.ru/ .
диплом с реестром купить диплом с реестром купить .
Прокапаться на дому: комфорт и здоровье
спортивный прогноз на сегодня http://prognozy-ot-professionalov4.ru .
купить диплом в балашове купить диплом в балашове .
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
компании по продвижению сайтов компании по продвижению сайтов .
купить диплом в владикавказе rudik-diplom10.ru .
В 2025 году условия меняются — важно заранее узнать, где заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1436839-vozrast-dlya-zaklyucheniya-kontrakta-v-armiyu-usloviya-svo-2025-v-rossii В статье подробно разобраны детали, как подписать контракт на СВО и получить все положенные льготы.
1win yutuq olish yo‘li https://1win5510.ru/
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
marketing agency seo https://reiting-runeta-seo.ru .
услуги сео http://www.reiting-kompanii-po-prodvizheniyu-sajtov.ru .
Adoro a erupcao de BetPrimeiro Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um vulcao em furia. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e escaldantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque vulcanico. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma chama de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que incendeia como uma tocha. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brasa, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, BetPrimeiro Casino e um cassino online que e uma cratera de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma brasa ardente, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como uma lava sem fim.
betprimeiro sports betting|
Adoro o clima insano de DiceBet Casino, parece um tornado de diversao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma bomba. A equipe do cassino manda um atendimento que e show, com uma ajuda que e um arraso. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Na real, DiceBet Casino vale cada segundo explorar esse cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
dicebet casino|
агентство seo агентство seo .
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
В 2025 году доступно больше возможностей, где можно заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/money/1550175-kontrakt-voennosluzhashego-rossiiskoi-federacii-osobennosti-i-izmeneniya-v-2025-godu-na-svo В материале описаны льготы для семей и пособия для детей.
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar016.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
купить диплом техникума кемерово купить диплом техникума кемерово .
купить виртуальный номер дешево
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
Мне нравится, что Автоновости Шина Про делают акцент на реальных фактах. Всё просто и по делу.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
готовые деревянные лестницы
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
лечение запоя
купить диплом строителя купить диплом строителя .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Продвижение сайта с помощью SEO — это стратегический шаг к росту и устойчивости бизнеса. Оптимизация помогает повысить видимость и улучшить поведенческие факторы. Это инвестиция, которая окупается в долгосрочной перспективе. Узнайте, как SEO помогает компаниям расти https://dev.neos.epss.ucla.edu/wiki/index.php?title=Поисковая_Раскрутка_Сайтов_Под_Яндекс_И_Гугл
Настоящий оазис удовольствия и покоя. Всё продумано до мелочей — интерьер, освещение, музыка. Девушка невероятно чувственная и заботливая. Рекомендую, проститутки недорого нск: https://sibirka.com/. Всё понравилось, спасибо за отличное настроение.
Предлагаем ветошь обтирочную https://vetosh-optom.ru для протирки и уборки. Цена от 45 руб/кг. В ассортименте трикотаж, махра, хлопок, белая и цветная ветошь. Продаём от 10 кг, работаем с оптовыми и розничными клиентами. Доставка по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленобласти, возможна отправка в другие регионы.
купить диплом в севастополе купить диплом в севастополе .
pin up telegram qo‘llab-quvvatlash pinup5007.ru
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar017.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Услуги нарколога на дому – это удобное решение для людей, которые нуждаются в профессиональной помощи при лечении зависимости. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru предлагает услуги опытных специалистов, готовых оказать медицинскую и эмоциональную поддержку. Нарколог на дом проведет диагностику зависимостей, обеспечит анонимное лечение и разработает медикаментозную терапию. Консультация нарколога может включать психотерапию в процессе лечения зависимости, что способствует восстановлению после зависимости. Также необходима поддержка для близких, чтобы оказать помощь им справиться с возникшими трудностями. Реабилитация на дому позволяет комфортно пройти курс лечения алкоголизма и других зависимостей, не покидая привычной обстановки. Профессиональная помощь доступна каждому, кто желает сделать первый шаг к новой жизни без зависимости.
прогнозы и ставки на футбол прогнозы и ставки на футбол .
https://alexander4u63owe9.bimmwiki.com/user
Злоупотребление алкоголем — это острое заболевание, требующее своевременного вмешательства и профессиональной помощи. В владимире доступен вызов нарколога на дом, что позволяет получить необходимую медицинскую помощь в случае алкогольной зависимости в комфортной обстановке. Признаки алкоголизма состоят в регулярном потреблении алкоголя, утрате контроля над объемом выпиваемого и появлении симптомов алкогольной зависимости. вызов нарколога на дом владимир Борьба с алкоголизмом можно начать с определения степени зависимости, которую проведет квалифицированный нарколог. Консультация нарколога способствует выявить степень зависимости и разработать индивидуальный план лечения. Важно учитывать о поддержке семьи, которая является важным фактором в процессе выздоровления. Последствия алкоголизма могут быть крайне тяжелыми, включая физические и психологические проблемы. Наркологическая помощь в владимире включает как медикаментозное лечение, так и программы реабилитации, направленные на восстановление пациента. Не затягивайте с решением проблемы, позаботьтесь о своей жизни и обратитесь за помощью!
лестница в доме на второй этаж железная
Та шо ви знаєте про кайф, поки не спробували молочний коктейль з морозивом ??
Капельница от запоя на дому: вопросы и ответы (владимир) Нарколог на дом в владимире становится все более востребованным. Специалисты предлагают медикаментозное лечение, включая капельницы для оперативного выхода из запоя. Симптоматика запоя может включать в себя как сильную головную боль, так и тошноту. При наличии таких симптомов важно быстро обратиться к специалистам для получения медицинской помощи. Консультация у нарколога позволит установить адекватный план лечения. Капельницы включают в себя витамины и медикаменты, способствующие восстановлению организма. Процедуры осуществляются в удобной обстановке, что минимизирует стресс. Реабилитация после запоя включает и психологическую поддержку. услуги нарколога на дому в владимире Важно помнить, что лечение алкоголизма – это процесс, требующий терпения и усилий. Нарколог на дом в владимире предоставляет не только услуги по выводу из запоя, но и дальнейшую реабилитацию. Выход из запоя возможен, и мы готовы поддержать вас на этом пути.
купить диплом в клинцах купить диплом в клинцах .
SEO-продвижение помогает вывести сайт на лидирующие позиции и удерживать их без переплат за рекламу. Этот процесс требует внимания и анализа, но эффект заметен уже через несколько месяцев. Оптимизация делает сайт удобным, быстрым и полезным. В итоге растёт доверие пользователей и количество заявок. Подробнее о преимуществах SEO читайте – http://onestopclean.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=835894
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
Je suis totalement electrifie par Donbet Casino, on dirait un ouragan de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est un veritable raz-de-maree, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le support est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support d’une puissance rare. Les paiements sont securises comme un bunker, parfois plus de promos percutantes seraient un plus. Pour resumer, Donbet Casino offre une experience aussi puissante qu’une eruption pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive comme un eclair, amplifie l’immersion dans un tourbillon de fun.
donbet|
можно ли купить диплом медсестры можно ли купить диплом медсестры .
Овсянка с ягодами — завтрак чемпионов.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Армейская служба по контракту начинается с вопроса — где заключить контракт? https://vc.ru/money/1550660-kontrakt-voennyi-chto-nuzhno-znat-o-kontrakte-na-svo-rossiya-2025 Здесь также указаны условия по денежным выплатам и надбавкам.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar018.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Алкогольный запой – это синдром‚ характеризующееся длительным приемом алкоголя‚ и это может вызвать к серьезным последствиям. Симптомы алкогольной зависимости включают необходимость в спиртном‚ что делает незамедлительное лечение запоя необходимым. В владимире медицинская помощь при запое предоставляется в специальных медицинских учреждениях‚ где предлагаются услуги нарколога; последствия запоя могут варьироваться от ухудшения состояния здоровья до психических расстройств. экстренный вывод из запоя владимир Экстренный вывод из запоя предполагает detox-процедуры‚ которые помогают организму очиститься от токсинов. Психологическая помощь при алкоголизме также играет ключевой ролью в восстановлении. Реабилитация алкоголиков в владимире предлагает комплексный подход к лечению‚ включая профилактику запоев и поддержку в период восстановления. Необходимо учитывать‚ что лечение алкоголизма требует профессиональной помощи для снижения рисков и повышения качества жизни.
I read this article fully about the resemblance of hottest and previous technologies, it’s awesome article.
Когда следует вызывать экстренную наркологическую помощь в владимире В жизни каждого человека могут возникнуть кризисные ситуации, связанные с зависимостью от алкоголя или наркотиков. В такие моменты необходимо понимать, как быстро и эффективно получить необходимую помощь. Срочный вызов нарколога на дом в владимире может спасти жизнь тем, кто испытывает признаки алкогольного отравления или другие острые состояния, связанные с зависимостями. Экстренная помощь от наркологической службы включает возможность вызвать нарколога на дом. Это актуально для людей, которые по разным причинам не могут или не хотят обращаться в медицинские учреждения. Чтобы предотвратить серьезные последствия, лечение алкоголизма часто требует помощи квалифицированных специалистов. Родственники играют ключевую роль в реабилитации наркоманов и алкоголиков; Психотерапия при зависимости помогает выявить причины и справиться с проблемами. Хотя адреса наркологических центров в владимире можно легко найти в интернете, иногда требуется экстренная помощь; нарколог на дом срочно владимир Важно помнить, что профилактика зависимости также имеет большое значение. Обращение к специалистам на ранних стадиях может предотвратить развитие серьезных проблем. Имейте в виду, что экстренные меры могут спасти чью-то жизнь.
Анонимный вызов врача нарколога — это важный шаг для людей, столкнувшихся с зависимостями при лечении зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir026.ru вы можете обратиться за помощью и поискать наркологической помощью. Это особенно важно для тех, кто испытывает проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками. Профессиональная помощь нарколога включают диагностику зависимостей и медицинскую помощь при наркотической зависимости. Анонимный нарколог может приехать на дом, что гарантирует приватность и удобство. Выездные специалисты предоставляют психологическую поддержку и проводят процессы реабилитации для зависимых. Виртуальная встреча с врачом позволяет быстро получить необходимые рекомендации. Лечение наркотиков анонимно — это возможность начать новую жизнь без опасений о предвзятости. Не теряйте возможности на перемены с помощью конфиденциальной медицинской помощи!
купить диплом техникума точно купить диплом техникума точно .
купить диплом техникума об окончании купить диплом техникума об окончании .
Оптимизация сайта помогает бизнесу привлекать заинтересованную аудиторию и повышать эффективность онлайн-присутствия. Работа с контентом, структурой и техническими аспектами улучшает позиции и повышает доверие пользователей. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии обеспечивают долгосрочный результат. В итоге сайт становится удобным и надёжным источником клиентов. Подробнее по ссылке: интернет магазин сео
Оптимизация сайта делает ресурс более удобным и привлекательным для посетителей. Работа с контентом, структурой страниц и техническими параметрами помогает улучшить позиции и увеличить трафик. Регулярный анализ и корректировка стратегии поддерживают стабильный результат. В результате сайт становится надёжным источником клиентов. Подробнее по ссылке http://dogetransparency.wiki/index.php/Эффективное_Сео_Продвижение_Сайтов_Любой_Тематики
топ агентств seo продвижения https://reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru .
купить диплом вуза с занесением в реестр купить диплом вуза с занесением в реестр .
https://www.live4cup.com/f-sp1827009-.html#p1827009
Здравствуйте!
VSU Masherova carries out joint implementation of scientific and educational projects, preparation of publications, participation in conferences, summer and winter schools, internships, language courses, training of highly qualified specialists and teaching staff.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vsu.by/abiturientam/priemnaya-kampaniya.html
проходной бал, Feedback from graduates VSU, витебск университет
ВГУ Машерова партнёры, [url=https://vsu.by/en/magistracy/specialities.html]Specialities Vitebsk university [/url], ролики
Удачи и успехов в учебе!
Продвижение сайта в поисковых системах позволяет компаниям получать клиентов без дополнительных затрат на рекламу. Оптимизация помогает улучшить видимость ресурса и привлечь заинтересованных посетителей. С помощью качественного контента и технической настройки достигается высокая конверсия. SEO — это инвестиция в долгосрочное развитие бизнеса. Подробнее об этапах продвижения читайте: https://mqbinfo.com/w/Сео_Продвижение_Сайтов_Для_Увеличения_Продаж
https://www.wowonder.xyz/read-blog/330309
технический перевод в металлургии dzen.ru/a/aPFFa3ZMdGVq1wVQ .
вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово .
я купил диплом с проводкой я купил диплом с проводкой .
В 2025 году условия меняются — важно заранее узнать, где заключить контракт на СВО. https://vc.ru/social/1483448-sluzhba-po-kontraktu-v-sevastopole-kontrakt-na-svo-rossiya-2025-i-ego-osobennosti В статье подробно рассказывается, как именно заключить контракт на службу по контракту.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar019.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
У місті Полтава https://u-misti.poltava.ua новини Полтави та області. Події, огляди та багато цікавого
ПРОКАПАТЬ ОТ АЛКОГОЛЯ: ВАЖНОСТЬ ДЕТОКСИКАЦИИ И ПОДДЕРЖКИ Проблема алкогольной зависимости затрагивает множества людей. Лечение алкоголизма часто стартует с детоксикации, которая включает прокапывание. Этот этап способствует вывести токсины из организма и облегчить абстинентный синдром.Капельницы от алкоголя содержат препараты для детоксикации, которые оздоровлению организма. Они способствуют восстановиться после запоя, обеспечивая необходимую медицинскую помощь. Важно помнить, что поддержка зависимых в этот период имеет большое значение.После детоксикации начинается реабилитация, где психотерапия при алкоголизме занимает ключевую роль. Специалисты поддерживают разобраться в причинах зависимости и дают советы по борьбе с зависимостями.На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru можно найти информацию о том, как правильно пройти лечение и получить поддержку. Здоровье является важный шаг к новой жизни без алкоголя.
Получите бесплатный вопрос юристу прямо сейчас!
является неотъемлемой частью. Непонимание юридических нюансов может негативно сказаться на жизни граждан.
Первый пункт, который стоит обсудить — это доступность юридической помощи. В настоящее время множество экспертов предоставляет консультации через интернет. Такой подход значительно облегчает получение правовой помощи.
Следующий важный момент — это выбор юриста. Важно, чтобы юрист имел хорошие рекомендации и подходящий опыт. Люди часто игнорируют эти факторы, что может привести к неудачам.
Третий аспект, который следует рассмотреть, — это стоимость юридических услуг. Размеры гонораров могут отличаться в зависимости от сложности предоставляемых услуг. Обсуждение условий и стоимости заранее крайне важно.
Наконец, необходимо помнить об ответственности юриста. Отсутствие должного уровня компетенции может иметь серьезные последствия для клиента. Поэтому выбирайте юриста с умом, чтобы избежать проблем.
У розділі Традиції та обряди стільки атмосферних історій!
купить диплом в люберцах купить диплом в люберцах .
I’ll immediately seize your rss as I can’t to find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service.
Do you have any? Kindly permit me understand so that I may just subscribe.
Thanks.
I got this web page from my pal who told me on the topic of this web site and now this time I am browsing this web page and reading very informative articles here.
https://staffinggoals.com/
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
купить диплом в соликамске купить диплом в соликамске .
J’adore la chaleur de VBet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui jaillit comme un volcan en furie. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et incandescentes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse eruptive, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, VBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino incandescent pour les volcanologues du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, facilite une experience de casino eruptive.
vbet чья компания|
купить диплом фармацевта купить диплом фармацевта .
https://vc.ru/money/1656723-kakie-obsledovaniya-prohodyat-pered-kontraktom-na-svo-medkomissiya-i-analizy
Капельница от запоя – это действительным способом оказания помощи в случае алкогольной зависимости. Вызов нарколога на дом даёт возможность быстро получить необходимую помощь при запое. Состав раствора капельницы как правило включает препараты для очищения организма, такие как физраствор, глюкоза, витамины и антиоксиданты. Действие капельницы сосредоточено на восстановлении водно-электролитного баланса, снятие симптомов абстиненции и улучшение общего состояния пациента. Капельница как способ лечения запоя обеспечивает быструю помощь при запое и способствует восстановлению после запоя. Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет избежать госпитализации, что делает процесс лечения более комфортным. Важно учитывать, что реабилитация после запоя может включать и психотерапевтические методы для борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Если вы или ваш близкий столкнулись с проблемой алкогольной зависимости, капельница от запоя может стать начальным этапом к излечению. В владимире профессиональные услуги по детоксикации тела оказывают многочисленные клиники для людей с зависимостью от алкоголя. Специалист-нарколог в владимире проведет диагностику и подберет медикаментозное лечение алкогольной зависимости. Медицинские капельницы для снятия похмелья способствуют быстрому улучшению состояния пациента. Процесс восстановления после алкогольной зависимости включает в себя реабилитацию от алкоголя и поддержку специалистов. Закажите медицинские услуги на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir028.ru для получения профессиональной помощи.
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar020.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Частный нарколог на дому в владимире предоставляет важную помощь тем, кто борется с зависимостями. Процесс лечения зависимостей может быть непростым процессом, но выездной нарколог предлагает комфортные условия и конфиденциальность. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir028.ru можно назначить встречу с наркологом, который встретится с вами на дому. Медицинская помощь на дому включает очистку организма и психологическую терапию для борьбы с зависимостями, что позволяет пациенту начать путь к отрыву от наркотиков или алкоголя. Реабилитационная программа разрабатывается с индивидуальным подходом, учитывающим особенности каждого клиента. Поддержка родственников играет ключевую роль в профилактике рецидива. Частный нарколог на дому обеспечивает не только лечение, но и эмоциональную поддержку, что является необходимым условием для достижения успеха в реабилитации зависимых.
Сайт konsultaciya-advokata51.ru предлагает вам разнообразные возможности. Юридическая консультация – это важный шаг для многих людей. Мы обеспечим вас экспертными консультациями.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на бесплатные адвокаты в москве.
Защита прав граждан — это важный аспект современного общества.
Важно обратить внимание на уровень профессионализма юристов. Наши юристы обладают необходимыми знаниями и опытом. Что бы вы ни выбрали, мы гарантируем качественное выполнение работы.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, доступных для разных категорий граждан. Вы сможете легко ознакомиться с нашими тарифами и предложениями. Мы уверены, что каждый найдет подходящее решение для себя.
Кроме того, мы предлагаем услуги онлайн. Виртуальные консультации становятся всё более популярными. Наши специалисты готовы ответить на ваши вопросы круглосуточно.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
У них є окремо звуки природи для релаксу — дуже атмосферно.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, sempre pronto para ajudar. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto algumas rodadas gratis extras seriam incriveis. No final, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao a cada momento para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Vale notar a navegacao e simples e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Abrir agora|
рейтинг seo организаций http://www.reiting-seo-kompaniy.ru .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Я не фанат овочів, але запечені баклажани — це шось!
где можно купить диплом техникума в омске где можно купить диплом техникума в омске .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
диплом настоящий купить с занесением в реестр https://www.frei-diplom2.ru .
купить диплом техника купить диплом техника .
купить диплом в кирово-чепецке http://www.rudik-diplom12.ru .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
купить диплом техникума в твери купить диплом техникума в твери .
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
https://easystaffingmd.com
купить диплом с занесением в реестр пенза купить диплом с занесением в реестр пенза .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Как предотвратить алкоголизм в Красноярске: рекомендации медиков Алкогольная зависимость — это сложная проблема‚ требующая внимания и действий. Важно знать о возможностях профилактики и лечения. Вызвать нарколога на дом в Красноярске для получения консультации специалиста. Врачи рекомендуют проводить профилактические меры‚ включая осведомленность о последствиях алкоголизма и поддержку семьи. вызвать нарколога на дом Красноярск В процесс лечения алкоголизма входят реабилитационные программы‚ позволяющие способствуют вернуть здоровье и социальную интеграцию. Наркологическая помощь является важной для работы с зависимыми‚ а также для предотвращения рецидивов. Здоровье и алкоголь — это вечная борьба‚ и поддержка в нужный момент может решающую роль.
https://vc.ru/money/1644974-artilleriya-na-svo-tehnika-vooruzhenie-i-sovremennye-sistemy-artillerista
купить диплом техникума с занесением пять плюс купить диплом техникума с занесением пять плюс .
Если у вас появились проблемы с зависимостямивызов нарколога становится необходимым шагом. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk019.ru готов предложить вам высококлассную помощь в лечении зависимостей. Признаки зависимости варьируются и могут быть разными, поэтому важно их вовремя идентифицировать. Обращение к врачу поможет определить оптимальные методы лечения алкоголизма или наркомании. Центр реабилитации дает возможность получить анонимную помощь и поддержку для родственников. Медицинская помощь при наркомании охватывает процесс восстановления после зависимости, что является важным этапом на пути к здоровью. Не откладывайте вызов нарколога, ведь это может спасти жизнь.
https://nikitafirst.com.ua/images/pages/index.php?joker_promokod.html
купить диплом в реестре купить диплом в реестре .
Цены и клиники для капельницы от запоя в Красноярске Проблема алкогольной зависимости требует серьезного подхода и профессиональной помощи. В Красноярске вы можете вызвать врача нарколога на дом, что дает возможность получить помощь при запое без визита в клинику. Использование капельницы от запоя способствует быстрому восстановлению организма и снижению симптомов. врач нарколог на дом Красноярск Лечение алкоголизма включает детоксикацию организма‚ которая может проводиться в домашних условиях. Врачи-наркологи предлагают анонимное лечение алкоголизма‚ что обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность. Стоимость капельниц может различаться в зависимости от клиники и объема предоставляемых услуг. Капельница для выведения из запоя — это эффективный и быстрый метод, позволяющий вернуть пациента к привычной жизни. Реабилитация зависимых включает не только детоксикацию‚ но и последующее восстановление после запоя. Наркологическая помощь в Красноярске доступна для всех‚ кто нуждается в поддержке и лечении.
Капельница от запоя – это действующий способ лечения при запое, который доступен от квалифицированный нарколог в городе Красноярск. Во время запоя тело переживает существенное истощение жидкости и отравление, что вызывает к симптомам похмелья. Необходимо предоставить медицинскую помощь, чтобы улучшить состояние больного. нарколог на дом Красноярск Детоксикация организма с помощью инфузий способствует быстрому выведению токсинов и возвращению к норме. Индивидуальный подход нарколога обеспечивает высокую результативность лечения на дому. Услуги медикаментов на дому позволяют не ложиться в больницу и сделать процесс лечения комфортным. Алкоголь негативно сказывается на здоровье катастрофически, поэтому восстановление после запоя включает восстановление после запоя и помощь специалиста. Комплексная терапия, включая инфузионную терапию, помогает восстановлению здоровья и полноценному восстановлению.
капитальный ремонт двигателя дизеля https://www.dzen.ru/a/aO5JcSrFuEYaWtpN .
кухни на заказ санкт петербург от производителя http://kuhni-spb-2.ru .
Пользуюсь DRINKIO давно, и они ни разу не подвели. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, всё доставляется аккуратно. Ассортимент радует, цены доступные. Очень удобно, что сервис работает круглосуточно. Всё проходит быстро и без лишних вопросов. Доставка алкоголя на дом по Москве, https://drinkio105.ru/
купить диплом в невинномысске купить диплом в невинномысске .
купить диплом в челябинске купить диплом в челябинске .
DRINKIO стал для меня настоящим открытием — оформление заказа занимает считанные минуты, а доставка всегда быстрая и чёткая. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, вежливые и опрятные. Радует, что можно оформить заказ в любое время суток, даже ночью. Ассортимент широкий, цены адекватные. Всё доставляется в идеальном состоянии, что тоже важно. Отличный выбор для тех, кому нужна доставка алкоголя на дом в Москве 24/7, https://drinkio105.ru/
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
her latest blog https://parkerturnersart.com
диплом купить с проводкой диплом купить с проводкой .
купить диплом в губкине https://rudik-diplom10.ru .
купить диплом в перми купить диплом в перми .
купить проведенный диплом провести купить проведенный диплом провести .
купить диплом магистра купить диплом магистра .
купить диплом техникума в ростове пять плюс купить диплом техникума в ростове пять плюс .
Доброго!
Сейчас самое время купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда без лишних документов. купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда — это надёжность и стабильность на долгие годы. купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда — это цифровая свобода и приватность. Выбирайте наш сервис, чтобы купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда с удобством. Если хотите остаться на связи, лучше купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда уже сегодня.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://polisportal.ru/fullnew-196-polnyj-gid-po-vyboru-i-ispolzovaniyu-virtualnogo-nomera-dlya-avito-bezopasnost-udobstvo-i-maksimalna.html
постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер
виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
http://www.mebelniy-prokat.ru Точки присутствия в разных районах города. Доступнее для личных встреч.
https://www.infarmbureau.org/membership/my-member-deals/john-deere
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Капельницы от алкоголя на дому — это результативный способ помощи алкоголизма, что даёт возможность быстро устранить симптомы абстиненции и повысить общее состояние больного. Помощь нарколога на дому становятся все более популярными, так как множество людей выбирают не проходить лечение в стационаре. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru Процедура включает в себя детоксикацию на дому, в которой медицинская помощь при алкоголизме осуществляется в комфортной обстановке. Капельница для снятия похмелья содержит препараты для детоксикации, способствующие помогают выведению токсинов из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Важно помнить о признаках абстинентного синдрома, таких как тревога, повышенное потоотделение и тремтение. Поддержка близких при алкоголизме играет ключевую роль в эффективном лечении и реабилитации после запоя. Домашняя терапия включает в себя не только прокапывание, но и рекомендации по профилактике алкогольной зависимости, что содействует предотвращению повторных срывов и сохранить трезвый образ жизни.
navigate to this web-site https://azapainters.com
Дабстеп-музика змінює сприйняття світу, занурюючи у ритми, що переносять в інші виміри. DJ Gafur Dubstep Radio — це місце, де справжні шанувальники Dubstep можуть насолоджуватись безперервним звучанням.
pop over to these guys https://protecprosltd.com
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
как купить легальный диплом https://frei-diplom5.ru/ .
discover here https://naturewreathpro.com
Срочная наркотическая помощь в Красноярске является ключевую роль в борьбе зависимостей. Если вы оказались с кризисной ситуацией, важно обратится в медицинскую клинику, где оказывают медицинскую помощь при алкогольной зависимости. Квалифицированные специалисты проводят процедуры детоксикации, чтобы удалить токсичные вещества из организма; затем начинается лечебный процесс, ориентированная преодоление после зависимости. Психологическая поддержка также играет важную роль в реабилитации. Сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk020.ru предлагает консультации нарколога, где вы получите ознакомиться о признаках зависимости и необходимых действиях. Не откладывайте обращение за необходимой помощью – это начало к выздоровлению.
Шоколадный кекс развалился в духовке, но я всё равно съел — вкусно ж! ??
websites https://rynovaworks.com
Капельница от запоя – это распространенный метод терапии, который может быть выполнен специалистом на дом анонимно в Красноярске. Главная задача процедуры – очищение организма и восстановление после алкогольной зависимости. Однако важно учитывать ограничения и побочные эффекты. Ограничения включают: серьезные болезни сердца и сосудов, аллергические реакции на компоненты капельницы и патологии почек. Побочные эффекты могут проявляться в виде боли в голове, тошнотных ощущений и аллергических реакций. нарколог на дом анонимно Красноярск Важно помнить, что помощь нарколога предполагают не только лечение алкогольной зависимости, но и профилактику рецидивов, реабилитацию и медицинское сопровождение. Конфиденциальное лечение с помощью капельниц может значительно облегчить состояние пациента и способствовать быстрому восстановлению.
Капельница от запоя: экстренная помощь при алкогольном отравлении Инфузионная терапия содержит жизненно важные вещества для восстановления водно-электролитного баланса и укрепления здоровья больного. Комплексное лечение зависимости включает в себя не только детоксикацию, но и долгосрочную терапию алкоголизма. Важно помнить о восстановлении после запоя, который может занять время и потребовать дополнительных усилий. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Экстренная помощь включает в себя оценку состояния пациента и персонализированный подход к лечению. При выявлении симптомов алкогольного отравления необходимо срочно обратиться за медицинской помощью. Помните, что здоровье — это самое главное, и профессиональная помощь в наркологической клинике поможет восстановить контроль над своей жизнью.
купить диплом мастера маникюра и педикюра купить диплом мастера маникюра и педикюра .
https://www.porn-city.com/ the best porno site ever! NO ADS!
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Стальные трубы, уголки, швеллеры и листы обеспечивают прочность конструкций. Качественный металлопрокат устойчив к коррозии и нагрузкам, что делает его незаменимым в создании долговечных сооружений. Современные технологии производства позволяют получать изделия с высокой точностью и разнообразием форм для любых задач: металлопрокат
Приветствую всех!
Сегодня все больше компаний используют рекламу у блогеров, чтобы найти новых клиентов.
Это направление быстро развивается, и результаты часто превосходят классический таргет. Этот подход показывается прекрасные результаты
Подробнее о том, как устроен рынок блогеров, можно прочитать в нашем материале — в нашем блоге
А что думаете вы?
индуктивные сенсоры
1xbet 1xbet .
1xbet giri? yapam?yorum http://www.1xbet-giris-4.com .
one x bet 1xbet-giris-5.com .
1xbet giri? 1xbet giri? .
1xbet guncel http://1xbet-giris-3.com .
Дабстеп у моєму житті з’явилося завдяки DJ Gafur Dubstep Radio. Тут не тільки класні треки, а й атмосфера, яка дозволяє повністю зануритися у музичний простір.
birxbet giri? http://1xbet-giris-1.com/ .
https://vc.ru/money/1652757-chasto-zadavaemye-voprosy-i-otvety-o-zaklyuchenii-kontrakta-na-svo
коммутация
Ich finde absolut irre DrueGlueck Casino, es bietet eine krasse Spielerfahrung. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist gigantisch, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die krachen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel und zuverlassig, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur Spieler, die auf Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck velkomstbonus|
Galera, resolvi compartilhar minha experiencia sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me ganhou de verdade. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos rodaram sem travar. O atendimento no chat foi respondeu em segundos, o que ja me deixou seguro. As retiradas foram mais velozes que imaginei, inclusive testei PIX e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que gostaria de ver mais brindes, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Resumindo, o Bingoemcasa me conquistou. Ja me sinto parte da comunidade
bingoemcasa cassino|
Ich bin suchtig nach Lowen Play Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein machtiger Sprung ins Spielvergnugen. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und kraftvoll, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Brullen wirkt. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad im Busch, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Lowen Play Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Sonnenaufgang, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
bestes löwen play casino|
Estou completamente encantado por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. As opcoes sao vastas como um desfile, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Eleva a diversao do jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, de vez em quando mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. No final, PlayPIX Casino e indispensavel para jogadores para quem aposta com cripto ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, facilita uma imersao total. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para competicao, oferece recompensas continuas.
https://playpixcasino.pro/|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Hervorzuheben ist die mobilen Apps, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com emocao atletica. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos adaptados para criptos. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os saques sao rapidos como um sprint, as vezes recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Alem disso o design e moderno e dinamico, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Outro destaque as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Saber mais|
аренда мебели для вечеринки Модное оформление для вечеринок. Оформление пространства с учетом тематики.
A thriving community supports Bedrock Edition by sharing tips, tricks, and content, making it a lively environment.
jenny 2 mod mcpe https://minecraft-bedrock-edition.com/mods/mob/jenny-2/
read more https://containergardenguru.com/
видео mailsco online стало популярным на сайте.
http://cs-headshot.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=681550#681550
learnshareconnect.shop – Content feels genuine and helpful, not just fluff, which I appreciate.
Капельница от запоя на дому: вопросы и ответы (Красноярск) Нарколог на дом в Красноярске становится все более востребованным. Специалисты предлагают медикаментозное лечение, включая капельницы для оперативного выхода из запоя. Симптомы запоя могут варьироваться от сильной головной боли до тошноты. При наличии таких симптомов важно быстро обратиться к специалистам для получения медицинской помощи. Обратившись к наркологу, вы сможете получить рекомендации по необходимому курсу лечения. Капельница содержит необходимые витамины и лекарства, которые восстанавливают организм. Процедуры осуществляются в удобной обстановке, что минимизирует стресс. Реабилитация после запоя включает и психологическую поддержку. нарколог на дом Красноярск Важно помнить, что лечение алкоголизма – это процесс, требующий терпения и усилий. Наркологи на дому в Красноярске предлагают как услуги по выводу из запоя, так и программы дальнейшей реабилитации. Реабилитация после запоя реальна, и мы готовы помочь вам в этом процессе.
everydayvaluecorner.shop – Super quick delivery and friendly service, couldn’t ask for more.
findyourperfectdeal.shop – Found unique items I hadn’t seen elsewhere, glad I discovered this store.
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
Прокапаться от алкоголя на дому — значимый этап для преодоления алкогольной зависимости. Процесс избавления от алкоголизма начинается с очищения организма, которая может быть проведена в домашних условиях . Основные подходы включают использование медикаментов и поддержку специалистов, которые помогут безопасно прекратить употребление . vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru Советы по трезвости и методы борьбы с зависимостью , такие как самопомощь при алкоголизме , имеют огромное значение в реабилитации . Безопасное прекращение употребления алкоголя — это шаг к новой, трезвой жизни.
Additionally, various platforms feature appealing bonuses and promotional incentives.
features of slot platforms https://superatou.com/understanding-online-slot-platforms/
liveandexplore.shop – Shipping was smooth, packaging was neat and arrived ahead of schedule.
Алкоголизм: лечение в домашних условиях становится все более популярным. Основные этапы включают домашней детоксикации и помощи при запое. С чего следует начать? Важно получить поддержку от близкихкоторые могут помочь в процессе.Психологическая поддержка и альтернативные методы могут стать хорошим дополнением к медикаментам от алкоголя. Программы по поддержанию трезвости и советы по отказу от спиртного помогут установить верное мышление. vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk021.ru Важно помнить о реабилитации дома, которая включает поддержку психолога и профилактику рецидива. Что делать, чтобы бросить пить самостоятельно? Начните с постановки ясной цели и находите свою мотивацию. Главное – это желание изменить свою жизнь и поддержка близких.
getinspiredtoday.click – The content variety keeps it fresh—always something new to check out.
modernlivingstyle.click – Affordable but stylish pieces, great value for upgrading my living space.
getinspiredtoday.click – User-friendly experience, felt confident exploring and reading freely.
Капельница от запоя – это распространенный метод помощи, который помогает людям справиться с алкогольной зависимостью. Врач нарколог на дом оказывает медицинскую помощь при алкогольной зависимости, проводя детоксикацию организма и возвращая его функции. Терапия запоя включает применение препаратов для капельницы, которые помогают ликвидации симптомов отмены.Важно помнить, что рецидив алкоголизма может произойти в любой момент. Предотвращение рецидивов включает как физическое лечение, так и психотерапию при алкоголизме, которая содействует пациентам понять корни своей проблемы и научиться справляться с психологическими барьерами. После окончания запоя важно пройти реабилитацию, чтобы предотвратить рецидивы. Нарколог на дом поддержит организовать этот процесс, предоставляя необходимые рекомендации для восстановления после запоя и поддерживая пациента на пути к новому, трезвому существованию.
https://www.diigo.com/item/note/8vt06/iu0t?k=2fa69a558dc754d4602b59f1bf78507f
staycuriousalways.click – Easy navigation and fast loading enhanced my experience significantly today.
https://vc.ru/money/1648933-bpla-dlya-razvedki-sposoby-vedeniya-nablyudeniya-i-vozdushnogo-poiska-celei
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this
site. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s tough
to get that “perfect balance” between usability and appearance.
I must say you’ve done a superb job with this. Also, the
blog loads very fast for me on Firefox. Superb
Blog!
1x bet giri? 1x bet giri? .
shopwithconfidence.click – Customer service responded fast and helped resolve my question easily.
1xbet giri? 2025 1xbet giri? 2025 .
https://non-gamstop.org/
keepgrowingforward.click – Found many new ideas to explore, keeps me inspired and moving forward.
discoverendlessideas.shop – Quality content and products, everything delivered exactly as described.
Хтось бачив матч Dr Pepper? Це була справжня битва гігантів на полі Battle Nexus, і вони дійсно показали свою майстерність.
birxbet birxbet .
купить диплом в обнинске http://rudik-diplom5.ru .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
uniquetrendstore.shop – Secure checkout process, felt confident shopping here.
globalmarketplacehub.shop – Recommend to anyone looking for reliable, interesting products and good service.
ссылка на сайт https://kra42at.cc
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
staycuriousalways.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
hardman4schools – Strong educational vision, visuals and tone reflect dedication beautifully.
discoveryourmoment.shop – Quality selection and reliable shipping, I’m impressed with the service provided.
Pinco casino-da futbol və e-idman mərcləri üçün koeffisentlər tez-tez yenilənir, ona görə canlı rejimdə qərar vermək rahatdır.
Çoxlu lokal ödəniş üsulu dəstəklənir, komissiyalar real vaxt göstərilir. Rəsmi giriş həmişə eyni ünvandır — pinco-casino-azerbaijan.biz.ua/; pinco azərbaycan tg elanlarına uymayın. Sürətli ödəniş üçün sevimli metodları saxlayıb bir kliklə istifadə etmək olur. Sürətli oyunlar və crash-mekanikalar qısa sessiyalar üçün ideal həll təqdim edir.
Mobil tətbiqdə bildirişləri yalnız maraqlandığınız liqalara açmaq məsləhətdir. iOS istifadəçiləri üçün PWA veb-tətbiqi ikonaya əlavə etməklə bir toxunuşda açılır.
Fikriniz və təkliflər üçün rəy forması hər səhifənin sonunda var. Şəxsi məlumatların işlənməsi siyasətində məqsəd və saxlanma müddəti göstərilir. Seçim etməkdə çətinlik varsa, tematik toplular — futbol mərcləri, slot hitləri və canlı oyunlar — kömək edir.
thebestplacetoshop.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
ואני רוצה שוב רוצה לשרוף בו. אני רוצה שהוא יראה שוב זה, לעולם לא תחשוב על זה, במיוחד שהוא, בעלה גניחות, מכות בישבן וחריקות מיטה, מתפזרות בחדר… אותו לטבעת הצמודה שלי! גנחנו בו זמנית והוא התחיל click here to find out more
newseasoncollection.shop – Affordable pricing for trendy pieces, totally happy with my haul.
купить диплом пту в реестре купить диплом пту в реестре .
https://factava.com.ua/karta-sum/
createandgrow.click – Quality content and tools that actually feel helpful and practical.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
uniquetrendstore.click – Loved the selection here, everything looks fresh and stylish.
Коли хочеш тиші — допомагає ранкова кава на балконі.
dreamcreateinspire.click – The layout is clean and easy to navigate, made exploring so simple.
купить диплом в новотроицке купить диплом в новотроицке .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Canlı izləmə və canlı mərc ekranları yan-yana açılır, gecikmə minimumdur.
Çoxlu lokal ödəniş üsulu dəstəklənir, komissiyalar real vaxt göstərilir. APK yükləmək istəyənlər üçün rəsmi səhifə budur — https://pinco-casino-azerbaijan.biz.ua; burada pinco yüklə addımları addım-addım göstərilib. Risk idarəsi üçün gündəlik və aylıq xərcləmə limitləri qurmaq mümkündür. Axtarış paneli ad, provayder və mexanika üzrə işləyir — nəticələr dərhal çıxır.
Riskli kombinlərdə cash-out planı əvvəlcədən müəyyənləşdirilməlidir. Matç mərkəzi canlı statistika və animasiya ilə təqvimi birləşdirir.
Şikayət forması və cavab müddətləri xidmət qaydalarında göstərilib. Şəxsi məlumatların işlənməsi siyasətində məqsəd və saxlanma müddəti göstərilir. Yeni reliz bildirişləri ilə provayderlərin son oyunlarını ilk siz sınaya bilərsiniz.
thinkcreategrow – Interface is clean, loads fast, and content is genuinely helpful.
joinourcreativeworld.click – Easy to navigate, found inspiring resources without scrolling too long.
discovernewworld.click – Customer service responded quickly when I had a small question earlier today.
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, garantissant un service premium. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! A noter le site est rapide et futuriste, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement cool les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. En resume, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
It’s not my first time to pay a visit this web page, i am browsing this website dailly and get good data from here everyday.
exploreopportunitiesnow.click – Articles and ideas keep coming, keeps me coming back for more.
changetheworld – Appreciate practical tips here; implemented one idea that improved workflow.
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, il procure une experience exquise. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et chic, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Aller en ligne|
Продвижение сайтов: как повысить видимость и конверсию https://admtog.ru/stati/prodvizhenie-sajtov-kak-povysit-vidimost-i-konversiju/
J’adore l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie blockchain. Le repertoire est riche et varie, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des promotions crypto rapides. Le support client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et fiable. Le processus est simple comme un hash, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est incontournable pour les fans de crypto pour les adeptes de sensations futuristes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un wallet, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des transactions fiables.
Lire entiГЁrement|
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
discoverendlessideas – I shared one article with family, they found it super helpful too.
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
Алматы, город контрастов, предлагает своим гостям и жителям широкий спектр услуг, включая услуги сопровождения. Эти услуги стали популярным выбором для тех, кто стремится к удобству и уверенности в любой ситуации.
Эскорт-агентства в Алматы астана проститутки РЅР° ночь предоставляют опытных спутников, которые готовы сопровождать вас на деловые встречи или светские вечера. Каждый спутник проходит строгий отбор, что гарантирует премиальное обслуживание.
Преимущества эскорт-услуг в Алматы включают конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход и гибкость в решении любых задач. Это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит комфорт и желает получить яркие эмоции.
Выбирая сопровождение в Алматы, вы делаете шаг к уверенности в любой жизненной ситуации.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk022.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
J’adore l’atmosphere rythmee de BassBet Casino, il procure une aventure groovy. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino vaut une jam session pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est simple et rythmee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis accro a BassBet Casino, il procure une experience dynamique. La variete des titres est rapide, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Le support est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un delta, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient une vague. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement fluviale, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourne comme un conte. La selection de jeux est enchantee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un chapitre. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En bonus le design est moderne et enchante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
Je suis completement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir immortel. La variete des titres est divine, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme des dieux, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un nectar. En bref, Olympe Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://olympefr.com/|
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Website https://useit2.ru/.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Discover the best PS2 games in Canada! A curated list of timeless classics, including action, RPGs, and sports titles. Relive the nostalgia of top PlayStation 2 hits loved by gamers: best PS2 games list Canada
https://casinoer-uden-nemid.com/
Вызов нарколога в владимире – важный шаг для тех‚ кто с трудностями зависимости. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru вы имеете возможность обратиться за квалифицированной помощью. Наркологическая помощь включает диагностику зависимости и анонимное лечение. Если у вас есть алкогольная или наркотическая зависимость‚ неотложный вызов врача поможет избежать осложнений. Центры реабилитации предлагают программы восстановления и поддержку семьи‚ что критично для успешного лечения. Консультация нарколога – это первый этап на пути к выздоровлению. Не откладывайте‚ просите за медицинской помощью уже сегодня!
yourtrustedonlinestore – Navigation is smooth, the layout is clean, content loads without distraction.
The Inheritance Games Canada: A thrilling mystery game where players unravel secrets, solve puzzles, and compete for a billionaire’s fortune. Perfect for fans of strategy and suspense: Inheritance Games plot summary
купить медицинский диплом медсестры купить медицинский диплом медсестры .
everytrendinone – Very user-friendly interface, things load fast, content is engaging and fresh.
купить диплом в бийске https://rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в бийске .
Лечение зависимости: вызов нарколога на дом Зависимость от наркотиков – это серьезная проблема, для решения которой необходима квалифицированная помощь. Не забывайте, что лечение наркомании начинается с консультации у специалиста. Полную информацию о вызове нарколога на дом вы найдете на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru. Лечение подразумевает проведение детоксикации организма и предоставление психологической помощи. Реабилитация зависимых часто бывает необходима и включает индивидуальные программы восстановления. Конфиденциальное лечение создает условия комфорта и безопасности для пациента. Домашняя терапия предоставляет необходимую помощь и особенно важна для тех, кто испытывает стеснение при обращении в медицинские учреждения. Лечение алкоголизма также возможно в домашних условиях, что способствует более быстрому восстановлению после зависимости. Квалифицированная помощь специалиста – ключ к успешной борьбе с зависимостями.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
В городе владимир доступна услуга по вызову нарколога на дом, доступная 24/7, обеспечивающая наркологические услуги для людей, страдающих от зависимости. Если вам или вашим близким требуется лечение алкоголизма, опытный нарколог окажет медицинскую помощь на дому, обеспечивая анонимное лечение. вызов нарколога владимир Если вы ищете надежное решение, вызов нарколога в владимире является первым шагом на пути к новой жизни.
Современная наркологическая помощь включает в себя работающие методы лечения зависимостей, такие как фармакотерапия и психотерапия для зависимых. Выездная наркология стала популярной благодаря индивидуальному подходу к каждому пациенту. Это позволяет проводить диагностику зависимостей и разрабатывать программу реабилитации, не выходя из домашнего уюта. Лечение наркомании нуждается в комплексном подходе. Консультация нарколога на дому даёт возможность обсудить проблемы и подобрать оптимальные варианты терапии. Помощь родственников играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления после зависимости. Профилактика рецидивов и регулярное наблюдение помогают избежать повторного срыва. Конфиденциальное лечение и реабилитация на дому гарантируют комфорт и безопасность, что имеет большое значение для тех, кто стесняется обращаться за помощью. Используя ресурсы, такие как vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru, можно найти необходимую информацию и поддержку, которая так необходима на пути к здоровью.
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: Prisma Games technology blog
successpartnersgroup – Very helpful resources, makes business strategy and growth easier today.
successpartnersgroup – Really motivating and informative, makes complex topics easier to understand quickly.
https://vc.ru/money/1680353-zapisatsya-dobrovolcem-na-svo-iz-krasnodara
nextgeninnovation – Layout is simple, user-friendly, and makes exploring innovation topics really enjoyable.
inspiredgrowthteam – A great platform for organizations looking to enhance team dynamics.
hardman4schools – The layout is simple yet powerful, delivering a message of trust.
urbanwearzone – Love the variety of clothes here, really stylish daily finds.
learnshareconnect – Content is varied and well‑written—it’s clear effort was put into this.
globalideasnetwork – Easy to navigate site, makes learning new ideas enjoyable always.
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
вывод из запоя смоленск
купить диплом фитнес инструктора купить диплом фитнес инструктора .
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
лечение запоя смоленск
Pinco casino-da futbol və e-idman mərcləri üçün koeffisentlər tez-tez yenilənir, ona görə canlı rejimdə qərar vermək rahatdır.
Hesabın verifikasiyası onlayn aparılır və sənədlər şifrəli kanalla yüklənir. Hesabınıza təhlükəsiz daxil olmaq üçün pinco casino login düyməsini istifadə edin və iki mərhələli girişi aktiv edin. AZN balansı aydın görünür, tranzaksiya tarixi filtrə ilə rahat axtarılır. Canlı kazino bölməsində blackjack, rulet və bakara masaları 24/7 açıqdır.
Canlı mərclərdə gecikməni nəzərə alıb əmsal kilidlərinə diqqət etmək lazımdır. iOS istifadəçiləri üçün PWA veb-tətbiqi ikonaya əlavə etməklə bir toxunuşda açılır.
Fikriniz və təkliflər üçün rəy forması hər səhifənin sonunda var. Şəxsi məlumatların işlənməsi siyasətində məqsəd və saxlanma müddəti göstərilir. Kampaniya təqvimi bonusları planlaşdırmağa və maksimum fayda götürməyə imkan verir.
привітання з днем народження швагра
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
вывод из запоя смоленск
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk023.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя смоленск
Хочете більше дізнатися про команду, яка вражає результатами? Зайдіть на Fanta і дізнайтесь, чим вони відрізняються від інших команд.
этот сайт champion casino
аренда мебели в москве на выставку Экспозиционное оборудование в Москве. Быстрая сборка и бережная перевозка.
shopandshineeveryday – The writing style is clear and friendly—makes reading fun rather than a chore.
Смотреть здесь casino vodka bet
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Здравствуйте!
Виртуальный номер для смс навсегда – это решение для тех, кто ценит простоту и удобство. Купите постоянный виртуальный номер и используйте его для регистрации аккаунтов и других задач. Мы предлагаем доступные цены и качественные услуги. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это свобода общения без ограничений. Закажите у нас и начните использовать прямо сейчас.
Полная информация по ссылке – купить виртуальный номер для авито
купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить постоянный виртуальный номер
купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер телефона
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
https://factava.com.ua/karta-chernihova/
купить диплом программиста купить диплом программиста .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
купить диплом в гатчине rudik-diplom5.ru .
1xbet turkiye 1xbet turkiye .
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
1xbet giri? g?ncel http://1xbet-4.com .
Я не знаю, як без кави зранку люди живуть ??
http://webd.francite.com/fr/services/forums/message.asp?id=736581&msgid=7058853&poster=0&ok=0
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
https://orb11ta.asia is online now!
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
https://vc.ru/money/1644035-reb-na-svo-rol-zashity-ot-dronov-i-primenenie-voisk-radioelektronnoi-borby
Перейти на сайт https://kra42at.at/
**memorylift**
memorylift is an innovative dietary formula designed to naturally nurture brain wellness and sharpen cognitive performance.
диплом техникума купить в диплом техникума купить в .
createimpactonline – The resources provided are incredibly helpful for scaling our nonprofit.
https://7173mustangs.com/members/stallionjoe.10966/#about
partnershippowerhouse – Appreciate how they break down complex partnership concepts into simple steps.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя цена
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
аренда мебели и оборудования Полное решение в аренду. Услуга под ключ для вашего мероприятия.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Рестораны в Москве предлагают разнообразные блюда и атмосферу, которые привлекают жителей и туристов.
где поесть рядом с парком горького https://restoran-rus.ru/
one x bet http://www.1xbet-7.com/ .
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
лечение запоя
xbet giri? https://1xbet-9.com/ .
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-smolensk024.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
קראו לי מאוד בעקשנות להצטרף לחגיגה שלהם, והחלטתי להיכנע. אחרי ששתיתי קצת וודקה, בגלל היכרות, ואלרה מושכת אותו חזק למעלה. עם תמיכה כזו, העלייה התבררה כפרשה ממש פשוטה. חצי דקה ומקס כבר היה https://coupleschoice.com/%D7%93%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%91%D7%90%D7%A9%D7%A7%D7%9C%D7%95%D7%9F/
mystylecorner – Great experience browsing through latest trends, very satisfied overall.
Таможенный брокер всегда держит связь и объясняет все шаги. Приятное сотрудничество https://tamozhenniiy-broker-moskva11.ru/
войти в 1вин войти в 1вин
Website https://useit2.ru/.
Я обожнюю дивитися на команди, які добре грають, і Smart Hamsters – Wild Dancer точно потрапляють до цієї категорії.
https://www.megacritic.ru/partner/gornolyzhnyye-kurorty-krasnodarskogo-kraya-trassy-razvlecheniya-i-prozhivaniye
https://casinosargentina.org/
exploreamazingideas – Content is varied and well‑written—it’s clear effort was put into this.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
mebelniy-prokat.ru Складские помещения и регулярное обслуживание. Поддержание чистоты.
купить диплом в златоусте купить диплом в златоусте .
https://www.reverbnation.com/otellotravel
Добрый день, друзья!
Сегодня современные проекты используют продвижение через инфлюенсеров, чтобы повысить узнаваемость.
Это направление быстро развивается, и результаты часто превосходят классический таргет. Этот подход показывается отличные результаты
Читайте подробный обзор по ссылке: https://digitalpromo-blog.blogspot.com/2025/09/blog-post.html
А что думаете вы?
findyourperfectdeal – Sharing with colleagues because it’s inspiring and worth a browse during breaks.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Чесно, шоколадний торт — це моя слабкість, без шансів ??
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
cat casino сайт
ДОСТУПНЫЙ ВЫВОД ИЗ ЗАПОЯ В владимире: МИФЫ И РЕАЛЬНОСТЬ Лечение алкоголизма – это сложный и многогранный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода. В владимире множество наркологических клиник предлагают лечение запоя и реабилитацию от запоя, однако имеются ложные представления о лечении алкоголизма, которые могут сбивать с толку. Во-первых, некоторые люди полагают, что вывод из запоя – это быстрое мероприятие. На самом деле, эффективные методы вывода из запоя включают детоксикацию и медико-психологическую помощь, что требует времени. Наркологическая клиника владимир в владимире предлагает реабилитационные программы, на которых специалисты помогают восстановиться после запоя. Важно отметить, что психотерапия имеет центральное значение в процессе лечения зависимости. Консультация нарколога способствует выявлению причин зависимости и созданию индивидуального плана лечения. Не стоит забывать, что лечение зависимости в владимире доступно и эффективно, если обратиться за помощью вовремя.
https://telegra.ph/1xbet-promo-code-registration-india-10-14
купить диплом тренера http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом тренера .
https://yk.kz/news/obshhestvo/rejting-luchshix-otelej-nizhnego-novgoroda-czenyi,-otzyivyi,-raspolozhenie-405301.html
mystylecorner – Love the variety of clothes here, really stylish daily finds.
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Капельницы для лечения похмелья – является эффективным средством для улучшения состояния организма после употребления алкоголя. В владимире медицинские услуги в виде вливание глюкозы и электролитов позволяет быстро облегчить симптомы похмелья, такие как головная боль, тошнота и слабость. Медицинские учреждения в владимире предоставляют услуги с использованием энтеросгеля для детоксикации. Восстановление водного баланса также имеет большое значение в процессе восстановления. Не забывайте о необходимости консультации врача прежде чем начинать лечение. Чтобы узнать больше посетите сайт vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir025.ru.
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. La variete des titres est raffinee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le support client est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Un plus le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. La variete des titres est eclatante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, offre des recompenses continues.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Реабилитационный центр для алкоголиков в владимире предоставляет возможность начать жизнь с чистого листа для тех, кто столкнулся с алкогольной зависимостью. Вызвать нарколога на дом можно для первичной консультации и оценки состояния. Лечение алкоголизма предполагает медицинское сопровождение и психотерапию, что обеспечивает индивидуальный подход к каждому человеку. Программа реабилитации включает процесс восстановления после алкогольной зависимости и адаптацию в обществе, а также поддержку родственников. Анонимные алкоголики помогают восстановить связи с людьми, переживающими схожие проблемы. Наркологическая помощь в нашем центре позволяет справиться с зависимостью и начать новую жизнь.
Je suis completement electrise par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un mix de DJ. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs lumineux. Boostant votre mise de depart. Le suivi est impeccable, offrant des solutions claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un drop, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient un banger. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter le design est moderne et lumineux, booste le plaisir de jouer. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
J’aime l’aura futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un n?ud blockchain. Le repertoire est opulent et divers, proposant des tables numeriques elegantes. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un algorithme, joignable en un clic. Le processus est lisse comme un smart contract, mais plus de promos dynamiseraient l’aventure. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui brille dans l’univers crypto pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Apprendre en ligne|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourne avec elegance. La variete des titres est rapide, avec des slots aux designs veloces. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le support client est veloce, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un sprint. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino vaut une course rapide pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement veloce, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. La variete des titres est rapide, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En bref, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie celeste. La selection de jeux est olympienne, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et sage, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la gloire. En bref, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le site est rapide et glorieux, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere blues de BassBet Casino, il procure une experience rythmee. Le catalogue est riche et varie, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a jammer. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient rythmees. En bref, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations blues ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinologinfr.com|
https://mebelniy-prokat.ru Восстановление собственными силами. Контроль качества всего каталога.
moved here https://meghansvineyard.com
Отличный сервис! Документы поданы в срок, сотрудники всегда на связи. Приятно сотрудничать, https://dmebroker.ru/
https://www.treeland.ru/sitemap
I every time spent my half an hour to read this webpage’s posts
daily along with a cup of coffee.
dailyessentialfinds – Love that they stock items I haven’t seen elsewhere — great discovery.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
https://sgcasinogreek.com/
buildsuccessnetwork – The membership/community features seem well-designed for collaborative growth.
best online poker real money
newest usa online casinos
online craps real money
partnershipgrowthhub – Plan to revisit when I map out our next collaboration strategy; looks promising.
innovationdriventeam – Appreciate how the advice blends innovation with teamwork; feels realistic and actionable.
powerofcollaboration – The layout is clean and navigation is easy, making exploration smooth.
Заказать проститутку в Балашихе: Быстро, дискретно, премиум-класс
Здесь вы сможете узнать больше: https://shluhi-balashiha.ru/
Тележка с подъемной платформой предназначена для работы в складских помещениях, производственных предприятий для транспортировки коробок, инструментов и других грузов. Способны поднимать и перемещать грузы весом до 0.3т на высоту до 900мм.
Простота эксплуатации — для работы с ними не нужны специальные навыки. Возможность подъема на высоту объемных и тяжелых грузов. Небольшие расходы на обслуживание — достаточно купить недорогие технические жидкости отечественного производства. Бесшумная работа независимо от нагрузки.
Арт. 700057.
Развернуть Свернуть.
Грузоподъемность: 500 кг. Высота подъема: 880 мм. Размер платформы: 850х500 мм. Колеса: 125х40 мм. Гарантия: 12 мес.
Грузоподъемность: 500 кг.
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Помощь наркологов – это набор действий‚ направленных на избавление от зависимостей. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir026.ru можно ознакомиться с информацией о наркологических клиниках ‚ предлагающих профессиональную помощь при алкоголизме и других зависимостях . Лечение начинается с детоксикации ‚ после которой проводятся встречи с врачами и персонализированное лечение. Психологическая поддержка и групповые занятия играют ключевую роль в восстановлении после зависимости . Также важна социальная адаптация и поддержка родственников ‚ что способствует профилактике рецидивов .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
https://multiup.io/50fbba2c465de911419816729bd635a6
pressbros – Cozy café vibe with creative flair; coffee and brunch look seriously inviting.
unitedvisionnetwork – The site layout is clean, easy to navigate and content feels relevant for growth.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
Лечение запоя в владимире ? это важная задача, которая требует квалифицированного вмешательства. Алкоголизм — это беда, способная сломать судьбы, и помощь при запое жизненно важна для всех, кто оказался в этой ситуации. В клиниках для лечения запоя предлагаются различные программы, направленные на выведение из запоя и реабилитацию после запоя . Цены на лечение алкогольной зависимости могут меняться в зависимости от клиники и качества обслуживания. Цены на лечение алкоголизма могут включать консультацию нарколога, медицинскую помощь при запое, а также услуги по выводу из запоя . лечение запоя владимир Помощь наркологов в владимире включает в себя как стационарное, так и outpatient лечение, что также влияет на стоимость . Программа лечения алкоголизма индивидуализирована и может включать детоксикационные процедуры, психологическую помощь и реабилитационные мероприятия. Комплексный подход к лечению зависимостей в владимире позволяет не только остановить алкогольное потребление, но и минимизировать риск рецидивов. Поэтому, если вам или вашим близким требуется помощь, важно не откладывать обращение к профессионалам.
аренда мебели на выставку цены Текущие тарифы на прокат оснащения для выставок. Прозрачное ценообразование и точный расчет.
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
businesssuccesshub – Bookmarking this as a resource; many useful templates and checklists.
Неотложная наркологическая помощь при запое в владимире: куда обращаться В случае алкогольной зависимости и запойного состояния крайне важно оперативно обратиться за медицинской помощью. В владимире доступна услуга вызова нарколога на дом‚ что является особенно удобным вариантом в экстренных случаях. Наркологические центры в городе предоставляют услуги по лечению запоев‚ включая детоксикацию и терапию алкогольной зависимости. Круглосуточная служба помощи готова оказать поддержку вам и вашим близким. Консультация нарколога поможет определить необходимые шаги для восстановления. Совместно с врачом можно разработать программу реабилитации алкоголиков и профилактики запойного состояния. Не забывайте о значении поддержки семьи алкоголика в процессе его лечения. Психотерапия при алкоголизме также может быть неотъемлемой частью лечения. Не откладывайте обращение за помощью — здоровье важнее всего! врач нарколог на дом владимир
trustedpartnergroup – Support/contact info is clearly displayed—nice for building trust with users.
Recommended Reading https://aidenandorla.com
ultimateprofitplan – Appreciate the realistic tone in their advice rather than exaggerated claims.
АЛЬТЕРНАТИВНЫЕ МЕТОДЫ ВЫВОДА ИЗ ЗАПОЯ В владимире: ЛЕГЕНДЫ И ФАКТЫ
connectforprogress – Excellent articles and real-life examples make the lessons stick better.
investprofitgrow – Good for someone who’s serious about growth, but as always, proceed carefully.
dailyessentialstore – The item I ordered arrived as described and in good condition.
visionaryfutureteam – Overall good find; this could be useful for teams aiming to innovate and grow together.
winwithus – Excellent platform for anyone looking to grow and build strong connections.
trustbridgealliance – The mobile experience is smooth, good for checking on the go.
professionalgrowthhub – Great resource for advancing careers, lots of practical advice and tools.
mcalpineinfo – The site appears to cover the “McAlpine Barge Incident” and has very minimal content so far.
1091m2love – Absolutely love the vibe here, great visuals and easy smooth navigation.
trustedleaderscircle – The layout is very clean, making browsing through content a smooth experience.
modernlifestylezone – Recommend this store to anyone looking to elevate their living space on a budget.
uniquedecorstore – Already planning my next order as they have new items weekly.
financialgrowthplan – The layout is clean, lots of good principles for long-term growth.
classyhomegoods – The color matching was accurate to the pictures, which is always refreshing.
Пользуемся услугами уже давно. Всё стабильно и качественно. Настоящие специалисты: таможенный брокер в Москве
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
Цьогорічний фестиваль Beta Festival став справжнім святом для меломанів. Виступи Richie Hawtin та Tale Of Us викликали справжній фурор серед гостей. Їхня музика буквально переповнювала простір емоціями. Adam Beyer завершив вечір своїм бездоганним сетом, залишивши в серцях гостей неймовірні враження.
their explanation https://lorivawind.com/
dailytrendstore – Just received my order, quality matches the photos almost exactly.
Паста с грибами — идеальный ужин после долгого дня.
Для юридических лиц этот брокер — идеальное решение. Вся отчётность прозрачная, документы всегда в порядке. Работаем с ними уже год: https://tamozhenniiy-broker-moskva11.ru/
successmindsetnetwork – Found some useful exercises on the site, will apply them this week for sure.
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
pmajoe4council – Clear campaign focus, design feels trustworthy and community-oriented.
advancedtradingtools – Would recommend to other traders looking for enhanced tools and decent support.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
купить дипломы о высшем с занесением купить дипломы о высшем с занесением .
Отличный сервис, особенно для юридических лиц, которые ценят время https://dmebroker.ru/
http://www.mebelniy-prokat.ru Выставочное пространство с personal визитом. Запись на посещение через сайт.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
reference https://elvirodream.com/
Платная наркологическая помощь в владимире набирает популярность. Клиники, занимающиеся лечением зависимостей, например, наркологическая клиника владимир предоставляют разнообразные услуги: от детоксикации организма до реабилитации наркозависимых. Психотерапия и консультирование по зависимостям способствуют осознанию причин зависимости и поиску путей к восстановлению. Алкогольные реабилитационные центры предлагают конфиденциальное лечение и персонализированный подход к каждому клиенту. Профессиональная поддержка наркологов, программа восстановления и медицинская помощь при наркозависимости играют ключевую роль в успешной реабилитации. Адаптация к социальной жизни после лечения имеет большое значение для снижения риска рецидивов. Более подробную информацию можно найти на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir027.ru.
где купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге где купить диплом техникума в екатеринбурге .
купить диплом хореографа купить диплом хореографа .
888starz uz, O’zbekistondagi eng yaxshi onlayn qimor sayti qimor o’ynash uchun ideal imkoniyatlar taqdim etadi. Bu onlayn kazino turli o’yinlar, bonuslar va qiziqarli aktsiyalar bilan to’la.
888starz uz ga kirishni juda qulay tarzda bajarish mumkin . O’yinchilar hech qanday muammosiz sayt orqali ro’yxatdan o’tishlari va o’yinlarga kirishishlari mumkin .
Har haftada yangi bonuslar va aktsiyalar taqdim etiladi . Bu o’yinchilarning qiziqishini oshirish uchun muhimdir .
888starz uz xavfsizlikni ta’minlashga katta e’tibor qaratadi . Ular o’z ma’lumotlarini himoya qilish uchun zamonaviy texnologiyalarni qo’llaydilar .
888starz apk ios https://888starzuzb.com/apk/
Цена капельницы от запоя в владимире: где найти лучшие предложения Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, с которой сталкиваются многие люди. Для лечения алкоголизма и выведения из запоя часто требуется медицинская помощь. Услуги нарколога в владимире, включая вызов врача на дом, востребованы среди тех, кто стремится избавиться от алкогольной зависимости. Капельница от запоя — это действенный метод восстановления организма после продолжительного приема алкоголя. Стоимость капельниц может отличаться в зависимости от клиники и используемых препаратов. К примеру, капельница на дому — это удобный способ, который позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке. Ценник на капельницу определяется составом препаратов и особенностями самой процедуры. В владимире можно найти различные предложения, но важно выбирать клиники с хорошей репутацией. Наркологические услуги включают не только капельницы, но и терапию при алкоголизме, что также стоит учитывать при выборе. Восстановление после запоя требует комплексного подхода, и лечение запойного состояния должно быть проведено профессионалами. Помните, что качественные медицинские услуги — это ваша инвестиция в собственное здоровье.
букмекерская контора регистрация онлайн букмекерская контора регистрация онлайн
Запойное состояние – это серьезная проблема‚ которая требует неотложной помощи нарколога. В владимире доступны круглосуточные услуги клиники наркологии‚ где вы можете получить необходимую медицинскую помощь. Капельницы для детоксикации помогут быстрому восстановлению после запоя. Процесс лечения алкоголизма включает как физическую‚ так и психологическую поддержку‚ а также помощь психолога. Консультация нарколога гарантирует индивидуальное внимание к каждому пациенту. Поддержка семьи играет важную роль в процессе восстановления. Не стоит откладывать‚ обращайтесь за помощью! помощь нарколога владимир
Как эффективно провести детоксикацию организма после запоя в владимире Преодоление запойной зависимости требует всестороннего подхода, включая очищение и реабилитацию. Симптомы похмелья могут быть тяжелыми, и важно выбрать правильные методы для детоксикации; Лекарственные препараты часто дополняются народными средствами, что повышает эффективность. лечение запоя Клиники по лечению алкоголизма предлагают программы детоксикации и реабилитацию после запоя. Забота родных и психологическая помощь играют ключевую роль в процессе. Профилактика запойного состояния включает в себя постоянный контроль за здоровьем и благополучием. Помните, что восстановление — это долгий путь, но возможный.
Таможенный брокер быстро оформил все документы и отправил отчёт: Таможенное оформление в Домодедово
https://vc.ru/money/1653984-kak-polzovatsya-pzrk-primenenie-perenosnyh-kompleksov-na-svo
urbanstylehub – The filters and categories are well organised — made shopping easy.
Капитальный ремонт Двиговичкофф https://dzen.ru/a/aPkGhHYePCku9uSe .
Таланти команди Ivanka виходять далеко за межі звичайного уявлення про сценічне шоу. Їхній виступ на Trance Illusion був схожий на справжній музичний спектакль, де кожен елемент був продуманий до дрібниць. PJ Zoe додала унікального стилю кожному треку завдяки своїм дизайнерським візуалізаціям, які буквально оживали на сцені. Мені ще не доводилося бачити нічого подібного. Якщо ви хочете відчути цю магію, дізнайтеся більше на їхньому сайті.
Где сейчас доступен официальный сайт Kraken?
Мы собрали все проверенные адреса площадки.
Переходите по проверенной ссылке > kra45 cc
Безопасное соединение и стабильная работа 24/7.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Профессиональная косметика Christina https://sinapple.ru/collection/phytomer/product/phytomer-spring-set
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is needed to get set up?
I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny?
I’m not very internet savvy so I’m not 100% sure.
Any suggestions or advice would be greatly appreciated. Thanks
https://mebelniy-prokat.ru Вебинары и мастер-классы от экспертов индустрии. Бесплатное участие желающим.
discover here https://dance-master-class.com/
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
Looking for effective strategies to increase my website’s organic traffic. Any advice?
https://casinozer77.com/
купить диплом в химках купить диплом в химках .
Вызов нарколога на дому в владимире ? это комфортабельное и действенное решение для тех, кто сталкивается с проблемами алкогольной зависимости . Круглосуточные услуги нарколога предоставляют профессиональную помощь, включая диагностику и лечение алкоголизма. Услуги нарколога на дому обеспечивают анонимное лечение и комфортные условия для пациента . Если требуется вывод из запоя, следует обратиться к опытному специалисту. Профессиональный нарколог проведет первичную консультацию, оценит здоровье пациента и разработает персонализированный план терапии. Поддержка семьи зависимого также играет важную роль в процессе реабилитации .Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Медицинская помощь на дому позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с посещением клиники . Круглосуточный доступ к наркологической помощи гарантирует, что в любой момент можно получить необходимую поддержку . Восстановление после запоя возможно благодаря комплексному подходу и вниманию к каждому пациенту .
купить диплом техникума или колледжа купить диплом техникума или колледжа .
Наркология – это значимая область медицины, которая фокусируется на лечении зависимостей. В владимире действует множество центров помощи наркозависимым, предлагающих различные программы реабилитации. Преодоление зависимостей от алкоголя и наркотиков требует персонализированного подхода, и помощь нарколога играет ключевую роль в этом процессе. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir028.ru вы можете узнать информацию о диагностике зависимостей и консультациях врача-нарколога. Кризисная помощь доступна для тех, кто оказался в острыми проблемами. Психологическая поддержка является незаменимой составляющей лечения, способствуя пациентам вернуться к нормальной жизни после зависимости. Анонимная помощь обеспечивает защиту данных, что особенно важно для многих пациентов. Здравоохранение в владимире включает в себя не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическую поддержку со стороны родных. Программы реабилитации способствуют пациентам приспособиться к жизни без веществ, что способствует восстановлению.
these details https://lukejohnhansen.com/
помощь при запое 24/7
Роберт Левандовски футбол дүйнөсүндөгү эң таасирдүү чабуулчулардын бири.
Левандовскинин жашоо образы көптөр үчүн мотивация. Левандовскинин трансфери Барселона үчүн чоң ийгилик болгон. Роберт Левандовски көп жолу “алтын бутсага” татыктуу болгон. Эгер сиз Левандовскинин биографиясын издеп жатсаңыз, http://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ шилтемесин колдонуңуз. Роберт Левандовски Барселона клубуна энергия кошту.
Левандовски спорттук тарбиянын маанисин ар дайым белгилейт. Левандовски жаракаттан кийин дагы күчтүү кайтып келген.
Левандовскинин туугандары тууралуу тарых да кызыктуу. Левандовски ийгиликке жөн эле жеткен эмес.
Капельница от запоя на дому для пожилых людей в владимире — это ключевой элемент в лечении запоя. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно предлагает услуги детоксикации на дому, что является особенно важным для пожилых людей. Симптомы запоя, такие как слабость и тревожность, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Лечение алкоголизма может включать капельницы, которые способствуют восстановлению водно-электролитного баланса. Однако важно помнить о рисках капельницы: аллергические реакции, осложнения при неправильном введении. Поэтому безопасность должна оставаться главным приоритетом. Помощь врача на дому позволяет избежать стресса при транспортировке больного. Забота о пожилых людях нуждается в особом внимании, и круглосуточная помощь специалиста обеспечивает нужный уход. Рекомендуется соблюдать указания врачей для успешного выхода из запоя.
Прочитала про секрети приготування хрустких вафель. Обов’язково зроблю!
learnsharegrow.shop – Appreciate the practical tips and advice shared on this site.
futuregoalsnetwork.shop – Great variety of products at unbeatable prices; highly recommend.
аренда мебели на выставку цены Актуальные цены на прокат оснащения для выставок. Прозрачное ценообразование и полная стоимость.
J’adore l’energie rythmee de BassBet Casino, il cree une ambiance de studio live. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, proposant des jeux de table styles. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino vaut une session live pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter le design est moderne et vibrant, ajoute une touche de rythme. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis ebloui par BassBet Casino, ca offre un eclat de plaisir. La selection de jeux est eclatante, proposant des jeux de table styles. L’offre de bienvenue est brillante. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un neon, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient lumineuses. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En plus la navigation est simple et lumineuse, booste le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les options de paris variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere aquatique de BassBet Casino, il procure une experience dynamique. La selection de jeux est dynamique, avec des slots aux designs aquatiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient dynamiques. En resume, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un lac, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere olfactive de Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
leadersunitedgroup.bond – The tone feels hopeful, which is refreshing on many sites.
globalpartnershipteam.shop – The layout is crisp and clear, makes exploring effortless.
Шоколадный фондан — мечта сладкоежки.
Роберт Левандовски тууралуу жаңылыктар ар дайым көңүлдү бурат.
Левандовски жубайы менен көп кайрымдуулук иштерин колдойт. Левандовскинин статистикасы футбол дүйнөсүндө өзгөчө. Роберт Левандовски дүйнөлүк футбол жылдызы. Эгер сиз Левандовскини жактырсаңыз, анда бул сайт сиз үчүн — Роберт Левандовски расмий барагы. Левандовски Барселонада өзүнүн тажрыйбасын көрсөтүүдө.
Левандовски өзүнүн эмгеги менен дүйнөгө белгилүү болгон. Роберт Левандовски фитнеске чоң маани берет.
Левандовскинин түпкү теги тууралуу маалымат көп талкууланат. Роберт Левандовски футбол тарыхындагы легенда.
https://ihm.sureshinternationalcollege.in/india-by-train-as-low-as-54999e/
Je suis captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. La selection de jeux est astronomique, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Le bonus d’entree est eclatant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, toujours pret a decoder. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, cependant des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les evenements communautaires decentralises, qui booste l’engagement.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
Regarder maintenant|
winmore.bond – Navigation is intuitive; I can find everything quickly and easily.
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Au final, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Tout accГ©der|
connectinnovationhub.bond – Looking forward to more updates and new features soo
trustandunity.bond – Navigation is intuitive, finding information is quick and effortless.
businessgrowthhub.shop – Looking forward to more updates and new features soon.
smartfashionboutique.bond – Navigation is intuitive, finding information is quick and effortless.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – A clean and professional design that makes navigation a breeze.
где купить диплом об окончании техникума где купить диплом об окончании техникума .
https://vc.ru/money/1656831-kak-stat-artilleristom-na-svo-trebovaniya-vozmozhnosti-i-karera
uniquefashionstyle.shop – (Note: I spotted a small typo in the URL above—a minor thing but worth checking.)
successpathway.bond – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
growthpoint.bond – Looking forward to seeing more updates and offerings from this site.
Левандовски Барселонага кошулгандан кийин команда күчөдү.
Инстаграмда Роберт Левандовскинин посттору абдан популярдуу. Роберт Левандовски карьерасында жүздөгөн гол салган. Роберт Левандовски көп жолу “алтын бутсага” татыктуу болгон. Барселона, Польша жана Роберт Левандовски тууралуу баарын https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ сайтынан билиңиз. Барселонадагы Левандовскинин оюнун күйөрмандар макташат.
Роберт Левандовски карьерасын үзүрлүү өткөрүүдө. Левандовски жаракаттан кийин дагы күчтүү кайтып келген.
Левандовскинин туугандары тууралуу тарых да кызыктуу. Роберт Левандовски карьерасын толук берилип өткөрөт.
useful source https://meadowfinreth.com/
createimpacttoday.shop – The products are not only beautiful but also support great causes.
Роберт Левандовски акыркы оюндарында мыкты оюн көрсөттү.
Роберт Левандовски денесин мыкты формада кармайт. Роберт Левандовски голдорунун саны ар жыл сайын өсүүдө. Левандовски футбол тарыхында өз изин калтырган. Барселона жана Левандовски тууралуу кеңири маалымат https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ порталында бар. Левандовски Барселонада өзүнүн тажрыйбасын көрсөтүүдө.
Левандовски футболго болгон сүйүүсүн эч качан жоготпойт. Левандовски жаракаттан кийин тез эле формасын кайтарды.
Левандовскинин ата-энеси да спорт менен алектенген. Роберт Левандовски карьерасын толук берилип өткөрөт.
куплю диплом младшей медсестры https://frei-diplom15.ru .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
discovernewpath.shop – The visuals are appealing and complement the content well.
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
1x bet giri? http://1xbet-12.com/ .
1xbet giri? 2025 1xbet giri? 2025 .
http://okna-plastic-4.ru – балконы под ключ с утеплением гипсокартоном с розетками с стеллажами дизайнерский ремонт
https://okna-plastic-7.ru – окна от производителя без наценок немецкие технологии контроль качества установка за 1 день
1xbet resmi giri? 1xbet resmi giri? .
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – Impressed with the product quality and packaging; exceeded expectations.
1xbet giri? g?ncel 1xbet giri? g?ncel .
https://okna-plastic-1.ru – окна от производителя без посредников немецкие технологии сертификаты изготовление за 1 день
mebelniy-prokat.ru Департамент проверки следит за состоянием мебели. Строгие стандарты к качеству.
buildbrand.bond – I appreciate how fast everything loads here; very responsive.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
1xbet 1xbet .
Класичні драматичні твори досі викликають емоції.
1xbet giri? adresi 1xbet giri? adresi .
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблематика, которая требует всестороннего метода к излечению. В городе владимир доступна помощь в любое время, в т.ч. вывод из запоя. Центры лечения алкоголизма предлагают услуги психотерапии и реабилитации, что становится необходимым этапом в излечении. Экстренная помощь и консультации специалистов помогают людям с зависимостью понять и принять свою зависимость. Психологическая поддержка включает индивидуальную терапию и групповые занятия, что способствует обмену опытом и эмоциональной поддержке. Программа восстановления способствует созданию стратегий отказа от алкоголя и новые навыки жизни без него. вывод из запоя круглосуточно владимир Следует отметить, что наркологическая помощь доступна в любое время, что даёт возможность каждому отыскать свой путь к восстановлению и счастливой жизни.
заказать кухню спб http://kuhni-spb-2.ru .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Как начать лечение алкоголизма в владимире: первый шаг к выздоровлению Алкогольная зависимость – серьезная проблема, требующая профессионального вмешательства. В владимире доступна круглосуточная помощь нарколога на дом, что позволяет начать лечение в удобное время. Консультация нарколога поможет выявить уровень зависимости и выбрать подходящую программу лечения. нарколог на дом круглосуточно владимир Медикаментозная терапия, широко используемая в реабилитационных центрах владимира, нацелена на облегчение абстинентного синдрома и восстановление здоровья. Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе выздоровления, обеспечивая эмоциональную стабильность. Анонимность в лечении создает более комфортные условия для пациента. Детоксикационная программа способствует очищению организма от токсинов, а реабилитационный процесс включает социальную адаптацию и меры по предотвращению рецидивов. Профессиональная помощь – залог успешного преодоления проблемы. Не упустите возможность изменить свою жизнь к лучшему!
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Snatch Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, aber mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Insgesamt, Snatch Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein super Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
https://snatch-casino.de/de-de/|
okna-plastic-5.ru/ – века окна оригинальные благородный белый с мультифункциональным стеклом с детским замком с москитной сеткой
https://okna-plastic-10.ru – окна от производителя без наценок европейское оборудование гарантия 5 лет изготовление за 1 день
пластиковые окна рехау – теплые оконные системы Рехау с установкой
Капельница от запоя – это значимая процедура, которая помогает скорейшему восстановлению здоровья человека, страдающего алкогольную зависимость. В владимире вызов нарколога для проведения этой процедуры становится всё более актуальным. Употребление алкоголя негативно влияет на организм, вызывая симптомам похмелья, такими как головная боль, тошнота и слабость.Лечение алкоголизма включает detox, который помогает детоксикации организма от токсинов. Капельница гарантирует поступление необходимых веществ, улучшая состояние пациента. Нарколог предоставляет профессиональную поддержку при запое, что способствует избежать серьёзных осложнений. вызов нарколога владимир Восстановление организма после запоя требует комплексном подходе, включая реабилитацию от алкоголя. Терапия запоя может включать как фармацевтические методы, так и психотерапевтическую помощь. Важно помнить, что здоровье – это главное, и оперативная помощь нарколога может спасти жизнь.
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в владимире – данная услуга, которая все более востребованной в наше время. Многие люди сталкиваются с проблемами, связанными с зависимостями, будь то алкоголь или наркотики. Квалифицированный нарколог предлагает помощь, помогая справится с этими сложными ситуациями. Вы можете вызвать нарколога на дом, если это необходимо. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать медицинские учреждения. Услуги нарколога в владимире включают диагностику зависимостей, консультацию нарколога и лечение зависимости. Важно помнить, что анонимное лечение зависимости также возможно.Помощь на дому гарантирует комфорт и сохранение конфиденциальности, что особенно актуально для лечения алкоголизма и реабилитации после наркомании; Психотерапия для людей с зависимостями – важный элемент, который помогает пациентам вернуться к нормальной жизни. Реабилитация зависимых в владимире проходит под контролем опытных специалистов, что обеспечивает высокое качество лечения. Не откладывайте решение проблемы! Получите помощь, вызвав нарколога на сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-vladimir029.ru.
https://www.sutori.com/en/story/1xbet-pakistan-promo-code-no-deposit-2026-100-15000-pkr–nqH96hKwZpV7RiYE9vDNAAUm
https://dzen.ru/a/aPRXjPraMEja6Ols
пластиковые окна на балкон цены – доступные стоимость на балконное остекление под ключ
kraken ios
https://xn--kr41-rzb.com
https://okna-plastic-6.ru – прямые поставки без посредников собственное производство гарантия 5 лет установка за 1 день
https://okna-plastic-9.ru – прямые поставки без наценок немецкие технологии контроль качества быстрые сроки
okna-plastic-7.ru – балконы под ключ алюминиевое панорамное с выездом с утеплением недорого с материалами евроремонт
Література стає цікавішою, якщо розумієш її сенс. Розбір творів допоможе в цьому.
Website https://cardsfm.ru/ .
Роберт Левандовски тууралуу жаңылыктар ар дайым көңүлдү бурат.
Роберт Левандовски фото жана видеолору дайыма талкууда. Левандовски канча гол салганы тууралуу маалымат ар дайым жаңыланып турат. Роберт Левандовски улуттук курама үчүн көп гол салган. Акыркы маектер жана жаңылыктар https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ сайтында. Роберт Левандовски Барселона менен титулдар үчүн күрөшүүдө.
Левандовски өзүнүн эмгеги менен дүйнөгө белгилүү болгон. Левандовски спорттук формасын жоготпойт.
Левандовскинин балдары да спортко жакын. Роберт Левандовски карьерасын толук берилип өткөрөт.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск .
unitedbygoal.bond – Appreciate the clear and concise information provided throughout.
http://okna-plastic-3.ru – лоджии под ключ с утеплением пластиком с выключателями с полками индивидуальный проект
Нужен безопасный вход на маркет?
> вход в кракен
Сохраняйте ссылку в закладки.
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
harrietlevinmillan.com – The tone is authentic and thoughtfully presented, which is refreshing.
mdcphilly.com – The visuals are strong and add to the appeal of the website.
аренда мебели для форума Профессиональное оснащение для конференций. Удобные модели и оперативный монтаж.
ks4thekids.com – The content is clear and shows focus; I like the purpose.
pp4fdr.org – The visuals and community voice make the site feel authentic and grounded.
https://pay-n-play.org/
как купить диплом техникума официального сайта как купить диплом техникума официального сайта .
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
brauhausschmitzoktoberfest.com – The use of imagery really helps set the mood—nice choice.
okna-plastic-10.ru/ – рехау окна качественные темный дуб с триплексом с микропроветриванием с жалюзи
clubinorout.com – I like how the content is organised and the tone looks friendly.
http://www.okna-plastic-4.ru – металлопластиковые системы для дома с доставкой с подарками цветные панорамные раздвижные с фурнитурой
https://okna-plastic-8.ru – заводские цены без наценок собственное производство контроль качества быстрые сроки
concernedaboutpollution.com – Pages load quickly and the navigation feels smooth and intuitive.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
grant-jt.com – Loading speed seems fast; the experience is smooth so far.
komunahouse.com – Overall, the brand presentation feels authentic and well-considered.
gailcooperspeaker.com – The design feels clean and easy to navigate which is refreshing.
berrybombselfiespot.com – Booking seems straightforward; that’s a plus for planning a visit.
mdcphilly.com – Pages load smoothly and the overall user experience is very pleasant.
https://www.okna-plastic-1.ru/ – реальные отзывы выполненные объекты рейтинг компаний сертификаты производители опыт работы
https://kraken-russia.com Россия
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр .
https://www.okna-plastic-9.ru/ – фото работ наши работы рейтинг компаний сертификаты партнеры опыт работы
Купить диплом колледжа в Ивано-Франковск https://educ-ua7.ru/ .
http://www.okna-plastic-5.ru – окна пластиковые для офиса с доставкой с подарками цветные нестандартные распашные с фурнитурой
http://www.okna-plastic-7.ru – прайс на окна с калькулятором с учетом комплектации прозрачные акционные по рекомендации с рассрочкой 0%
reindeermagicandmiracles.com – The site’s branding fits perfectly with what they’re offering—nice match.
I wanted to thank you for this excellent read!! I certainly
enjoyed every little bit of it. I’ve got you book marked to check
out new things you post…
brucknerbythebridge.com – I appreciate the clear presentation of location and transport links.
купить диплом в вольске http://rudik-diplom3.ru .
https://okna-plastic-2.ru/ – выбрать окна в Москве с расчетом по фото с заменой советских окон на теплые с выгодой
meetkatemarshall.com – I appreciated the categorization of posts; makes exploring topics really easy.
я купил диплом с проводкой я купил диплом с проводкой .
купить свидетельство о браке купить свидетельство о браке .
купить диплом в нефтекамске купить диплом в нефтекамске .
купить легальный диплом техникума купить легальный диплом техникума .
Мятный чай реально помогает, если нервничаешь перед сном.
купить диплом образцы купить диплом образцы .
https://vc.ru/money/1643497-kak-stat-snaiperom-svo-put-podgotovki-i-obucheniya-boica
http://okna-plastic-10.ru/ – окна ПВХ Москва с выездом бесплатная доставка инженер-замерщик в удобное время
купить диплом в биробиджане купить диплом в биробиджане .
http://okna-plastic-6.ru – отделка балконов с утеплением пластиком с выключателями с полками индивидуальный проект
shemplymade.com – I like the handcrafted vibe; it makes the brand feel personal.
http://www.okna-plastic-8.ru – прайс на окна с калькулятором с учетом размеров без скрытых платежей праздничные для новых клиентов с отсрочкой
moeinclub.com – The content covers a wide range of topics which can appeal to many interests.
Як не витрачати зайві гроші в подорожах? Кращі поради та ідеї тут: дивитися!
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
купить диплом в мичуринске https://www.rudik-diplom11.ru .
https://mebelniy-prokat.ru Быстрая заявка с оперативной обработкой. Простая навигация и полная информация.
https://okna-plastic-4.ru – заводские цены без посредников собственное производство сертификаты изготовление за 1 день
https://okna-plastic-7.ru – заводские цены без переплат немецкие технологии гарантия 5 лет установка за 1 день
casa-nana.net – The site is clean and welcoming, and does a good job communicating its mission.
electmikemontes.com – The visuals are minimal yet effective—good balance.
купить диплом москва легально https://frei-diplom1.ru .
http://www.okna-plastic-1.ru – стоимость окон с калькулятором с учетом размеров прозрачные праздничные для новых клиентов с отсрочкой
https://vc.ru/money/1654879-operator-bpla-na-svo-kontraktnaya-sluzhba
http://okna-plastic-10.ru – балконы под ключ с утеплением гипсокартоном с выключателями с стеллажами индивидуальный проект
https://www.okna-plastic-5.ru – металлопластиковые окна в Подмосковье под ключ со скидкой в кредит качественные европейского качества Rehau трехкамерные энергосберегающие
okna-plastic-8.ru – остекление балконов теплое панорамное по области с освещением недорого с материалами евроремонт
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui groove comme une voix soul. Le catalogue est riche en emotions, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Le suivi est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et vibrant, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. En bref, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le design est moderne et soul, booste le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de legendes. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent comme par magie, toujours pret a transformer. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le design est moderne et enchante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un riff. Le catalogue est riche et varie, avec des slots aux designs rythmiques. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient rythmees. En bref, BassBet Casino vaut une jam session pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
http://okna-plastic-2.ru/ – пластиковые окна Москва в любом районе бесплатный монтаж консультация специалиста срочный выезд
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Avec des depots instantanes. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un banquet, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un cosmos chiffre. La selection de jeux est astronomique, avec des slots aux themes innovants. Le bonus d’accueil est eclatant. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite cosmique, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des transactions fiables.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
http://okna-plastic-9.ru/ – пластиковые окна Москва во всех округах бесплатный монтаж технический специалист выезд в день обращения
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir raffine. La selection de jeux est exquise, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Un autre atout les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Aller voir|
аренда мебели форум Конференц-мебель для деловых встреч. Эргономичное оснащение и профессиональная сборка.
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
https://www.okna-plastic-6.ru/ – реальные отзывы наши работы рейтинг компаний лицензии поставщики надежная компания
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. La selection de jeux est somptueuse, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. En resume, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
http://www.impressariocasinoappfr.com|
окна пластиковые в частный дом – надежные пластиковые окна для частного дома под ключ
https://verde-el.com/
медтехника http://medicinskaya-tehnika.ru/ .
поставка медицинского оборудования поставка медицинского оборудования .
Це не просто так, але футболістів часто порівнюють, щоб визначити, хто з них найкращий. Але кожен має свої унікальні сильні сторони.
наркологическая служба http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru/ .
окна пвх – российские конструкции для дачи
1xbet g?ncel 1xbet g?ncel .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
оборудование для больниц http://www.medicinskoe–oborudovanie.ru .
клиника наркологическая москва narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru .
поменять окна – профессиональная замена старых окон на современные с гарантией
https://okna-plastic-4.ru – окна от производителя без посредников европейское оборудование контроль качества изготовление за 1 день
готовые пластиковые окна для дачи – качественные готовые окна для загородного дома с установкой
Website https://remonttermexov.ru/ .
https://www.okna-plastic-1.ru – пластиковые окна в Москве от производителя со скидкой в кредит надежные российского производства Veka трехкамерные шумозащитные
http://www.okna-plastic-9.ru – металлопластиковые системы для офиса с доставкой с подарками под дерево панорамные глухие с подоконниками
muralspotting.com – I’d love to see a map view or interactive feature for locating murals.
okna-plastic-7.ru – остекление балконов теплое панорамное в Москве с утеплением недорого с гарантией эконом
https://okna-plastic-5.ru/ – выбрать окна в регионе с примеркой по размерам с заменой советских окон на современные с выгодой
Looking for effective strategies to increase my website’s organic traffic. Any advice?
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
купить диплом занесением реестр украины https://www.frei-diplom2.ru .
http://okna-plastic-2.ru/ – пластиковые окна Москва во всех округах бесплатная доставка консультация специалиста выезд в день обращения
https://ivory-frog-s2pbv6.mystrikingly.com/
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/metizy-klyuchevye-harakteristiki-i-rekomendatsii-po-vyboru/
okna-plastic-10.ru/ – века окна оригинальные золотой дуб с триплексом с противовзломной фурнитурой с роллетами
mebelniy-prokat.ru Карта сайта для легкой ориентации. Просто и быстро.
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
купить свидетельство о рождении купить свидетельство о рождении .
catherinewburton.com – The visuals are calming and the tone is personable—nice choice.
vsmphotography.com – Navigation to galleries and contact info is intuitive; I found what I needed quickly.
https://www.okna-plastic-8.ru – пластиковые окна в Подмосковье от производителя по выгодной цене с рассрочкой теплые немецкие Rehau однокамерные энергосберегающие
http://www.okna-plastic-6.ru – окна цены с калькулятором с учетом установки без скрытых платежей сезонные для новых клиентов с рассрочкой 0%
toddstarnesbooktour.com – I like the visuals—they match the theme of a book tour and create excitement.
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
createandgrow.shop – The layout appears clean and user-friendly; nice visual clarity.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – The visuals are inviting and the interface feels smooth.
okna-plastic-3.ru – остекление балконов алюминиевое полное по области с освещением быстро с материалами эконом
купить диплом об окончании техникума в оренбурге купить диплом об окончании техникума в оренбурге .
findwhatyoulove.shop – The branding is consistent and gives the store a polished identity.
startsomethinggreat.shop – The branding is consistent and gives the store a polished identity.
theperfectgiftshop.com – The site loads quickly and works smoothly on mobile too.
shopandsmilealways.shop – Overall a good first impression; user-friendly and pleasant to explore.
Пицца с ветчиной — честно, можно есть хоть каждый день.
simplybestchoice.shop – The site loads quite fast; browsing feels smooth on mobile too.
shopandsmilealways.shop – The branding feels simple and clean; consistent visual tone.
geteventclipboard.com – The visuals are clean, supporting the purpose without distraction.
https://www.okna-plastic-8.ru – пластиковые окна в Москве под ключ со скидкой с гарантией качественные немецкие Rehau двухкамерные энергосберегающие
Купить диплом техникума в Мариуполь http://www.educ-ua7.ru .
[url=https://okna-plastic-4.ru/]okna-plastic-4.ru[/url] – остекление балконов алюминиевое панорамное с выездом с отделкой качественно с гарантией премиум
как легально купить диплом о как легально купить диплом о .
uniquetrendstore – Always a pleasure shopping here, never disappoints with selections.
http://okna-plastic-1.ru – отделка балконов с утеплением гипсокартоном с розетками с шкафами индивидуальный проект
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании можем помочь. Купить диплом бакалавра в Нижнем Новгороде – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-nizhnem-novgorode
купить диплом в спб с занесением в реестр http://frei-diplom6.ru .
shopwithconfidence – Customer support helped me instantly, very impressed with service quality.
купить диплом в комсомольске-на-амуре купить диплом в комсомольске-на-амуре .
Another aspect that makes MCPEDL worthwhile is the community’s active participation.
minecraft pe shaders https://mcpedl-minecraft.com/textures-minecraft-pe/shaders/
https://500px.com/p/codeprom11o?view=photos
okna-plastic-9.ru – остекление балконов теплое частичное с выездом с освещением быстро с материалами премиум
https://www.buellmotorcycle.com/profile/codeprom11o42019/profile
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
купить диплом в северодвинске купить диплом в северодвинске .
newseasoncollection – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
купить диплом в реестре купить диплом в реестре .
купить диплом монтажника купить диплом монтажника .
joinourcreativeworld – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
купить диплом в михайловске https://www.rudik-diplom4.ru .
inspireeverydaylife – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
okna-plastic-2.ru – балконы под ключ алюминиевое частичное по области с освещением быстро с гарантией евроремонт
smartchoiceoutlet – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
mebelniy-prokat.ru Все в одном месте включая декор помимо мебели. Координация всего для вашего удобства.
lifestyleinspirationhub – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
shopthebesttoday – Excellent customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
shopforhappiness – Highly recommend this shop, never disappointed with my purchases.
купить диплом в каменске-шахтинском http://rudik-diplom10.ru .
https://www.sony.edu.pe/profile/bestfreebonous15206/profile
discovernewworld – Fantastic variety of products, always something new and exciting.
staycuriousalways – Great shopping experience, fast delivery and quality items every time.
пластиковые окна в видном – надежные оконные системы в Ленинском районе с гарантией
купить диплом в сарове купить диплом в сарове .
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
okna-plastic-8.ru/ – рехау окна качественные темный дуб с мультифункциональным стеклом с противовзломной фурнитурой с жалюзи
мостбет ком https://www.mostbet12031.ru
okna-plastic-6.ru/ – рехау окна качественные темный дуб с i-стеклом с противовзломной фурнитурой с роллетами
bestdealsforlife – Fast delivery and packaging was perfect, highly recommended for everyone.
купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр купить диплом университета с занесением в реестр .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
discoveryourmoment – Love the variety of products, always something new to explore.
пластиковые окна калькулятор онлайн – быстрый расчет стоимости окон онлайн
Je suis epoustoufle par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui groove comme une voix soul. Les titres sont d’une richesse envoutante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec un groove parfait, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Le processus est simple et vibrant, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme une chanson, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. Egalement genial les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’ai une passion cyclonique pour Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir veloce. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. En resume, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
casinospinitfr.com|
пластиковые окна с установкой в москве – надежные пластиковые окна под ключ от производителя
J’adore l’atmosphere musicale de BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. Les options sont vastes comme un album, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est melodieux, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme un riff, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient melodieuses. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un riff, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
J’adore l’ambiance delicate de Impressario Casino, il evoque un jardin parfume. Les titres proposes sont d’une finesse rare, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Boostant votre capital initial. Le service client est irreprochable, toujours pret a aider. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, bien que plus de promotions regulieres ajouteraient du charme. Au final, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les passionnes de sensations raffinees ! En plus le design est moderne et soigne, ce qui rend chaque session plus lumineuse. Un atout les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©bloquer plus|
Відвідавши Австралійський Фестиваль Природи, я зрозуміла, що такі події варто відвідувати всією родиною. Тут є щось цікаве для кожного, від дитини до дорослого. Більше інформації про фестивалі – на сайті Australia Department[/url>.
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. La variete des titres est eclatante, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement cool les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Commencer Г apprendre|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fees. La selection de jeux est enchantee, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En bonus le design est moderne et enchante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
This site really has all of the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
https://kra41c.com
J’ai une passion brulante pour Impressario Casino, il evoque un tapis rouge scintillant. La collection de jeux est eclatante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et gracieux, parfois plus de promotions regulieres ajouteraient du prestige. Au final, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui captive pour les passionnes de sensations prestigieuses ! A souligner le design est moderne et scintillant, ce qui rend chaque session plus glamour. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir tout de suite|
thinkcreategrow – Inspiring content that motivates me to take action every day.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un cosmos chiffre. La selection de jeux est astronomique, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus d’accueil est eclatant. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite cosmique, toujours pret a resoudre. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction blockchain, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! De plus le site est rapide et futuriste, ajoute une touche de sophistication. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des transactions fiables.
Continuer maintenant|
http://www.okna-plastic-1.ru – металлопластиковые системы для квартиры с замером по специальной цене под дерево панорамные распашные с откосами
окна пластиковые цены в москве – доступные цены на оконные системы с установкой
https://mebelniy-prokat.ru Финансовая прозрачность для заинтересованных лиц. Честный бизнес без секретов.
are replica shoes fake – what’s a replica shoe
globalmarketplacehub – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
пластиковые окна цена – актуальные прайс на пластиковые окна от производителя
everytrendinone – Easy checkout and secure payment made shopping worry-free this time.
http://okna-plastic-2.ru – отделка балконов с остеклением гипсокартоном с освещением с шкафами индивидуальный проект
brightfuturedeals – Great site that sparks creativity and gives me new perspectives daily.
learnshareconnect – The website layout is clean and navigation feels very intuitive today.
discovergreatthings – Love discovering fresh items here; keeps the space feeling updated and fun.
findyourperfectdeal – The writing style is clear and friendly—makes reading fun rather than a chore.
yourjourneybegins – Wonderful site with inspiring products that brighten every day, so glad.
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My blog covers a lot of the same topics as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
kra42 at
https://vc.ru/money/1681478-normy-pitaniya-dlya-kontraktnikov-na-svo-chto-vhodit-v-racion
купить диплом в анжеро-судженске https://www.rudik-diplom13.ru .
okna-plastic-9.ru/ – века окна качественные благородный белый с триплексом с микропроветриванием с москитной сеткой
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
купить окна kbe – качественные продукцию KBE от производителя
окна kbe цена – доступные стоимость на продукцию KBE в Москве
куплю диплом младшей медсестры http://www.frei-diplom14.ru .
blinkiesdonutsca – Loved stopping by, donuts were fresh and service was super friendly.
https://www.okna-plastic-3.ru/ – реальные отзывы портфолио топ производителей лицензии партнеры история компании
купить диплом в самаре http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в самаре .
realherschel – Overall a positive experience so far, happy to have discovered them.
http://okna-plastic-10.ru – лоджии под ключ с утеплением пластиком с освещением с стеллажами евростандарт
Як на мене, найкраща спеція — це копчена паприка.
tabitoshigoto – I love that they focus on real locations with authentic local details.
okna-plastic-8.ru – остекление лоджий алюминиевое панорамное с выездом с отделкой быстро с гарантией эконом
http://okna-plastic-4.ru/ – окна ПВХ Москва в любом районе бесплатная доставка инженер-замерщик выезд в день обращения
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
Враження від фестивалю цього року залишилися неймовірними. Adam Beyer створив настільки потужний сет, що публіка буквально завмирала під кожну композицію. Його стиль поєднував індустріальні мотиви з мелодійністю, яка пробирала до глибини душі. Amelie Lens продемонструвала свою майстерність у створенні ритмів, які резонували з кожним рухом. А виступ Richie Hawtin був справжнім техно-шедевром, що створював відчуття подорожі крізь час і простір.
http://okna-plastic-1.ru – отделка балконов с обшивкой пластиком с выключателями с полками дизайнерский ремонт
прокат мебели москва Прокат мебели в городе для дома. Разнообразие моделей и лояльные тарифы.
ohmydrifter – Overall a solid blog with distinct voice—worth following if you like this style.
cs-nippon-cp – I checked the site but couldn’t find a clear description of what it offers.
http://www.okna-plastic-9.ru – ПВХ конструкции для офиса с монтажом по акции белые панорамные глухие с откосами
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
hopeandlace – Their portfolio appears creative and professional, great for anyone looking for event design.
http://okna-plastic-7.ru/ – пластиковые окна Москва с выездом бесплатный монтаж технический специалист в удобное время
trabas007hoki – Customer support section seemed minimal—hard to tell how responsive they are.
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/metizy-klyuchevye-harakteristiki-i-rekomendatsii-po-vyboru/
http://www.okna-plastic-5.ru – окна цены бесплатно с учетом установки без скрытых платежей праздничные по рекомендации с рассрочкой 0%
motivilovesmusic – For now, treat it as a lower-certainty option until more background is found.
http://okna-plastic-2.ru/ – пластиковые окна Москва в любом районе бесплатный монтаж инженер-замерщик выезд в день обращения
Website https://useit2.ru/.
hanayaka-na-life – Good selection of items, I found something I’ve been looking for.
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely feel this web site needs a great deal more attention. I?ll probably be back again to read through more, thanks for the information!
hawaiineiartcontest – The guidelines look quite specific about species eligibility and artwork format. :contentReference[oaicite:0]index=0
Ищете альтернативу KRAKEN?
Вот ещё вариант: https://krakr.cc
wrestlingac – Great starting point for wrestling-enthusiasts, just be sure to cross-check key information when using it in a broader research context.
Excellent, what a weblog it is! This website gives helpful facts to us, keep it up.
https://kra42c.com
https://www.okna-plastic-10.ru – пластиковые окна в Московской области от производителя недорого с рассрочкой надежные российского производства KBE однокамерные энергосберегающие
foruminvestmali – The website appears to have been last significantly updated around 2019, which raises a question about its ongoing relevance. :contentReference[oaicite:3]index=3
https://okna-plastic-8.ru/ – заказать окна в Москве с примеркой по фото с ремонтом старых окон на пластиковые с выгодой
okna-plastic-6.ru – остекление лоджий холодное панорамное по области с освещением быстро с работой премиум
envolavecning – No visible social-media links or clear contact details right away, which is a little concerning.
остекление и утепление лоджии цена – окончательная стоимость на комплексные работы в Москве
https://www.okna-plastic-9.ru/ – фото работ выполненные объекты топ производителей разрешения поставщики история компании
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
https://mebelniy-prokat.ru Онлайн-визуализация по шоуруму. Изучите детали не выходя из дома.
he said
uniswap exchange
http://www.okna-plastic-7.ru – стоимость окон с калькулятором с учетом комплектации прозрачные сезонные для новых клиентов с отсрочкой
https://princesscasino-de.com/
okna-plastic-4.ru/ – века окна качественные темный дуб с i-стеклом с противовзломной фурнитурой с роллетами
keyword.
Сохраняйте рабочие адреса KRAKEN и проверяйте их перед входом.
На Trance Illusion команда Ivanka показала, як можна поєднати технології зі звуком, створюючи неповторну атмосферу. Світлові шоу від PJ Mia вразили точністю і гармонією, створюючи справжній ефект занурення у музику.
okna-plastic-10.ru/ – рехау окна оригинальные благородный белый с мультифункциональным стеклом с детским замком с москитной сеткой
купить диплом в самаре купить диплом в самаре .
http://www.okna-plastic-6.ru – окна пластиковые для квартиры с монтажом по акции цветные стандартные распашные с откосами